Abstract
We evaluated the status of Clonorchis sinensis infection and potential risk factors among residents of riverside areas (Geumgang) in Muju-gun, Jeollabuk-do (Province), Korea. From January to February 2010, a total of 349 (171 males, 178 females) stool samples were collected and examined by the formalin-ether concentration technique. Also, village residents were interviewed using questionnaires to obtain information about C. sinensis infection-related risk factors. Overall egg-positive rate of C. sinensis was 13.2%. Egg-positive rates were significantly higher in males, farmers, and residents who had lived there more than 20 years, and in residents who had eaten raw freshwater fish than in opposite groups, respectively. However, there was no significant difference between age groups, education levels, cigarette smoking, alcohol drinking, health status, past history of infection, and experience of clonorchiasis medication and examination. Logistic regression analysis was performed to determine risk factors for clonorchiasis. On univariate analysis, the odds ratios for males, farmers, those who had lived there more than 20 years, and who had eaten raw freshwater fish were 2.41, 4.44, 3.16, and 4.88 times higher than those of the opposites, respectively. On multivariate analysis, the odds ratio of residents who had eaten raw freshwater fish was 3.2-fold higher than that of those who had not. These results indicate that residents living in Muju-gun, along the Geum River, Korea, have relatively high C. sinensis egg-positive rates, and the habit of eating raw freshwater fish was the major factor for the maintenance of clonorchiasis.
-
Key words: Clonorchis sinensis, prevalence, risk factor, Geum River basin
INTRODUCTION
Parasitic infections were regarded as major public health problems in the past in Korea. Over the last 50 years, the prevalence of such infections has decreased rapidly, accompanying the increase in GNP, improvements in sanitation and hygiene, changes in agricultural management, and a nationwide control plan [
1]. Infection by soil-transmitted helminths, such as
Ascaris and
Trichuris, has decreased dramatically: the egg-positive rates for these parasites were 54.9% and 65.4% in 1971 and 0.03% and 0.41% in 2012, respectively [
2]. However, the pattern of the prevalence of foodborne trematode infections seems to be quite different from that of soil-transmitted helminth infections. Among foodborne trematode infections prevailing in the Republic of Korea (=Korea),
Clonorchis sinensis infection is known to be the most important endemic disease, and its endemicity has remained at relatively high levels in riverside areas [
3,
4,
5,
6].
C. sinensis is the most common human liver fluke in East Asian countries, including Korea, China, and Vietnam [
7,
8,
9]. Currently, it is estimated that more than 200 million people are at risk of infection, 15-20 million people are infected, and 1.5-2.0 million show symptoms or complications [
7]. Human infection occurs when metacercariae in the flesh or skin of freshwater fish are ingested by a human host. As second intermediate hosts of
C. sinensis, 40 species of freshwater fish have been reported in Korea [
10]. Thus, eating raw freshwater fish is believed to be the leading risk factor for
C. sinensis infection [
4,
8,
9]. Most infected humans experience no symptoms; however, a part of the infected population with heavy worm burdens and/or chronic infection with complications may suffer from severe clinical manifestations, such as epigastric pain, tenderness, fever, jaundice, and diarrhea [
7]. Several studies have demonstrated its carcinogenic properties in humans, and it was reclassified as a group 1 biocarcinogens by the International Agency for Research on Cancer in 2009 [
11]. Recently, clonorchiasis has been associated with atopy and high levels of total serum IgE [
12].
C. sinensis infection remains an issue of major public health concerns in Korea. National surveys revealed egg-positive rates of
C. sinensis in the general population as 4.6% in 1971, 1.8% in 1976, 2.6% in 1981, 2.7% in 1986, 2.2% in 1992, 1.4% in 1997, 2.4% in 2004, and 1.9% in 2012 [
2]. In 2013, June et al. [
4] reported
C. sinensis egg-positive rates of residents living in 5 river basins of 9.3% in Geum-gang, 7.9% in Han-gang, 21.5% in Seomjin-gang, 4.8% in Youngsan-gang, and 13.8% in Nakdong-gang. These data indicate that the egg-positive rates in residents living in those river basins differed considerably, and that it was still being actively transmitted in endemic areas of Korea.
The Geum River basin is an endemic area for clonorchiasis. There have been several surveys on the prevalence of
C. sinensis infection in the Geum River previously [
3,
4,
6,
13,
14,
15,
16]; however, there was no up-to-date survey report. Thus, to evaluate the recent epidemiological characteristics of
C. sinensis infection in residents of Muju-gun County, Jeollabuk-do (Province), living near the Geum River, we examined the prevalence of
C. sinensis infection and clonorchiasis-related risk factors in survey participants using stool examinations and a questionnaire survey.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Area surveyed and population
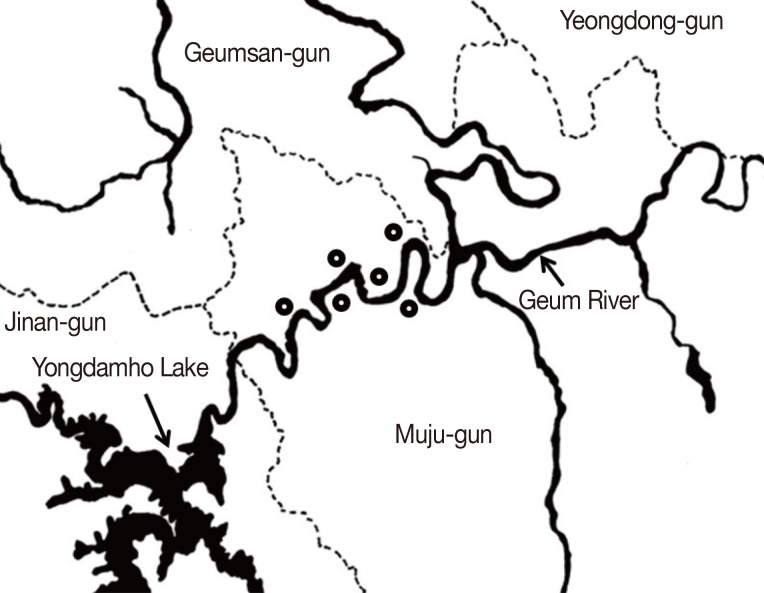
This epidemiological study was undertaken during the period of January to February 2010. In total, 349 residents (171 males, 178 females) from 6 villages in Bunam-myeon, Muju-gun in Jeollabuk-do Province, Korea, were examined (
Fig. 1). The age of the subject population ranged from 4 to 90 years old (average, 51.3±19.7 years). Written or oral consent was obtained from all the participants. The study protocol was approved by the IRB committee of Chungnam National University School of Medicine, Daejeon, Korea.
Stool specimens were collected in plastic containers and transferred to the laboratory of the Korea National Institutes of Health, Osong, Chungcheongbuk-do. A part (1 g) of each fecal sample was fixed with 10% neutral formalin in a 10-ml tube. These formalin-fixed stool specimens were further processed to the formalin ether concentration technique to identify the presence of C. sinensis eggs. C. sinensis egg-positive residents were administered with praziquantel at the dose of 25 mg/kg ×3 times in a single day. Also, individuals positive for parasites other than C. sinensis were treated with appropriate anti-parasitic drugs at the end of the study.
Questionnaire survey
We conducted a questionnaire survey of the participants to evaluate correlations between C. sinensis infection and risk factors. Each participant was interviewed by a community health practitioner working in the village. The structured questionnaire contained 2 parts: sociodemographic characteristics and clonorchiasis-related risk factors.
Statistical analyses
The results of fecal examination and the questionnaires were analyzed using the SPSS software (ver. 16.0; Chicago, Illinois, USA). Differences in continuous variables among groups were tested using a 2-tailed Mann Whitney U test and Student's t-test. Factors that showed a significant association with the C. sinensis egg-positive rate were used in univariate and multivariate logistic regression analyses. A univariate analysis of the relationship between C. sinensis infection and clonorchiasis-related risk factors was conducted. A multiple logistic regression analysis was done to eliminate confounding factors. Differences between the 2 groups were considered significant when the P-value was<0.05.
RESULTS
Characteristics of participating residents
The characteristics of the 349 participants are summarized in
Table 1. There were 171 males (49.0%) and 178 females (51.0%). The percentages of participants who were <65 and ≥ 65 years old were 51.9% and 48.1%, respectively. Among participants, more than two-thirds were farmers, non-smokers, and who had lived for more than 20 in the surveyed area. More than a half did not drink alcohol and felt generally healthy. According to education levels, the percentages of participants who were uneducated, graduated from elementary school, or middle school were 31.2%, 41.5%, and 27.2%, respectively.
We also checked the clonorchiasis-related behavior of the participants. The percentage who had eaten raw freshwater fish was 61.6%, and it was 77.2% in males. Of the participants, 25.2% had experience of C. sinensis infection in the past, and 23.2% of them had received treatment. The percentage of participants who was undergone a previous clonorchiasis examination was 63.6%.
Analysis of C. sinensis egg-positive cases
The results from the stool examinations are summarized in
Table 2. The overall egg-positive rate for
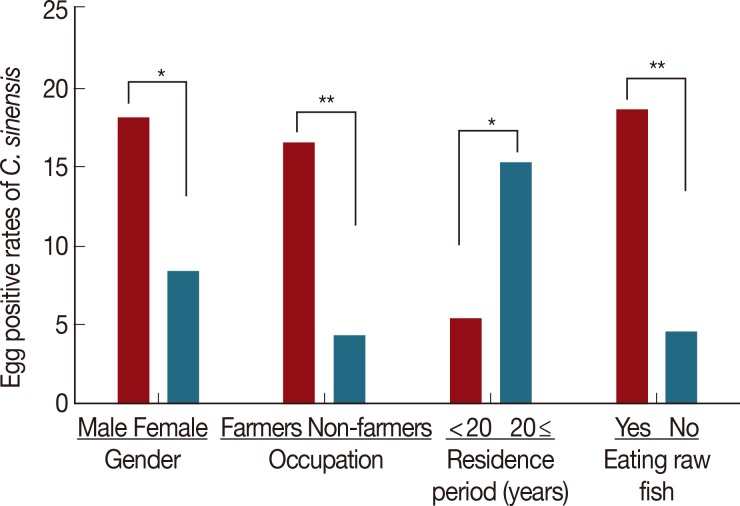
C. sinensis was 13.2% (46/349 cases). The egg-positive rates were significantly higher in males (18.1%,
P=0.011), farmers (16.5%,
P<0.001), residents who had lived there more than 20 years (15.3%,
P=0.032), and residents who had eaten raw freshwater fish (18.6%,
P<0.001) than in females (8.4%), non-farmers (4.3%), residents who had lived there less than 20 years (5.4%), and residents who had not eaten raw freshwater fish (4.5%), respectively (
Fig. 2).
C. sinensis egg-positive rates were somewhat higher in those who graduated from elementary school, alcohol drinkers, and those who had undergone previous C. sinensis examinations than those of the opposite group for each variable. However, the egg-positive rates showed no statistically significant difference by age group, education level, cigarette smoking, alcohol drinking, health status, past history of infection, or experience of past clonorchiasis medication or examination.
Correlation between C. sinensis infection and infection-related risk factors
To evaluate the relationship between
C. sinensis infection and clonorchiasis-related risk factors, we selected those factors that showed statistically significant differences among groups, such as gender, occupation, residence period, and raw freshwater fish consumption, and then analyzed the results by logistic regression (
Table 3).
On univariate analysis, the odds ratios for males, farmers, those who had lived there more than 20 years, and who had eaten raw freshwater fish were 2.41, 4.44, 3.16, and 4.88 times higher than those of the opposites, respectively. On multivariate analysis, the risk of infection was 3.2-fold higher in those with the habit of raw freshwater fish consumption than in those without the habit, while gender, occupation, and residence period were confounding factors. Thus, eating raw fish was found to be the major factor for maintenance of clonorchiasis in this region.
DISCUSSION
The liver fluke,
C. sinensis, is currently the most important parasite infecting humans in Korea. According to the results of a national survey, the prevalence rate of clonorchiasis was 1.4% in 1997, 2.4% in 2004, and 1.9% in 2012. However, the prevalence of
C. sinensis infection is much higher in riverside areas. In 2006, the total egg-positive rate of
C. sinensis was 11.1% among residents living in the river basins of South Korea [
6]. The
C. sinensis egg-positive rate was as high as 8.1%, on average, in riverside areas surveyed in 2007 [
5]. The egg-positive rates of
C. sinensis observed in the Geum River basin were 12.0% in 1981 [
16], 4.6% in 2006 [
6], and 3.1% in 2007 [
5]. In more details, the egg-positive rates for
C. sinensis in Muju-gun were 40.4% in 1994 [
13], 7.6% in 2007 [
15], and 13.2% in the present study. However, the current prevalence of Muju-gun is still high. To lower the
C. sinensis-positive rate, it is necessary to manage riverside endemic areas continuously. For example, as a result of continuous management at Gokseong-gun in the Seomjin River basin, the positive rate was reported to have decreased from 19.0% in 1999 to 11.3% in 2005 [
17].
In this study, we used the formalin ether sedimentation technique for microscopic examination of the stools. The formalin-ether sedimentation procedure is recommended as being the easiest to perform, allowing recovery of the broadest range of organisms, and being the easiest subject to technical error [
18]. However, the eggs of
C. sinensis are similar in size and shape to those of minute intestinal flukes, including
Heterophyes heterophyes and
Metagonimus yokogawai. A PCR approach has proven to be an accurate diagnostic procedure. However, eggs of the liver fluke and heterophyid intestinal flukes cannot be differentiated by the opercular shoulder, although the appearance of muskmelon pattern on the egg shell of the liver fluke is helpful for diagnosis [
19]. Our diagnosis of
C. sinensis eggs was based on the presence of muskmelon patterns on the egg shell surface.
Many factors determine the infection status of clonorchiasis in any region. Generally, the prevalence of
C. sinensis is higher in males and in inhabitants living in rural areas, and increases with age [
3,
4,
8,
20]. We also found that egg-positive rates were higher among residents who had lived longer in the area and eaten raw freshwater fish, and also higher in males than in females. This may be related to Korean culture, in which drinking alcohol and consuming raw freshwater fish are more common among men than women; men participate in social activities that involve drinking and raw freshwater fish consumption more frequently than women. Those findings were consistent with previous reports from Vietnam and China [
8,
20]. Also, in our study population, the egg-positive rate of clonorchiasis of farmers was significantly higher than in non-farmers. That is why the survey areas are basically rural agricultural regions, so residents who have lived for a long time were almost farmers. Like the residents who had lived more than 20 years were significantly higher prevalence of clonorchiasis than those of the opposite, the prevalence of farmers were significantly higher than those of non-farmers. In the present study, the egg-positive rate was higher in those ≥65 years old than those <65 years old, although the difference was not significant. Similar to previous reports, this may be due to an accumulation effect of reinfection or superinfection with age because epidemiological studies indicate that humans do not develop any resistance to reinfection or superinfection by this parasite [
7].
The 4.5% of
C. sinensis infection among the participants in this study was not reporting raw fish eating experience, which is probably due to under-reporting or the possibility of cross-contamination during the cooking process. Because metacercariae of
C. sinensis are mucilaginous and may stick to cooking utensils and so could theoretically contaminate other food [
20]. In the present study, 14.8% rate in those with previous experience of infection indicates the possibility of reinfection. Repeated infection with
C. sinensis is known to increase the risk of cholangiocarcinoma [
7]. Clonorchiasis is a significant risk factor for cholangiocarcinoma in humans, as confirmed in several studies [
21,
22,
23]. Two hospital-based case control studies in Korea demonstrated that radiological, serological, and parasitological evidence correlated significantly with an increased risk of both intrahepatic and extrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma [
21,
22]. By analysis of endemicity of clonorchiasis and the Korean National Cancer Incidence Database for 1999-2005, the relative risk of cholangiocarcinoma by liver flukes was 4.7 (95% CI=2.8-8.4) and ~10% of cholangiocarcinoma in Korea was estimated due to
C. sinensis infection [
23].
According to the results of this study, the habit of raw freshwater fish consumption increased the risk of
C. sinensis infection by 3.2 and 4.8 times (4.9 in univariate analysis, 3.2 in multivariate analysis). There were strong association between raw fish consumption and the prevalence of
C. sinensis infection; thus, the major risk factor for
C. sinensis infection is the consumption of raw freshwater fish. An obvious means of reducing infection would be to change such dietary habits; however, the habit of raw freshwater fish consumption is not going to be changed in a short period of time [
7,
20]. Accordingly, in community health surveys, we need to consider using the habit of raw freshwater fish consumption as a screening tool to select high-risk areas or individuals susceptible to
C. sinensis infection [
24].
Limitation of this study include that our study only sampled residents living close to the river and examined only a small number of individuals based on their proximity to primary healthcare posts. In conclusion, the overall egg-positive rate for C. sinensis in Muju-gun, Jeollabuk-do was 13.5%. These data showed that this area still has a high prevalence of infection with C. sinensis, and the habit of eating raw freshwater fish was the major factor in the maintenance of clonorchiasis. Our data have updated the status of clonorchiasis along the Geum River basin, showing some decrease, compared with previous reports.
Chungnam National University
Notes
-
We have no conflict of interest related to this work.
ACKNOWLEDGMENT
This study was financially supported by a research fund of Chungnam National University, Daejeon, Korea in 2011.
References
- 1. Kim TS, Cho SH, Huh S, Kong Y, Sohn WM, Hwang SS, Chai JY, Lee SH, Park YK, Oh DK, Lee JK. Working Groups in National Institute of Health. Korea Association of Health Promotion. A nationwide survey on the prevalence of intestinal parasitic infections in the Republic of Korea, 2004. Korean J Parasitol 2009;47:37-47.
- 2. Korea Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Korea National Institute of Health. National survey of the prevalence of intestinal parasitic infections in Korea, 2012. The 8th Report. Osong Chungcheongbuk-do, Korea. 2013.
- 3. Lee GS, Cho IS, Lee YH, Noh HJ, Shin DW, Lee SG, Lee TY. Epidemiological study of clonorchiasis and metagonimiasis along the Geum-gang (River) in Okcheon-gun (county), Korea. Korean J Parasitol 2002;40:9-16.
- 4. June KJ, Cho SH, Lee WJ, Kim C, Park KS. Prevalence and risk factors of clonorchiasis among the populations served by primary healthcare posts along five major rivers in South Korea. Osong Public Health Res Perspect 2013;4:21-26.
- 5. Kim HK, Cheun HI, Cheun BS, Lee KY, Kim TS, Lee SE, Lee WJ, Cho SH. Prevalence of Clonorchis sinensis infections along the five major rivers in Republic of Korea, 2007. Osong Public Health Res Perspect 2010;1:43-49.
- 6. Cho SH, Lee KY, Lee BC, Cho PY, Cheun HI, Hong ST, Sohn WM, Kim TS. Prevalence of clonorchiasis in southern endemic areas of Korea in 2006. Korean J Parasitol 2008;46:133-137.
- 7. Hong ST, Fang Y. Clonorchis sinensis and clonorchiasis, an update. Parasitol Int 2012;61:17-24.
- 8. Dang TC, Yajima A, Nguyen VK, Montresor A. Prevalence, intensity and risk factors for clonorchiasis and possible use of questionnaires to detect individuals at risk in northern Vietnam. Trans R Soc Trop Med Hyg 2008;102:1263-1268.
- 9. Qian MB, Chen YD, Fang YY, Tan T, Zhu TJ, Zhou CH, Wang GF, Xu LQ, Zhou XN. Epidemiological profile of Clonorchis sinensis infection in one community, Guangdong, People's Republic of China. Parasit Vectors 2013;6:194.
- 10. Cho SH, Sohn WM, Na BK, Kim TS, Kong Y, Eom K, Seok WS, Lee T. Prevalence of Clonorchis sinensis metacercariae in freshwater fish from three latitudinal regions of the Korean Peninsula. Korean J Parasitol 2011;49:385-398.
- 11. Bouvard B, Baan R, Straif K, Grosse Y, Secretan B, El Ghissassi F, Benbrahim-Tallaa L, Guha N, Freeman C, Galichet L, Cogliano V. WHO International Agency for Research on Cancer Monograph Working Group. A review of human carcinogens. Part B: biological agents. Lancet Oncol 2009;10:321-322.
- 12. Choi MH, Chang YS, Lim MK, Bae YM, Hong ST, Oh JK, Yun EH, Bae MJ, Kwon HS, Lee SM, Park HW, Min KU, Kim YY, Cho SH. Clonorchis sinensis infection is positively associated with atopy in endemic area. Clin Exp Allergy 2011;41:697-705.
- 13. Kim CH, Na YE, Kim NM, Shin DW, Chang DY. Intestinal parasite and Clonorchis sinensis infection among the inhabitants in the upper stream of Taechong Dam, Kumgang (River). Korean J Parasitol 1994;32:207-214.
- 14. June KJ, Park JY, Park DS, Jho KN, Jho JS, Kim SC, Suk ES, Shin DS, Lee EK, Kim ON. Prevalence of clonorchiasis, knowledge and intention to change behavior of village people living in the catchment area of community health posts along the Geum River. J Korean Acad Rural Health Nurs 2009;4:5-12.
- 15. Park DS. Current status of Clonorchis sinensis infection and its related factors among the residents of rural communities. J Korean Acad Rural Health Nurs 2007;2:33-42.
- 16. Seo BS, Lee SH, Cho SY, Chai JY, Hong ST, Han IS, Sohn JS, Cho BH, Ahn SR, Lee SK, Chung SC, Kang KS, Shim HS, Hwang IS. An epidemiologic study of clonorchiasis and metagonimiasis in riverside areas In Korea. Korean J Parasitol 1981;19:137-150.
- 17. Park MD, Shin JH, Sohn SJ, Park J, Kim SI. Clonorchis sinensis intervention at a Sumjin riverside area. J Agric Med Community Health 2009;34:135-142.
- 18. Garcia LS. Diagnostic Medical Parasitology. 5th ed. Washington DC, USA. ASM Press. 2007, pp 423-438.
- 19. Kaewkes S. Taxonomy and biology of liver flukes. Acta Trop 2003;88:177-186.
- 20. Zhang R, Gao S, Geng Y, Huang D, Yu L, Zhang S, Cheng J, Fu Y. Epidemiological study on Clonorchis sinensis infection in Shenzhen area of Zhujiang delta in China. Parasitol Res 2007;101:179-183.
- 21. Choi BI, Han JK, Hong ST, Lee KH. Clonorchiasis and cholangiocarcinoma: etiologic relationship and imaging diagnosis. Clin Microbiol Rev 2004;17:540-552.
- 22. Choi D, Lim JH, Lee KT, Lee JK, Choi SH, Heo JS. Cholangiocarcinoma and Clonorchis sinensis infection: A case-control study in Korea. J Hepatol 2006;44:1066-1073.
- 23. Shin HR, Oh JK, Lim MK, Shin A, Kong HJ, Jung KW, Won YJ, Park S, Park SJ, Hong ST. Descriptive epidemiology of cholangiocarcinoma and clonorchiasis in Korea. J Korean Med Sci 2010;25:1011-1016.
- 24. Yajima A, Cong DT, Trung DD, Cam TD, Montresor A. Cost comparison of rapid questionnaire screening for individuals at risk of clonorchiasis in low- and high-prevalence communities in northern Vietnam. Trans R Soc Trop Med Hyg 2009;103:447-451.
Fig. 1Location of surveyed areas in Bunam-myeon, Muju-gun, Jeollabuk-do, Korea. Dot (

); survey areas in Muju-gun along the Geum River basin.
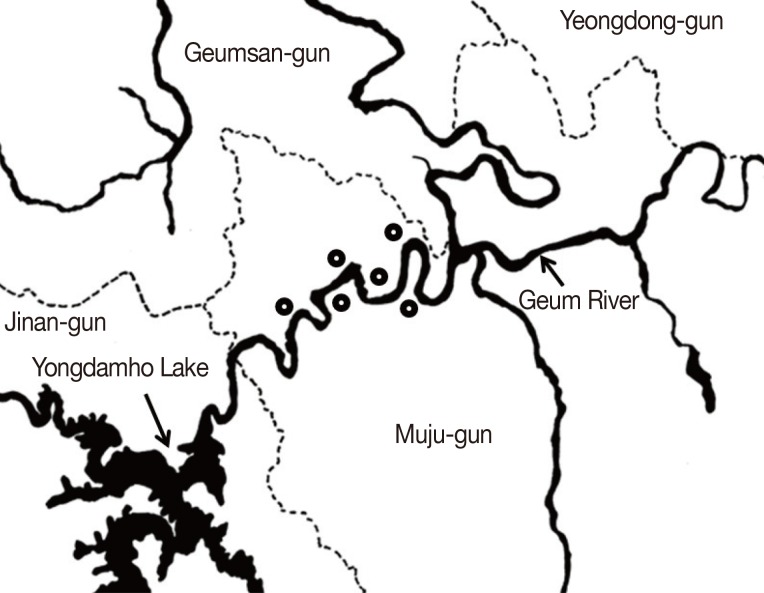
Fig. 2Risk factors for clonorchiasis in Muju-gun along the Geum River basin, Korea. This figure shows the egg positive rates of C. sinensis according to variables of the surveyed residents. Significant differences of C. sinensis egg positive rates between the 2 groups were *P<0.05 and **P<0.001, respectively.
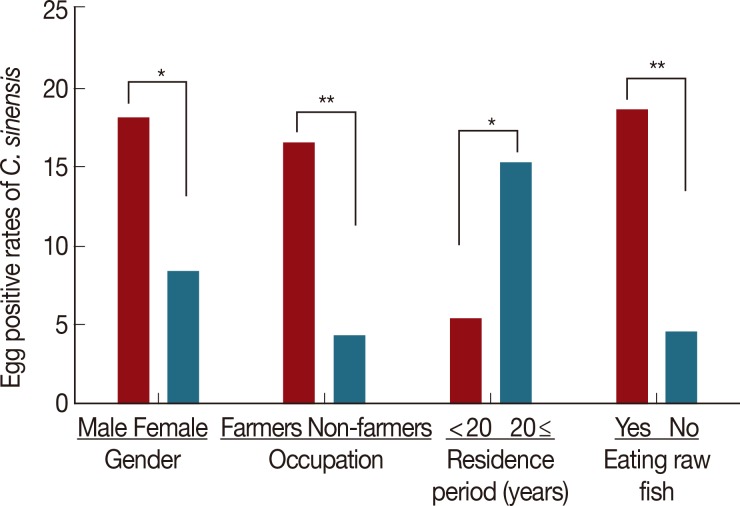
Table 1.Distribution of surveyed population according to sociodemographic and behavioral characteristics
Table 1.
|
Variables |
Male (%) |
Female (%) |
Total (%) |
|
Age (years) |
|
|
|
|
< 65 |
88 (51.5) |
93 (52.2) |
181 (51.9) |
|
65 and over |
83 (48.5) |
85 (47.8) |
168 (48.1) |
|
Educational level |
|
|
|
|
Uneducated |
35 (20.5) |
74 (41.6) |
109 (31.2) |
|
Elementary school |
75 (43.8) |
70 (39.3) |
145 (41.5) |
|
Middle school ≤ |
61 (35.7) |
34 (19.1) |
95 (27.2) |
|
Occupation |
|
|
|
|
Farmers |
127 (74.3) |
128 (71.9) |
255 (73.1) |
|
Non-farmers |
44 (25.7) |
50 (28.1) |
94 (26.9) |
|
Residence period (years) |
|
|
|
|
< 20 |
41 (24.0) |
33 (18.5) |
74 (21.2) |
|
20 and over |
130 (76.0) |
145 (81.5) |
275 (78.8) |
|
Cigarette smoking |
|
|
|
|
Yes |
70 (40.9) |
16 (9.0) |
86 (24.6) |
|
No |
101 (59.1) |
162 (91.0) |
263 (75.4) |
|
Alcohol drinking |
|
|
|
|
Yes |
96 (56.1) |
37 (20.8) |
133 (38.1) |
|
No |
75 (43.9) |
141 (79.2) |
216 (61.9) |
|
Health status |
|
|
|
|
Healthy |
104 (60.8) |
92 (51.7) |
196 (56.2) |
|
Unhealthy |
67 (39.2) |
86 (48.3) |
153 (43.8) |
|
Raw freshwater fish consumption |
|
|
|
|
Yes |
132 (77.2) |
83 (46.6) |
215 (61.6) |
|
No |
39 (22.8) |
95 (53.4) |
134 (38.4) |
|
Past history of clonorchiasis |
|
|
|
|
Yes |
57 (33.3) |
31 (17.4) |
88 (25.2) |
|
No |
114 (66.7) |
147 (82.6) |
261 (74.8) |
|
Medication experience for clonorchiasis |
|
|
|
|
Yes |
54 (31.6) |
27 (15.2) |
81 (23.2) |
|
No |
117 (68.4) |
151 (84.8) |
268 (76.8) |
|
Experience of C. sinensis examination |
|
|
|
|
Yes |
114 (66.7) |
108 (60.7) |
222 (63.6) |
|
No |
57 (33.3) |
70 (39.3) |
127 (36.4) |
|
Total |
171 (100.0) |
178 (100.0) |
349 (100.0) |
Table 2.Egg-positive rates of C. sinensis according to the sociodemographic and behavioral characteristics
Table 2.
|
Variables |
Positive (%) |
Negative (%) |
Total (%) |
P-value |
|
Gender |
|
|
|
0.011 |
|
Males |
31 (18.1) |
140 (81.9) |
171 (100.0) |
|
|
Females |
15 (8.4) |
163 (91.6) |
178 (100.0) |
|
|
Age (years) |
|
|
|
0.874 |
|
< 65 |
23 (12.7) |
158 (87.3) |
181 (100.0) |
|
|
65 and over |
23 (13.7) |
145 (86.3) |
169 (100.0) |
|
|
Educational level |
|
|
|
0.055 |
|
Uneducated |
13 (11.9) |
96 (88.1) |
109 (100.0) |
|
|
Elementary school |
26 (17.9) |
119 (82.1) |
145 (100.0) |
|
|
Middle school ≤ |
7 (7.4) |
88 (92.6) |
95 (100.0) |
|
|
Occupation |
|
|
|
< 0.001 |
|
Farmers |
42 (16.5) |
213 (83.5) |
255 (100.0) |
|
|
Non-farmers |
4 (4.3) |
90 (95.7) |
94 (100.0) |
|
|
Residence period (years) |
|
|
|
0.032 |
|
< 20 |
4 (5.4) |
70 (94.6) |
74 (100.0) |
|
|
20 and over |
42 (15.3) |
233 (84.7) |
275 (100.0) |
|
|
Cigarette smoking |
|
|
|
0.199 |
|
Yes |
15 (17.4) |
71 (82.6) |
86 (100.0) |
|
|
No |
31 (17.4) |
232 (88.2) |
263 (100.0) |
|
|
Alcohol drinking |
|
|
|
0.102 |
|
Yes |
23 (17.3) |
110 (82.7) |
133 (100.0) |
|
|
No |
23 (10.6) |
193 (89.4) |
216 (100.0) |
|
|
Health status |
|
|
|
0.752 |
|
Healthy |
27 (13.8) |
169 (86.2) |
196 (100.0) |
|
|
Unhealthy |
19 (12.4) |
134 (87.6) |
153 (100.0) |
|
|
Raw freshwater fish consumption |
|
|
|
< 0.001 |
|
Yes |
40 (18.6) |
175 (81.4) |
215 (100.0) |
|
|
No |
6 (4.5) |
138 (95.5) |
134 (100.0) |
|
|
Past history of clonorchiasis |
|
|
|
0.589 |
|
Yes |
13 (14.8) |
75 (85.2) |
88 (100.0) |
|
|
No |
33 (12.6) |
228 (87.4) |
261 (100.0) |
|
|
Medication experience for clonorchiasis |
|
|
|
0.854 |
|
Yes |
11 (13.6) |
70 (86.4) |
81 (100.0) |
|
|
No |
35 (13.1) |
233 (86.9) |
268 (100.0) |
|
|
Experience of C. sinensis examination |
|
|
|
0.324 |
|
Yes |
20 (15.7) |
107 (84.3) |
127 (100.0) |
|
|
No |
26 (11.7) |
196 (88.3) |
222 (100.0) |
|
|
Total |
46 (13.2) |
303 (86.8) |
349 (100.0) |
|
Table 3.Egg-positive rates of C. sinensis and 4 risk factors among residents of riverside areas in Muju-gun, Jeollabuk-do, Korea
Table 3.
|
Variablesa
|
Positive No. (%) |
Univariate analysis
|
Multivariate analysisb
|
|
OR (95% CI)b
|
OR (95% CI) |
|
Gender |
|
|
|
|
Males |
31 (18.1) |
2.41 (1.25-4.64) |
1.80 (0.89-3.63) |
|
Females |
15 (8.4) |
1 |
1 |
|
Occupation |
|
|
|
|
Farmers |
42 (16.5) |
4.44 (1.55-12.74) |
2.74 (0.91-8.27) |
|
Non-farmers |
4 (4.3) |
1 |
1 |
|
Residence period (years) |
|
|
|
|
20 and over |
42 (15.3) |
3.16 (1.09-9.10) |
2.00 (0.65-6.11) |
|
< 20 |
4 (5.4) |
1 |
1 |
|
Raw freshwater fish consumption |
|
|
|
|
Yes |
40 (18.6) |
4.88 (2.01-11.85) |
3.20 (1.25-8.17) |
|
No |
6 (4.5) |
1 |
1 |