Abstract
Acanthamoeba keratitis has been increasing in recent years. Main risk factors are contact lens wear and their cleaning solutions. Most contact lens wearers use multipurpose disinfecting solutions (MPDS) for cleansing and disinfecting microorganisms because of its convenience. We determined amoebicidal effects of MPDS made in Korea and their cytotoxicity on human corneal epithelium cells. Fifteen commercial MPDS (A to O) were tested for their amoebicidal effects on Acanthamoeba castellanii trophozoites and cysts by using a most probable number (MPN) technique. Among them, 7 kinds of MPDS showed little or no amoebicidal effects for 24 hr exposure. Solutions A, B, G, H, L, and O showed positive amoebicidal effects, and solutions M and N killed almost all trophozoites and cysts after 24 hr exposure. However, 50%-N solution showed 56% cytotoxicity on human corneal epithelial cells within 4 hr exposure, and 50%-O solution also showed 62% cytotoxicity on human cells within 4 hr exposure. Solution A did not show any cytotoxicity on human cells. These results revealed that most MPDS made in Korea were ineffective to kill Acanthamoeba. The solutions having amoebicidal activity also showed high levels of cytotoxicity on human corneal epithelial cells. New formulations for improved MPDS that are amoebicidal but safe for host cells are needed to prevent Acanthamoeba keratitis.
-
Key words: Acanthamoeba castellanii, multipurpose disinfecting solution (MPDS), cytotoxicity
INTRODUCTION
Acanthamoeba is an opportunistic protozoan pathogen distributed at the environment and can cause granulomatous encephalitis and keratitis [
1]. The recent increased incidence in
Acanthamoeba infection is due to acquired immune deficiency syndrome, while that for keratitis is due to the increased use of contact lenses [
2]. The precise mechanism of
Acanthamoeba keratitis associated with contact lenses is not fully understood, but the use of ineffective lens disinfection systems, homemade saline, tap water, and contamination of lens storage cases have been cited as important risk factors for the disease [
3–
6].
Cleaning and disinfection of contact lenses are essential to avoid lens related infection of the cornea. Contact lens disinfection solutions have an important role in safe contact lens wears. The most popular lens disinfecting products are multipurpose disinfecting solution (MPDS), which are designed for cleaning, disinfecting, rinsing, and storing contact lenses using a single formulation [
7,
8]. Most of these solutions contain polyhexamethylene biguanide (PHMB) or polyquad (polyquaternium-1) [
8,
9]. Santodomingo-rubido et al. [
8] reported that 6 commercially available MPDS showed significantly higher disinfection capabilities against bacterial species. The susceptibility of
Acanthamoeba to contact lens disinfecting solutions was variable depending on the stage of the organism (trophozoite or cyst), type and dilution of disinfecting solution, and length of exposure time [
10]. Most commercially available MPDS are ineffective against
Acanthamoeba, especially the cyst of
Acanthamoeba [
10,
11]. Resistance to biocides during encystation of
Acanthamoeba has been observed [
12].
In addition, these disinfecting agents in MPDS are associated with cytotoxic effects. MPDS induced varying levels of irreversible tissue sensitivity reactions [
9]. Several MPDS showed a progressive dose-dependent increase in cytotoxicity for higher concentrations [
8]. This suggests that the formulations of MPDS need to assess the amoebicidal effects and cytotoxicity, and balance amoebicidal effectiveness with low cytotoxicity.
For foreign made MPDS, several in vitro studies have investigated the amoebicidal effects and cytotoxicity on human cells; however, those of MPDS made in Korea have not yet been reported. The aim of this study was to determine and compare the amoebicidal effects and cytotoxicity on human corneal epithelium cells of 15 kinds of Korean MPDS.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Amoeba cultivation and encystation
Acanthamoeba castellanii Castellani was obtained from the American Type Culture Collection (ATCC 30011) (Rockville, Maryland, USA).
A. castellanii trophozoites were axenically cultured in PYG medium (0.75% proteose peptone, 0.75% yeast extract, and 1.5% glucose) at 25°C incubator.
A. castellanii encystation was induced in an encystation media (0.1 M KCl, 0.008 M MgSO
4, 0.0004 M CaCl
2, and 0.02 M 2-amino-2-methyl-1,3-propanediol pH 9.0) for 3 days [
13]. Mature cysts were counted under a light microscope after treating them with 0.5% SDS, and encystation ratios were calculated [
14].
Determination of amoebicidal activity
All tested MPDS made in Korea and their respective contents are listed in
Table 1. All MPDS were taken from their original wrappings and were used before their stated expiry date. Amoebicidal activity of MPDS was determined using a most probable number (MPN) technique for amoebic enumeration [
15]. Trophozoites or cysts were exposed to 15 MPDS and a control solution (0.9% PAS). Aliquots (0.1 ml) of trophozoite or cyst culture were added to 9.9 ml of each MPDS and control in sterile glass bottles to give initial concentrations of 104 trophozoites or cysts/ml. All bottles were incubated in a 25°C incubator at predefined intervals (0, 4, 8, and 24 hr), and 1 ml aliquots from each MPDS and the control solution were placed in 9 ml of Dey Engley (DE) broth for disinfectant neutralization. These were sealed and incubated at 25°C for 15 min. Seventeen 1-ml aliquots of the one in 10 dilution prepared in DE broth were inoculated onto agar plates covered with heat-killed bacteria. The 6-well tissue culture plates were used for the 1-ml aliquots, and the wells of 12-well plates were used for the 0.1- and 0.01-ml aliquots. All plates were sealed and incubated at 25°C. The plates were examined for the presence of viable trophozoites after 3 and 7 days of incubation. Each MPDS was tested in triplicate against trophozoites and cysts.
Human corneal epithelial (HCE) cells were cultured in endothelial cell growth media kits (KGMTM BulletKitTM) (Lonza, Portsmouth, New Hampshire, USA) in 5% CO2 incubator. Monolayered HCE cells were placed in 96-well plates and incubated with 3 kinds of MPDS or control media in 5% CO2. Cytopathic effects (CPE) were assessed visually after Giemsa staining and measurement of optical density at 590 nm, with 0.1 ml of cells solubilized in 5% SDS. Percent CPE was calculated according to the following formula: % CPE=100 − [(OD of experimental well − OD of HCE alone)/OD of control cells] ×100. The CPE assay was performed in triplicate.
Statistical analysis
Data are expressed as mean±SD in 3 independent experiments. Statistical significance was analyzed using an unpaired Student’s t-test. A P-value of <0.05 was interpreted as statistically significant.
RESULTS
Amoebicidal activity of MPDS
To determine the amoebicidal activity of Korean MPDS, the most probable number (MPN) technique was used. All tested Korean MPDS and their respective contents were listed in
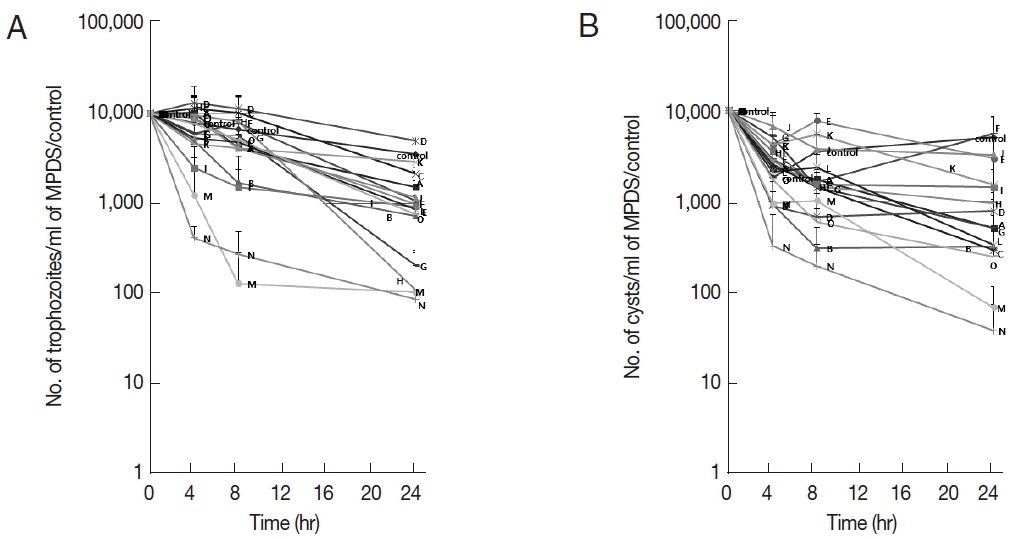
table 1. Fifteen kinds of MPDS and control solution were tested for amoebicidal activity. The average and standard deviation from MPN at 0, 4, 8, and 24 hr of trophozoites and cysts after incubation with MPDS were shown in
Table 2. The trophozoites and cysts MPN average and SD were presented respectively in
Fig. 1. No significant difference was detected between trophozoites and cysts. After an exposure time of 4 hr, solution N showed high amoebicidal activity to trophozoites and cysts. After 8 hr of exposure, solution N and M showed moderate amoebicidal activity to trophozoites (
Fig. 1A). After 24 hr of exposure, solution N and M killed almost all trophozoites and cysts (
Fig. 1A, B). Solutions A, B, G, H, L, and O showed positive amoebicidal effects with 24 hr exposure (
Table 2;
Fig. 1). Especially, solutions G and H showed moderate amoebicidal activity to trophozoites. However, cysts were more resistant to solutions G and H than solutions N and M. Among 15 MPDS made in Korea, solutions N and M showed higher amoebicidal effects to trophozoites and cysts than the others but not enough to eradicate the amoeba.
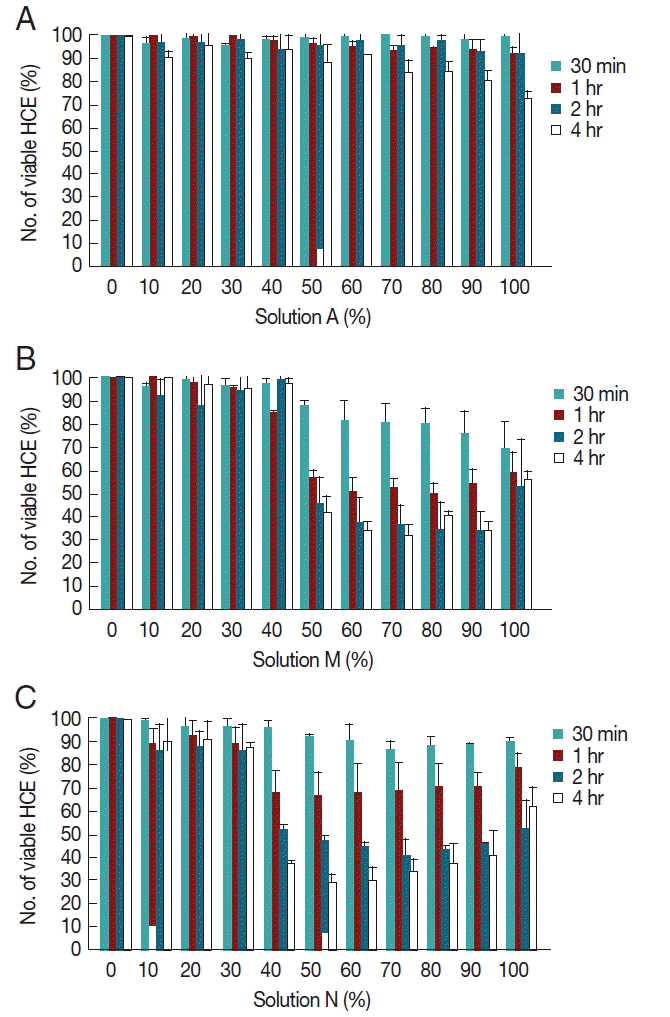
To investigate the cytopathic effects of MPDS which possessed amoebicidal effects, solutions A, N, and M were incubated with human corneal epithelial cells for 30 min, 1 hr, 2 hr, and 4 hr. The concentrations of MPDS were designed so that a linear range of 0% to 100% (
Fig. 2). A few amoebicidals effective MPDS-A was not cytotoxic at any of the concentrations tested (
Fig. 2A). Solution A was cytotoxic for higher concentrations (70–100%) after 4 hr exposure; however, the solution is dilute to appropriate concentrations by eye drops.
Moderate amoebicidal solution M showed 58% cytopathic effects at 50% concentration and 4 hr exposure (
Fig. 2B). Even at 1 hr exposure to 50% diluted solution M, 43% cytopathic effects were shown. The best amoebicidal solution N showed 62% cytopathic effects at 50% concentration and 4 hr exposure, and 32% cytopathic effects at 50% concentration and 1 hr exposure (
Fig. 2C). Both of these solutions M and N showed a time-dependent cytotoxicity towards HCE cells. These results showed that amoebicidal solutions also have various ranges of cytopathic effects against human cells.
DISCUSSION
MPDS have a broad antimicrobial activity and minimal cytotoxicity. We have first evaluated the amoebicidal activity of 15 MPDS made in Korea and their cytopathic effects on human corneal epithelial cells at various concentrations and times. Only 2 of the 15 MPDS (solutions N and M) showed moderate amoebicidal effects (
Table 2;
Fig. 1). However, those amoebicidal MPDS also showed cytopathic effects (
Fig. 2B, C). Both amoebicidal activity and cytotoxicity were closely dependent on the agents used in the formulation of the MPDS. Cytotoxicity of PHMB (polyhexamethylene biguanide) was apparent at 10 ppm during incubation with HCE cells for 30 min [
16], and 0.02% PHMB showed 46% lysis of the HCE cells within 10 min [
17]. The buffering and isotonic agents tested showed various strengths of cytotoxicity, and the surfactant agents also showed various strengths of cytotoxicity [
8].
All tested MPDS in this study and their ingredients are listed in
Table 1. However, the concentrations of their contents are not shown in detail. Different concentrations of PHMB among MPDS seemed to result in various degrees of amoebicidal effects and cytopathic effects.
Table 2 and
Fig. 1 showed no significant differences between trophozoites and cysts. Action mechanisms of PHMB may explain this to kill both
Acanthamoeba trophozoites and cysts by inhibiting the membrane function [
18].
A limitation of this study was that no details of all reagents are mentioned in the manufacturer’s instructions, and all MPDS were not tested yet for their potential cytotoxicity. Amoebic numbers within each control replicate must be confirmed. Currently, MPDS are used widely for cleaning, disinfecting, rinsing, and storing contact lenses, but the amoebicidal activity and cytotoxicity of these solutions have not been determined.
In this report, we investigated that most of the MPDS made in Korea were ineffective or insufficient to kill
Acanthamoeba, and the amoebicidal effective solutions also showed cytotoxicity on human corneal epithelial cells. These results suggested that the development of a new disinfection system with higher amoebicidal effects and a reduced cytotoxicity on HCE cells is needed to prevent
Acanthamoeba keratitis. The development of a more streamlined and commercial solution would be a major step in the future. New combination of autophagy inhibitors or cellulose synthesis inhibitors with low concentration of PHMB were suggested as a potential future treatment [
17,
19].
Notes
-
CONFLICT OF INTEREST
We have no conflict of interest related to this work.
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS
This research was supported by Basic Science Research Program through the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF) funded by the Ministry of Science, ICT & Future Planning (grant no. NRF-2015R1D1A1A01057265).
Fig. 1A most probable number of Acanthamoeba after incubation with 15 kinds of MPDS (solution A- solution O) and control solution. (A) Amoebicidal effects of MPDS on trophozoites. (B) Amoebicidal effects of MPDS on cysts. MPDS N and M showed moderate amoebicidal effects. Values indicate the mean (±SD) of 3 experiments.

Fig. 2Cytopathic effects of MPDS on human corneal epithelial cells. (A) Cytopathic effects of serially diluted MPDS-A on HCE cells for 30 min, 1 hr, 2 hr, and 4 hr exposure. (B) Cytopathic effects of serially diluted MPDS-M on HCE cells for 30 min, 1 hr, 2 hr, and 4 hr exposure. (C) Cytopathic effects of serially diluted MPDS-N on HCE cells for 30 min, 1 hr, 2 hr, and 4 hr exposure. A few amoebicidals effective MPDS-A was not cytotoxic at any of the concentrations tested. However, moderate amoebicidal effective MPDS-M and N showed various strengths of cytopathic effects on HCE cells. Data are expressed as mean±SD in 3 independent experiments.
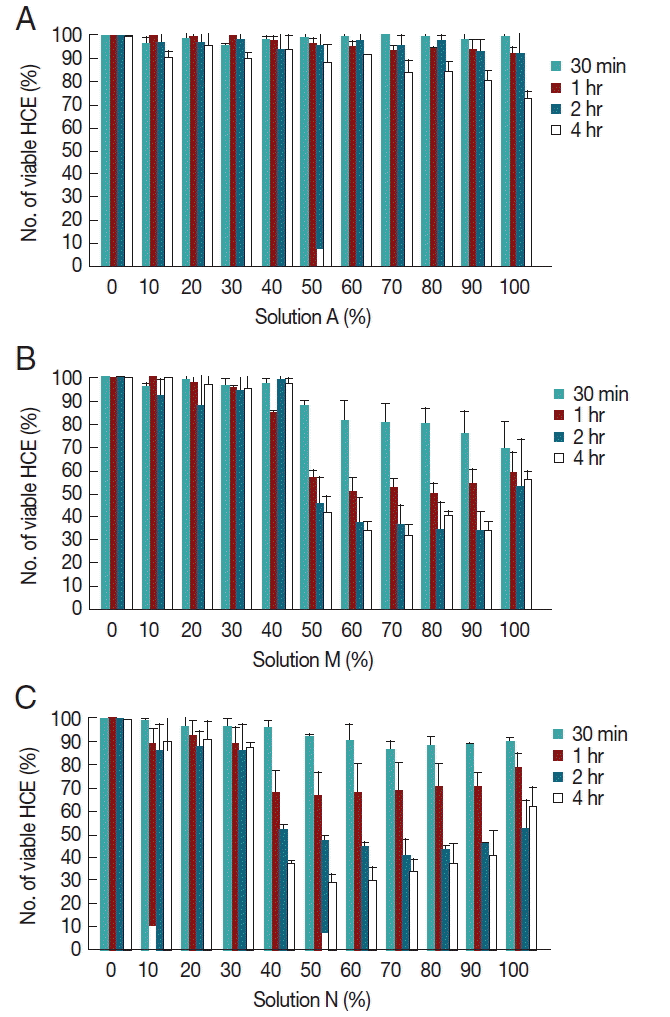
Table 1Ingredients of MPDS and manufacturers
Table 1
|
MPDS |
Manufacturer |
Preservative |
Buffer system |
Cleaning or lubricating agent |
Chelating agent |
Others |
|
A |
H. |
PHMB |
- |
- |
- |
NaCl |
|
B |
H. |
PHMB |
- |
- |
- |
- |
|
C |
M. |
PHMB |
- |
poloxamer 407 |
edetate hydrate (EDTA) |
NaCl |
|
D |
L. |
PHMB |
- |
- |
- |
NaCl, H2O, hydroxypropyl methylcellulose |
|
E |
N. |
-a
|
sodium borate, sodium bicarbonate |
sodium phosphate |
- |
povidone, tetronicselectant1107 |
|
F |
K. |
PHMB |
- |
- |
- |
- |
|
G |
K. |
PHMB |
- |
- |
- |
- |
|
H |
K. |
PHMB |
- |
- |
- |
- |
|
I |
J. |
20% PHMBb
2.5 mg/100 ml |
- |
- |
- |
potassium sorbate 52 mg, sodium hyaluronate 20 mg |
|
J |
J. |
20% PHMB
5 μl/100 ml |
- |
- |
- |
sodium hyaluronate 20 mg/100 ml |
|
K |
J. |
20% PHMB
2.5 mg/100 ml |
- |
- |
- |
potassium sorbate 52 mg |
|
L |
J. |
20% PHMB
0.1 mg/100 ml |
- |
- |
- |
hydroxypropylcellulose 2910 0.1 g |
|
M |
C. |
PHMB |
- |
- |
- |
- |
|
N |
P. |
20% PHMB |
sodium borate, boric acid |
ploxamine 1107 |
disodium edetate hydrate (EDTA-2Na), sodium chloride |
30% etidronic acid tetrasodium, hydroxypropyl methylcellulose |
|
O |
P. |
PHMB 0.00001% |
sodium borate, boric acid, D-sorbitol |
ploxamer 407 |
disodium edetate hydrate (EDTA-2Na), sodium chloride |
hydroxypropylcellulose, H2O |
Table 2
Table 2
|
MPDS |
Avg (SD) count at 0 hr |
Avg (SD) count at 4 hr |
Avg (SD) count at 8 hr |
Avg (SD) count at 24 hr |
|
|
|
|
|
Trophozoites |
Cysts |
Trophozoites |
Cysts |
Trophozoites |
Cysts |
Trophozoites |
Cysts |
|
Control |
10,000 (0) |
10,000 (0) |
7,867 (2136) |
1,800 (557) |
6,633 (2,136) |
3,533 (1,850) |
3,500 (0) |
5,000 (3,593) |
|
|
A |
10,000 (0) |
10,000 (0) |
10,167 (5,380) |
2,300 (557) |
4,133 (1,097) |
1,733 (451) |
1,533 (961) |
500 (0) |
|
|
B |
10,000 (0) |
10,000 (0) |
5,000 (3,593) |
920 (710) |
1,703 (1,633) |
300 (205) |
736.7 (836) |
310 (381) |
|
|
C |
10,000 (0) |
10,000 (0) |
11,400 (3,984) |
2,510 (2,582) |
10,167 (5,380) |
1,400 (954) |
2,133 (2,829) |
287 (189) |
|
|
D |
10,000 (0) |
10,000 (0) |
13,133 (6,772) |
890 (750) |
11,400 (3,984) |
667 (144) |
5,000 (3,593) |
767 (462) |
|
|
E |
10,000 (0) |
10,000 (0) |
8,933 (6,120) |
4,133 (1,097) |
4,767 (1,097) |
7,667 (7,217) |
996.7 (1,223) |
2,917 (2,270) |
|
|
F |
10,000 (0) |
10,000 (0) |
6,000 (2,848) |
2,900 (1,039) |
7,867 (2,136) |
1,607 (1,698) |
1,087 (1,182) |
5,517 (9,082) |
|
|
G |
10,000 (0) |
10,000 (0) |
6,000 (2,848) |
5,083 (4,184) |
5,633 (3,356) |
1,400 (954) |
206.7 (100) |
507 (523) |
|
|
H |
10,000 (0) |
10,000 (0) |
9,600 (7,275) |
2,767 (2,470) |
8,300 (6,736) |
1,437 (1,789) |
110 (101) |
940 (1,268) |
|
|
I |
10,000 (0) |
10,000 (0) |
2,500 (1,732) |
3,533 (1,850) |
1,517 (831) |
1,517 (831) |
933.3 (318) |
1,400 (1,825) |
|
|
J |
10,000 (0) |
10,000 (0) |
8,933 (6,120) |
6,633 (2,136) |
4,133 (1,097) |
3,700 (1,609) |
1,167 (611) |
3,223 (5,094) |
|
|
K |
10,000 (0) |
10,000 (0) |
4,633 (3,868) |
4,133 (1,097) |
4,133 (1,097) |
5,400 (3,700) |
2,900 (557) |
1,503 (1,740) |
|
|
L |
10,000 (0) |
10,000 (0) |
5,367 (3,233) |
2,100 (1,249) |
4,767 (1,097) |
2,333 (1,106) |
863.3 (686) |
327 (369) |
|
|
M |
10,000 (0) |
10,000 (0) |
1,243 (1,955) |
933 (318) |
130 (156) |
1,007 (1,037) |
104 (178) |
67 (45) |
|
|
N |
10,000 (0) |
10,000 (0) |
416.7 (144) |
317 (380) |
273.3 (216) |
190 (137) |
87 (117) |
37 (35) |
|
|
O |
10,000 (0) |
10,000 (0) |
7,700 (7,422) |
1,733 (1,533) |
5,133 (3,453) |
580 (624) |
756.7 (845) |
243 (227) |
References
- 1. Marciano-Cabral F, Cabral G. Acanthamoeba spp. as agents of disease in humans. Clin Microbiol Rev 2003;16:273-307.
- 2. Marciano-Cabral F, Puffenbarger R, Cabral GA. The increasing importance of Acanthamoeba infections. J Eukaryot Microbiol 2000;47:29-36.
- 3. Stevenson RW, Seal DV. Has the introduction of multi-purpose solutions contributed to a reduced incidence of Acanthamoeba keratitis in contact lens wearers? A review. Cont Lens Anterior Eye 1998;21:89-92.
- 4. Stehr-Green JK, Bailey TM, Visvesvara GS. The epidemiology of Acanthamoeba keratitis in the United States. Am J Ophthalmol 1989;107:331-336.
- 5. Seal DV, Kirkness CM, Bennett HG, Peterson M. Keratitis Study Group. Acanthamoeba keratitis in Scotland: risk factors for contact lens wearers. Cont Lens Anterior Eye 1999;22:58-68.
- 6. Houang E, Lam D, Fan D, Seal D. Microbial keratitis in Hong Kong: relationship to climate, environment and contact-lens disinfection. Trans R Soc Trop Med Hyg 2001;95:361-367.
- 7. Stiegemeier MJ, Friederichs GJ, Hughes JL, Larsen S, Movic W, Potter WB. Clinical evaluation of a new multi-purpose disinfecting solution in symptomatic contact lens wearers. Cont Lens Anterior Eye 2006;29:143-151.
- 8. Santodomingo-Rubido J, Mori O, Kawaminami S. Cytotoxicity and antimicrobial activity of six multipurpose soft contact lens disinfecting solutions. Ophthalmic Physiol Opt 2006;26:476-482.
- 9. Choy CK, Cho P, Boost MV. Cytotoxicity and effects on metabolism of contact lens care solutions on human corneal epithelium cells. Clin Exp Optom 2012;95:198-206.
- 10. Zanetti S, Fiori PL, Pinna A, Usai S, Carta F, Fadda G. Susceptibility of Acanthamoeba castellanii to contact lens disinfecting solutions. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 1995;39:1596-1598.
- 11. Hiti K, Walochnik J, Haller-Schober EM, Faschinger C, Aspöck H. Viability of Acanthamoeba after exposure to a multipurpose disinfecting contact lens solution and two hydrogen peroxide systems. Br J Ophthalmol 2002;86:144-146.
- 12. Turner NA, Russell AD, Furr JR, Lloyd D. Emergence of resistance to biocides during differentiation of Acanthamoeba castellanii. J Antimicrob Chemother 2000;46:27-34.
- 13. Bowers B, Korn ED. The fine structure of Acanthamoeba castellanii (Neff strain). II. Encystment. J Cell Biol 1969;41:786-805.
- 14. Aqeel Y, Siddiqui R, Khan NA. Silencing of xylose isomerase and cellulose synthase by siRNA inhibits encystation in Acanthamoeba castellanii. Parasitol Res 2013;112:1221-1227.
- 15. Beattie TK, Seal DV, Tomlinson A, McFadyen AK, Grimason AM. Determination of amoebicidal activities of multipurpose contact lens solutions by using a most probable number enumeration technique. J Clin Microbiol 2003;41:2992-3000.
- 16. Yanai R, Yamada N, Ueda K, Tajiri M, Matsumoto T, Kido K, Nakamura S, Saito F, Nishida T. Evaluation of povidone-iodine as a disinfectant solution for contact lenses: antimicrobial activity and cytotoxicity for corneal epithelial cells. Cont Lens Anterior Eye 2006;29:85-91.
- 17. Moon EK, Kim SH, Hong Y, Chung DI, Goo YK, Kong HH. Autophagy inhibitors as a potential antiamoebic treatment for Acanthamoeba keratitis. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 2015;59:4020-4025.
- 18. Kong HH, Chung DI. Ultrastructural changes of Acanthamoeba cyst of clinical isolates after treatment with minimal cysticidal concentration of polyhexamethylene biguanide. Korean J Parasitol 1998;36:7-13.
- 19. Moon EK, Hong Y, Chung DI, Goo YK, Kong HH. Potential value of cellulose synthesis inhibitors combined with PHMB in the treatment of Acanthamoeba keratitis. Cornea 2015;34:1593-1598.