Evolution of Genetic Polymorphisms of Plasmodium falciparum Merozoite Surface Protein (PfMSP) in Thailand
Article information
Abstract
Plasmodium falciparum malaria is a major public health problem in Thailand due to the emergence of multidrug resistance. The understanding of genetic diversity of malaria parasites is essential for developing effective drugs and vaccines. The genetic diversity of the merozoite surface protein-1 (PfMSP-1) and merozoite surface protein-2 (PfMSP-2) genes was investigated in a total of 145 P. falciparum isolates collected from Mae Sot District, Tak Province, Thailand during 3 different periods (1997-1999, 2005-2007, and 2009-2010). Analysis of genetic polymorphisms was performed to track the evolution of genetic change of P. falciparum using PCR. Both individual genes and their combination patterns showed marked genetic diversity during the 3 study periods. The results strongly support that P. falciparum isolates in Thailand are markedly diverse and patterns changed with time. These 2 polymorphic genes could be used as molecular markers to detect multiple clone infections and differentiate recrudescence from reinfection in P. falciparum isolates in Thailand.
Malaria remains one of the most important public health problems in several tropical countries. Plasmodium falciparum infection causes clinical symptoms ranging from asymptomatic to the rarer complications of severe manifestations. Cerebral malaria (CM) is one of the major pathological complications of P. falciparum infection in humans manifesting as coma that can lead to death. The emergence and spread of resistance of P. falciparum to antimalarial drugs is an important factor for malaria control in endemic areas [1]. The resistance of P. falciparum has occurred to all classes of antimalarial drugs except artemisinin and its derivatives. The understanding of genetic diversity of malaria parasites is essential for developing effective drugs and vaccines. The merozoite surface protein-1 (MSP-1) of P. falciparum is a major surface protein with an approximate molecular size of 190 kDa. MSP-1 exerts a key role in erythrocyte invasion by the merozoite [2]. It is a target of human immune responses [3] and a promising candidate for a blood stage subunit vaccine [4]. MSP-2 of P. falciparum is another candidate antigen for a subunit malaria vaccine [5]. The objective of this study was to investigate genetic diversity of PfMSP-1 and PfMSP-2 genes in blood samples collected from 145 patients with uncomplicated P. falciparum malaria in Mae Sot District of Thailand during the 3 different study periods.
A total of 145 blood samples were collected from patients attending the malaria clinic in Mae Sot District, Tak Province during 3 different periods, i.e., 1997-1999 (n=49), 2005-2007 (n=50), and 2009-2010 (n=46). Approval of the study protocol was obtained from the Ethics Committees of Ministry of Public Health, Thailand. Tak Province has been reported as the province with highest malaria incidence with approximately equal ratio of P. falciparum and P. vivax. Two milliliters of blood samples were collected by venipuncture prior to treatment with standard regimens for P. falciparum (a 3-day artesunate-mefloquine combination) and collected into EDTA collecting tubes. Giemsa-stained thin and thick blood smears were prepared and examined microscopically for P. falciparum. Parasite genomic DNA was extracted from whole blood using Chelex extraction method and used as the template for PCR amplification.
The amplification of PfMSP-1 and PfMSP-2 was carried out using PCR technique [6]. In the reaction, primer pairs corresponding to the conserved sequences spanning the polymorphic regions consisted of forward-5'GAAGATGCAGTATTGACAGG3' and reverse-5'GAGTTCTTTAATAGTGAACAAG3' for MSP-1 and forward-5'GAGTTCTTTAATAGTGAACAAG3' and reverse-5'CCTGTACCTTTATTCTCTGG3' for MSP-2 [6]. The reaction volume was 20 µl containing 1 µM of each of primer, 0.5 U of Taq polymerase, 1x of buffer with KCl (Fermentas, Burlington, Canada), 2.5 mM of MgCl2 (Fermentas), 0.5 mM of dNTP and DNA template. PCR was performed under 1 cycle of 5 min at 94℃, then 30 cycles of 1 min at 94℃, 1 min at 50℃, 1 min at 72℃, and final extension at 72℃ for 5 min of amplification condition. PCR products were analyzed on a 2% agarose gel containing ethidium bromide. The variation in size of the amplified products was observed.
The genetic diversity pattern of PfMSP-1 and PfMSP-2 were analyzed using GeneTools software (SYNGENE™, Cambridge, UK). This software automatically compensates for smiling or distorted bands and tracks. Molecular weight or base pair values can be calculated using 2 standards for comfirmation. Comparison of difference in gene patterns during 3 different periods of sample collection was performed using the chi-square test (SPSS version 12.0 software, SPSS Inc., Chicago, Illinois, USA). Statistical significance level was set at P=0.05.
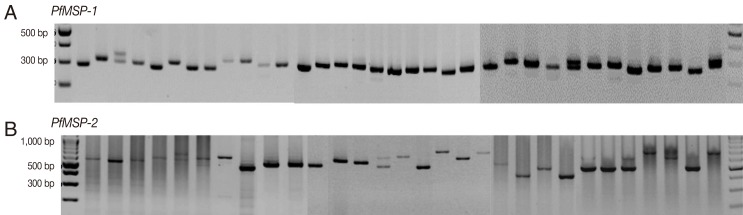
The amplification results of 145 samples during the 3 study periods (1997-1999, 2005-2007, and 2009-2010) were successful in 46 (94%), 50 (100%), and 46 (100%) for PfMSP-1 and 33 (67%), 29 (58%), and 39 (85%) for PfMSP-2, respectively. Both P. falciparum genes were highly polymorphic (Fig. 1) with different gene patterns in samples collected during the 3 periods (Tables 1-2). The dominant polymorphic sizes of PfMSP-1 and PfMSP-2 detected during 1997-1999, 2005-2007, and 2009-2010 were 300 and 500 bp, 300 and 480 bp, and 310 and 650 bp, respectively. The multiple clone infections were detected by 2 or more PCR fragments. A significant difference in the pattern of PfMSP-1 was observed between isolates collected during the period 1997-1999 vs 2005-2007 (P=0.002), 2005-2007 vs 2009-2010 (P<0.001), and between 1997-1999 vs 2009-2010 (P=0.028). For the pattern of PfMSP-2, significant difference was found between isolates collected during the period 1997-1999 vs 2005-2007 (P=0.050).

Summary of polymorphic sizes of PfMSP-1 in Plasmodium falciparum isolates collected during the 3 different study periods (1997-1999, 2005-2007, and 2009-2010)

Summary of polymorphic sizes of PfMSP-2 in Plasmodium falciparum isolates collected during the 3 different study periods (1997-1999, 2005-2007, and 2009-2010)
The polymorphic sizes of the combined PfMSP-1/PfMSP-2 were more diversed than each individual gene alone; 25, 23, and 32 patterns of PfMSP-1/PfMSP-2 polymorphisms were observed (Table 3). The dominant combination pattern found in samples collected during the period 1997-1999, 2005-2007, and 2009-2010 were 300/500, 300/610, and 310/650, respectively. A total of 5 (15.5%), 3 (17.8%), and 7 (18.4%) samples collected during the 3 periods showed multiple clone infections, respectively.
Several malarial proteins have been proposed as vaccine candidate antigens but MSP-1 is the most promising candidate [7,8]. Results of the phase 1-2b clinical trial of a MSP-2 based vaccine showed that 1 allelic type included in the vaccine may be more effective against malaria parasite [9]. P. falciparum MSP-2, apical membrane antigen-1 (AMA-1), and circumsporozoite protein (CSP) are also under investigation as candidate antigens for the development of malaria vaccine [10,11]. The polymorphisms of PfMSP-1 and PfMSP-2 have been investigated in isolates collected from several malaria endemic areas [12-16]. All showed highly polymorphic patterns of these 2 genes. High levels of PfMSP-1 and PfMSP-2 polymorphisms and multiple clonal infections were reported in 3 malaria endemic regions of Lao PDR [13]. Similarly, sequence analysis of PfMSP-1 block 2 in P. falciparum isolates collected from Myanmar demonstrated 14 different genotypes (5 for K1 type and 9 for MAD20 type), whereas 22 genotypes (7 for FC27 type and 15 for 3D7 type) were found with PfMSP-2 block 3 [12]. A recent report from Republic of Congo revealed high polymorphisms and multiple clones of P. falciparum isolates [15]. Moreover, isolates collected from Malawi, Tanzania, Uganda, Burkina Faso, and São Tomé exhibited highly polymorphic and low allele frequencies of PfMSP-1, PfMSP-2, and glurp, with a total of 17 PfMSP-1, 116 PfMSP-2, and 14 glurp genotypes [16]. In contrast, relatively low levels of genetic diversity were found in isolates collected from Haiti (9 PfMSP-1 genotypes) [14].
The results of the present study confirmed the genetic variations of PfMSP-1 and PfMSP-2 in isolates collected from Mae Sot District, the endemic area of Thailand with highest malaria incidence. Moreover, the combination of PfMSP-1/PfMSP-2 was relatively more polymorphic, and thus appropriate for application to detect multiple clone infections and differentiate recrudescence from reinfection in P. falciparum isolates in Thailand. The low efficacy of vaccine candidate antigens observed in various clinical trials would be due to the highly variable genetic polymorphisms of PfMSP-1 and PfMSP-2 in P. falciparum isolates.
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS
This work was supported by the Commission on Higher Education, Ministry of Education, Thailand, and the National Research University Project of Thailand Office of Higher Education Commission of Thailand.
Notes
We have no conflict of interest related with this study.