Abstract
We report here a case of strongyloidiasis in a 72-year-old diabetic patient (woman) accompanied by gastrointestinal stromal tumor receiving imatinib therapy, first diagnosed as hypereosinophilic syndrome and treated with steroids for uncontrolled eosinophilia. She suffered from lower back pain and intermittent abdominal discomfort with nausea and diagnosed with gastrointestinal stromal tumor. After post-operative imatinib treatment eosinophilia persisted, so that steroid therapy was started under an impression of hypereosinophilic syndrome. In spite of 6 months steroid therapy, eosinophilia persisted. Stool examination was performed to rule out intestinal helminth infections. Rhabditoid larvae of Strongyloides stercoralis were detected and the patient was diagnosed as strongyloidiasis. This diagnosis was confirmed again by PCR. The patient was treated with albendazole for 14 days and her abdominal pain and diarrhea improved. This case highlights the need for thorough investigation, including molecular approaches, to test for strongyloidiasis before and during steroid therapies.
-
Key words: Strongyloides stercoralis, imatinib, gastrointestinal stromal tumor (GIST), PCR, hypereosinophilic syndrome
INTRODUCTION
Strongyloidiasis, caused by
Strongyloides stercoralis, is one of the most neglected tropical diseases and is highly under-reported in low-endemic areas [
1,
2]. Transmission is usually through the skin by third-stage larvae, but the nematode can also replicate within the host as an autoinfection [
3].
S. stercoralis can cause a wide spectrum of diseases such as acute strongyloidiasis, chronic strongyloidiasis, hyperinfection syndrome, and disseminated infections depending on host immunity [
4]. However, strongyloidiasis is frequently under-diagnosed since many infections are asymptomatic and conventional diagnostic tests based on parasitological examinations are not sufficiently sensitive [
5]. Clinical suspicion is important for strongyloidiasis diagnosis. While eosinophilia is a frequently observed as initial finding in patients with strongylodiasis [
6], it is also found in various other underlying conditions [
7]. Moreover, unknown eosinophilia is often encountered in clinical laboratories and this hypereosinophilia syndrome (HES) can be treated with imatinib [
8].
Strongyloidiasis recorded in Korea have been mainly of intestinal or hyperinfections and counted over 40 cases [
9-
14]. This infection is also known to be triggered by immune deficient status, e.g., lymphoma, leukemia, immunosuppressant therapy, organ transplantation, and coinfection with the human T cell lymphotropic virus type-1 [
4,
15-
17]. Interestingly, strongyloidiasis can present as a colonic mass [
18]; and thus discrimination from gastrointestinal lymphoma may be sometimes difficult. In contrast with gastrointestinal lymphoma, however, the report of strongyloidiasis with gastrointestinal stromal tumor (GIST) is limited. Here, we report a case of strongyloidiasis in a diabetic patient accompanied by gastrointestinal stromal tumor, who was initially diagnosed as hypereosinophilic syndrome (HES) and treated with steroid therapy for persistent eosinophilia uncontrolled by imatinib treatment.
CASE RECORD
A 72-year-old woman was admitted with chief complaints of lower back pain and intermittent abdominal discomfort with nausea that had lasted for 1 year. She had a medical history of type 2 diabetes mellitus and hypertension. She was transferred for a 6.5×6.5 cm mesenteric mass detected by CT at a private clinic. She underwent small bowel segmental resection and was diagnosed with GIST. During 9 months follow-up after the operation, eosinophilia persisted despite imatinib treatment. Laboratory tests revealed eosinophilia (3,760/mm3, 45.8%), anemia (hemoglobin, 11.4 g/dl), uncontrolled blood glucose (Hb A1c, 9.1%), high levels of immunoglobulin E (IgE, 326 IU/ml), and free light chain kappa (31.1 mg/dl). Serological evaluations for common parasitic infections (clonorchiasis, paragonimiasis, sparganosis, cysticercosis, and toxocariasis) were positive only for cysticercosis IgG (0.415; cut-off value, 0.234). Because there was no other evidence of cysticercosis, steroid therapy was started for HES. Although the patient received steroid therapy for 6 months, she presented with persistent eosinophilia and aggravated abdominal pain with diarrhea.
Physical examination revealed multiple erythematous patches on her buttocks; the patient also reported intermittent itching on her buttocks. Enhanced abdomino-pelvic CT showed edematous wall thickening and enhancement with moderate ascites involving the jejunum, ileum, and ascending colon. She was treated with ceftriazone and trizel for a clinical suspicion of enterocolitis. Stool examination was performed to evaluate the eosinophilia that remained uncontrolled despite the steroid therapy. The formalin-ether concentration method revealed
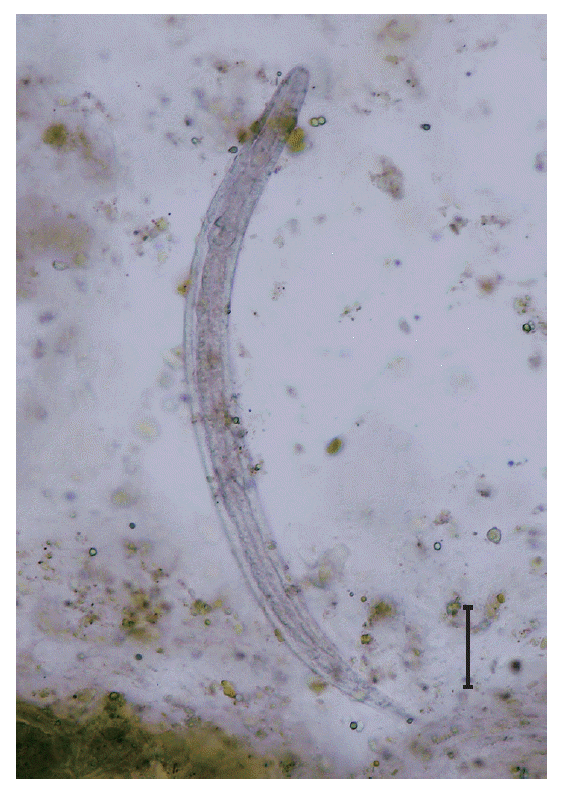
S. stercoralis rhabditoid larvae of 320 to 325 μm in length and 15 to 18 μm in width (
Fig. 1). Colonoscopy showed multiple aphthous ulcerative lesions throughout the colon, indicating chronic colitis. Eosinophilic colitis without evidence of
S. stercoralis larvae was noted in a colonic biopsy. Fecal specimens were cultured using the Baermann’s funnel method; however, filariform larvae were not observed until after 72 hr in culture. Therefore, we identified
S. stercoralis in stool samples by PCR using specific primers as previously described [
19]. The patient was treated with 400 mg of albendazole twice a day for 14 days and her abdominal pain and diarrhea improved.
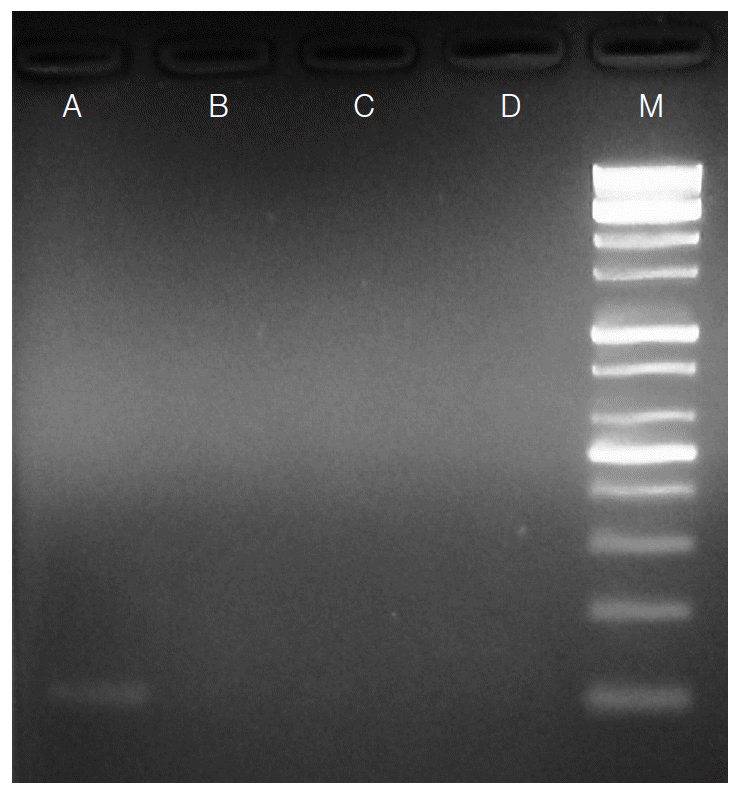
S. stercoralis larvae were no longer detected in stool examination and PCR in the follow-up examinations (
Fig. 2), and the eosinophilia was improved.
DISCUSSION
Clinicians often encounter eosinophilia persisting for at least 6 months without recognizable causes such as asthma, allergic disorders, or malignancies, in addition to parasitic infections. It is difficult for clinicians to investigate all possible causes of eosinophilia. In addition to eosinophilia, our patient also reported frequent nausea, abdominal discomfort, loose stool, and itching around her buttocks. The symptoms worsened with change of treatment from imatinib to steroid therapy; this might reflect an autoinfection stage by
S. stercoralis. Non-response to imatinib, a treatment option for both GIST and HES [
8,
20], might conversely indicate that this case had a relatively low probability of clonal eosinophilia [
21]. A thorough work-up for secondary eosinophilia including stool examination should have been performed at that time. Stool examination is an easy, economical, and essential tool to detect parasitic infections in clinical use, but the usefulness of stool examination has been underestimated because of its relatively low sensitivity, especially in non-endemic countries. Moreover, examination of multiple stools is imperative in clinical laboratories, considering the intermittent shedding of parasite ova in stools, but is labor-intensive. Thus, some researchers have proposed the Triple-Faeces-Test protocol for reliable detection of parasites using multiple sampling with a sodium acetate, acetic acid, and formalin fixative method or PCR [
22,
23].
The current case showed that molecular testing could be helpful for rapid confirmation of strongyloidiasis. While serological tests using enzyme immunoassays could be useful for diagnosing immunocompetent individuals, they are not currently available in Korea [
24]. There was no pathological evidence of
S. stercoralis in this case, although intestinal strongyloidiasis is typically diagnosed based on histological findings from biopsies [
25]. Thus, PCR offered confirmation for the definitive diagnosis of
S. stercoralis infection. There has been some debate if molecular procedures or traditional methods such as direct smear, formalin ether concentration, and various culture methods offer better detection rates, but study results vary according to the study design [
5,
26]. However, we believe PCR may be a sensitive and useful modality for detecting
S. stercoralis in stool samples, with sensitivity comparable to formalin-ether concentrations.
We nearly missed this strongyloidiasis, and the correct diagnosis was delayed for 1 year after the onset of symptoms because of the low index of suspicion. Fortunately, the patient did not develop hyperinfection syndrome despite long-term steroid therapy. Notably, many strongyloidiasis cases have been fatal in immunocompromised patients [
9,
12]; thus, proper screening of potentially infected individuals is essential before administering steroid therapy. Although gastrointestinal lymphoma has been reported associated with strongyloidiasis, strongyloidiasis is scarcely reported in a patient with GIST before. This case presents strongyloidiasis triggered by steroid therapy in a diabetic patient with GIST receiving imatinib therapy and suggests the usefulness of molecular investigations to completely rule out strongyloidiasis.
Notes
-
We have no conflict of interest related to this work.
This work was supported by the funding from the Korean Society of Clinical Microbiology (2014).
Fig. 1.A rhabditoid larva of Strongyloides stercoralis visible in the stool using formalin-ether concentration method. ×400. Bar=50 μm.

Fig. 2.Agarose-gel electrophoresis of PCR products amplified by Strongyloides stercoralis-specific primers using genomic DNA extracted from stool samples. Lane A: Positive PCR product (114 bp) from a stool sample in which S. stercoralis larvae were found by formalin-ether concentration method. Lanes B-D: Negative PCR products of the patient’s stool samples (follow-ups). Lane M: 100 bp DNA marker ladder.

References
- 1. Olsen A, van Lieshout L, Marti H, Polderman T, Polman K, Steinmann P, Stothard R, Thybo S, Verweij JJ, Magnussen P. Strongyloidiasis-the most neglected of the neglected tropical diseases? Trans R Soc Trop Med Hyg 2009;103:967-972.
- 2. Schar F, Trostdorf U, Giardina F, Khieu V, Muth S, Marti H, Vounatsou P, Odermatt P. Strongyloides stercoralis: global distribution and risk factors. PLoS Negl Trop Dis 2013;7:e2288.
- 3. Potter A, Stephens D, De Keulenaer B. Strongyloides hyperinfection: a case for awareness. Ann Trop Med Parasitol 2003;97:855-860.
- 4. Keiser PB, Nutman TB. Strongyloides stercoralis in the immunocompromised population. Clin Microbiol Rev 2004;17:208-217.
- 5. Requena-Mendez A, Chiodini P, Bisoffi Z, Buonfrate D, Gotuzzo E, Munoz J. The laboratory diagnosis and follow up of strongyloidiasis: a systematic review. PLoS Negl Trop Dis 2013;7:e2002.
- 6. Gonzalez A, Gallo M, Valls ME, Munoz J, Puyol L, Pinazo MJ, Mas J, Gascon J. Clinical and epidemiological features of 33 imported Strongyloides stercoralis infections. Trans R Soc Trop Med Hyg 2010;104:613-616.
- 7. Rothenberg ME. Eosinophilia. N Engl J Med 1998;338:1592-1600.
- 8. Schaller JL, Burkland GA. Case report: rapid and complete control of idiopathic hypereosinophilia with imatinib mesylate. MedGenMed 2001;3:9.
- 9. Choi SI, Hong SW, Lee KG. Hyperinfection syndrome with Strongyloides stercoralis: report of a case. Korean J Pathol 1989;23:359-364.
- 10. Lee SK, Shin BM, Khang SK, Chai JY, Kook J, Hong ST, Lee SH. Nine cases of strongyloidiasis in Korea. Korean J Parasitol 1994;32:49-52.
- 11. Kim J, Joo HS, Kim DH, Lim H, Kang YH, Kim MS. A case of gastric strongyloidiasis in a Korean patient. Korean J Parasitol 2003;41:63-67.
- 12. Kim J, Joo HS, Ko HM, Na MS, Hwang SH, Im JC. A case of fatal hyperinfective strongyloidiasis with discovery of autoinfective filariform larvae in sputum. Korean J Parasitol 2005;43:51-55.
- 13. Kim HO, Kim JH, Cheon YH, Suh YS, Lim MH, Heo ST, Sohn WM, Ko GH, Bae IG. A case of duodenal ulcer due to coinfection with Strongyloides stericoralis and cytomegalovirus. Infect Chemother 2010;42:431-433.
- 14. Cho JY, Kwon JG, Ha KH, Oh JY, Jin MI, Heo SW, Lee GH, Cho CH. A case of steroid-induced hyperinfective strongyloidiasis with bacterial meningitis. Korean J Gastroenterol 2012;60:330-334.
- 15. Genta RM, Miles P, Fields K. Opportunistic Strongyloides stercoralis infection in lymphoma patients. Report of a case and review of the literature. Cancer 1989;63:1407-1411.
- 16. Devault GAJ, King JW, Rohr MS, Landreneau MD, Brown ST, McDonald JC. Opportunistic infections with Strongyloides stercoralis in renal transplantation. Rev Infect Dis 1990;12:653-671.
- 17. Gotuzzo E, Terashima A, Alvarez H, Tello R, Infante R, Watts DM, Freedman DO. Strongyloides stercoralis hyperinfection associated with human T-cell lymphotropic virus type-1 infection in Perú. Am J Trop Med Hyg 1999;60:146-149.
- 18. Sethi S, Kheraj R, Sethi N, Wadhwa V. A case of strongyloidiasis presenting as a colonic mass. Am J Gastroenterol 2014;109:20.
- 19. Moghaddassani H, Mirhendi H, Hosseini M, Rokni M, Mowlavi G, Kia E. Molecular diagnosis of Strongyloides stercoralis infection by PCR detection of specific DNA in human stool samples. Iran J Parasitol 2011;6:23-30.
- 20. Nishida T, Doi T, Naito Y. Tyrosine kinase inhibitors in the treatment of unresectable or metastatic gastrointestinal stromal tumors. Expert Opin Pharmacother 2014;15:1979-1989.
- 21. Fazel R, Dhaliwal G, Saint S, Nallamothu BK. Clinical problem-solving. A red flag. N Engl J Med 2009;360:2005-2010.
- 22. Vandenberg O, Van Laethem Y, Souayah H, Kutane WT, van Gool T, Dediste A. Improvement of routine diagnosis of intestinal parasites with multiple sampling and SAF-fixative in the triple-faeces-test. Acta Gastroenterol Belg 2006;69:361-366.
- 23. Bruijnesteijn van Coppenraet LE, Wallinga JA, Ruijs GJ, Bruins MJ, Verweij JJ. Parasitological diagnosis combining an internally controlled real-time PCR assay for the detection of four protozoa in stool samples with a testing algorithm for microscopy. Clin Microbiol Infect 2009;15:869-874.
- 24. Anderson NW, Klein DM, Dornink SM, Jespersen DJ, Kubofcik J, Nutman TB, Merrigan SD, Couturier MR, Theel ES. Comparison of three immunoassays for detection of antibodies to Strongyloides stercoralis. Clin Vaccine Immunol 2014;21:732-736.
- 25. Santos RB, Fonseca LE Jr, Santana AT, Silva CA, Guedes JC. Clinical, endoscopic and histopathological profiles of parasitic duodenitis cases diagnosed by upper digestive endoscopy. Arq Gastroenterol 2011;48:225-230.
- 26. Sultana Y, Jeoffreys N, Watts MR, Gilbert GL, Lee R. Real-time polymerase chain reaction for detection of Strongyloides stercoralis in stool. Am J Trop Med Hyg 2013;88:1048-1051.
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by

- Global prevalence and correlation of intestinal parasitic infections in patients with colorectal cancer: a systematic review and meta-analysis
Maryam Hataminejad, Bahareh Basirpour, Melika Baharlou, Masoumeh Gholami Koohestan, Hajar Ziaei Hezarjaribi, Bahman Rahimi Esboei, Shirzad Gholami, Seyed Abdollah Hosseini, Reza Saberi
BMC Gastroenterology.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - A case of disseminated strongyloidiasis diagnosed by worms in the urinary sediment
Young-Ha Lee
Parasites, Hosts and Diseases.2024; 62(2): 238. CrossRef - From past to present: opportunities and trends in the molecular detection and diagnosis of Strongyloides stercoralis
Abigail Hui En Chan, Urusa Thaenkham
Parasites & Vectors.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Seropositivity Rates of Strongyloides stercoralis Antibody in the Southeastern Region of Republic of Korea: A Single-Center Retrospective Study
Taehwa Kim, Seungjin Lim
The Korean Journal of Parasitology.2022; 60(3): 181. CrossRef - Importance of detection of Strongyloides stercoralis DNA in fecal samples from patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus
Márcia Carolina Mazzaro, Émelin Alves dos Santos, Gessica Baptista de Melo, Priscila Duarte Marques, Laura Vilela Souza, Jefferson Elias-Oliveira, Bruna Campos da Silva, Ronaldo César Borges Gryschek, Fabiana Martins de Paula, Rosângela Maria Rodrigues
Clinics.2022; 77: 100060. CrossRef - Phylogenetic Positioning of a Strongyloides stercoralis Isolate Recovered from a Korean Patient and Comparison with Other Asian Isolates
Jaeho Bae, Mi Jin Jeong, Dong hoon Shin, Hyun Woo Kim, Sung Ho Ahn, Jun Ho Choi, Hak Sun Yu
The Korean Journal of Parasitology.2020; 58(6): 689. CrossRef - Report of the Korean Association of External Quality Assessment Service on Clinical Parasitology (2018–2019)
Suhak Jeon, Eun Jeong Won, Yu Jeong Lee, Moon-Ju Kim, Myung Geun Shin, Jong Hee Shin
Journal of Laboratory Medicine and Quality Assurance.2020; 42(4): 177. CrossRef - Strongyloides stercoralis infection in a patient with rheumatoid arthritis and type 2 diabetes mellitus: a case-based review
Alireza Ashiri, Molouk Beiromvand, Abdollah Khanzadeh
Clinical Rheumatology.2019; 38(11): 3093. CrossRef - Strongyloidiasis Current Status with Emphasis in Diagnosis and Drug Research
Tiago Mendes, Karen Minori, Marlene Ueta, Danilo Ciccone Miguel, Silmara Marques Allegretti
Journal of Parasitology Research.2017; 2017: 1. CrossRef