Abstract
Leishmania (L.) tropica is a causative agent of cutaneous leishmaniasis, and occasionally of visceral or viscerotropic leishmaniasis in humans. Murine models of Leishmania infection have been proven to be useful for elucidation of mechanisms for pathogenesis and immunity in leishmaniasis. The aim of this study was to establish a murine model for human viscerotropic leishmaniasis, and the growth pattern of L. tropica was studied in different tissues of BALB/c mice in order to find out whether the parasite visceralizes in this murine model. L. major was used as a control as this species is known to cause a progressive infection in BALB/c mice. L. tropica or L. major was injected into the footpad of mice, and thickness of footpad, parasite loads in different tissues, and the weight of the spleen and lymph node were determined at different intervals. Results showed that L. tropica visceralizes to the spleen and grows there while its growth is controlled in footpad tissues. Dissemination of L. tropica to visceral organs in BALB/c mice was similar to the growth patterns of this parasite in human viscerotropic leishmaniasis. The BALB/c model of L. tropica infection may be considered as a good experimental model for human diseases.
-
Key words: Leishmania tropica, BALB/c mouse, murine model, visceral leishmaniasis, viscerotropic leishmaniasis
INTRODUCTION
Leishmania tropica is a causative agent of cutaneous leishmaniasis in humans. It can occasionally be a causative agent of visceral or viscerotropic leishmaniasis in humans (
Mebrahtu et al., 1989;
Sacks et al.,1995;
Guessous-Idrissi et al., 1997;
Yaghoobi-Ershadi et al., 2002;
Jacobson, 2003;
Murray et al., 2005;
Alborzi et al., 2006;
Mohebali et al., 2006).
L. tropica can also cause a systemic leishmania infection (
Magill et al., 1993), which was called as "viscerotropic" leishmaniasis to distinguish it from "visceral" leishmaniasis, which is frequently considered to be the same as kala-azar caused by
L. donovani (
Magill et al., 1993). Viscerotropic leishmaniasis is a comparatively mild form of visceral leishmaniasis caused by
L. tropica, and is a feature of this disease (
Hyams et al., 2001). Murine models of
Leishmania infection have been shown to be useful for studying pathogenesis and immunity of this disease (
Sacks and Noben-Trauth, 2002). BALB/c mice have been used as a model for
L. tropica infection (
Lira et al., 1998;
Mahmoudzadeh-Niknam, 2004;
Mahmoudzadeh-Niknam and McKerrow, 2004;
Mahmoudzadeh-Niknam et al., 2007). The aim of the present study was to find out whether BALB/c mice may be considered as an experimental model for human viscerotropic leishmaniasis.
Dissemination of parasites is an important factor in murine models of
L. major infection. Dissemination into the spleen, as a visceral organ, is associated with a susceptible phenotype, whereas containment of the parasite in the skin and lymph nodes is associated with a resistant phenotype in mice (
Laskay et al., 1995;
Nicolas et al., 2000). It is not known whether
L. tropica disseminates to the visceral organs in BALB/c mice. Lira et al. (
1998) reported that
L. tropica remains in the skin and lymph nodes in BALB/c mice and does not disseminate to the spleen. However, our previous study suggested that
L. tropica disseminates into the spleen (
Mahmoudzadeh-Niknam, 2004). In the present study, we carried out a detailed experiment to study the potential of
L. tropica to disseminate to the spleen in BALB/c mice. We also studied the parasite growth patterns in different tissues throughout the course of infection.
L. major was used as a control for a disseminating species, and its visceralization as well as growth patterns were compared with
L. tropica throughout the course of infection.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Mice
Inbred BALB/c mice, 6~8 week-old females, were used throughout the experiments. These mice were obtained from the animal breeding facility of Pasteur Institute of Iran.
Parasites
Leishmania tropica strain MHOM/AF/88/KK27 is a cutaneous
L. tropica isolated from Afghanistan, and was initially described by Dr. R. Killick-Kendrick (
Lira et al., 1998). It was a gift from Dr. D. Sacks (Laboratory of Parasitic Diseases, National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Disease, National Institute of Health, Bethesda, Maryland, USA). The
L. major strain MRHO/IR/75/ER is an isolate from Iran, and was a gift from Dr. M. Mohebali (School of Public Health, Tehran University of Medical Sciences, Tehran, Iran). The parasites were grown at 23-24℃ in 50-ml disposable centrifuge tubes containing 4 ml of culture medium. The culture medium consisted of 2 ml NNN and 2 ml RPMI-1640 medium (Sigma Chemical Co., St. Louis, Missouri, USA). The NNN medium consisted of 12% rabbit blood (with sodium citrate as an anticoagulant), 1.35% glucose (Sigma Chemical Co.), 1.4% agar (Merck, Darmstadt, Germany), and 0.6% (w/v) NaCl (Arasto Pharmaceutical Chemicals Co., Saveh, Iran). Penicillin (100 IU/ml) and streptomycin (100 µg/ml) were used as antibiotics. The parasite growth was determined by daily counting of viable parasites in culture. The promastigotes were considered stationary, if the number of viable parasites was approximately the same on 2 consecutive days. The stationary phase of promastigote growth reached 7-9 days after the beginning of promastigote cultures from starting concentration of 10
6 promastigotes per milliliter.
Infection
Mice were infected subcutaneously with 106 live stationary phase promastigotes in the right hind footpad. Disease evolution was monitored by measurement of the thickness of footpad at weekly intervals. The thickness was determined by a dial-gauge caliper (Mitutoyu, Kawasaki, Kanagawa, Japan). The footpad thickness increase due to the infection was defined as the difference between the thickness of the infected footpad and the thickness of the uninfected contralateral footpad.
Parasite load assay
The parasite load assays were carried out as previously described (
Sacks and Melby, 1998). Footpad tissues, draining lymph nodes, or spleens were homogenized in 400, 1000, and 1,000 µl of RPMI 1640, respectively. One hundred microliters from each homogenate were diluted by 2-fold serial dilutions in consecutive wells.
Groups of 5-10 BALB/c mice were infected with 106 stationary phase promastigotes of either L. major or L. tropica. The infection was done by injecting into the right hind footpad of mice. The disease evolution was monitored by determination of the footpad thickness at weekly intervals. Parasite burdens were determined in the footpads, draining lymph nodes, and spleens at 4 intervals: day 10, and mo 1, 4, and 6 post-infection (PI). The weight of the spleen and lymph node were recorded at intervals mentioned above. The study was approved by Ethical Committee of Pasteur Institute of Iran.
Statistical analysis
Footpad thicknesses were compared between different experimental groups by the Student's t-test. Parasite loads in each group were calculated by the geometric means of reciprocal titers of individual tissue samples in that group. Geometric mean titers were compared by the Student's t-test. The weights of spleens and lymph nodes were compared between different groups by nonparametric Mann-Whitney U test. P-values less than 0.05 were considered significant.
RESULTS
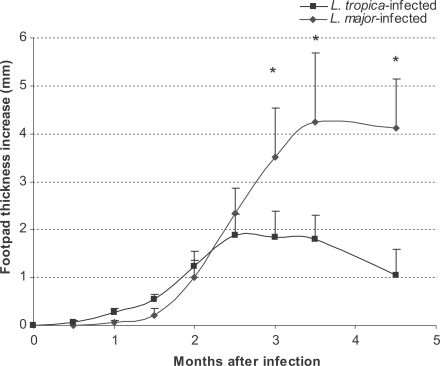
Lesion development in footpads
Lesion development in footpads was followed up for 6 mo after infection. The results are shown in
Fig. 1. The footpad thickness increased progressively until the end of the experiment in
L. major-infected mice (
Fig. 1). However, the footpad thickness in
L. tropica-infected mice increased only up to 3 mo PI and regressed thereafter. This pattern was the same as reported previously (
Lira et al., 1998;
Mahmoudzadeh-Niknam, 2004).
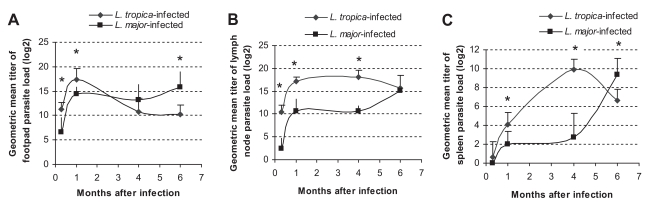
The parasite loads in
L. major and
L. tropica-infected mice are shown in
Fig. 2. The parasite load of
L. major-infected footpads increased up to 1 mo after infection (
P ≤ 0.001) and remained high until the end of the experiment, i.e., 6 mo after the injection. This pattern was quite different in
L. tropica-infected footpads: the parasite load increased up to 1 mo, decreased from mo 1 to mo 4 (
P ≤ 0.05) and remained low from mo 4 to 6 PI. The parasite load of lymph nodes in
L. tropica-infected mice increased up to mo 1 (
P ≤ 0.001), remained the same from mo 1 to mo 4 (
P ≤ 0.21), and from mo 4 to mo 6 (
P ≤ 0.11). The parasite load of lymph nodes in
L. major-infected mice increased from day 10 to mo 1 (
P ≤ 0.001), remained the same from mo 1 to mo 4 (
P ≤ 0.9), and increased from mo 4 to mo 6 (
P ≤ 0.001). The parasite load of the spleen in
L. major-infected mice increased from day 10 to mo 1 (
P ≤ 0.003), remained the same from mo 1 to mo 4 (
P ≤ 0.5), and increased from mo 4 to mo 6 (
P ≤ 0.001). The parasite load of the spleen in
L. tropica-infected mice increased from day 10 to mo 1 (
P ≤ 0.001), from mo 1 to mo 4 (
P ≤ 0.001), and decreased from mo 4 to mo 6 (
P ≤ 0.001). For the purpose of having a preliminary evaluation of the long-term outcome of
L. tropica infection in BALB/c mice, parasite loads of the footpad, lymph node, and spleen were determined in 4 mice at mo 11 after
L. tropica infection. Results showed that the parasite loads at mo 11 PI were not significantly different from those at mo 6 PI (data not shown).
Parasite loads of
L. tropica and
L. major in different tissues of infected BALB/c mice are compared in
Fig. 2. In the footpad, the parasite load of
L. tropica was higher than that of
L. major at day 10 (
P ≤ 0.002) and day 30 (
P ≤ 0.01) after infection. However, the parasite load of
L. major became higher than the parasite load of
L. tropica at mo 4 and mo 6 after the infection (
P ≤ 0.009 for mo 6). In lymph nodes, the parasite load of
L. tropica was statistically higher than the parasite load of
L. major at day 10, mo 1, and mo 4 after the infection (
P ≤ 0.001 for all intervals). In the spleen, the
L. tropica parasite load was higher than the
L. major parasite load at mo 1 (
P ≤ 0.01) and mo 4 (
P ≤ 0.001) after the infection. However, the
L. major parasite load in the spleen became higher than the
L. tropica parasite load 6 mo after the infection (
P ≤ 0.01).
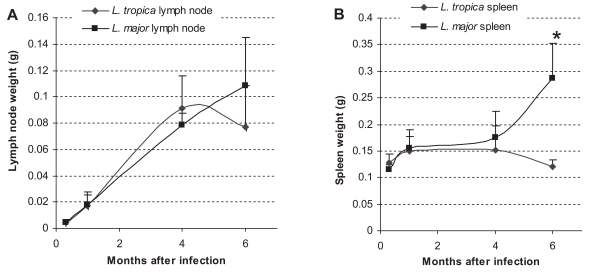
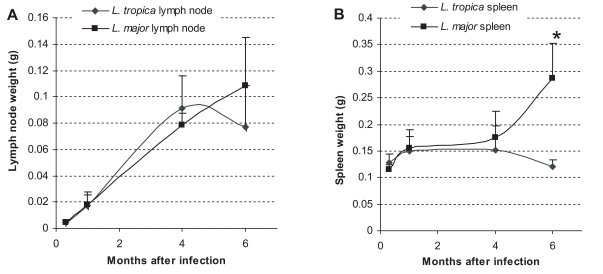
The spleen and lymph node weights in
L. major and
L. tropica-infected BALB/c mice are shown in
Fig 3. In
L. major-infected mice, the weight of the spleen and lymph node increased progressively throughout the experiment. The weight increase in
L. major-infected spleen was statistically significant at mo 1 (
P ≤ 0.01) and mo 6 (
P ≤ 0.005) after the infection. The weight increase of the
L. major-infected lymph node was statistically significant at mo 1(
P ≤ 0.004), mo 4 (
P ≤ 0.001), and mo 6 (
P ≤ 0.04) after the infection. The general trend of the increase was in accordance with the increase in parasite loads in the same organ at the corresponding time. In
L. tropica-infected mice, the weight of the spleen increased slightly until mo 1, and remained steady until mo 4, after then diminished. It was noteworthy that these slight differences were not statistically significant. The weight of the lymph node in
L. tropica-infected mice increased progressively and significantly between day 10 and mo 1 (
P ≤ 0.002), and from mo 1 to mo 4 (
P ≤ 0.001). The weight reduced slightly, but insignificantly by mo 6. Comparison of the spleen weights between
L. tropica and
L. major-infected mice showed that the spleen weight was significantly greater in
L. major-infected spleen in comparison to the
L. tropica-infected spleen at mo 6 PI. The weight of spleens at other intervals or the lymph node weights throughout the experiment were not statistically different between
L. tropica and
L. major-infected mice.
DISCUSSION
There are numerous examples of the tissue specific growth of
Leishmania parasites. Different growth rates of parasites in infected organs are a remarkable aspect of visceral leishmaniasis (
Wilson et al., 2005).
L. donovani promastigotes inoculated into the skin of hamsters multiply during the first week after the inoculation (
Wilson et al., 1987), and the cutaneous infection is eventually controlled locally. Despite these local responses, the organism is able to disseminate to visceral organs (
Wilson et al., 1987).
L. chagasi in mice multiply rapidly in the first 4 weeks in the liver, but they are cleared by week 8 PI. In contrast to the liver, parasites grow slowly in the spleen and bone marrow, where they can persist for life of the animal (
Engwerda and Kaye, 2000). There are localized immune responses in the liver and spleen of infected animals, which lead to an apparent "tropism" and unique patterns of localized growth or cure of parasite infection (
Wilson et al., 2005). Tissue specific activity of cytokines has been reported in BALB/c mice infected by
L. donovani (
Engwerda et al., 1998). It has been reported that the effect of antibodies on the host immune responses against
Leishmania pifanoi infection is selectively expressed at cutaneous sites of infection (
Colmenares et al., 2002).
The outcome of the disease in murine leishmaniasis can be influenced by many factors, including the parasite dose, route and site of inoculation, and developmental stage of the parasite. All these variables were carefully controlled for L. tropica and L. major in our experiment. The developmental stage of the parasite seems to be critical in this experimental model. The "stationary phase" was determined in our study by daily counting of the parasite, which is more accurate than the time course of parasite culture.
Leishmania tropica infection in BALB/c mice is not fatal and results in a chronic, non-healing, and non-ulcerating disease (
Lira et al., 1998). This outcome is in contrast to the outcome of
L. major infection in BALB/c mice, which results in progressive, non-healing, and destructive lesions (
Lira et al., 1998). Our data shows that
L. major infection in BALB/c mice results in an increase of footpad lesions (
Fig. 1), increase of parasite load in the footpad, lymph node, and spleen (
Fig. 2), and increase in the weight of lymph node and spleen (
Fig. 3). These data confirm that
L. major results in a destructive, progressive, and non-healing infection in BALB/c mice. On the other hand,
L. tropica infection in BALB/c mice results in a decrease in footpad lesions (
Fig. 1), decrease of parasite load in the footpad and spleen (
Fig. 2), non-increasing weight of the spleen throughout the course of infection, and non-increasing lymph node weight at the later phase of infection (
Fig. 3). These data clearly shows that
L. tropica results in a non-healing, non-fatal, and chronic infection in BALB/c mice. These findings are compatible with our previous report (
Mahmoudzadeh-Niknam, 2004) and another report (
Lira et al., 1998).
Our data shows that the L. tropica parasite load of footpads at mo 4 PI is significantly lower than the parasite load at mo 1 PI. This difference is suggestive of formation of more protective immune responses in footpads against L. tropica in later phases of infection. In contrast to L. tropica, no reduction of the parasite load of footpads is seen in L. major-infected BALB/c mice in the course of infection, showing no protective immune responses against L. major.
An important finding in our data is that L. tropica-infected BALB/c mice controls parasite growth at footpad tissues, while the parasite continues to grow in visceral organs. As far as we know, this kind of growth patterns is the first report in BALB/c mice for Leishmania species causing cutaneous infections. The logical conclusion from our data is that we should consider both the skin and visceral organs for evaluation of protection in this model of L. tropica infection and protection only at footpad level is not indicative of general protective immune responses in this model.
In order to study the tissue specific growth of
L. tropica in BALB/c mice, we determined parasite loads in the footpad, lymph node, and spleen at specified intervals after infection. Our results confirmed that
L. tropica, like
L. major, disseminate to the spleen and persist there for a long time. The growth of
L. tropica in the spleen is compatible with our previous suggestive data (
Mahmoudzadeh-Niknam, 2004), which showed that
L. tropica disseminated to the spleen of BALB/c mice at the time point of 4 mo after infection. The present data is the first definitive report for dissemination of
L. tropica to the spleen of BALB/c mice. Our data is not compatible with the other report (
Lira et al., 1998). In a study of Lira et al. (
1998), one million promastigotes from each growth phase (logarithmic-phase, stationary-phase, and metacyclic) of
L. tropica (the same strain used in our study) were inoculated subcutaneously into the footpad of BALB/c mice, and no dissemination to spleen were observed until 9 mo after infection. However, the reason for this discrepancy is not clear.
Viscerotropic leishmaniasis is a comparatively mild form of visceral
Leishmania infection caused by
L. tropica (
Hyams et al., 2001). Viscerotropic leishmaniasis patients have a visceral involvement with no cutaneous manifestations (
Hyams et al., 2001). There are several reports from various parts of the world suggesting that
L. tropica can cause visceral leishmaniasis (
Mebrahtu et al., 1989;
Sacks et al., 1995;
Guessous-Idrissi et al., 1997;
Mohebali et al., 2006;
Alborzi et al., 2006). Our data shows that
L. tropica infection visceralizes in BALB/c mice and survives more efficiently in visceral organs than in skin tissues. The visceralizing growth pattern of
L. tropica in BALB/c mice resembles the parasite growth patterns in human viscerotropic leishmanisis that are caused by the same
Leishmania species. The BALB/c model of
L. tropica infection may, therefore, prove to be an experimental model of these unusual cases of human visceral leishmaniasis caused by
L. tropica. This murine model can be useful for study of the disease pathophysiology as well as therapeutic and vaccine studies.
In summary, our data shows that L. tropica results in a non-healing, chronic, and non-destructive infection in BALB/c mice, which disseminates to the spleen. These features are suggestive of a useful experimental model for viscerotropic leishmaniasis in humans. More studies, including the testing of multiple isolates of L. tropica, are needed to elucidate the details of this interesting murine model of L. tropica infection.
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS
Kind advices from Dr. David Sacks (Laboratory of Parasitic Diseases, National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Disease, National Institute of Health, Bethesda, Maryland, USA) in the design and execution of the experiments are highly appreciated. Critical reading of the manuscript by Dr. David Sacks and Dr. Mary Wilson (University of Iowa, Iowa City, Iowa, USA) are also highly appreciated. We are thankful to Dr. M. H. Alimohammadian (Immunology Department of Pasteur Institute of Iran) for managerial supports.
References
Fig. 1Footpad thickness of L. tropica and L. major-infected BALB/c mice. Mice were infected with 106 parasites in the footpad. Asterisks (*) shows statistically significant differences (P ≤ 0.05) between the 2 groups.
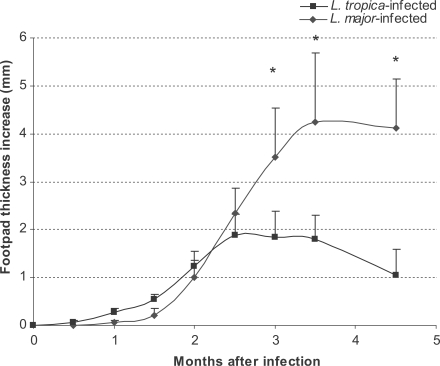
Fig. 2Parasite loads of L. tropica and L. major-infected BALB/c mice in (A) footpad, (B) lymph node, and (C) spleen at the indicated time points after infection with 106 parasites in the footpad. Asterisks (*) shows statistically significant differences (P ≤0.05) between L. tropica and L. major-infected tissues.
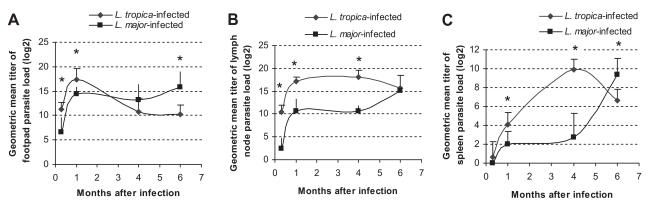
Fig. 3Weight of lymph node (A) and spleen (B) in L. tropica and L. major-infected BALB/c mice. Mice were infected with 106 parasites in the footpad. Asterisks (*) shows statistically significant differences (P ≤ 0.05) between L. tropica and L. major-infected tissues.