Abstract
Entamoeba histolytica, which causes amoebic colitis and occasionally liver abscess in humans, is able to induce host cell death. However, signaling mechanisms of colon cell death induced by E. histolytica are not fully elucidated. In this study, we investigated the signaling role of NOX in cell death of HT29 colonic epithelial cells induced by E. histolytica. Incubation of HT29 cells with amoebic trophozoites resulted in DNA fragmentation that is a hallmark of apoptotic cell death. In addition, E. histolytica generate intracellular reactive oxygen species (ROS) in a contact-dependent manner. Inhibition of intracellular ROS level with treatment with DPI, an inhibitor of NADPH oxidases (NOXs), decreased Entamoeba-induced ROS generation and cell death in HT29 cells. However, pan-caspase inhibitor did not affect E. histolytica-induced HT29 cell death. In HT29 cells, catalytic subunit NOX1 and regulatory subunit Rac1 for NOX1 activation were highly expressed. We next investigated whether NADPH oxidase 1 (NOX1)-derived ROS is closely associated with HT29 cell death induced by E. histolytica. Suppression of Rac1 by siRNA significantly inhibited Entamoeba-induced cell death. Moreover, knockdown of NOX1 by siRNA, effectively inhibited E. histolytica-triggered DNA fragmentation in HT29 cells. These results suggest that NOX1-derived ROS is required for apoptotic cell death in HT29 colon epithelial cells induced by E. histolytica.
-
Key words: Entamoeba histolytica, host cell death, HT29 colon epithelial cell, reactive oxygen species (ROS), NADPH oxidase 1 (NOX1)
INTRODUCTION
Tissue-invasive intestinal protozoan parasite,
Entamoeba histolytica, causes colitis and liver abscess in human beings [
1]. During infection, trophozoites of
E. histolytica degrade mucin layer that covers the colon epithelium and then subsequently results in contact-dependent colon cell death [
2].
E. histolytica-induced colon cell death is crucial for provocation of neutrophil-mediated tissue inflammation in the amoeba-infected colon lesions [
3]. Adherence of amoebae to host cells through amoebic gal-lectin and host β
2-integrin induces host cell death in vitro [
4,
5]. Host cell death induced by
E. histolytica does not involve either of the two common cell death signaling pathways of death receptors or mitochondria [
6]. It has been reported that intracellular Ca
2+ [
7], calpain [
8], caspase-3 [
9], or protein tyrosine phosphatases [
10,
11] can be a signaling molecule required for
E. histolytica-induced host cell death. However, the signaling mechanisms responsible for amoeba-induced host cell death are not fully understood.
NADPH oxidase (NOX)-derived reactive oxygen species (ROS) act as intracellular second messengers for a variety of cellular receptor signal transduction pathways, and they play pivotal roles in various biological activities, including host defense, cell growth and differentiation, stimulation of pro-inflammatory genes, and cell death [
12]. In phagocytes, NOX2 has been well known to function as antibacterial host defenses [
13]. Recently, 6 homologs of NOX2, including NOX1, NOX3, NOX4, NOX5, dual oxidase 1 (DUOX1), and DUOX2 have been highly expressed in non-phagocytic cells. It is of particular interest that NOX1 expression is abundant in colon tissues and HT29 colonic epithelial tumor cell line [
14]. NOX1 plays a crucial role in host defense against symbiotic or infectious microbes in the colon [
15,
16]. For example, NOX1-derived ROS was produced in guinea pig colon epithelial cells stimulated by recombinant flagellin from
Salmonella enteritidis [
17]. In the context of host cell death induced by
E. histolytica, there is also accumulating evidence that diphenyleneiodonium chloride (DPI)-sensitive NOXs are required for ROS-dependent cell death in neutrophils [
18] and Caco2 colon epithelial cells [
19] induced by
E. histolytica. However, the functional role of NOX1-derived ROS in cell death of HT29 colon epithelial cells induced by
E. histolytica has not been elucidated. In this study, using NOX inhibitor DPI and siRNA specific for NOX1, we show that NOX1-derived ROS is closely involved in
E. histolytica-induced cell death of HT29 colonic epithelial cells.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Reagents
DPI, pan-caspase inhibitor z-VAD-FMK and rotenone were purchased from EMD Biosciences (Darmstadt, Hesse, Germany). Dichlorodihydrofluorescein diacetate (H2DCFDA) and 5-(and 6)-chloromethyl SNARF-1 were purchased from Molecular Probes (Eugene, Oregon, USA). Rabbit polyclonal antibodies against human NOX1 or Rac1 were purchased from Abcam (Cambridge, UK). Unless stated otherwise, all other reagents were purchased from Sigma-Aldrich (St. Louis, Missouri, USA).
Cultivation of E. histolytica trophozoites and HT29 colon epithelial tumor cell line
E. histolytica (HM1:IMSS strain) trophozoites were subcultivated in screw-capped glass tubes containing TYI-S-33 medium at 37℃. After cultivation for 48 hr, trophozoites in the logarithmic growth phase were harvested and washed with RPMI 1640 medium supplemented with 2 g/L NaHCO3, 50 mg/L gentamicin, 1 g/L human serum albumin, and 10% (v/v) heat-inactivated fetal bovine serum (FBS) and were suspended in the culture medium before being incubated with host cells. HT29 cells (American Type Culture Collection, Manassas, Virginia, USA) were maintained in RPMI 1640 medium or minimal essential medium (MEM) containing 10% heat-inactivated FBS, 100 U/ml penicillin, and 100 µg/ml streptomycin at 37℃ in a humidified 5% CO2 incubator. Amoebae and HT29 cells were always 99% viable before experiments as determined by trypan blue exclusion tests.
Measurement of E. histolytica-induced cell death in HT29 cells
HT29 cells (5×105 cells/sample) seeded in tissue culture plates were incubated with live E. histolytica trophozoites at a ratio of 5:1 and 10:1 for 30 min or 60 min at 37℃ in a CO2 incubator. The percentage of dead HT29 cells was determined by staining with trypan blue dye or propidium iodide (PI). Trypan blue staining for dead cells was performed on at least 300 cells. Flow cytometric analysis following PI staining was performed with a FACScan on at least 3,000 cells from host cell fraction. To assay amoeba-induced DNA fragmentation, HT29 cells (4×106 cells/sample) were co-incubated with E. histolytica trophozoites at a ratio of 10:1 for 30 min or 60 min at 37℃ in a humidified CO2 incubator. To elucidate the role of amoebic galactose binding lectin in DNA fragmentation induced by E. histolytica, HT29 cells were incubated with E. histolytica trophozoites for 30 min or 60 min in the presence of D-galactose (50 mM). After incubation, the cells were harvested and DNA was extracted using ApopLadder Ex™ (TaKaRa, Shiga, Japan). The DNA samples were separated by electrophoresis on a 2% agarose gel and were visualized by ethidium bromide.
To determine the role of caspases or NOX in PI influx or DNA fragmentation in HT29 cells induced by E. histolytica, HT29 cells were pretreated with DMSO (0.5 or 1 %, v/v), pan-caspase inhibitor z-VAD-FMK (100 µM), or NOX inhibitor DPI (50 µM) for 30 min at 37℃ before being incubated with E. histolytica.
Measurement of intracellular ROS production in HT29 cells
Intracellular ROS accumulation in HT29 cells was measured by staining cells with the green fluorescence probe H2DCF-DA, which is rapidly oxidized to highly fluorescent DCF in the presence of intracellular H2O2, and was analyzed by flow cytometry. Briefly, HT29 cells (4×105 or 1×105 cells/sample, respectively) seeded in tissue culture plates were preloaded with 5 µM H2DCF-DA for 30 min and washed twice with culture medium. Washed cells were incubated with or without E. histolytica trophozoites at a ratio of 5:1 or 10:1 for up to 10 min at 37℃ in a CO2 incubator. Mean DCF fluorescence intensities of the amoeba-treated HT29 cells were compared with those of the non-treated control cells.
In addition, intracellular ROS accumulation in HT29 cells induced by amoebic trophozoites was confirmed by inverted fluorescence microscopy (×200). In particular, to clearly distinguish between live amoebae and HT29 cells, we added prestained amoebae with 10 µM SNARF-1 (red color) to the cell cultures. The production of intracellular ROS (green color) was observed under an inverted fluorescence microscopy.
Reverse transcription-PCR (RT-PCR)
Total RNA was obtained from HT29 cells using the TRI reagent (Molecular Research Center, Cincinnati, Ohio, USA) and was reverse-transcribed using ProSTAR first strand RT-PCR kit (Stratagene, La Jolla, California, USA). PCR was performed with specific primer sets for NOX1: NOX1, forward 5' ATGGGAAACTGGGTGGTTA-3' and reverse 5'-TAGCTGAAGTTACCATGAGAA-3'. Cycling conditions were as follows: 5 min at 95℃, followed by 35 cycles of 30 sec at 95℃, 30 sec at 60℃, and 30 sec at 72℃, with a final amplification for 7 min at 72℃. PCR products were examined on 2% agarose gels.
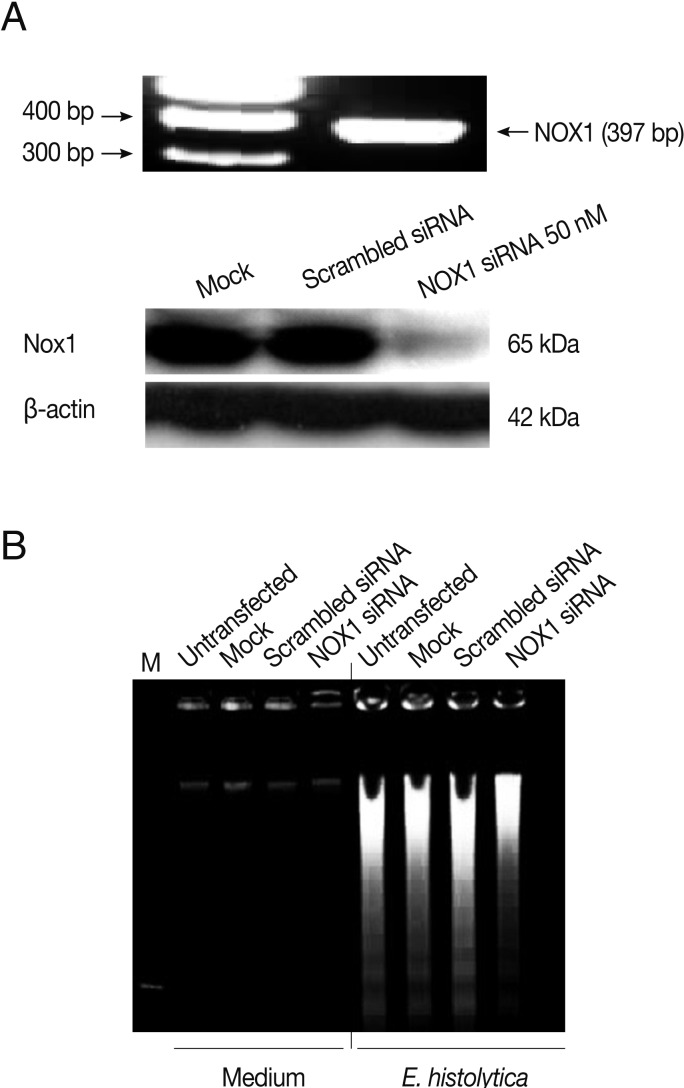
Knockdown of NOX1 and Rac1 in HT29 cells by siRNA
NOX1 siRNA, Rac1 siRNA, and the control siRNA were purchased from Dharmacon (Lafayette, Colorado, USA). In mock transfections, all reagents were used except for the siRNA. The siRNA cellular transfections were performed according to the manufacturer's instructions. To optimize the conditions of siRNA treatment, HT29 cells treated with 50 nM of siRNAs for varying periods of incubation (24, 48, or 72 hr) were examined. The cells were viable throughout the course of all experiments, as determined by trypan blue exclusion assays (data not shown). At 24, 48, and 72 hr post-transfection, the efficiency of siRNA-mediated knockdown of NOX1 or Rac1 was confirmed by western blotting using Ab to NOX1, Rac1 or β-actin as the loading control. At 48 hr post-transfection, the transfected HT29 cells were washed, placed in fresh cell culture medium, and co-incubated with E. histolytica for cell death assays.
Immunoblot analysis
HT29 cells (1×106 cells/sample), transfected with or without siRNAs, were lysed in lysis buffer (20 mM Tris-HCl, pH 7.5, 60 mM β-glycerophosphate, 10 mM EDTA, 10 mM MgCl2, 10 mM NaF, 2 mM dithiothreitol, 1 mM Na2VO4, 1 mM 4-amidinophenylmethane sulfonyl fluoride hydrochloride, 1% NP-40, and 5 µg/ml leupeptin) on ice for 30 min. Whole cell lysates were resolved in 10% SDS-PAGE gels, transferred to a membrane, and probed with specific antibodies to Rac1, NOX1, or β-actin at 4℃ overnight. The membranes were then soaked with horseradish-peroxidase (HRP)-conjugated anti-rabbit antibody at room temperature for 1 hr. Immunoreactivity was detected using LumiGLO (Cell Signaling Technology, Beverly, Massachusetts, USA).
Statistical analysis
Results are expressed as mean±SEM from at least three independent experiments. Statistical analyses were conducted using the Student's t-test. Values with P<0.05 were considered statistically significant.
RESULTS
Adherence of E. histolytica induced caspase-independent cell death in HT29 cells
E. histolytica-induced cell death in HT29 cells was determined through trypan blue, PI exclusion tests, or DNA fragmentation assays. As shown in
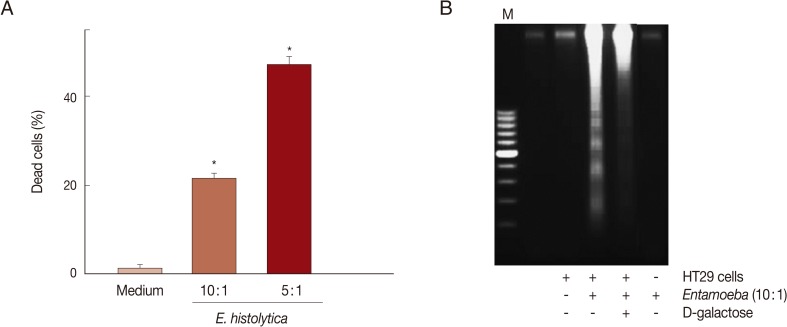
Fig. 1A, when HT29 cells were incubated with
E. histolytica trophozoites for 60 min at 10:1 and 5:1 ratios, the percentages of dead cells stained with trypan blue were 21.3% and 47.3%, respectively. In contrast, only 1.3% of cells incubated with medium alone were dead. Co-incubation of HT29 cells with
E. histolytica at a ratio of 10:1 for 60 min resulted in the marked appearance of DNA laddering (
Fig. 1B), which is a typical pattern for apoptotic cell death. Moreover, addition of 50 mM D-galactose remarkably retarded
E. histolytica-induced nuclear DNA fragmentation in HT29 cells (
Fig. 1B). The amoebic trophozoites themselves did not show laddering pattern (
Fig. 1B). To assess whether caspase activation is involved in
E. histolytica-induced HT29 cell death, HT29 cells pretreated with a pan-caspase inhibitor (z-VAD-FMK) were incubated with
E. histolytica trophozoites for 60 min at 10:1 ratio. The pro-death effect of amoebae on PI influx or DNA fragmentation was not prevented by pretreatment with 100 µM z-VAD-FMK (
Fig. 2A and B). To examine involvement of NOX-derived ROS in colon cell death induced by
E. histolytica, we pretreated HT29 cells for 30 min with a NADPH oxidase inhibitor (DPI) prior to exposure to live trophozoites. Pretreatment with 50 µM DPI strongly retarded amoebic-induced DNA fragmentation in HT29 cells (
Fig. 2B).
Incubation with E. histolytica induces DPI-sensitive intracellular ROS generation in HT29 cells
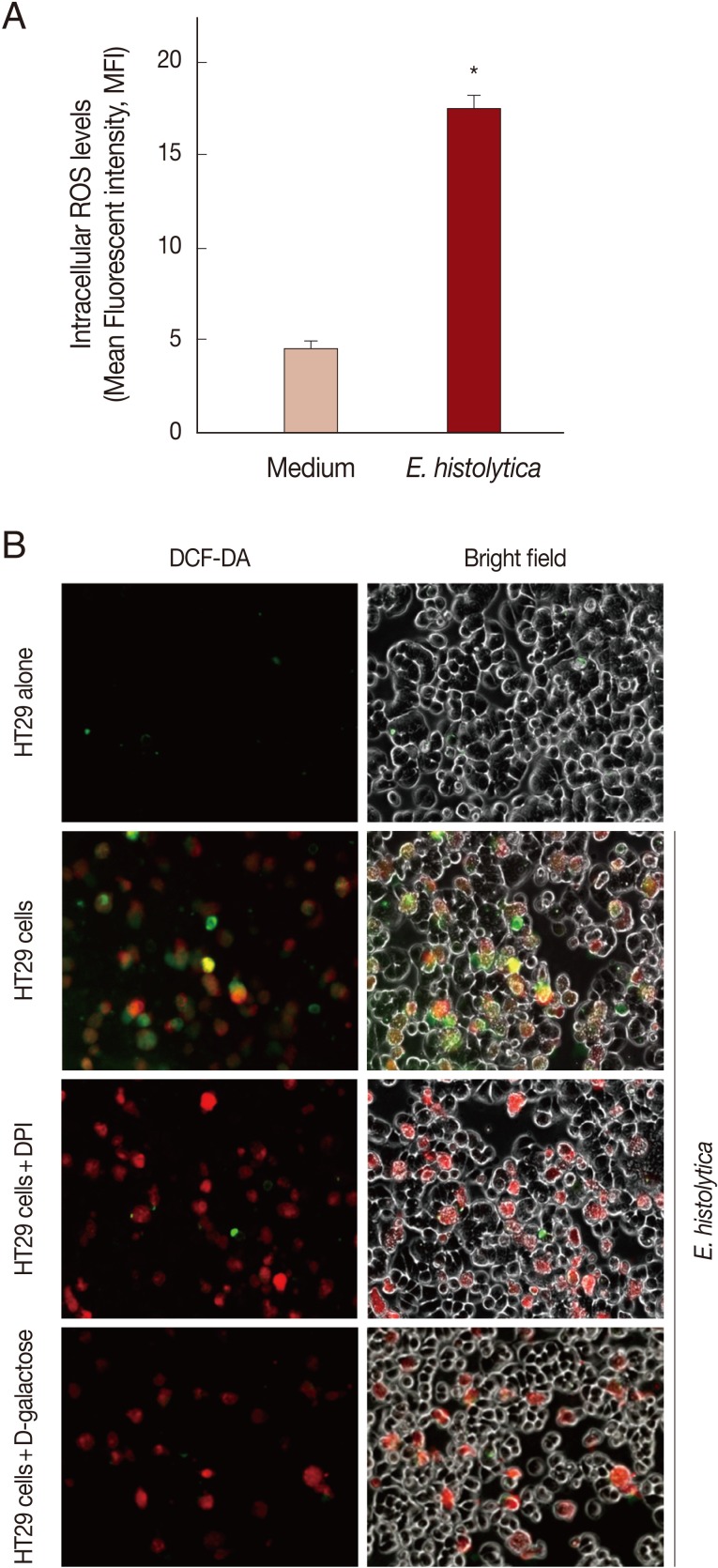
As shown in
Fig. 3A, when using flow cytometer, mean fluorescence intensity (MFI) of DCF fluorescence in HT29 cells incubated with live trophozotes for 5 min at a 10:1 ratio was about 3.8-fold increased compared to results for cells incubated with medium alone. No DCF fluorescence was observed in amoebic trophozoites themselves (data not shown). As shown in
Fig. 3B by inverted fluorescence microscopy, HT29 cells co-incubated with live amoebic trophozoites prestained with SNARF-1 (red fluorescence) showed strong ROS responses (green fluorescence) as compared to cells incubated with medium alone. In contrast, treatment with 50 µM DPI and 50 mM D-galactose almost completely abolished the generation of intracellular ROS in HT29 cells.
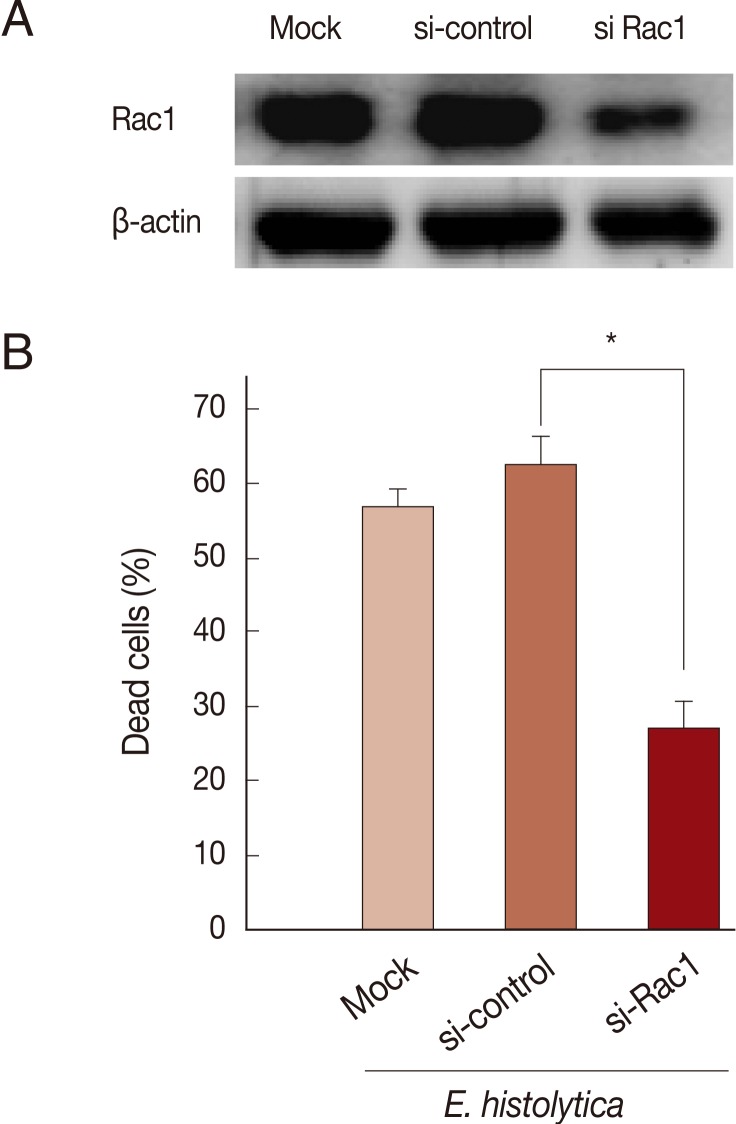
Rac GTPase is an important activator of NOX1 [
20]. To address the role of constitutive activity of Rac1 in
E. histolytica-induced cell death, we designed small interference RNA (siRNA) to selectively knock down Rac1 protein levels. As shown in
Fig. 4A, Rac1 siRNA efficiently (about 60%) inhibited the Rac1 protein expression in HT29 cells compared to siRNA control group. As shown in
Fig. 4B, mock transfection in HT29 cells did not prevent
Entamoeba-induced cell death. However, when transfected HT29 cells with Rac1 siRNA were incubated with
E. histolytica, the percentage of dead cells stained with PI was reduced about 50% compared to that with control siRNA (
Fig. 4B). We examined the gene expression of the catalytic subunits of NOX1 in colon cells. HT29 cells expressed NOX1 protein at high levels (
Fig. 5A). As shown in
Fig. 5A, compared to scrambled siRNA, either mRNA or protein expression for NOX1 was effectively suppressed in HT29 cells by transfection with 50 nM NOX1 siRNA. As shown in
Fig. 5B, compared to control siRNA, NOX1 siRNA effectively inhibited
E. histolytica-induced DNA fragmentation in HT29 cells.
DISCUSSION
We have demonstrated that NOX1-derived ROS participates in cell death of HT29 colon epithelial cells induced by
E. histolytica. Amoeba-induced HT29 cell death was not inhibited by pretreatment with pan-caspase inhibitor. These results suggest that HT29 colon cells induced by amoebic trophozoites undergo to cell death in a caspase-independent mechanism.
E. histolytica-induced cell death in HT29 cells was strongly inhibited by pretreatment with a NOX inhibitor, DPI. Indeed, mRNA and protein for NOX1 was found to be highly expressed in HT29 colon cells. Moreover, Rac1 protein, which is an important cytosolic factor for NOX1 activation [
27], was highly expressed in HT29 cells. Suppression of Rac1 level by siRNA resulted in significant reduction of
Entamoeba-induced cell death in HT29 cells. Furthermore, knockdown of NOX1 protein expression by specific siRNA prevented efficiently
Entamoeba-induced DNA fragmentation in HT29 cells, suggesting that NADPH oxidase-derived ROS plays an important role in apoptotic cell death of colon epithelial cells induced by
E. histolytica. All together, these results strongly suggest that NOX1 is required for ROS-mediated apoptotic cell death in HT29 colon cells induced by
E. histolytica. Our in vitro finding can extend to in vivo scene that adherence of amoebic trophozoites to colon epithelial cells triggers the activation of NOX1 enzymes leading to ROS-dependent cell death, which can be a host defense mechanism to regulate acute inflammation during early phase of human amoebiasis.
Our previous report [
18] has shown that ROS generation and caspase-3 works independently in the process of apoptosis in human neutrophils induced by
E. histolytica, suggesting that there are two pro-death channels in human neutrophils for determination of apoptotic death in response to
E. histolytica. However, when we used HT29 colon epithelial cells, a previous report has shown that calpain inhibitor or calpain siRNA reduced
E. histolytica-induced cell death [
21], suggesting that ROS as well as calpain may participate in the process of HT29 cell death. Although it is evident that calpain can regulate activation of caspase-3 in Jurkat T cells [
8], pretreatment with a cell permeable calpain inhibitor, calpeptin, did not work to inhibit
E. histolytica-induced cell death. These results suggest that signaling molecules involved in cell death induced by
E. histolytica may vary in various immune cells.
In this study, we found that incubation with
E. histolytica induced intracellular ROS generation and cell death in HT29 cells in a contact-dependent manner. Signaling interaction between amoebic Gal/GalNAc lectin and glycosylated receptors in host side may cause
E. histolytica-induced host cell death [
3]. Integrin is a typical adhesion molecule interacting with mammalian galectin [
22]. Recently, we presented evidence that there might be a signaling association between β
2 integrin on human neutrophils and amoebic galectin in
E. histolytica-induced host cell apoptosis [
5]. Moreover, it remains a possibility that amoebic galectin might directly associate with glycosylated residues of NOX2 since human NOX2 (gp91
phox) is a glycosylated protein, and the carbohydrate chains are largely composed of N-acetylglucosamine and galactose [
23]. A recent paper regarding on the lectin interaction to glycosylated residues of NOX2 supports our possibility [
24]. Therefore, further studies to find out signaling interaction between amoebic gal-lectin and glycosylated receptors with high galactose side chains can lead to better understanding the secret of real parasitism in the view of tightly regulated signaling talk between host and amoeba in vivo.
A large number of studies about cell death of non-phagocytic cells via NOX activation have been documented [
25,
26]. In this study, by using both general NOX inhibitor DPI and siRNA for NOX1, we have demonstrated that ROS generated from NOX1 can contribute to
E. histolytica-induced HT29 colon cell death. Our finding was consistent with our previous report on signaling involvement of NOX1-derived ROS in cell death of Caco2 colon epithelial cells induced by
E. histolytica [
19]. NOX1 is highly expressed in the colon epithelial cells [
27] and its distribution increases from the ascending to descending colon segments, in parallel with the increased bacterial burden [
28]. Therefore, NOX1 in colon epithelial cells could be activated during cell death in response to amoebic adhesion during early phase of the amebiasis. Among 7 NOX isoforms, NOX5, DUOX1 and DUOX2, which harbor calcium binding site EF-hands, are known to be activated by elevation of intracellular Ca
2+ [
29]. Indeed, NOX5-derived ROS has been reported to mediate cell death of prostatic tumor cell line stimulated with calcium ionophore A23187 [
30]. Conversely, ROS has been reported to induce elevation of intracellular Ca
2+ from intracellular storage [
31]. Moreover,
E. histolytica-induced host cell death can occur in a calcium- or ROS-dependent manner [
18,
32]. Therefore, deeper excavation regarding whether there is a cross talk between calcium and NOX-derived ROS, and whether calcium-dependent NOX5 can contribute to ROS-dependent host cell death induced by
E. histolytica should be needed.
In conclusion, we show that NOX1-derived ROS, but not caspases, participates in cell death of HT29 colon epithelial cells induced by E. histolytica. This finding provides a clue to unveil the functional role of NOX1 in the context of human colon cell death leading to tissue pathology during early phase of human amebiasis.
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS
This study was supported by the Korea Research Foundation Grant funded by the Korea Government (MOEHRD, Basic Research Promotion Fund) (KRF-2006-311-E00256).
References
- 1. Stanley SL Jr. Amoebiasis. Lancet 2003;361:1025-1034.
- 2. Moncada D, Keller K, Ankri S, Mirelman D, Chadee K. Antisense inhibition of Entamoeba histolytica cysteine proteases inhibits colonic mucus degradation. Gastroenterology 2006;130:721-730.
- 3. Petri WA, Haque R, Mann BJ. The bittersweet interface of parasite and host: lectin-carbohydrate interactions during human invasion by the parasite Entamoeba histolytica. Annu Rev Microbiol 2002;56:39-64.
- 4. Berninghausen O, Leippe M. Necrosis versus apoptosis as the mechanism of target cell death induced by Entamoeba histolytica. Infect Immun 1997;65:3615-3621.
- 5. Sim S, Park SJ, Yong TS, Im KI, Shin MH. Involvement of beta 2-integrin in ROS-mediated neutrophil apoptosis induced by Entamoeba histolytica. Microbes Infect 2007;9:1368-1375.
- 6. Seydel KB, Stanley SL Jr. Entamoeba histolytica induces host cell death in amebic liver abscess by a non-Fas-dependent, non-tumor necrosis factor alpha-dependent pathway of apoptosis. Infect Immun 1998;66:2980-2983.
- 7. Ragland BD, Ashley LS, Vaux DL, Petri WA. Entamoeba histolytica: target cells killed by trophozoites undergo DNA fragmentation which is not blocked by Bcl-2. Exp Parasitol 1994;79:460-467.
- 8. Kim KA, Lee YA, Shin MH. Calpain-dependent calpastatin cleavage regulates caspase-3 activation during apoptosis of Jurkat T cells induced by Entamoeba histolytica. Int J Parasitol 2007;37:1209-1219.
- 9. Huston CD, Houpt ER, Mann BJ, Hahn CS, Petri WA. Caspase 3-dependent killing of host cells by the parasite Entamoeba histolytica. Cell Microbiol 2000;2:617-625.
- 10. Teixeira JE, Mann BJ. Entamoeba histolytica-induced dephosphorylation in host cells. Infect Immun 2002;70:1816-1823.
- 11. Kim KA, Lee YA, Shin MH. Calpain-dependent cleavage of SHP-1 and SHP-2 is involved in the dephosphorylation of Jurkat T cells induced by Entamoeba histolytica. Parasite Immunol 2010;32:176-183.
- 12. Forman HJ, Torres M. Reactive oxygen species and cell signaling: respiratory burst in macrophage signaling. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 2002;166:S4-S8.
- 13. Lambeth JD. Nox enzymes and the biology of reactive oxygen. Nat Rev Immunol 2004;4:181-189.
- 14. Geiszt M, Lekstrom K, Brenner S, Hewitt SM, Dana R, Malech HL, Leto TL. NAD(P)H oxidase 1, a product of differentiated colon epithelial cells, can partially replace glycoprotein 91phox in the regulated production of superoxide by phagocytes. J Immunol 2003;171:299-306.
- 15. Kuwano Y, Kawahara T, Yamamoto H, Teshima-Kondo S, Tominaga K, Masuda K, Kishi K, Morita K, Rokutan K. Interferon-gamma activates transcription of NADPH oxidase 1 gene and upregulates production of superoxide anion by human large intestinal epithelial cells. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol 2006;290:C433-C443.
- 16. Kim JS, Bokoch GM. Anthrax edema toxin inhibits Nox1-mediated formation of reactive oxygen species by colon epithelial cells. J Innate Immun 2009;1:145-152.
- 17. Kawahara T, Kuwano Y, Teshima-Kondo S, Takeya R, Sumimoto H, Kishi K, Tsunawaki S, Hirayama T, Rokutan K. Role of nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate oxidase 1 in oxidative burst response to Toll-like receptor 5 signaling in large intestinal epithelial cells. J Immunol 2004;172:3051-3058.
- 18. Sim S, Yong TS, Park SJ, Im KI, Kong Y, Ryu JS, Min DY, Shin MH. NADPH oxidase-derived reactive oxygen species-mediated activation of ERK1/2 is required for apoptosis of human neutrophils induced by Entamoeba histolytica. J Immunol 2005;174:4279-4288.
- 19. Kim KA, Kim JY, Lee YA, Song KJ, Min D, Shin MH. NOX1 participates in ROS-dependent cell death of colon epithelial Caco2 cells induced by Entamoeba histolytica. Microbes Infect 2011;13:1052-1061.
- 20. Miyano K, Koga H, Minakami R, Sumimoto H. The insert region of the Rac GTPases is dispensable for activation of superoxide-producing NADPH oxidases. Biochem J 2009;422:373-382.
- 21. Jang YS, Song KJ, Kim JY, Lee YA, Kim KA, Lee SK, Shin MH. Calpains are involved in Entamoeba histolytica-induced death of HT-29 colonic epithelial cells. Korean J Parasitol 2011;49:177-180.
- 22. Lei CX, Zhang W, Zhou JP, Liu YK. Interactions between galectin-3 and integrinbeta3 in regulating endometrial cell proliferation and adhesion. Hum Reprod 2009;24:2879-2889.
- 23. Harper AM, Chaplin MF, Segal AW. Cytochrome b-245 from human neutrophils is a glycoprotein. Biochem J 1985;227:783-788.
- 24. Gorudko IV, Mukhortava AV, Caraher B, Ren M, Cherenkevich SN, Kelly GM, Timoshenko AV. Lectin-induced activation of plasma membrane NADPH oxidase in cholesterol-depleted human neutrophils. Arch Biochem Biophys 2011;516:173-181.
- 25. Cristóvão AC, Choi DH, Baltazar G, Beal MF, Kim YS. The role of NADPH oxidase 1-derived reactive oxygen species in paraquat-mediated dopaminergic cell death. Antioxid Redox Signal 2009;11:2105-2118.
- 26. Coyoy A, Valencia A, Guemez-Gamboa A, Morán J. Role of NADPH oxidase in the apoptotic death of cultured cerebellar granule neurons. Free Radic Biol Med 2008;45:1056-1064.
- 27. Geiszt M, Leto TL. The Nox family of NAD(P)H oxidases: host defense and beyond. J Biol Chem 2004;279:51715-51718.
- 28. Bedard K, Krause KH. The NOX family of ROS-generating NADPH oxidases: physiology and pathophysiology. Physiol Rev 2007;87:245-313.
- 29. Bedard K, Lardy B, Krause KH. NOX family NADPH oxidases: not just in mammals. Biochimie 2007;89:1107-1112.
- 30. Brar SS, Corbin Z, Kennedy TP, Hemendinger R, Thornton L, Bommarius B, Arnold RS, Whorton AR, Sturrock AB, Huecksteadt TP, Quinn MT, Krenitsky K, Ardie KG, Lambeth JD, Hoidal JR. NOX5 NAD(P)H oxidase regulates growth and apoptosis in DU 145 prostate cancer cells. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol 2003;285:C353-C369.
- 31. Granados MP, Salido GM, González A, Pariente JA. Dose-dependent effect of hydrogen peroxide on calcium mobilization in mo-use pancreatic acinar cells. Biochem Cell Biol 2006;84:39-48.
- 32. Ravdin JI, Moreau F, Sullivan JA, Petri WA Jr, Mandell GL. Relationship of free intracellular calcium to the cytolytic activity of Entamoeba histolytica. Infect Immun 1988;56:1505-1512.
Fig. 1Co-incubation with Entamoeba histolytica induces cell death in HT29 colon cells. (A) Percentage of dead cells in HT29 cells incubated with live trophozoites of E. histolytica. Data are presented as means±SEM from 5 independent experiments. Significant differences from controls are as follows. *P<0.05. (B) Addition of D-galactose inhibits DNA fragmentation in HT29 cells induced by E. histolytica. The figure is representative of 3 separate experiments showing similar results.
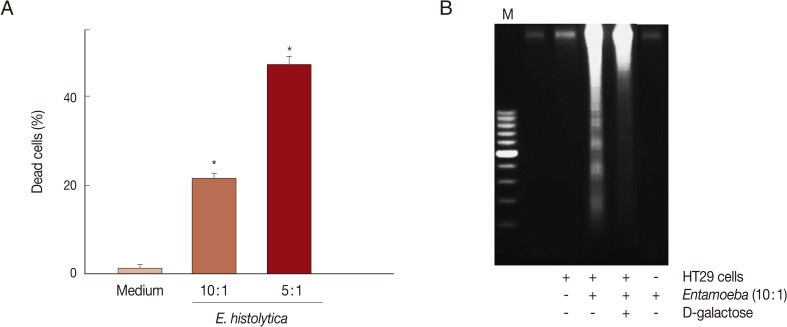
Fig. 2NOX-derived ROS, but not caspases are involved in cell death of HT29 cells induced by E. histolytica. (A) Effect of pan-caspase inhibitor z-VAD-fmk (100 µM) on PI influx in HT29 cells induced by E. histolytica. Data are presented as means±SEM from 4 independent experiments. (B) Effect of z-VAD-fmk or NADPH oxidase inhibitor (DPI) on E. histolytica-induced DNA fragmentation in HT29 cells. The figure is representative of 3 separate experiments showing similar results.
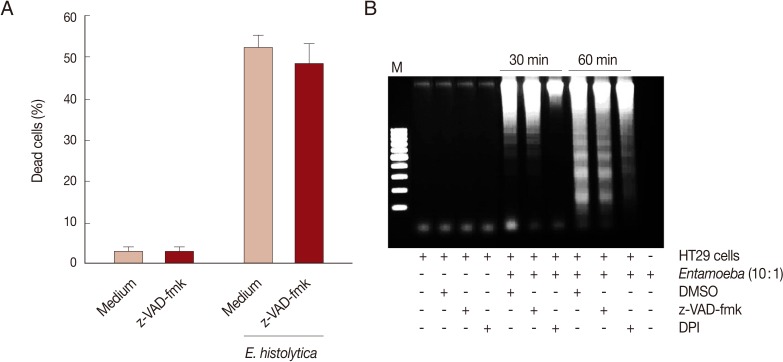
Fig. 3Incubation with live trophozoites of E. histolytica induces ROS generation in HT29 cells. (A) Incubation with E. histolytica induces ROS generation in HT29 cells. Data are presented as means±SEM from 3 independent experiments. Significant differences from controls are as follows; *P<0.05. (B) Visualization of intracellular ROS accumulation in HT29 cells adhered to live trophozoites of E. histolytica. The production of intracellular ROS in HT29 cells was observed by inverted fluorescence microscopy (×200).
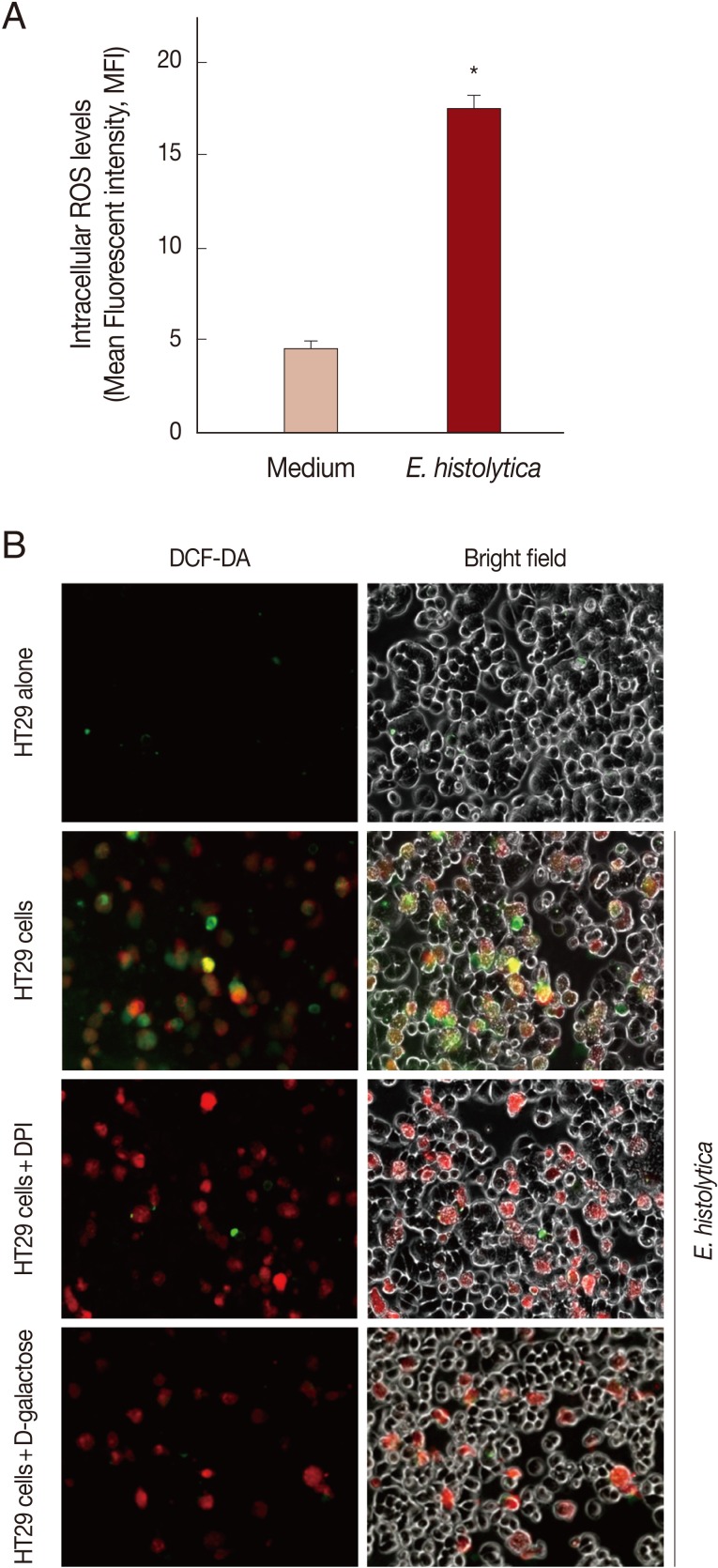
Fig. 4Transfection with Rac1 siRNA inhibits E. histolytica-induced cell death in HT29 cells. (A) Analysis of Rac1 protein levels following Rac1 siRNA in HT29 cells. Blots are representative of 3 independent experiments. (B) Effect of Rac1 siRNA on PI influx in HT-29 cells induced by E. histolytica. Data are means±SD of 3 experiments done in triplicate. Significant differences from controls are as follows; *P<0.05.
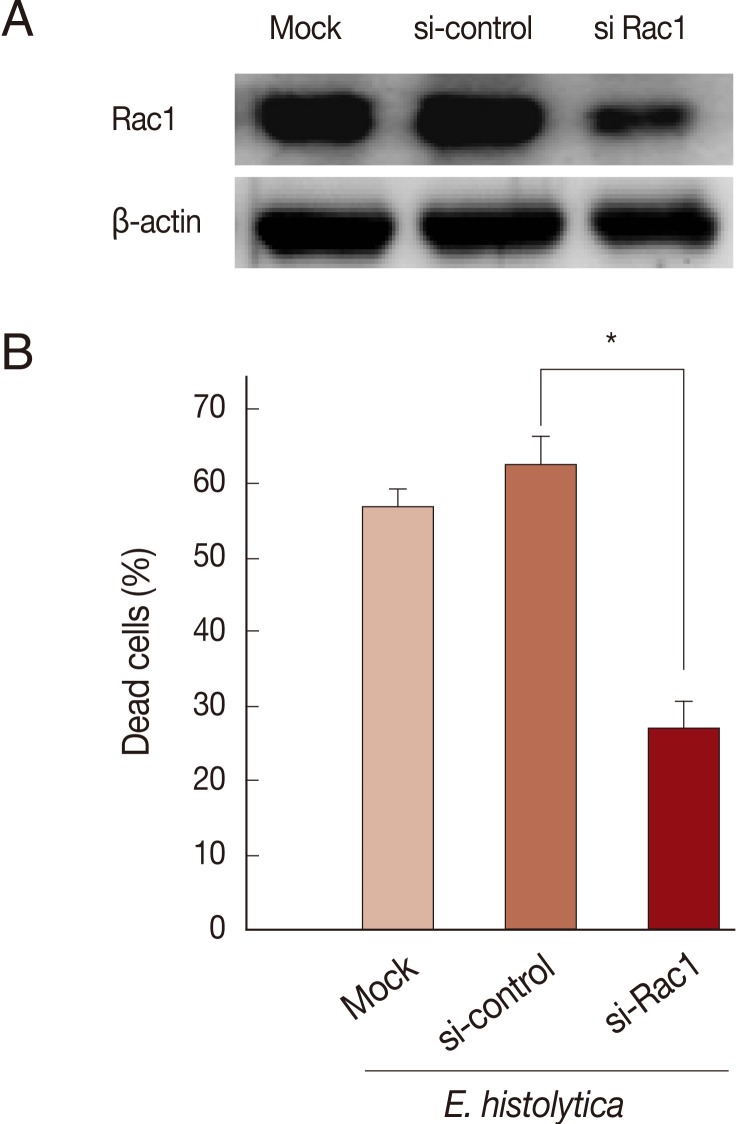
Fig. 5Transfection with NOX1 siRNA inhibits E. histolytica-induced ROS generation and cell death in HT29 cells. (A) Analysis of rac1 gene or protein levels following NOX1 siRNA in HT29 cells. Blots are representative of 3 independent experiments. (B) Effect of NOX1 siRNA on E. histolytica-induced DNA fragmentation in HT29 cells. The figure is representative of 3 separate experiments showing similar results.