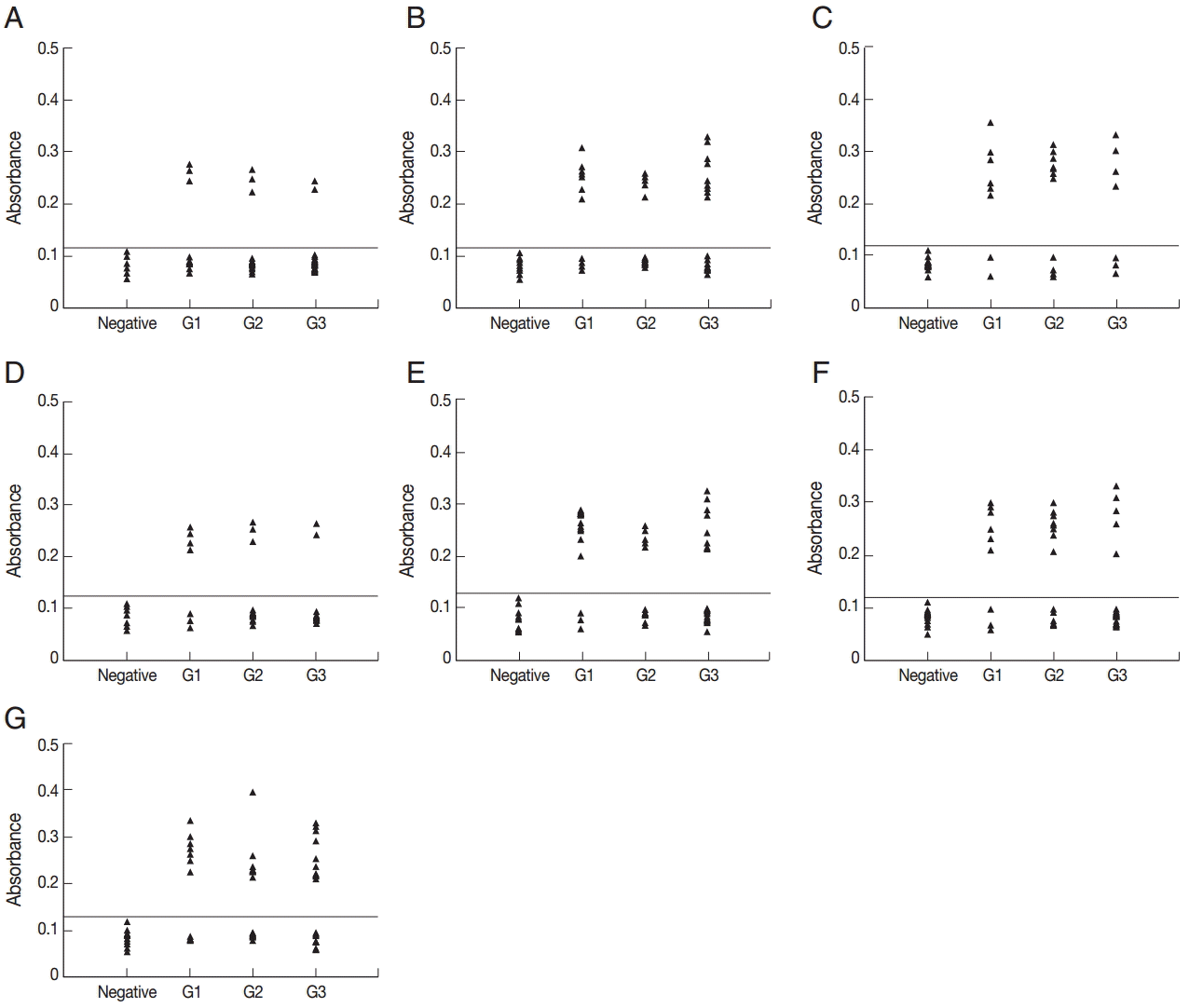Abstract
The study of antigenic epitopes from Toxoplasma gondii has not only enhanced our understanding of the structure and function of antigens, the reactions between antigens and antibodies, and many other aspects of immunology, but it also plays a significant role in the development of new diagnostic reagents and vaccines. In the present study, T. gondii GRA6 epitopes were identified using bioinformatics tools and a synthetic peptide technique. The potential B cell epitopes of GRA6 predicted by bioinformatics tools concentrated upon 3 regions of GRA6, 1-20 aa, 44-103 aa, and 172-221 aa. Ten shorter peptides from the 3 regions were synthesized and assessed by ELISA using pig sera from different time points after infection. Three of the 10 peptides (amino acids 44-63, 172-191, and 192-211) tested were recognized by all sera and determined to be immunodominant B-cell epitopes of GRA6. The results indicated that we precisely and accurately located the T. gondii GRA6 epitopes using pig sera collected at different time points after infection. The identified epitopes may be very useful for further studies of epitope-based vaccines and diagnostic reagents.
-
Key words: Toxoplasma gondii, GRA6, epitope, pig antibody
INTRODUCTION
Toxoplasma gondii is an obligate intracellular parasite that infects a variety of mammals and birds, causing toxoplasmosis. Toxoplasmosis is a zoonotic protozoan disease that is distributed worldwide.
T. gondii is an important foodborne parasite that is primarily transmitted from animals to humans through the consumption of infected meat [
1]. In some countries, pork is the most common meat consumed, and several ethnic groups consume raw pork. Pigs are considered the primary source of human infections with
T. gondii [
2]. Toxoplasmosis is a source of significant economic loss for swine farmers because of gross lesions in infected animals, which result in the carcass being condemned at the time of slaughter, the expense associated with treatment, and weight loss associated with clinical toxoplasmosis [
3]. The development of effective diagnostic reagents or vaccines is very important for worldwide public health and economic repercussions of
T. gondii infection.
The life cycle of
T. gondii is relatively complex, and its antigenic component can change in specificity or makeup during different development stages; therefore, the newly synthesized multiepitope antigen is one of the most promising antigens for the development of effective diagnostic reagents or vaccines [
4-
9]. However, the study of epitope-based vaccines and diagnostic reagents is highly dependent on the accurate identification of B-cell epitopes and T-cell epitopes. Therefore, the identification of protein epitopes will be very important for diagnostic purposes and for the development of peptide vaccines [
10-
12].
Among dense granule antigens (GRAs), GRA6 was also demonstrated to be useful for designing novel and alternative diagnostic methods for toxoplasmosis or vaccines [
13-
17]. The
gra6 gene does not contain any introns and is a single copy in the genome of
T. gondii. It encodes a 32-kDa secreted protein. GRA6 localized in the dense granules and in the parasitophorous vacuole closely associated to the network. GRA6 plays an important role in the pathogenicity of
T. gondii [
18] to date.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Serum samples
A total of 51 T. gondii-positive sera samples previously collected from pigs (n=32) experimentally infected with the Gansu Jingtai strain (isolated from a pig with acute toxoplasmosis) in our laboratory were evaluated in this study. The experimental protocol was approved by the Ethical Committee of the Lanzhou Veterinary Research Institute, Chinese Academy of Agricultural Sciences, China. Twelve pig serum samples were collected at the time of presentation of clinical symptoms (G1), 18 follow-up samples were collected on days 14 to 35 after the onset of symptoms (G2), and 21 samples were collected on days 60 to 120 after the onset of symptoms (G3). The presence of Toxoplasma IgM and IgG antibodies was determined by T. gondii lysate antigen-ELISA. The G1 and G2 samples were positive for IgM and IgG against T. gondii. The G3 samples were positive for IgG against T. gondii. Ten serum samples negative for T. gondii IgM and IgG were used as controls.
Amplification, cloning, and sequencing of the GRA6 gene
The complete GRA6 gene sequence was obtained as described by Wang et al. [
12].
T. gondii DNA was obtained from Gansu Jingtai strain tachyzoites using the Universal Genomic DNA Extraction kit (TaKaRa Biotechnology Co., Ltd, Dalian, China), and the GRA6 sequence was amplified using the primers 5´-GCGAATTCATGGCACACGGTGGCATCT-3´ and 5´-ATGCGGCCGCTTAAAAATCAAACTCATTC-3´. The PCR amplification was performed using the TaKaRa TaqTM kit according to the manufacturer’s instructions. The sample was subjected to an initial denaturation (94°C for 5 min), 35 cycles of denaturation (94°C for 1 min), annealing (60°C for 30 sec) and elongation (72°C for 1 min), and a final extension at 72°C for 10 min. The PCR-generated fragment was purified and cloned into the pMD-18T vector (TaKaRa Biotechnology). The recombinant plasmid was used to transform
Escherichia coli JM 109 competent cells, and the recombinant cells were selected on LB plates with ampicillin (100 mg/L), X-Gal (5-bromo-4-chloro-3-indolyl-β-D-galactopyranoside; 70 mg/L), and IPTG (isopropyl β-D-thiogalactopyranoside; 80 μM) at 37°C for 24 hr (ampicillin, X-Gal and IPTG were from TaKaRa Biotechnology). Positive colonies were inoculated into LB liquid medium containing ampicillin (100 mg/L) and incubated at 37°C for 16 hr. The recombinant plasmid was extracted using a Plasmid Purification kit (TaKaRa Biotechnology). The positive colonies identified by PCR were sequenced by TaKaRa Biotechnology.
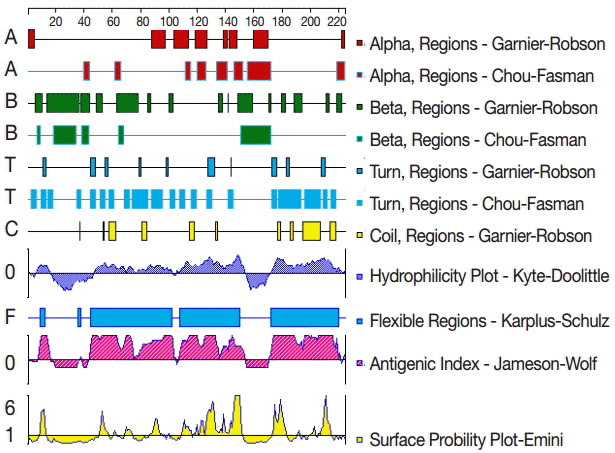
To analyze the GRA6 B cell epitopes, the deduced amino acid sequence of GRA6 was analyzed using the PROTEAN subroutine in the DNASTAR software package. This subroutine uses the Garnier-Robson [
20] and Chou-Fasman [
21] algorithms for predicting the alpha, beta, and turn regions, the Garnier-Robson algorithm for predicting the coil regions, the Kyte-Doolittle [
22] algorithm for predicting hydrophilicity, the Karplus-Schultz [
23] algorithm for predicting flexibility, the Emini [
24] algorithm for predicting surface probability, and the Jameson-Wolf [
25] algorithm for predicting antigenicity. Based on this analysis, the peptides with good hydrophilicity, high accessibility, high flexibility, and strong antigenicity were selected as the antigen epitopes. These peptides were chemically synthesized by GL Biochem Ltd (Shanghai, China). The peptide sequences are shown in
Table 1.
Enzyme-linked immunoassays specific for each peptide were performed as described by Cardona et al. [
26] with minor modifications. The microplates were coated with 100 μl (10 µg/ml) of each peptide diluted in carbonate buffer, pH 9.6 (Na
2CO
3: 0.159 g/100 mL; NaHCO
3: 0.293 g/100 ml). The plates were incubated for 1 hr at 37°C, then for 48 hr at 4°C, and 1 hr at 37°C. Non-specific ligand sites were blocked with 100 μl 2% casein phosphate buffer for 1 hr at 37°C. The plates were washed and incubated with 100 μl serum diluted to 1:100 in 5% casein phosphate buffer for 1 hr at 40°C. After washing, 100 μl rabbit anti-pig peroxidase-conjugated IgG (Sigma) diluted to 1:4,000 in 6% casein phosphate buffer was added for 20 min at 37°C. After the washes, the horseradish peroxidase activity was detected using TMB for 30 min at 37°C and stopped with a 5% H
2SO
4 solution. ELISA experiments were repeated twice. The absorbance of duplicates for each serum sample was measured at 450 nm. A positive cut-off point was determined by estimating the mean average absorbance of 10 negative controls plus 2 SDs.
To determine the specificity of the anti-peptide antibody, ELISA using irrelevant peptides from the BL21 of the orf virus previously synthesized by our laboratory (sequence: VDVQSKDKDADELRE) was also performed as described above. As controls, ELISA using excretory/secretory antigen (ESA) and recombinant GRA6 from the RH strain of T. gondii previously expressed by our laboratory was also performed as described above, with minor modifications. Briefly, non-specific ligand sites were blocked with 100 μl 5% BSA phosphate buffer. Pig sera were diluted 1:100 in PBS and used as the primary antibody. The rabbit anti-pig peroxidase-conjugated IgG diluted 1:8,000 in PBS was used as the secondary antibody.
RESULTS
The secondary structure of GRA6 was predicted by the Garnier-Robson and Chou-Fasman algorithms based on the sequence of the GRA6 gene. A flexibility plot, hydrophilicity plot, surface probability plot, and antigenic index for GRA6 were obtained using the Karplus-Schulz, Kyte-Doolittle, Emini, and Jameson-Wolf algorithms, respectively (
Fig. 1). Based on the results obtained with these methods, potential B cell epitopes on GRA6 were predicted, including 1-20 aa, 44-63 aa, 54-73 aa, 64-83 aa, 74-93 aa, 84-103 aa, 172-191 aa, 182-201 aa, 192-211 aa, and 202-221 aa.
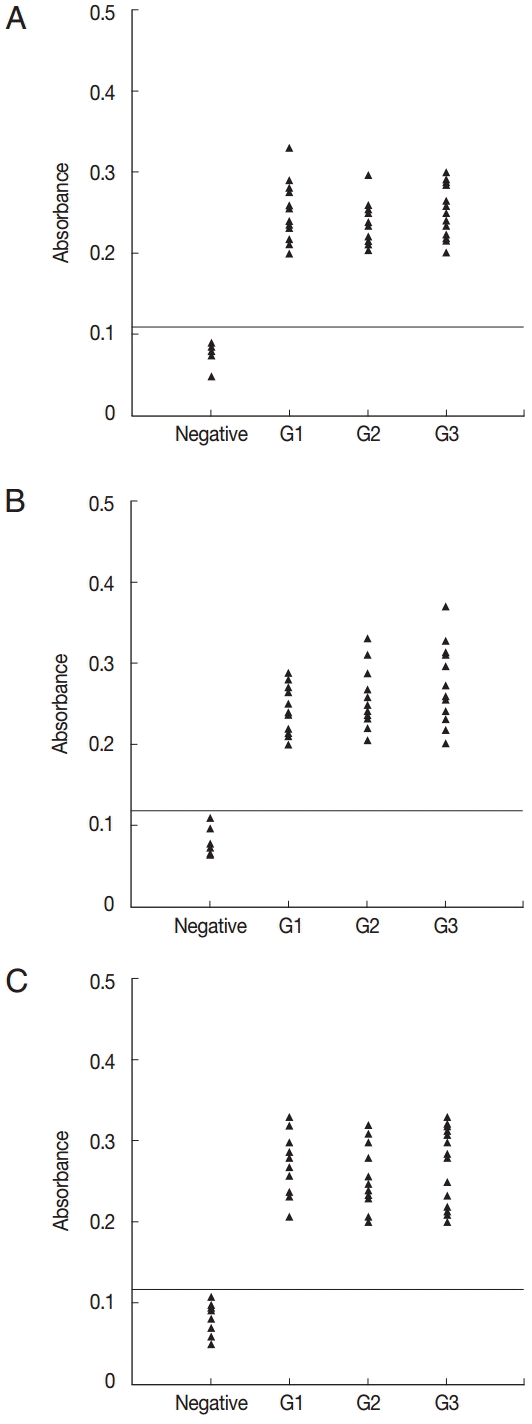
All of the 10 predicted epitope peptides were evaluated by ELISA using pig sera from various time points after infection. P2, P7, and P9 were recognized by all sera. The results of ELISA for 3 peptides, P2, P10, and P11, are shown in
Fig. 2. For each of the 3 peptides, no significant differences were found between the mean absorbances of the 3 groups (G1, G2, and G3) as determined by ANOVA. Furthermore, no significant differences were found between the mean absorbances of the 3 peptides, P2, P7, and P9. The other 7 peptides were recognized by selection of sera from various time points after infection (
Fig. 3). The number of positive samples/tested for each peptide was as follows: P1:8/51, P3:25/51, P4:18/51, P5:9/51, P6:27/51, P8:20/51, and P10:31/51.
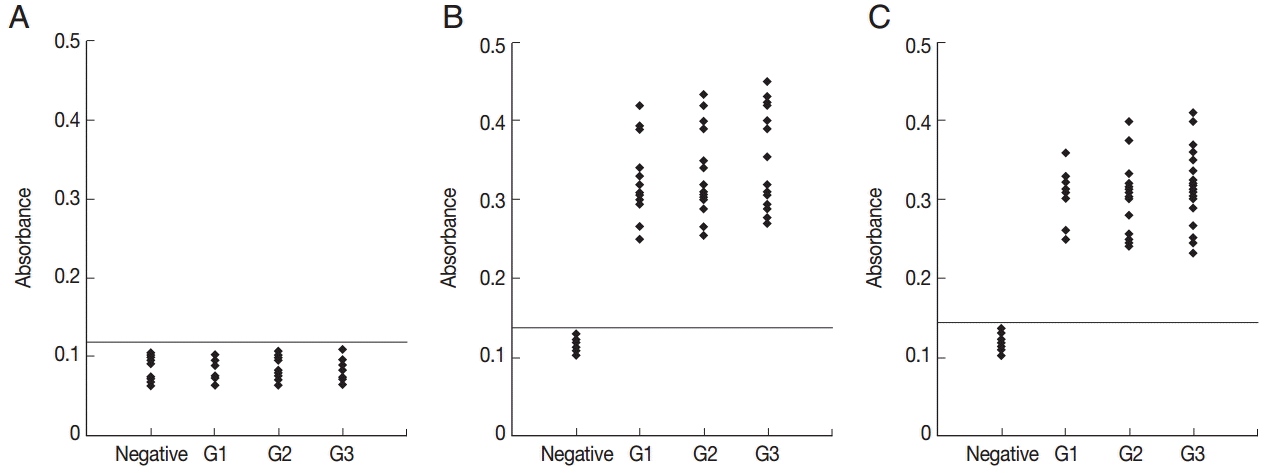
To determine the specificity of the anti-peptide antibody, ELISA using an irrelevant peptide was also performed. This peptide did not react with the sera (
Fig. 4A). To compare the serological reactivity of the peptides with ESA and recombinant GRA6, ELISA using ESA and recombinant GRA6 was also performed. A total of 51 serum samples reacted with ESA (
Fig. 4B) and recombinant GRA6 (
Fig. 4C).
DISCUSSION
The adoption of immunoinformatics methods for the prediction of antigenic epitopes has become an indispensable tool for epitope localization. These methods can reduce the blindness and improve the accuracy of epitope identification. In addition, such techniques are economical and effective and can substantially reduce experimental costs. Bioinformatics has been widely used in the analysis of protein epitopes [
10-
12]. In the present study, the secondary structure of GRA6 was predicted by the Garnier-Robson and Chou-Fasman algorithms based on the sequence of the GRA6 gene. A flexibility plot, hydrophilicity plot, surface probability plot, and antigenic index for GRA6 were obtained using the Karplus-Schulz, Kyte-Doolittle, Emini, and Jameson-Wolf algorithms, respectively. The variability, fragment mobility, and hydrophilicity are important features of antigenic epitopes. The existence of flexible regions, such as coil and turn region, provides powerful evidence for epitope identification [
27].
In the past, several experimental techniques were developed for mapping antibody interacting residues on an antigen, including the identification of interacting residues from the structure of antibody-antigen complexes. Synthetic peptide technique is a popular approach, which primarily identifies sequential epitopes [
28]. Many researchers have applied this technique to study epitopes [
6,
10-
12,
26,
29]. Using this technique and bioinformatics tools, we found that many regions of GRA6, particularly the regions represented by peptides P2, P7, and P9, are involved in the pig antibody response, and strong reactivity with the
T. gondii-infected pig sera was observed. The reactivity of these epitopes does not seem to be dependent upon the time of infection. The identification of B cell epitopes is important for understanding antigenic structure and parasite-antibody interactions at the molecular level and may assist in the design of vaccines and diagnostic reagents.
Many tools for identifying and predicting B cell epitopes have been developed previously [
28]. Conformational epitope selection relies on the determination of the tertiary structure of an antigen to identify residues that interact with antibodies. The experimental techniques required to determine the tertiary structure of the antigen, such as crystallography, are expensive and time-consuming, and the mapping of conformational epitopes has been severely hampered. The majority of methods and databases have focused on the identification of linear epitopes [
30]. In the present study, linear epitopes were analyzed using synthetic peptide techniques and bioinformatics tools, and 3 of the 10 predicted epitope peptides were confirmed by synthetic peptide techniques. The use of a molecular biology method in combination with a bioinformatics method is a useful method to screen for linear epitopes.
We have precisely located the epitopes of T. gondii GRA6 using pig sera collected at different time points after infection. The identification of specific epitopes targeted by the host antibody response is important both for understanding the natural response to infection and for the development of epitope-based vaccines and diagnostic methods. The identification of B cell epitopes is an attractive area of study. There are more linear and conformational B cell epitopes than previously predicted; therefore, the number of identified epitopes should also increase with further studies.
Notes
-
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
This study was supported by grants from the Natural Science Foundation of Gansu Province, China (no. 145RJZA234).
Fig. 1.The secondary structures, flexibility, hydrophilicity, surface probability, and antigenicity index for T. gondii GRA6. The alpha, beta, and turn regions were predicted by Garnier-Robson and Chou-Fasman algorithms, respectively. The coil regions were predicted by Garnier-Robson algorithm. The hydrophilicity, flexibility, surface probability, and antigenicity were predicted by Kyte-Doolittle, Karplus-Schultz, Emini, and Jameson-Wolf algorithms, respectively. Based on this analysis, the peptides with good hydrophilicity, high accessibility, high flexibility, and strong antigenicity were selected as the antigen epitopes.
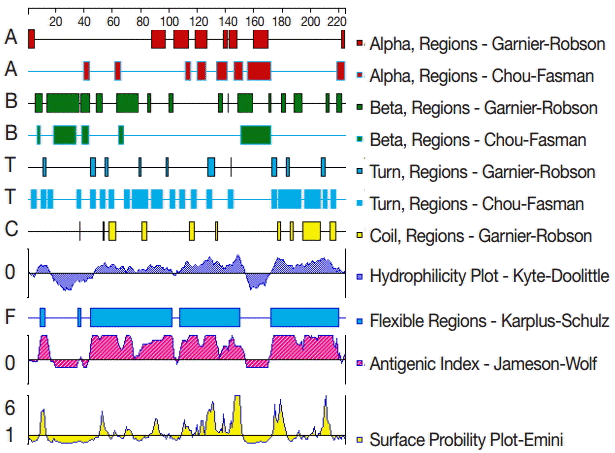
Fig. 2.ELISA of IgG antibodies against different peptides in the 4 groups of pig sera, showing the absorbances targeting P2 (A), P7 (B), and P9 (C), respectively. The cut-off point for the assay is indicated by the horizontal line. G1, Serum samples collected at the time of presentation of clinical symptoms; G2, Serum samples collected on days 14 to 35 after the onset of symptoms; G3, Serum samples collected on days 60 to 120 after the onset of symptoms.

Fig. 3.ELISA of IgG antibodies against different peptides in the 4 groups of pig sera, showing the absorbances targeting P1 (A), P3 (B), P4 (C), P5 (D), P6 (E), P8 (F), and P10 (G), respectively. The cut-off point for the assay is indicated by the horizontal line. G1, Serum samples collected at the time of presentation of clinical symptoms; G2, Serum samples collected on days 14 to 35 after the onset of symptoms; G3, Serum samples collected on days 60 to 120 after the onset of symptoms.

Fig. 4.ELISA of IgG antibodies against an irrelevant peptide (A), ESA (B), and recombinant GRA6 (C) in the 4 groups of pig sera. The cut-off point for the assay is indicated by the horizontal line. G1, Serum samples collected at the time of presentation of clinical symptoms; G2, Serum samples collected on days 14 to 35 after the onset of symptoms; G3, Serum samples collected on days 60 to 120 after the onset of symptoms.
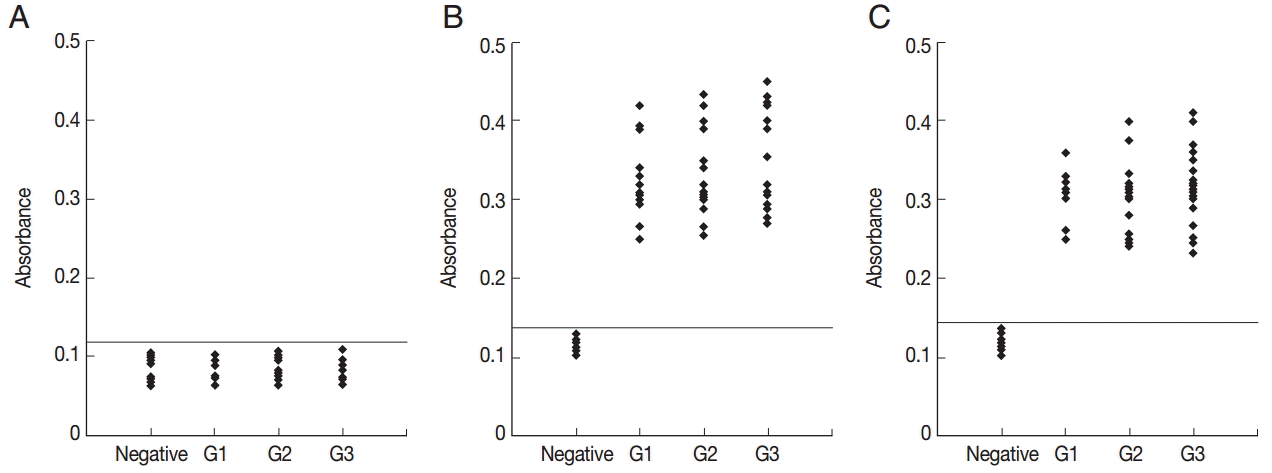
Table 1.Sequences of synthesized peptides
Table 1.
|
Peptides |
Start and end position |
Sequence |
|
P1 |
1-20 aa |
MAHGGIYLRQKRNFCPLTVS |
|
P2 |
44-63 aa |
ADSGGVRQTPSETGSSGGQQ |
|
P3 |
54-73 aa |
SETGSSGGQQEAVGTTEDYV |
|
P4 |
64-83 aa |
EAVGTTEDYVNSSAMGGGQG |
|
P5 |
74-93 aa |
NSSAMGGGQGDSLAEDDTTS |
|
P6 |
84-103 aa |
DSLAEDDTTSDAAEGDVDPF |
|
P7 |
172-191 aa |
RRTGRRSPQEPSGGGGGNDA |
|
P8 |
182-191 aa |
PSGGGGGNDAGNNAGNGGNE |
|
P9 |
192-211 aa |
GNNAGNGGNEGRGEGGEDDR |
|
P10 |
202-221 aa |
GRGEGGEDDRRPLHPGSVNE |
References
- 1. Dubey JP, Baker DG, Davis SW, Urban JF, Shen SK. Persistence of immunity to toxoplasmosis in pigs vaccinated with a non-persistent strain of Toxoplasma gondii. Am J Vet Res 1994;55:982-987.
- 2. Ortega-Pacheco A, Acosta-Viana KY, Guzman-Marin E, Uitzil-Álvarez B, Rodríguez-Buenfil JC, Jimenez-Coello M. Infection dynamic of Toxoplasma gondii in two fattening pig farms exposed to high and low cat density in an endemic region. Vet Parasitol 2011;175:367-371.
- 3. Wang YH, Zhang DL, Wang GX, Yin H, Wang M. Immunization with excreted-secreted antigens reduces tissue cyst formation in pigs. Parasitol Res 2013;112:3835-3842.
- 4. Cong H, Gu QM, Yin HE, Wang JW, Zhao QL, Zhou HY, Li Y, Zhang JQ. Multi-epitope DNA vaccine linked to the A2/B subunit of cholera toxin protect mice against Toxoplasma gondii. Vaccine 2008;26:3913-3921.
- 5. Darcy F, Maes P, Gras-Masse H. Protection of mice and nude rats against toxoplasmosis by a multiple antigenic peptide construction derived from Toxoplasma gondii P30 antigen. J Immunol 1992;149:3636-3641.
- 6. Godard I, Estaquier J, Zenner L, Bossus M, Auriault C, Darcy F, Gras-Masse H, Capron A. Antigenicity and immunogenicity of P30-derived peptides in experimental models of toxoplasmosis. Mol Immunol 1994;31:1353-1363.
- 7. Wang YH, Wang M, Wang GX, Pang AN, Fu BQ, Yin H, Zhang DL. Increased survival time in mice vaccinated with a branched lysine multiple antigenic peptide containing B- and T-cell epitopes from T. gondii antigens. Vaccine 2011;29:8619-8623.
- 8. Dai JF, Jiang M, Wang YY, Qu LL, Gong RJ, Si J. Evaluation of a recombinant multiepitope peptide for serodiagnosis of Toxoplasma gondii infection. Clin Vaccine Immunol 2012;19:338-342.
- 9. Maksimov P, Zerweck J, Maksimov A, Hotop A, Gross U, Pleyer U, Spekker K, Däubener W, Werdermann S, Niederstrasser O, Petri E, Mertens M, Ulrich RG, Conraths FJ, Schares G. Peptide microarray analysis of in silico-predicted epitopes for serological diagnosis of Toxoplasma gondii infection in humans. Clin Vaccine Immunol 2012;19:865-874.
- 10. Wang YH, Wang GX, Zhang DL, Yin H, Wang M. Screening and identification of novel B cell epitopes of Toxoplasma gondii SAG1. Parasit Vectors 2013;6:125.
- 11. Wang YH, Wang GX, Zhang DL, Yin H, Wang M. Identification of novel B cell epitopes within Toxoplasma gondii GRA1. Exp Parasitol 2013;135:606-610.
- 12. Wang YH, Wang GX, Ou JT, Yin H, Zhang DL. Analyzing and identifying novel B cell epitopes within Toxoplasma gondii GRA4. Parasit Vectors 2014;6:125.
- 13. Golkar M, Shokrgozar MA, Rafati S, Musset K, Assmar M, Sadaie R, Cesbron-Delauw MF, Mercier C. Evaluation of protective effect of recombinant dense granule antigens GRA2 and GRA6 formulated in monophosphoryl lipid A (MPL) adjuvant against Toxoplasma chronic infection in mice. Vaccine 2007;25:4301-4311.
- 14. Lecordier L, Fourmaux MP, Mercier C, Dehecq E, Masy E, Cesbron-Delauw MF. Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assays using the recombinant dense granule antigens GRA6 and GRA1 of Toxoplasma gondii for detection of immunoglobulin G antibodies. Clin Diagn Lab Immunol 2000;7:607-611.
- 15. Hiszczyńska-Sawicka E, Kur J, Pietkiewicz H, Holec L, Gąsior A, Myjak P. Efficient production of the Toxoplasma gondii GRA6, p35 and SAG2 recombinant antigens and their applications in the serodiagnosis of toxoplasmosis. Acta Parasitol 2005;50:249-254.
- 16. Golkar M, Azadmanesh K, Khalili G, Khoshkholgh-Sima B, Babaie J, Mercier C, Brenier-Pinchart MP, Fricker-Hidalgo H, Pelloux H, Cesbron-Delauw MF. Serodiagnosis of recently acquired Toxoplasma gondii infection in pregnant women using enzyme-linked immunosorbent assays with a recombinant dense granule GRA6 protein. Diagn Microbiol Infect Dis 2008;61:31-39.
- 17. Elyasi H, Babaie J, Fricker-Hidalgo H, Brenier-Pinchart MP, Zare M, Sadeghiani G, Assmar M, Pelloux H, Golkar M. Use of dense granule antigen GRA6 in an immunoglobulin G avidity test to exclude acute Toxoplasma gondii infection during pregnancy. Clin Vaccine Immunol 2010;17:1349-1355.
- 18. Lecordier L1, Moleon-Borodowsky I, Dubremetz JF, Tourvieille B, Mercier C, Deslée D, Capron A, Cesbron-Delauw MF. Characterization of a dense granule antigen of Toxoplasma gondii (GRA6) associated to the network of the parasitophorous vacuole. Mol Biochem Parasitol 1995;70:85-94.
- 19. Feliu V, Vasseur V, Grover HS, Chu HH, Brown MJ, Wang J, Boyle JP, Robey EA, Shastri N, Blanchard N. Location of the CD8 T cell epitope within the antigenic precursor determines immunogenicity and protection against the Toxoplasma gondii parasite. PLoS Pathog 2013;9:e1003449.
- 20. Garnier J, Robson B. The GOR method for predicting secondary structures in proteins. In Fasman GD ed, Prediction of protein structure and the principles of protein conformation. New York, USA. Plenum Press; 1989, pp 417-465.
- 21. Chou PY, Fasman GD. Prediction of the secondary structure of proteins from their amino acid sequence. Adv Enzymol 1987;47:45-148.
- 22. Kyte J, Doolittle RF. A simple method for displaying the hydropathic character of a protein. J Mol Biol 1982;157:105-132.
- 23. Karplus PA, Schulz GE. Prediction of chain flexibility in proteins: a tool for the selection of peptide antigens. Naturwissenschaften 1985;72:212-213.
- 24. Emini EA, Hughes JV, Perlow DS, Boger J. Induction of hepatitis A virus-neutralizing antibody by a virus-specific synthetic peptide. J Virol 1985;55:836-839.
- 25. Jameson BA, Wolf H. The antigenic index: a novel algorithm for predicting antigenic determinants. Comput Appl Biosci 1988;181:212-213.
- 26. Cardona N, de-la-Torre A, Siachoque H, Manuel A. Patarroyo Jorge E. Gomez-Marin. Toxoplasma gondii: P30 peptides recognition pattern in human toxoplasmosis. Exp Parasitol 2009;123:199-202.
- 27. Zhang ZW, Zhang YG, Wang YL, Pan L, Fang YZ, Jiang ST, Lu JL, Zhou P. Screening and identification of B cell epitopes of structural proteins of foot-and-mouth disease virus serotype Asia I. Vet Microbiol 2010;140:25-33.
- 28. Frank R. The SPOT-synthesis technique. Synthetic peptide arrays on membrane supports-principles and applications. J Immunol Methods 2002;267:13-26.
- 29. Siachoque H, Guzman F, Burgos J, Patarroyo ME, Marin JEG. Toxoplasma gondii: Immunogenicity and protection by P30 peptides in a murine model. Exp Parasitol 2006;114:62-65.
- 30. Vita R, Zarebski L, Greenbaum JA, Emami H, Hoof I, Salimi N, Damle R, Sette A, Peters B. The immune epitope database 2.0. Nucleic Acids Res 2010;38:D854-D862.