Abstract
Toxoplasma gondii is a protozoan parasite with a broad range of intermediate hosts. Chickens as important food-producing animals can also serve as intermediate hosts. To date, experimental studies on the pathogenicity of T. gondii in broiler chickens were rarely reported. The objective of the present study was to compare the pathogenicity of 5 different T. gondii strains (RH, CN, JS, CAT2, and CAT3) from various host species origin in 10-day-old chickens. Each group of chickens was infected intraperitoneally with 5×108, 1×108, 1×107, and 1×106 tachyzoites of the 5 strains, respectively. The negative control group was mockly inoculated with PBS alone. After infection, clinical symptoms and rectal temperatures of all the chickens were checked daily. Dead chickens during acute phage of the infection were checked for T. gondii tachyzoites by microscope, while living cases were checked for T. gondii infection at day 53 post-inoculation (PI) by PCR method. Histopathological sections were used to observe the pathological changes in the dead chickens and the living animals at day 53 PI. No significant differences were found in survival periods, histopathological findings, and clinical symptoms among the chickens infected with the RH, CN, CAT2, and CAT3 strains. Histopathological findings and clinical symptoms of the JS (chicken origin) group were similar to the others. However, average survival times of infected chickens of the JS group inoculated with 5×108 and 1×108 tachyzoites were 30.0 and 188.4 hr, respectively, significantly shorter than those of the other 4 mammalian isolates. Chickens exposed to 108 of T. gondii tachyzoites and higher showed acute signs of toxoplasmosis, and the lesions were relatively more severe than those exposed to lower doses. The results indicated that the pathogenicity of JS strain was comparatively stronger to the chicken, and the pathogenicity was dose-dependent.
-
Key words: Toxoplasma gondii, chicken, pathogenicity
INTRODUCTION
Toxoplasmosis is caused by infection with the obligate intracellular parasite
Toxoplasma gondii. The parasite infects virtually all warm-blooded animals including humans, livestock, marine mammals, and avian species [
1]. The pathogenicity of
T. gondii infection in different hosts varies widely [
2]. Mice, marsupials, and new world monkeys were most susceptible to
T. gondii, while chickens, cattle, horses, deer, pigs, and goats were resistant [
3]. Usually, the pathogenicity of
T. gondii strains to animals is considered to be related to the genotypes of the parasite [
4]. However, recent studies indicated that mouse pathogenicity and genetic types were not strictly correlated, and there was no clear evidence that the mouse pathogenicity could be equated with pathogenicity in humans and livestock [
5-
7]. Previous studies reported that 5 different
T. gondii strains of various host species origin displayed variable degrees of clinical illness and antibody levels in young pigs [
8]. Therefore,
T. gondii sources might be an important factor related to the pathogenicity.
Chickens always display chronic infection without apparent clinical signs to toxoplasmosis [
9]. However, the seropositive rate of
T. gondii infection was very high from 30-50% in free-range chickens [
10,
11] to 100% in backyard chickens [
12,
13]. The chicken is one of the major food resources for humans. Therefore, it can be considered as a potential source of the disease.
Up to now, many strains of T. gondii have been isolated from different animals. Theoretically, all of the strains could infect chickens through the cat, the only final host of T. gondii. Thus, comparison of the pathogenicity of different animal source strains of T. gondii to chickens is important for understanding of the pathological mechanisms of this parasite in chickens. In the present study, we report different pathogenicity to chickens of 5 strains of T. gondii from avian or mammals.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
T. gondii strains and cell culture
All
T. gondii strains used here were isolated by bioassay method from different vertebrate hosts. The chicken strain “JS” (Type I) was obtained as described previously [
14]. The strain “RH” (Type I) of human congenital origin, “CN” (Type I) of swine congenital origin and “CAT” (Type I) of feline congenital origin were well conserved in liquid nitrogen in the Laboratory of Veterinary Molecular and Immunological Parasitology, Nanjing Agricultural University, China.
T. gondii tachyzoites were grown and maintained in HeLa (human cervix carcinoma) cells obtained from the German Collection of Microorganisms and Cell Cultures (DSMZ, Braunschweig, Germany) as described previously [
15]. All these 5
T. gondii strains were identified by PCR-RFLP method as described previously [
14]. Then, tachyzoites were harvested, washed by centrifugation using PBS, and finally diluted in PBS with the dose of 5×10
8, 1×10
8, 1×10
7, and 1×10
6 in 1 ml for inoculation.
Animals and experimental design
A total of 210 broiler chickens (1 day old) were obtained from a commercial farm in Nanjing City of Jiangsu Province, China. During the experimental period, all the chickens were given commercially available complete fodder mix, tap water ad libitum without any drugs, and submitted to similar management as in broiler chickens farming systems.
At 10 days of age, the chickens were allocated randomly into 21 groups with 10 birds in each group. In the 20 infected groups, tachyzoites of the 5 isolates were infected intraperitoneally with doses of 5×108, 1×108, 1×107, and 1×106, respectively, while the negative control (-Ve) group was mockly inoculated with PBS alone.
Animal ethics
This study was performed in strict accordance with the recommendations in the Guide for the Care and Use of Laboratory Animals of the Animal Care and Ethics Committee of Nanjing Agricultural University (approval no. 200709005). The Nanjing Agricultural University is approved for animal studies by the China National Institutes of Health under Animal Welfare Assurance no. C3158.
Serological examinations
Before inoculation, sera from all the chickens were collected. Both
Toxoplasma circulating antigens (TCA) and
Toxoplasma circulating antibodies (TCAb) were checked with the chicken TCA ELISA kit (DRE73521, R&B Scientific, Calabasas, California, USA) and chicken TCAb ELISA kit (DRE73549, R&B Scientific), respectively. The procedures of the test were the same to that published previously [
11].
Post inoculation, clinical symptoms of chickens including appetite, consciousness, and appearance were observed, and rectal temperatures were recorded by a clinical thermometer every day.
Survival time of chickens
The survival time of each animal was recorded every 12 hr post inoculation (PI). For those chickens not died until day 53 PI, the survival time was recorded as 53 days (1,272 hr).
Observation of tachyzoites during acute stage of infection
For the dead cases during acute stage of infection, impression smears of the soft internal tissues were used to microscopically check the T. gondii tachyzoites.
Identification of the infection by PCR
On day 53 of the experiment, all the living chickens were slaughtered humanely and all the soft organs (heart, liver, spleen, lungs, kidneys, and brain) were sampled, mixed, and used for DNA extraction and screened for infection with
T. gondii by PCR. PCR was performed with a 341 bp fragment of the internal transcribed spacer 1 (ITS-1) gene of
T. gondii as the target by a pair of primers, 5´-AGTTTAGGAAGCAATCTGAAAGCACATC-3´ and 5´-GATTTGCATTCAAG AAGCGTGATAGTAT-3´ as described previously [
16]. In brief, PCR reactions (25 μl) were performed in 2.5 mM of MgCl2, 0.4 μM of each primer, 2.5 μl 1×rTaq buffer, 0.25 mM of each deoxyribonucleotide, 0.625 U of rTaq DNA polymerase (TaKaRa, Tokyo, Japan), and 3 μl of DNA sample in a thermocycler (Biometra, Göttingen, Germany) under the following conditions: after an initial denaturation at 94˚C for 5 min, 35 cycles of 94˚C for 30 sec (denaturation), 55˚C for 30 sec (annealing), 72˚C for 30 sec (extension), and followed by a final extension at 72˚C for 7 min. The positive control of
T. gondii DNA and negative control (no-DNA control) were included in each run. Each amplicon (13 μl) was examined by agarose gel electrophoresis to validate amplification efficiency.
For the dead cases during acute phage and the living chickens at day 53 PI, pathological sections were observed for histopathological changes on the main tissues. In brief, tissue samples collected from the heart, liver, spleen, lungs, kidneys, and brain were fixed in 10% buffered formalin for 48 hr. Trimmed tissues were washed under running water for 12 hr, dehydrated, and embedded in paraffin wax. Five μm thick sections were cut on a rotary microtome, stained with hematoxylin and eosin, and observed under an Olympus BX-51 light microscope. Digital photomicrographs were taken using an Olympus DP 25 digital camera.
Statistical analysis
Statistical analysis was carried out using the SPSS statistical package (SPSS 13, SPSS Inc., Chicago, Illinois, USA). Differences between groups were tested by the non-parametric test. Differences between groups were considered significant at P<0.05. Correlations between groups were tested with Pearson’s rank correlation coefficient.
RESULTS
TCA and TCAb in serum
Before inoculation, all the chickens were found negative for TCA and TCAb which indicated that all the chickens were not infected with T. gondii.
Clinical symptoms
All chickens inoculated with 5×108 tachyzoites showed serious anorexia and apathy after infection. While chickens inoculated with 1×108 tachyzoites showed moderate anorexia and apathy except for the JS group which showed more severe than the other 4 mammalian strains inoculated groups.
Chickens inoculated with 1×10
7 showed slight anorexia and apathy only. There were no clinical symptoms in the 1×10
6 group and negative control group during the experiment. The rectal temperatures of all the infection groups experienced a marked increase and peaked on the second day PI. The rectal temperatures of all chickens inoculated with 1×10
8, 1×10
7, or 1×10
6 tachyzoites were similar (
Table 1), and there were no significant differences among them. The rectal temperatures of all chickens inoculated with 5×10
8 tachyzoites showed no significant differences. At the 3rd day, the chickens inoculated with 5×10
8 tachyzoites of the JS strain showed significantly higher temperatures than that inoculated with lower dosages of all 5 strains. The chickens inoculated with 5×10
8 tachyzoites of the other 4 strains showed no significant differences of temperatures from the lower dosage groups.
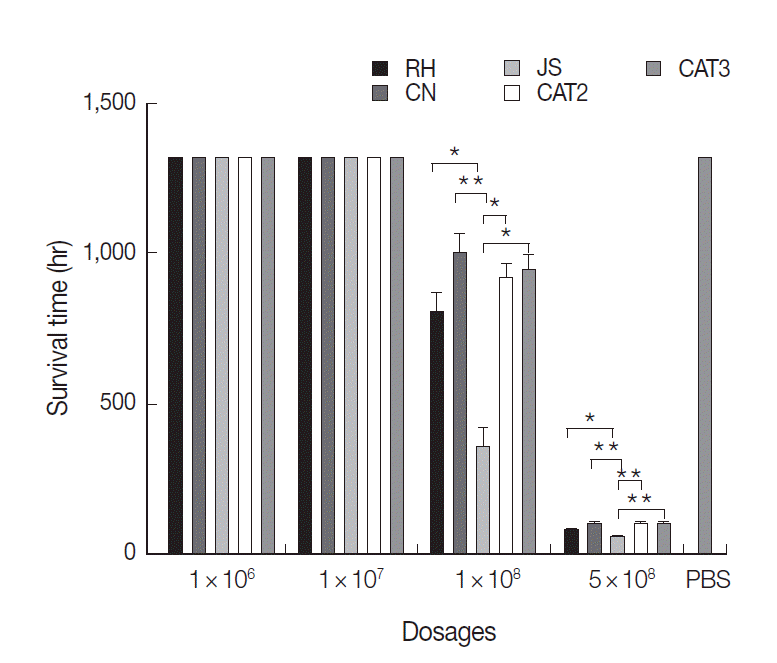
The chickens inoculated with 5×10
8 tachyzoites all died at day 3 PI. The average survival time of RH, CN, JS, CAT2, and CAT3 infected groups with this dosage was 51.6, 56.4, 30.0, 58.8, and 56.4 hr, respectively (
Fig. 1). The survival time of the JS group was significantly shorter than that of the other 4 infected groups (
P<0.05), while there were no significant differences among the 4 mammalian isolates (
P>0.05) inoculated groups.
Chickens inoculated with 1×10
8 tachyzoites became severely ill. With this dosage, 8 chickens died in the JS group, while 4, 2, 3, and 3 chickens died in RH, CN, CAT2, and CAT3 groups, respectively (
Fig. 1). The average survival time of the JS group was significantly shorter than that of the other 4 infected groups (
P<0.05). Similarly, there were no significant differences among the 4 mammalian strains (
P>0.05) inoculated groups. There were no deaths in the 1×10
7 group, 1×10
6 group, and negative control group during the experiment.
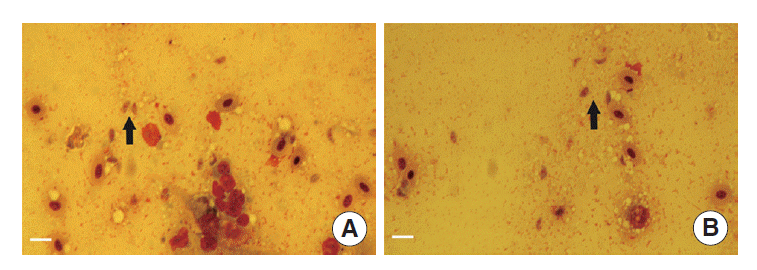
The tachyzoites were detected in all livers, spleens, kidneys, and lungs of dead chickens during the acute stage (as shown in
Fig. 2A,
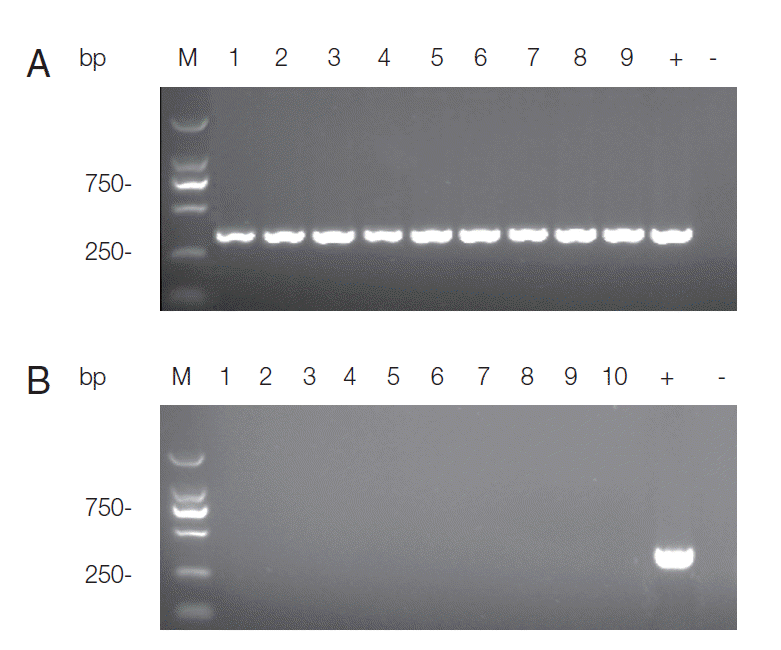
B). Specific DNA was detected in all living chickens at the end of the experiment. There was no apparent difference in the expression levels of ITS1 between different infection dose and
T. gondii strain groups. The detection results of RH group were shown in
Fig. 3A. All the samples in negative control group remained negative for PCR detection (
Fig. 3B).
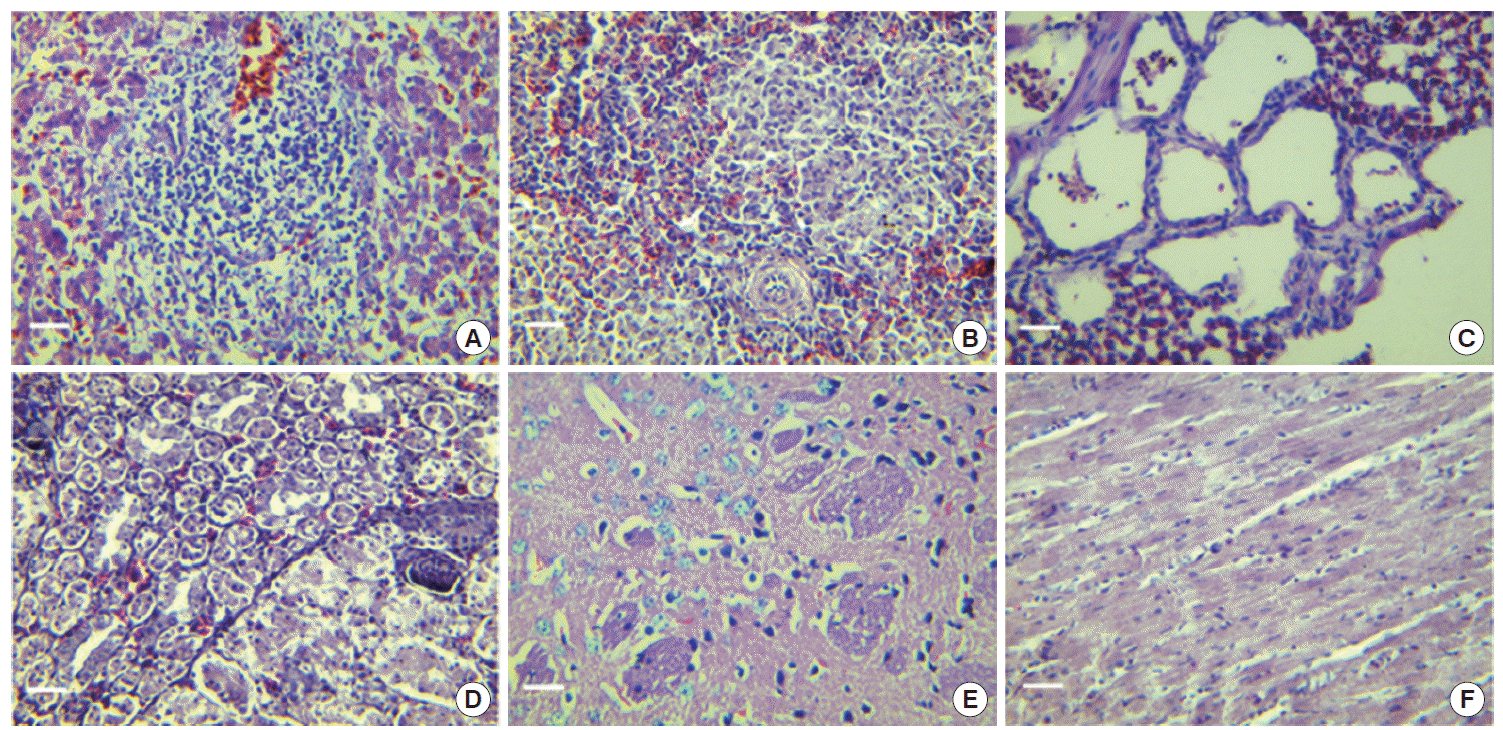
Macroscopic examination of autopsied organs showed congested and intumescent lungs, livers, spleens, and kidneys of the dead cases during the acute stage, without visible changes in hearts (
Table 2). The livers (
Fig. 4A) showed infiltrations of lymphocyte and mononuclear cells in the parenchymatous tissue and portal area. Congestion, enlargement of the hepatic sinusoids, and focal necrosis of hepatocytes were particularly evident in these cases. The spleens showed considerable changes (
Fig. 4B). Congestion and enlargement of the splenic sinusoid were obvious, and numerous infiltrations of eosinophils and neutrophils were detected in the spleen parenchymatous tissues as well.
Main pathological changes of lungs were interstitial pneumonia (
Fig. 4C). Numerous lymphocytes, monocytes, eosinophils, and neutrophils infiltrated within the bronchial alveoli. Swollen alveolar wall and engorged blood capillaries were particularly evident. As shown in
Fig. 4D, the main pathological changes of kidneys were interstitial nephritis, enlargement and engorgement of blood capillaries, hemorrhage of renal interstitium, and swelling of glomeruli. The only histopathological changes of the brains were degeneration of nerve cells (
Fig. 4E). As shown in
Fig. 4F, no pathological changes were found in the heart.
No histopathological changes were observed in any of the living chickens of the infected groups and the negative control group at the end of the experiment (
Table 2).
DISCUSSION
Chickens are usually considered to be resistant to infection with
T. gondii and always display chronic infection without apparent clinical signs to toxoplasmosis [
9]. There are only a few reports of clinical toxoplasmosis in chickens worldwide [
12]. Recently, Goodwin et al. [
17] reported peripheral neuritis in 3 chickens from Georgia, USA, while Dubey et al. [
18] reported that 3 birds died suddenly out of a group of 14 backyard chickens in Illinois. Torticollis and lateral recumbency were the only clinical signs [
18]. Up to now, worldwide prevalence of
T. gondii infection in chickens was reported, and viable
T. gondii was isolated in many parts of the world from free-range chickens [
19-
24]. These indicated that eating undercooked chicken meat might lead to transmission of the parasite to humans. To date, experimental studies of histopathological lesions of
T. gondii infection in broiler chickens were relatively rare. Our previous study indicated that chickens under 14 days old were susceptible to a high dose infection of
T. gondii [
25]. Thus, 10 days old chickens were used as experimental animals in this study.
In the present study, 4 doses of 5×108, 1×108, 1×107, and 1×106 tachyzoites were applied to infect chickens. The results showed that the sensitivity of chickens to T. gondii presented dose-dependent responses. The infection with more than 1×107 tachyzoites of all the 5 strains resulted in death, clinical signs, and pathological changes of the organs. The infection of 1×106 tachyzoites did not produce death, clinical signs, or pathological changes. This indicated that the infection dose is an important factor to the pathogenicity of the parasite.
In a previous research, we found that the JS strain was more virulent for the 7-day-old chickens than the RH strain [
25]. In the present study, we found that the survival times of chickens infected with 5×10
8 and 1×10
8 tachyzoites of the JS strain were significantly shorter than that of the other 4 strains, and there were no significant differences among the 4 mammal strains. These results were in accordance with that reported in young pigs [
8]. These findings together suggested that the virulence of
T. gondii might be related to the sources of the strain origin and the mammalian strains might be less virulent to chickens. However, the exact mechanisms of these differences need to be further investigated.
In a previous study, we showed that the RH strain from humans could infect chickens and persisted in chickens for 53 days [
25]. In this study, we used 5 strains of
T. gondii from the human, chicken, swine, and feline. The results showed that the tachyzoites of all 5 strains could be observed by microscopy in the liver, spleen, kidneys, and lungs during the acute stage, and the DNA of
T. gondii could be detected by specific PCR at the end of the experiment. These findings were in accordance with that of the previous report [
26]. These suggested that most of the strains of
T. gondii from other animals could infect chickens and persist in chickens. It also intensified the importance of chicken infection of
T. gondii in public health.
To date, little has been published regarding the histopathological changes of
T. gondii in broiler chickens. In the present study, birds exposed to a high dose of
T. gondii tachyzoites showed acute signs of toxoplasmosis with obvious histopathological lesions. The main histopathological changes of the dead cases were hyperemia, hemorrhage, and infiltration of numerous pro-inflammatory cells. These findings were in agreement with the results obtained in young chickens [
26].
In this study, no tissue cysts were found in the histopathological sections of the brain, heart, and other main organs of infected chickens at day 53 PI. Similar results were also reported [
26-
28]. These results together indicated that
T. gondii might not form cysts in chickens. Another possibility was that
T. gondii really formed cysts in chickens, but the numbers were rare and we could not observe them in tissue sections. However, the DNA of
T. gondii could be detected by specific PCR at day 53 PI. This showed that
T. gondii could persist in the chicken tissues for a long time. The real type of
T. gondii presented in chicken tissues in the late stage of infection should be further studied.
In the present research, DNA of T. gondii could be detected by specific PCR at day 53 PI, and the expression levels of ITS1 seems to be almost the same in the different groups infected with 1×108, 1×107, and 1×106 tachyzoites, respectively. One possibility was that the vast majority of T. gondii tachyzoites were cleaned up by the host immune system and resulted in almost equal residuals of tachyzoites, and thus PCR could not differentiate the differences of tachyzoites between different groups. Another possibility was that the general PCR was not suitable to distinguish the different expressions of the gene. However, the exact reasons for the same expression levels of ITS1 at day 53 PI should be further investigated.
Notes
-
We have no conflict of interest related to this work.
This work was supported by the Special Fund for Public Welfare Industry of Ministry of Agriculture of China (200903036-04) and the Priority Academic Program Development of Jiangsu Higher Education Institutions (PAPD).
Fig. 1.Survival time of chickens post intraperitoneal infection with T. gondii. Results are expressed as mean±SD. Statistically significant differences (P<0.05 and P<0.01) are indicated as * and **, respectively.

Fig. 2.Observations of T. gondii in tissues of dead chickens. (A) Tachyzoites (arrows) in the chicken’s liver (Wright stain, magnification ×400). (B) Tachyzoite (arrow) in the chicken’s spleen (Wright stain, magnification ×400). Bar =10 μm.

Fig. 3.Agarose gel electrophoresis of PCR products for T. gondii ITS-1 fragment. DNA extracted from a mixture of the heart, liver, spleen, lung, kidney, and brain of each chicken was used for PCR. (A) PCR detection results of RH group infected with 1×106, 1×107, and 1×108 tachyzoites, respectively. Three samples for each group were presented. Lanes 1-3 represent 1×106 group; Lanes 4-6 represent 1×107 group; Lanes 7-9 represent 1×108 group; +: product of positive control; -: product of negative control. (B) Detection results of samples in negative control group. Lane M: DL2000 marker; Lanes 1-10: PCR products of each chicken; +: product of positive control; -: product of negative control.

Fig. 4.Characteristic histopathological changes of dead chickens in acute infection with T. gondii (H-E stain, magnification ×400). (A), liver; (B), spleen; (C), lung; (D), kidney; (E), brain; (F), heart. Bar=20 μm.

Table 1.Rectal temperature of chickens post intraperitoneally infected with T. gondii
Table 1.
|
Dosage |
Strain |
Rectal temperature (minimum to maximum, ˚C)
|
|
Day 1 |
Day 2 |
Day 3 |
Day 4 |
Day 5 |
Day 6-53 |
|
5 × 108
|
RH |
40.1-40.9 |
43.1-43.7 |
42.8-43.5B
|
NS |
NS |
NS |
|
CN |
40.3-40.7 |
43.0-43.9 |
42.9-43.6B
|
NS |
NS |
NS |
|
JS |
40.2-40.8 |
43.1-43.8 |
43.1-43.7A
|
NS |
NS |
NS |
|
CAT 2 |
40.0-40.7 |
43.2-43.9 |
42.7-43.5B
|
NS |
NS |
NS |
|
CAT 3 |
40.1-40.9 |
43.0-43.6 |
42.9-43.4B
|
NS |
NS |
NS |
|
RH |
40.0-40.8 |
42.9-43.8 |
42.0-42.7B
|
41.4-42.2 |
40.3-40.8 |
40.0-40.7 |
|
1 × 108
|
CN |
40.2-40.9 |
42.8-43.9 |
42.0-42.8B
|
41.5-42.2 |
40.1-40.9 |
40.2-40.9 |
|
1 × 107
|
JS |
40.1-40.9 |
42.6-44.0 |
42.2-42.8B
|
41.2-42.4 |
40.5-40.8 |
40.3-40.8 |
|
1 × 106
|
CAT 2 |
40.1-40.9 |
42.7-43.8 |
42.0-42.9B
|
41.1-42.3 |
40.2-40.7 |
40.2-40.7 |
|
CAT 3 |
40.0-40.7 |
42.8-43.8 |
42.1-42.6 |
41.2-42.5 |
40.0-40.7 |
40.2-40.8 |
|
Negative control |
PBS |
40.1-40.8 |
40.0-40.9 |
40.2-41.0 |
40.1-40.8 |
40.2-40.8 |
40.2-40.7 |
Table 2.Histopathological lesions in various organs of chickens post intraperitoneally infected with T. gondii
Table 2.
|
Dosage |
|
Organs
|
|
Liver |
Spleen |
Lung |
Kidney |
Heart |
Brain |
|
5 × 108
|
Dead chicken |
Lymphocytic infiltration, congestion and necrosis |
Acidophilic and neutrophil infiltration, congestion |
Interstitial pneumonia, lymphocytic, acidophilic and neutrophil infiltration |
Interstitial nephritis, congestion and hemorrhage |
No |
Degeneration |
|
Living chicken |
NS |
NS |
NS |
NS |
NS |
NS |
|
1 × 108
|
Dead chicken |
Lymphocytic infiltration and congestion |
Acidophilic and neutrophil infiltration |
Interstitial pneumonia, l ymphocytic and monocytic infiltration |
Interstitial nephritis and hemorrhage |
No |
Degeneration |
|
Living chicken |
No |
No |
No |
No |
No |
No |
|
1 × 107
|
Living chicken |
No |
No |
No |
No |
No |
No |
|
1 × 106
|
Living chicken |
No |
No |
No |
No |
No |
No |
|
Negative control |
Living chicken |
No |
No |
No |
No |
No |
No |
References
- 1. Dubey JP, Sundar N, Hill D, Velmurugan GV, Bandini LA, Kwok OC, Majumdar D, Su C. High prevalence and abundant atypical genotypes of Toxoplasma gondii isolated from lambs destined for human consumption in the USA. Int J Parasitol 2008;38:999-1006.
- 2. Innes EA. Toxoplasmosis: comparative species susceptibility and host immune response. Comp Immunol Microbiol Infect Dis 1997;20:131-138.
- 3. Gustafsson K, Uggla A. Serologic survey for Toxoplasma gondii infection in the brown hare (Lepus europaeus P.) in Sweden. J Wildl Dis 1994;30:201-204.
- 4. Howe DK, Honore S, Derouin F, Sibley LD. Determination of genotypes of Toxoplasma gondii strains isolated from patients with toxoplasmosis. J Clin Microbiol 1997;35:1411-1414.
- 5. Dubey JP, Choudhary S, Kwok OC, Ferreira LR, Oliveira S, Verma SK, Marks DR, Pedersen K, Mickley RM, Randall AR, Arsnoe D, Su C. Isolation and genetic characterization of Toxoplasma gondii from mute swan (Cygnus olor) from the USA. Vet Parasitol 2013;195:42-46.
- 6. Zhou Y, Zhang H, Cao J, Gong H, Zhou J. Isolation and genotyping of Toxoplasma gondii from domestic rabbits in China to reveal the prevalence of type III strains. Vet Parasitol 2013;193:270-276.
- 7. Wang L, Chen H, Liu D, Huo X, Gao J, Song X, Xu X, Huang K, Liu W, Wang Y, Lu F, Lun ZR, Luo Q, Wang X, Shen J. Genotypes and mouse virulence of Toxoplasma gondii isolates from animals and humans in China. PLoS One 2013;8:e53483.
- 8. Jungersen G, Jensen L, Riber U, Heegaard PM, Petersen E, Poulsen JS, Bille-Hansen V, Lind P. Pathogenicity of selected Toxoplasma gondii isolates in young pigs. Int J Parasitol 1999;29:1307-1319.
- 9. Zou J, Huang XX, Yin GW, Ding Y, Liu XY, Wang H, Chen QJ, Suo X. Evaluation of Toxoplasma gondii as a live vaccine vector in susceptible and resistant hosts. Parasit Vectors 2011;4:168.
- 10. Zhu J, Yin J, Xiao Y, Jiang N, Ankarlev J, Lindh J, Chen Q. A sero-epidemiological survey of Toxoplasma gondii infection in free-range and caged chickens in northeast China. Vet Parasitol 2008;158:360-363.
- 11. Zhao G, Shen B, Xie Q, Xu LX, Yan RF, Song XK, Hassan IA, Li XR. Detection of Toxoplasma gondii in free-range chickens in China based on circulating antigens and antibodies. Vet Parasitol 2012;185:72-77.
- 12. Dubey JP. Toxoplasma gondii infections in chickens (Gallus domesticus): prevalence, clinical disease, diagnosis and public health significance. Zoonoses Public Health 2010;57:60-73.
- 13. Dubey JP, Rajendran C, Costa DG, Ferreira LR, Kwok OC, Qu D, Su C, Marvulo MF, Alves LC, Mota RA, Silva JC. New Toxoplasma gondii genotypes isolated from free-range chickens from the Fernando de Noronha, Brazil: unexpected findings. J Parasitol 2010;96:709-712.
- 14. Zhao GW, Shen B, Xie Q, Xu LX, Yan RF, Song XK, Adam HI, Li XR. Isolation and Molecular Characterization of Toxoplasma gondii from Chickens in China. Journal of Integrative Agriculture 2012;11:1347-1353.
- 15. More G, Maksimov P, Pardini L, Herrmann DC, Bacigalupe D, Maksimov A, Basso W, Conraths FJ, Schares G, Venturini MC. Toxoplasma gondii infection in sentinel and free-range chickens from Argentina. Vet Parasitol 2012;184:116-121.
- 16. Yan C, Yue CL, Yuan ZG, Lin RQ, He Y, Yin CC, Xu MJ, Song HQ, Zhu XQ. Molecular and serological diagnosis of Toxoplasma gondii infection in experimentally infected chickens. Vet Parasitol 2010;173:179-183.
- 17. Goodwin MA, Dubey JP, Hatkin J. Toxoplasma gondii peripheral neuritis in chickens. J Vet Diagn Invest 1994;6:382-385.
- 18. Dubey JP, Webb DM, Sundar N, Velmurugan GV, Bandini LA, Kwok OC, Su C. Endemic avian toxoplasmosis on a farm in Illinois: clinical disease, diagnosis, biologic and genetic characteristics of Toxoplasma gondii isolates from chickens (Gallus domesticus), and a goose (Anser anser). Vet Parasitol 2007;148:207-212.
- 19. Lindstrom I, Sundar N, Lindh J, Kironde F, Kabasa JD, Kwok OC, Dubey JP, Smith JE. Isolation and genotyping of Toxoplasma gondii from Ugandan chickens reveals frequent multiple infections. Parasitology 2008;135:39-45.
- 20. Dubey JP, Morales ES, Lehmann T. Isolation and genotyping of Toxoplasma gondii from free-ranging chickens from Mexico. J Parasitol 2004;90:411-413.
- 21. Dubey JP, Venturini MC, Venturini L, Piscopo M, Graham DH, Dahl E, Sreekumar C, Vianna MC, Lehmann T. Isolation and genotyping of Toxoplasma gondii from free-ranging chickens from Argentina. J Parasitol 2003;89:1063-1064.
- 22. Dubey JP, Gomez-Marin JE, Bedoya A, Lora F, Vianna MC, Hill D, Kwok OC, Shen SK, Marcet PL, Lehmann T. Genetic and biologic characteristics of Toxoplasma gondii isolates in free-range chickens from Colombia, South America. Vet Parasitol 2005;134:67-72.
- 23. Dubey JP, Vianna MC, Sousa S, Canada N, Meireles S, Correia da Costa JM, Marcet PL, Lehmann T, Darde ML, Thulliez P. Characterization of Toxoplasma gondii isolates in free-range chickens from Portugal. J Parasitol 2006;92:184-186.
- 24. Zhao G, Shen B, Xie Q, Xu LX, Yan RF, Song XK, Hassan IA, Li XR. Detection of Toxoplasma gondii in free-range chickens in China based on circulating antigens and antibodies. Vet Parasitol 2012;185:72-77.
- 25. Wang S, Zhao G, Wang W, Xie Q, Zhang M, Yuan C, Hassan IA, Liu X, Xu L, Yan R, Song X, Li X. Pathogenicity of two Toxoplasma gondii strains in chickens of different ages infected via intraperitoneal injection. Avian Pathol 2014;43:91-95.
- 26. Derakhshanfar A, Hatam G, Sohrabi K, Mirzaei M. Clinical, serological and histopathological signs of toxoplasmosis in broiler chickens (Gallus domesticus) after experimental infection. Comparative Clinical Pathology 2012;21:1379-1382.
- 27. Kaneto CN, Costa AJ, Paulillo AC, Moraes FR, Murakami TO, Meireles MV. Experimental toxoplasmosis in broiler chicks. Vet Parasitol 1997;69:203-210.
- 28. Dubey JP, Ruff MD, Camargo ME, Shen SK, Wilkins GL, Kwok OC, Thulliez P. Serologic and parasitologic responses of domestic chickens after oral inoculation with Toxoplasma gondii oocysts. Am J Vet Res 1993;54:1668-1672.