Eosinophil and IgE responses of IL-5 transgenic mice experimentally infected with Nippostrongylus brasiliensis
Article information
Abstract
Eosinophil and IgE responses of interleukin (IL)-5 transgenic and normal C3H/HeN mice were studied after experimental infection with Nippostrongylus brasiliensis (Nb). Intestinal worms were recovered at day 5 post-infection (PI), and numbers of total white blood cells (WBC) and eosinophils, and total serum IgE and anti-hapten (dinitrophenyl) (DNP) specific IgE titers, were measured at days 0, 14 and 21 PI. IL-5 mice appeared resistant to Nb infection showing a significantly lower worm recovery rate than normal mice (P<0.05). Total WBC and eosinophil counts (/mm3) were significantly increased in Nb infected normal mice (P<0.05), but unchanged (total WBC) or decreased (eosinophils) in IL-5 mice at day 21 PI. The total serum IgE level remarkably increased in normal mice, but only a little in IL-5 mice at days 14 and 21 PI. Priming with DNP brought about more remarkable increases of the total and anti-DNP specific IgE in normal mice than in IL-5 mice. The results show that IL-5 mice are resistant to Nb infection, and that eosinophil and IgE responses in these mice are not augmented by Nb infection.
INTRODUCTION
Interleukin (IL)-5 transgenic mice are those genetically converted to produce high levels of IL-5, eosinophils, and antibodies including IgM and IgE (Tominaga et al., 1991, 1993). They are now popularly used as a useful animal model to study host immunity to parasites (Dent et al., 1997; Hokibara et al., 1997; Shin et al., 1997; Sugaya et al., 1997). In relation to IL-5 mice, one of questions is whether their elevated eosinophil and IgE levels are further augmented by a helminthic infection. Moreover, it is of great interest whether they could protect themselves from infection with various kinds of helminths.
Nippostrongylus brasiliensis (Nb) is an intestinal nematode of rodent hosts, which migrates through the lung before reaching to the intestine. Eosinophilia, elevated serum IgE, mucosal mastocytosis and goblet cell hyperplasia are characteristic immune responses of the host to this nematode infection (Rennick et al., 1990; Abe et al., 1993; Uchikawa et al., 1994; Chen et al., 1995). One or more of these factors may be directly related with host protective mechanisms. Goblet cells, for example, are known to play a vital role for expulsion of Nb from the intestine of normal murine hosts (Abe et al., 1992, 1993).
IL-5 transgenic mice were found resistant to Nb infection, and eosinophils were suggested to play a key role for the protection (Shin et al., 1997). IgE, the level of which is also high in IL-5 mice (Tominaga et al., 1991, 1993), was reported not important for protection of mice against Nb (Watanabe et al., 1988), but it should be further documented. Meanwhile, studies on eosinophil and serum IgE responses in Nb infected IL-5 mice have been lacking. Therefore, the present study was undertaken to confirm resistance of IL-5 mice to Nb infection, and to observe their eosinophil and IgE responses.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Parasite
Nippostrongylus brasiliensis (Nb) has been maintained in our laboratory by repeated passages in female Sprague-Dawley rats. Infective third stage larvae (L3) were harvested from fecal culture on charcoal granules through Baermann's apparatus (Beaver et al., 1984) filled with warm saline. They were washed with saline, counted, and injected subcutaneously to mice with the dose of 500 larvae per mouse.
Animals
Transgenic mice carrying the mouse IL-5 gene (= IL-5 mice) with the background of C3H/HeN, 10-12 week-old females, were bred in our laboratory. These mice were constructed by inserting IL-5 cDNA in the exon of beta-globin gene and ligating with mouse metallothionein promotor (Tominaga et al., 1991). Normal female C3H/HeN mice were purchased from Shizuoka Laboratory Animal Center Inc. (Hamamatsu, Japan).
Experimental grouping, blood and serum sampling
Five IL-5 mice and 5 normal age-matched C3H/HeN mice were prepared for worm recovery from the intestine at day 5 post-infection (PI), of which experiments were repeated three times. To observe eosinophil, total serum IgE, and anti-DNP (dinitrophenyl) specific IgE responses, IL-5 mice and normal C3H/HeN mice were divided into 4 groups; Nb infection only (n=5), no infection (n=5), Nb infection with DNP-Keyhole lympet hemocyanin (DNP-KLH) injected (n=5), and no infection but DNP-KLH injected group (n=5), and bled from the tail vein at days 0, 14 and 21 PI to collect blood and sera.
Worm recovery
At day 5 PI, infected IL-5 and normal mice were sacrificed under ether anesthesia, and worms were harvested from the small intestine. The intestine was opened longitudinally on a wire mesh in a Baermann's apparatus and incubated in warm saline for 3 hr. Worms were collected from the bottom of the test tube, and counted under a dissecting microscope.
Cell counts
Total white blood cell (WBC) counts (/mm3) were done by staining of the blood with Turk's solution. The number of eosinophils (/mm3) in the peripheral blood was calculated using the total WBC counts and differential percentages of leukocytes on thin blood films stained with modified Giemsa (Diff-Q, Fisher Sci., USA). WBC and eosinophil counts were done at days 0 and 21 PI.
Serum IgE assay
Total serum IgE levels of 4 groups of mice at days 0, 14 and 21 PI were measured by a sandwitch enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA). Rat anti-mouse IgE monoclonal antibody (6HD5) was purified from culture supernatant using protein G-agarose (Genzyme, Cambridge, USA). Horseradish-peroxidase-labeled goat anti-mouse IgE (Nordic, California, USA) was used as the secondary antibody. ABTS [2,2-azinobis(3-ethylbenzthiazoline sulfonic acid)] (Sigma, St. Louis, USA) solution was used as a substrate. Quantitation of the total serum IgE was done using the standard curve of anti-DNP mouse IgE antibody (Yamasa Corp., Chiba, Japan).
Hapten-carrier effects on IgE response
In order to observe carrier effects of Nb for production of anti-hapten (DNP) specific IgE antibodies (Kojima and Ovary, 1975a, 1976), mice were injected with DNP-KLH 21 days prior to Nb infection, and DNP-Nb soluble antigen was injected 14 days after Nb infection. Mice were bled 7 days later to collect sera.
Passive cutaneous anaphylaxis (PCA)
Anti-DNP specific IgE titers were measured by PCA in normal Sprague-Dawley rats (280-300 g, males) as previously described (Kojima and Ovary, 1976). Briefly, the back skin of the rat was shaved and 0.1 ml of serum dilutions (1:10, 1:40, 1:160, 1:640, 1:2,560, and 1:10,240) were serially injected intradermally. Rats were then challenged intravenously with 1 mg of DNP-bovine serum albumin (BSA) in 1 ml of saline containing 1% Evans blue dye 2 hr later. Reciprocals of the last dilution giving a threshold reaction (5 mm in diameter) were taken as the titer of IgE antibodies.
Statistical test
The data were expressed as the mean ± SD (standard deviation). The statistical significance was analyzed by Student's t test. P values lower than 0.05 were considered statistically significant.
RESULTS
Worm recovery
The number of intestinal Nb adult worms recovered at day 5 PI was significantly different between two different genetic backgrounds of mice (P<0.001); normal C3H/HeN and IL-5 transgenic (Table 1). IL-5 mice appeared highly resistant against Nb infection showing only 3.7% of the worm recovery rate, in contrast to normal C3H/HeN mice which revealed 30.8% of the worm recovery rate (Table 1). Two other repeated experiments revealed similar results.
Total WBC counts
The total WBC count (/mm3) in the peripheral blood of Nb infected C3H/HeN mice at day 21 PI was 15,900 ± 2,672, a significantly higher value compared with 10,360 ± 3,661 of uninfected C3H/HeN mice (P<0.05) (Fig. 1). In case of IL-5 mice, however, those infected with Nb showed total WBC count of 54,040 ± 14,520, which showed no significant difference from their uninfected counterparts, 53,900 ± 13,442 (P>0.05) (Fig. 1).
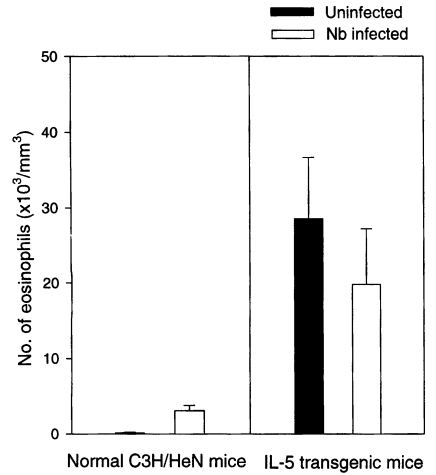
Eosinophil numbers
The blood eosinophil count (/mm3) was 3,121 ± 714 in Nb infected C3H/HeN mice at day 21 PI, which was a more than 20-fold increased value of uninfected group (P<0.05) (Fig. 2). But the eosinophil count of Nb infected IL-5 mice was 19,749 ± 7,474, significantly lower than that of uninfected IL-5 mice, 28,539 ± 8,114 (P<0.05) (Fig. 2).
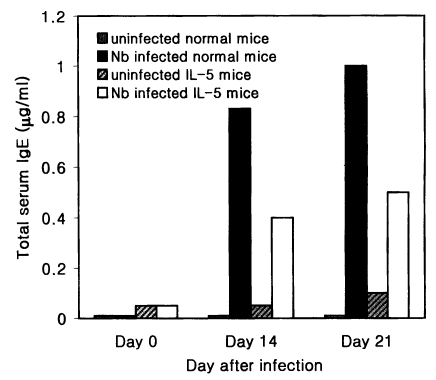
Total serum IgE levels
The total serum IgE level of Nb infected C3H/HeN mice was 0.83 and 1.0 µg/ml on average at days 14 and 21 PI, respectively, which were 83- and 100-fold higher values of uninfected C3H/HeN mice (Fig. 3). In IL-5 mice, however, the mean level of the total serum IgE at days 14 and 21 PI was 0.4 and 0.5 µg/ml, respectively, in Nb infected group, which were only 8- or 5-fold higher than in uninfected counterparts (Fig. 3).
Total serum IgE levels in DNP-KLH primed mice
The total serum IgE level was found to increase 28 and 67 folds in hapten (DNP-KLH) primed Nb infected C3H/HeN mice at days 14 and 21 PI, respectively, compared with hapten injected uninfected mice (Fig. 4). However, in IL-5 mice, Nb infection brought about only 7- and 10-fold increases of the total IgE at days 14 and 21 PI, respectively, by DNP priming (Fig. 4).

Total serum IgE levels (average values, n=5) in hapten (DNP-KLH) primed normal C3H/HeN and IL-5 transgenic mice experimentally infected with Nippostrongylus brasiliensis (at days 0, 14 and 21 PI). Hapten priming was done 21 days before Nb infection, and hapten-carrier (DNP-Nb soluble antigen) was injected at day 14 PI. Nb infected IL-5 mice reveal weaker responses than Nb infected normal mice.
Anti-DNP specific IgE levels in DNP-KLH primed mice
In DNP-primed C3H/HeN mice, anti-DNP specific IgE titer, as measured by PCA reaction on the rat skin, was fairly high (1:160) in uninfected mice and increased 64 folds by Nb infection at day 21 PI (Table 2). In unprimed C3H/HeN mice, however, the titer was negligible (lower than 1:10) in uninfected mice, and increased to 1:160 by Nb infection (Table 2).
Anti-DNP-specific IgE titers of sera from normal and IL-5 transgenic mice infected with Nippostrongylus brasiliensis as revealed by the passive cutaneous anaphylaxis (PCA) reaction
In IL-5 mice, the anti-DNP specific IgE titer was 1:20 in uninfected controls and increased to 1:1,280 in Nb infected group (Table 2). In unprimed IL-5 mice, the titer was lower than 1:10 irrespective of Nb infection.
DISCUSSION
IL-5 is produced chiefly from CD4+ helper T2 (Th2) cells but can also from CD4-CD8- T cells, upon various stimulations including helminthic infections (Coffman et al., 1989; Takamoto et al., 1995). IL-5 regulates generation of eosinophil precursors in the bone marrow and promotes development and differentiation of eosinophils in the peripheral blood (Takatsu et al., 1994). IL-5 also induces terminal differentiation of B cells to immunoglobulin-secreting cells (Takatsu et al., 1988).
After IL-5 transgenic mice were developed, it was found that they constitutively produce high levels of eosinophils and serum IgE together with elevated IL-5 (Tominaga et al., 1991, 1993). In humans and rats, there is evidence that eosinophils and IgE may be important in host defense against helminths such as schistosomes (Capron et al., 1981; Gounni et al., 1994). Therefore, it is a question whether they could protect themselves from helminthic infections.
Several papers on this subject were published, but conflicting results were demonstrated. Whereas IL-5 mice could protect themselves from Nb (Shin et al., 1997) or Angiostrongylus cantonensis (Sugaya et al., 1997) infection, they failed to protect from Schistosoma mansoni (Dent et al., 1997) or Toxocara canis (Sugane et al., 1996; Hokibara et al., 1997) infection. The reasons for this discrepancy remained to be further elucidated.
The present study confirmed resistance of IL-5 mice to Nb infection, whereas normal mice were highly susceptible to the same infection. In normal Nb infected mice, eosinophilia was about 20% at day 21 PI and total serum IgE level increased 80-100 folds compared with uninfected controls. In case of IL-5 mice, before Nb infection, they already revealed 40-60% eosinophilia and 10-fold higher level of IgE than normal mice. Interestingly, however, their eosinophilia was not further enhanced but reduced a little after Nb infection, and increase of serum IgE concentration was not so remarkable after Nb infection compared with normal Nb infected mice.
For the resistance of IL-5 mice to Nb infection, eosinophils were suggested to play a key role, since an adoptive transfer of eosinophils from IL-5 mice into normal mice resulted in a reduction of worm recovery (Shin et al., 1997). Moreover, the protection was strongly suggested to occur during the migration stage of Nb, because IL-5 mice revealed a significantly lower worm recovery rate at lungs than normal mice from as early as 1.5 days PI (Shin et al., 1997). In this study, the reduced level of eosinophilia in IL-5 mice after Nb infection may have resulted from sequestration of some proportion of eosinophils in the skin and lungs in order to kill migrating Nb larvae.
Participation of IgE in the protective mechanisms of mice against Nb infection seems less probable, because IgE-independent protection of mice against Nb was already documented using IgE-deficient SJA/9 mice (Watanabe et al., 1988) or IL-4 deficient mice (Urban et al., 1998). In this study, however, strong serum IgE responses were observed in normal C3H/HeN mice after Nb infection at days 14 and 21 PI, regarding it as a secondary response rather than a protective mechanism. But in Nb infected IL-5 mice the response was not so remarkable and the real level of serum IgE concentration was only a half of Nb infected normal mice. There could be two reasons. One is that IgE of IL-5 mice may have been utilized by the host to control Nb infection, and another may be no significant production of IgE even after Nb infection. The former seems less probable because IgE in IL-5 mice is not Nb-specific and Nb is quickly eliminated before stimulation of specific IgE production by host B cells.
Measurement of specific IgE is very difficult because of its very low concentration in sera. Therefore, in the present study, hapten (DNP)-carrier (Nb) effect (Kojima and Ovary, 1975a, 1976) was studied in IL-5 and normal mice. It is well known that using Nb as a carrier protein anti-hapten specific IgE production can be induced very strongly, and at this time the induced Th cells are Nb specific (Kojima and Ovary, 1975a, 1975b). Whereas total serum IgE and anti-DNP specific IgE levels of uninfected normal mice primed with DNP were negligible, they were strikingly elevated in DNP-primed Nb infected normal mice. This result suggests that Nb played an excellent carrier role, inducing carrier-specific Th cells. In IL-5 mice, however, total and anti-DNP specific IgE responses were both remarkably lower than in normal mice, strongly indicating that Nb failed to survive and stimulate Th cells in the host animal.
In conclusion, IL-5 mice appeared to be constitutively resistant to Nb infection, and for this reason eosinophilia and IgE responses are not augmented after Nb infection, but rather decreased a little (eosinophils) or insignificantly increased (IgE).
Notes
This study was supported by a grant from the Seoul National University College of Medicine Research Fund (1997).