1. Larsen CS. Biological changes in human populations with agriculture.
Ann Rev Anthropol 1995;24:185-213.

2. Kim MJ, Ki HC, Kim S, Chai JY, Seo M, Oh CS, Shin DH. Parasitic infection patterns as correlated with urban-rural recycling of night soils in Korea and other East Asian countries: the archaeological and historical evidence.
Korean Studies 2014;38:51-74.

3. Wheelwright J. Days of Dysevolution Discovery 2015;32-39.
4. Barnes E. Diseases and Human Evolution. Albuquerque, USA. University of New Mexico Press. 2005.
6. Ruffer MA. Note on the presence of “
Bilharzia haematobia” in Egyptian mummies of the twentieth dynasty (1250–1000 BC).
Br Med J 1910;1:16.


7. Ferreira LF, Araújo A, Confalonieri U. Congresso Brasileiro De Parasitologia, editors. 2. Resumos. Campinas, SP: 1979. Subsidios para a Paleoparasitologia do Brasil I-Parasitos encontrados em coprólitos no município de Unai, Minas Gerais. p 56.


8. Ferreira LF, Reinhard K, Araújo A. Fundamentos da Paleoparasitologia. Rio de Janeiro, Brazil. Editora Fiocruz. 2011, p 484.


9. Seo M, Araujo A, Reinhard K, Chai JY, Shin DH. Paleoparasitological studies on mummies of the Joseon Dynasty, Korea.
Korean J Parasitol 2014;52:235-242.

10. Le Bailly M, Gonçalves ML, Lefèvre C, Roper DC, Pye JW, Araujo A, Bouchet F. Parasitism in Kansas in the 1800s: a glimpse to the past through the analysis of grave sediments from Meadowlark cemetery.
Mem Inst Oswaldo Cruz 2006;101( suppl 2):53-56.


11. Le Bailly M, Landolt M, Bouchet F. First World War German soldier intestinal worms: an original study of a trench latrine in France.
J Parasitol 2012;98:1273-1275.

12. Reinhard KJ, Araújo A, Sianto L, Costello JG, Swope K. Chinese liver flukes in latrine sediments from Wong Nim’s Property, San Bernardino, California: archaeoparasitology of the Caltrans District Headquarters.
J Parasitol 2008;94:300-303.

13. Mitchell PD, Anastasiou E, Syon D. Human intestinal parasites in crusader Acre: evidence for migration with disease in the medieval period. Int J Paleopathol 2011;1:132-137.
14. Seo M, Oh CS, Chai JY, Lee SJ, Park JB, Lee BH, Park JH, Cho GH, Hong DW, Park HU, Shin DH. The Influence of differential burial preservation on the recovery of parasite eggs in soil samples from Korean Medieval tombs.
J Parasitol 2010;96:366-370.

15. Schulz S, Kroeger A. Soil contamination with Ascaris lumbricoides eggs as an indicator of environmental hygiene in urban areas of north-east Brazil. J Trop Med Hyg 1992;95:95-103.
16. Uga S, Ono K, Kataoka N, Safriah A, Tantular IS, Dachlan YP, Ranuh IG. Contamination of soil with parasite eggs in Surabaya, Indonesia.
Southeast Asian J Trop Med Public Health 1995;26:730-734.



17. Uga S, Nagnaen W, Chongsuvivatwong V. Contamination of soil with parasite eggs and oocysts in southern Thailand.
Southeast Asian J Trop Med Public Health 1997;28( suppl 3):14-17.

18. Chongsuvivatwong V, Uga S, Nagnaen W. Soil contamination and infections by soil-transmitted helminths in an endemic village in southern Thailand.
Southeast Asian J Trop Med Public Health 1999;30:64-67.


19. Callen EO, Cameron TWM. A prehistoric diet as revealed in coprolites.
New Scientist 1960;8:35-40.

20. Criscione CD, Anderson JD, Sudimack D, Peng W, Jha B, Williams-Blangero S, Anderson TJ. Disentangling hybridization and host colonization in parasitic roundworms of humans and pigs.
Proc Biol Sci 2007;274:2669-2677.

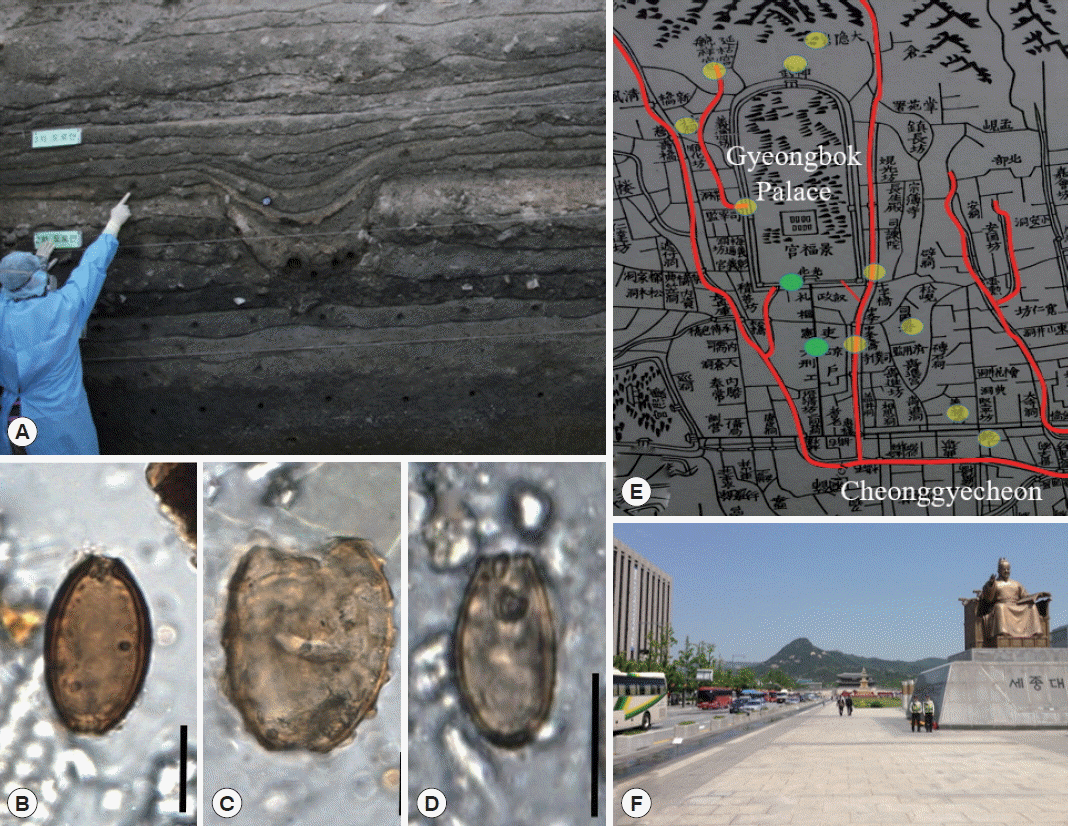
21. Shin DH, Oh CS, Lee SJ, Chai JY, Kim J, Lee SD, Park JB, Choi IH, Lee HJ, Seo M. Paleo-parasitological study on the soils collected from archaeological sites in old district of Seoul City. J Arch Sci 2011;38:3555-3559.
22. Shin DH, Shim SY, Jeong HJ, Kim MJ, Lee MH, Kim KY, Lee IH, Kim G, Chai JY, Oh CS, Seo M. A Paleoparasitological Study on the Capital Area of the Ancient Korean Kingdom.
J Parasitol 2015;101:458-461.


23. Shin DH, Oh CS, Shin YM, Cho CW, Seo M. The pattern of ancient parasite egg contamination in the private residence, alley, ditch and streambed soils of old Seoul City, the capital of Joseon dynasty.
Int J Paleopathol 2013;3:208-213.


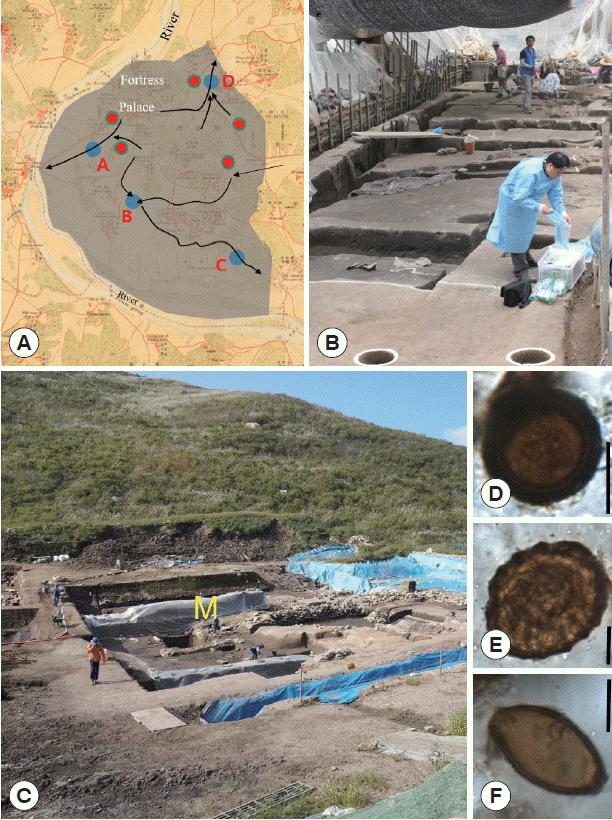
24. Kim MJ, Seo M, Oh CS, Chai JY, Lee J, Kim GJ, Ma WY, Choi SJ, Reinhard K, Araujo A, Shin DH. Paleoparasitological study on the soil sediment samples from archaeological sites of ancient Silla Kingdom in Korean peninsula.
Quart Int 2016;405:80-86.


25. Monckton A. Environmental archaeology in Leicestershire. Transactions of the Leicestershire.
Arch Hist Soc 1995;69:32-41.

26. Matsui A, Kanehara M, Kanehara M. Palaeoparasitology in Japan-discovery of toilet features. Mem Inst Oswaldo Cruz 2003;98( suppl 1):127-136.
27. Fernandes A, Ferreira LF, Gonçalves ML, Bouchet F, Klein CH, Iguchi T, Sianto L, Araujo A. Intestinal parasite analysis in organic sediments collected from a 16th-century Belgian archeological site. Cad Saude Publica 2005;21:329-332.
28. da Rocha GC, Harter-Lailheugue S, Le Bailly M, Araújo A, Ferreira LF, da Serra-Freire NM, Bouchet F. Paleoparasitological remains revealed by seven historic contexts from “Place d’Armes”, Namur, Belgium. Mem Inst Oswaldo Cruz 2006;101( suppl 2):43-52.
29. Mitchell PD, Stern E, Tepper Y. Dysentery in the crusader kingdom of Jerusalem: and ELISA analysis of two medieval latrines in the City of Acre (Israel).
J Arch Sci 2008;35:1849-1853.

30. Nesaki M. The human manure distribution of the Edo Era and the view of raw sewages. Hosei J Human Env 2008;9:1-21.
31. Tajima K. The marketing of urban human waste in the early modern Edo/Tokyo Metropolitan area. Env Urbain/Urban Env 2007;1:13-30.
32. Kim HJ. The great dredging works on Cheonggye-cheon in the Choson Dynasty. J Korea Water Resources Ass 2004;37:22-25.
33. Ki HC, Bae JH, Shin DH. Historical study on factors inducing soil-transmitted helminth infection among people of old Seoul City during Joseon Dynasty. Uisahak (Med Hist) 2013;22:89-132.
38. Miksic JN. Water, urbanization, and disease in Ancient Indonesia.
Archeol Papers Am Anthropol Assoc 2008;9:167-184.

39. Shin DH, Oh CS, Chung T, Yi YS, Chai JY, Seo M. Detection of parasite eggs from a moat encircling the royal palace of Silla, the ancient Korean Kingdom.
J Arch Sci 2009;36:2534-2539.