Abstract
To investigate the potential role of transforming growth factor (TGF)-β1 in liver fibrosis during Echinococcus granulosus infection, 96 BALB/c mice were randomly divided into 2 groups, experimental group infected by intraperitoneal injection with a metacestode suspension and control group given sterile physiological saline. The liver and blood samples were collected at days 2, 8, 30, 90, 180, and 270 post infection (PI), and the expression of TGF-β1 mRNA and protein was determined by real-time quantitative RT-PCR and ELISA, respectively. We also evaluated the pathological changes in the liver during the infection using hematoxylin and eosin (H-E) and Masson staining of the liver sections. Pathological analysis of H-E stained infected liver sections revealed liver cell edema, bile duct proliferation, and structural damages of the liver as evidenced by not clearly visible lobular architecture of the infected liver, degeneration of liver cell vacuoles, and infiltration of lymphocytes at late stages of infection. The liver tissue sections from control mice remained normal. Masson staining showed worsening of liver fibrosis at the end stages of the infection. The levels of TGF-β1 did not show significant changes at the early stages of infection, but there were significant increases in the levels of TGF-β1 at the middle and late stages of infection (P<0.05). RT-PCR results showed that, when compared with the control group, TGF-β1 mRNA was low and comparable with that in control mice at the early stages of infection, and that it was significantly increased at day 30 PI and remained at high levels until day 270 PI (P<0.05). The results of this study suggested that increased expression of TGF-β1 during E. granulosus infection may play a significant role in liver fibrosis associated with E. granulosus infection.
-
Key words: Echinococcus granulosus, TGF-β1, Liver fibrosis
INTRODUCTION
Hepatic hydatidosis is a zoonotic disease due to
Echinococcus granulosus infection, which is common in regions with developed animal husbandry. It passes directly through skin erosions and causes liver damage through mechanical pressure and toxic damage to the liver, and it always results in granulomatous immunopathology, liver failure, and splenomegaly [
1]. This is a serious threat to human health. Though surgery combined with drug therapy or comprehensive therapeutic and preventive measures are available for clinical management of hepatic hydatidosis, the overall therapeutic efficiency of these options is not encouraging [
2,
3]. Therefore, development of more effective preventive and therapeutic measures is still the focus of current researches. There is a complex network among the liver cells, inflammatory cells, and cytokines. The study shows that the transforming growth factor, TGF-β1, plays an important role in wound healing after tissue and organ damage and associated with fibrous lesions [
4-
9]. TGF-β1 plays a critical role in liver fibrosis, and its over expression in the liver can cause serious liver fibrosis. However, whether TGF-β1 in hepatic hydatidosis has any association with liver fibrosis has not been studied. In this study, we used
E. granulosus-infected mice as our model and investigated the changes in TGF-β1 expression in serum and liver tissues during liver infection, and found that TGF-β1 expression in
E. granulosus-infected liver is associated with liver fibrosis.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Animal studies
Four-week-old, 10-12 g, female BLAB/C mice were randomly divided into 2 groups with 48 animals in each group, the experimental group infected with E. granulosus and the control group given normal saline. The mice were provided by the Experimental Animal Center of Xinjiang Medical University, Xinjiang, China. All the animal research protocols were approved by the Animal Care and User Committee of Xinjiang Medical University.
Main reagents
Rabbit anti-TGF-β1 antibody was purchased from the Beijing Boosen Biotechnology Co. (Beijing, China). Generic antibodies were purchased from Beijing Chinese fir biological company. Trizol was purchased from Invitrogen (Carlsbad, California, USA). Masson trichrome staining kit was purchased from Fuzhou Maixin Biological Formulation Company (China).
Design and synthesis of primers
The primers used for detection of TGF-β1 mRNA were designed with DNAman software and synthesized by Invitrogen company.
Infection of mice with E. granulosus and collection of samples
The capsule fluids from the fresh sheep liver infected with E. granulosus was collected aseptically by a syringe into 50 ml sterile centrifuge tube, and kept it at room temperature for a while to sediment the protoscolex. The sediments of the protoscolex were collected after rinsing several times with saline. The number, morphology, and the survival rate of the protoscolex were determined by staining with 0.5% Iraqi Red Dyes. The survival rate was determined to be over >90%. The protoscolices were resuspended at 2,000 per ml with normal saline supplemented with 500 U/ml penicillin and 100 μg/ml streptomycin, and used for infection of mice by injecting 0.2 ml of the suspension. The control group was injected with an equal volume of normal saline per mouse.
At days 2, 8, 30, 90, 180, and 270 post infection (PI), the blood samples were collected from the mice by performing retro-orbital blood collection procedures, and the sera were isolated from the blood samples and stored at -80˚C freezer until determination of cytokines by ELISA. After blood collection, the mice were sacrificed by cervical dislocation, and the livers were removed. The part of the livers was placed in 10% formaldehyde solution for more than 24 hr for fixation before histological staining. The remaining parts of the liver was immediately frozen with liquid nitrogen, and kept in -80˚C freezer before isolation of total RNA for real-time fluorescence quantitative PCR (qRT-PCR).
H-E and Masson staining
The fixed liver tissues were paraffin embedded, sectioned, and H-E and Masson stained. The degree of liver fibrosis was graded after observation under a microscope as detailed in
Table 1 [
10].
TGF-β1 levels in serum samples were determined by sandwich ABC-ELISA kit following the protocol provided by the manufacturer. The lowest detection limit of the kit was 5 pg/ml.
Determination of TGF-β1 mRNA by qRT-PCR
Total RNA was extracted from the frozen liver samples and converted to cDNA by reverse transcription kit (Thermo Fisher Scientific Inc., San Jose, California, USA). For determination of TGF-β1 mRNA, we performed qRT-PCR using specific primers and SYBR Green/ROX qPCR Master Mix. We used GAPDH as internal control.
Statistical analysis
Data were expressed as mean±SD, and the statistical significances were analyzed by SPSS 17.0 software. The P-values of less than 0.05 were determined as statistically significant.
RESULTS
Gross anatomical changes in mice infected with E. granulosus
The mice in the experimental group were found to have no abnormal changes in the liver and peritoneal cavity after 2 and 8 days after infection; However, at day 30 PI, the spleen and lymph nodes were enlarged, the intestinal mucosa and liver of the mice appeared to have small amount of fine-grained spine ball tissues, and there were small vesicles in the inoculation area. At day 90 PI, mouse liver lobules and intestinal mucosa appeared to have different sizes of vesicles and clustering, and it was hard to separate from the liver. At day 180 PI, the abdominal adhesions were easily seen, the abdominal cavity and liver E. granulosus vesicles have drastically increased in sizes, and it was hard to separate from the surrounding tissues. The liver was damaged by E. granulosus, as revealed by smaller sizes with grey red color. At day 270 PI, the lesions were all over the liver, the liver was almost completely eroded, and the surrounding liver tissue was not clear. At this time, the infection in the liver was easily seen to be infiltrated into the chest cavity. The control group mouse liver showed no E. granulosus vesicle tissues, and the color of the liver was bright red.
Pathological changes in livers of mice infected with E. granulosus
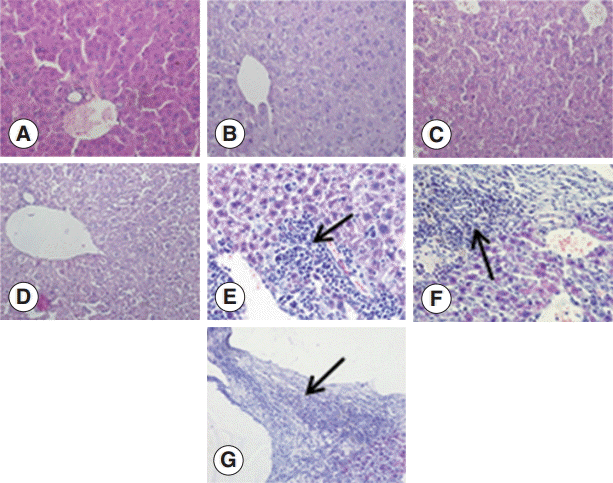
To investigate the changes in the livers after infection in detail, we examined the liver sections after staining with H-E. The structure of the liver tissue was normal in non-infected mice, and the structure of hepatic leaflets was complete. The boundary of the liver cells was clear, and the arrangement was neat with no inflammatory cell invasion. In contrast, the infected mice livers showed differences in changes at different time points after infection. At the early infection stages (days 2 and 8 PI), the liver cells were arranged in neat, clear boundary, and there was no obvious changes. At day 30 PI, the infiltration of inflammatory cells was increased, and at day 90 PI, the infiltration of inflammatory cells further aggravated. There could be seen proliferation of the bile duct, necrosis of hepatocytes, and proliferation of liver cells. At day 180 PI, the formation of fibrous capsule wall of
E. granulosus was easily seen. Also, the proliferation of fibroblast cells and infiltration of inflammatory cells in the periphery of the capsule wall and structural damage of hepatic leaflets were visible. In fibrous connective tissues and the
E. granulosus cyst wall adjacent to the visible band of inflammatory cells, sometimes granuloma nodules were seen. At day 270 PI, the hepatic portal area contained diffused fibrous hyperplasia, fibrosis, and fibrous tissue around the liver cells. Necrosis of the liver tissue and
E. granulosus cyst wall could be seen (
Fig. 1).
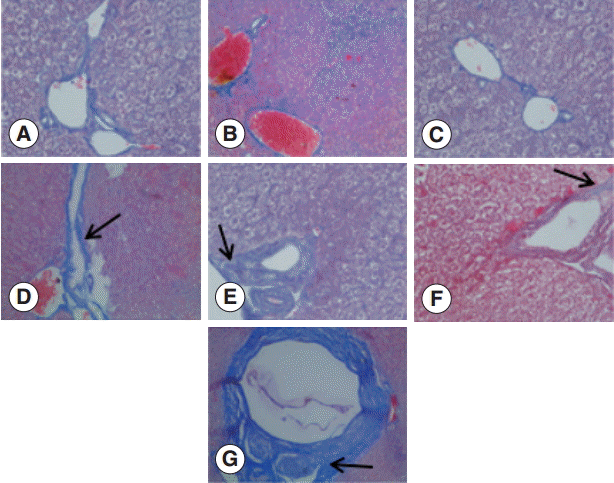
The collagen in the livers of the control group was mainly located in the portal area and central vascular wall with small quantity. In contrast, the collagen staining in the livers of the experimental group was significantly increased compared with the control group mainly in the periportal fibrous tissue hyperplasia, Di's gap,
E. granulosus cyst wall, granuloma, and around the calcification and necrosis tissues. It was distributed as cords or patches. The degree of hepatic fibrosis gradually increased with the extension of the infection time. At days 2 and 8 PI, there were no obvious changes in the collagen content, but at day 30 PI, the portal area and central vascular wall showed a small blue collagen, and at day 90 PI the liver collagen fibers were seen around hydatid cysts, surrounded by the calcification and necrosis tissues. At day 180 PI, the findings included the emergence of a large number of collagen fibers in the portal area and concentric fibrosis changes around the bile duct; the degree of fibrosis was increased with the development of the disease course, and a small amount of fibrosis tissue extended to the leaflets (
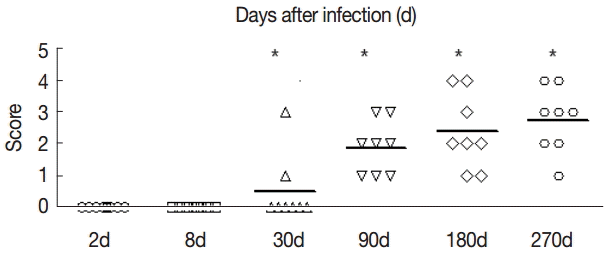
Fig. 2). Hepatic fibrosis grading was shown in
Fig. 3.
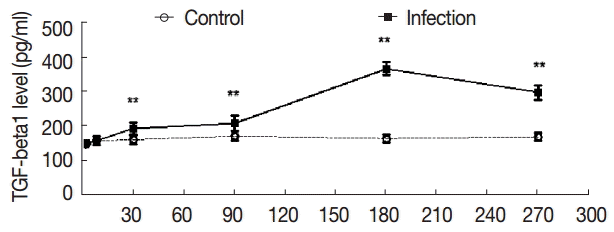
The serum levels of TGF-β1 in the control group were not high compared with the control group, and the serum levels of TGF-β1 were not significantly changed in the experimental group from day 2 to day 8 (t
2d=-0.353, p
2d=0.730; t
8d=-0.237, p
8d=0.816); The levels of TGF-β1 were elevated at day 30 PI (t
30d=-4.161, p
30d=0.001). At day 180 PI, the serum levels of TGF-β1 reached the peak in the experimental group (t
180d=-25.709, p
180d=0.000), and at day 270 PI, the serum levels of TGF-β1 were sustained, and the difference was statistically significant (t
270d=-14.900, p
270d=0.000) (
Fig. 4).
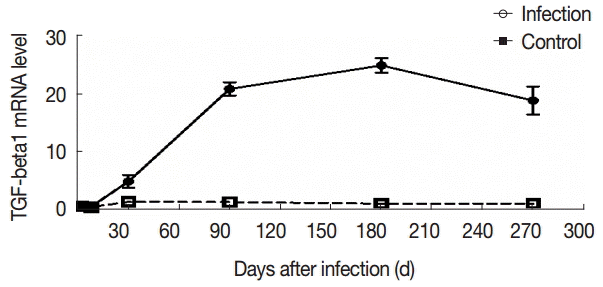
To further evaluate the changes in TGF-β1 in local areas, we determined the transcript levels of TGF-β1 in the liver samples of mice infected with
E. granulosus. Compared with the control group, there were no significant changes in the expression of TGF-β1 mRNA in the liver of the infected mice at days 2 and 8 PI (t
2d=-1.821, p
2d=0.090; t
8d=-1.972, p
8d=0.069). However, the expression of TGF-β1 mRNA was increased significantly after day 30 PI (t
30d=-17.984, p
30d=0.000), and this level was sustained at days 90 and 180 PI (t
90d=-5.555, p
90d=0.000; t
180d=-5.900, p
180d=0.000). The expression of TGF-β1 mRNA was decreased at day 270 PI, but the expression was significantly increased compared with the control group (t
270d=-3.672, p
270d=0.003) (
Fig. 5).
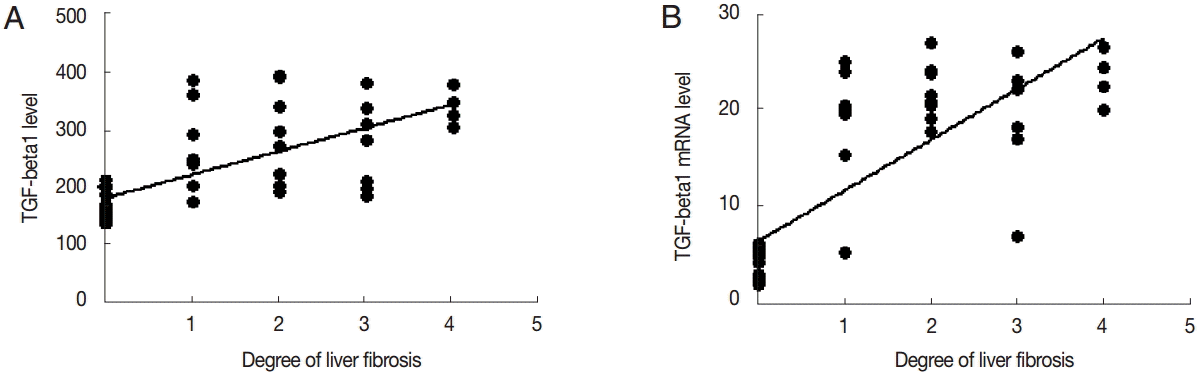
TGF-β1 levels in the serum was positively correlated with the degree of liver fibrosis (
r=0.478,
P<0.01). The expression level of TGF-β1 mRNA was positively correlated with the degree of liver fibrosis (
r=0.644,
P<0.01) (
Fig. 6).
DISCUSSION
The common causes of liver fibrosis are ethanol, ischemia, parasites, HBV and HCV virus infections, autoimmune disease, non-alcoholic fatty liver disease, drug toxicity, and liver toxin and other factors. These factors induce liver cell damage, which leads to changes in liver cells and accumulation of inflammatory cells in the damaged liver. The inflammatory cells activate and release large amounts of cytokines and soluble factors. The sustained inflammation in the liver will lead to liver fibroblast activation, differentiation, and proliferation, followed by liver fibrosis [
11-
14]. Liver fibrosis affects the function of the liver, and further development can lead to cirrhosis and even liver failure and liver cancer. The early liver fibrosis is reversible, but cirrhosis is essentially irreversible. Therefore, it is important to prevent and treat liver fibrosis at its early stage. After parasitizing the host’s organs, the parasite cysts (internal capsule) grow in size, and enlarged parasite cysts press the surrounding tissues and organs which will lead to infiltration of inflammatory cells, proliferation of fibroblasts, and continuous fibrosis. As a consequence, enlarged cyst formation occurs without clear boundaries with surrounding tissues [
15,
16]. The studies showed that TGF-β1 is a multifunctional cytokine and involved in many biological processes, such as tumor development, inflammatory cell differentiation, and the development of fibrosis and tissue repairs [
17,
18]. Herbert et al. [
19] found that TGF-β and IL-10 can protect the liver by inhibition of liver inflammation in acute stages of liver diseases. TGF-β1 levels in diseased tissues and organs will improve greatly, especially in the areas with fiber lesions. If exogenous TGF-β1 used for laboratory animals, it will lead to fibrosis in tissues and organs and then causes excessive deposition of extracellular matrices. In experimental treatment of anti-TGF-β1, it can suppress the formation of fibrosis. It is proved that TGF-β1 is the major factor in regulation of the development of liver fibrosis, and accumulation of TGF-β1 is closely related with liver fibrosis [
20]. Therefore, understanding the dynamic changes and role of TGF-β1 in the development of liver fibrosis is critical for understanding the mechanisms of liver fibrosis and its therapy. However, the role of TGF-β1 and its changes in the liver during
E. granulosus infection has not been addressed.
Our results demonstrated that infection of the liver with E. granulosus increased TGF-β1 mRNA and protein expressions in liver tissues and elevated the levels of expression correlated with the development of parasitic cysts in the liver and liver fibrosis. Therefore, our data provided the first evidence of increased liver TGF-β1 and its association with liver fibrosis in an animal model of E. granulosus infection. In this study, we also established a mouse model to study the pathological changes of the liver and dynamic changes of TGF-β1 in cystic echinococcosis-induced fibrosis in the liver. Masson staining showed that the liver fibrosis got worse when the infection lasted. Liver tissue immunohistochemical staining and blood serum ELISA for TGF-β1 showed increased expression levels of TGF-β1 in E. granulosus-infected BALB/c mice, particularly around the granulomas, parasite-surrounding liver cells, fibroblasts, and sinusoidal endothelial cells in the late stage of infection. It might indicate that, in the middle and late stages of infection, TGF-β1 can activate hepatic stellate cells and promote liver fibrosis accompanied with inflammatory infiltration of neutrophils and fibroblasts. Meanwhile, with the growth of hydatids, severe inflammatory responses occurred around the fibrous layer, separated from host organs. This can effectively avoid the host immune responses, and it is beneficial to the growth and erosion of the parasite.
The results of this study showed that the expression of TGF-β1 mRNA began to increase after day 90 PI. TGF-β1 mRNA in the liver tissue was significantly higher and reached the peak in the late infection stage (days 180 and 270 PI). It is indicated that, at the transcriptional level, TGF-β1 in the middle and late stages of
E. granulosus infection is highly expressed. At the same time, the correlation analysis showed that TGF-β1 mRNA expression has some relation with
E. granulosus infection and liver fibrosis, which suggests that TGF-β1 is a multifunctional cytokine, which can promote the cell proliferation and behaves as inflammatory mediators. It may be one of the important initiating factors of liver fibrosis [
21]. Based on extensive research in the future, if we could predict the levels of cytokines as auxiliary indices in the diagnosis of liver fibrosis, it is worth to further study the expression levels and its predictive values in diagnosis of liver fibrosis.
This study showed that the mouse model of E. granulosus infection can lead to liver fibrosis, and the level of TGF-β1 in the middle and late stages of infection is highly expressed and positively correlated with liver fibrosis. This reminds that anti-TGF-β1 therapy may benefit the treatment of E. granulosus infection, but it also requires in depth studies involved with patients with cystic hydatid infection. The findings from such studies will lead to development of more favorable treatment options in neutralizing the effect of TGF-β1 and ultimately improve the patient's quality of life and survival time.
Notes
-
We have no conflict of interest related to this work.
This work was supported by grants from Chinese National Natural Science Foundation (nos. 81260253, 31160194, 30960358, 81160378, 81160200, 31000411, and 81060135).
Fig. 1.Pathological changes of Echinococcus granulosus-infected mouse livers. (A) H-E staining of liver tissues of a control mouse. (B-G) H-E staining of E. granulosus-infected mice at days 2 (B), 8 (C), 30 (D), 90 (E), 180 (F), and 270 (G). (E) Arrow indicates proliferation of the bile duct, necrosis of hepatocytes, and proliferation of liver cells. (F) Arrow shows the formation of fibrous capsule wall and E. granulosus cyst wall. (G) Arrow indicates the hepatic portal area containing diffuse fibrous hyperplasia, fibrosis, and fibrotic tissues around the liver cells. ×400 for all the panels.
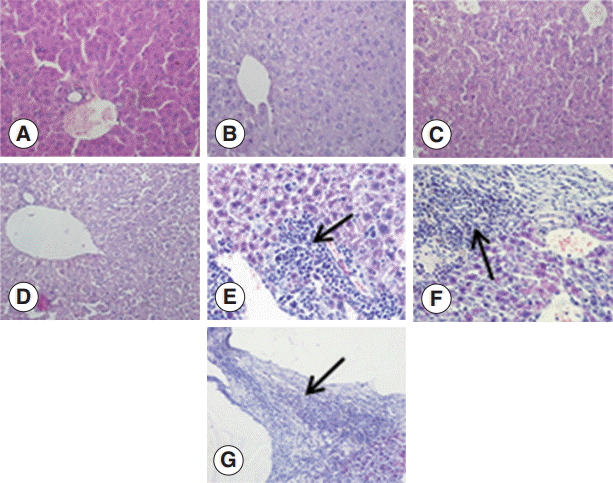
Fig. 2.Changes in liver fibrosis after infection of mice with E. granulosus. (A) Masson staining of the livers of a control mouse. (B-G) Masson staining of the livers of mice infected with E. granulosus at days 2 (B), 8 (C), 30 (D), 90 (E), 180 (F), and 270 (G). (D) Arrow shows the formation of a small blue collagen. (E) Arrow indicates liver collagen fibers around hydatid cysts. (F) Arrow shows the emergence of a large number of collagen fibers in the portal area and concentric fibrosis changes around the bile duct. (G) Arrow indicates the concentric fibrosis changes around the bile duct and a small amount of fibrotic tissues extended to the leaflets. ×400 for all the panels.

Fig. 3.The fibrosis ratings of the livers of infected mice by Masson dye staining. The liver tissue was collected at days 2, 8, 30, 90, 180, and 270 after infection. Significant differences were noted between the infection group and the control group (P<0.05).
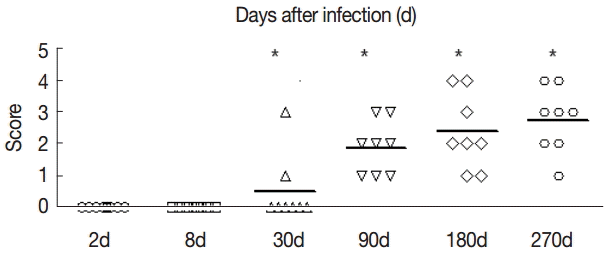
Fig. 4.Dynamic changes of serum concentrations of TGF-β1 (pg/ml). Mouse sera were collected at different time points after infection as indicated, and the levels of TGF-β1 were detected by ELISA. Quantitative results were shown. **P<0.01, between the experimental group and the control group.
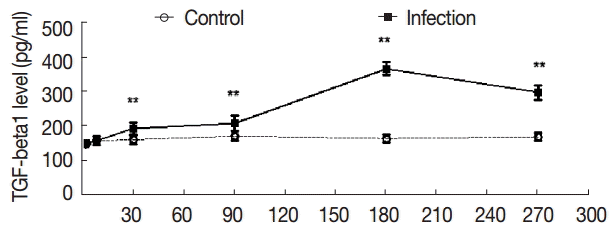
Fig. 5.The changes in mRNA expression of TGF-β1 in liver tissues of mice infected with E. granulosus. The amount of TGF-β1mRNA was measured in the liver tissues from infected and uninfected control mice by qPCR at different time points. Quantitative results were shown. P<0.01, between the experimental group and the control group.
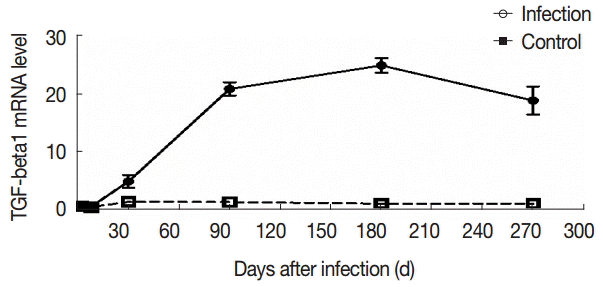
Fig. 6.Correlation analysis of TGF-β1 expression and liver fibrosis. Correlation analysis of serum TGF-β1 (A) or liver TGF-β1 mRNA expression (B) and hepatic fibrosis.
Table 1.Grading criteria for hepatic fibrosis stages
Table 1.
|
Score |
Fibrosis degree |
|
0 |
No fibrosis |
|
1 |
Fibrous connective tissue is confined to the portal area or the portal area to expand, lobular development tendency |
|
2 |
Fibrosis connective tissue hyperplasia was significantly more than 2/3 and accompanied by grade 1 Change |
|
3 |
The connective tissue of the fibrosis enters the central venous of the hepatic lobe |
|
4 |
Fibrosis connective tissue multiple diffuse hyperplasia in the whole leaflet, Pseudo leaflet formation, And have the same change with S3 |
References
- 1. Wen H, Wulamu M, Wang H. The echinococcosis learning tutorial. Xinjiang, China. Xinjiang People's Publishing House. 2009. 7:57-63 (in Chinese).
- 2. Leggatt GR, McManus DP. Sequence homology between two immunodiagnostic fusion proteins from Echinococcus multilocularis. Int J Parasitol 1992;22:831-833.
- 3. Ito A. Introduction of ongoing research projects on echinococcosis at Asahikawa Medical College and some comments on the surveillance, prevention and control of alveolar echinococcosis in Japan. Hokkaido Igaku Zasshi 2001;76:3-8.
- 4. Friedman SL. Evolving challenges in hepatic fibrosis. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol 2010;7:425-436.
- 5. Gorelik L, Flavell RA. Transforming growth factor-beta in T-cell biology. Nat Rev Immunol 2002;2:46-53.
- 6. Ray K. Liver: hepatic stellate cells hold the key to liver fibrosis. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol 2014;11:74.
- 7. Kocabayoglu P, Friedman SL. Cellular basis of hepatic fibrosis and its role in inflammation and cancer. Front Biosci (Schol Ed) 2013;5:217-230.
- 8. Tsolaki E, Athanasiou E, Gounari E, Zogas N, Siotou E, Yiangou M, Anagnostopoulos A, Yannaki E. Hematopoietic stem cells and liver regeneration: differentially acting hematopoietic stem cell mobilization agents reverse induced chronic liver injury. Blood Cells Mol Dis 2014;53:124-132.
- 9. Hu X, Rui W, Wu C, He S, Jiang J, Zhang X, Yang Y. Compound Astragalus and Salvia miltiorrhiza extracts suppress hepatocarcinogenesis by modulating transforming growth factor-β/Smad signaling. J Gastroenterol Hepatol 2014;29:1284-1291.
- 10. Zhai W, Wang T, Zhou X. The diagnosis of chronic hepatitis, grading and staging. Chinese Digest Magazine 1996;5:277.
- 11. Gressner OA, Rizk MS, Kovalenko E, Weiskirchen R, Gressner AM. Changing the pathogenetic roadmap of liver fibrosis? Where did it start; where will it go? J Gastroenterol Hepatol 2008;23:1024-1035.
- 12. Friedman SL. Hepatic stellate cells: protean, multifunctional, and enigmatic cells of the liver. Physiol Rev 2008;88:125-172.
- 13. Bataller R, Brenner DA. Liver fibrosis. J Clin Invest 2005;115:209-218.
- 14. Le Bousse-Kerdilès MC, Martyré MC, Samson M. Cellular and molecular mechanisms underlying bone marrow and liver fibrosis: a review. Eur Cytokine Netw 2008;19:69-80.
- 15. Baker RJ, Fischer JE. Mastery of Surgery. 4th ed. Philadelphia, USA. Lippincott Williams and Willkins Inc; 2001, pp 1082-1099.
- 16. Wilson MS, Mentink-Kane MM, Pesce JT, Ramalingam TR, Thompson R, Wynn TA. Immunopathology of schistosomiasis. Immunol Cell Biol 2007;85:148-154.
- 17. Dong C. Th17 cells in development: an updated view of their molecular identity and genetic programming. Nat Rev Immunol 2008;8:337-348.
- 18. Martin-Martin N, Slattery C, McMorrow T, Ryan MP. TGF-β1 mediates sirolimus and cyclosporine A-induced alteration of barrier function in renal epithelial cells via a noncanonical ERK 1/2 signaling pathway. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol 2011;301:1281-1292.
- 19. Herbert DR, Orekov T, Perkins C, Finkelman FD. IL-10 and TGF-β redundantly protect against severe liver injury and mortality during acute schistosomiasis. J Immunol 2008;181:7214-7220.
- 20. Liu X, Hu H, Yin JQ. Therapeutic strategies against TGF-β signaling pathway in hepatic fibrosis. Liver Int 2006;26:8-22.
- 21. Breitkopf K, Lahme B, Tag CG, Gressner AM. Expression and matrix deposition of latent transforming growth factor beta binding proteins in normal and fibrotic rat liver and transdifferentiating hepatic stellate cells in culture. Hepatology 2001;33:387-396.