Abstract
Laboratory workers, in resource-poor countries, still consider PCR detection of Giardia lamblia more costly and more time-consuming than the classical parasitological techniques. Based on 2 published primers, an in-house one-round touchdown PCR-RFLP assay was developed. The assay was validated with an internal amplification control included in reactions. Performance of the assay was assessed with DNA samples of various purities, 91 control fecal samples with various parasite load, and 472 samples of unknown results. Two cysts per reaction were enough for PCR detection by the assay with exhibited specificity (Sp) and sensitivity (Se) of 100% and 93%, respectively. Taking a published small subunit rRNA reference PCR test results (6%; 29/472) as a nominated gold standard, G. lamblia was identified in 5.9% (28/472), 5.2%, (25/472), and 3.6% (17/472) by PCR assay, RIDA® Quick Giardia antigen detection test (R-Biopharm, Darmstadt, Germany), and iodine-stained smear microscopy, respectively. The percent agreements (kappa values) of 99.7% (0.745), 98.9% (0.900), and 97.7% (0.981) were exhibited between the assay results and that of the reference PCR, immunoassay, and microscopy, respectively. Restriction digestion of the 28 Giardia-positive samples revealed genotype A pattern in 12 and genotype B profile in 16 samples. The PCR assay with the described format and exhibited performance has a great potential to be adopted in basic clinical laboratories as a detection tool for G. lamblia especially in asymptomatic infections. This potential is increased more in particular situations where identification of the parasite genotype represents a major requirement as in epidemiological studies and infection outbreaks.
-
Key words: Giardia lamblia, PCR-RFLP, genotype, asymptomatic human infection
INTRODUCTION
Giardia is a unicellular parasite that infects a wide range of vertebrate hosts, including humans [
1]. Six species have been identified for this intestinal parasite. To date,
Giardia lamblia (syn.
G. duodenalis or
G. intestinalis) is the only species associated with human infections [
2]. Infection is usually transmitted through ingestion of infective cysts, the environmental stage [
1]. Infection occurs worldwide, but mostly affects populations in the developing countries [
3]. Infection is commonly asymptomatic but mild to moderate self-limiting diarrhea occurs in some cases [
3]. In other cases, diarrhea may be severe, prolonged, and even threatening to life [
2,
3]. According to a recent study,
G. lamblia has 7 genotypes, frequently referred to as assemblages, named alphabetically from A to G [
4]. Although assemblage E has been isolated recently from human feces [
5], most of infections occurring in humans have been attributed to genotypes A and B [
4,
6]. Due to the great genetic diversity between the 2 genotypes, assemblages A and B have been considered by a number of investigators as 2 distinct species [
7].
The diagnosis of
Giardia infection relies entirely on laboratory diagnosis. Examination of feces with classical wet mount microscopy is frequently employed as a rapid, cheap, and simple method [
8,
9]. However, microscopy offers a low sensitivity and depends to a great extent on the skill of the person who is carrying out the test. Several antigen detec tion kits, frequently recognized as “coproantigen” kits are commercially available cost-effective diagnostic methods, alternative to microscopy [
9,
10]. However, these kits have reported lower specificity and sensitivity than that obtained with the PCR-based detection tools. PCR is a more important method not only for epidemiological studies, but also as a diagnostic tool for low-density
Giardia infections [
11].
Despite several PCR-based diagnostic assays which have been described [
12-
17], the implementation of the majority of these assays into microbiology laboratories, particularly in resource-poor countries, is still challenging. This may be related to a number of reasons. First, the majority of these assays rely on multi-step procedures for
Giardia DNA extraction and subsequent PCR amplification. Second, most of the assays lack standardization and proper clinical evaluations. Finally, for poor countries where
Giardia infection predominates, PCR is still considered an expensive technique in comparison to the conventional diagnostic methods.
In this study, we aimed to develop a simple, internally-controlled, and cost-effective PCR-RFLP assay for detection and characterization of G. lamblia clinical isolates in human feces. The assay performance was investigated in comparison to microscopy and a rapid immunoassay with fecal samples collected from asymptomatic Giardia human infections. The agreements between PCR assay results and that of the rapid immunoassay, microscopy, and the reference PCR were also investigated.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Giardia strains
The WB-assemblage A (ATCC
® 50803) and GS-assemblage B strains (ATCC
® 50581) were purchased from the American Type Culture Collection (Rockville, Maryland, USA) and grown in the laboratory using a modified TYI-S-33 medium as described previously [
18].
A total of 563 fecal specimens were collected from those submitted to the Microbiology Department at 2 public hospitals at Taif region, Western Saudi Arabia, for routine parasitological examinations. The initial 91 samples were subjected to parasitological examinations with composite gold standard tests comprising of iodine-stained microscopy method [
9], RIDA
® Quick
Giardia rapid kit (R-Biopharm, Darmstadt, Germany), and small subunit (SSU) rRNA PCR [
19]. According to the test results, 4 groups of control samples were prepared and used while estimating the diagnostic performance of the assay. Group-1 included 15 samples diagnosed as
Giardia-positive by the 3 methods. Group-2 involved 22 samples described as
Giardia-negative with microscopy but were positive for
Giardia coproantigen and DNA. Group-3 contained 9 samples that were
Giardia-negative by microscopy and rapid immunoassay but were
Giardia DNA-positive with the reference PCR. Lastly, group-4 comprised of 45
Giardia-negative samples with 3 individual assays. Microscopic examination of these
Giardia-negative samples revealed
Entamoeba histolytica/dispar, Dientamoeba fragilis, Blastocystis hominis, and
Hymenolepis nana in 7, 3, 4, and 2 samples, respectively.
Subsequently, the remaining 472 samples were used to validate the diagnostic PCR assay. Fresh specimens were examined by the routine wet mount microscopy followed by the rapid immunoassay test within 2-3 days after collection. The remainder of each specimen was adequately labeled and kept without any preservative at -20˚C till PCR examination.
DNA extraction protocol
Nucleic acid was directly extracted from whole fecal samples, cultured
Giardia trophozoites,
Giardia cysts-spiked feces, or purified
Giardia cysts suspension using the QIAamp
® Stool Mini Kit (Qiagen, Valencia, California, USA) following an amended kit’s protocol [
20]. Briefly, extraction was performed using 200 µl of feces and eluted into 50 µl of the elution buffer. The lysis temperature was raised to the boiling point for 10 min, and the incubation time of the InhibitEX tablet was extended to 5 min. Also, a pre-cooled ethanol was used for nucleic acid precipitation.
Approximately 455 bp of
Giardia glutamate dehydrogenase gene (
gdh) sequence was amplified using 2 previously described specific primers; GDHeF and GDHiR [
21]. Amlifications were carried out in 96-well Techne
TM TC-4000 thermal cycler (Techne, Cambridge, UK). Following optimization experiments, reactions were set up with 10 pmol of each primer, 1 µl of DNA extract, 1X Go Taq
® green buffer, 0.2 mM of each dNTP (Bioline, London, UK), 1.5 mM MgCl2, 1% DMSO, and 1 U of GoTaq
® HotStart (Promega, Madison, Wisconsin, USA) as final concentrations.
Reaction of 20 µl volumes were prepared and run with a touchdown PCR protocol as follows: Initial denaturation was set up at 94˚C for 4 min, followed by 10 cycles of the touchdown stage with denaturation at 94˚C for 30 sec and annealing temperature at 67˚C for 30 sec. Then, the annealing temperature was decreased to 57˚C by 1˚C per cycle for the first 10 cycles. Extension temperature used was 72˚C for 30 sec and the subsequent 30 cycles were as follows; denaturation at 94˚C for 30 sec, annealing at 57˚C for 30 sec, and extension at 72˚C for 30 sec. A final extension step at 72˚C for 7-10 min was included.
PCR products were analyzed on ethidium bromide-stained 1-2% agarose gels (Sigma, Dorset, UK) in an in-house electrophoresis tank. Gels were viewed by UV illumination and photographed using a gel documentation system (Kodak, Rochester, New York, USA). The GeneRulerTM 100 bp DNA molecular weight marker (Fermentas, York, UK) was used as the size standard in gel electrophoresis.
Construction of PCR amplification controls
PCR reaction was set up with 1 µl of DNA extract of cultured WB strain. The PCR product (i.e., amplicon) was gel-purified with YORBIO Gel/PCR DNA Purification Kit (Yorkshire Bioscience, York, UK) and subsequently cloned into pCR
®4-TOPO vector (Invitrogen, Paisley, UK) following the standard procedures [
22]. The plasmid was then propagated in
Escherichia coli (Top10) and subsequently purified with the Wizard Plus Miniprep isolation kit (Promega, Leiden, Netherlands) prior to sending for bidirectional sequencing (Eurofins MWG, Germany). Stocks of the plasmid construct were prepared for subsequent PCR reactions as an external control (EC).
Based on the retrieved EC sequence, an internal control (IC) of ≈ 300 bp was constructed through deleting ≈ 155 bp between the flanking primer sequences using the same approach that we have practiced in an earlier study [
23]. Briefly, a forward primer (AGA AGC TTC TCA CAG GCA AGA ACG TCA A) and a reverse primer (ATA AGC TTA TGA CCT CGT TGT CGG ACT T) were manually-designed with
HindIII restriction enzyme recognition sequence plus 2 additional nucleotides incorporated at the 5´ terminus of each. An inverse PCR was set up and as a result, an amplicon of ≈ 4.2 kb was produced. The amplicon was gel purified, subjected to restriction diggestion, and religated on itself forming plasmid with the new construct. Plasmid was propagated in
E. coli (DH5α), and stocks of DNA was prepared as described above.
Serial dilutions of EC plasmid DNA (1 ng-0.05 fg/µl) were prepared, subjected to PCR amplifications, and the lowest concentration with amplicon on gel was defined as the lower detection limit (LDL). Ten-fold serial dilutions of IC plasmid DNA (1 ng-0.1 fg/µl) were prepared and co-amplified with the EC plasmid DNA with concentration equal to the LDL, in 1 tube as a duplex PCR. The lowest dilution, consistently detectable with the primary PCR target on gel, was defined as the optimum concentration of IC.
Cyst purification, counting, and seeding experiment
Three
G. lamblia cyst-positive fecal samples were pooled, concentrated, and purified initially with modified formol-ether concentration [
9] and then by the sucrose density-gradient centrifugation techniques as previously described [
24]. Cysts were counted under the microscope with a modified Fuchs-Rosenthal counting chamber (Hausser Scientific, Horsham, Pennsylvania, USA) following the manufacturer’s protocol. Suspensions of PBS, 1 ml each, with ≈ 10
6 of
Giardia cysts were prepared, labelled, and stored at -20˚C till usage.
Decimal serial dilutions of 106 cysts-spiked 200 μl-aliquot of Giardia-free fecal material were prepared and subjected to DNA extraction. The retrieve DNA extracts were amplified, and the lowest dilution that showed product on the gel was defined as the LDL.
Restriction digestion
Amplification products of 28
Giardia-positive samples, including samples with discordant results with microscopy and the immunoassay were gel-purified. In 20 µl volume reactions, ≈ 1 µg of the purified DNA was subjected to restriction digestion with 2U
Nla IV (Roche, Burgess Hill, UK) in the presence of 1×reaction buffer. Digestion was carried out at 37˚C for 1-3 hr. Restriction digest profiles were analyzed on 2% high resolution grade agarose (Fisher Biotech, Loughborough, UK) stained with ethidium bromide and analyzed according to the restriction patterns described elswhere [
21].
This research was carried out following an approval gained from the Local Directorate of Health and from the ethics committee of Taif University, Saudi Arabia. Permissions were also taken from patients attending hospitals to use their biological materials during the specified research period.
Statistical analysis
Data were collected and statistically analyzed with SPSS 17.0 software (SPSS Inc., Chicago, Illinois, USA). The diagnostic sensitivity (Se), specificity (Sp), positive predictive value (PPV), and negative predictive value (NPV) were assessed using chi-square tests against the combined gold standard test results. The agreement of the diagnostic assay results with the other tests was done with Kappa statistics (κ). Confidence intervals (CI) of proportions (95%) were calculated based on binomial distribution. The
gdh copy number per 1 nanogram of plasmid DNA was calculated following a previously described equation [
25].
RESULTS
Constructed plasmids
Two recombinant plasmids were constructed in the current study.
Table 1 shows a number of important features for the 2 plasmids. The lowest concentration of the EC plasmid DNA that was successfully amplified and detected on gel, as a sole target of amplification, was 0.5 fg which corresponds to ≈ 100 copies of the
gdh target gene locus. The estimated optimal concentration of IC DNA was 0.9-3.6 fg per reaction (
Fig. 1). Stocks with the described concentrations were prepared, aliquoted, carefully labeled, and used as an EC and IC for the PCR assay in the subsequent amplification reactions.
Three estimates of LDL of the assay were described according to the type and purification degree of the template DNA. The assay detected a minimum of 0.5 fg of EC plasmid DNA, corresponding to ≈ 100 copies of the
gdh gene (
Fig. 2A). Moreover, concentration of ≈ 2 pg of genomic DNA (WB and GS strains) was the LDL, which matched to ≈ 12 copies of the
Giardia genome (
Fig. 2B). Lastly,
Giardia DNA was successfully extracted and subsequently amplified from all spiked samples down to ≈ 100 cysts per extract (200 μl), corresponding to ≈ 2 cysts per PCR reaction (
Fig. 2C).
The assay successfully amplified DNA sequences from all
Giardia-positive control stool samples except 3 samples which belonged to group-3. Running an additional PCR round with 1 µl of the PCR product as a template, the primary target DNA was identified in these 3 samples. Importantly, no amplification was detected for
G. lamblia specific DNA in any of the
Giardia-negative control samples (n=45). Equally important, the IC target DNA was successfully amplified in all samples (
Fig. 3). Based on these results, the PCR assay was found to exhibit Se, Sp, NPV, and PPV of ≈ 93%, 100%, ≈ 94%, and 100%, respectively (
Table 2).
G. lamblia DNA was exhibited in 5.9% (28/472) of samples by the diagnostic PCR assay. Giardia coproantigen was identified in 5.2% (25/472) of samples by RIDA® Quick kit. The reference PCR assay demonstrated G. lamblia DNA in 6.1% (29/472) of samples. With iodine-stained microscopy ≈ 8% of samples were positives for Giardia and/or other intestinal parasites. G. lamblia cysts were demonstrated in 3.6% (17/472) of the examined feces. Out of these 17 Giardia-positive samples, 12 were sole Giardia infections while the remaining 5 samples were found mixed with other intestinal parasites. Giardia cysts were concomitantly found in 2 samples with E. histolytica/dispar cysts, in 2 samples with B. hominis cysts and in 1 sample with D. fragilis. Lastly, B. hominis, E. histolytica/E. dispar, H. nana, and D. fragilis were also demonstrated as sole infections in 8, 7, 2, and 1 Giardia-negative sample, respectively.
Aggreament with other test results
Table 3 shows the percent of agreement between PCR assay results and that of the other tests. All
Giardia-positive samples by microscopy were also positives by the immunoassay and 2 PCR assays. All
Giardia-positive samples by the immunoassay were also positive by 2 PCR assays, apart from 1 sample. No significant PCR inhibition was noticed in all
Giardia-negative samples.
G. lamblia genotypes
DNA products of all 28 Giardia-positive samples by the developed assay were subjected to restriction digestion by Nla IV, and 12 restriction profiles were G. lamblia genotype A while the remaining 16 profiles were G. lamblia genotype B. None of the examined samples showed mixed genotypes.
DISCUSSION
In earlier studies, a variety of genetic loci including (SSU) rRNA,
gdh, triose phosphate isomerase,
β-giardin, and elongation factor 1-α have been used as the target gene loci for
Giardia PCR assays [
7]. The (SSU) rRNA gene sequence is short and highly conserved among the major
G. lamblia genotypes, thus it has been mainly used in PCR detection assays [
19]. Conversely, the other genes have frequently been used in detection and characterization studies [
12-
17].
In the current study, we developed a simple PCR assay for identification and subsequent discrimination of
Giardia clinical isolates in human feces based on specified
gdh gene sequence. A simple method was selected to extract and purify
Giardia DNA directly from feces without any sample preparatory steps. The whole method was carried out in 1-2 ml scale, hence permitting the use of inexpensive table-top microfuges and heating blocks that are available at most of the basic laboratories. Extraction of 24-sample batch was carried out in ≈ 120 min. The commercial kit-based extraction method has been proved useful for extraction of more than 1 protozoan DNA directly from feces [
20].
Being an enzymatic reaction, PCR is amenable to inhibition by substances in feces or accidentally brought into reactions [
26]. PCR inhibition gives rise to false negative results that are not acceptable in clinical laboratory settings. Thus, we validated our PCR assay with an IC with a minimal additional cost. The concomitant use of IC with the primary amplification target in a duplex PCR worked properly without causing alteration to the diagnostic efficiency of the assay. No significant inhibition was noticed for all DNA retrieved from feces which reflects the high efficiency of the extraction protocol adopted in the study, consistent with our previous findings [
20].
The analytical sensitivity of the assay was demonstrated, and ≈ 2 pg of genomic DNA was sufficient for detection, in agreement with the original study [
21]. Read et al. [
21] reported identical sensitivity but for a semi-nested assay with DNA purified from a cultured strain p1c10, representative of
G. lamblia, genotype A. Although nested or semi-nested PCR assays help in increasing the sensitivity and specificity of the target sequence detection, assays with that formats also cause more elevation of assay cost, duration, and increase the risk of PCR carry-over contamination [
27]. Also in this study, another estimate for the analytical sensitivity which reflected to some extent the efficiency of both the extraction and amplification steps, was undertaken in this study. Assuming that the cyst count seeded in stool aliquots was precise and the DNA extraction was carried out from all cysts with equal efficiency, ≈ 2 cysts were sufficient for identification. It is important to announce that, in view of the estimated assay sensitivity and
Giardia cysts excretion rates that have been reported in human infections [
28], this sensitivity is considered acceptable.
The diagnostic performance of the assay was addressed using high quality control samples that were prepared in the study. A sensitivity of 93% and a specificity of 100% were demonstrated by the assay. The 3
Giardia-positive control samples that could not be picked up by the assay were assumed to be of low parasite loads. The exhibited outstanding assay specificity may be related to the high specificity of primers, the usage of the touchdown protocol, and inclusion of 1% DMSO in the reaction, as previously stated [
29,
30]. Subsequently, the assay was validated on a panel of stool samples with blinded results.
Giardia infection was detected in the study population with a prevalence rate of 5.9%, slightly lower than that described previously. According to earlier reports,
Giardia has been found in 8.5-17.0% of population from Taif [
31,
32]. Moreover, prevalence rates of 3-9% have been described in other Saudi populations [
33,
34]. Much higher rates have been recorded for
Giardia infections in developing countries outside Saudi Arabia [
35]. Certainly, these prevalence variations among studies may be explained by the differences in the study design, target population, sampling size, and the adopted parasitological examination [
36].
The restriction digestion profiles of 28
Giardia DNA-positive samples were successfully analyzed. Both genotypes A and B were described in the study population. The identification of
Giardia clinical isolate is far important not only for epidemiological studies but for infection control programs as well. The correlation between each genotype and clinical picture of
Giardia infection has been investigated but still uncertain. While a number of investigators have linked genotype A with mild infection and genotype B with severe infection [
37], others have found the above correlations insignificant [
28]. These associations could not be investigated in this study because the clinical data extracted from hospital records were not sufficient.
Like any new diagnostic tool, evaluation of our PCR assay has to be carried out continuously. A larger prospective clinical study including samples from various geographic locations covering both endemic and non-endemic regions has to be done in the future. Moreover, further measures for improving the assay have to be searched for in view of the rapidly evolving PCR technology. The assay could be improved more in the future by inclusion of more detection targets of clinically-related and epidemiologically relevant enteric pathogens (viruses, bacteria, and/or parasites)-attributed diarrhea. Moreover, the simple kit-based extraction protocol and the single-round PCR amplification adopted in the PCR assay make the assay highly amenable for partial or complete automation with subsequent reduction in cost, time, and human error.
In conclusion, we developed a diagnostic PCR-based assay coupled with restriction digestion polymorphism for identification of Giardia clinical isolates in human feces. The assay was proved simple, relatively cost-effective, highly specific, adequately sensitive, and reliable. The assay offers a great potential to be used as a diagnostic test in clinical laboratories, particularly in developing countries. Future studies are required for further evaluation, and future measures have to be sought for more improvement of the assay in view of the rapidly progressing PCR technology with more reduction of PCR reagents and machines.
Notes
-
We have no conflict of interest related to this study.
Authors are grateful for help and support given by all staff and technicians at the Medical Laboratory Department, College of Applied Medical Sciences, Taif University, Saudi Arabia.
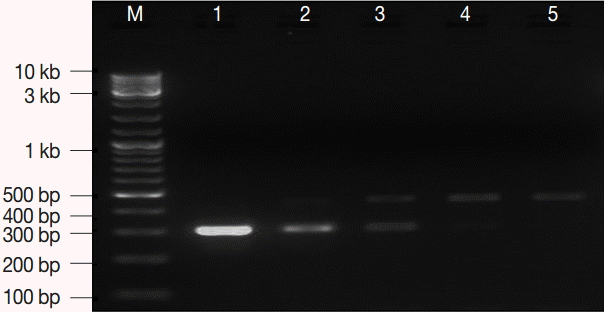
Fig. 1.The optimum concentration of internal control (IC). M, GeneRuler™ 100 bp DNA marker; lane 1, 7.2 fg; lane 2, 3.6 fg; lane 3, 1.8 fg; lane 4, 0.9 fg; lane 5, 0.4 fg. IC concentration of 0.9-3.6 fg per μl was optimum.

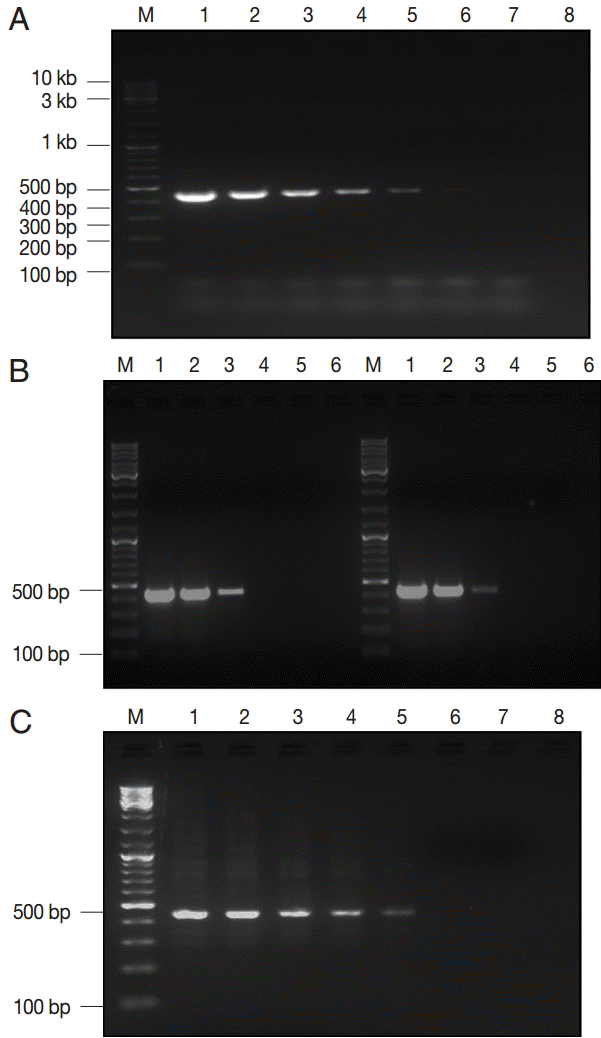
Fig. 2.The lower detection limit (LDL) of PCR assay using 3 kinds of DNA samples of various purities. (A) Serial dilutions of recombinant plasmid DNA. Lane 1, 50 pg/reaction; lane 2, 0.5 pg; lane 3, 50 fg; lane 4, 5 fg; lane 5, 0.5 fg; lane 6, 0.05 fg; lane 7, 0.005 fg. (B-left) Serial dilutions of genomic DNA sample of Giardia WB strain (assemblage A). Lane 1, 160 pg/reaction; lane 2, 16 pg; lane 3, 1.6 pg; lane 4, 0.16 pg; lane 5, 16 fg; (B-right) Serial dilutions of genomic DNA sample of Giardia GS strain (assemblage B). Lane 1, 200 pg/reaction; lane 2, 20 pg; lane 3, 2 pg; lane 4, 0.2 pg; lane 5, 20 fg. (C) Serial dilutions of Giardia-negative feces spiked with 105 Giardia cysts. Lane 1, 106 cysts; lane 2, 105 cysts; lane 3, 104 cysts; lane 4, 103 cysts; lane 5, 102 cysts; lane 6, 101 cysts; lane 7, 100 cysts; lane 8; empty. M, GeneRuler™ 100 bp DNA marker.
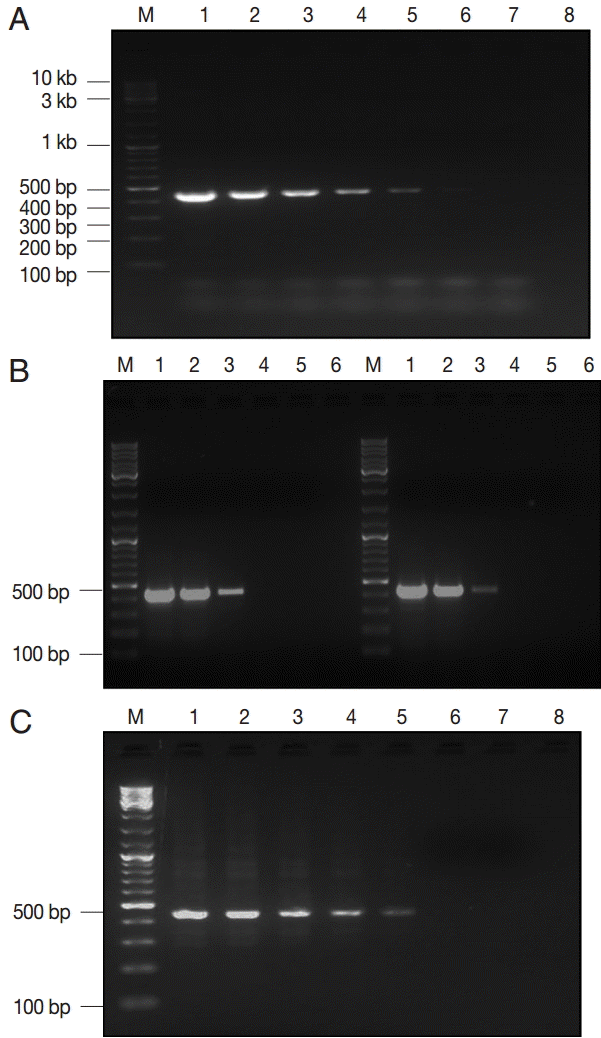
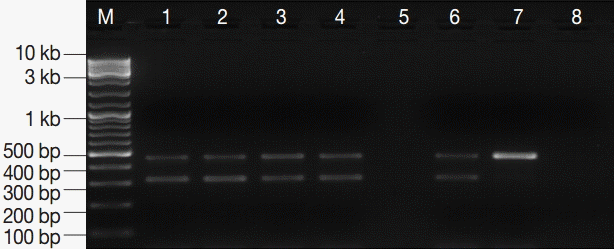
Fig. 3.PCR amplification products of G. lamblia positive stool samples. M, GeneRuler™ 100 bp DNA marker; lanes 1-4, G. lamblia-positive stool samples; lane 5, empty; lane 6, EC and IC (PCR-positive control); lane 7, EC alone; lane 8, DNA-free master mix (PCR negative control).
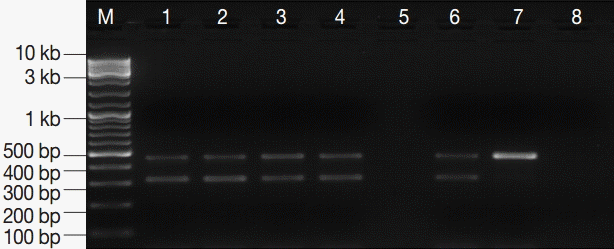
Table 1.Important features of external control (EC) and internal control (IC) plasmids constructed in the study
Table 1.
|
Feature |
EC |
IC |
|
Cloning vector |
pCR4®-TOPO |
pCR4®-TOPO plus gdh insert (455 bp) |
|
Plasmid length |
≈ 4.4 kb |
≈ 4 kb |
|
G. lamblia strain |
WB laboratory strain |
WB laboratory strain |
|
Cloned sequence (bp) |
Primary target gdh sequence (≈ 450 bp) |
Modified gdh sequence (≈ 300 bp) |
|
Flanking PCR primers |
GDHeF and GDHiR |
GDHeF and GDHiR |
|
E. coli strain (storage) |
Top10 |
DH5α |
|
Antibiotics used for colony selection |
Ampicillin |
Ampicillin or erythromycin |
|
gdh copy number per 1 ng of plasmid DNA |
≈ 2.11 × 108
|
≈ 2.1 × 108
|
|
HindIII restriction digestion |
NA |
One band of ≈ 4 kb |
Table 2.Diagnostic performance parameters of PCR assay using 91 control fecal samples against a nominated composite gold standard test comprising microscopy, immunoassay, and a reference PCR assay
Table 2.
|
Test |
Diagnostic performance parameters
|
|
No. of false positive |
No. of false negative |
Sensitivity
|
Specificity
|
PPV
|
NPV
|
|
% |
95% CI |
% |
95% CI |
% |
95% CI |
% |
95% CI |
|
PCR assay |
0 |
3a
|
93.4 |
82.0-98.5 |
100 |
92.0-100 |
100 |
91.7-100 |
93.7 |
82.7-98.6 |
Table 3.Correlation of results between PCR assay and other tests on 472 clinical stool samples
Table 3.
|
Test |
PCR assay results
|
Agreements (%)
|
Kappa (κ) test 95% CI |
|
Positive (No=28) |
Negative (No=444) |
Prevalence (5.9%) |
PPA |
NPA |
Overall |
|
Microscopy |
17 |
455 |
3.6% |
60.7 |
100 |
97.7 |
κ = 0.745 95% CI = [0.60-0.88] |
|
RIDA® Quick kit |
25a
|
447 |
5.2% |
85.7 |
99.7 |
98.9 |
κ = 0.900 95% CI = [0.81-0.98] |
|
Reference PCR |
29 |
443 |
6.1% |
96.5 |
100 |
99.7 |
κ = 0.981 95% CI = [0.94-1.00] |
References
- 1. Robertson LJ. Introduction to Giardia duodenalis: the parasite and the disease. Giardia as a foodborne pathogen. New York. USA. Springer. 2013, pp 1-7.
- 2. Monis PT, Caccio SM, Thompson RC. Variation in Giardia: towards a taxonomic revision of the genus. Trends Parasitol 2009;25:93-100.
- 3. Cacciò SM, Sprong H. Epidemiology of giardiasis in humans. Vienna, Austria. Springer. 2011, pp 17-28.
- 4. Pallant L, Barutzki D, Schaper R, Thompson RC. The epidemiology of infections with Giardia species and genotypes in well cared for dogs and cats in Germany. Parasit Vectors 2015;8:2.
- 5. Foronda P, Bargues MD, Abreu-Acosta N, Periago MV, Valero MA, Valladares B, Mas-Coma S. Identification of genotypes of Giardia intestinalis of human isolates in Egypt. Parasitol Res 2008;103:1177-1181.
- 6. Cacciò SM, Ryan U. Molecular epidemiology of giardiasis. Mol Biochem Parasitol 2008;160:75-80.
- 7. Thompson RC, Monis P. Giardia-from genome to proteome. Adv Parasitol 2012;78:57-95.
- 8. Smith HV, Mank TG. Diagnosis of human giardiasis. Vienna, Austria. Springer. 2011, pp 353-377.
- 9. McHardy IH, Wu M, Cohen RS, Couturier MR, Humphries RM. Clinical laboratory diagnosis of intestinal protozoa. J Clin Microbiol 2014;52:712-720.
- 10. El-Nahas HA, Salem DA, El-Henawy AA, El-Nimr HI, Abdel-Ghaffar HA, El-Meadawy AM. Giardia diagnostic methods in human fecal samples: a comparative study. Cytometry B Clin Cytom 2013;84:44-49.
- 11. Platts-Mills JA, Operario DJ, Houpt ER. Molecular diagnosis of diarrhea: current status and future potential. Curr Infect Dis Rep 2012;14:41-46.
- 12. Stroup S, Tongjai S, Swai N, Maro A, Kibiki G, Houpt ER. Dual probe DNA capture for sensitive real-time PCR detection of Cryptosporidium and Giardia. Mol Cell Probes 2012;26:104-106.
- 13. Boadi S, Polley SD, Kilburn S, Mills GA, Chiodini PL. A critical assessment of two real-time PCR assays targeting the (SSU) rRNA and gdh genes for the molecular identification of Giardia intestinalis in a clinical laboratory. J Clin Pathol 2014;67:811-816.
- 14. Vanni I, Cacciò SM, van Lith L, Lebbad M, Svärd SG, Pozio E, Tosini F. Detection of Giardia duodenalis assemblages A and B in human feces by simple, assemblage-specific PCR assays. PLoS Negl Trop Dis 2012;6:e1776.
- 15. Stark D, Al-Qassab SE, Barratt JLN, Stanley K, Roberts T, Marriott D, Harkness J, Ellis JT. Evaluation of multiplex tandem real-time PCR for detection of Cryptosporidium spp., Dientamoeba fragilis, Entamoeba histolytica, and Giardia intestinalis in clinical stool samples. J Clin Microbiol 2011;49:257-262.
- 16. Elwin K, Fairclough HV, Hadfield SJ, Chalmers RM. Giardia duodenalis typing from stools: a comparison of three approaches to extracting DNA, and validation of a probe-based real-time PCR typing assay. J Med Microbiol 2014;63:38-44.
- 17. Haque R, Roy S, Siddique A, Mondal U, Rahman SM, Mondal D, Houpt E, Petri WA. Multiplex real-time PCR assay for detection of Entamoeba histolytica, Giardia intestinalis, and Cryptosporidium spp. Am J Trop Med Hyg 2007;76:713-717.
- 18. Keister DB. Axenic culture of Giardia lamblia in TYI-S-33 medium supplemented with bile. Trans R Soc Trop Med Hyg 1983;77:487-488.
- 19. Hopkins RM, Meloni BP, Groth DM, Wetherall JD, Reynoldson JA, Thompson RC. Ribosomal RNA sequencing reveals differences between the genotypes of Giardia isolates recovered from humans and dogs living in the same locality. J Parasitol 1997;83:44-51.
- 20. Hawash Y. DNA extraction from protozoan oocysts/cysts in feces for diagnostic PCR. Korean J Parasitol 2014;52:263-271.
- 21. Read CM, Monis PT, Thompson RC. Discrimination of all genotypes of Giardia duodenalis at the glutamate dehydrogenase locus using PCR-RFLP. Infect Genet Evol 2004;4:125-130.
- 22. Green MR, Sambrook J. Molecular cloning: a laboratory manual. 4th ed. New York, USA. Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press. 2012.
- 23. Hawash Y, Ghonaim MM, Al-Hazmi AS. Internal amplification control for a Cryptosporidium diagnostic PCR: construction and clinical evaluation. Korean J Parasitol 2015;53:147-154.
- 24. Stibbs HH, Samadpour M, Mannings JF. Enzyme immunoassay for detection of Giardia lamblia cyst antigens in formalin-fixed and unfixed human stool. J Clin Microbiol 1988;26:1665-1669.
- 25. Whelan JA, Russel NB, Whelan MA. A method for the absolute quantification of cDNA using real time PCR. J Immunol Methods 2003;278:261-269.
- 26. Schrader C, Schielke A, Ellerbroek L, Johne R. PCR inhibitorsoccurrence, properties and removal. J Appl Microbiol 2012;113:1014-1026.
- 27. Porter-Jordan K, Rosenberg EI, Keiser JF, Gross JD, Ross AM, Nasim S, Garrett CT. Nested polymerase chain reaction assay for the detection of Cytomegalovirus overcomes false positives caused by contamination with fragmented DNA. J Med Virol 1990;30:85-91.
- 28. Kohli A, Bushen OY, Pinkerton RC, Houpt E, Newman RD, Sears CL, Lima AA, Guerrant RL. Giardia duodenalis assemblage, clinical presentation and markers of intestinal inflammation in Brazilian children. Trans R Soc Trop Med Hyg 2008;102:718-725.
- 29. Hecker KH, Roux KH. High and low annealing temperatures increase both specificity and yield in touchdown and stepdown PCR. Biotechniques 1996;20:478-485.
- 30. Obradovic J, Jurisic V, Tosic N, Mrdjanovic J, Perin B, Pavlovic S, Djordjevic N. Optimization of PCR conditions for amplification of GC-rich EGFR Promoter Sequence. J Clin Lab Anal 2013;27:487-493.
- 31. Hawash Y. Evaluation of an immunoassay-based algorithm for screening and identification of Giardia and Cryptosporidium antigens in human faecal specimens from Saudi Arabia. J Parasitol Res 2014;213745:doi:10.1155/2014/213745.
- 32. Shalaby I, Gherbawy Y, Banaja A. Molecular characterization of Giardia parasite isolated from stool samples collected from different hospitals in Taif City (Saudi Arabia). Trop Biomed 2011;28:487-496.
- 33. El-Sheikh SM, El-Assouli SM. Prevalence of viral, bacterial and parasitic enteropathogens among young children with acute diarrhea in Jeddah, Saudi Arabia. J Health Popul Nutr 2001;19:25-30.
- 34. Abahussain NA. Prevalence of intestinal parasites among expatriate workers in Al-Khobar, Saudi Arabia. J Family Community Med 2005;3:17-21.
- 35. Muhsen K, Levine MM. A systematic review and meta-analysis of the association between Giardia lamblia and endemic pediatric diarrhea in developing countries. Clin Infect Dis 2012;55(suppl 4):271-293.
- 36. Hörman A, Korpela H, Sutinen J, Wedel H, Hänninen ML. Meta-analysis in assessment of the prevalence and annual incidence of Giardia spp. and Cryptosporidium spp. infections in humans in the Nordic countries. Int J Parasitol 2004;34:1337-1346.
- 37. Homan WL, Mank TG. Human giardiasis: genotype linked differences in clinical symptomatology. Int J Parasitol 2001;31:822-826.