Abstract
This study investigated the effect of breast-feeding in protection against protozoan infection in infants with persistent diarrhea. Infants were classified into 2 groups; 161 breast-fed infants and the same number of non-breast-fed infants. Microscopic examinations of stool were done for detection of parasites and measuring the intensity of infection. Moreover, serum levels of IgE and TNF-α were measured by ELISA. Cryptosporidium spp., Entamoeba histolytica/Entamoeba dispar, Giardia lamblia, and Blastocystis sp. were demonstrated in infants with persistent diarrhea. The percentage of protozoan infections was significantly lower in breast-fed infants than that in the non-breast-fed infants. The levels of IgE and TNF-α were significantly lower in the breast-fed group than in the non-breast-fed group. There were significant positive associations between the serum levels of IgE and TNF-α and the intensity of parasite infection in the breast-fed group. It is suggested that breast-feeding has an attenuating effect on the rate and intensity of parasite infection.
-
Key words: Entamoeba histolytica, Entamoeba dispar, Giardia lamblia, Cryptosporidium, Blastocystis, breast-feeding, breast milk, diarrhea, intestinal protozoa, IgE, TNF-α
INTRODUCTION
Protozoan parasites such as
Cryptosporidium spp.,
Entamoeba histolytica, and
Giardia lamblia [
1] cause diarrhea which still remains a leading cause of morbidity and mortality among infants in low- and middle-income countries [
2]. As infections with parasites, particularly
G. lamblia and
Cryptosporidium spp., are the most likely causes of persistent diarrhea (>14 days) [
3], pediatricians had strong suspicion from the symptoms and clinical courses of these infants that the causes of persistent diarrhea should be intestinal protozoan infections (IPI), i.e., infections caused by pathogenic protozoa in the intestine [
4].
Breast-feeding provides significant protection against many diseases including diarrhea in infancy [
5]. This is attributable to a complex of acquired and innate factors unique to human milk including immunoglobulins [
6,
7], oligosaccharides, glycoconjugates, lactoferrin, antimicrobial compounds [
8], leukocytes, cytokines, and other agents [
9,
10]. Breast-fed infants have a lower prevalence of gastrointestinal infections including IPI than formula-fed infants [
9,
10]. However, there are little conflicting opinions concerning breast-milk and anti-infective functions [
11,
12]. Detailed investigations are still limited.
IgE is considered to play a central role in protective immunity against parasites, not only helminths [
13] but also some protozoa such as
G. intestinalis (synonymous with
G. lamblia and
G. duodenalis) [
14].
TNF-α is an important inflammatory cytokine in immune regulation and resistance to various microbes including protozoa [
15]. This cytokine is known to be of significant importance in the pathogenesis of inflammatory bowel diseases, and anti-TNF agents have proven to be effective in the treatment of chronic active inflammatory bowel diseases and fistulizing disease [
16].
Thus, the present study was designed to investigate the breast-feeding in protection against IPI by comparing breast-fed with non-breast-fed infants with persistent diarrhea.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Subjects and methods
This study was carried out with 322 infants (146 boys and 176 girls, 2-6 months old) who presented with persistent diarrhea (minimum of 3 loose stools/day for more than 14 days) in spite of an anti-bacterial drug, nifuroxazide. They had been enrolled from inpatient wards and outpatient clinics of the Pediatric Department of University Hospital, Minia District, Egypt, between January 2011 and March 2012. These infant cases were divided into 2 equal groups of 161 each. The first group comprised of 161 partially breast-fed infants (79 boys and 82 girls, mean±SD=4.5±1.1 months old) and the second an equal number of non-breast-fed infants (some were having formula alone, and some bovine milk, 67 boys and 94 girls, 4.4±1.2 months old). There was no difference in sex between these 2 groups. The sample characteristics (age, parent socio-economic levels, and residency) of these 2 groups were similar.
The breast-fed infants had been breast-fed since birth, while non-breast-fed infants had received a formula since 1 or 2 weeks after birth. Formula was dissolved in tap water, which had been boiled and cooled down.
Ethical considerations
Verbal consent was obtained from the parents of these infants. All procedures were conducted according to the ethical standards approved by the Institutional Human Ethics Committee, Faculty of Medicine, Minia University, Egypt.
Stool examinations
Stool samples were collected in a clean plastic container once per infant but several stool samples were collected on alternate days to detect parasites because cysts of G. lamblia are excreted intermittently. Fecal specimens were transported to the laboratory of Parasitology Department, Faculty of Medicine, Minia University, Egypt to be examined by different techniques for parasitic infections within 1-3 hr after collection.
For microscopic examinations, direct wet smear methods, namely saline wet mount and iodine wet mount, were applied. The technique of formol-ether sedimentation was used to concentrate the cysts or oocysts of the protozoa.
A same amount of stools (50 mg) from each of all infants was mixed with 10 ml of fixation buffer (sodium-acetate acetic acid formalin, SAF) and incubated for 1 hr for fixation and inactivation. The suspension was passed through 4 layers of cotton netting and centrifuged at 2,000 g for 5 min. Two smears were dried in air, fixed with methanol, and then examined using 2 different stains: acid fast stain (modified Ziehl-Neelsen stain) for identification of
Cryptosporidium spp. and Giemsa stain for identification of
Blastocystis sp. The intensity of infection was scored as follows by ×1,000 magnification: 1, very low infection (1 parasite per field); 2, mild infection (2 parasites per field); 3, moderate infection (3 parasites per field); 4, heavy infection (4 or more parasites per field) [
17].
Blood samples were collected from arm vein and sera were stored at -20℃ until use. The serum levels of IgE and TNF-α were measured using commercially available ELISA kits (MYM Laboratory and Medical Supply, Inc., San Diego, California, USA, and Anogen, Ontario, Canada, respectively) according to the manufacturers' guidelines.
Statistical analysis
Data were coded and verified prior to data entry. No data were double-entered. As the data were distributed as normal, results of the studies were reported as mean±SD. The Statistical Package of SPSS version 16 for Windows was used for data entry and analysis. Descriptive statistics were calculated. The χ2-test was used to compare proportions of parasite detection between groups and of sex difference between groups. The Student's t-test was used to compare means between groups. Regression analysis was used for estimating the relationships between serum levels of IgE and TNF-α and the intensity of the infection. P<0.05 was considered to be statistically significant.
RESULTS
Parasite detection and infection intensity among infants with persistent diarrhea
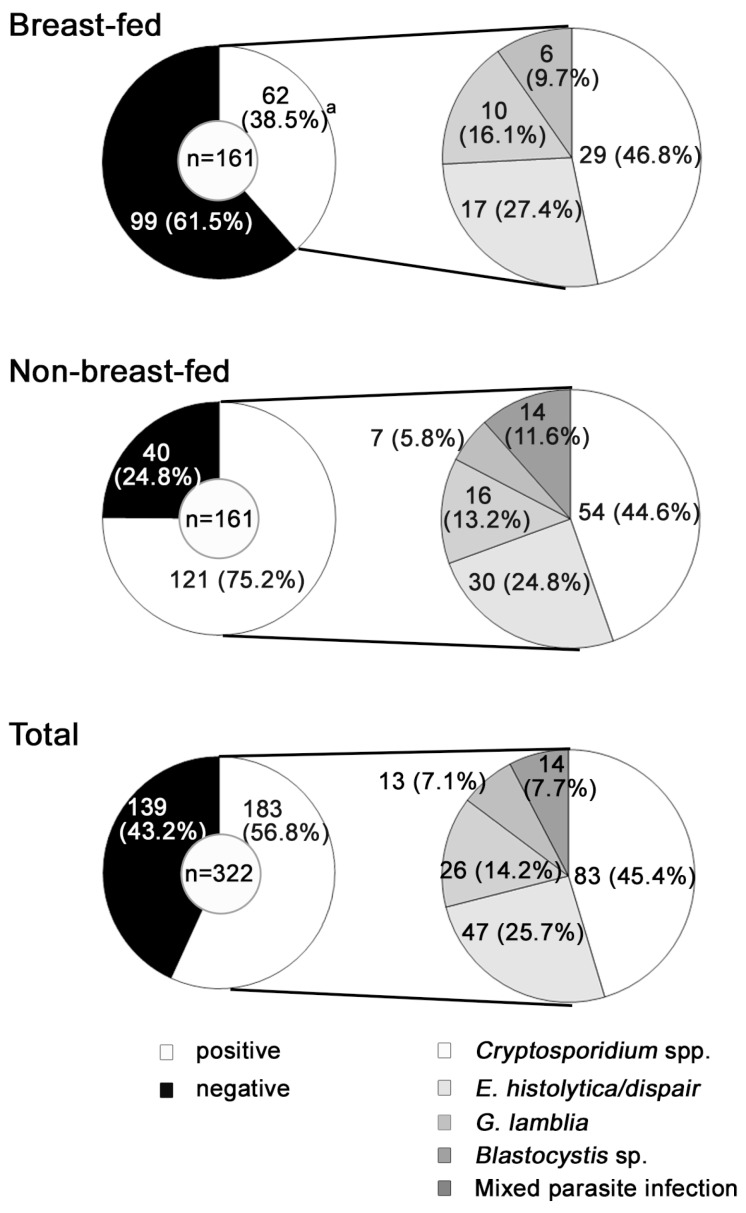
Protozoa were detected in 62 breast-fed infants (38.5%), a significantly lower incidence than that in non-breast-fed infants, among which 121 (75.2%) were infected (
Fig. 1).
Cryptosporidium spp. was the most common protozoan detected in both groups, followed by
E. histolytica/
E. dispar,
G. lamblia, and
Blastocystis sp. Mixed parasitic infections were observed only in the non-breast-fed group. The intensity of single parasitic infection of the breast-fed group was significantly less than that of the non-breast-fed group (
Table 1).
Serum levels of IgE and TNF-α were summarized in
Table 2. In the breast-fed group, the serum levels of IgE and TNF-α of parasite positive infants were significantly elevated (514.8±95.2 IU/ml and 6.2±0.7 pg/ml, respectively) compared with the levels in parasite negative infants (118.1±15.9 IU/ml and 3.5±0.5, respectively) (
P<0.01). In non-breast-fed group, the serum levels of IgE and TNF-α of parasite positive infants were also significantly elevated (645.9±67.8 IU/ml and 7.7±1.2 pg/ml, respectively) than those of parasite negative infants (121.1±9.6 IU/ml and 3.7±0.3 pg/ml, respectively) (
P<0.01). In addition, the serum levels of IgE and TNF-α of parasite-infected infants were significantly lower in the breast-fed group (514.8±95.2 IU/ml and 6.2±0.7 pg/ml, respectively) than those in the non-breast-fed group (645.9±67.8 IU/ml and 7.7±1.2 pg/ml, respectively) (
P<0.01). The serum levels of IgE and TNF-α of infants infected with each parasite were significantly lower in the breast-fed group than in the non-breast-fed group (
P<0.01) (data not shown). There were no significant differences in the serum levels of IgE and TNF-α of the parasite-non-infected infants between the breast-fed and non-breast-fed groups.
There were no significant differences in the serum levels of IgE between parasite-infected boys (487.8±97.2 IU/ml and 653.1±67.3 IU/ml, respectively) and girls (534.3±90.0 IU/ml and 641.7±68.2 IU/ml) of the parasite infected breast-fed and non-breast-fed groups. However, the serum levels of TNF-α in the breast-fed group were significantly lower in parasite-infected boys (5.8±0.8 pg/ml) than in parasite-infected girls (6.5±0.6 pg/ml) (P<0.05).
Relation between serum levels of IgE and TNF-α and parasite infection intensity
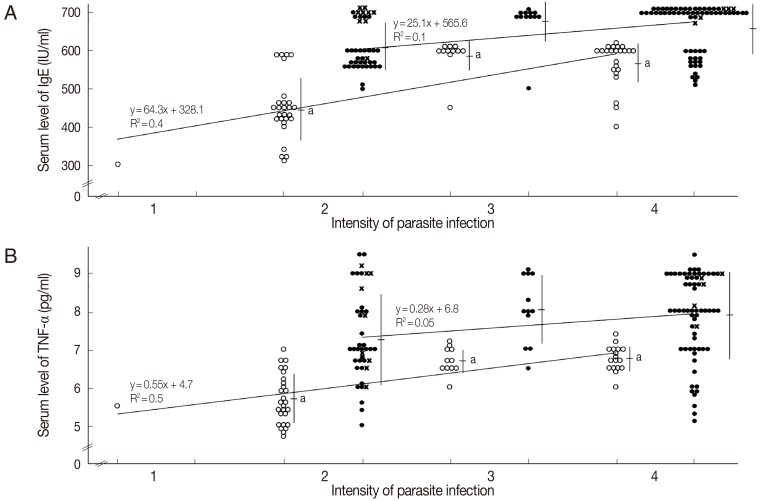
There was a significant positive correlation between the infection intensity and the serum levels of IgE (
Fig. 2A) and TNF-α (
Fig. 2B) in the breast-fed group. On the other hand, in the non-breast-fed group, there was a positive correlation between them, although there were no significant differences. The serum level of IgE tended to be higher in infants infected with 2 parasites than in those with a single parasite in the non-breast-fed group. With regard to the comparison in the same infection intensity, the levels of IgE and TNF-α in the breast-fed group were significantly lower than those in the non-breast-fed group (
P<0.01) (
Fig. 2).
DISCUSSION
Persistent diarrhea should prompt investigation for protozoan infections, mainly of
Giardia and
Cryptosporidium [
3]. Protozoan parasites, which were detected in the study, were the main causes of diarrhea. Diarrhea was not with an acute onset and was not associated with high fever or vomiting. Infants, infected with protozoan parasites, were treated successfully with anti-protozoan drugs.
This study clearly indicated that the percentage of protozoan parasite-infected infants in the breast-fed group was significantly less than that of the non-breast-fed group. The numbers of infants infected with the same protozoan parasites in the breast-fed group were also significantly lower than those of the non-breast-fed group. In addition, the intensities of parasite infections were less in the breast-fed group than those in the non-breast-fed group. Increased risks of persistent diarrhea are environment-related, such as poor hygiene [
18]. In this study, both macroenvironmental measures (provision of a safe and adequate water supply, and hygienic waste disposal) and microenvironmental measures (hand washing, hygienic storage and use of water, and avoidance of stale/cold-storage infant foods in tropical environments) [
18] were poor in both groups. Lack of access to clean water, sanitation, and hygiene are strong drivers for IPI [
4]. Thus, scaling-up environmental control measures and safe water and hygiene strategies is important to prevent children from persistent diarrhea [
18].
IgE activates platelets and induces cytotoxic functions against parasites [
19]. An elevation in total IgE levels was also reported even in helminth and protozoan infectious diseases such as cryptosporidiosis and giardiasis [
13,
14,
20-
22]. Excretory and secretory proteins released by
G. intestinalis are responsible for production of a specific IgE [
14]. In this study, the serum level of IgE was significantly elevated in both parasite-infected groups compared to the non-infected infants. The IgE levels of infants infected with the respective parasites of the breast-fed group were significantly lower than those of the non-breast-fed group in this study. The IgE level and the intensity of parasite infections were related in the breast-fed group. In addition, the IgE level of the breast-fed group was lower than that of the non-breast-fed group with the same intensity of parasite infections. Some factors such as immune activation by protozoa might be different between the breast-fed and non-breast-fed groups. This will be the subject of a future study. The higher total IgE levels in non-breast-fed infants were not due to cow's milk-specific IgE; such antibodies could not be detected in cow's-milk infant group [
23]. Regarding the relation of breast-feeding and IgE levels in the early childhood of healthy infants, there are some contradictory reports. Total IgE level was significantly lower in breast-fed infants compared with formula-fed infants, while another report showed that no feeding-related differences in the IgE level in the first 6 months of life [
24,
25].
Protozoan infections of the intestinal tissue will lead to a robust inflammatory process and production of a wide range of cytokines including TNF-α that is elevated in the gastrointestinal tract of some forms of inflammatory colitis, cryptosporidiosis,
E. histolytica-related diarrhea, and giardiasis [
26-
30]. In this study, the serum level of TNF-α was also significantly higher in infants infected with parasites than those uninfected. In addition, the level of infected infants was significantly lower in the breast-fed group than that in the non-breast-fed group. The serum level of TNF-α in the breast-fed group was also significantly lower than that in the non-breast-fed group with the same intensity of parasite infections. Tumor necrosis factor-induced nitric oxide production by macrophages leads to cytotoxicity of
E. histolytica in vitro [
31].
The serum levels of TNF-α of male infants were significantly lower than those of female infants in the infected breast-fed group. Gender differences exist in the incidence, morbidity, and mortality associated with diseases with an inflammatory component [
32]. The relationship between TNF-α levels and gender will be a topic for further studies. There were no significant differences in IgE levels between parasite-infected boys and girls in this study, in agreement with the previous report [
20].
The present study showed positive relationships between the intensity of infection and serum levels of IgE and TNF-α in the breast-fed group. Thus, the serum levels of IgE and TNF-α may be a marker of the intensity of infection and an indicator for therapy and prognosis in infants with persistent diarrhea.
The present study revealed the effect of breast-feeding on lowering the rate and ameliorating the intensity of protozoan parasite infections. The spread of breast-feeding by education and encouragement of mothers, with attention to transmission of pathogens such as human immunodeficiency virus through breast-feeding, can prevent protozoa-caused diarrhea, the main cause of death in infants [
33].
Notes
-
We have no conflict of interest related with this study.
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS
The authors would like to thank Prof. Nabil Shokrany Gabr, Head of Department of Parasitology, Faculty of Medicine, Minia University, Egypt for his continuous advice through the technical procedures. The authors would also like to thank Prof. Refaat M. Khalifa, Department of Parasitology, Faculty of Medicine, Assuit University, Egypt for his continuous advice.
References
- 1. Pierce KK, Kirkpatrick BD. Update on human infections caused by intestinal protozoa. Curr Opin Gastroenterol 2009;25:12-17.
- 2. Fischer Walker CL, Perin J, Aryee MJ, Boschi-Pinto C, Black RE. Diarrhea incidence in low- and middle-income countries in 1990 and 2010: a systematic review. BMC Public Health 2012;12:220.
- 3. Cheng AC, McDonald JR, Thielman NM. Infectious diarrhea in developed and developing countries. J Clin Gastroenterol 2005;39:757-773.
- 4. Speich B, Marti H, Ame SM, Ali SM, Bogoch II, Utzinger J, Albonico M, Keiser J. Prevalence of intestinal protozoa infection among school-aged children on Pemba Island, Tanzania, and effect of single-dose albendazole, nitazoxanide and albendazole-nitazoxanide. Parasit Vectors 2013;6:3.
- 5. Section on Breastfeeding. Breastfeeding and the use of human milk. Pediatrics 2012;129:e827-e841.
- 6. Korpe PS, Liu Y, Siddique A, Kabir M, Ralston K, Ma JZ, Haque R, Petri WA Jr. Breast milk parasite-specific antibodies and protection from amebiasis and cryptosporidiosis in Bangladeshi infants: a prospective cohort study. Clin Infect Dis 2013;56:988-992.
- 7. Tellez A, Winiecka-Krusnell J, Paniagua M, Linder E. Antibodies in mother's milk protect children against giardiasis. Scand J Infect Dis 2003;35:322-325.
- 8. Gillin FD, Reiner DS, Wang CS. Human milk kills parasitic intestinal protozoa. Science 1983;221:1290-1292.
- 9. Morrow AL, Ruiz-Palacios GM, Altaye M, Jiang X, Guerrero ML, Meinzen-Derr JK, Farkas T, Chaturvedi P, Pickering LK, Newburg DS. Human milk oligosaccharides are associated with protection against diarrhea in breast-fed infants. J Pediatr 2004;145:297-303.
- 10. Chirico G, Marzollo R, Cortinovis S, Fonte C, Gasparoni A. Antiinfective properties of human milk. J Nutr 2008;138:1801S-1806S.
- 11. Hernell O, Ward H, Bläckberg L, Pereira ME. Killing of Giardia lamblia by human milk lipases: an effect mediated by lipolysis of milk lipids. J Infect Dis 1986;153:715-720.
- 12. Granot E, Golan D, Berry EM. Breast-fed and formula-fed infants do not differ in immunocompetent cell cytokine production despite differences in cell membrane fatty acid composition. Am J Clin Nutr 2000;72:1202-1205.
- 13. Erb KJ. Helminths, allergic disorders and IgE-mediated immune responses: where do we stand? Eur J Immunol 2007;37:1170-1173.
- 14. Jiménez JC, Fontaine J, Grzych JM, Dei-Cas E, Capron M. Systemic and mucosal responses to oral administration of excretory and secretory antigens from Giardia intestinalis. Clin Diagn Lab Immunol 2004;11:152-160.
- 15. Derouich-Guergour D, Brenier-Pinchart MP, Ambroise-Thomas P, Pelloux H. Tumour necrosis factor-α receptors: role in the physiopathology of protozoan parasite infections. Int J Parasitol 2001;31:763-769.
- 16. Kuhbacher T, Fölsch UR. Practical guidelines for the treatment of inflammatory bowel disease. World J Gastroenterol 2007;13:1149-1155.
- 17. Utzinger J, Botero-Kleiven S, Castelli F, Chiodini PL, Edwards H, Köhler N, Gulletta M, Lebbad M, Manser M, Matthys B, N'Goran EK, Tannich E, Vounatsou P, Marti H. Microscopic diagnosis of sodium acetate-acetic acid-formalin-fixed stool samples for helminths and intestinal protozoa: a comparison among European reference laboratories. Clin Microbiol Infect 2010;16:267-273.
- 18. Bhutta ZA, Ghishan F, Lindley K, Memon IA, Mittal S, Rhoads JM. Persistent and chronic diarrhea and malabsorption: Working Group report of the second World Congress of Pediatric Gastroenterology, Hepatology, and Nutrition. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr 2004;39:S711-S716.
- 19. Joseph M, Gounni AS, Kusnierz JP, Vorng H, Sarfati M, Kinet JP, Tonnel AB, Capron A, Capron M. Expression and functions of the high-affinity IgE receptor on human platelets and megakaryocyte precursors. Eur J Immunol 1997;27:2212-2218.
- 20. Durmaz B, Yakinci C, Köroğlu M, Rafiq M, Durmaz R. Concentration of total serum IgE in parasitized children and the effects of the antiparasitic therapy on IgE levels. J Trop Pediatr 1998;44:121.
- 21. Allam AF, Abou-Shousha SA, Abou Shamaa LA. Antibody profile, interferon-γ and nutritional status in cryptosporidial infection among school children. J Egypt Soc Parasitol 2002;32:755-766.
- 22. Matowicka-Karna J, Dymicka-Piekarska V, Kemona H. IFN-gamma, IL-5, IL-6 and IgE in patients infected with Giardia intestinalis. Folia Histochem Cytobiol 2009;47:93-97.
- 23. Björkstén F, Saarinen UM. IgE antibodies to cow's milk in infants fed breast milk and milk formulae. Lancet 1978;2:624-625.
- 24. Saarinen UM, Björkstén F, Knekt P, Siimes MA. Serum IgE in healthy infants fed breast milk or cow's milk-based formulas. Clin Allergy 1979;9:339-345.
- 25. Juto P, Björkstén B. Serum IgE in infants and influence of type of feeding. Clin Allergy 1980;10:593-600.
- 26. Kasper LH, Buzoni-Gatel D. Ups and downs of mucosal cellular immunity against protozoan parasites. Infect Immun 2001;69:1-8.
- 27. Rojas-Cartagena C, Flores I, Appleyard CB. Role of tumor necrosis factor receptors in an animal model of acute colitis. Cytokine 2005;32:85-93.
- 28. Kirkpatrick BD, Noel F, Rouzier PD, Powell JL, Pape JW, Bois G, Alston WK, Larsson CJ, Tenney K, Ventrone C, Powden C, Sreenivasan M, Sears CL. Childhood cryptosporidiosis is associated with a persistent systemic inflammatory response. Clin Infect Dis 2006;43:604-608.
- 29. Peterson KM, Shu J, Duggal P, Haque R, Mondal D, Petri WA Jr. Association between TNF-α and Entamoeba histolytica diarrhea. Am J Trop Med Hyg 2010;82:620-625.
- 30. Muñoz-Cruz S, Gómez-García A, Millán-Ibarra J, Giono-Cerezo S, Yépez-Mulia L. Giardia lamblia: interleukin 6 and tumor necrosis factor-alpha release from mast cells induced through an Ig-independent pathway. Exp Parasitol 2010;126:298-303.
- 31. Blazquez S, Zimmer C, Guigon G, Olivo-Marin JC, Guillén N, Labruyère E. Human tumor necrosis factor is a chemoattractant for the parasite Entamoeba histolytica. Infect Immun 2006;74:1407-1411.
- 32. Cooper GS, Stroehla BC. The epidemiology of autoimmune diseases. Autoimmun Rev 2003;2:119-125.
- 33. Kourtis AP, Butera S, Ibegbu C, Belec L, Duerr A. Breast milk and HIV-1: vector of transmission or vehicle of protection? Lancet Infect Dis 2003;3:786-793.
Fig. 1Intestinal protozoa isolated from feces of 322 infants with persistent diarrhea according to feeding state. The detailes of the mixed parasite infection from non-breast-fed group were as follows: Cryptosporidium spp. and E. histolytica/dispar; 4 (3.3%), Cryptosporidium spp. and G. lamblia; 4 (3.3%), and Cryptosporidium spp. and Blastocystis sp.; 6 (5.0%). aP<0.05 between breast-fed vs. non-breast-fed.

Fig. 2Serum levels of IgE and TNF-α and intensity of parasite infection. (A) IgE. (B) TNF-α. Open circles, breast-fed group; filled circles, non-breast-fed group. X, infants infected with mixed parasites. Values are means±SD. aP<0.01 between breast-fed and non-breast-fed group in same intensity of parasite infections.

Table 1.Parasite intensity of infected infants with persistent diarrhea according to feeding state
Table 1.
|
|
Breast-fed |
Non-breast-fed |
Total |
|
Parasite intensity |
Single parasite infection |
2.9 ± 0.9a
|
3.3 ± 0.9 |
3.1 ± 1.0 |
|
Mixed parasite infections |
- |
2.7 ± 1.0 |
2.7 ± 1.0 |
|
Total |
2.9 ± 0.9 |
3.2 ± 0.9 |
3.1 ± 1.0 |
Table 2.The levels of serum IgE and TNF-α in infants with persistent diarrhea
Table 2.
|
Protozoa |
Breast-fed (n = 161)
|
Non-breast-fed (n = 161)
|
|
IgE (IU/ml) |
TNF-α (pg/ml) |
IgE (IU/ml) |
TNF-α (pg/ml) |
|
Positive (n = 183) |
514.8 ± 95.2a,b
|
6.2 ± 0.7a,b
|
645.9 ± 67.8b
|
7.7 ± 1.2b
|
|
Boys (n = 72) |
487.8 ± 97.2 |
5.8 ± 0.8c
|
653.1 ± 67.3 |
7.7 ± 1.1 |
|
Girls (n = 111) |
534.3 ± 90.0 |
6.5 ± 0.6 |
641.7 ± 68.2 |
7.7 ± 1.2 |
|
Negative (n = 139) |
118.1 ± 15.9 |
3.5 ± 0.5 |
121.1 ± 9.6 |
3.7 ± 0.3 |