Abstract
Ascaris suum eggs are inactivated by composting conditions; however, it is difficult to find functional changes in heat-treated A. suum eggs. Here, unembryonated A. suum eggs were incubated at 20℃, 50℃, and 70℃ in vitro, and the gene expression levels related to viability, such as eukaryotic translation initiation factor 4E (IF4E), phosphofructokinase 1 (PFK1), and thioredoxin 1 (TRX1), and to apoptosis, such as apoptosis-inducing factor 1 (AIF1) and cell death protein 6 (CDP6), were evaluated by real-time quantitative RT-PCR. No prominent morphological alterations were noted in the eggs at 20℃ until day 10. In contrast, the eggs developed rapidly, and embryonated eggs and hatched larvae began to die, starting on day 2 at 50℃ and day 1 at 70℃. At 20℃, IF4E, PFK1, and TRX1 mRNA expression was significantly increased from days 2-4; however, AIF1 and CDP6 mRNA expression was not changed significantly. IF4E, PFK1, and TRX1 mRNA expression was markedly decreased from day 2 at 50℃ and 70℃, whereas AIF1 and CDP6 mRNA expression was significantly increased. The expressions of HSP70 and HSP90 were detected for 9-10 days at 20℃, for 3-5 days at 50℃, and for 2 days at 70℃. Taken together, incremental heat increases were associated with the rapid development of A. suum eggs, decreased expression of genes related to viability, and earlier expression of apoptosis-related genes, and finally these changes of viability- and apoptosis-related genes of A. suum eggs were associated with survival of the eggs under temperature stress.
-
Key words: Ascaris suum, egg, temperature, viability, apoptosis, real-time quantitative RT-PCR
Ascaris suum is an intestinal roundworm in pigs, with a life cycle identical to that of
Ascaris lumbricoides [
1].
A. suum eggs are able to survive a variety of treatment conditions [
2]. The longevity of infective
A. suum eggs represents an important public health issue because of the widespread use of pig manure as a fertilizer, including Korea [
3]. Some reports have demonstrated that
A. suum infects humans frequently [
4-
6]. Thus, when organic waste is reused in agriculture or gardening, pathogenic agents must be inactivated [
2].
Composted livestock excrement can be an effective, hygienically safe, and economical organic fertilizer [
7]. During the composting of organic wastes, temperatures of 65-71℃ have been measured on days 4-6 in the middle of a composting manure pile [
8], and several reports have demonstrated the inactivation of
Ascaris eggs over the temperature range used for sludge treatment [
2,
7-
9]. However, it is difficult to find functional changes in genes or proteins related to viability, apoptosis, and heat stress in
A. suum eggs during composting. Eukaryotic translation initiation factor 4E (IF4E), phosphofructokinase 1 (PFK1), and thioredoxin 1 (TRX1) genes are involved in the development, cell cycle control, mammalian glycolytic pathway, anti-inflammatory and antiapoptotic effects, antioxidative effects [
10-
12], apoptosis-inducing factor 1 (AIF1), and cell death protein 6 (CDP6) genes related with apoptosis. Here,
A. suum eggs were incubated in vitro at 20℃, 50℃, and 70℃, and the morphological characteristics, mRNA expression levels of IF4E, PFK1, TRX1, AIF1, and CDP6; and the protein levels of heat shock protein (HSP) 70 and HSP90 were evaluated by microscopy, real-time quantitative reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction (real-time qRT-PCR), and western blotting, respectively.
A. suum eggs were collected from the uteri of female adult worms and shaken for 5 min in 0.5% sodium hypochlorite to remove their outer proteinaceous coating. After washing with physiologic saline (0.9% NaCl), eggs were transferred to a Petri dish and incubated with physiologic saline at 20℃, 50℃, and 70℃ for 40 days to examine the survival period of the eggs. About 200 eggs were examined in each case, and the development of the eggs was evaluated under a microscope on the basis of morphological changes in the germinal cells and the presence of viable larvae in the eggs or hatched larvae. We also evaluated the expression levels of genes or proteins related to viability, apoptosis, and heat stress for 10 days.
Real-time qRT-PCR analyses of IF4E, PFK1, TRX1, AIF1, and CDP6 expressions were performed using the ABI StepOne Real-Time PCR System (Applied Biosystems, Foster City, California, USA). All assays used a similar amplification efficiency, with a ΔCT experimental design for relative quantification. The reactions were performed in triplicate in a 20-µl reaction volume containing 10 µl of the expression probe (Power SYBR Green PCR Master mix; Applied Biosystems), 1 µl of forward (F)-primer, 1 µl of reverse (R)-primer, 2 µl of cDNA, and 6 µl of distilled water. The resulting calibration graph (CT vs. log unit of the standard template) correlates CT values with the amount of template in the reaction. This calibration was performed separately for every amplicon. To standardize the amount of cDNA used, the housekeeping gene encoding elongation factor 1-α (EF1α) served as an endogenous control. The amplification program consisted of 10 min at 95℃ followed by 40 cycles of 15 sec at 95℃ and 1 min at 60℃. The oligonucleotides used were: EF1α-F, 5'-CCCTTAGACTGCCTCTCCAAGAC-3'; EF1α-R, 5'-CGACCGACTTCACCTCGGTGGTA-3'; IF4E-F, 5'-GTATTTGAAGGCGGATCGAA-3'; IF4E-R, 5'-GACCACCCTTGACGTTGTTT-3'; PFK1-F, 5'-CATCTCCCTTTGATCGCATT-3'; PFK1-R, 5'-GGCTTCTTCGGCTAACTCCT-3'; TRX1-F, 5'-GAGCTCGAGGGTGAAGGTTT-3'; TRX1-R, 5'-TGACATCACCGTTGGATTTG-3'; AIF1-F, 5'-ACCTTCTAATCGGTGCAGGA-3'; AIF1-R, 5'-CGCCATACCACCAAAGTTCT-3'; CDP6-F, 5'-GGAGTGGCAAGTTCTTCGAG-3'; and CDP6-R, 5'-ACCTCTGTTACGCCAAGCAT-3'. All samples were analyzed separately, and the average expression value (geometric mean) for each gene is presented.
HSP70 and HSP90 expressions were analyzed by western blotting. Eggs were lysed in SDS-PAGE loading buffer (2% SDS, 62.5 mM Tris-HCl, 10% glycerol, 50 mM dithiothreitol, and 0.01% bromophenol blue; pH 6.8) and heated at 98℃ for 5 min. Proteins (50 µg) were resolved by SDS-PAGE using 15% acrylamide and then transferred to PVDF membranes (BioRad, Hercules, California, USA) by a semidry transfer method. The membranes were then blocked overnight at 4℃ with 1× PBS/0.1% Tween 20 (TPBS) plus 5% (w/v) non-fat dry milk and incubated for 3 hr at room temperature with monoclonal anti-HSP70 and anti-HSP90 antibodies (1: 5,000 dilution; Sigma, St. Louis, Missouri, USA). After washing in TPBS, the membranes were incubated with HRP-conjugated rabbit anti-mouse (Sigma) secondary antibodies for 1 hr at room temperature and then washed 4 times in TPBS for 10 min each. The blots were developed using an enhanced chemiluminescence detection kit (Amersham, Buckinghamshire, UK) and visualized by autoradiography.
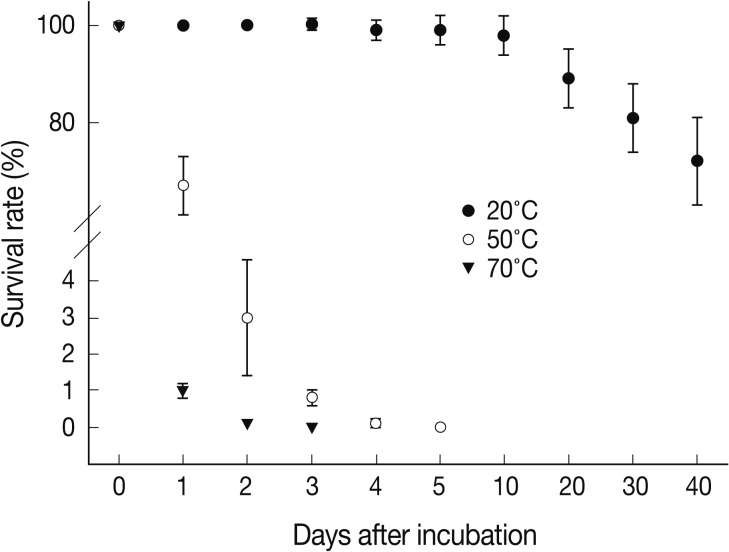
We measured the survival periods of
A. suum eggs incubated at 20℃, 50℃, and 70℃ for 40 days. As shown in
Fig. 1, at 20℃, > 99% of the eggs survived until day 10. On day 20, the percentage of viable
A. suum eggs was 89±6%. On day 40, 72±9% of the eggs were viable. However, at 50℃, about 67% of the eggs were viable on day 1, and 97% of the eggs or larvae were inactivated on day 2. Almost all eggs were devitalized by day 4. At 70℃, eggs started to die on day 1, and almost all eggs were dead on day 2. We also assessed the morphological characteristics of
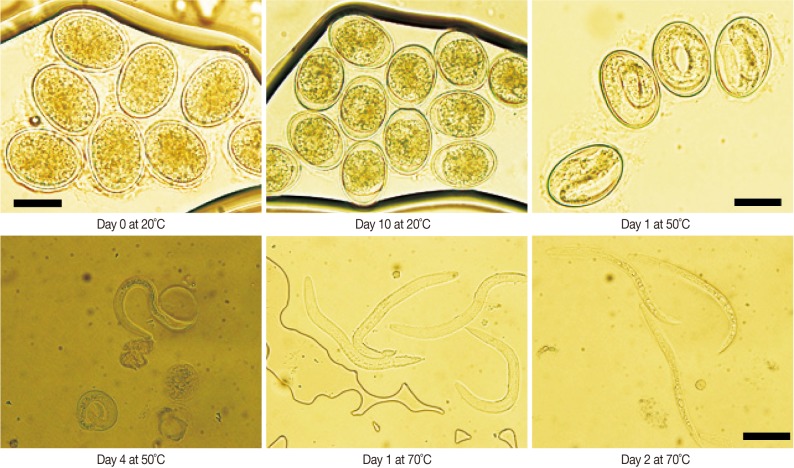
A. suum eggs during development at different temperatures for 10 days (
Fig. 2). At 20℃, no morphological alterations compared to day 0 were noted until day 5. On day 10, 1% of the eggs were in the cleavage stage. During incubation at 50℃, about 35% of the eggs were embryonated on day 1. On day 2, the eggs were further developed; thus, 85±4% of the eggs were observed to be in the larval stage. On day 4, the eggs were in the larval stage or hatching naturally, and most of hatched larvae or embryonated eggs were dead. Among the eggs incubated at 70℃, 62% were in the larval stage on day 1, and most of them were not viable. On day 2, all observed embryos were in the larval stage or hatching naturally, and almost all of the hatched larvae or larval-stage eggs were dead.
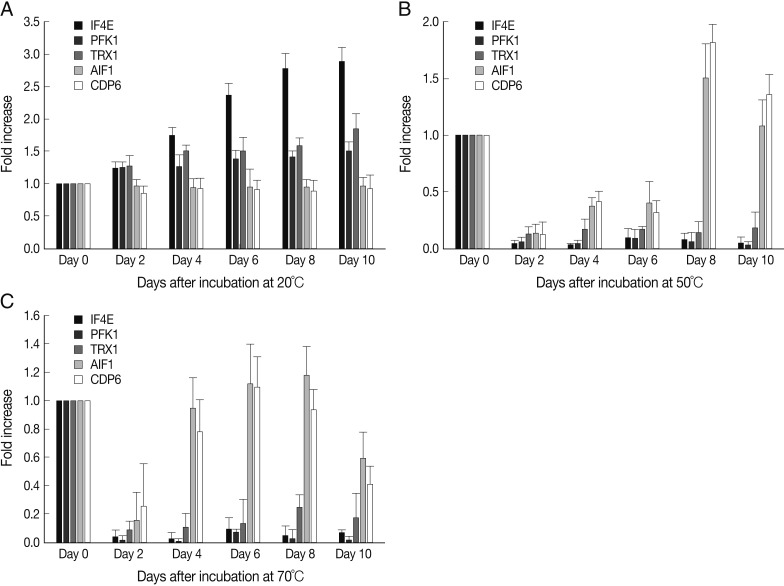
To quantify the functional changes in
A. suum eggs under different heat stress conditions, mRNA expressions of viability- and apoptosis-related genes were evaluated for 10 days (
Fig. 3). At 20℃, IF4E mRNA expression was significantly increased on day 4 compared with day 0, and this level increased slowly until day 8, after which the level remained constant. PFK1 and TRX1 mRNA expressions were significantly increased on day 2 (
P<0.05), after which similar levels were maintained until day 10. However, AIF1 and CDP6 mRNA expression was not significantly changed during the experimental period. At 50℃ and 70℃, IF4E, PFK1, and TRX1 mRNA expressions were markedly decreased on day 2 (
P<0.01), after which very low levels were maintained until day 10. However, AIF1 and CDP6 mRNA expressions were markedly decreased on days 2-6 at 50℃ or 70℃ (
P<0.01), and then increased from day 8 at 50℃ and day 4 at 70℃.
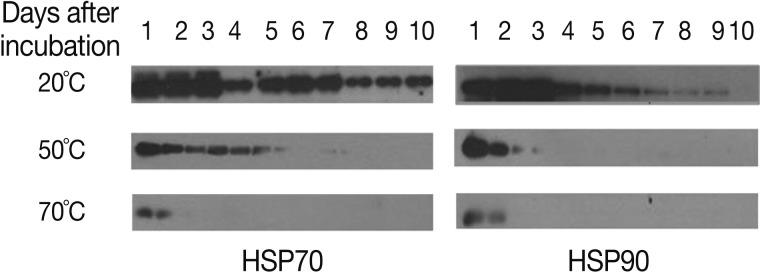
HSPs are induced by a variety of stressors, including heat, free radicals, and heavy metals. We assessed the expression levels of HSP70 and HSP90 to evaluate the heat stress response of
A. suum eggs (
Fig. 4). At 20℃, HSP70 derived from
A. suum eggs was detected for 10 days, with high levels during days 1-3, after which a decrease was observed. Similar to HSP70 expression, HSP90 levels were high until day 3 and then tapered slowly. HSP70 and HSP90 were detected during days 1-5 at 50℃ and days 1-3 at 70℃. At 50℃, the expression levels of HSP70 and HSP90 were the highest on day 1, and then decreased. At 70℃, HSP70 and HSP90 protein expression was detected on days 2 and 1, respectively, and their expression levels were much lower than those observed in eggs incubated at 20 or 50℃.
Pigs are the main host for
A. suum, and it is estimated that approximately 10-50% of pigs are infected by
A. suum worldwide [
13-
15]. Following the ingestion of
A. suum egg-contaminated food and water by humans or other mammals, larvae reach the liver and lung alveoli via the bloodstream, resulting in eosinophilic pneumonia, liver lesions, myelitis, and visceral larva migrans, characterized by neurological symptoms, including encephalomyeloradiculoneuropathy [
5,
6]. Thus, the inactivation of helminth eggs by fermentation or composting is critical for minimizing risks to the environment and public health.
Our results demonstrate that the devitalization of
A. suum eggs occurred in a temperature-dependent manner. Almost all
A. suum eggs were alive for 20 days at 20℃, whereas inactivation started prominently from days 2 and 1 at 50℃ and 70℃, respectively. The complete devitalization of unembryonated
A. suum eggs during the composting of organic wastes has been reported at temperatures ranging from 49℃ to 64℃ [
8]. Hamer [
3] also suggested that temperatures between 60℃ and 72℃ were sufficient for pathogen inactivation. Compared with the report of Cruez et al. [
16], who incubated unembryonated
A. suum eggs at 28℃, our timeline of egg development at 20℃ was somewhat delayed. These data suggest that temperature is critically important in the devitalization of
Ascaris eggs, although pH, ammonia concentration, and anaerobic conditions are also involved in the composting process.
Here, we evaluated the expression levels of genes related to viability and apoptosis by real-time qRT-PCR. The expression periods of these viability-related genes were decreased in a temperature-dependent manner. At 20℃, IF4E, PFK1, and TRX1 mRNA levels were significantly increased, which may present the development of A. suum eggs. However, A. suum eggs started to die at 50℃ and 70℃, thus the mRNA levels of IF4E, PFK1, and TRX1 were sharply decreased. In addition, the expression of these apoptosis-related genes appeared early with incremental temperature increases. In particular, AIF1 and CDP6 mRNA levels were significantly high from day 8 and 4 at 50℃ and 70℃, respectively. These results may be reflected as the signals of heat-treated eggs or the remains of dead eggs.
HSPs are involved in the transport, folding, and assembly of proteins and serve to maintain cell homeostasis by functioning as molecular chaperones [
17]. In this study, we found that the proteins HSP70 and HSP90 were expressed at higher levels for a longer period in eggs incubated at 20℃ than in those incubated at 50℃ or 70℃. This expression pattern is similar to that for viability-related gene expression. Interestingly, HSP70 protein was expressed for longer periods than HSP90 at all temperatures analyzed. These differences may be due to the different regulatory systems between HSP70 and HSP90. Based on the quantitative evaluation of genes or proteins related to viability, apoptosis, and heat stress, the expression periods and levels of these genes or proteins were concomitant with the survival periods of the eggs according to incubation temperature.
In this study, we quantified the functional changes in genes or proteins related to viability, apoptosis, and heat stress in A. suum eggs at composting temperatures. The expression periods of IF4E, PFK1, and TRX1 were shortened with incremental temperature increases, whereas AIF1 and CDP6 were expressed earlier at increased temperatures. The protein expression levels and periods of HSP70 and HSP90 were decreased with incremental temperature increases. The functional changes in these genes or proteins were correlated with survival of the eggs under heat stress conditions. Our results confirmed those of previous studies showing that the inactivation of A. suum eggs is strongly dependent on temperature.
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS
The present research has been performed according to a planning project of Korea Institute of Planning and Evaluation for Technology in Food, Agriculture, Forestry, and Fisheries, and the authors are grateful to financial support for this project (grant number 608010-5).
References
- 1. Leles D, Gardner SL, Reinhard K, Iñiguez A, Araujo A. Are Ascaris lumbricoides and Ascaris suum a single species? Parasit Vectors 2012;5:42.
- 2. Collick AS, Inglis S, Wright P, Steenhuis TS, Bowman DD. Inactivation of Ascaris suum in a biodrying compost system. J Environ Qual 2007;36:1528-1533.
- 3. Hamer G. Solid waste treatment and disposal: effects on public health and environmental safety. Biotechnol Adv 2003;22:71-79.
- 4. Pinelli E, Willers SM, Hoek D, Smit HA, Kortbeek LM, Hoekstra M, de Jongste J, van Knapen F, Postma D, Kerkhof M, Aalberse R, van der Giessen JW, Brunekreef B. Prevalence of antibodies against Ascaris suum and its association with allergic manifestations in 4-year-old children in the Netherlands: The PIAMA birth cohort study. Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis 2009;28:1327-1334.
- 5. Inatomi Y, Murakami T, Tokunaga M, Ishiwata K, Nawa Y, Uchino M. Encephalopathy caused by visceral larva migrans due to Ascaris suum. J Neurol Sci 1999;164:195-199.
- 6. Sakakibara A, Baba K, Niwa S, Yagi T, Wakayama H, Yoshida K, Kobayashi T, Yokoi T, Hara K, Itoh M, Kimura E. Visceral larva migrans due to Ascaris suum which presented with eosinophilic pneumonia and multiple intra-hepatic lesions with severe eosinophil infiltration--outbreak in a Japanese area other than Kyushu. Intern Med 2002;41:574-579.
- 7. Vinnerås B. Comparison of composting, storage and urea treatment for sanitising of faecal matter and manure. Bioresour Technol 2007;98:3317-3321.
- 8. Szabová E, Juris P, Papajová I. Sanitation composting process in different seasons. Ascaris suum as model. Waste Manag 2010;30:426-432.
- 9. Pecson BM, Barrios JA, Jiménez BE, Nelson KL. The effects of temperature, pH, and ammonia concentration on the inactivation of Ascaris eggs in sewage sludge. Water Res 2007;41:2893-2902.
- 10. Goodfellow IG, Roberts LO. Eukaryotic initiation factor 4E. Int J Biochem Cell Biol 2008;40:2675-2680.
- 11. Mor I, Cheung EC, Vousden KH. Control of glycolysis through regulation of PFK1: Old friends and recent additions. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol 2011;76:211-216.
- 12. Watanabe R, Nakamura H, Masutani H, Yodoi J. Anti-oxidative, anti-cancer and anti-inflammatory actions by thioredoxin 1 and thioredoxin-binding protein-2. Pharmacol Ther 2010;127:261-270.
- 13. Nissen S, Poulsen IH, Nejsum P, Olsen A, Roepstorff A, Rubaire-Akiiki C, Thamsborg SM. Prevalence of gastrointestinal nematodes in growing pigs in Kabale District in Uganda. Trop Anim Health Prod 2011;43:567-572.
- 14. Ismail HA, Jeon HK, Yu YM, Do C, Lee YH. Intestinal parasite infections in pigs and beef cattle in rural areas of Chungcheongnam-do, Korea. Korean J Parasitol 2010;48:347-349.
- 15. Lai M, Zhou RQ, Huang HC, Hu SJ. Prevalence and risk factors associated with intestinal parasites in pigs in Chongqing, China. Res Vet Sci 2011;91:e121-e124.
- 16. Cruz LM, Allanson M, Kwa B, Azizan A, Izurieta R. Morphological changes of Ascaris spp. eggs during their development outside the host. J Parasitol 2012;98:63-68.
- 17. Rupik W, Jasik K, Bembenek J, Widłak W. The expression patterns of heat shock genes and proteins and their role during vertebrate's development. Comp Biochem Physiol A Mol Integr Physiol 2011;159:349-366.
Fig. 1Survival days of Ascaris suum eggs at 20℃, 50℃, and 70℃ of incubation for 40 days. At each time, about 200 eggs were evaluated under a microscope on the basis of morphological changes in triplicate. Data are presented as the mean±SD of 200 A. suum eggs and are representative of 2 separate experiments.

Fig. 2Microscopic findings of A. suum eggs at 20℃, 50℃, and 70℃ of incubation for 10 days. Fertilized A. suum eggs were 48 to 73 µm long and 32 to 52 µm wide. Scale bar=50 µm.

Fig. 3Expression levels of eukaryotic translation initiation factor 4E (IF4E), phosphofructokinase 1 (PFK1), thioredoxin 1 (TRX1), apoptosis-inducing factor 1 (AIF1), and cell death protein 6 (CDP6) of A. suum eggs at 20℃ (A), 50℃ (B), and 70℃ (C) of incubation. Cellular RNA was extracted from 200 A. suum eggs, and the mRNA expressions of IF4E, PFK1, TRX1, AIF1, and CDP6 were evaluated by real-time quantitative reverse transcription-PCR (real-time qRT-PCR). Data are expressed as RQ (relative quantity), and differences are shown in the figures as the expression ratio of the normalized target gene. Data are presented as the mean±SD and are representative of 2 separate experiments.

Fig. 4Expression patterns of HSP70 and HSP90 of A. suum eggs at 20℃, 50℃, and 70℃ of incubation by western blot. Data are representative of 2 separate experiments.