Abstract
In the era of (pre) elimination setting, the prevalence of malaria has been decreasing in most of the previously endemic areas. Therefore, effective cost- and time-saving validated pooling strategy is needed for detection of malaria in low transmission settings. In this study, optimal pooling numbers and lowest detection limit were assessed using known density samples prepared systematically, followed by genomic DNA extraction and nested PCR. Pooling strategy that composed of 10 samples in 1 pool, 20 µl in 1 sample, was optimal, and the parasite density as low as 2 p/µl for both falciparum and vivax infection was enough for detection of malaria. This pooling method showed effectiveness for handling of a huge number of samples in low transmission settings (<9% positive rate). The results indicated that pooling of the blood samples before DNA extraction followed by usual nested PCR is useful and effective for detection of malaria in screening of hidden cases in low-transmission settings.
-
Key words: Plasmodium falciparum, Plasmodium vivax, malaria, pooling strategy, low-transmission setting, nested PCR
INTRODUCTION
Malaria morbidity and mortality have been decreasing globally, and malaria risk has been reduced by 37% since 2000 [
1]. The number of countries moving forwards for malaria elimination is increasing. At the same time, drug resistance against falciparum and vivax malaria have been reported in some endemic countries [
2,
3]. Therefore, World Health Organization (WHO) initiated the elimination of the artemisinin resistance against falciparum malaria in drug resistance foci, Greater Mekong Subregion, by 2020 [
4]. For this elimination approach, surveillance of malaria especially for submicroscopic asymptomatic infection that may harbor the drug resistant parasite [
5] is critical. Rapid diagnostic tests (RDT) and malaria microscopy are recommended as parasitological methods for diagnosis of clinical malaria [
6]. However, the low-level parasitemia that cannot be detected by these routine diagnosis tests is not uncommon in endemic areas [
7-
10]. Moreover, there is no ideal method for detection of asymptomatic parasitemia in low-transmission settings [
6,
11]. Meanwhile, many molecular based detection methods such as nested-PCR [
12,
13], real-time PCR [
9,
14], and recently reverse-transcriptase PCR [
15], are used in parallel detection of low-level parasitemia.
Most of the molecular-based methods are costly and time-consuming for handling of huge numbers of samples at the same time. To overcome these obstacles, pooling strategy has been considered before molecular-based amplification procedures [
9,
16]. However, most of the pooling approaches that was conducted only after DNA extraction will not save the time and cost for individual DNA extraction. Moreover, previously documented pooling methods also did not show the assessment on effectiveness and validation with known parasite count samples to identify the lowest detection limit of the pooling strategy. Therefore, in this study, high through-put sensitive pooling strategy was proposed and validated using known positive and negative samples.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Blood sample preparation
All of the blood samples were collected under aseptic conditions and transferred into EDTA tubes and then kept in a -80˚C deep freezer until analysis. For the positive and negative control blood samples, all were confirmed by RDT (SDFK80, Standard Diagnostics, Yongin, Korea), microscopy, and nested PCR before the pooling procedure. In this experiment, blood that had different parasite counts of
Plasmodium falciparum or
P. vivax; 200 parasites per microliter (p/µl), 20 p/µl, 2 p/µl, and 0.2 p/µl were prepared according to the procedures described for preparation of laboratory quality control samples for malaria RDTs [
17].
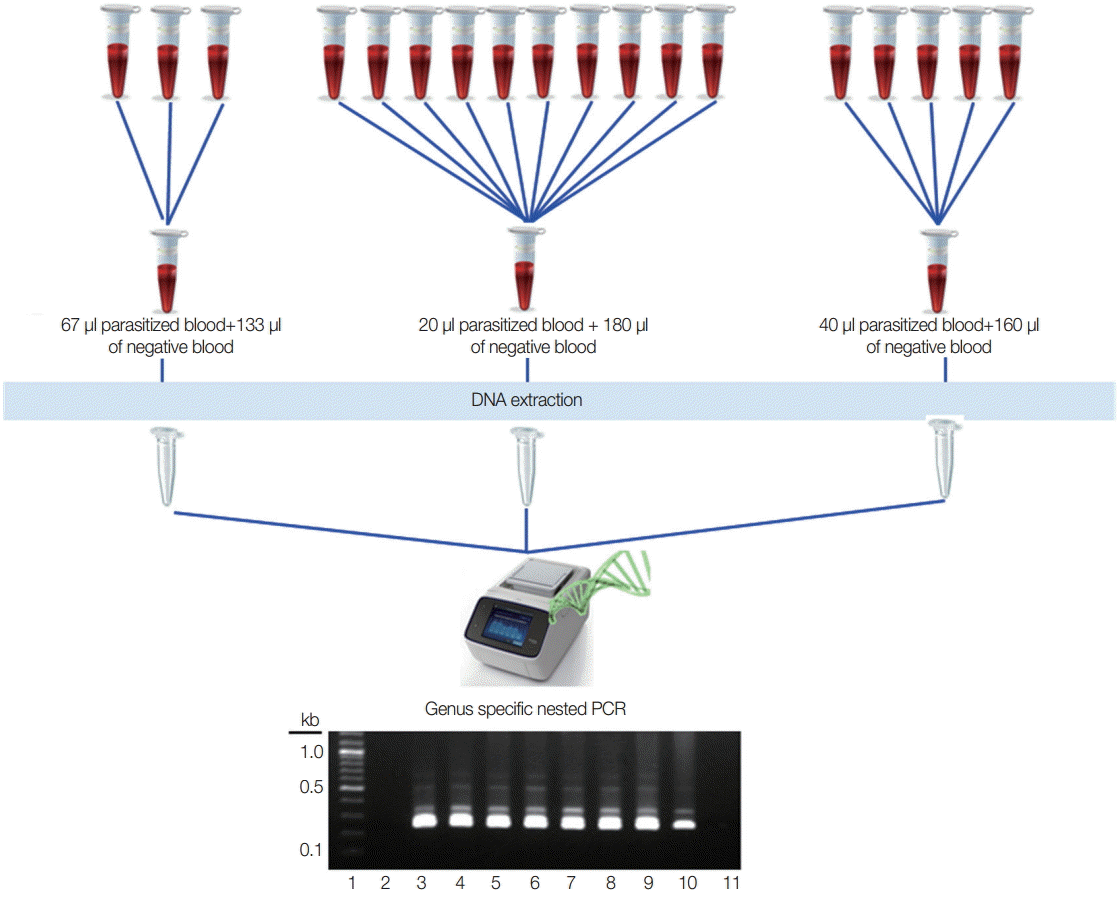
Different numbers of samples in each pool were assessed to know the optimal pooling, and 200 µl of the pooled blood was used for DNA extraction. Two of the known vivax malaria blood samples (parasite count 200 p/µl and 20 p/µl) were used for 3 different pools that represented 3 samples in 1 pool (67 µl of parasitized blood with 133 µl of negative blood), 5 samples in 1 pool (40 µl of parasitized blood with 160 µl of negative blood), and 10 samples in 1 pool (20 µl of parasitized blood with 180 µl of negative blood). Two-hundred microliters from each positive and negative sample were used directly for DNA extraction (
Fig. 1). All of the blood samples were used for genomic DNA extraction by using QIAamp Blood Mini kit (Qiagen, Valencia, California, USA) in accordance with the manufacturer's instructions.
Nested PCR to amplify the small subunit ribosomal RNA gene [
13] was used to detect
Plasmodium infection. Briefly, amplification was conducted using Accupower premix (Bioneer, Daejon, Korea) in a final volume of 20 µl, which included 250 nM primers, 0.25 mM each of deoxyribonucleoside triphosphate, 10 mM Tris-hydrochloric acid, 30 mM magnesium chloride, 1.0 unit of
Taq polymerase, and 10 µl of the genomic DNA as template. The primers used for genus and species identification were shown in
Table 1. The reaction condition consisted of initial denaturing 95˚C for 5 min followed by 35 cycles of 95˚C for 30 sec, 55˚C for 1 min and 72˚C for 2 min, and a final extension step of 10 min at 72˚C. After nested-1 PCR, 2 µl of the PCR product was used for nested-2 reaction, and amplification reaction was the same as above except for annealing temperature of 60˚C for 30 sec for 30 cycles. After amplification, 1% agarose gel electrophoresis was done at 100 volt for 30 min, and gel results were documented by UV transilluminator.
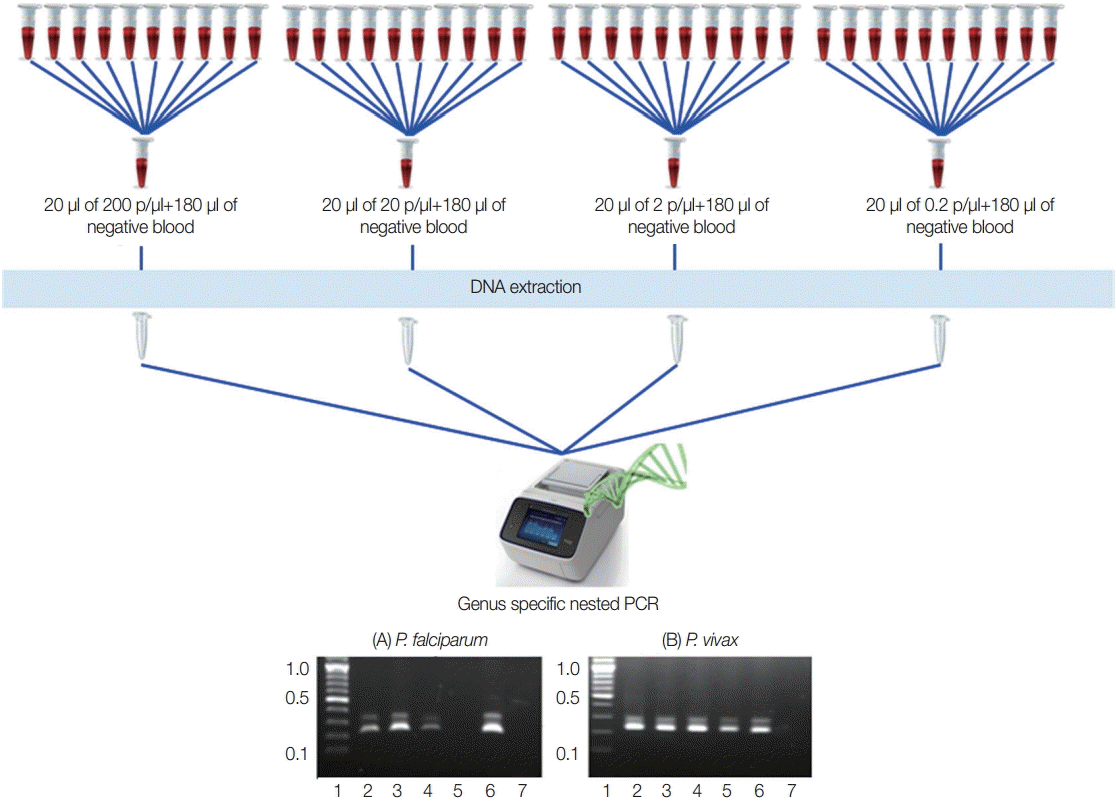
To identify the lowest detection limit of individual samples inside the pools, different parasite counts of the blood were used. Twenty microliter (20 µl) of the different parasite count of
P. falciparum and
P. vivax that have 200 p/µl, 20 p/µl, 2 p/µl, and 0.2 p/µl were prepared and diluted with 180 µl of known negative control blood samples in individual tubes to become 200 µl. DNA extraction and nested PCR were also conducted as described above (
Fig. 2).
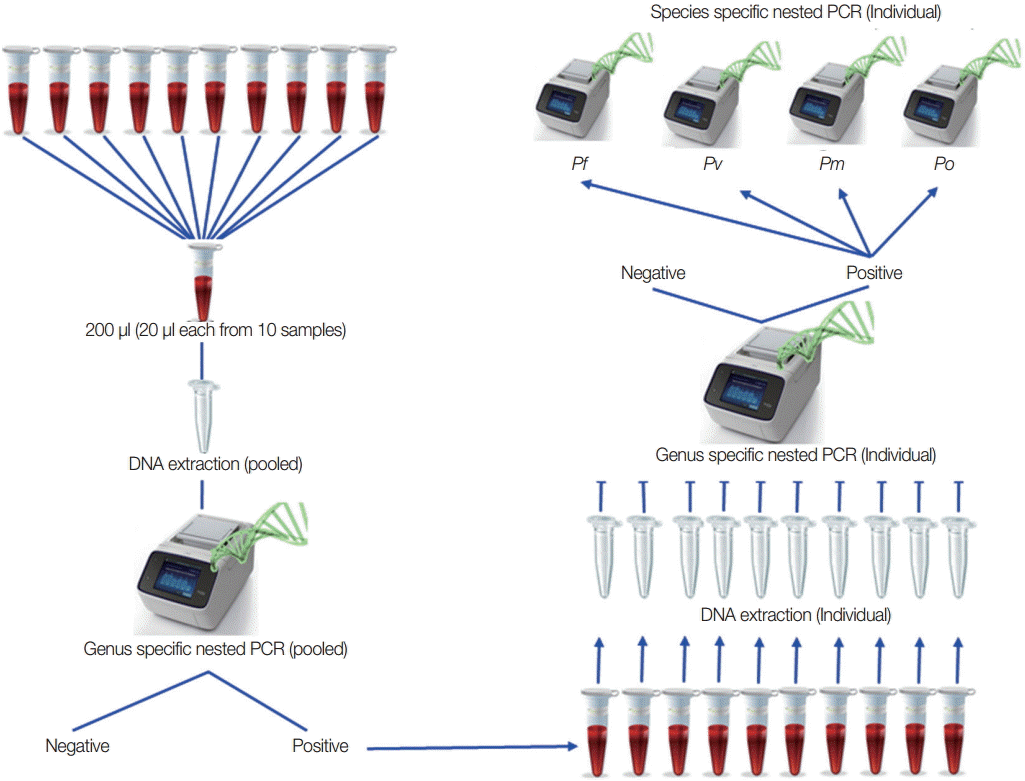
Based on the result of the optimal number in each pool and the lowest volume for each samples, field samples from low-transmission areas were used to detect malaria infection by this pooling strategy as purposed in
Fig. 3 to confirm the pooling strategy. All of the positive individual samples were checked to identify the species. For field sample collection, ethical clearance from the Ethical Review Committee of the Department of Medical Research, Myanmar was obtained (approval no. 49/Ethics 2014). The study was registered in
www.clinicaltrial.gov (identifier: NCT02708199).
The effectiveness of the pooling method in this study was assessed by comparing the possible maximum number of the test by routine individual handling of the samples, with this pooling method to estimate the usefulness of the pooling method for different prevalence of malaria.
RESULTS
For optimal number of the pools, 2 independent experiments were performed using 200 p/µl and 20 p/µl of the blood. Among the different numbers of pools, all become positive clearly even in 10 samples in 1 pool at 20 p/µl parasitized blood (
Fig. 1).
To assess the lowest detection limit of this pooling strategy, 2 independent experiments were carried out using quality control blood samples that contained 200 p/µl, 20 p/µl, 2 p/µl, and 0.2 p/µl of falciparum and vivax infections that are most prevalence species. Both of the results indicated that minimum 1 positive vivax sample that had as few as 0.2 p/µl can be detected by this approach. Meanwhile, 2 p/µl of falciparum malaria can be detected by this method (
Fig. 2).
To validate these pooling methods, 1,004 filed samples collected from local residents who had no signs and symptoms of malaria in low-transmission settings were used. According to the polling strategy, 101 pools were prepared, and nested PCR was done. Among them, 22 pools became genus positive, and 220 individual genomic DNA extractions were carried out. Subsequent genus-specific PCR showed that 27 samples (2.7% of all samples) were infected with Plasmodium, and species-specific PCR resulted in 22 vivax infections, 3 falciparum, and 2 malariae infections in these genus positive samples. Among them, only 2 vivax samples showed microscopy positive and all were negative by RDT (HRP2 and vivax-specific pLDH based SDFK80, Standard Diagnostics).
We also compared the total number of the test by routine individual handling of the samples with the maximum possible number of the test by this pooling method to estimate the effectiveness. According to this calculation, the parasite positive rate less than 9 was suitable for this pooling strategy (
Table 2).
DISCUSSION
In the era of malaria pre-elimination, blood smear positive rate is usually less than 5% in febrile patients. If the blood smear positive rate becomes less than 1 case per 1,000 population at risk per year, it is time to initiate the elimination of malaria [
4]. At the same time, the detection of asymptomatic infections in local residents are important to treat properly, so that the source of the transmission will be terminated [
8].
Although microscopic examination is still the gold standard test for the diagnosis of clinical malaria, RDT is recommended as the diagnostic method particularly in areas where there is no reliable microscopic facility [
6]. The detection limit for microscopy is 20 p/µl by an expert microscopist, and 50 p/µl by good microscopist [
20], while the detection limit of the RDT was 200 p/µl [
21]. Meanwhile, molecular-based detection such as PCR can detect even less than 5 p/µl [
22]. However, in mass-surveys collecting a huge number of samples from local residents, individual DNA extraction and amplification led to time- and reagent-consuming. Therefore, pooling strategy has to be considered.
Pooling specimens reduces the number of assays for screening of infectious diseases. It is useful and effective in screening for many diseases, including genome-wide studies and other infectious diseases, such as HIV [
23] and hepatitis viruses [
24]. Regarding the malaria diagnosis by molecular means, a pooling method was proposed by Bharti et al. [
25] since 2009 by using serum samples. Similarly, pooling of the genomic DNA before amplification [
9,
16] was reported in detection of malaria in asymptomatic cases. The pooling method that applied only after DNA extraction cannot save the reactions for DNA extraction. However, there is no methodology that has been documented and validated for blood pooling before DNA extraction showing the optimal pooling number and lower detection limit, including consideration of effectiveness based on the positive rate especially for low-transmission settings.
In this methodology, the optimal pooling number was assessed using 200 p/µl and 2 p/µl confirmed parasite density of blood, and 10 samples in 1 pool showed to be positive by nested PCR. Therefore, 10 samples in 1 pool with each sample composed of 20 p/µl are good enough for pooling blood before DNA extraction. Moreover, the lowest parasite density detected after the pooling method was also examined, and at least 2 p/µl of the blood in 1 sample can be detected correctly. The pooling strategy may give false negative results for very low parasitemia cases but it is still higher in sensitivity than microscopy [
25].
Moreover, the effectiveness of the pooling methods has been considered by comparing the number of tests by routine individual sample handling, with the maximum possible number of the test by the pooling method. Based on this comparison, when the parasite positive rate was 4%, a half of genomic DNA extractions can be saved that is effectively useful for most of the (pre) elimination setting where the positive rate is less than 9%. In conclusion, pooling of the blood samples before DNA extraction followed by usual nested-PCR method is effective for detecting malaria and screening of hidden cases in low-transmission settings.
Notes
-
We have no conflict of interest related to this study.
The authors would like to express their gratitude towards authorities from Department of Medical Research and Department of Health, Myanmar for allowing the collection of field blood samples for this study. All of the participants in this study are acknowledged. This work was supported by a grant from the Korea International Cooperation Agency (KOICA), the Korea Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (KCDC), 2013 Research Grant from Kangwon National University (no. C1009819-01-01), and Korea Association of Health Promotion (2016_02).
Fig. 1.Experimental design for optimal number of the pooling strategy. Lane 1, 100 bp DNA ladder; lane 2, negative blood only (200 μl); lane 3, parasitized blood only (200 μl of 200 p/μl); lane 4, parasitized blood only (200 μl of 20 p/μl); lane 5, 67 μl of 200 p/μl with 133 μl of negative blood; lane 6, 40 μl of 200 p/μl with 160 μl of negative blood; lane 7, 20 μl of 200 p/μl with 180 μl of negative blood; lane 8, 67 μl of 20 p/μl with 133 μl of negative blood; lane 9, 40 μl of 20 p/μl with 160 μl of negative blood; lane 10, 20 μl of 20 p/μl+180 μl of negative blood; lane 11, negative control for PCR reaction.
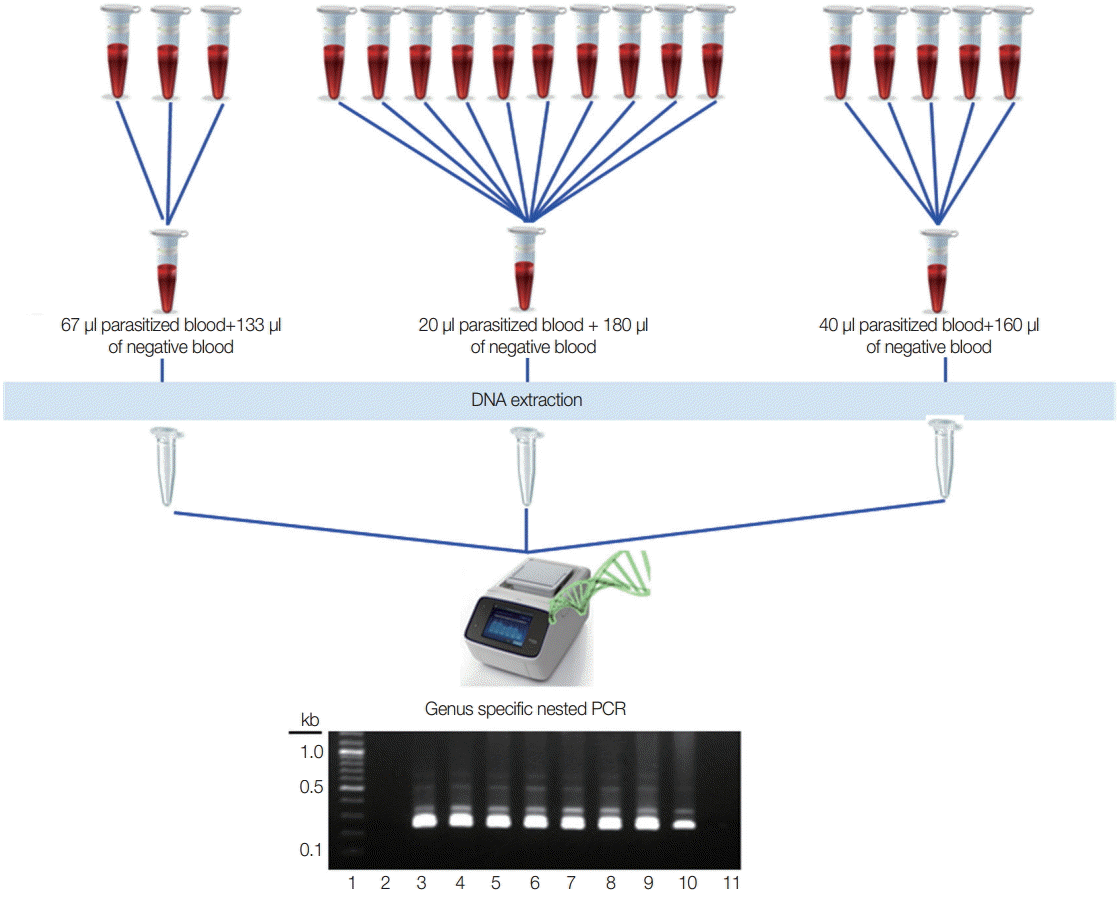
Fig. 2.Experimental design for lowest detection limit of pooling strategy. Falciparum and vivax were done independently. (A) P. falciparum. (B) P. vivax. Lane 1, ladder (100 bp); lane 2-5, 20 μl each of 200 p/μl, 20 p/μl, 2 p/μl, and 0.2 p/μl of parasite blood with 180 μl of negative blood, respectively; lane 6, falciparum control (3D7) or known vivax sample; lane 7, negative control for PCR reaction.
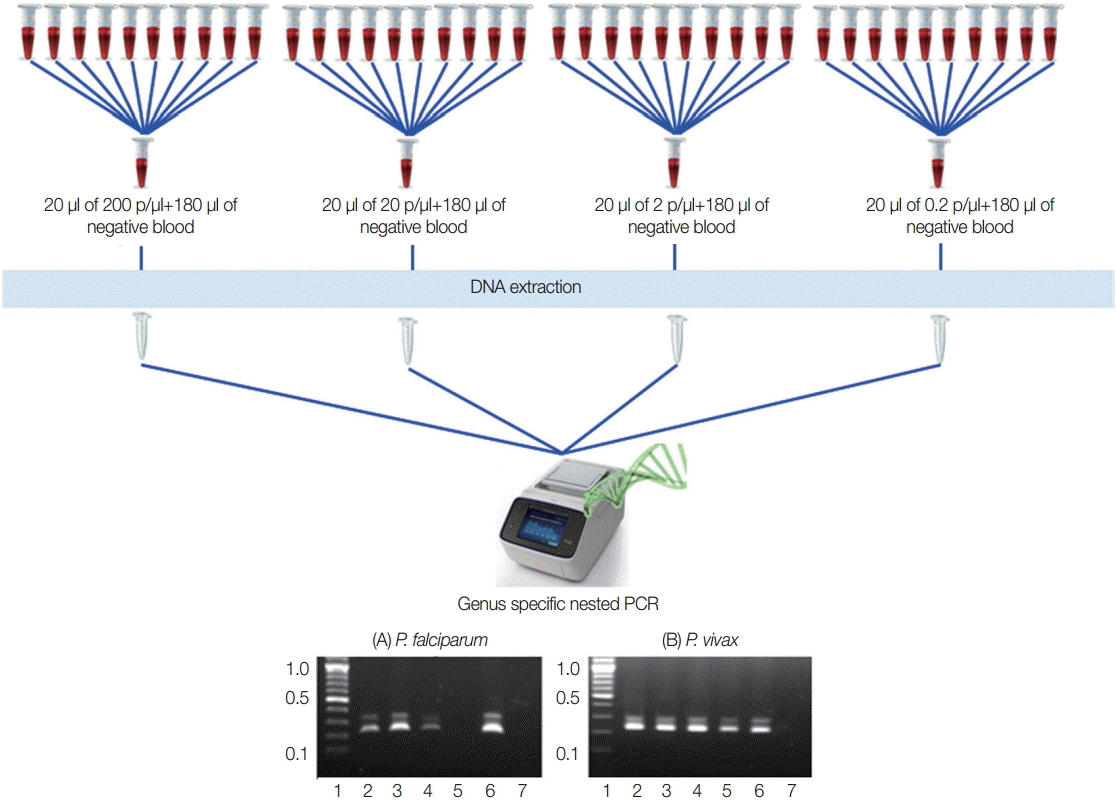
Fig. 3.Proposed pooling strategy. Twenty microliters (20 μl) from each sample and 10 samples in 1 pool were prepared, and DNA extractions were done for each pooled sample. Using these genomic DNA from each pool, genus-specific PCR was done. Only genus positive pools were selected for individual DNA extraction followed by genus-specific PCR to get individual positive samples. Species identification was done on these individual genus positive samples.
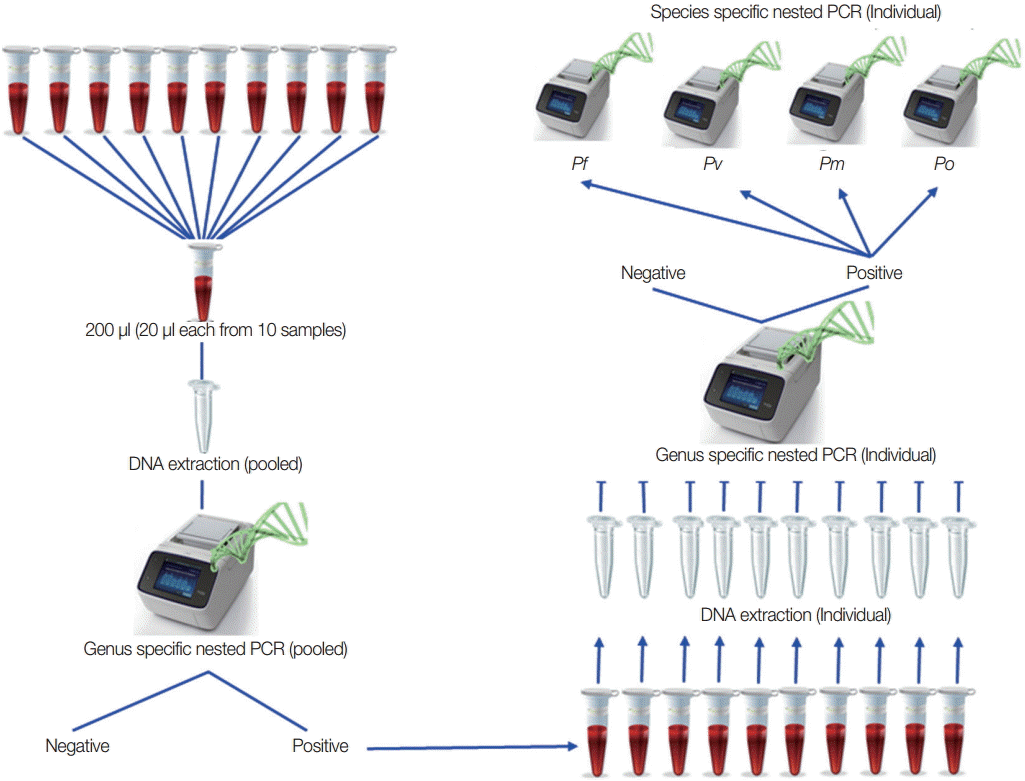
Table 1.The pairs of primers used for genus and species detection
Table 1.
|
Primers |
Primer and probe sequences (5'→3') |
Genus/species |
Amplicon size (bp) |
|
Primary PCR |
|
|
|
|
rPLU1_F |
TCA AAG ATT AAG CCA TGC AAG TGA |
Genus |
-1,670 |
|
rPLU5_R |
CCT GTT GTT GCC TTA AAC TTC |
|
|
|
Secondary PCR |
|
|
|
|
rPLU3_F |
TTT TTA TAA GGA TAA CTA CGG AAA AGC TGT |
Genus |
240 |
|
rPLU4_R |
TAC CCG TCA TAG CCA TGT TAG GCC AAT ACC |
|
|
|
rFAL1_F |
TTA AAC TGG TTT GGG AAA ACC AAA TAT ATT |
Pf |
206 |
|
rFAL2_R |
ACA CAA TGA ACT CAA TCA TGA CTA CCC GTC |
|
|
|
rVIV1_F |
CGC TTC TAG CTT AAT CCA CAT AAC TGA TAC |
Pv |
121 |
|
rVIV1_R |
ACT TCC AAG CCG AAG CAA AGA AAG TCC TTA |
|
|
|
rMAL1_F |
ATA ACA TAG TTG TAC GTT AAG AAT AAC CGC |
Pm |
145 |
|
rMAL2_R |
AAA ATT CCC ATG CAT AAA AAA TTA TAC AAA |
|
|
|
rOVA3_F |
CGG GGA AAT TTC TTA GAT TGC |
Po |
456 |
|
rOVA4_R |
GAG AAA CAG CAT GAA TTG CG |
|
|
Table 2.Logistic calculation on the effectiveness of the pooling strategy
Table 2.
|
Possible positive rate |
No. of pools |
Maximum possible no. of positive pools |
Total no. of test by pooling method |
Total no. of test by routine individual methoda
|
No. of test saved by pooling methoda
|
|
1 |
10 |
1 |
20 |
100 |
80 |
|
2 |
10 |
2 |
30 |
100 |
70 |
|
3 |
10 |
3 |
40 |
100 |
60 |
|
4 |
10 |
4 |
50 |
100 |
50 |
|
5 |
10 |
5 |
60 |
100 |
40 |
|
6 |
10 |
6 |
70 |
100 |
30 |
|
7 |
10 |
7 |
80 |
100 |
20 |
|
8 |
10 |
8 |
90 |
100 |
10 |
|
9 |
10 |
9 |
100 |
100 |
0 |
|
10 |
10 |
10 |
110 |
100 |
-10 |
|
> 10 |
10 |
10 |
110 |
100 |
-10 |
References
- 1. World Health Organization. World Malaria Report 2015. Geneva, Switzerland. World Health Organization. 2015.
- 2. World Health Organization. Emergency response to artemisinin resistance in the Greater Mekong Subregion. Regional framework for action 2013-2015. Geneva, Switzerland. WHO. 2013, p 32.
- 3. World Health Organization. Global report on antimalarial drug efficacy and drug resistance: 2000-2010. Geneva, Switzerland. 2010.
- 4. World Health Organization. Strategy for Malaria Elimination in the Greater Mekong Subregion (2015–2030). World Health Organization Regional Office for the Western Pacific. 2015.
- 5. Ganguly S, Saha P, Guha SK, Biswas A, Das S, Kundu PK, Maji AK. High prevalence of asymptomatic malaria in a tribal population in eastern India. J Clin Microbiol 2013;51:1439-1444.
- 6. World Health Organization. Guidelines for treatment of malaria. 3rd ed. Geneva, Switzerland. WHO. 2015.
- 7. Okell L, Ghani A, Lyons E, Drakeley C. Submicroscopic infection in Plasmodium falciparum endemic populations: a systematic review and meta-analysis. J Infect Dis 2009;200:1509-1517.
- 8. Bousema T, Okell L, Felger I, Drakeley C. Asymptomatic malaria infections: detectability, transmissibility and public health relevance. Nat Rev Microbiol 2014;12:833-840.
- 9. Wang B, Han SS, Cho C, Han JH, Cheng Y, Lee SK. Comparison of microscopy, nested-PCR, and real-time PCR assays using high-throughput screening of pooled samples for diagnosis of malaria in asymptomatic carriers from areas of endemicity in Myanmar. J Clin Microbiol 2014;52:1838-1845.
- 10. Starzengruber P, Fuehrer H, Ley B, Thriemer K, Swoboda P, Habler V. High prevalence of asymptomatic malaria in South-Eastern Bangladesh. Malar J 2014;13:1-10.
- 11. Lo E, Zhou G, Oo W, Afrane Y, Githeko A, Yan G. Low parasitemia in submicroscopic infections significantly impacts malaria diagnostic sensitivity in the highlands of western Kenya. PLoS One 2015;10:e0121763.
- 12. Snounou G, Singh B. Nested PCR analysis of Plasmodium parasites. Methods Mol Med 2002;72:189-203.
- 13. Singh B, Bobogare A, Cox-Singh J, Snounou G, Abdullah MS, Rahman HA. A genus- and species-specific nested polymerase chain reaction malaria detection assay for epidemiologic studies. Am J Trop Med Hyg 1999;60:687-692.
- 14. Imwong M, Hanchana S, Malleret B, Rénia L, Day NPJ, Dondorp A, Nosten F, Snounou G, White NJ. High-throughput ultrasensitive molecular techniques for quantifying low-density malaria parasitemias. J Clin Microbiol 2014;52:3303-3309.
- 15. Adams M, Joshi SN, Mbambo G, Mu AZ, Roemmich SM, Shrestha B, Strauss KA, Johnson NE, Oo KZ, Hlaing TM, Han ZY, Han KT, Thura S, Richards AK, Huang F, Nyunt MM, Plowe CV. An ultrasensitive reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction assay to detect asymptomatic low-density Plasmodium falciparum and Plasmodium vivax infections in small volume blood samples. Malar J 2015;14:1-5.
- 16. Taylor S, Juliano J, Trottman P, Griffin J, Landis S, Kitsa P. High-throughput pooling and real-time PCR-based strategy for malaria detection. J Clin Microbiol 2010;48:512-519.
- 17. World Health Organization. Methods Manual for Laboratory Quality Control Testing of Malaria RDTs. WHO Global Malaria Programme. 2014.
- 18. Bailey NTJ. The Mathematical Theory of Infectious Diseases and Its Applications. Nature Publishing Group. 1975, pp 1-413.
- 19. Diekmann O, Heesterbeek JAP. Mathematical Epidemiology of Infectious Diseases: Model building, Analysis and Interpretation. Nature Publishing Group. 2000, pp 1-303.
- 20. World Health Organization. WHO Evidence Review Group on Malaria Diagnosis in Low Transmission Settings. Geneva, Switzerland. 2013.
- 21. World Health Organization. Policy brief on malaria diagnostics in low-transmission settings. Geneva, Switzerland. 2014.
- 22. Coleman RE, Sattabongkot J, Promstaporm S, Maneechai N, Tippayachai B, Kengluecha A, Rachapaew N, Zollner G, Miller RS, Vaughan JA, Thimasarn K, Khuntirat B. Comparison of PCR and microscopy for the detection of asymptomatic malaria in a Plasmodium falciparum/vivax endemic area in Thailand. Malar J 2006;5:121-121.
- 23. Stramer SL, Glynn SA, Kleinman SH, Strong DM, Caglioti S, Wright DJ, Dodd RY, Busch MP. Detection of HIV-1 and HCV infections among antibody-negative blood donors by nucleic acid-amplification testing. N Engl J Med 2004;351:760-768.
- 24. Mine H, Emura H, Miyamoto M, Tomono T, Minegishi K, Murokawa H, Yamanaka R, Yoshikawa A, Nishioka K. High throughput screening of 16 million serologically negative blood donors for hepatitis B virus, hepatitis C virus and human immunodeficiency virus type-1 by nucleic acid amplification testing with specific and sensitive multiplex reagent in Japan. J Virol Methods 2003;112:145-151.
- 25. Bharti AR, Letendre SL, Patra KP, Vinetz JM, Smith DM. Malaria diagnosis by a polymerase chain reaction-based assay using a pooling strategy. Am J Trop Med Hyg 2009;81:754-757.