Abstract
Toxoplasma gondii atypical type II genotype was diagnosed in a pet peach-faced lovebird (Agapornis roseicollis) based on histopathology, immunohistochemistry, and multilocus DNA typing. The bird presented with severe neurological signs, and hematology was suggestive of chronic granulomatous disease. Gross post-mortem examination revealed cerebral hemorrhage, splenomegaly, hepatitis, and thickening of the right ventricular free wall. Histologic sections of the most significant lesions in the brain revealed intralesional protozoan organisms associated with malacia, spongiform changes, and a mild histiocytic response, indicative of diffuse, non-suppurative encephalitis. Immunohistochemistry confirmed the causative organisms to be T. gondii. DNA isolated from the brain was used to confirm the presence of T. gondii DNA. Multilocus genotyping based on SAG1, altSAG2, SAG3, BTUB, GRA6, c22-8, c29-2, L358, PK1, and Apico markers demonstrated the presence of ToxoDB PCR-RFLP genotype #3 and B1 gene as atypical T. gondii type II. The atypical type II strain has been previously documented in Australian wildlife, indicating an environmental transmission route.
-
Key words: Toxoplasma gondii, toxoplasmosis, peach-faced lovebird, encephalitis, genotyping
Toxoplasma gondii is a ubiquitous, cyst-forming, apicomplexan parasite renowned for its ability to infect all endothermic vertebrates, i.e., mammals and birds [
1]. Potentially all birds can become intermediate hosts for
T. gondii, as indicated by seroprevalence in over 38 species of wild birds across 8 avian orders [
1]. Subclinical and chronic infection is prevalent in many avian species; however, susceptibility to infection and disease varies across species [
1]. Reports of acute disease and death suggest that psittacines, passerines, columbiformes, and galliformes are most susceptible to clinical infection [
1,
2]. Reports of lethal toxoplasmosis in psittacines have been seen in native Australian and New Zealand parrots, captive psittacines in North and South America, a Swanson’s lorikeet (
Trichoglossus moluccanus), 2 budgerigars (
Melopsittacus undulatus) in Switzerland and the Netherlands, and experimentally infected budgerigars in the United States [
1-
6]. To our knowledge we report the first
T. gondii-associated lethal encephalitis in a pet peachfaced lovebird (
Agapornis roseicollis).
The susceptibility and severity of toxoplasmosis in individuals and among species varies, and insights into the population structure and unique genetic polymorphisms of
T. gondii strains may explain strain-specific disease states or increased biological potential for virulence [
7]. The current understanding of
T. gondii genetic diversity suggests that both clonal and recombinant (atypical or nonarchetypal) isolates of the lineages I, II, III, and the more recent, type 12, exist [
8,
9]. The types II, III, and 12 have been isolated from birds of prey species and a virulent type II from a black-winged lory (
Eos cyanogenia) in North America [
4,
9]. Atypical or nonarchetypal genotypes are typically reported from birds in South America and geographically isolated regions such as New Zealand and Australia [
10,
11]. Atypical type II isolates were described as the causative agent of mortality in native New Zealand bird species and a type I/III variant was isolated from a diseased Valley quail (
Callipepla californica) in Brazil [
6,
12]. In Australia, molecular genotyping studies have revealed the presence of atypical type II strains in marsupials and marine mammals, but there is no genetic data on
T. gondii isolates from birds [
11,
13-
15].
The aim of this study was to genetically characterize
T. gondii infection in a case of lethal toxoplasmosis in a pet peach-faced lovebird (
A. roseicollis) and describe the disease and microscopic lesions. A female peach-faced lovebird of unknown age was presented with ataxia to the Avian Reptile and Exotic Pet Hospital at the Camden Campus of the University of Sydney in August 2014. The lovebird was found free-flying outside and adopted by the owner 1 year prior to its presentation. During this time, it was confined to the house, and the owner did not have a cat. The bird did eat the owner’s food, but any meat eaten was thoroughly cooked. Observations during physical examination revealed feather destruction of the contour feathers over the sternum. The lovebird had a mild polycythemia (PCV 66%, normal range 20-57%), hyperproteinemia (estimated total protein 53 g/L, normal range 24-46 g/L), a leucocytosis (40,600 cells/µl, normal range 4,000-16,000 cells/µl), heterophilia (25,578 cells/µl, normal range 1,600-12,000 cells/µl), and a monocytosis (6,902 cells/µl, normal range less than 1,800 cells/µl) [
16]. Plasma uric acid was elevated (715 µmol/L, normal range 178-287 µmol/L) and there was a mild increase in creatinine phosphokinase (1411 U/L, normal range less than 400 U/L). Whole body radiographs were not diagnostic. The lovebird was treated with fluid therapy and azithromycin. A transient improvement was observed followed by a general deterioration in neurological signs. A week after the first presentation, the lovebird’s ataxia had worsened, it had intention tremors, and a head tilt. The bird was euthanized at the owner’s request.
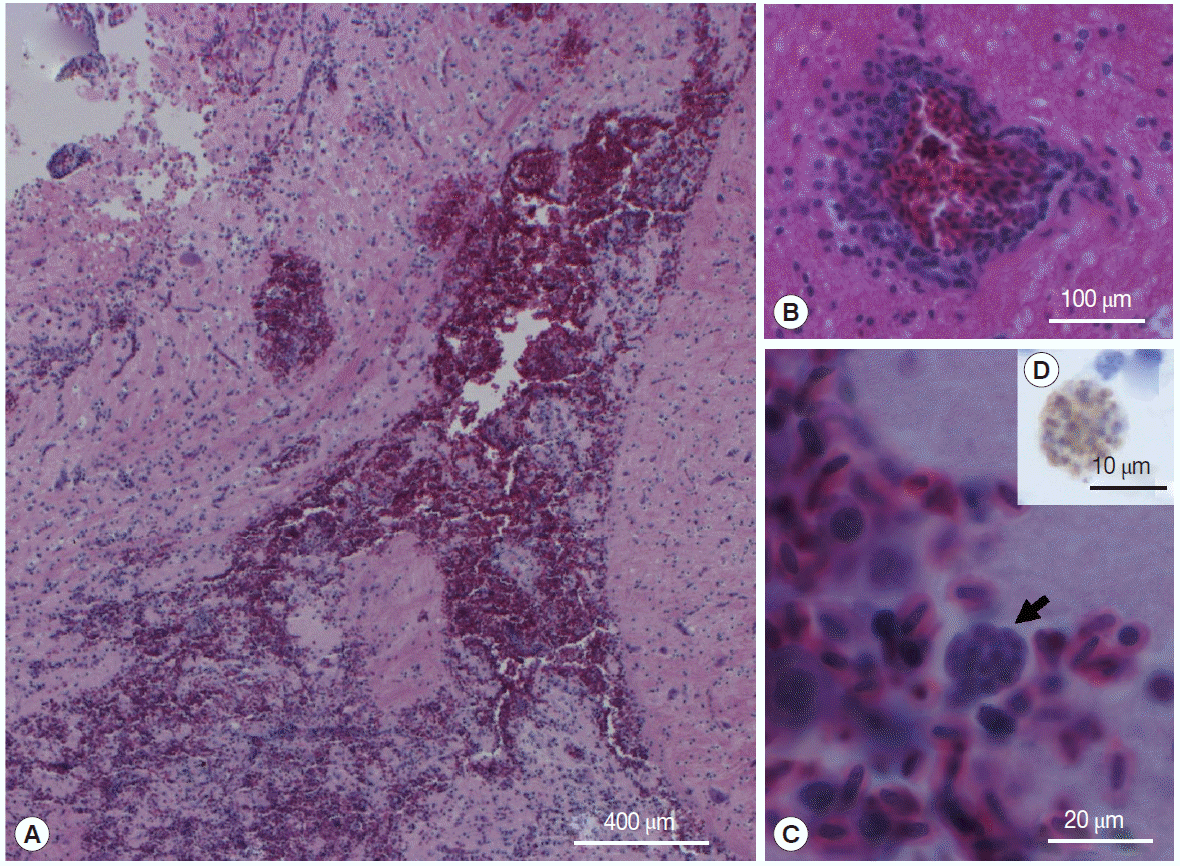
At necropsy, representative samples of the brain, spleen, liver, proventriculus, and heart tissue were processed for histological examinations using standard procedures. The most significant histopathological finding was diffuse, non-suppurative encephalitis. This was characterized by a focally extensive area of hemorrhage in the caudal cerebrum (
Fig. 1A), accompanied by malacia, lymphoplasmacytic cuffing (
Fig. 1B), spongiform changes in the white matter and gliosis, and a mild histiocytic response. Clusters of intracytoplasmic organisms were seen where the hemorrhage was most extensive (
Fig. 1C). The spleen was twice the normal size, with depletion of histiocytes and lymphocytes. The liver had a mild, multifocal periportal lymphoplasmacytic response, and many scattered hepatocytes had shrunken nuclei or were pyknotic. There was moderate to marked thickening of the proventricular lamina propria. The wall of the right atrium and right ventriculus was thickened and there was significant hypertrophy of the myofibres. Tachyzoites in the brain stained positive with anti-
T. gondii antibody (
Fig. 1D) and were negative with the negative control. Immunohistochemical staining was used to differentiate
T. gondii stages from other cyst-forming coccidia in the brain as previously described [
13].
Samples of the fresh brain were stored at -20˚C prior to DNA extraction. Genomic DNA was extracted from 25 mg of brain tissue using the Bioline Isolate II Genomic DNA kit (Bioline, Alexandria, New South Wales, Australia), and the phylogenetically informative portion of the D1/D2 domain of the large subunit rRNA gene (LSU) was PCR amplified and directly sequenced. The obtained LSU sequence (GenBank no. KT314077) unambiguously matched to
T. gondii LSU. To identify the genotype of
T. gondii, nested PCR amplification was applied to
T. gondii-specific genetic markers at B1,
SAG1,
alt-SAG2,
SAG3,
BTUB,
GRA6,
c22-8,
c29-2,
L358,
PK1, and
Apico loci [
17]. The sequenced loci revealed the presence of
T. gondii type II alleles, with the exception of B1 and
Apico (
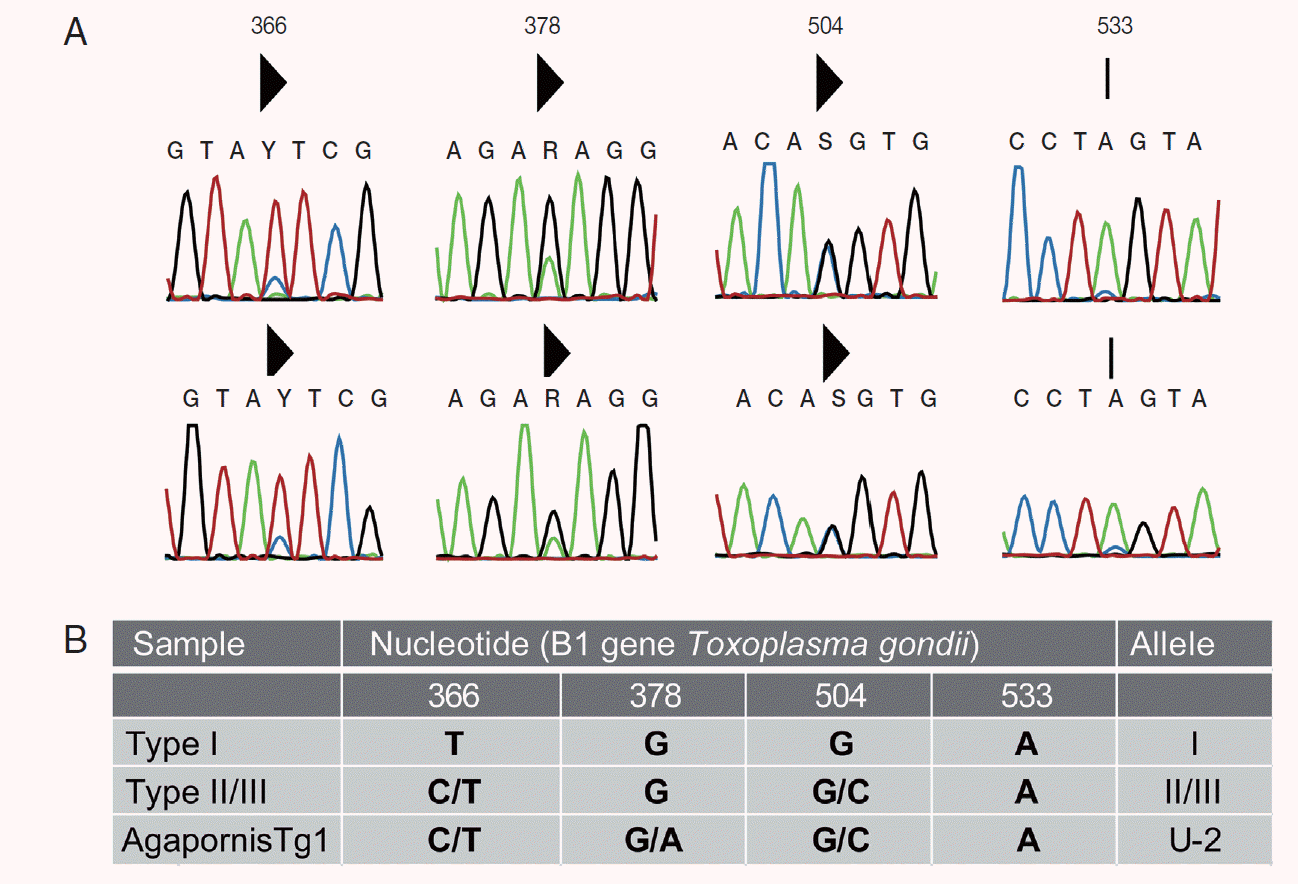
Table 1). Two nucleotide peaks were detected at 3 nucleotide positions (positions 366, 378, and 504) in the lovebird B1 sequence, when compared with the B1 reference sequence (
Fig. 2B). The guanine/adenine polymorphism at position 378 is not found in classical strain types I, II, and II, but has been described in other Australian mammals [
11,
13-
15]. Dinucleotide peaks at positions 366 and 504 are consistent with strain type II or III (
Fig. 2A). A SNP at position 178 in the
Apico locus corresponds with archetypical type I allele. The RFLP genotype of the peach-faced lovebird is ToxoDB #3 atypical type II (ToxoDB isolate ID: AgapornisTg1).
Presence of
Chlamydia spp. was ruled out by a TaqMan qPCR test targeting the 23S ribosomal DNA [
18], and DNA from the lovebird tested negative for the presence of
Psittacine beak and feather disease virus capsid DNA by PCR [
19].
Clinical signs associated with acute toxoplasmosis in passerines, columbiformes, and galliformes commonly include diarrhea, depression, and dyspnea, which are explained by the tissue distribution of
T. gondii cysts or tachyzoite-associated lesions in the enteric system, central nervous system, and lungs [
1,
20,
21]. In contrast, reports of clinical toxoplasmosis in psittacines more often describe nonspecific signs such as feather fluffing and reduced activity [
1-
3,
20,
21]. Histologically, toxoplasmosis in psittacines is reported to be most severe in the heart, lung, liver, and spleen, and is characterized by myocarditis, pneumonia, hepatic necrosis, and splenomegaly in association with disseminated tissue cysts [
20,
21]. The histological findings of this investigation are mostly consistent with those previously reported in psittacines. The exception in this case is the finding of diffuse, non-suppurative encephalitis, and signs of ataxia.
T. gondii-associated encephalitis has not been previously reported in a naturally infected psittacine, and documentation of toxoplasmosis in captive lovebirds does not exist, and therefore is not often considered a differential. Our findings show that toxoplasmosis should be considered in birds with neurologic signs. The post-mortem examination on this bird was incomplete so the presence or absence of lesions in the kidneys and lungs was not documented. However, the presence of a hypertrophy of the right ventricle could be consistent with increased resistance to outflow as the result of chronic pulmonary disease.
Hematological findings in birds with toxoplasmosis are not typically reported [
1-
4,
6,
9,
12,
20,
21]. The hematological findings in this study suggested that the lovebird was experiencing a chronic granulomatous disease, which was supported by histopathology of the brain lesions. These findings suggest that hematology may prove to be a useful tool for narrowing the differential diagnosis list for birds with toxoplasmosis. Important differential diagnoses for these types of hematological changes include
Chlamydia psittaci infections, mycobacteriosis, and systemic fungal infections [
22]. The latter 2 can cause encephalitis or, in fungal infections, brain infarcts, although these lesions are uncommon.
C. psittaci infection was ruled out by PCR assay. Determining the nature of the brain lesion antemortem would have required advanced imaging techniques. Hyperuricemia was most likely secondary to dehydration, since the owner noted that the bird had difficulty in drinking due to ataxia.
Perhaps one of the most common causes of immune suppression in parrots is infection with the psittacine beak and feather disease virus and infection in lovebirds is common [
23]. This bird was negative for this virus; however, it is not known if other factors might have been impacting its immune function.
The recent expansion in the use of DNA sequencing for molecular genotyping has enabled the identification of unique polymorphisms and genetic diversity of
T. gondii isolates, particularly in wildlife [
17]. Molecular genotyping has increased the knowledge of
T. gondii strain types in Australian marsupials and marine mammals, which give clues to the epidemiology of
T. gondii in wildlife [
11,
14,
15]. Our finding of an atypical type II strain (ToxoDB RFLP genotype #3) in a pet peach-faced lovebird has also been previously identified in a free-ranging common wombat (
Vombatus ursinus) in Australia, suggesting that exposure to resistant
T. gondii oocysts in the environment is a likely transmission route [
11]. The same atypical type II strain has also been reported in pet Eurasian siskins (
Spinus spinus) and Oriental skylarks (
Alauda gulgula) in China, which are bred in semi-free range systems and share the same environment with people in urban areas [
24].
While it is highly unlikely that direct transmission of
T. gondii from a pet bird to humans could occur, due to the confinement of oocysts to the gastrointestinal tract and tissue cysts to internal organs, pet birds may be indicators of the risk of environmental transmission to any intermediate host [
24]. Infection in this case is presumably as a consequence of
T. gondii oocyst ingestion. Felids are the definitive host for
T. gondii, and the risk of oocyst contamination in waterways or soil is increased in urban areas with high cat populations [
1]. As the owner did not have a cat, the direct route of exposure is not known. However, it is most likely that the infection was a result of ingestion of oocyst-contaminated food or water.
Notes
-
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest related to this work.
The study was supported by the Faculty of Veterinary Science, University of Sydney, Australia through an internal support and DVC-R compact support for the Honours project of M. Cooper. S. Donahoe is supported by the International Postgraduate Research Scholarship (IPRS) and an Australian Postgraduate Award (APA) tenable at The University of Sydney. We thank the Veterinary Pathology Diagnostic Services, The University of Sydney, for performing Chlamydia spp. test.
Fig. 1.Peach-faced lovebird (Agapornis roseicollis) brain lesion with extensive hemorrhage (A), lymphoplasmacytic cuffing (B), and intralesional cysts (arrow) (C); H&E stain. Inset (D) is anti-T. gondii antibody positive bradyzoites in the lovebird brain; IHC stain.

Fig. 2.Bidirectional B1 sequence chromatographs showing the single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) (A). Solid triangle above the sequence indicates a double peak. Sequence residues Y=C/T, R=G/A, and S=G/C. A SNP at nucleotide position 533 that has been previously identified in Australian wildlife was not called by CLC Main Workbench in isolate AgapornisTg1. (B) Summary of polymorphisms in the B1 gene compared to type I and II/III reference strains. “U” indicates a nonarchtypal allele; I, II, or III refers to the archetypal allele from the type I, II, or III strain. B1 PCR was run using MyTaq Red Mix (Bioline, Australia). Amplification products were bidirectionally sequenced (Macrogen Inc., Seoul, South Korea), assembled using CLC Main Workbench v 6.9 including “secondary peak calling” tool set to cut off of 0.2 (QIAGEN, CLC Bio, Aarhus, Denmark).

Table 1.Genotyping results determined by bidirectional sequencing of the 11 DNA markers, followed by virtual RFLP (NEBcutter, New England Biolabs Inc.) and comparison to type I (GT1), type II (ME49), and type III (CTG) reference sequences from ToxoDB (
http://toxodb.org/toxo/)
Table 1.
|
Genotype/Isolate ID |
B1 |
SAG1 |
alt- SAG2 |
SAG3 |
BTUB |
GRA6 |
C22-8 |
C29-2 |
L358 |
PK1 |
Apico |
|
Type I (ToxoDB #10)*/GT1 |
I |
I |
I |
I |
I |
I |
I |
I |
I |
I |
I |
|
Type II (ToxoDB #1)*/ME49 |
II or III |
II or III |
II |
II |
II |
II |
II |
II |
II |
II |
II |
|
Type III (ToxoDB #2)*/VEG |
II or III |
II or III |
III |
III |
III |
III |
III |
III |
III |
III |
III |
|
Atypical type II (ToxoDB #3)/AgapornisTg1 |
U-2a
|
II or III |
II |
II |
II |
II |
II |
II |
II |
II |
I |
References
- 1. Dubey JP. A review of toxoplasmosis in wild birds. Vet Parasitol 2002;106:121-153.
- 2. Hartley J, Booth R, Slocombe RF, Dubey JP. Lethal toxoplasmosis in an aviary of kakarikis (Cyanoramphus spp.) in Australia. J Parasitol 2008;94:1424-1425.
- 3. Donatti RV, Marques MV, Ecco R, Preis IS, Shivaprasad HL, Vilela DA, Martins NR. Fatal toxoplasmosis in a vinaceous Amazon parrot (Amazona vinacea). Avian Dis 2012;56:774-777.
- 4. Dubey JP, Parnell PG, Sreekumar C, Vianna MCB, Young RWD, Dahl E, Lehmann T. Biologic and molecular characteristics of Toxoplasma gondii isolates from striped skunk (Mephitis mephitis), Canada goose (Branta canadensis), black-winged Lory (Eos cyanogenia), and cats (Felis catus). J Parasitol 2004;90:1171-1174.
- 5. Kajerová V, Literák I, Bártová E, Sedlák K. Experimental infection of budgerigars (Melopsittacus undulatus) with a low virulent K21 strain of Toxoplasma gondii. Vet Parasitol 2003;116:297-304.
- 6. Howe L, Hunter S, Burrows E, Roe W. Four cases of fatal toxoplasmosis in three species of endemic New Zealand birds. Avian Dis 2014;58:171-175.
- 7. Grigg ME, Bonnefoy S, Hehl AB, Suzuki Y, Boothroyd JC. Success and virulence in Toxoplasma as the result of sexual recombination between two distinct ancestries. Science 2001;294:161-165.
- 8. Sibley LD, Khan A, Ajioka JW, Rosenthal BM. Genetic diversity of Toxoplasma gondii in animals and humans. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci 2009;364:2749-2761.
- 9. Dubey JP, Velmurugan GV, Rajendran C, Yabsley MJ, Thomas NJ, Beckmen KB, Sinnett D, Ruid D, Hart J, Fair PA, McFee WE, Shearn-Bochsler V, Kwok OC, Ferreira LR, Choudhary S, Faria EB, Zhou H, Felix TA, Su C. Genetic characterisation of Toxoplasma gondii in wildlife from North America revealed widespread and high prevalence of the fourth clonal type. Int J Parasitol 2011;41:1139-1147.
- 10. Dardé ML. Toxoplasma gondii, "new" genotypes and virulence. Parasite 2008;15:366-371.
- 11. Donahoe SL, Slapeta J, Knowles G, Obendorf D, Peck S, Phalen DN. Clinical and pathological features of toxoplasmosis in freeranging common wombats (Vombatus ursinus) with multilocus genotyping of Toxoplasma gondii type II-like strains. Parasitol Int 2015;64:148-153.
- 12. Casagrande RA, Pena HF, Cabral AD, Rolim VM, de Oliveira LG, Boabaid FM, Wouters AT, Wouters F, Cruz CE, Driemeier D. Fatal systemic toxoplasmosis in Valley quail (Callipepla californica). Int J Parasitol Parasites Wildl 2015;4:264-267.
- 13. Donahoe SL, Rose K, Slapeta J. Multisystemic toxoplasmosis associated with a type II-like Toxoplasma gondii strain in a New Zealand fur seal (Arctocephalus forsteri) from New South Wales, Australia. Vet Parasitol 2014;205:347-353.
- 14. Pan S, Thompson RCA, Grigg ME, Sundar N, Smith A, Lymbery AJ. Western Australian marsupials are multiply infected with genetically diverse strains of Toxoplasma gondii. PLoS One 2012;7:e45147.
- 15. Parameswaran N, Thompson RCA, Sundar N, Pan S, Johnson M, Smith NC, Grigg ME. Nonarchetypal Type II-like and atypical strains of Toxoplasma gondii infecting marsupials of Australia. Int J Parasitol 2010;40:635-640.
- 16. Fudge AM. Laboratory reference ranges for selected avian, mammalian, and reptilian species. In Fudge AM ed, Laboratory Medicine: Avian and Exotic Pets. Philadelphia, Pennsylvania, USA. WB Saunders; 2000, pp 375-400.
- 17. Su C, Shwab EK, Zhou P, Zhu XQ, Dubey JP. Moving towards an integrated approach to molecular detection and identification of Toxoplasma gondii. Parasitology 2010;137:1-11.
- 18. Ehricht R, Slickers P, Goellner S, Hotzel H, Sachse K. Optimized DNA microarray assay allows detection and genotyping of single PCR-amplifiable target copies. Mol Cell Probes 2006;20:60-63.
- 19. Heath L, Martin DP, Warburton L, Perrin M, Horsfield W, Kingsley C, Rybicki EP, Williamson AL. Evidence of unique genotypes of beak and feather disease virus in southern Africa. J Virol 2004;78:9277-9284.
- 20. Hartley WJ, Dubey JP. Fatal toxoplasmosis in some native Australian birds. J Vet Diagn Invest 1991;3:167-169.
- 21. Howerth EW, Rich G, Dubey JP, Yogasundram K. Fatal toxoplasmosis in a red lory (Eos bornea). Avian Dis 1991;35:642-646.
- 22. Campbell TM, Ellis DK. Avian and Exotic Animal Haematology and Cytology. 3rd ed. Ames, Iowa, USA. Blackwell Publishing; 2007, pp 3-50.
- 23. Phalen DN. Implications of viruses in clinical disorders. In Harrison GJ, Lightfoot T eds, Clinical Avian Medicine. 2. Palm Beach. Florida, USA. Spix Publishing Inc; 2006, pp 573-586.
- 24. Cong W, Meng QF, Song HQ, Zhou DH, Huang SY, Qian AD, Su C, Zhu XQ. Seroprevalence and genetic characterization of Toxoplasma gondii in three species of pet birds in China. Parasit Vectors 2014;7:152.