Abstract
This study aimed at constructing a draft genome of the adult female worm Toxocara canis using next-generation sequencing (NGS) and de novo assembly, as well as to find new genes after annotation using functional genomics tools. Using an NGS machine, we produced DNA read data of T. canis. The de novo assembly of the read data was performed using SOAPdenovo. RNA read data were assembled using Trinity. Structural annotation, homology search, functional annotation, classification of protein domains, and KEGG pathway analysis were carried out. Besides them, recently developed tools such as MAKER, PASA, Evidence Modeler, and Blast2GO were used. The scaffold DNA was obtained, the N50 was 108,950 bp, and the overall length was 341,776,187 bp. The N50 of the transcriptome was 940 bp, and its length was 53,046,952 bp. The GC content of the entire genome was 39.3%. The total number of genes was 20,178, and the total number of protein sequences was 22,358. Of the 22,358 protein sequences, 4,992 were newly observed in T. canis. Following proteins previously unknown were found: E3 ubiquitin-protein ligase cbl-b and antigen T-cell receptor, zeta chain for T-cell and B-cell regulation; endoprotease bli-4 for cuticle metabolism; mucin 12Ea and polymorphic mucin variant C6/1/40r2.1 for mucin production; tropomodulin-family protein and ryanodine receptor calcium release channels for muscle movement. We were able to find new hypothetical polypeptides sequences unique to T. canis, and the findings of this study are capable of serving as a basis for extending our biological understanding of T. canis.
-
Key words: Toxocara canis, de novo synthesis, genomics, next generation sequencing
INTRODUCTION
Toxocara canis is the most important parasitic pathogen that causes visceral larva migrans.
T. canis is an intestinal nematode found in dogs; however, if embryonated eggs or larvae are introduced to humans, the larvae migrate to the liver, lungs, eyes, or brain, but cannot reach the intestine. The seropositivity rate for toxocariasis has been estimated to be 5% in Korea [
1].
We determined the genome sequence of this worm using next-generation sequencing and de novo assembly. The goal of this study was to present a draft genome of
T. canis. During the course of this study, a draft genome of
T. canis was published by another research group [
2]; however, there were some of software tools of already old ones. Therefore, we continued the study and obtained distinct results in our draft genome of
T. canis. In this study, we used more recent versions or new tools as follows: Jellyfish, SOAPec, and GATK for sequencing; RepeatRunner, MAKER, PASA, and Blast2GO for structural annotation. These results may be able to provide insights into the taxonomy of
T. canis, host-parasite interactions, drug development, treatment protocols, and strategies to control
T. canis.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Materials
Female adult specimens of T. canis were obtained from the intestines of dogs in a slaughterhouse in Chungju, Chungcheongbuk-do, Korea. We used the female worm because its number is greater in the dog intestine than that of the male worm. Adult worms were frozen in liquid nitrogen immediately after removal from the dog intestine. The frozen worms were transferred to the laboratory, and DNA was extracted using a genomic DNA purification kit, catalog no. A1120 (Promega, Madison, Wisconsin, USA). RNA was extracted using an RNA extraction kit, ReliaPrepTM RNA Miniprep Systems, catalog no. Z6011 (Promega).
Overall methodology
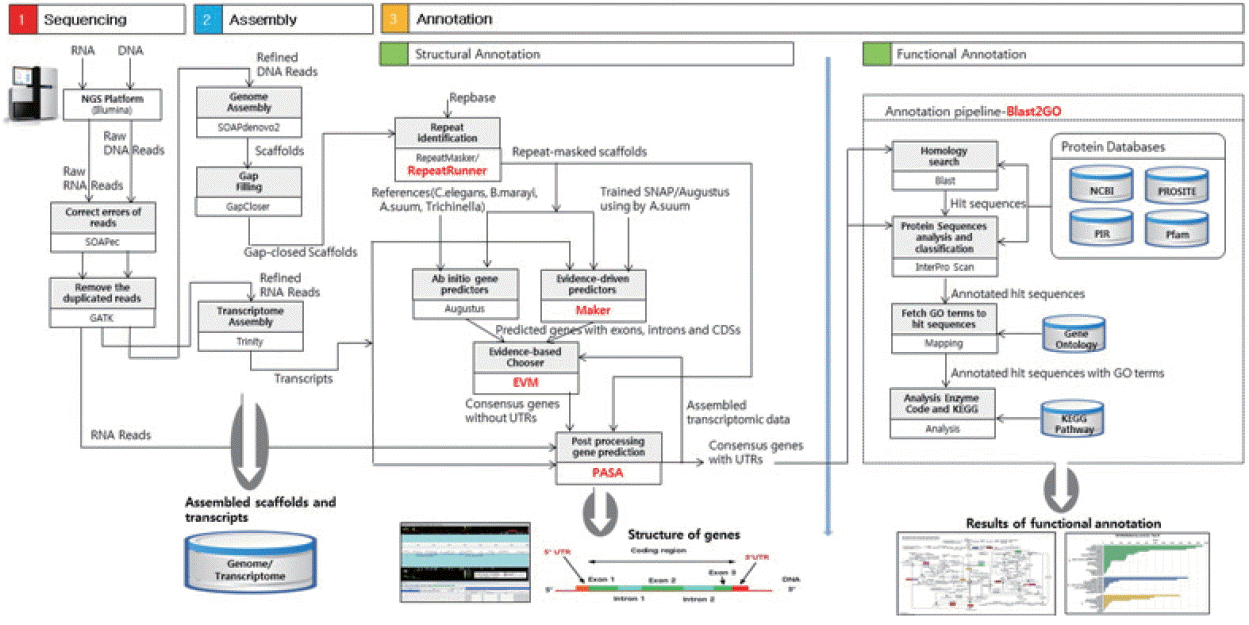
Fig. 1 presents an overview of our methodology, which involved 3 steps: 1) a sequencing step, in which the raw DNA/RNA reads of a genome were obtained and a stringent filtering process was carried out to obtain a clean and usable set of reads; 2) an assembly step, in which the preprocessed reads were used to construct contigs, scaffolds, and to fill the intra-scaffold gaps; and 3) an annotation step, consisting of 2 sub-steps (structural and functional annotations), in which genes were identified within the genome and the functions of the encoded proteins were deduced, respectively.
Sequencing
Paired-end DNA reads of T. canis (with a ~350 Mbp genome) were obtained using a Genome Analyzer IIx (Ilumina, San Diego, California, USA). The library sizes used were 170 bp, 400 bp, 1,900 bp, 2,900 bp, and 10 Kbp. The read data for which the insert size was short (less than or equal to 400 bp) were produced using the paired-end method, while those with a longer insert size were obtained using the mate-pair method. In total, we generated 121.1 Gbp of DNA reads (equal to 317.5-fold coverage of the entire genome) with an average read length of 101 bp.
Libraries for the RNA reads were also sequenced using the Genome Analyzer IIx (Ilumina). Paired-end libraries were sequenced in reads with a length of 101×2 nucleotides. The insert sizes for library production were 200 to 300 bp, and the total size of the RNA read data obtained was 4.5 Gbp. DNA and RNA sequencing was done at the Laboratory of an author, Dr. Jong-Il Kim.
In order to remove errors and to improve the quality of the assembly results through a purification process, k-mer analysis was performed. The k-mer distribution of a simple random genome sequence is expected to be a Poisson distribution [
3]. We used Jellyfish [
4], which is a fast and memory-efficient system, and performed a k-mer frequency analysis to filter out reads with lower k-mer frequency, which could result from a sequencing error. For all of the read data, an error correction tool, SOAPec (version 2.01) [
5], was used for read trimming and base correction, with the k-mer size set to 17. Next, GATK [
6] was used to remove duplicate read pairs, and only 1 read pair from the duplicates was kept. All remaining data were used for de novo assembly.
We assembled the
T. canis genome using SOAPdenovo 2 (version 2.04.240) [
7], which adopted the de Bruijn graph algorithm to construct contigs. The de Bruijn graph is an efficient way to represent a sequence in terms of its k-mer components, and captures overlaps of length k−1 between the k-mer components. In order to obtain a maximally efficient k-mer size, we performed a preliminary experiment using only a subset of all data. Multiple contig assemblies were performed with a range of k-mers between 21 and 71, and k = 41 was selected as the optimal size on the basis of 3 parameters: N50, N90, and the average length of the contig sequences.
We first assembled the short insert size reads (170 bp) into contigs using subsequence overlap information. We then constructed scaffolds with longer insert size reads, step by step from the shortest (400 bp) to the longest (10 Kbp) insert size. In order to fill the intra-scaffold gaps, we used GapCloser (version 1.12), a stand-alone tool in the SOAPdenovo package [
7]. With GapCloser, the paired-end information was used as long as 1 read was well-aligned on the scaffolds, while another read was located in a gap region, and then these reads were locally assembled. The N50 length is defined such that half of the nucleotides reside in contigs or scaffolds having a length of at least N50 length.
All preprocessed RNA reads were assembled using Trinity (version 2014-07–17) [
8] which used the de Bruijn graph algorithm to recover transcript isoforms. Trinity combines 3 independent software modules: Inchworm, Chrysalis, and Butterfly, each of which is applied sequentially to process large volumes of RNA reads. Inchworm assembles the RNA data into contigs (unique sequences of transcripts) via greedy k-mer extension. Trinity was run on the paired-end sequences with a default k-mer size of 25. The RNA reads were assembled into 81,629 contigs with an N50 of 940 bp, an average length of 650 bp, and a total length of 53,047 Kbp.
Repetitive elements are ubiquitous in eukaryotic genomes and complicate genome annotation. RepeatMasker (version 4.0.5) [
9] was used in conjunction with RepeatRunner [
10] for repeat identification, characterization, and masking in the 10,853 scaffold sequences that were produced. The repeat libraries used were Repbase (version 2014-01–31) [
11] and the Comparative Genomics Library [
12].
De novo gene prediction was performed on the repeat masked scaffolds using Augustus [
13]. Augustus provides a fast and easy way of determining gene structures such as introns, exons, coding sequences, start codons, end codons, and protein sequences without external evidence such as expressed sequence tags or protein alignment. Given enough high-quality gene model parameters, Augustus predicts significantly more genes correctly than any other ab initio program [
14]. We ran Augustus with the system-provided model parameters trained on
Caenorhabditis elegans, Trichinella spiralis, and Brugia malayi, and predicted 14,281, 16,074, and 8,631 genes, respectively for these 3 genomes closely related to the
T. canis genome. The threshold of the E-value was set to 10
−5. We also used MAKER [
15] to train Augustus and created a parameter file for
Ascaris suum. Using the parameter file for
A. suum, Augustus predicted that 3,611 genes would be present in the
T. canis genome.
MAKER [
14,
15] is an evidence-based gene prediction pipeline that uses a set of gene predictors and additional evidence (including protein similarity and transcriptome information) to generate a set of high-quality gene predictions. The inputs to MAKER include the genomic scaffolds to be annotated, an assembled transcriptome, and protein sequences for alignment. We ran the first iteration on MAKER combining evidence from the known transcriptome and protein sequences of
A. suum and the ab initio predictions of SNAP [
16] and Augustus. For additional evidence, we downloaded 18,542 transcripts and 18,542 protein sequences of
A. suum from Wormbase (available from
http://www.wormbase.org/).
A. suum was chosen because it is a well-studied species that is closely related to
T. canis [
17]. Using the output of the previous iteration, we trained Augustus and also modeled SNAP HMM (hidden Markov model). In the second iteration step, masked
T. canis scaffolds were run through MAKER using the trained parameter files of SNAP and Augustus, and with transcriptome-based predictions turned on. Using the MAKER pipeline, we predicted 6,883 protein-coding genes.
All gene structures predicted by the previous methods were combined into a consensus gene set using Evidence Modeler (EVM) [
18]. EVM attempts to choose the single prediction whose intron-exon structure represents the best consensus gene structure from the overlapping predictions using a scoring method based on user-generated weight parameters. We used EVM to combine 4 ab initio gene predictions from Augustus (trained on
C. elegans,
T. spiralis, B. malayi, and
A. suum) and 1 evidence-based gene prediction from MAKER, in combination with
T. canis transcriptomic data from the PASA (program to assemble spliced alignments) assemblies [
18]. In our experiment, 2 gene prediction tools, Augustus and MAKER, were given an equal weight (weight = 1 for each), while the assembled transcriptomic data (33,323 contig sequences) were given the highest weight (weight = 10) for revising the annotation. The final count of the consensus gene set was 21,459 genes.
However, EVM is not designed to model alternative splicing isoforms. We ran the PASA pipeline (version 2.0.2) [
19] to update the EVM consensus predictions to add alternate splicing and untranslated region sequences based on assembled transcriptomic data, and predicted the presence of 20,178 protein-coding genes.
We first performed a homology search for 22,358 protein sequences acquired from 20,178 genes using Blastp in Blast2GO [
20] against the National Center for Biotechnology Information non-redundant protein database (January 2016), and homologs were identified with an E-value of cutoff of 10
−5. Blast2GO provides 2 Blast execution methods: LocalBlast and CloudBlast. We used Blastp based on CloudBlast, since mass sequence alignment was necessary to improve the search performance due to the presence of many protein sequences and long sequences. In the next mapping step, we first retrieved gene ontology (GO) terms associated with the hit sequences obtained in the Blastp search and updated them using the integrated InterProScan 5 (version 5.16–55.0) function. The functional GO terms were then assigned to protein sequences. We also generated enzyme codes and KEGG pathway annotations by mapping the GO terms to their enzyme codes.
RESULTS
Total length of draft genome
DNA and RNA reads of
T. canis was sequence.
T. canis draft genome was obtained with an N50 of 108 Kbp and a total length of 314 Mbp. The GC content of the assembled draft genome was 39.3%. Total 20,178 gene structures, with an average exon length of 172 bp and an average number of 7.09 exons, were predicted. The detailed results are summarized in
Table 1 as follows: The total number of scaffolds was 10,853; the total size of scaffolds 341,776,187 bp, and the N50 length 108,950 bp. Data were deposited to GenBank available from:
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/nuccore/LYYD00000000.
Homology of 22,358 protein sequences extracted from 20,178
T. canis genes was compared with those of closely related species, such as
C. elegans,
T. spiralis, B. malayi, and
A. suum using Blastp.
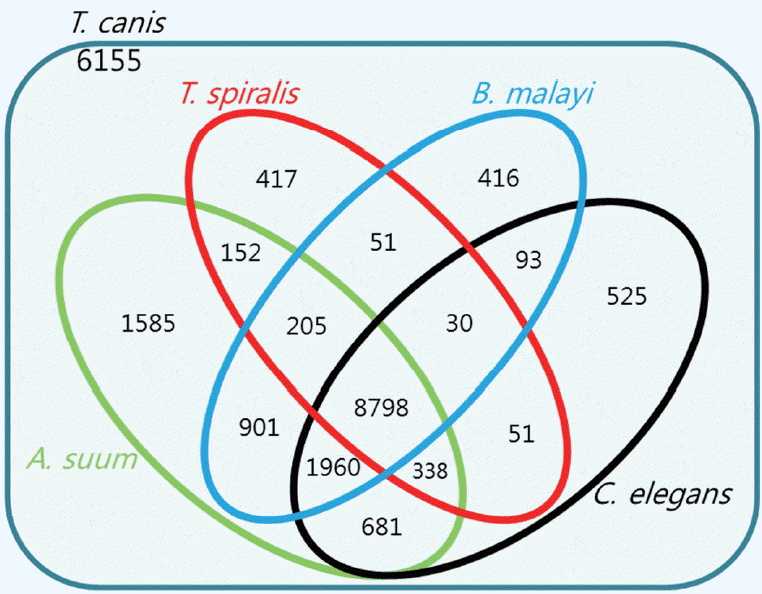
Fig. 2 showed the number of homologs between
T. canis and the 4 other closely related species, defined as the number of pairs with reciprocal best hits. The E-value threshold value was set to 10
−5. Most of the predicted
T. canis genes had a homolog either in
C. elegans (n=12,476; 55.8%),
T. spiralis (n=10,042; 44.9%),
B. malayi (n=12,454; 55.7%), or
A. suum (n=14,620; 65.3%). As shown in
Fig. 2, the
T. canis genes were most similar to those of
A. suum. A total of 8,798 genes were homologous among all 5 species, while 6,155 genes were unique to
T. canis relative to the other 4 species.
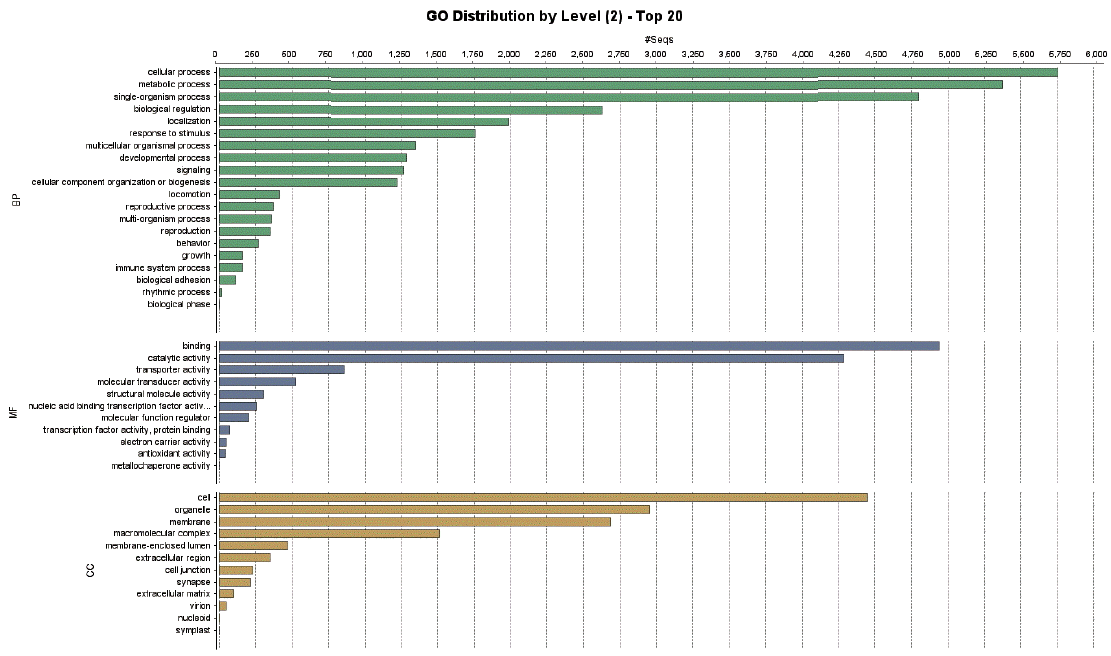
A total of 9,283 protein sequences (41.5%) were successfully annotated and classified into the 3 main GO functional categories: biological processes, molecular functions, and cellular components.
Fig. 3 showed the distribution of the assigned GO terms for the
T. canis protein sequences, using a GO level of 2. In the biological processes category, most sequences were classified as cellular processes, metabolic processes, and single-organism processes. In the molecular functions category, most sequences were related to binding activity, catalytic activity, and transporter activity, and in the cellular components category, most sequences corresponded to the cell overall, organelles, and membrane. GO level data were not comparable to other nematodes because there were no classification data from other nematodes whole genome sequences.
Domains of protein sequences were analyzed with using InterProScan, contained in Blast2GO, before mapping GO terms to protein sequences. With this tool, it was possible to search for protein sequence names and identify the domain or family of each protein from several protein databases, such as Pfam, PROSITE, PIR and others. Total 2,299 domains were found from 22,358 protein sequences. Additionally, domains were searched for
C. elegans and
A. suum. Number of protein sequences and number of domains were as follows: 22,358 and 2,299 for
T. canis; 23,906 and 2,769 for
C. elegans, and 18,542 and 2,786 for
A. suum. The quantity of sequences in each domain of those closely related species and in the
T. canis domain in
Table 2 were analyzed for correlations, and the Spearman correlation coefficient was obtained. When the top 200 domains were compared, the correlation coefficient between
T. canis and
C. elegans was 0.8368 and the correlation between
T. canis and
A. suum was 0.9063. When only the upper 50 domains were compared, the correlation coefficient between
T. canis and
C. elegans was 0.6984 and the correlation coefficient between
T. canis and
A. suum was 0.917.
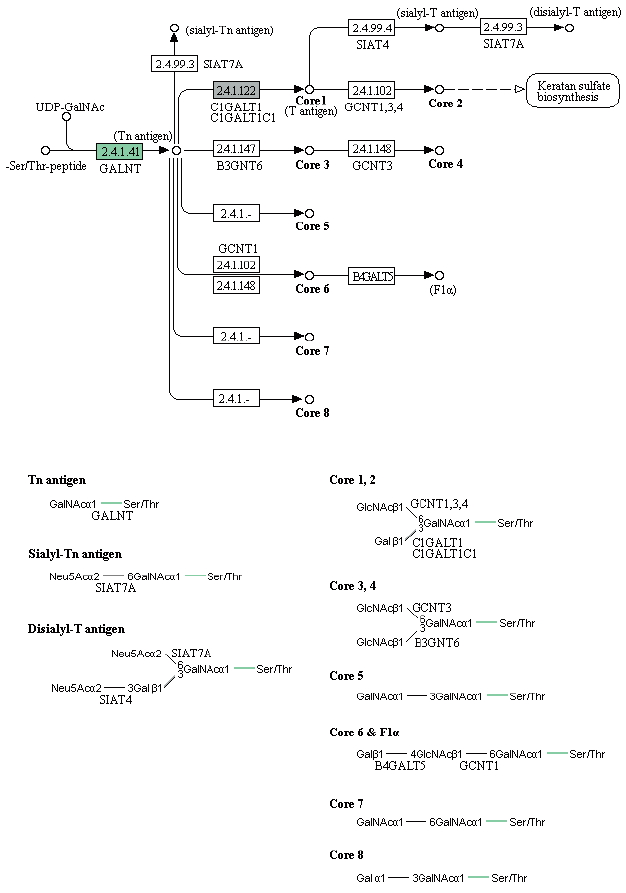
Enzymes related to the KEGG pathway were analyzed in order to assess interactions among genes. The number of enzyme pathways was 127. As an example, the mucin type O-glycan biosynthesis pathway was shown in
Fig. 4. It was presented because it is not well-known topic out of nematode pathways; however, mucin type O-glycan is one of the common pathways in nematode parasites and free-living nematode and presented as a sample of KEGG pathway [
21]. Each box contained an enzyme code, and colored boxes refer to the enzymes obtained from
T. canis genes. Nine sequences and the following 2 enzymes were found: 3-beta galatosyltransferase and N-acetylgalatosaminyltransferase.
T-cell and B-cell regulation
Sequences coding for proteins, such as E3 ubiquitin-protein ligase cbl-b and antigen T-cell receptor, zeta chain, were found. Sequences for the following proteins protective against stress were found: heat shock protein 70, heat shock protein 90 (partial), superkiller viralicidic activity 2-like 2, and macrophage migration inhibitory factor.
Cuticle metabolism
Endoprotease bli-4 is essential for the production of cuticle. Additionally, sequences were found for the nematode cuticle collagen domain protein and cuticle protein isoform b-like. These were components of the cuticle, which is essential for
T. canis because it both provides protection from the external environment and allows the absorption of nutrients [
22].
Mucin production
Mucin is also produced in the host intestinal mucosa. Since T. canis also has an intestine, it is possible for T. canis to produce mucin. Mucin protects the epithelial cells of intestinal mucosa by forming a gel. We found sequences coding for 2 types of mucin protein: mucin 12Ea and polymorphic mucin variant C6/1/40r2.1.
Muscle movement
In
T. canis, muscle movement is essential for migration into the host intestine and to extraintestinal organs such as the liver, lung, brain, eye, and distant organs. Sequences coding for the tropomodulin-family protein and ryanodine receptor calcium release channels were found. Tropomodulin-family protein is a member of a family of tropomyosin-binding proteins that regulates the tropomyosin-actin interaction in non-muscle cells and tissues [
23]. Tropomyosin is a protein essential for muscle contraction, whereas ryanodine receptor calcium releases channels contribute to muscle contraction through calcium influx into the cell and calcium release from the cell.
DISCUSSION
Our results were comparable to the previous draft genome of
T. canis published by Zhu et al. [
2]. We obtained 1,583 more putative genes (20,178 vs 18,595). This discrepancy may have been due to the size of the database that was annotated, as it is possible that the databases may have had more genes and proteins recently. Differences were also found in the total number of scaffolds (10,853 vs 22,857), the N50 length (108,950 bp vs 375,067 bp), the GC content (39.3% vs 40.0%), the average gene length (6,055 bp vs 8,416 bp), the average number of exons per gene (7.09 vs 7.4), the average exon length (172 bp vs 156 bp), the average intron length (793 bp vs 1,133 bp), and the average coding sequence length (1,077 bp vs 1,156 bp).
The previous
T. canis draft genome was also included for homology comparison [
1]. In this work, the methods of sequencing, annotation, and homology searches were not significantly different than those used in the previous draft genome study; but we used more recent versions of new tools such as PASA and Evidence Modeler. Therefore, it increased the accuracy of gene structure analysis, which made it possible to find more reliable 4,992 unique protein-coding genes. The prominent functions of the proteins encoded by these genes included cuticle metabolism, mucin production, and muscle movement. The cuticle of parasitic nematodes is a protective organ and a metabolic site for nutrients. Genes relating to cuticle metabolism will be able to provide basic data for the development of drugs targeted against nematodes. Mucin production is also essential for nematodes to survive in the host intestine. Both the host and the parasites produce mucin, which protects intestinal epithelial cells. Genes for 2 types of mucin protein, mucin 12Ea and polymorphic mucin variant C6/1/40r2.1, were identified in the present study. Those proteins can be studied for further mechanisms of mucin secretion. In mucin biosynthesis, O-glycosylation is the essential posttranslational modification of proteins. It regulates protein conformation and sorting, the development of
T. canis, and enzymes. A basic knowledge of O-glycan pathways has already been well established in vertebrates. Therefore, knowledge of the corresponding nematode systems may also be helpful in elucidating the regulatory factors of this pathway. Although there were reports on the mucin type O-glycan biosynthesis in nematodes, its specific function was not still clear [
21]. However, other RNAi data of those genes involved in glycosylation pathways told us that it is required for proteoglycan modification of the cell surface metabolism in
C. elegans embryos [
24]. The muscle movement of nematodes is also essential for migration and survival. Sequences coding for tropomyosin and ryanodine receptor calcium release channel were identified. Their mechanism of action may inform further searches for movement-related genes. The present draft genome may provide basic genomic information of
T. canis, allowing research into specific genes to be carried out more easily.
Notes
-
CONFLICT OF INTEREST
The authors have no conflict of interest related to this work.
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS
This work was supported by the Hallym University Research Fund (HRF-201411-013) and by the Basic Science Research Program through the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF) funded by the Ministry of Science, ICT, and Future Planning (nos. 2014R1A2A1A11052141 and 2014R1A1A3052083).
Fig. 1Overview of the genome analysis process. The overall workflow of the genomic analysis of Toxocara canis is shown, and all software tools and annotation databases used are also summarized. For acquisition of more exact results of structural annotation, new tools such as RepeatRunner, Maker, EVM, and PASA were used. For functional annotation, Blast2GO was used.
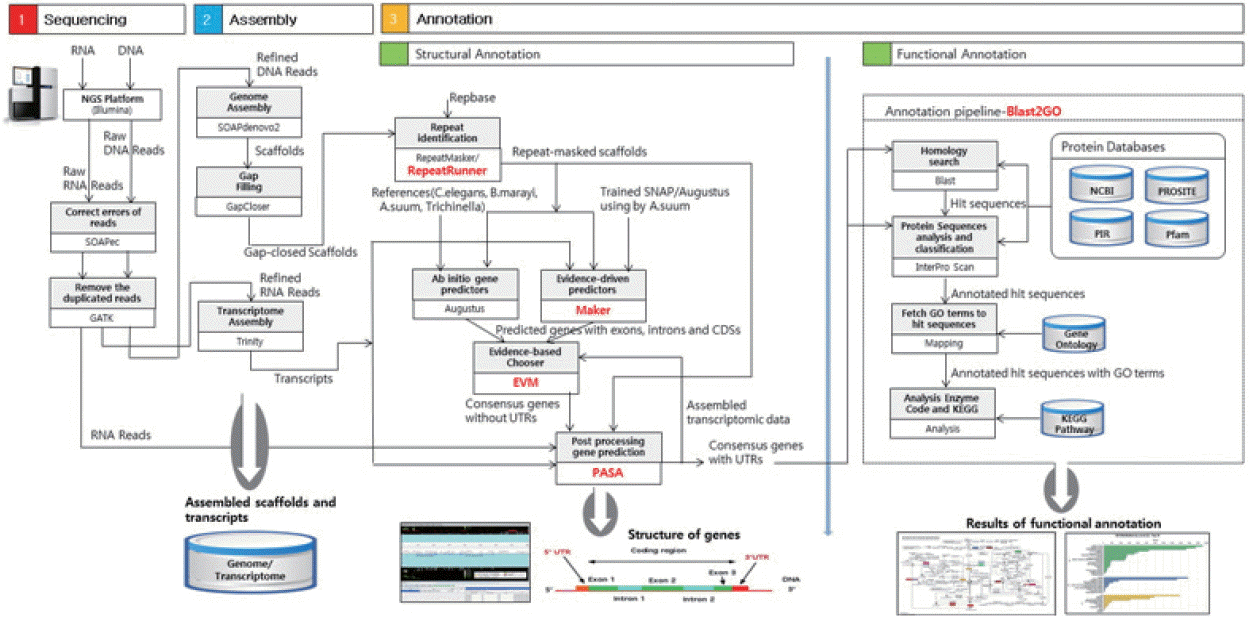
Fig. 2Venn diagram showing the results of the homology comparison of Toxocara canis ortholog genes with other closely related species.
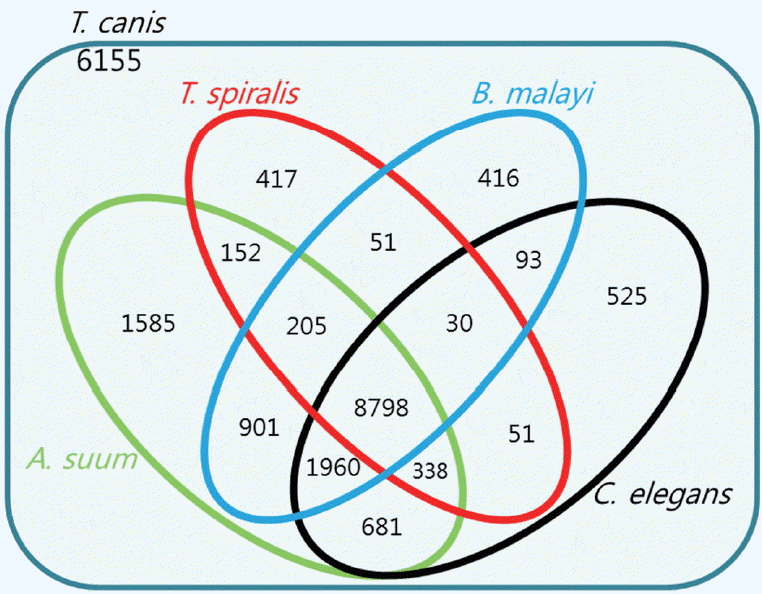
Fig. 3Distribution of gene ontology functional terms for Toxocara canis protein sequences. The graphs show level-2 annotations for biological processes (BP), molecular functions (MF), and cellular components (CC).
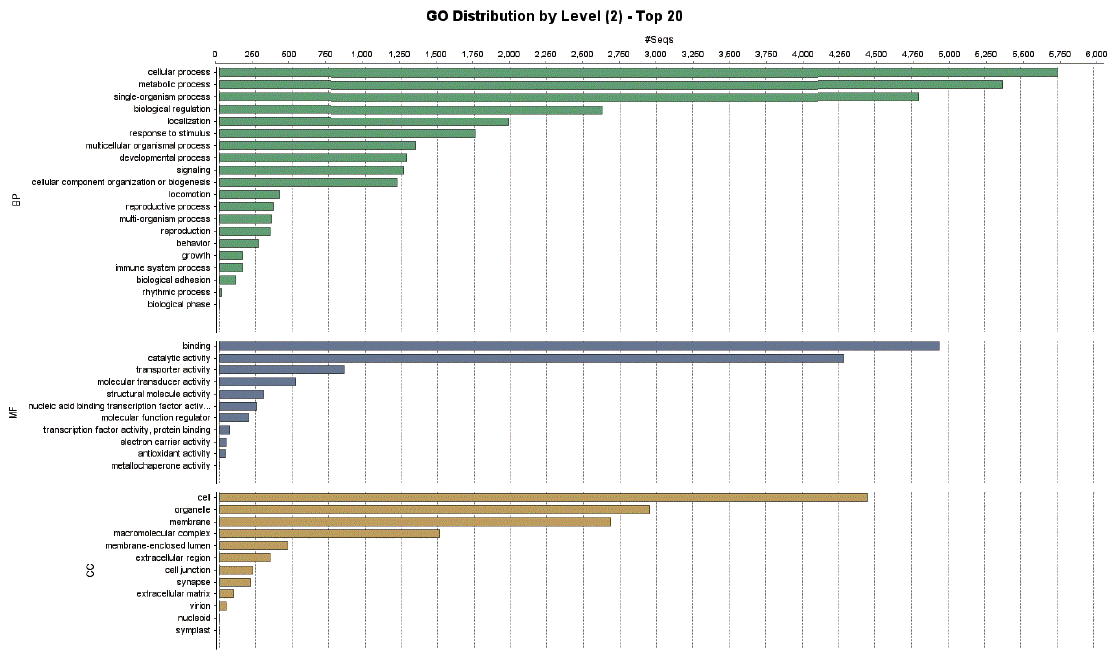
Fig. 4KEGG map for the mucin type O-glycan biosynthesis pathway.
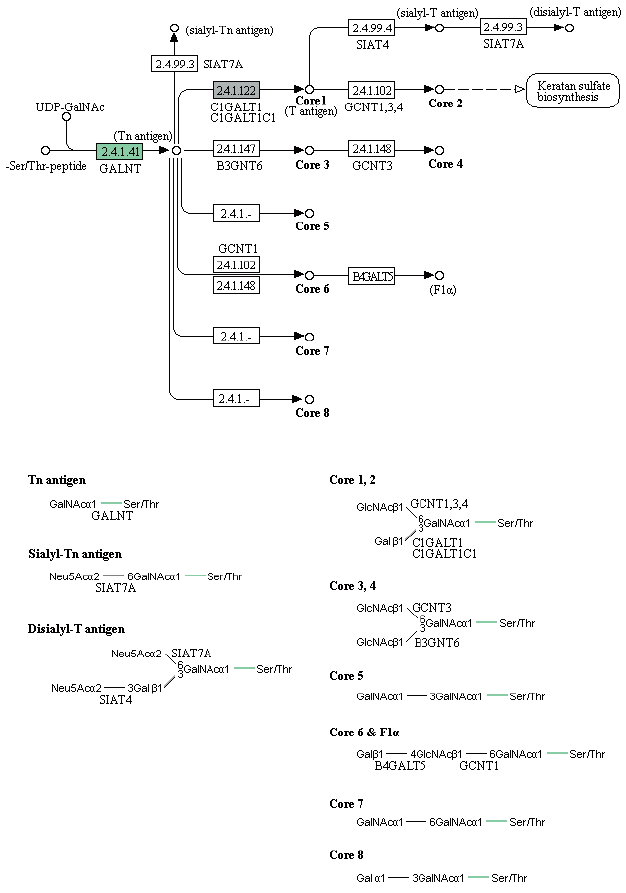
Table 1Features of the Toxocara canis draft genome
Table 1
|
Items |
Size or number |
|
Total number of scaffolds |
10,853 |
|
Total size of scaffolds (bp) |
341,776,187 |
|
N50 length (bp) |
108,950 |
|
GC content of the entire genome (%) |
39.3 |
|
Total number of genes |
20,178 |
|
Average gene length (bp) |
6,055 |
|
Average exon number per gene |
7.09 |
|
Average exon length (bp) |
172 |
|
Average intron length (bp) |
793 |
|
Average coding sequence length (bp) |
1,077 |
Table 2Domain information obtained from the Toxocara canis genome
Table 2
|
Ranking |
Domain name |
No. of sequences |
|
1 |
P-loops containing nucleoside triphosphate hydrolase |
699 |
|
2 |
Protein kinase domain |
541 |
|
3 |
Protein kinase-like domain |
440 |
|
4 |
G protein-coupled receptors, rhodopsin-like, 7TM |
308 |
|
5 |
Serine/threonine/dual-specificity protein kinase, catalytic domain |
293 |
|
6 |
WD40/YVTN repeat-like-containing domain |
288 |
|
7 |
Immunoglobulin-like fold |
264 |
|
8 |
Major facilitator superfamily domain |
253 |
|
9 |
EF-hand domain pair |
244 |
|
10 |
RNA recognition motif domain |
217 |
|
11 |
Zinc finger, RING/FYVE/PHD-type |
207 |
|
12 |
Nucleotide-binding alpha-beta plait domain |
200 |
|
13 |
WD40-repeat-containing domain |
180 |
|
14 |
Pleckstrin homology-like domain |
179 |
|
15 |
NAD(P)-binding domain |
175 |
|
16 |
Ankyrin repeat-containing domain |
174 |
|
17 |
Armadillo-like helical |
174 |
|
18 |
Armadillo-type fold |
174 |
|
19 |
Zincfinger,C2H2 |
174 |
|
20 |
Serine-threonine/tyrosine-protein kinase catalytic domain |
171 |
|
21 |
Alpha/beta-hydrolase fold |
166 |
|
22 |
Homeodomain-like |
165 |
|
23 |
Immunoglobulin-like domain |
159 |
|
24 |
PDZ domain |
148 |
|
25 |
Tetratricopeptide-like helical domain |
147 |
|
26 |
Zinc finger, RING-type |
146 |
|
27 |
Epidermal growth factor-like domain |
145 |
|
28 |
Winged helix-turn-helix DNA-binding domain |
145 |
|
29 |
Nematode cuticle collagen, N-terminal |
139 |
|
30 |
Reverse transcriptase domain |
139 |
References
- 1. Kim YH, Huh S, Chung YB. Seroprevalence of toxocariasis among healthy people with eosinophilia. Korean J Parasitol 2008;46:29-32.
- 2. Zhu XQ, Korhonen PK, Cai H, Young ND, Nejsum P, von Samson-Himmelstjerna G, Boag PR, Tan P, Li Q, Min J, Yang Y, Wang X, Fang X, Hall RS, Hofmann A, Sternberg PW, Jex AR, Gasser RB. Genetic blueprint of the zoonotic pathogen Toxocara canis. Nat Commun 2015;6:6145.
- 3. Melsted P, Pritchard JK. Efficient counting of k-mers in DNA sequences using a bloom filter. BMC Bioinformatics 2011;12:333.
- 4. Marcais G, Kingsford C. A fast, lock-free approach for efficient parallel counting of occurrences of k-mers. Bioinformatics 2011;27:764-770.
- 5. Beijing Genomics Institute. SOAPec [Internet]; Shenzen, China: Beijing Genomics Institute; [cited 2016 Jan 2]. Available from: http://soap.genomics.org.cn/about.html
- 6. Broad Institute. GATK [Internet]; Cambridge, MA, USA: Broad Institute; [cited 2016 Jan 2]. Available from: https://www.broadinstitute.org/gatk
- 7. Luo R, Liu B, Xie Y, Li Z, Huang W, Yuan J, He G, Chen Y, Pan Q, Liu Y, Tang J, Wu G, Zhang H, Shi Y, Liu Y, Yu C, Wang B, Lu Y, Han C, Cheung DW, Yiu SM, Peng S, Xiaoqian Z, Liu G, Liao X, Li Y, Yang H, Wang J, Lam TW, Wang J. SOAPdenovo2: an empirically improved memory-efficient short-read de novo assembler. GigaScience 2012;1:18.
- 8. Broad Institute. Trinity [Internet]; Cambridge, MA, USA: Broad Institute; [cited 2016 Jan 2]. Available from: http://trinityrnaseq.sourceforge.net
- 9. Institute for Systems Biology. RepeatMasker [Internet]; Seattle, WA, USA: Institute for Systems Biology; [cited 2016 Jan 2]. Available from: http://repeatmasker.org
- 10. Smith CD, Edgar RC, Yandell M, Smith DR, Celniker SE, Myers EW, Karpen GH. Improved repeat identification and masking in Dipterans. Gene 2007;389:1-9.
- 11. Jurka J. Repbase Update: a database and an electronic journal of repetitive elements. Trends Genetics 2000;9:418-420.
- 12. Yandell M. Comparative genomics library (CGL) [internet]; Available from: http://www.yandell-lab.org/software/cgl.html
- 13. Stanke M, Tzvetkova A, Morgenstern B. AUGUSTUS at EGASP: using EST, protein and genomic alignments for improved gene prediction in the human genome. Genome Biology 2006;7(suppl):1-8.
- 14. Cantarel BL, Korf I, Robb SM, Parra G, Ross E, Moore B, Holt C, Sánchez Alvarado A, Yandell M. MAKER: an easy-to-use annotation pipeline designed for emerging model organism genomes. Genome Res 2008;18:188-196.
- 15. Holt C, Yandell M. MAKER2: an annotation pipeline and genome-database management tool for second-generation genome projects. BMC Bioinformatics 2011;12:491.
- 16. Johnson AD, Handsaker RE, Pulit SL, Nizzari MM, O’Donnell CJ, de Bakker PI. SNAP: A web-based tool for identification and annotation of proxy SNPs using HapMap. Bioinformatics 2008;24:2938-2939.
- 17. Jex AR, Liu S, Li B, Young ND, Hall RS, Li Y, Yang L, Zeng N, Xu X, Xiong Z, Chen F, Wu X, Zhang G, Fang X, Kang Y, Anderson GA, Harris TW, Campbell BE, Vlaminck J, Wang T, Cantacessi C, Schwarz EM, Ranganathan S, Geldhof P, Nejsum P, Sternberg PW, Yang H, Wang J, Wang J, Gasser RB. Ascaris suum draft genome. Nature 2011;479:529-533.
- 18. Haas BJ, Salzberg SL, Zhu W, Pertea M, Allen JE, Orvis J, White O, Buell CR, Wortman JR. Automated eukaryotic gene structure annotation using EVidenceModeler and the program to assemble spliced alignments. Genome Biol 2008;9:R7.
- 19. Institute for Genomic Research. PASA [Internet]; La Jolla, CA, USA: Institute for Genomic Research; [cited 2016 Jan 2]. Available from: http://pasapipeline.github.io
- 20. Conesa A, Götz S, García-Gómez JM, Terol J, Talón M, Robles M. Blast2GO: a universal tool for annotation, visualization and analysis in functional genomics research. Bioinformatics 2005;21:3674-3676.
- 21. Staudacher E. Mucin-type O-glycosylation in invertebrates. Molecules 2015;20:10622-10640.
- 22. Page AP, Stepek G, Winter AD, Pertab D. Enzymology of the nematode cuticle: a potential drug target? Int J Parasitol Drugs Drug Resist 2014;4:133-141.
- 23. Fowler VM. Tropomodulin: a cytoskeletal protein that binds to the end of erythrocyte tropomyosin and inhibits tropomyosin binding to actin. J Cell Biol 1990;111:471-481.
- 24. Wang H, Spang A, Sullivan MA, Hryhorenko J, Hagen FK. The terminal phase of cytokinesis in the Caenorhabditis elegans early embryo requires protein glycosylation. Mol Biol Cell 2005;16:4202-4213.