Abstract
Human diphyllobothriasis is a widespread fish-borne zoonosis caused by the infection with broad tapeworms belonging to the genus Diphyllobothrium. In mainland China, so far 20 human cases of Diphyllobothrium infections have been reported, and the etiologic species were identified as D. latum and D. nihonkaiense based on morphological characteristics or molecular analysis. In the present study, proglottids of diphyllobothriid tapeworms from 3 human cases that occurred in Heilongjiang Province, China were identified as D. nihonkaiense by sequencing mitochondrial cytochrome c oxidase subunit I (cox1) and NADH dehydrogenase subunit 5 (nad5) genes. Two different cox1 gene sequences were obtained. One sequence showed 100% homology with those from humans in Japan. The remaining cox1 gene sequence and 2 different nad5 gene sequences obtained were not described previously, and might reflect endemic genetic characterizations. D. nihonkaiense might also be a major causative species of human diphyllobothriasis in China. Meanwhile, the finding of the first pediatric case of D. nihonkaiense infection in China suggests that infants infected with D. nihonkaiense should not be ignored.
-
Key words: Diphyllobothrium nihonkaiense, molecular identification, human, cox1 gene, nad5 gene
INTRODUCTION
Human diphyllobothriasis is a widespread fish-borne zoonosis caused by the infection with broad tapeworms belonging to the genus
Diphyllobothrium. It has been estimated that 20 million people are affected globally [
1]. Humans as the most suitable definitive host become infected through eating raw or undercooked freshwater or marine fish harboring plerocercoid larvae, which develop into adult tapeworms in the small intestine after ingestion. In most of cases, patients may remain asymptomatic until expulsion of proglottids of the adult parasite in feces, while others can suffer from mild digestive troubles, such as abdominal pain, diarrhea, and abdominal discomfort. Occasionally,
Diphyllobothrium latum infection can cause malignant anemia due to the consumption of vitamin B12 by the tapeworm. Several outbreaks caused by
Diphyllobothrium had a significant impact on economy and public health [
2,
3].
The application of molecular methods based on the sequencing of mitochondrial and nuclear genes resulted in a better understanding of the genus
Diphyllobothrium. To date, about 18 species of
Diphyllobothrium have been reported to infect humans, with
D. latum and
Diphyllobothrium nihonkaiense being the most common [
4]. Human diphyllobothriasis has been reported in Europe [
3,
5-
7], North America [
8,
9], South America [
2,
10,
11], and Asia [
12-
15]. In mainland China, a total of 20 human cases have been documented since the first report in 1927 (
Table 1) [
14-
21]. All of them were initially identified as
D. latum infection based on morphological characteristics of the worm, with 3 out of them being confirmed molecularly [
14,
21]; however, 5 out of them have been re-verified as
D. nihonkaiense infection on the basis of molecular analysis recently [
15].
D. nihonkaiense is relatively common in humans in Japan, Korea, and Far Eastern Federal District of Russia [
7,
22-
24]. In addition, there have been case reports of human
D. nihonkaiense infection in France, Switzerland, Canada, New Zealand, and China [
6,
9,
15,
25-
27]. In the present study, to understand the situation of
Diphyllobothrium infection in Heilongjiang Province, China, we identified the proglottids of diphyllobothriid tapeworms from 3 human cases in Heilongjiang Province, China by sequencing mitochondrial cytochrome
c oxidase subunit I (
cox1) and NADH dehydrogenase subunit 5 (
nad5) genes.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Ethics statement
This research study was approved by the Medical Ethics Review Committee of Harbin Medical University, Harbin, China. Meanwhile, the Medical Ethics Review Committee of Harbin Medical University exempted the individual informed consent targeting molecular identification of the proglottids of tapeworms because the specimens were obtained after they were excreted in the feces.
Cases and proglottids collection
Between 2012 and 2014, total 3 strobilae (a chain of proglottids) of diphyllobothriid tapeworms were collected from 3 human cases that occurred in Heilongjiang Province, the northeastern part of China. The first patient was a 27-year-old woman residing in Harbin, who expelled some fragments of a flat white worm in the feces. She stated that she frequently consumed raw or undercooked fish, such as salmons, and had never traveled abroad. The second patient was a 39-year-old woman inhabiting Fuyuan, a county city near the Heilong River, who liked eating raw or undercooked salmons and had ever been to Russia. She passed some white living proglottids in the feces. The third patient was a 17-month-old girl born in Harbin. Her parents mentioned that they regularly ate raw fish dishes, such as salmons, and the girl was fed the delicious dishes once in a while. Her parents found some white flat segments in the girl’s feces. The whole family did not have histories of overseas travel. Macroscopic examination of the 3 proglottids showed that each segment was wider than long. Microscopic examination of the fecal samples of 3 patients showed the eggs that were yellowish in color and elliptical in shape, with a broad operculum at one end, and belonged to Diphyllobothrium spp. eggs. Several proglottids of each tapeworm were preserved in 70% ethanol at 4˚C until the DNA extraction.
DNA extraction and PCR amplification
Prior to DNA extraction, each proglottid specimen was washed 3 times with PBS to remove ethanol. The genomic DNA of
Diphyllobothrium was extracted from approximately 25 mg proglottid tissue of each tapeworm using a DNeasy blood and tissue kit (Qiagen, Hilden, Germany) according to the manufacturer-recommended procedures. The DNA was eluted in 200 µl of AE elution buffer and was stored at -20˚C until further use in PCR analysis. The mitochondrial
cox1 and
nad5 genes of
Diphyllobothrium were amplified using previously published primers, respectively [
14]. The reaction mixtures contained 2 µl DNA, 0.1 mM premixed solution of dNTP, 5 pmol of each primer, 2.5 µl PCR buffer (10×), 0.5 U of TaqDNA polymerase, and enough water for the final volume of 25 µl. Approximately 885 bp of the
cox1 gene and 1,028 bp of
nad5 gene were amplified, respectively, with the same cycle parameters as follows: an initial denaturation step at 94˚C for 3 min; 35 cycles at 94˚C for 1 min, 50˚C to 60˚C for 30 sec, and 72˚C for 1 min 30 sec; followed by a final extension step at 72˚C for 10 min [
28]. Each DNA preparation was analyzed at least 3 times by PCR at both
cox1 and
nad5 loci. All PCR amplifications were run with non-template water control. All amplicons were fractionated in 1.5% agarose gel electrophoresis and visualized under UV light after ethidium bromide staining.
All PCR products of 2 genes positive for
Diphyllobothrium were sequenced with the PCR primers at each locus after being purified on an ABI PRISM
TM 3730 DNA Analyzer (Applied Biosystems, Foster City, California, USA), using a Big Dye Terminator v 3.1 Cycle Sequencing kit (Applied Biosystems). Sequence accuracy was confirmed by 2-directional sequencing. Nucleotide sequences obtained in the present study were subjected to BLAST searches (
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/blast/) and then aligned and analyzed with each other.
Diphyllobothrium reference sequences were downloaded from Gen-Bank using the program Clustal X 1.83 (
http://www.clustal.org/). Two neighboring-joining trees were constructed at
cox1 and
nad5 loci, respectively, using the program Mega 5 (
http://www.megasoftware.net/) on the basis of the evolutionary distances calculated by Kimura-2-parameter model. The reliability of the 2 trees was assessed using the bootstrap analysis with 1,000 replicates.
RESULTS
All 3 proglottids were identified as D. nihonkaiense based on cox1 and nad5 genes. The representative nucleotide sequences obtained in the present study were deposited in the GenBank database under the following accession nos.: KP273585 and KP273586 (cox1), and KP273587 and KP273588 (nad5).
Two different
cox1 gene sequences were obtained from 3 proglottids of tapeworms. One sequence (KP273585) (n=2) showed 100% homology with those from humans in Japan (AB781787 and AB573405). The remaining one (KP273586) was novel and had 99.8% similarity with the reference sequence AB781787, with 2 base differences at nucleotide sites 540 (T to C) and 789 (T to C). However, both codons (CGC and CGT), and both codons (TGC and TGT) could be translated into the amino acids arginine (R) and cystine (C), respectively (
Table 1). Two
nad5 gene sequences obtained were not described previously and had 99.8% and 99.7% similarity with the complete genomic sequences of
Diphyllobothrium (AB268585 and EF420138), respectively, with 1 base difference between one another. One sequence (KP273587) (n=2) had 2 base differences at nucleotide sites 624 (C to T) and 816 (G to A), and the remaining one (KP273588) had 3 base differences at nucleotide sites 315 (A to G), 624 (C to T), and 816 (G to A) compared to the reference sequence AB268585; however, each both codons (TTA and TTG; TTC and TTT; TCG and TCA) could be translated into the amino acids leucine (L), phenylalanine (F) and serine (S), respectively (
Table 1).
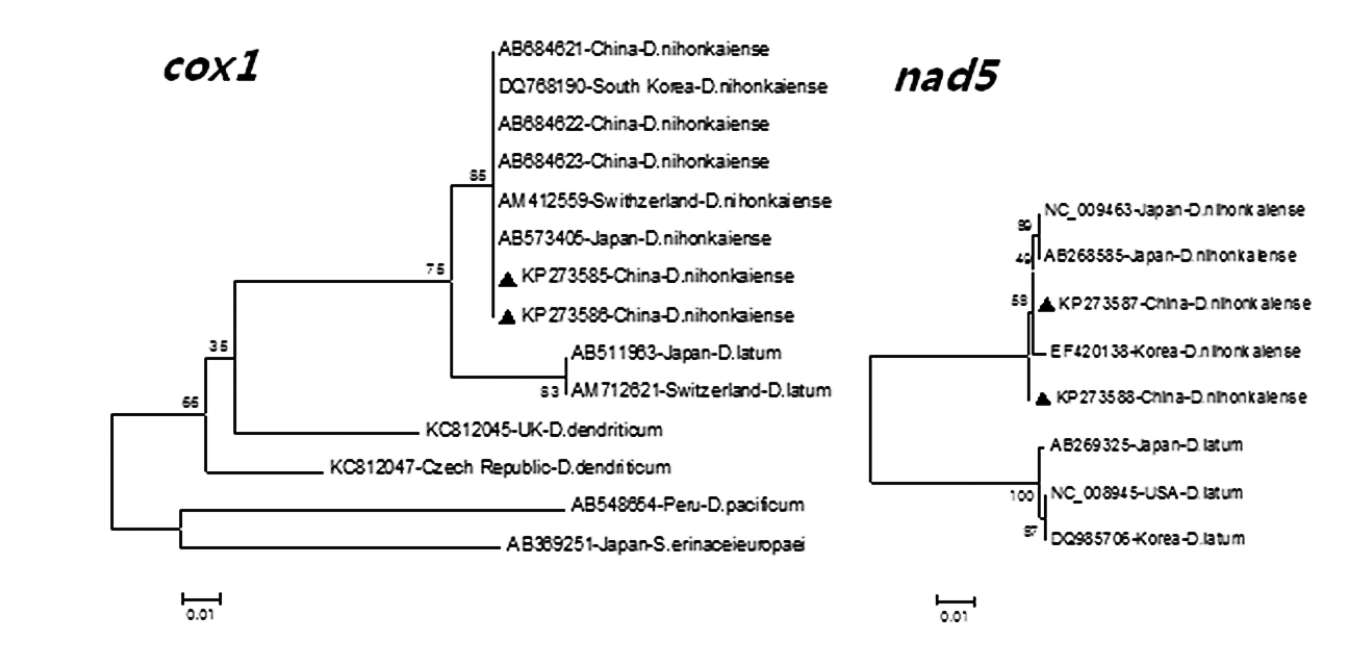
Phylogenetic analyses based on 2 neighbor-joining trees at
cox1 and
nad5 loci also showed that all 3 proglottids of tapeworms in the northeast of China (=Heilongjiang Province) were
D. nihonkaiense (
Fig. 1). By analysis of the
cox1 gene sequence (KP273586) with the previous sequence of
D. nihonkaiense (AB684621-AB684623) in Shanghai, a total of 10 polymorphic sites were shown; however, different codons at different variant sites could be translated into the same amino acids, respectively, except at nucleotide sites 373, which codon (ATC) and codon (GTC) could be translated into amino acids isoleucine and valine, respectively (
Table 2).
DISCUSSION
So far 20 human cases of
Diphyllobothrium infections have been reported in mainland China since 1927 (
Table 3) and the etiologic agents initially were identified as
D. latum based on morphological characteristics, with 3 out of them were confirmed molecularly. Recently, 5 out of these cases have been reconfirmed as
D. nihonkaiense infection by Chen et al. [
15] for the first time on the basis of molecular analysis, this inconformity was considered that
D. latum and
D. nihonkaiense were almost indistinguishable morphologically, and laboratory workers usually identified the
Diphyllobothrium species according to previously reported cases in the area.
In the present study, 3 tapeworm samples from human cases of Heilongjiang Province were identified as
D. nihonkaiense molecularly. The application of molecular markers based on species-specific suitable genes for accurately identifying
Diphyllobothrium species is helpful in accumulating the geographical and epidemiological information associated to this parasite. As mitochondrial DNA is known to be more powerful than nuclear DNA due to its rapid sequence evolution [
29], and the sequences of mitochondrial
cox1 and
nad5 genes of
Diphyllobothrium spp. were available in the GenBank database, we applied
cox1 and
nad5 genes to identify the 3 tapeworms.
This is the second report of human infection with
D. nihonkaiense in mainland China. In fact, for many years whenever eggs of
Diphyllobothrium spp. in fecal smears or proglottids were observed in this area, the identification was made invariably as “
D. latum”. However, 3
Diphyllobothrium isolates in our study, in combination with the previous 5 isolates re-identified, a total of 8
Diphyllobothrium isolates have been identified as
D. nihonkaiense molecularly in mainland China. Thus, it is strongly suggested that some previous diphyllobothriasis cases may have been misdiagnosed only based on morphological characteristics, and
D. nihonkaiense may be the major causative species of human diphyllobothriasis in China. Similar results have been reported in Korea. Most of the previous diphyllobothriasis cases were thought to be caused by
D. latum; however, they were re-confirmed as
D. nihonkaiense infections [
22,
30]. Thus, it is necessary to molecularly analyze for specific diagnoses of
D. nihonkaiense and
D. latum infection in humans.
D. nihonkaiense was first identified by Yamane et al. [
31] in Japan in 1986. The cestode is also common in humans in Japan, Korea, and the Russian Far East [
12,
22-
24]. Pacific salmons (
Oncorhynchus spp.), especially the chum salmon (
Oncorhynchus keta) and sockeye salmon (
Oncorhynchus nerka) serve as its second intermediate hosts [
7,
32,
33]. Plerocercoid larvae can be found in the musculature, liver, and gonads of these fish. A report showed that plerocercoid larvae of
D. nihonkaiense with infection rates as high as 51.1% (24/47) were found in immature chum salmon commonly referred to as
tokishirazu [
34]. However, never plerocercoid larvae have been found in freshwater or marine fish in China. It is better to detect plerocercoid larvae in fish to find and identify the
Diphyllobothrium species other than
D. latum and
D. nihonkaiense in China in the near future.
In the present study, since all 3 patients had the history of consumption of raw or undercooked salmons, it seems likely that the infection sources of D. nihonkaiense in the 3 patients might be salmons. However, it is difficult to identify the salmon species based on sashimi, sushi, and other salmon dishes. As the second patient had ever been to the Russian Far East, whether she became infected in China or Russia is unclear. It is surprising that the third patient was a 17-month-old girl. She is the first pediatric case of D. nihonkaiense infection in China, and is also the youngest patient infected with D. nihonkaiense based on molecular identification worldwide so far. It should not be ignored that infants can be infected with D. nihonkaiense.
In the present study, the
cox1 gene sequence (KP273586) was novel, with 2 base differences compared to the reference sequence AB781787; 2
nad5 gene sequences were not described previously, having 99.8% and 99.7% similarity with the complete genomic sequences of
Diphyllobothrium (AB268585 and EF420138), respectively (
Table 1). However, these base substitutions were synonymous mutations and did not affect the respective amino acid translations due to the degeneracy of amino acids. The
cox1 gene sequence and 2
nad5 gene sequences possibly reflected endemic genetic characterizations of
D. nihonkaiense in China.
The cases of human diphyllobothriasis may increase with increasing consumption of salmons and other fish, and growing popularity of raw fish dishes, such as sashimi and sushi, in Heilongjiang Province, even in China. It seems that the general public is not aware of the potential risk for diphyllobothriasis posed by consumption of raw or uncooked freshwater or marine fish. Thus, it is necessary for the general public, especially food handlers and consumers to provide some information about the risk associated with eating habits to prevent more people from being infected with diphyllobothriasis. Freezing fish at -20˚C for at least 24 hr, or -35˚C for 15 hr, or cooking fish at 55˚C or more for at least 5 min is sufficient to kill plerocercoid larvae of Diphyllobothrium spp. possibly present in fresh fish to prevent transmission of the parasites.
Notes
-
We have no conflict of interest related to this work.
This work was financially supported by the Heilongjiang Province Education Bureau (grant no. 12531346).
Fig. 1.Comparison of phylogenies of different species within Diphyllobothrium based on cox1 and nad5 gene sequences. Two phylogenetic trees were constructed using the neighbor-joining distance method analysis with a Kimura-2-parameter model. The reliability of 2 trees was assessed using the bootstrap analysis with 1,000 replicates. The triangles indicate the sequences of Diphyllobothrium from the present study.

Table 1.Differences in bases and amino acids at cox1 and nad5 loci of D. nihonkaiense
Table 1.
|
Gene |
Accession no./case |
Homology (%) |
Codon (amino acida)/Nucleotide positionb
|
|
cox1
|
AB781787 |
Ref. sequence |
CGT(R)/540 |
TGT(C)/789 |
|
|
KP273585/ case 1,2 |
100 |
CGT(R)/540 |
TGT(C)/789 |
|
|
KP273586/ case 3 |
99.8 |
CGC(R)/540 |
TGC(C)/789 |
|
|
nad5
|
AB268585 |
Ref. sequence |
TTA(L)/315 |
TTC(F)/624 |
TCG(S)/816 |
|
KP273587/ case 1,2 |
99.8 |
TTA(L)/315 |
TTT(F)/624 |
TCA(S)/816 |
|
KP273588/ case 3 |
99.7 |
TTG(L)/315 |
TTT(F)/624 |
TCA(S)/816 |
Table 2.Variations at polymorphic sites within cox1 gene sequences of D. nihonkaiense in China
Table 2.
|
GenBank accession no.a
|
Nucleotide at position
|
|
87 |
96 |
373b
|
480 |
504 |
540 |
600 |
642 |
717 |
789 |
|
KP273585 |
G |
C |
A |
A |
T |
T |
T |
A |
C |
T |
|
KP273586 |
G |
C |
A |
A |
T |
C |
T |
A |
C |
C |
|
AB684621 |
G |
T |
G |
A |
T |
T |
C |
C |
C |
T |
|
AB684622 |
G |
C |
A |
G |
T |
T |
T |
A |
T |
T |
|
AB684623 |
A |
C |
A |
A |
C |
T |
T |
A |
C |
T |
Table 3.Cases of human diphyllobothriasis in mainland China from 1927 to 2014
Table 3.
|
Place of residence |
No. of cases |
Suspected source of infection (no.) |
Morphological identification (no.)/Molecular identification (no.) |
Ref. |
|
Beijing |
2 |
Unknown (2) |
D. latum (2)/Untested (2) |
[16, 17] |
|
Fujian |
2 |
Plecoglossus altivelis (1) |
D. latum (2)/Untested (2) |
[18, 19] |
|
|
Raw salmon (1) |
|
|
|
Guangzhou |
1 |
Unknown (1) |
D. latum (1)/Untested (1) |
[17] |
|
Heilongjiang |
7a
|
Raw fish (2) |
D. latum (7)/D. latum (1), D. nihonkaiense (1), Untested (5) |
[14, 15, 17, 20] |
|
|
Raw salmon (1) |
|
|
|
|
Unknown (4) |
|
|
|
Jilin |
2 |
Raw fish (1) |
D. latum (2)/D. latum (1), Untested (1) |
[14, 17] |
|
|
Raw salmon (1) |
|
|
|
Shanghai |
6 |
Raw salmon (5) |
D. latum (6)/D. latum (1), D. nihonkaiense (4), Untested (1) |
[15, 17, 21] |
|
|
Unknown (1) |
|
|
References
- 1. Scholz T, Garcia HH, Kuchta R, Wicht B. Update on the human broad tapeworm (genus Diphyllobothrium), including clinical relevance. Clin Microbiol Rev 2009;22:146-160.
- 2. Sampaio JL, de Andrade VP, Lucas Mda C, Fung L, Gagliardi SM, Santos SR, Mendes CM, Eduardo MB, Dick T. Diphyllobothriasis, Brazil. Emerg Infect Dis 2005;11:1598-1600.
- 3. Jackson Y, Pastore R, Sudre P, Loutan L, Chappuis F. Diphyllobothrium latum outbreak from marinated raw perch, Lake Geneva, Switzerland. Emerg Infect Dis 2007;13:1957-1958.
- 4. Kim HJ, Eom KS, Seo M. Three cases of Diphyllobothrium nihonkaiense infection in Korea. Korean J Parasitol 2014;52:673-676.
- 5. Dupouy-Camet J, Peduzzi R. Current situation of human diphyllobothriasis in Europe. Euro Surveill 2004;9:31-35.
- 6. Yera H, Estran C, Delaunay P, Gari-Toussaint M, Dupouy-Camet J, Marty P. Putative Diphyllobothrium nihonkaiense acquired from a Pacific salmon (Oncorhynchus keta) eaten in France; genomic identification and case report. Parasitol Int 2006;55:45-49.
- 7. Chai JY, Darwin Murrell K, Lymbery AJ. Fish-borne parasitic zoonoses: status and issues. Int J Parasitol 2005;35:1233-1254.
- 8. Dick TA, Nelson PA, Choudhury A. Diphyllobothriasis: update on human cases, foci, patterns and sources of human infections and future considerations. Southeast Asian J Trop Med Public Health 2001;32:59-76.
- 9. Wicht B, Scholz T, Peduzzi R, Kuchta R. First record of human infection with the tapeworm Diphyllobothrium nihonkaiense in North America. Am J Trop Med Hyg 2008;78:235-238.
- 10. Mercado R, Yamasaki H, Kato M, Muñoz V, Sagua H, Torres P, Castillo D. Molecular identification of the Diphyllobothrium species causing diphyllobothriasis in Chilean patients. Parasitol Res 2010;106:995-1000.
- 11. Santos FL, de Faro LB. The first confirmed case of Diphyllobothrium latum in Brazil. Mem Inst Oswaldo Cruz 2005;100:585-586.
- 12. Yamane Y, Shiwaku K. Chapter III: Diphyllobothrium nihonkaiense and other marine-origin cestodes. In Otsuru M, Kamegai S, Hayashi S eds, rogress of Medical Parasitology in Japan, Vol. 8. Tokyo, Japan. Meguro Parasitological Museum; 2003, pp 245-249.
- 13. Park SH, Jeon HK, Kim JB. Four additional cases of Diphyllobothrium nihonkaiense infection confirmed by analysis of COX1 gene in Korea. Korean J Parasitol 2015;53:105-108.
- 14. Guo AJ, Liu K, Gong W, Luo XN, Yan HB, Zhao SB, Hu SN, Jia WZ. Molecular identification of Diphyllobothrium latum and a brief review of diphyllobothriosis in China. Acta Parasitol 2012;57:293-296.
- 15. Chen S, Ai L, Zhang Y, Chen J, Zhang W, Li Y, Muto M, Morishima Y, Sugiyama H, Xu X, Zhou X, Yamasaki H. Molecular detection of Diphyllobothrium nihonkaiense in humans, China. Emerg Infect Dis 2014;20:315-318.
- 16. Lin CS, Wu LT. Report of a preliminary health survey of Pinchiang (Chinese City of Harbin). Natl Med J Chin 1927;13:24-28. (in Chinese).
- 17. Wu GL. Human Parasitology. 4th ed. Beijing, China. People's Medical Publishing House; 2013.
- 18. Chen BJ, Li LS, Lin JX, Li YS, Li YR. A human case report of Diphyllobothrium latum infected by consumption of raw Plecoglossus altivelis. J Trop Dis Parasitol 2005;3:126. (in Chinese).
- 19. Li Y, Li L, Jiang D, Chen Y. A human case report of Diphyllobothrium latum due to eating raw salmon. Chin J Parasitol Parasit Dis 2013;31:494. (in Chinese).
- 20. Li Y, Wen JS, Shu J, Zhang WZ. A human case report of Diphyllobothrium latum infected in Heilongjiang Province. Chin J Parasitol Parasit Dis 2009;27:296. (in Chinese).
- 21. Li H, Chen SH, Zhang YN, Ai L, Chen JX. A human case report of Diphyllobothrium latum at Shanghai, China. J Anim Vet Adv 2012;11:3073-3075.
- 22. Jeon HK, Kim KH, Huh S, Chai JY, Min DY, Rim HJ, Eom KS. Morphologic and genetic identification of Diphyllobothrium nihonkaiense in Korea. Korean J Parasitol 2009;47:369-375.
- 23. Kim KH, Jeon HK, Kang S, Sultana T, Kim GJ, Eom K, Park JK. Characterization of the complete mitochondrial genome of Diphyllobothrium nihonkaiense (Diphyllobothriidae: Cestoda), and development of molecular markers for differentiating fish tapeworms. Mol Cells 2007;23:379-390.
- 24. Arizono N, Shedko M, Yamada M, Uchikawa R, Tegoshi T, Takeda K, Hashimoto K. Mitochondrial DNA divergence in populations of tapeworm Diphyllobothrium nihonkaiense and its phylogenetic relationship with Diphyllobothrium klebanovskii. Parasitol Int 2009;58:22-28.
- 25. Wicht B, de Marval F, Peduzzi R. Diphyllobothrium nihonkaiense (Yamane et al., 1986) in Switzerland: first molecular evidence and case reports. Parasitol Int 2007;56:195-199.
- 26. Shimizu H, Kawakatsu H, Shimizu T, Yamada M, Tegoshi T, Uchikawa R, Arizono N. Diphyllobothriasis nihonkaiense: possibly acquired in Switzerland from imported Pacific salmon. Intern Med 2008;47:1359-1362.
- 27. Yamasaki H, Kuramochi T. A case of Diphyllobothrium nihonkaiense infection possibly linked to salmon consumption in New Zealand. Parasitol Res 2009;105:583-586.
- 28. Park JK, Kim KH, Kang S, Jeon HK, Kim JH, Littlewood DT, Eom KS. Characterization of the mitochondrial genome of Diphyllobothrium latum (Cestoda: Pseudophyllidea) - implications for the phylogeny of eucestodes. Parasitology 2007;134:749-759.
- 29. Rostami Nejad M, Taghipour N, Nochi Z, Mojarad EN, Mohebbi SR, Harandi MF, Zali MR. Molecular identification of animal isolates of Echinococcus granulosus from Iran using four mitochondrial genes. J Helminthol 2012;86:485-492.
- 30. Choi S, Cho J, Jung BK, Kim DG, Jeon SJ, Jeon HK, Eom KS, Chai JY. Diphyllobothrium nihonkaiense: wide egg size variation in 32 molecularly confirmed adult specimens from Korea. Parasitol Res 2015;114:2129-2134.
- 31. Yamane Y, Kamo H, Bylund G, Wikgren BJ. Diphyllobothrium nihonkaiense sp. nov. (Cestoda: Diphyllobothriidae)–revised identification of Japanese broad tapeworm. Shimane J Med Sci 1986;10:29-48.
- 32. Yoshida M, Hasegawa H, Takaoka H, Miyata A. A case of Diphyllobothrium nihonkaiense infection successfully treated by oral administration of Gastrografin. Parasitol Int 1999;48:151-155.
- 33. Ando K, Ishikura K, Nakakugi T, Shimono Y, Tamai T, Sugawa M, Limviroj W, Chinzei Y. Five cases of Diphyllobothrium nihonkaiense infection with discovery of plerocercoids from an infective source, Oncorhynchus masou ishikawae. J Parasitol 2001;87:96-100.
- 34. Suzuki J, Murata R, Yanagawa Y, Araki J. Identification of Diphyllobothrium nihonkaiense by PCR-based approach. Clin Parasitol 2006;17:22-24. (in Japanese).