Abstract
Autophagy-related protein 8 (Atg8) is an essential component of autophagy formation and encystment of cyst-forming parasites, and some protozoa, such as, Acanthamoeba, Entamoeba, and Dictyostelium, have been reported to possess a type of Atg8. In this study, an isoform of Atg8 was identified and characterized in Acanthamoeba castellanii (AcAtg8b). AcAtg8b protein was found to encode 132 amino acids and to be longer than AcAtg8 protein, which encoded 117 amino acids. Real-time PCR analysis showed high expression levels of AcAtg8b and AcAtg8 during encystation. Fluorescence microscopy demonstrated that AcAtg8b is involved in the formation of the autophagosomal membrane. Chemically synthesized siRNA against AcAtg8b reduced the encystation efficiency of Acanthamoeba, confirming that AcAtg8b, like AcAtg8, is an essential component of cyst formation in Acanthamoeba. Our findings suggest that Acanthamoeba has doubled the number of Atg8 gene copies to ensure the successful encystation for survival when 1 copy is lost. These 2 types of Atg8 identified in Acanthamoeba provide important information regarding autophagy formation, encystation mechanism, and survival of primitive, cyst-forming protozoan parasites.
-
Key words: Acanthamoeba castellanii, encystation, autophagy protein 8, isoform
INTRODUCTION
Autophagy is an essential tool that enables cell survival under nutrient-limiting conditions in eukaryotes and during encystation of protozoan parasites [
1,
2]. Autophagy is a fundamental cellular process for survival during starvation, cellular differentiation, cell death, and aging by eliminating unwanted or unnecessary organelles and recycling components for reuse. Several protozoan parasites have complex life cycles that are environmentally dependent and involve drastic changes in morphology and metabolism, and autophagy is responsible for changes in cellular composition during differentiation [
2].
Autophagy has been studied in greatest detail in
Saccharomyces cerevisiae, and to date, at least 34 types of autophagy-related genes (Atg) have been identified, including the key protein, autophagy-related protein 8 (Atg8) [
3]. Atg proteins are categorized into 6 functional units [
4], namely, Atg1 protein kinase and its regulators, Atg12-Atg18 complex, the Atg8 system, the Atg12 system, the autophagy-specific phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase complex, and Atg9. Furthermore, it has been established that Atg8-PE (phosphatidylethanolamine) and Atg16-Atg5-Atg12 complex are essential for autophagosome formation [
5,
6].
Atg8 (AcAtg8) and Atg16 (AcAtg16) were identified in encysting
A. castellanii, and were found to play essential roles in autophagosome formation and in the encystation of
Acanthamoeba [
7,
8]. Other autophagy-related proteins of
Acanthamoeba, such as, Atg3 (AcAtg3), encystation-mediating serine protease (EMSP), encystation-mediating cysteine protease (EMCP), and cysteine protease inhibitor (AcStefin) have also been identified and characterized [
9-
12].
In this study, we focused on an isoform of Atg8 involved in autophagosome formation and encystation of protozoa. Previously, we identified and characterized one Atg8 gene in encysting
Acanthamoeba (AcAtg8) [
7]. Yeast possesses one Atg8 protein, whereas human has 7 isoforms, that is, GATE16, GABARAP, GABARAPL1, LC3A, LC3B, LC3B2, and LC3C [
3]. On the other hand,
Entamoeba invadens and
Dictyostelium discoideum have one Atg8 gene each [
2,
13].
Recently, using the sequences of autophagy-related genes in the cDNA database of A. castellanii Neff (Tang et al., not published), we cloned the full open reading frame (ORF) of the Atg8 isoform of A. castellanii Castellani (AcAtg8b) (GenBank no. KC524507). We found it interesting that a primitive protozoan parasite, such as, Acanthamoeba, has 2 types of Atg8 genes. We identified and characterized AcAtg8b as an encystation-mediating factor with AcAtg8. In addition, we discusses the role of AcAtg8b in Acanthamoeba during encystation.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Cultivation of Acanthamoeba
Acanthamoeba castellanii Castellani was obtained from the American Type Culture Collection (ATCC #30011).
Acanthamoeba trophozoites were cultured axenically in Peptone-Yeast-Glucose (PYG) medium at 25℃ in a Sanyo incubator (San Diego, California, USA) [
14]. Encystation was induced as previously described by Bowers and Korn [
15]. The morphological changes of cells to cysts were observed, and sodium dodecyl sulfate (SDS, 0.5% final concentration) was added for 10 min to solubilize trophozoites. The encystation ratios were calculated by counting cysts through hematocytometer under a light microscope.
Real-time PCR
Total RNA was purified using the TRIzol Reagent (Gibco BRL, Rockville, Maryland, USA) and cDNA synthesis was conducted using the RevertAid™ First Strand cDNA synthesis kit (Fermentas, Hanover, Indiana, USA). Real-time PCR was performed using the GenAmp 5700 SDS (Biosystems, Barcelona, Spain), using the following thermocycler program for all genes: 10 min of pre-incubation at 95℃ followed by 40 amplification cycles of 15 sec at 95℃ and 1 min at 60℃. Individual reactions were carried out in 20 µl volumes in a 96-well plate containing 20 ng of cDNA, 10 µl of 2×buffer, 3.5 mM MgCl2, 0.2 mM dNTPs, different concentrations of sense and antisense primers (sense 5'-CCGAGTTCCTGTGATCGTTGA and antisense 5'-AGCTGTGTGACGGCAATATCG for AcAtg8b, sense 5'-AAGGAAGCACATGAAGCTGAGC and antisense 5'-CCATCCTCGTCCTTGTACTTGG for AcAtg8), 0.025 U/µl of DNA polymerase, and 1:66,000 SYBR Green (Bionics, Seoul, Korea). All reactions were conducted using a SYBR Premix Ex TaqTM (Takara, Shiga, Japan).
The 18s rDNA (sense 5'-TCCAATTTTCTGCCACCGAA and antisense 5'-ATCATTACCCTAGTCCTCGCGC) was used as a reference gene [
8]. Real-time quantitative PCR was performed to determine relative gene expression data using the 2
-ΔΔCT method [
16].
In order to investigate the intracellular localization of AcAtg8b, its gene was cloned into a pUb vector with
Acanthamoeba ubiquitin promoter and enhanced green fluorescent protein (EGFP) reporter gene [
14]. The AcAtg8b gene was PCR amplified with primers that included sites for NcoI at the 5'end and SpeI at the 3'end, and the products were inserted into the pUb vector upstream of the EGFP gene. This plasmid was then transfected into viable
A. castellanii. Approximately 4×10
5 cells per well were seeded into a 6-well culture plate in 3 ml of PYG medium and incubated overnight at 25℃. Transient transfection was performed using the Superfect transfection reagent (Qiagen, Valencia, California, USA) as previously described [
14].
Amoebae expressing EGFP were selected and allowed to adhere to a Falcon cell culture dish (BD, Piscataway, New Jersey, USA). Cells were observed using a LSM 5 EXCITER Scalable confocal system (ZEISS, Hamburg, Germany). EGFP- and LysoTracker Red DND 99-mediated fluorescence was achieved using band-pass filters that provided excitation and emission wavelengths of 500-530 nm and 570-590 nm, respectively.
Gene silencing methodology
Small interfering RNA (siRNA) targeting AcAtg8b and AcAtg8 were synthesized by Sigma-Proligo (Boulder, Colorado, USA), based on its cDNA sequence. The siRNA duplex with sense (5'-CCAUCUUCCUCUUCGUGAAdTdT) and anti-sense (5'-UUCACGAAGAGGAAGAUGGdTdT) against AcAtg8b, and siRNA duplex with sense (5'-GAACUCAUGUCGCACAUCUTT) and anti-sense (5'-AGAUGUGCGACAUGAGUUCTT) against AcAtg8 sequences were used. The siRNA (4 µg) was transfected into
A. castellanii trophozoites at a cell density of 4×10
5 per well as previously described [
7].
RESULTS
Sequence alignment of AcAtg8b
Based on the cDNA sequence database of
A. castellanii Neff, the full-length ORF of Atg8 (autophagy protein 8 isoform) from
A. castellanii Castellani (AcAtg8b) was cloned (Genbank no. KC524507). The deduced amino acid sequence of AcAtg8b showed 75% sequence similarity with that of AcAtg8 (data not shown). When the amino acid sequence of AcAtg8b was aligned with those of other Atg8 proteins, AcAtg8b was found to be homologous at a tyrosine kinase phosphorylation site (boxed area) and a C-terminal glycine residue, which is removed by Atg4 protease (arrowhead) (
Fig. 1).
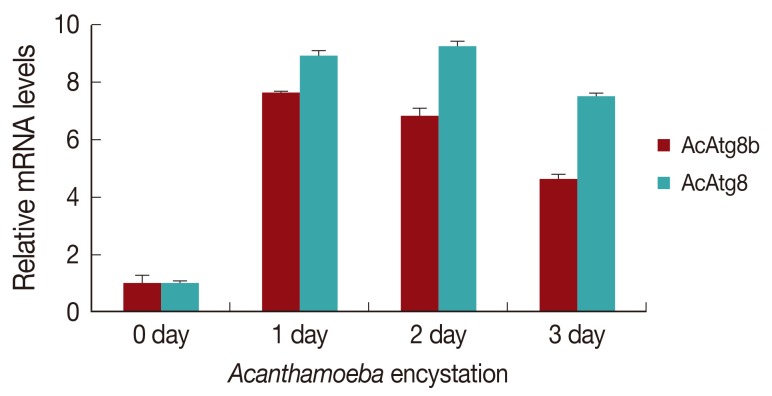
AcAtg8 and AcAtg8b showed higher expression levels during encystation than trophozoites (
Fig. 2). We believe that AcAtg8 showed higher expression levels during encystation (
Fig. 2) than has been previously reported [
8], because a fresh strain was used for this experiment. AcAtg8b mRNA was highly expressed at day 1 and day 2 (
Fig. 2, by 7-8 fold) after encystation induction. This increase may have been due to the formation of autophagosomal membrane during the early stage of encystation.
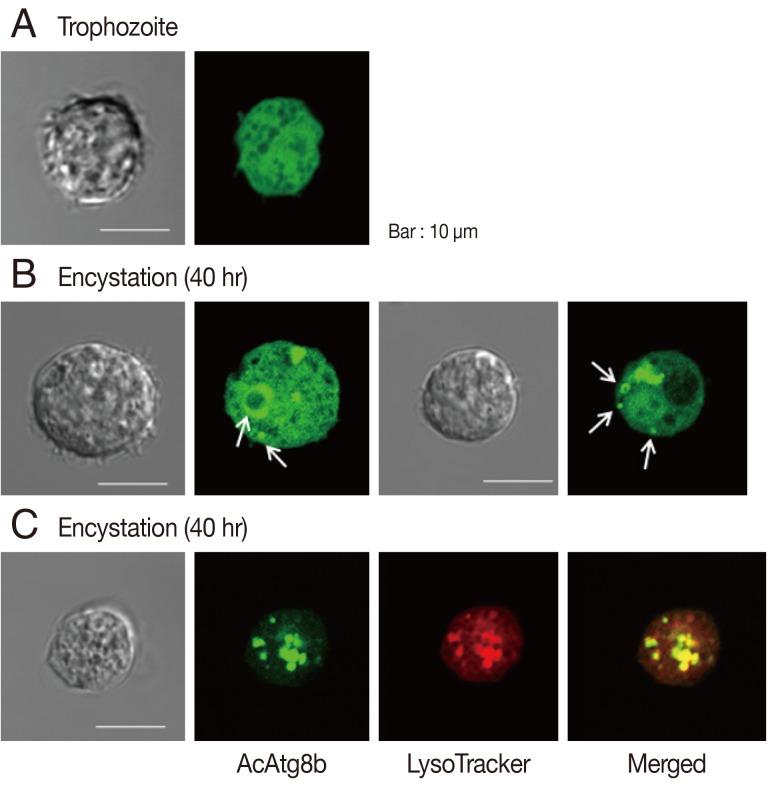
To determine the intracellular localization of AcAtg8b protein,
Acanthamoeba transfected with EGFP-AcAtg8b were examined under a light microscope (
Fig. 3). As shown in
Fig. 3A, EGFP-AcAtg8b exhibited a dispersed fluorescence pattern in the cytoplasm. Transfected amoebae were transferred to the encystment medium, and 24-40 hr later fluorescent vacuole structures appeared (
Fig. 3B, white arrows). EGFP-AcAtg8b fusion proteins on membranes were identified as autophagosomal membrane proteins by co-localization analysis using the LysoTracker as an autophagosome marker (
Fig. 3C).
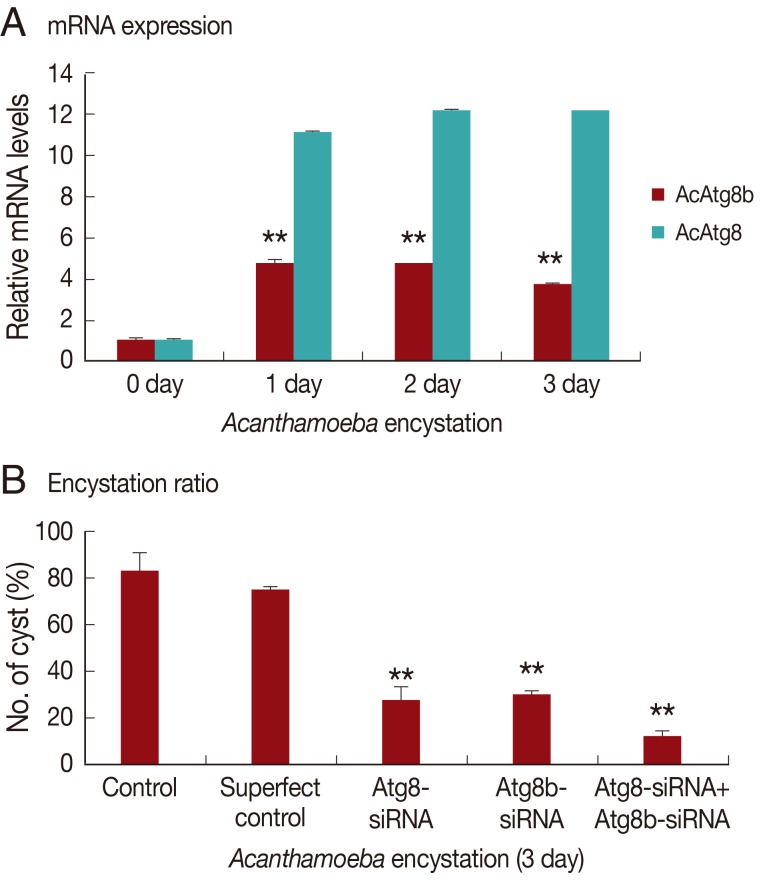
To determine the role of AcAtg8b in encystation of
Acanthamoeba, siRNA against AcAtg8b was used to reduce the expression of AcAtg8b. A siRNA transfection efficiency of 84% was achieved by FACS (data not shown). As shown in
Fig. 4A, AcAtg8b mRNA expression during encystation was reduced in siRNA-transfected cell versus the wild type as shown in
Fig. 2. Furthermore, AcAtg8b siRNA transfection did not affect the expression of AcAtg8 during encystation (
Fig. 4A). In addition, AcAtg8b siRNA-transfected trophozoites were transferred to the encystation medium to determine the effect of AcAtg8b knockdown on encystation. The number of mature cysts formed was found to be lower for AcAtg8b siRNA-transfected cells (
Fig. 4B). Treatment with AcAtg8b-siRNA had a similar effect to treatment with AcAtg8-siRNA on
Acanthamoeba encystation. However, treatment with AcAtg8b-siRNA plus AcAtg8-siRNA markedly reduced the encystation ratio of
Acanthamoeba (
Fig. 4B). These results suggest that AcAtg8 and AcAtg8b are required for encystation of
Acanthamoeba.
DISCUSSION
Atg8 is a major factor in the autophagic process during various differentiation stages of eukaryotic cells. Atg8 genes have been duplicated and lost during evolution in specific lineages (
Table 1). Man has 7 types of Atg8 homologues (1 GATE-16, 2 GABARAPs, and 4 LC3s), but
Drosophila has only 2 GABARAP genes. The primitive protozoan parasite,
A. castellanii expresses 2 types of Atg8 genes (AcAtg8 and AcAtg8b) during encystation, whereas other primitive protozoan parasites, such as,
Entamoeba and
Dictyostelium possess one Atg8 gene [
2,
13]. Moreover, in
Giardia lamblia, the Atg8 gene system is completely absent, although some key genes associated with autophagy, such as, TOR, Atg1, and Atg16, were identified by genome analysis in
Giardia [
17].
In this study, it was found that AcAtg8b participated in autophagosome formation and was essential for elongation of the autophagic membrane (
Fig. 3). Furthermore, amoeba transfected with AcAtg8b siRNA did not transform into mature cysts (
Fig. 4). In the present study, we did not differentiate between the functions of AcAtg8 and AcAtg8b during the encystation of
Acanthamoeba. However, levels of participation of AcAtg8b and AcAtg8 in encystation were similar. When we transfected
Acanthamoeba with siRNA against AcAtg8, complete inhibition of encystation was not achieved [
7], which suggests that another Atg8, such as, Atg8b, participates in the process. As shown in
Fig. 4A, the expression of Atg8 was not changed by siRNA treatment of Atg8b. Although their expression seems to be independent, participation of AcAtg8b and AcAtg8 in encystation was similar. Therefore, they are not able to rescue each other.
Although man possesses 7 types of Atg8 genes, their precise functions are unclear. Each Atg8 subfamily (GATE-16, GABARAP, and LC3) has a distinctive sequence feature [
3]. Position 18 in the GATE-16 subfamily is typically a serine or an alanine residue, whereas in the GABARAP subfamily this position is occupied by a glycine residue, and in the LC3 subfamily the corresponding position (position 20), is typically a valine, alanine, or sometimes a serine residue. Position 40 in GABARAP and position 42 in the LC3 are conserved and typically are basic, whereas the corresponding position in GATE-16 family is not well conserved. In
Acanthamoeba, position 18 in AcAtg8 and AcAtg8b correspond to alanine (
Fig. 1). However, position 40 of AcAtg8 and AcAtg8b is occupied by different amino acid residues, for example, AcAtg8b includes a basic residue, K (lysine), whereas AcAtg8 includes an acidic residue, D (aspartic acid) (
Fig. 1). Unfortunately, the present study does not shed light on functional implications of these sequence features.
Both AcAtg8 and AcAtg8b were highly expressed during encystation probably because they were needed to enable the establishment of autophagy rapidly. Mitochondria are a major target of autophagy in
Acanthamoeba, as compared with trophozoites, significantly fewer mitochondria remained in mature cysts [
12]. To degrade a large number of mitochondria, various types of autophagy may be needed. Recent studies suggest that mitochondrial autophagy may be a selective process (known as mitophagy). In yeast, 3 main mitophagy-related genes, namely, Uth1p (a specific membrane protein), Aup1p (a mitochondrial protein), and Atg32 (an autophagy-related gene) have been reported [
18-
20]. Although we searched for mitophagy-related genes in our
Acanthamoeba database and other databases, we were unable to find any.
Therefore, identification of Atg8 isoforms in
Acanthamoeba has an important meaning. Autophagy in
Acanthamoeba involves random engulfment of cellular components, including mitochondria (data not shown), and later, the targeted degradation of mitochondria might occur via a cyst-specific cysteine proteinase (CSCP) [
12]. Data from experiments using CSCP siRNA could support this hypothesis. In order to understand the complete mechanism of autophagy in encysting
Acanthamoeba, an investigation of mitophagy-related genes and the specific function of AcAtg8b is needed.
Here, we identified and characterized an Atg8 isoform in encysting Acanthamoeba (AcAtg8b). AcAtg8b was found to play an important role in autophagy and in the encystation of Acanthamoeba. Additional studies on AcAtg8b would undoubtedly accelerate our understanding of autophagy and of the cellular differentiation that occurs in cyst forming protozoan parasites such as Acanthamoeba.
National Research Foundation of KoreaNRF-2012R1A6A3A01015188
Notes
-
We have no conflict of interest related with this study.
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS
This research was supported by the Basic Science Research Program through the National Research Foundation of Korea funded by the Ministry of Education, Science and Technology (Grant no. NRF-2012R1A6A3A01015188). The authors wish to thank Professor Petrus Tang (Department of Parasitology, and Bioinformatics Center, Chang Gung University) for providing the sequence information of Atg8 from Acanthamoeba castellanii Neff.
References
- 1. Levine B, Klionsky DJ. Development by self-digestion: molecular mechanisms and biological functions of autophagy. Dev Cell 2004;6:463-477.
- 2. Picazarri K, Nakada-Tsukui K, Nozaki T. Autophagy during proliferation and encystation in the protozoan parasite Entamoeba invadens. Infect Immun 2008;76:278-288.
- 3. Shpilka T, Weidberg H, Pietrokovski S, Elazar Z. Atg8: an autophagy-related ubiquitin-like protein family. Genome Biol 2011;12:226-236.
- 4. Suzuki K, Ohsumi Y. Molecular machinery of autophagosome formation in yeast, Saccharomyces cerevisiae. FEBS Lett 2007;581:2156-2161.
- 5. Kuma A, Mizushima N, Ishihara N, Ohsumi Y. Formation of the approximately 350-kDa Apg12-Apg5.Apg16 multimeric complex, mediated by Apg16 oligomerization, is essential for autophagy in yeast. J Biol Chem 2002;277:18619-18625.
- 6. Mizushima N, Noda T, Yoshimori T, Tanaka Y, Ishii T, George MD, Klionsky DJ, Ohsumi M, Ohsumi Y. A protein conjugation system essential for autophagy. Nature 1998;395:395-398.
- 7. Moon EK, Chung DI, Hong YC, Kong HH. Autophagy protein 8 mediating autophagosome in encysting Acanthamoeba. Mol Biochem Parasitol 2009;168:43-48.
- 8. Song SM, Han BI, Moon EK, Lee YR, Yu HS, Jha BK, Danne DB, Kong HH, Chung DI, Hong Y. Autophagy protein 16-mediated autophagy is required for the encystation of Acanthamoeba castellanii. Mol Biochem Parasitol 2012;183:158-165.
- 9. Lee JY, Song SM, Moon EK, Lee YR, Jha BK, Danne DB, Cha HJ, Yu HS, Kong HH, Chung DI, Hong Y. Cysteine Protease Inhibitor (AcStefin) Is Required for Complete Cyst Formation of Acanthamoeba. Eukaryot Cell 2013;12:567-574.
- 10. Moon EK, Chung DI, Hong YC, Kong HH. Characterization of a serine proteinase mediating encystation of Acanthamoeba. Eukaryot Cell 2008;7:1513-1517.
- 11. Moon EK, Chung DI, Hong Y, Kong HH. Atg3-mediated lipidation of Atg8 is involved in encystation of Acanthamoeba. Korean J Parasitol 2011;49:103-108.
- 12. Moon EK, Hong Y, Chung DI, Kong HH. Cysteine protease involving in autophagosomal degradation of mitochondria during encystation of Acanthamoeba. Mol Biochem Parasitol 2012;185:121-126.
- 13. Eichinger L, Pachebat JA, Glöckner G, Rajandream MA, Sucgang R, Berriman M, Song J, Olsen R, Szafranski K, Xu Q, Tunggal B, Kummerfeld S, Madera M, Konfortov BA, Rivero F, Bankier AT, Lehmann R, Hamlin N, Davies R, Gaudet P, Fey P, Pilcher K, Chen G, Saunders D, Sodergren E, Davis P, Kerhornou A, Nie X, Hall N, Anjard C, Hemphill L, Bason N, Farbrother P, Desany B, Just E, Morio T, Rost R, Churcher C, Cooper J, Haydock S, van Driessche N, Cronin A, Goodhead I, Muzny D, Mourier T, Pain A, Lu M, Harper D, Lindsay R, Hauser H, James K, Quiles M, Madan Babu M, Saito T, Buchrieser C, Wardroper A, Felder M, Thangavelu M, Johnson D, Knights A, Loulseged H, Mungall K, Oliver K, Price C, Quail MA, Urushihara H, Hernandez J, Rabbinowitsch E, Steffen D, Sanders M, Ma J, Kohara Y, Sharp S, Simmonds M, Spiegler S, Tivey A, Sugano S, White B, Walker D, Woodward J, Winckler T, Tanaka Y, Shaulsky G, Schleicher M, Weinstock G, Rosenthal A, Cox EC, Chisholm RL, Gibbs R, Loomis WF, Platzer M, Kay RR, Williams J, Dear PH, Noegel AA, Barrell B, Kuspa A. The genome of the social amoeba Dictyostelium discoideum. Nature 2005;435:43-57.
- 14. Kong HH, Pollard TD. Intracellular localization and dynamics of myosin-II and myosin-IC in live Acanthamoeba by transient transfection of EGFP fusion proteins. J Cell Sci 2002;115:4993-5002.
- 15. Bowers B, Korn ED. The fine structure of Acanthamoeba castellanii (Neff strain). II. Encystment. J Cell Biol 1969;41:786-805.
- 16. Livak KJ, Schmittgen TD. Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) Method. Methods 2001;25:402-408.
- 17. Bagchi S, Oniku AE, Topping K, Mamhoud ZN, Paget TA. Programmed cell death in Giardia. Parasitology 2012;139:894-903.
- 18. Kanki T, Wang K, Cao Y, Baba M, Klionsky DJ. Atg32 is a mitochondrial protein that confers selectivity during mitophagy. Dev Cell 2009;17:98-109.
- 19. Kissová I, Deffieu M, Manon S, Camougrand N. Uth1p is involved in the autophagic degradation of mitochondria. J Biol Chem 2004;279:39068-39074.
- 20. Tal R, Winter G, Ecker N, Klionsky DJ, Abeliovich H. Aup1p, a yeast mitochondrial protein phosphatase homolog, is required for efficient stationary phase mitophagy and cell survival. J Biol Chem 2007;282:5617-5624.
Fig. 1Alignment of amino acid sequences of Atg8 isoforms (Atg8 and Atg8b) from
Acanthamoeba castellanii Castellani and those of
Entamoeba invadens,
Dictyostelium discoideum, and
Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Clustal W (
http://www.ch.embnet.org/sofrware/ClustalW.html) was used to produce the alignment. Degree of conservation is represented by shadings. The conserved tyrosine kinase phosphorylation site is boxed (□) and the C-terminal glycine residue is indicated by the arrowhead (▼).
'*' indicates amino acid position 18, and
'**' indicates position 40.

Fig. 2Expression levels of AcAtg8b mRNA measured by real-time PCR performed during encystation. A significant increase in AcAtg8b expression was observed during encystation (■). AcAtg8 was used as a positive control (░), and 18s rDNA was used as a reference control. The experiments were repeated 3 times and the average values are presented with error bars representing standard deviations.

Fig. 3Intracellular localization of AcAtg8b during encystation. Expressed EGFP-AcAtg8b showed a dispersed distribution in the cytoplasm of trophozoites (A). After transfer to encystment medium and incubation for 40 hr, large or small fluorescent circular structures were observed (B, white arrows). These structures colocalized with LysoTracker Red DND-99, a marker of autophagy (C).

Fig. 4Inhibition of encystation by AcAtg8b siRNA. Atg8b expression was inhibited in AcAtg8b siRNA transfected cells during encystation (A-■). However, AcAtg8b-siRNA did not affect AcAtg8 expression (A-░). Down-regulating the AcAtg8b gene, significantly inhibited mature cyst formation (B). The experiments were repeated 3 times and the average values are presented with error bars representing standard deviations. **The means are significantly different at P<0.01 by the Student's t-test.

Table 1.Atg8 subfamilies in metazoan lineages
Table 1.
|
Lineage |
Representative species |
Number of genes |
|
Mammals |
Homo sapience
|
7 |
|
Mollusks |
Aplysia californica
|
4 |
|
Flat worms |
Schmidtea mediterranea
|
3 |
|
Nematodes |
Caenorhabditis elegans
|
2 |
|
Insects |
Drosophila melanogaster
|
2 |
|
Protozoa |
Acanthamoeba castellanii
|
2 |
|
Plasmodium falciparum
|
1 |
|
Leishmania major
|
1 |
|
Entamoeba invadens
|
1 |
|
Dictyostelium discoideum
|
1 |
|
Yeast |
Saccharomyces cerevisiae
|
1 |