Abstract
After bathing at a hot spring resort, a 75-year-old man presented to the emergency department because of seizure-like attack with loss of conscious. This is the first case of primary amebic meningoencephalitis (PAM) caused by Naegleria fowleri in Taiwan. PAM was diagnosed based on detection of actively motile trophozoites in cerebrospinal fluid using a wet-mount smear and the Liu's stain. The amoebae were further confirmed by PCR and gene sequencing. In spite of administering amphotericin B treatment, the patient died 25 days later.
-
Key words: Naegleria fowleri, meningoencephalitis, fatal case, amphotericin B, Taiwan
INTRODUCTION
Naegleria fowleri,
Acanthamoeba spp., and
Balamuthia mandrillaris have been recognized as etiologic agents of encephalitis [
1,
2].
N. fowleri causes primary amebic meningoencephalitis (PAM), a rapidly fatal disease, while
Acanthamoeba spp. and
B. mandrillaris cause chronic granulomatous encephalitis [
3].
N. fowleri is commonly found in warm freshwater environments such as hot springs, lakes, natural mineral water, and resort spas frequented by tourists [
4]. Infection can occur when
N. fowleri enter the nasal passages, attach to the olfactory mucosa, and migrate along the olfactory nerve tracts, crossing the cribriform plate to the brain [
5]. Once
N. fowleri infects the central nervous system (CNS), it divides rapidly and death can occur within 1 to 2 weeks [
1].
CASE REPORT
A 75-year-old man presented to a local hospital complaining of headache, fever, and right arm myoclonic seizures. He had mild leukocytosis; however, there was no indication of intracerebral hemorrhage or other obvious abnormalities. He was transferred to Chung Shan Medical University Hospital (Taichung, Taiwan) due to sudden onset of convulsion and right side limbs weakness. The neurologist diagnosed a CNS infection and seizure of unknown etiology and admitted the patient to Coronary Care Unit for further evaluation and treatment.
Laboratory studies showed a total leukocyte count of 12,190/µl (with 94.6% neutrophils, 3.0% lymphocytes, and 2.2% monocytes), and a platelet count of 148,000/µl. The clinical biochemistry data showed blood urea nitrogen at 22.48 mg/dl, a blood sugar (ac) level of 175 mg/dl, a blood sugar (pc) level of 255 mg/dl, and C-reactive protein level of 2.85 mg/dl. The serologic result for HIV was negative. Blood cultures of bacteria and fungi were negative. Magnetic resonance (MR) imaging of the patient's brain showed that sagittal and axial post-gadolinium T1-weighted images revealed diffuse leptomeningeal enhancement along the brain surface, including the brainstem, frontal lobe, and cerebellum. A contrast-enhanced computed tomography (CT) scan showed diffuse leptomeningeal enhancement and subarachnoid and intraventricular hemorrhages.
A lumbar puncture was performed and showed slightly-turbid cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) with 4 mg/dl glucose, 954.1 mg/dl protein, and a leukocyte count of 560/µl with 90.5% neutrophils, 5.0% lymphocytes, and 4.5% monocytes. India ink preparations, acid-fast stains and Gram stains for bacteria and fungi were all negative. The CSF was negative for viral detection. Also, CSF cultures for bacteria and fungi were negative.
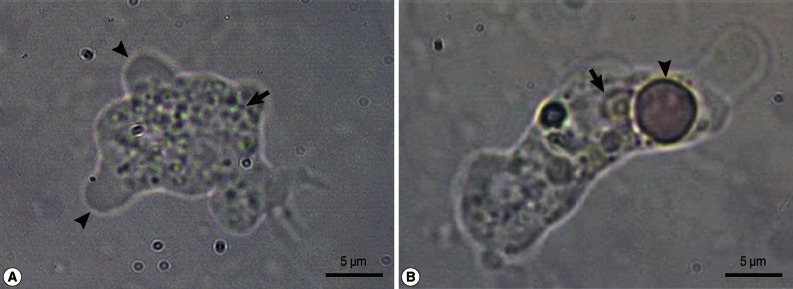
A wet-mount CSF smear revealed numerous trophozoites of approximately 10-25 µm size, which moved rapidly and directionally by pseudopodia. The cytoplasm of the trophozoites contained granular, abundant vacuoles. The amoeba was identified as
N. fowleri (
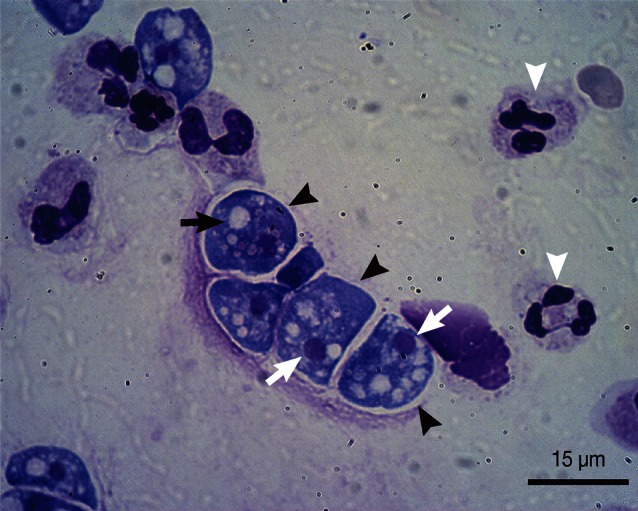
Fig. 1). A cytospin preparation was used to examine the CSF and the CSF sediment preparations were fixed with Liu's stain, which revealed amoebae containing nuclei and numerous cytoplasmic vacuoles (
Fig. 2).
N. fowleri infection was diagnosed and intravenous amphotericin B (50 mg q.d.) was started.
The CSF specimen obtained during hospitalization was examined at the Centers for Disease Control (CDC) of Taiwan.
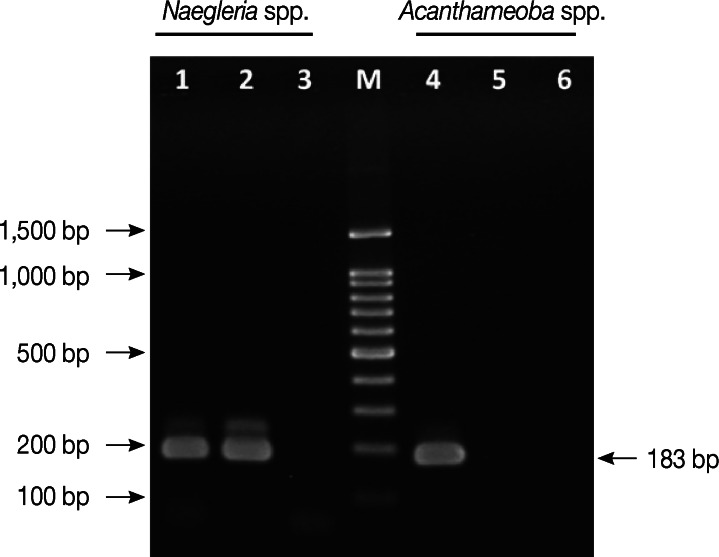
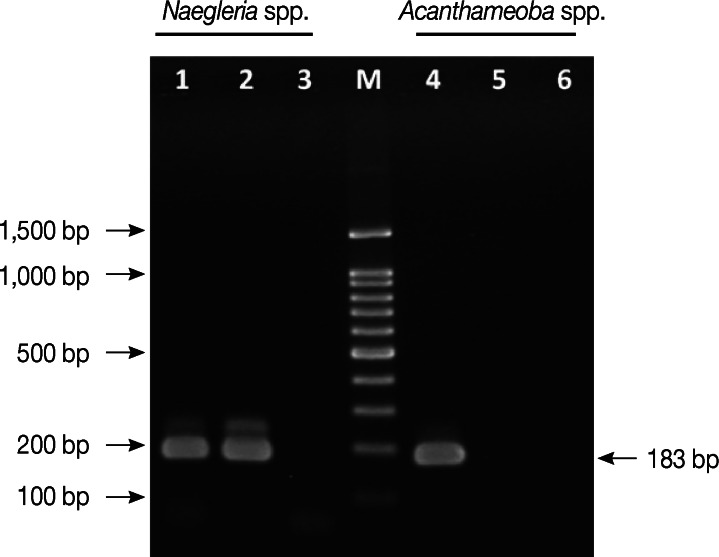
N. fowleri infection was confirmed by PCR analysis using the primers Nae3-F (5'-CAA ACA CCG TTA TGA CAG GG-3') and Nae3-R (5'-CTG GTT TCC CTC ACC TTA CG-3') to amplify fragments of a 183-bp product [
6]. For the detection of
Acanthamoeba spp., primers AcantF900 (5'-CCC AGA TCG TTT ACC GTG AA-3') and AcantR1100 (5'-TAA ATA TTA ATG CCC CCA ACT ATC C-3') were used to amplify fragments of a 180 bp product [
7].
N. fowleri Carter strain (American Type Culture Collection; ATCC no. 22758, Manassas, Virginia, USA) and
A. castellanii Neff strain (ATCC 30010) were used as positive controls. The PCR products (
Fig. 3) were visualized after electrophoresis on 2% agarose gels, where only a 183 bp amplicon of
Naegleria spp. was detected in the CSF specimen, but no band for
Acanthamoeba spp. was detected. For further confirmation, the PCR product was subjected to DNA sequencing to identify the species. The 183 bp PCR product showing higher similarity percentage to
N. fowleri using the BLAST algorithm at the National Center for Biotechnology Information (NCBI) website (
http://blast.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/). Although amphotericin B treatment was started immediately, the patient fell into coma. After 21 days of hospitalization, his health condition showed unstable hemodynamics and brain death. At 25 days post-treatment (beginning of treatment), the patient sustained to suffer from severe shock, followed by PAM and multiple organ failure leading to the patient's death.
DISCUSSION
N. fowleri is a thermophilic amoeba that grows well in tropical and subtropical climates and can tolerate temperatures up to 45℃ [
1,
8]. Warm fresh water coupled with a bacterial food supply is an ideal habitat for amoebae.
N. fowleri has a tendency to live in naturally or artificially heated water in spas, hot springs, warm rivers, ponds, lakes, saunas and indoor swimming pools [
1,
9]. In this case, the CDC of Taiwan analyzed the hot springs and confirmed the water contained
N. fowleri. Thus, the hot springs were possibly the source of infection. Based on these results, hot spring water may be a threat to human health, and exposure to warm fresh water should be considered a possible causative agent of amoebic meningoencephalitis. Also, it is important to rapidly detect thermotolerant amoebae in hot springs where people swim and bathe because of the possible impact on human health.
Based on clinical and laboratory diagnoses,
N. fowleri causes PAM, which is difficult to distinguish from bacterial meningoencephalitis. Therefore, it usually leads to an incorrect diagnosis. Once the CSF analysis indicates purulent meningitis without bacteria, PAM should be suspected [
2,
3]. The diagnosis is confirmed by further examination of CSF wet mounts for motile trophozoites. However, failure to visualize the amoeba does not exclude PAM, and the diagnosis is often missed when
Naegleria organisms are mistaken for atypical mononucleocytes or lymphocytes in the CSF.
CT and MR imaging may be normal in early PAM, with subsequent evidence of brain edema and basilar meningeal enhancement. However, PAM imaging features are non-specific [
10,
11]. Recently, a triplex real-time TaqMan PCR assay was developed as a rapid laboratory diagnostic tool for simultaneous identification of
Acanthamoeba spp.,
B. mandriallaris, and
N. fowleri [
7]. This approach may provide a relatively rapid means of detection to enhance identification of amoebae that are not easily distinguished by conventional cultivation and microscopic methods. PCR methodology for specific amplification of
N. fowleri DNA can identify amoeba in CSF. This method is sufficiently sensitive to detect individual amoeba and is often employed as a confirmatory test for
N. fowleri identification.
PAM is an acute disease, in which
N. fowleri can grow to large numbers by feeding on bacteria. Thus, early diagnosis is essential in order to initiate appropriate antimicrobial therapy before the amoebae do extensive damage [
1].
N. fowleri is highly sensitive to the antifungal drug amphotericin B; however, PAM survival rate is low and few patients survive [
13]. In our case, amphotericin B was ineffective possibly due to 1) high infectious dose, 2) rapid onset of disease, 3) delay in diagnosis, or 4) patient's immune system may have been compromised. In our case, PAM developed within several days following exposure to contaminated water, and caused death on day 25 after beginning of the chemotherapy. Therefore, we propose that critical points in determining PAM survival case include early diagnosis and treatment initiation, the infectious dose of amoebae, the virulence of the infecting strain, and the health status of the patient.
This is the first PAM case that occurred in Taiwan following bathing in hot spring. Rapid diagnosis was made by microscopic examination to visualize motile amoebae, and the diagnosis was further confirmed by PCR and sequencing. In spite of amphotericin B treatment, the patient passed away on day 25 after beginning of the treatment. The presence of N. fowleri in hot spring water poses a threat to human health. Thus, the relationship between public hygiene and the quality of hot spring water is worthy of future investigations.
References
- 1. Schuster FL, Visvesvara GS. Free-living amoebae as opportunistic and non-opportunistic pathogens of humans and animals. Int J Parasitol 2004;34:1001-1027.
- 2. Visvesvara GS, Moura H, Schuster FL. Pathogenic and opportunistic free-living amoebae: Acanthamoeba spp., Balamuthia mandrillaris, Naegleria fowleri, and Sappinia diploidea. FEMS Immunol Med Microbiol 2007;50:1-26.
- 3. da Rocha-Azevedo B, Tanowitz HB, Marciano-Cabral F. Diagnosis of infections caused by pathogenic free-living amoebae. Interdiscip Perspect Infect Dis 2009;2009:251406.
- 4. Heggie TW. Swimming with death: Naegleria fowleri infections in recreational waters. Travel Med Infect Dis 2010;8:201-206.
- 5. Martinez AJ, Visvesvara GS. Free-living, amphizoic and opportunistic amebas. Brain Pathol 1997;7:583-598.
- 6. Schild M, Gianinazzi C, Gottstein B, Müller N. PCR-based diagnosis of Naegleria sp. infection in formalin-fixed and paraffin-embedded brain sections. J Clin Microbiol 2007;45:564-567.
- 7. Qvarnstrom Y, Visvesvara GS, Sriram R, da Silva AJ. Multiplex real-time PCR assay for simultaneous detection of Acanthamoeba spp., Balamuthia mandrillaris, and Naegleria fowleri. J Clin Microbiol 2006;44:3589-3595.
- 8. de Jonckheere J, Voorde H. The distribution of Naegleria fowleri in man-made thermal waters. Am J Trop Med Hyg 1977;26:10-15.
- 9. Tyndall RL, Ironside KS, Metler PL, Tan EL, Hazen TC, Fliermans CB. Effect of thermal additions on the density and distribution of thermophilic amoebae and pathogenic Naegleria fowleri in a newly created cooling lake. Appl Environ Microbiol 1989;55:722-732.
- 10. Kidney DD, Kim SH. CNS infections with free-living amebas: neuroimaging findings. AJR Am J Roentgenol 1998;171:809-812.
- 11. Schumacher DJ, Tien RD, Lane K. Neuroimaging findings in rare amebic infections of the central nervous system. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 1995;16:930-935.
- 12. Carter RF. Sensitivity to amphotericin B of a Naegleria sp. isolated from a case of primary amoebic meningoencephalitis. J Clin Pathol 1969;22:470-474.
- 13. Vargas-Zepeda J, Gómez-Alcalá AV, Vásquez-Morales JA, Licea-Amaya L, De Jonckheere JF, Lares-Villa F. Successful treatment of Naegleria fowleri meningoencephalitis by using intravenous amphotericin B, fluconazole and rifampicin. Arch Med Res 2005;36:83-86.
Fig. 1Motile forms of Naegleria fowleri trophozoites in cerebrospinal fluid. (A) A motile N. fowleri, showing directional movements by means of blunt, bulbous pseudopodia (arrowheads), with granular cytoplasm (arrow). (B) The trophozoite is characterized by a nucleus (arrow) and phagocytizing an erythrocyte (arrowhead).
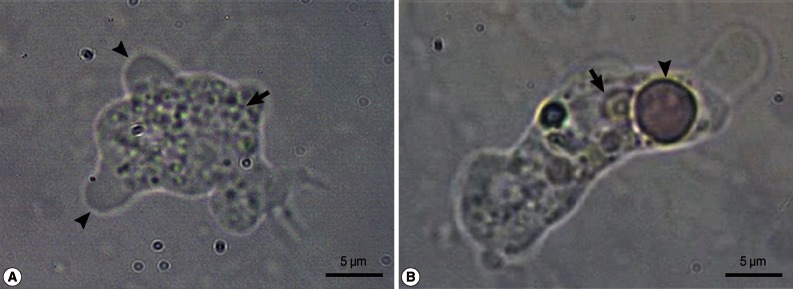
Fig. 2Liu's stain of a cerebrospinal fluid specimen. Microscopic examination revealed numerous Naegleria fowleri trophozoites (black arrowheads) containing nuclei (blank arrows) and numerous cytoplasmic vacuoles (black arrow). Blank arrowheads indicate leukocytes.
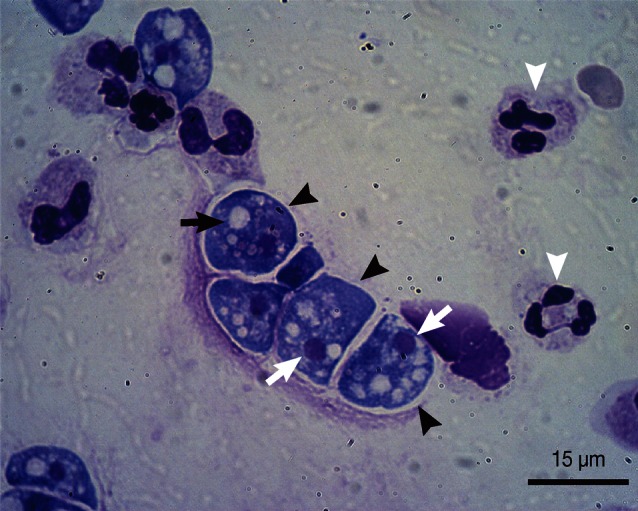
Fig. 3Identification of Naegleria fowleri by PCR. Lane 1. Positive control for Naegleria spp. Lane 2. DNA from the patient CSF for Naegleria spp. Lane 3. Negative control for Naegleria spp. Lane 4. Positive control for Acanthamoeba spp. Lane 5. DNA from the patient CSF for Acanthamoeba spp. Lane 6. Negative control for Acanthamoeba spp. M; 100-bp DNA ladder.