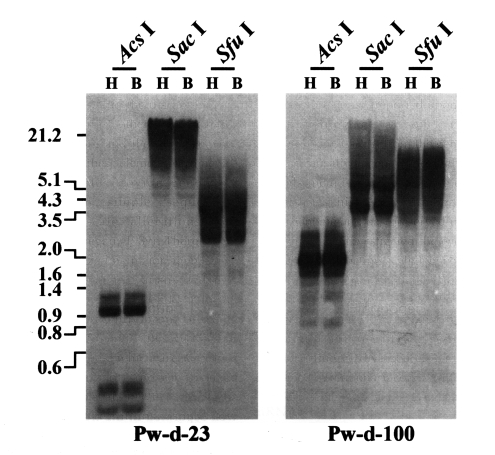
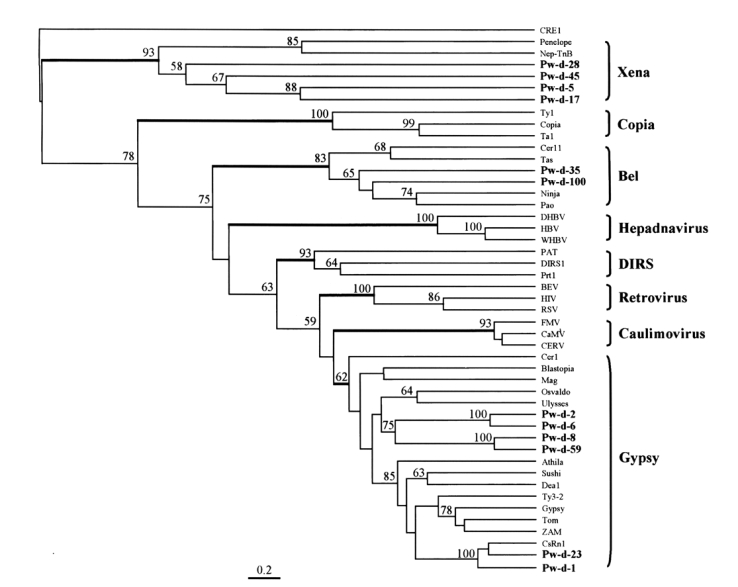
1. Abe H, Kanehara M, Terada T, et al. Identification of novel random amplified polymorphic DNAs (RAPDs) on the W chromosome of the domesticated silkworm,
Bombyx mori, and the wild silkworm,
B. mandarina, and their retrotransposable element-related nucleotide sequences.
Genes Genet Syst 1998;73:243-254.

2. Altschul SF, Madden TL, Schaffer AA, et al. Gapped BLAST and PSI-BLAST: a new generation of proteindatabase search programs.
Nucleic Acids Res 1997;25:3389-3402.

3. Bae YA, Moon SY, Kong Y, Cho SY, Rhyu MG. CsRn1, a novel active retrotransposon in a parasitic trematode,
Clonorchis sinensis, discloses a new phylogenetic clade of
Ty3/gypsy-like LTR retrotransposons.
Mol Biol Evol 2001;18:1474-1483.

4. Blair D, Xu ZB, Agatsuma T. Paragonomiasis and the genus
Paragonimus.
Adv Parasitol 1999;42:113-222.

5. Blesa D, Martínez-Sebastián MJ. Bilbo, a non-LTR retrotransposon of
Drosophila subobscura: a clue to the evolution of LINE-like elements in
Drosophila.
Mol Biol Evol 1997;14:1145-1153.

6. Boeke JD, Garfinkel DJ, Styles CA, Fink GR.
Ty elements transpose through an RNA intermediate.
Cell 1985;40:491-500.

7. Bowen NJ, McDonald JF. Genomic analysis of
Caenorhabditis elegans reveals ancient families of retroviral-like elements.
Genome Res 1999;9:924-935.

8. Brindley PJ, Laha T, McManus DP, Loukas A. Mobile genetic elements colonizing the genomes of metazoan parasites.
Trends Parasitol 2003;19:79-87.

9. Chomczynski P. A reagent for the single-step simultaneous isolation of RNA, DNA, and proteins from cell and tissue samples. Biotechniques 1993;15:532-534.
10. Cook JM, Martin J, Lewin A, Sinden RE, Tristem M. Systematic screening of
Anopheles mosquito genomes yields evidence for a major clade of Pao-like retrotransposons.
Insect Mol Biol 2000;9:109-117.

11. Copeland CS, Brindley PJ, Heyers O, et al.
Boudica, a retrovirus-like long terminal repeat retrotransposon from the genome of the human blood luke
Schistosoma mansoni.
J Virol 2003;77:6153-6166.

12. Dalle Nogare DE, Clark MS, Elgar G, Frame IG, Poulter RT.
Xena, a full-length basal retroelement from tetraodontid fish.
Mol Biol Evol 2002;19:247-255.

13. Drew AC, Brindley PJ. A retrotransposon of the non-long terminal repeat class from the human blood fluke
Schistosoma mansoni. Similarities to the chicken-repeat-1-like elements of vertebrates.
Mol Biol Evol 1997;14:602-610.

14. Evgen'ev MB, Zelentsova H, Shostak N, et al.
Penelope, a new family of transposable elements and its possible role in hybrid dysgenesis in
Drosophila virilis.
Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 1997;94:196-201.

15. Felder H, Herzceg A, de Chastonay Y, Aeby P, Tobler H, Muller F.
TAS, a retrotransposon from theparasitic nematode
Ascaris lumbricoides.
Gene 1994;149:219-225.

17. Finnegan DJ. Transposable elements.
Curr Opin Genet Dev 1992;2:861-867.

18. Kido Y, Saitoh M, Murata S, Okada N. Evolution of the active sequences of the
Hpa I short interspersed elements.
J Mol Evol 1995;41:986-995.

19. Kidwell MG, Lisch D. Transposable elements as sources of variation in animals and plants.
Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 1997;94:7704-7711.

20. Labrador M, Farre M, Utzet F, Fontdevila A. Interspecific hybridization increase transposition rates of
Osvaldo.
Mol Biol Evol 1999;16:931-937.

21. Li WH, Gu Z, Wang H, Nekrutenko A. Evolutionary analyses of the human genome.
Nature 2001;409:847-849.

22. Malik HS, Burke WD, Eickbush TH. The age and evolution of non-LTR retrotransposable elements.
Mol Biol Evol 1999;16:793-805.

23. Malik HS, Eickbush TH. Molecular evolution of the integrase domain in the Ty3/Gypsy class of LTR retrotransposons. J Virol 1999;73:5186-5190.
24. Malik HS, Eickbush TH. Phylogenetic analysis of ribonuclease H domains suggests a late, chimeric origin of LTR retrotransposable elements and retroviruses.
Genome Res 2001;11:1187-1197.

25. Manninen O, Kalendar R, Robinson J, Schulman AH. Application of
BARE-1 retrotransposon markers to the mapping of a major resistance gene for net blotch in barley.
Mol Gen Genet 2000;264:325-334.

26. Nicholas KB, Nicholas HB Jr. GeneDoc: a tool for editing and annotation multiple sequence alignments; 1997. Distributed by the authors (
www.cris.com/~ketchup/genedoc.html)
27. O'Neill RJ, O'Neill MJ, Graves JA. Undermethylation associated with retroelement activation and chromosome remodeling in an interspecific mammalian hybrid.
Nature 1998;393:68-72.

28. Page RD. Tree View: an application to display phylogenetic trees on personal computers.
Comput Appl Biosci 1996;12:357-358.

29. Park GM, Lee KJ, Im KI, Park H, Yong TS. Occurrence of a diploid type and a new first intermediate host of a human lung fluke,
Paragonimus westermani, in Korea.
Exp Parasitol 2001;99:206-212.

30. Peterson-Burch BD, Voytas DF. Genes of the Pseudoviridae (
Ty1/copia retrotransposons).
Mol Biol Evol 2002;19:1832-1845.

31. Pringle CR. Virus taxonomy-1999. The universal system of virus taxonomy, updated to include the new proposals ratified by the International Committee onTaxonomy of Viruses during 1998.
Arch Virol 1999;144:421-429.

32. Regev A, Lamb MJ, Jablonka E. The role of DNA methylation in invertebrates: developmental regulation or genome defense?
Mol Biol Evol 1998;15:880-891.

33. SanMiguel P, Tikhonov A, Jin YK, et al. Nested retrotransposons in the intergenic regions of the maize genome.
Science 1996;274:765-768.

34. Thompson JD, Gibson TJ, Plewniak E, Jeanmougin F, Higgins DG. The ClustalX windows interface: flexible strategies for multiple sequence alignments aided by quality analysis tools.
Nucleic Acids Res 1997;25:4876-4882.

35. Tristem M. Amplification of divergent retroelements by PCR. Biotechniques 1996;20:608-612.
36. Xiong Y, Eickbush TH. Origin and evolution of retroelements based upon their reverse transcriptase sequences. EMBO J 1990;9:3353-3362.
37. Zhao XP, Si Y, Hanson RE, et al. Dispersed repetitive DNA has spread to new genomes since polyploid formation in cotton. Genome Res 1998;8:479-492.