Abstract
Outbreaks of tick-borne disease cases in Santa Catarina, Brazil are known, but the presence of the pathogen DNA has never been determined. In this study, the first survey of Anaplasma marginale, Babesia bigemina, and Babesia bovis DNA on blood samples of 33 cattle from an outbreak in Ponte Alta Municipality, Santa Catarina, Brazil, has been carried out. A multiplex PCR detected 54.5% of animals were co-infected with 2 or 3 parasites, while 24.2% were infected with only 1 species. The most prevalent agent was B. bigemina (63.6%) followed by A. marginale (60.6%). This is the first report of tick-borne disease pathogens obtained by DNA analysis in Southern Brazil.
-
Key words: Babesia bovis, Babesia bigemina, Anaplasma marginale, multiplex-PCR, Brazil
INTRODUCTION
Babesia bovis and
Babesia bigemina in conjunction with
Anaplasma marginale are intraerythrocytic pathogens that are responsible for the most prevalent and costly tick-borne diseases (TBDs) of cattle worldwide [
1]. The Brazilian cattle industry estimates that losses reach about 500 million US dollars annually, according to data from Ministry of Agriculture, with these agents [
2].
B. bovis and
B. bigemina belong to the phylum Apicomplexa, Order Piroplasmid, and are the causative agents of bovine babesiosis in Latin America, where the only known vector is the host tick
Rhipicephalus (
B.)
microplus [
3]. Cattle suffering from babesiosis show massive destruction of erythrocytes because of the multiplication of hemoparasites inside these cells [
4] with high morbidity and mortality worldwide [
5].
A. marginale, is an intraerythrocytic rickettsia from family Anaplasmataceae [
6] responsible for important economic losses in cattle in tropical and subtropical areas throughout the world, including Latin America [
7]. Anaplasmosis can also be transmitted by bloodsucking flies, horseflies, and mosquitoes [
8].
A. marginale infection in the clinical signs consist of hemolytic anemia, jaundice, dyspnea, tachycardia, fever, fatigue, lacrimation, salivation, diarrhea, frequent urination, anorexia, and abortion, which in some cases can lead the animal to death in less than 24 hr [
9].
The state of Santa Catarina in Southern Brazil has presented several outbreaks of TBD but without an efficient differential diagnosis. This lack of information on the causative agent of TBD causes small farmers use incorrect drugs for treatment of the disease. The aim of this work is to assess what are the causative agents of TBD in 1 outbreak in Santa Catarina, using the multiplex PCR. We report here the first molecular detection of A. marginale, B. bovis, and B. bigemina from cattle in Southern Brazil.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Description of an outbreak
From November 2010 to March 2011, a total of 33 bovine blood samples were collected from Ponte Alta Municipality, Santa Catarina, Brazil, where an outbreak of tick-borne disease occurred. Samples were collected at 3 different properties of beef cattle from Limousin and Charolais bred with ages between 8 months and 4 years. Three animals showed characteristic clinical signs of tick-borne diseases, and other samples were collected from animals of the aforementioned properties. The properties had the presence of Rhipicephalus (B.) microplus ticks.
Sample size determination
The determination of the sample size was based on statistical and epidemiological concepts, considering the population of cattle in Ponte Alta Municipality of 16,200 animals. The minimum number of samples (n=28) was calculated based on consideration of the disease prevalence of 10% TBD, using the proposal methodology by De Canno Roe [
10], for an infinite population (n), with 95% reliability.
DNA was extracted from whole blood using phenol-chloroform method. Briefly, 200 µl of whole blood was mixed with lysis buffer (10 mM Tris pH 7.4, 10 mM NaCl, 25 mM EDTA, 1% SDS) with 100 µg/ml of proteinase K (Sigma, St. Louis, Missouri, USA) and incubated at 42℃ for 12 hr. Subsequently, 3 washes with phenol, phenol-chloroform (1:1), and chloroform, respectively, were performed, centrifuging to 14,000 g for 10 min and removing the supernatant. The DNA was precipitated with isopropanol and then washed with 70% ethanol. The tubes were placed in an oven at 37℃ until complete evaporation of the alcohol. The resulting DNA was eluted in 50 µl of Milli-Q water-free DNAse and stored at -20℃.
Multiplex PCR conditions
PCR amplification was carried out on genomic DNA extracted from cattle blood samples, and analyzed by multiplex PCR for the screening of B. bovis, B. bigemina, and A. marginale.
Briefly, PCR assay was performed in a total volume of 25 µl containing 80 ng of the genomic DNA and 8.5
pmoles of each primer pair (
Table 1); 1U
Taq DNA polymerase, GoTaq® Hot Start Polymerase (Promega; Madison, Wisconsin, USA), 0.2 mM dNTPs, 25 mM MgCl
2, 5 µl buffer (5X Green GoTaq® Flexi buffer (Promega) and ultra-pure water to make the final volume. Amplification involved a hot start of 5 min at 95℃, followed by 35 cycles of 1 min at 95℃, 1 min at 58℃, 1 min at 72℃, and a final extension step of 10 min at 72℃.
The amplified PCR products were subjected to electrophoresis on 2% agarose gel stained with ethidium bromide, visualized under UV light, and photographed in trans-illuminator apparatus. The amplicons molecular sizes were estimated by including a 100 bp ladder standard (Ludwig Biotecnologia, Porto Alegre, Brazil). DNA positive controls of A. marginale, B. bigemina, and B. bovis were kindly provided by Dr. Luciana Brito Gatto, Embrapa Porto Velho, RO and Dr. Odilon Vidotto, UEL, PR. Negative control was distilled water.
Sequencing
Purified PCR products were then ligated into the p-GEM T easy® vector (Promega) and cloned by transformation into DH5 α
Escherichia coli calcium competent cells. Single picked colonies were grown overnight, and plasmids were purified using the QIAGEN plasmid purification kit (QIAGEN, Hilden, Germany). To confirm plasmids contain the correct insert, between 1 and 2 µg DNA was purified from positive colonies and sequenced by a commercial sequencing service (ACTGene, Porto Alegre, Brazil). All high quality DNA sequences (Phred P20) were analyzed using the Phred/Phrap/Consed package [
11]. The identity of the sequences were confirmed with the BLAST tool (
www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/blast) [
12].
RESULTS
Thirty-three blood samples from Ponte Alta Municipality, Santa Catarina, Brazil were examined for infection with
A. marginale,
B. bigemina, and
B. bovis using multiplex PCR method. A summary of the results is shown in
Table 2. When the samples were assayed using multiplex PCR, 3 and 5 animals were found to have single infections with
A. marginale and
B. bigemina, respectively. Further 1, 2, and 12 animals had doubled infections with
B. bigemina/
B. bovis,
A. marginale/
B. bovis, and
A. marginale/
B. bigemina, respectively. Three animals had multiple infections with the 3 organisms, and 7 were negative. As shown in
Table 3,
B. bigemina is the most prevalent agent (63.6%) followed by
A. marginale (60.6%). An example of the results obtained using multiplex PCR on field samples is illustrated in
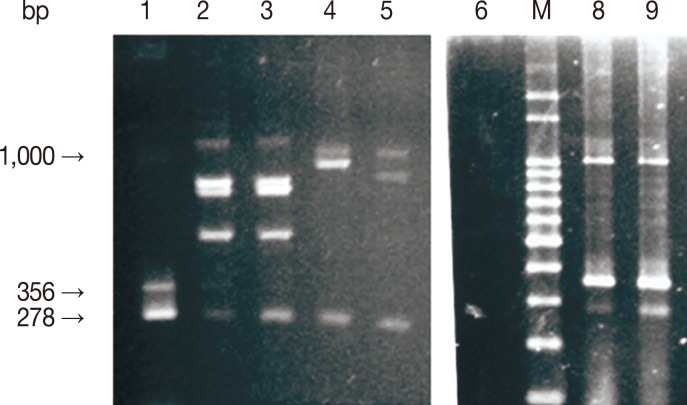
Fig. 1.
The identity of the amplicons was guaranteed by sequencing, demonstrating identity with sequences deposited in GenBank, respectively, with 93% (DQ501244.1) to A. marginale, 99% (AF027149) to B. bovis, and 83% of (S45366) for B. bigemina.
DISCUSSION
In this study, multiplex PCR was used for the first time to detect TBD agents in cattle blood samples from an outbreak occurred in Santa Catarina, Brazil. The multiplex PCR showed high specificity for use in epidemiological studies as described [
13,
14,
15,
16].
The state of Santa Catarina is in enzootic stability for TBD [
17], since the distribution of
A. marginale and
Babesia sp. were closely associated with the presence of the cattle tick
R. (
B.)
microplus which is highly prevalent in Santa Catarina state [
18] and by the high level of seroprevalence for
Babesia sp. [
19]. However, due to climatic factors, the study area can be considered in some periods of the year in enzootic instability [
20].
The prevalence of TBD agents in Southern Brazil are mainly based on serological analysis [
2,
21,
22]. In the state of Santa Catarina, only 2 papers were published, and they demonstrated high seroprevalence to
B. bigemina and
B. bovis [
23,
24]. In the same region, no studies were conducted on the prevalence of
A. marginale. Despite knowledge of the circulation of TBD agents, to date, no work on molecular analysis was conducted in the state of Santa Catarina.
The results obtained using the field samples clearly indicate the prevalence of mixed infections in the field, so the multiplex PCR will facilitate the assessment of risk factors associated with TBD and this is important for improved design and implementation of cost-effective control strategies in endemic and non-endemic regions [
25]. Multiplex PCR results obtained from field samples showed that 54.5% of animals were co-infected with 2 or 3 parasites, while 24.2% were infected with only 1 species. In Turkey [
16], it was found that 24% of animals were co-infected with
A. marginale and/or
B. bovis, and a prevalence of 12% dual infection with
B. bovis and
B. bigemina was observed in single PCR in Egypt [
26]. Comparisons with other data are not possible due to the lack of researches using multiplex PCR for detection of these pathogens.
Of the 3 tick-borne diseases investigated in the present study,
B. bigemina and
A. marginale were found to be most prevalent with 63.6% and 60.6% prevalence rate, respectively. The low infection rate for
B. bovis (18.2%) infections in cattle was related with low parasitemia during the acute phase of the disease, a feature of these agent [
27]. Cattle that survive initial infection and also calves partially resistant to this disease remain persistently infected [
28] with very low parasite levels that are sufficient for transmitting infection to ticks. Such cattle are potentially an important factor in the maintenance of
B. bovis in endemic areas as well as a suspect source for introduction and spread of the disease to non-endemic areas where competent vectors are present [
29]. These results highlight the situation in Santa Catarina where, although infection with
A. marginale and
B. bigemina appears to be the main risk, there is also a clear risk of co-infection between the 3 pathogens.
In conclusion, we could confirm that in Santa Catarina, like other states in Southern Brazil, the 3 TBD pathogens are circulating and knowledge of these data should be available to producers and government agencies.
Universidade do Estado de Santa Catarina
Notes
-
We have no conflict of interest related to this work.
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS
This work was supported by Universidade do Estado de Santa Catarina (UDESC), Brazil. Mariana Feltrin Canever was a fellowship of PIC program from UDESC, Brazil.
References
- 1. Suarez CE, Noh S. Emerging perspectives in the research of bovine babesiosis and anaplasmosis. Vet Parasitol 2011;180:109-125.
- 2. Almeida MB, Tortelli FP, Riet-Correa B, Ferreira JLM, Soares MP, Farias NAR, Riet-Correa F, Schild AL. Tristeza parasitária bovina na região sul do Rio Grande do Sul: estudo retrospectivo de 1978-2005. Pesq Vet Bras 2006;26:237-242.
- 3. Guglielmone AA. Epidemiology of babesiosis and anaplasmosis in South and Central America. Vet Parasitol 1995;57:109-119.
- 4. Bock R, Jackson L, de Vos A, Jorgensen W. Babesiosis of cattle. Parasitology 2004;129:S247-S269.
- 5. McCosker PJ. The global importance of babesiosis. In Ristic M, Krier JP eds, Babesiosis. New York, USA. Academic Press. 1981, pp 1-24.
- 6. Hornok S, Földvári G, Elek V, Naranjo V, Farkas R, de La Fuente J. Molecular identification of Anaplasma marginale and rickettsial endosymbionts in blood-sucking flies (Diptera: Tabanidae, Muscidae) and hard ticks (Acari: Ixodidae). Vet Parasitol 2008;154:354-359.
- 7. Harrus S, Baneth G. Drivers for the emergence and re-emergence of vector-borne protozoal and bacterial diseases. Int J Parasitol 2005;35:1309-1318.
- 8. Kocan KM, de La Fuente J, Blouin EF, Coetzee JF, Ewing SA. The natural history of Anaplasma marginale. Vet Parasitol 2010;167:95-107.
- 9. Vidotto O, Marana ERM. Diagnóstico em anaplasmose bovina. Ciência Rural (Santa Maria) 2001;31:361-368.
- 10. Thrusfield M. Veterinary Epidemiology. 3rd ed. Oxford, UK. Blackwell Publishing Co.. 2003, pp 46-69.
- 11. Ewing B, Green P. Base-calling of automated sequencer traces using phred. II. Error probabilities. Genome Res 1998;8:186-194.
- 12. Altschul SF, Madden TL, Schäffer AA, Zhang J, Zhang Z, Miller W, Lipman DJ. Gapped BLAST and PSI-BLAST: a new generation of protein database search programs. Nucl Acids Res 1997;25:3389-3402.
- 13. Figueroa JV, Chieves LP, Jonhson GS, Buening GM. Multiplex polymerase chain reaction based assay for the detection of Babesia bigemina, Babesia bovis, and Anaplasma marginale DNA in bovine blood. Vet Parasitol 1993;50:69-81.
- 14. Oliveira-Sequeira TCG, Oliveira MCS, Araujo JP Jr, Amarante AFT. PCR-based detection of Babesia bovis and Babesia bigemina in their natural host Boophilus microplus and cattle. Int J Parasitol 2005;35:105-111.
- 15. Silva MG, Henriques G, Sánchez C, Marques PX, Suarez CE, Oliva A. First survey for Babesia bovis and Babesia bigemina infection in cattle from Central and Southern regions of Portugal using serological and DNA detection methods. Vet Parasitol 2009;166:66-72.
- 16. Bilgic HB, Karagenç T, Simuunza M, Shiels B, Tait A, Eren H, Weir W. Development of a multiplex PCR assay for simultaneous detection of Theileria annulata, Babesia bovis, and Anaplasma marginale in cattle. Exp Parasitol 2013;133:222-229.
- 17. Nuerberg S, Serra-Freire NM. O carrapato e a tristeza parasitária bovina no estado de Santa Catarina. Rev Bras Med Vet 1995;17:257-259.
- 18. Souza AP, Gonzales JC, Ramos CI, Paloschi CG, Moraes AN. Variação sazonal de Boophilus microplus no Planalto Catarinense. Pesq Agrop Bras 1988;23:627-630.
- 19. Madruga CR, Aycardi E, Kessler RH, Schenk MAM, de Figueiredo GR, Curvo JBE. Níveis de anticorpos anti-Babesia bigemina e Babesia bovis em bezerros da raça Nelore, Ibagé e cruzamento de Nelore. Pesq Agrop Bras 1984;19:1163-1168.
- 20. Mahoney DF, Ross DR. Epizootiological factors in the control of bovine babesiosis. Aust Vet J 1972;48:292-298.
- 21. Schetters TPM, Kleuskens J, Scholtes N, Gorenflot A. Parasite localization and dissemination in the Babesia-infected host. Ann Trop Med Parasitol 1998;92:513-519.
- 22. Osaki SC, Vidotto O, Marana ERM, Vidotto MC, Yoshihara E, Pacheco RC, Igarashi M, Minho AP. Occurrence of antibodies against Babesia bovis and studies on natural infection in Nelore cattle, in Umuarama municipality, Paraná State, Brazil. Rev Bras Med Vet 2002;11:77-83.
- 23. Dalagnol AA, Martins E, Madruga CR, Gomes R, Schenk MAM, Kessler RH, Gratão G, Gales ME, Schenk JAP, Andrease M, Bianchini I, Miguita M. Prevalência de agentes da tristeza parasitária bovina em bovinos de corte na região de clima cfb-SC. Agrop Cat 1999;12:46-47.
- 24. Souza AP, Bellato V, Sartor AA, Farias LM. Prevalência de anticorpos anti-Babesia em bovinos no Planalto Norte de Santa Catarina. Rev Ciênc Agrove 2002;1:21-23.
- 25. Simuunza M, Weir W, Courcier E, Tait A, Shiels B. Epidemiological analysis of tick-borne diseases in Zambia. Vet Parasitol 2011;175:331-342.
- 26. Adham FK, Abd-El-Samie EM, Gabre RM, Hussein HE. Detection of tick blood parasites in Egypt using PCR assay I-Babesia bovis and Babesia bigemina. Parasitol Res 2009;105:721-730.
- 27. Kessler RH, Madruga CR, Schenk MAM, Ribeiro OC. Babesiose cerebral por Babesia bovis (Babés 1888 Starcovici 1893) em bezerros no Estado de Mato Grosso do Sul. Pesq Agrop Bras 1983;18:931-935.
- 28. Brown WC, Norimine J, Knowles DP, Goff WL. Immune control of Babesia bovis infection. Vet Parasitol 2006;138:75-87.
- 29. Howell JM, Ueti MW, Palmer GH, Scoles GA, Knowles DP. Persistently infected calves as reservoirs for acquisition and transovarial transmission of Babesia bovis by Rhipicephalus (Boophilus) microplus. J Clin Microbiol 2007;45:3155-3159.
- 30. Figueroa JV, Chieves LP, Johnson GS, Buening GM. Detection of Babesia bigemina-infected carriers by polymerase chain reaction amplification. J Clin Microbiol 1992;30:2576-2582.
- 31. Suarez CE, Palmer GH, Jasmer DP, Hines SA, Perryman LE, McElwain TF. Characterization of the gene encoding a 60-kilodalton Babesia bovis merozoite protein with conserved and surface exposed epitopes. Mol Biochem Parasitol 1991;46:45-52.
- 32. Lew AE, Bock RE, Minchin CM, Masaka S. A msp1α polymerase chain reaction assay for specific detection and differentiation of Anaplasma marginale isolates. Vet Microbiol 2002;86:325-335.
Fig. 1Analysis of mPCR products by agarose gel electrophoresis. M, 100 bp molecular size marker; lanes 1, 8, and 9, positive mPCR controls; lane 6, negative mPCR control (distilled water); lanes 2-3 (B. bigemina/B. bovis), 4 (B. bigemina/A. marginale), and 5 (B. bigemina/A. marginale), template DNA. Arrows indicate 278, 356, and 1,000 base pair amplicons, respectively, for B. bigemina, B. bovis, and A. marginale) generated using primer sets described in materials and methods.
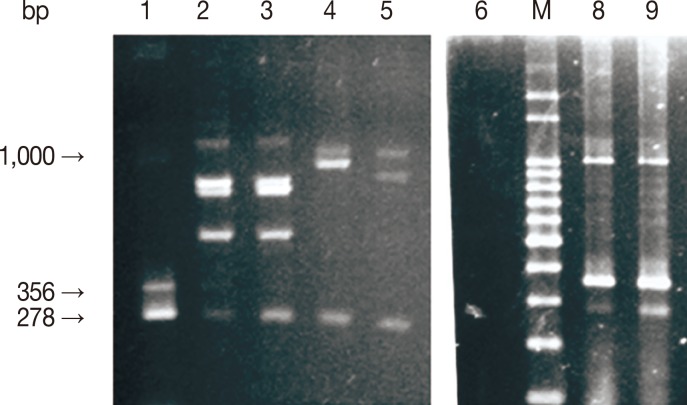
Table 1.Oligonucleotide primer sequences used in multiplex PCR
Table 1.
|
Pathogen |
Primer |
Sequence (5´-3´) |
Amplicon size (bp) |
References |
|
Babesia bigemina
|
BiIA |
CAT CTA ATT TCT CTC CAT ACC CCT CC |
278 pb |
[30] |
|
BiIB |
CCT CGG CTT CAA CTC TGA TGC CAA AG |
|
|
|
Babesia bovis
|
BoF BoR |
CAC GAG GAA GGA ACT ACC GAT GTT GA |
356 pb |
[31] |
|
|
CCA AGG AGC TTC AAC GTA CGA GGT CA |
|
|
|
Anaplasma marginale
|
1773F |
TGT GCT TAT GGC AGA CAT TTC C |
1,000 pb |
[32] |
|
2957R |
AAA CCT TGT AGC CCC AAC TTA TCC |
|
|
Table 2.Multiplex PCR test on field bovine blood samples
Table 2.
|
No. of PCR positive animals
|
No. of PCR negative animals |
Total no. of animals |
|
Am |
Bbi |
Bbo |
Am/Bbi |
Am/Bbo |
Bbi/Bbo |
Am/Bbi/Bbo |
|
Multiplex PCR |
3 |
5 |
0 |
12 |
2 |
1 |
3 |
7 |
33 |
|
Percentage (%) |
24.2 (n = 8) |
54.6 (n = 18) |
21.2 |
100 |
Table 3.Blood samples from 33 cattle using specific PCR amplification and number of samples showing simultaneous specific PCR amplification of 2 or 3 of the targeted micro-organisms
Table 3.
Detection of pathogen DNA
|
Co-detection of pathogen DNA
|
Number of animals infected/ number of samples (%)
|
Number of animals infected/ number of samples (%)
|
|
Am |
Bbi |
Bbo |
Am/Bbi |
Am/Bbo |
Bbi/Bbo |
Am/Bbi/Bbo |
|
20/33 (60.6) |
21/33 (63.6) |
6/33 (18.2) |
12/33 (36.4) |
2/33 (6.1) |
1/33 (3.0) |
3/33 (9.1) |