1. Elliott I, Pearson I, Dahal P, Thomas NV, Roberts T, et al. Scrub typhus ecology: a systematic review of
Orientia in vectors and hosts.
Parasit Vectors 2019;12(1):513
https://doi.org/10.1186/s13071-019-3751-x



2. Bhate R, Pansare N, Chaudhari Sp, Barbuddhe SB, Choudhary VK, et al. Prevalence and phylgenetic analysis of
Orientia tsutsugamushi in rodents and mites from Central India.
Vector Borne Zoonotic Dis 2017;17(11):749-754
https://doi.org/10.1089/vdz.2017.2159


3. Ha JH, Lee DH, Park JS, Cho OH, Kim DH, et al. Isolation and genetic characterization of
Orientia tsutsugamushi from scrub typhus patients in Gyeongsangnam-do, Korea.
J Bacteriol Virol 2016;46(4):275-282
https://doi.org/10.4167/jbv.2016.46.4.275

4. Roh JY, Song BG, Park WI, Shin EH, Park C, et al. Coincidence between geographical distribution of
Leptotrombidium scutellare and scrub typhus incidence in South Korea.
PLoS One 2014;9(12):e113193
https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone0113193



6. Kelly DJ, Fuerst PA, Ching WM, Richards AL. Scrub typhus: the geographic distribution of phenotypic and genotypic variants
Orientia tsutsugamushi
.
Clin Infect Dis 2009;48(suppl):203-230
https://doi.org/10.1086/596576


8. Choi YJ, Lee IY, Song HJ, Kim J, Park HJ, et al. Geographical distribution of
Orientia tsutsugamushi strains in chiggers from three provinces in Korea.
Microbiol Immun 2018;62(9):547-553
https://doi.org/10.1111/1348-0421.12639


9. Bahk YY, Ahn SK, Lee J, Kwon HW, Hong SJ, et al. Monitoring chigger mites for
Orientia tsutsugamushi in field small mammals in Hwaseong-si, Gyeonggi-do, Korea, 2019–2020.
Korean J Parasitol 2021;59(3):319-324
https://doi.org/10.3347/kjp.2021.59.3.319



10. Shim SK, Choi EN, Yu KO, Park HJ, Kim CM, et al. Characterisation of
Orientia tsutsugamushi genotypes from wild rodents and chigger mites in Korea.
Clin Microbiol Infect 2009;15(suppl):311-312
https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1469-0691.2008.02254.x


11. Mills JN, Corneli A, Young JC, Garrison LE, Khan AS, et al. Hantavirus pulmonary syndrome-United States: updated recommendation for risk reduction. MMWR Recomm Rep 2002;51(RR-9):1-12.
12. Ree HI. Fauna and key to the chigger mites of Korea (Acarina: Trombiculidae and Leeuwenhoekiidae). Korea J Syst Zool 1990;6:57-70.
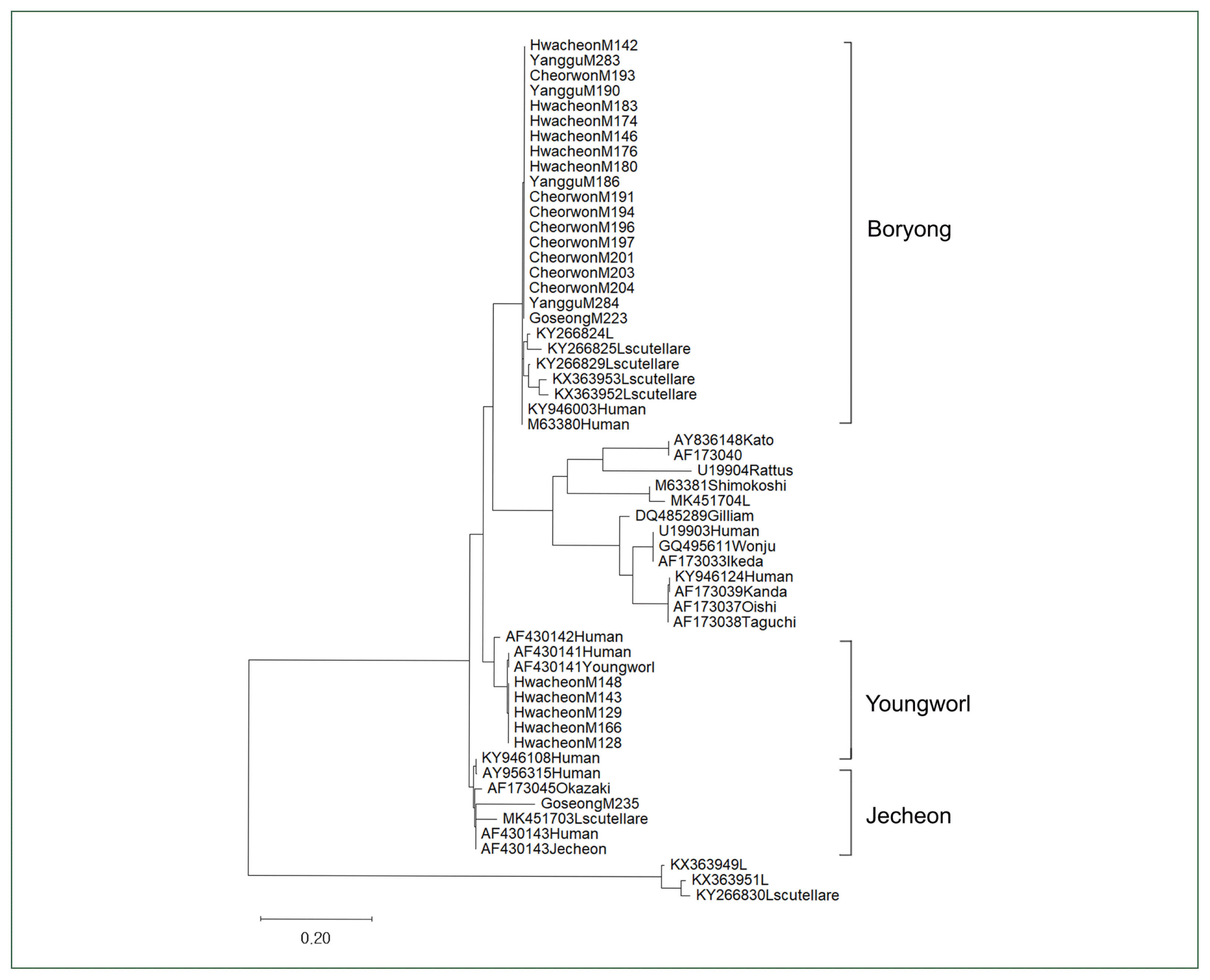
14. Kumar S, Stecher G, Li M, Knyaz C, Tamura K. MEGA X: molecular evolutionary genetics analysis across computing platforms.
Mol Biol Evol 2018;35(6):1547-1549
https://doi.org/10.1093/molbev/msy096



17. Tamura K, Stecher G, Peterson D, Filipski A, Kumar S. MEGA6: molecular evolutionary genetics analysis Version 6.0.
Mol Biol Evol 2013;30(12):2725-2729
https://doi.org/10.1093/molbev/mst197



18. Lee IY, Kim HC, Lee YS, Seo JH, Lim JW, et al. Geographical distribution and relative abundance of vectors of scrub typhus in the Republic of Korea.
Korean J Parsitol 2009;47(4):381-386
https://doi.org/10.3347/kjp.2009.47.4.381



19. Lee IY, Lim JW, Seo JH, Kim HC, Lee KJ, et al. Geographical distribution and epidemiologic factors of chigger mites on
Apodemus agrarius during autumn in Korea.
Korean J Parasitol 2021;59(5):473-479
https://doi.org/10.3347/kjp.2021.59.5.473



20. Kim SY, Gill B, Song BG, Chu H, Park WI, et al. Annual fluctuation in chigger mite populations and
Orientia tsutsugamushi infections in scrub typhus endemic regions of South Korea.
Osong Public Health Res Perpect 2019;10(6):351-358
https://doi.org/10.24171/j.phrp.2019.10.6.05



21. Lee IY, Ree HI, Hong HK. Seasonal prevalence and geographical distribution of trombiculid mites (Acarina: Trombiculidae) in Korea. Korean J Zool 1993;36(3):408-415 (in Korean).
22. Ree HI, Chang WH, Kee SH, Lee IY, Jeon SH. Detection of
Orientia tsutsugamushi DNA in individual trombiculids using polymerase chain reaction in Korea.
Med Entomol Zool 1997;48(3):197-209
https://doi.org/10.7601/mez.48.197

23. Ree HI, Lee IY, Jeon SH, Yoshida Y. Geographical distribution of vectors and sero-strains of tsutsugamushi disease at mid-south inland of Korea.
Korean J Parasitol 1997;35(3):171-179
https://doi.org/10.3347/kjp.1997.35.3.171


24. Kim HC, Lee IY, Cheong ST, Richards AL, Gu SH, et al. Serosurveillance of scrub typhus in small mammals collected from military training sites near the DMZ, northern Gyeonggi-do, Korea and analysis of the relative abundance of chiggers from mammals examined.
Korean J Parasitol 2010;48(3):237-243
https://doi.org/10.3347/kjp.2010.48.3.237



26. Park SW, Lee CK, Kwak YG, Moon C, Kim BN, et al. Antigenic drift of
Orientia tsutsugamushi in South Korea as identified by the sequence analysis of a 56-kDa protein-encoding gene.
Am J Trop Med Hyg 2010;83(4):930-935
https://doi.org/10.4269/ajtmh.2010.09-0791



27. Noh MS, Lee YJ, Chu CS, Gwack J, Youn SK, et al. Are there spatial and temporal correlations in the incidence distribution of scrub typhus in Korea?
Osong Public Health Res Perspect 2013;4(1):39-44
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.phrp.2013.01.002