Abstract
Heishui county, located in northwest Sichuan province, southwestern China, is an endemic area of zoonotic visceral leishmaniasis (VL) and is the most intractable area. VL is never destroyed in it. Asymptomatic dogs (Leishmania parasites have been diagnosed but clinically healthy) are considered to be a potential reservoir host in zoonotic VL area, and most can lead to infection of individuals, that is a new challenge for controlling VL in humans. The present study aimed to assess the Leishmania infection rate of asymptomatic dogs in Heishui county. Total 105 asymptomatic domestic dogs were gathered from 4 districts in Heishui county to investigate the infection rate with serological and molecular methods based on ELISA and kinetoplast minicircle DNA(kDNA) PCR, respectively. Out of 105 dogs, 44 (41.9%) were positive by more than 1 method; 21 (20.0%) were positive by ELISA, and 30 (28.6%) were positive by kDNA-PCR. Our study showed that Leishmania infection of domestic dogs which is clinically healthy is prevalent in the studied district, and the asymptomatic dogs infected by Leishmania may be the primary reason for the prevalence of visceral leishmaniasis in the area.
-
Key words: Leishmania, epidemiology, asymptomatic dog, China
Visceral leishmaniasis (VL) regarded as the main public health problem is currently distributed throughout 6 provinces or autonomous regions, including Sichuan in China [
1]. So far, there has been a continuous transmission of VL in Sichuan, and more than 400 cases have been reported in this province from 2004 to 2010 [
2,
3]. Recent epidemiological studies have demonstrated that most cases are reported from the northwest of Sichuan, including Heishui county [
1].
Heishui county is an endemic area of zoonotic visceral leishmaniasis (ZVL) [
4]. Prevention and control of VL in this area is the most intractable since domestic dogs may have become the main reservoir for children infection (under 5 years old) [
5]. Furthermore,
Leishmania infection of dogs may lead to different clinical forms; in addition to severe clinical forms, asymptomatic forms may have remained for a long time in some dogs, which are normally ignored in prevention and cure [
6]. Therefore, to develop effective strategy for control VL in endemic areas, asymptomatic dogs infected with
Leishmania must be accurately and fleetly identified at first. In recent years, the transmission of VL between humans and dogs, especially in poor rural areas, has become exacerbated, mainly resulted from an increasing number of domestic dogs, most of which are homeless as a result of the 5·12 Wenchuan earthquake outbreak.
Therefore, the focus of this study was to investigate the Leishmania-infection rate of asymptomatic dogs using the molecular method which we have established and provided as a simple and suitable tool for diagnosis of VL in asymptomatic dogs. In addition, we also used a serological method to detect Leishmania infection among asymptomatic dogs from the areas of endemicity in Heishui county.
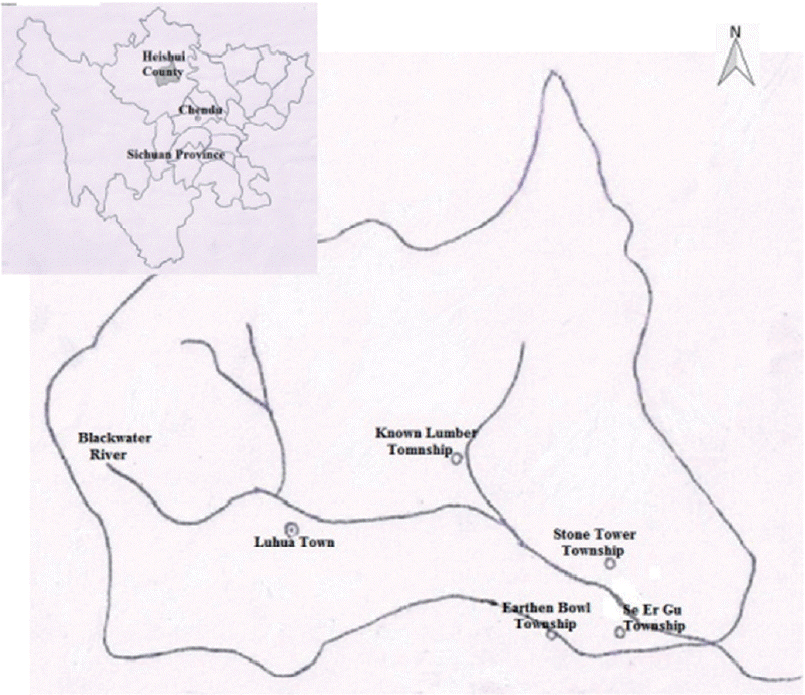
Heishui county belongs to Aba Tibetan and Qiang Autonomous Prefecture, in which 92% of the residents is Tibetan. It is located in the mountain area of northwestern Sichuan, southwestern China, where the mountains are steep with ravines crossbar. The main river, Heishui river, is a tributary of Minjiang river with a rapid flow. It is the high-altitude monsoon climate. Geography, climate, and other natural conditions are poor. Economy is mainly agriculture, followed by forestry and animal husbandry. Its latitude is between 31°35′N and 32°38′N, and its longitude is between 102°35′E and 103°30′E. The county covers an area of 4,356 km
2, and its altitude is 3,544 meters. It currently has 59,607 inhabitants (as of 2009). VL is prevalent in the county every year from September to May. The study was conducted in 4 district towns, where VL cases have been reported successively for 3 years, including Known Lumber Township, Earthen Bowl Township, Se Er Gu Township, and Stone Tower Township in Heishui county (
Fig. 1).
The investigation took place in early May 2010 in Heishui county, when the dogs infected with Leishmania were still asymptomatic. Domestic dogs in this study were from poor rural areas of 4 selected towns. Samples were collected from 105 domestic dogs (older than 6 months) through door-to-door visits. A 10-ml peripheral blood was collected by cephalic venipuncture; 5 ml blood was allowed to clot, and then centrifuged for 5 min at 3,400 rpm for obtaining serum, which were then stored in −20°C for ELISA to confirm anti-Leishmania antibodies, and aliquots of 5 ml blood containing anticoagulant EDTA-heparin was used for DNA extraction, after centrifugation for 10 min at 2,500 rpm, and the buffy coats including leukocytes and presumed parasites were immediately removed. For negative controls, 10 dogs from a non-endemic area of ZVL (Jiaxiang county of Shandong province) were selected to collect blood samples.
To detect anti-Leishmania antibodies, serum was tested by ELISA using LSM-Ab ELISA Kit (R&D Systems, Minneapolis, Minneapolis, USA) basis on the manufacturer’s instructions. Absorbance measured was the 450 nm using FilterMax F5 (Molecular Devices, Sunnyvale, California, USA). The minimum level of detection (cut-off) was the absorbance of positive standard, with the concentration of 1.5 IU/ml.
DNA from all whole bloods was extracted using the QIAamp DNA Mini Kit (Qiagen, Hilden, Germany) according to the manufacturer’s instructions. The DNA from Leishmania isolate (L.d. SD1 isolate, MHOM/CN/SD1) was obtained with phenol-chloroform method, that served as the positive control in PCR. The extracted DNA was resuspended in 50 μl of TE buffer (1 M Tris-HCl, 0.5 M EDTA, pH 8.0) and stored at −20°C until use.
The PCR was conducted in accordance with our previous study to confirm
Leishmania infection [
7]. Two pairs of
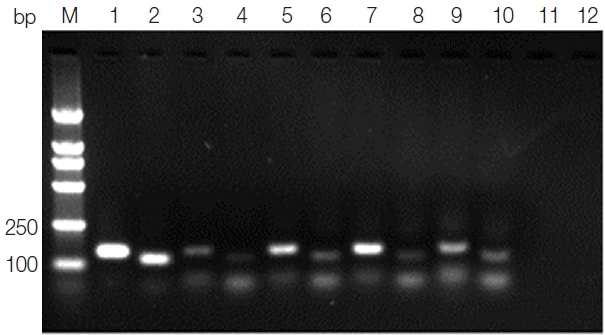
Leishmania genus-specific primers (forward primer: K13A 5′-GTGGGGGAGGGGCGTTCT-3′ and reverse primer: K13B5′-ATTTTACACCAACCCCCAGTT-3′; forward primer: RV1 5′-CTTTTCTGGTCCCGCGGGTAGG-3′ and reverse primer: RV2 5′-CCACCTGGCCTATTTTACACCA-3′) were designed to amplify a 120 bp fragment and a 145 bp fragment, respectively, from the conserved region of the kinetoplast DNA minicircle (kDNA) (GenBank no. AF169140.1) of the
Leishmania genus. The amplified product was analyzed by electrophoresis in 2% agarose gel. Both the 120 bp fragment and the 145 bp fragment that appeared in the same amplified sample were considered to be a positive result.
Prevalence rates were compared according to assays and districts using the chi-square test, and the statistical significance was indicated by a P<0.05. Analysis was performed by SPSS statistical software (Version 17.0).
Total 105 samples were analyzed by ELISA and PCR in the present study. Among them, 21 dogs (20.0%) were positive using ELISA (
Table 1). Meanwhile,
Leishmania DNA was detected in 30 samples (28.6%) by kDNA-PCR (
Table 1;
Fig. 2). There were 44 (41.9%) dogs positive by more than 1 diagnostic test. Eight dogs showed positive results by both ELISA and PCR methods, 13 samples were positive by ELISA but negative by PCR, whilst 22 samples were positive by PCR but not by ELISA. There was no statistical difference according to 4 districts using the chi-square test among infection rates by PCR (
P=0.969) and ELISA (
P=0.906), respectively.
PCR and ELISA as the serological and molecular methods recommended respectively by many government organs, including China and Korea [
8,
9], were used to investigate
Leishmania infection in asymptomatic dogs. Although no statistical difference was observed between ELISA and PCR to investigate the infection rates of the same district (
Table 1), there were different infection rates between assays, being consistent with previous investigations [
10–
15]. The probable reasons are the inherent limitations of both serological and molecular methods in the diagnosis of asymptomatic dogs, sample preparation, operation of experiments, and the immune reactivity of asymptomatic dogs to
Leishmania. Serological tests are not optimal for the detection of exposed or newly infected dogs, since dogs infected with
Leishmania (especially if they are asymptomatic) might not seroconvert immediately after infection or they may develop immune responsiveness oriented toward a self-healing cellular immune reaction, thus serological tests may lead to false-negative results [
14]. Additionally, serological methods frequently display cross reactivity with sera from other pathogens [
16,
17]. PCRs can make up for the above-mentioned inherited defects of serology and are more appropriate for
Leishmania surveillance in asymptomatic dogs. For example, in a previous study [
14], 37% of seronegative asymptomatic dogs from an area of endemicity were positive by PCR. Although PCR methods have high sensitivity, there are many inhibitors for PCR. Some negative results are probably due to the presence of
Leishmania parasites in blood aliquots assay and missing in the aliquots for DNA extraction; thus, it will not be enough to be amplified by PCR [
13]. So, discrepancies between the diagnostic methods were observed.
The accordance rate of 2 diagnostic methods in the present finding was 7.6% (
Table 1), which was consistent with previous investigations. Silva et al. [
18] inquired into the frequency of positive serological tests (ELISA) with positive PCR results for the diagnosis of asymptomatic infections. Low agreements (8.2%, 4.1%) between PCR and ELISA emerged, and no association was observed between the results of PCR and serological testing [
18]. The low accordance rate of 2 diagnostic methods highlighted the difficulty in assessment of the infection status of asymptomatic dogs. Although low agreement was obtained between the results of ELISA and PCR, PCR was more appropriate for our epidemiological surveillance of
Leishmania infection in asymptomatic dogs, since this method directly evaluated the presence of parasite DNA [
19,
20]. However, 2 pairs of primers both targeted the kDNA in this study, which is a limitation of the present study. Although samples of our study came from an endemic area where trypanosomatids-infected dogs are rare [
21], the possibility of cross reactivity in PCR assay cannot be ruled out. However, a number of articles related to our paper have already been published in some journals and added to Science Citation Index. Lachaud et al. [
22] and Costa et al. [
23] have reported that 2 pairs of primers (K13A-K13B and RV1-RV2) were highly specific among genus
Leishmania and could detect
Leishmania in 100% of symptomatic infected dogs. In China, PCR used the K13A-K13B as the primer, and ELISA was performed to evaluate the prevalence of canine
Leishmania infantum infection in Jiuzhaigou county of Sichuan province, which confirmed that 2 pair primers of PCR targeting the same gene kDNA were feasible to investigate
L. infantum infection among asymptomatic dogs [
8].
The findings in the present study indicated that
Leishmania infection was prevalent among asymptomatic dogs in the studied districts of Heishui. The rate in Heishui was higher than those of neighboring districts [
24], broadly in line with other districts of China [
25], and higher than Brazil [
26], but lower than some countries in the Mediterranean region [
27]. Our findings are utility for understanding of the asymptomatic dog infection rate, and the data presented provide evidence to consider the asymptomatic dogs as the primary reason for the prevalence of visceral leishmaniasis in the area. Since domestic dogs have a close relationship with human beings, once they are infected with
Leishmania, it will be easy to spread to individuals. As a matter of fact, there are neither concerns of
Leishmania-infected asymptomatic dogs nor effective strategies for controlling visceral leishmaniasis transmission through these dogs by now. However, it is necessary to detect
Leishmania infection in asymptomatic dogs before individuals are infected, to make effective management measures to deal with domestic dogs, and to prevent and control infection of
Leishmania among domestic dogs. Meanwhile, the route of domestic dog contamination and the risk of VL spreading to human populations should be further studied.
In summary, the results demonstrated that Leishmania infection was so highly prevalent among asymptomatic dogs that effective management measures should be made to reduce and interdict Leishmania infection in domestic dogs in Heishui county, and asymptomatic dogs may be the primary reason for the prevalence of VL in this area.
The study got the approval by Animal Ethical Committee (IACUC) of the Shandong Academy of Medical Sciences, Shandong Institute of Parasitic Disease, and obtained oral informed consent from dog owners.
Notes
-
CONFLICT OF INTEREST
The authors declare no conflict of interest related to this work.
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS
The authors are indebted to the Animal Husbandry and Bureau of Heishui and the owners of domestic dogs for the donation of the animals used in this study.
Fig. 1Map of selected 4 districts for survey of Leishmania infection among asymptomatic dogs in Heishui county, Sichuan province, China.
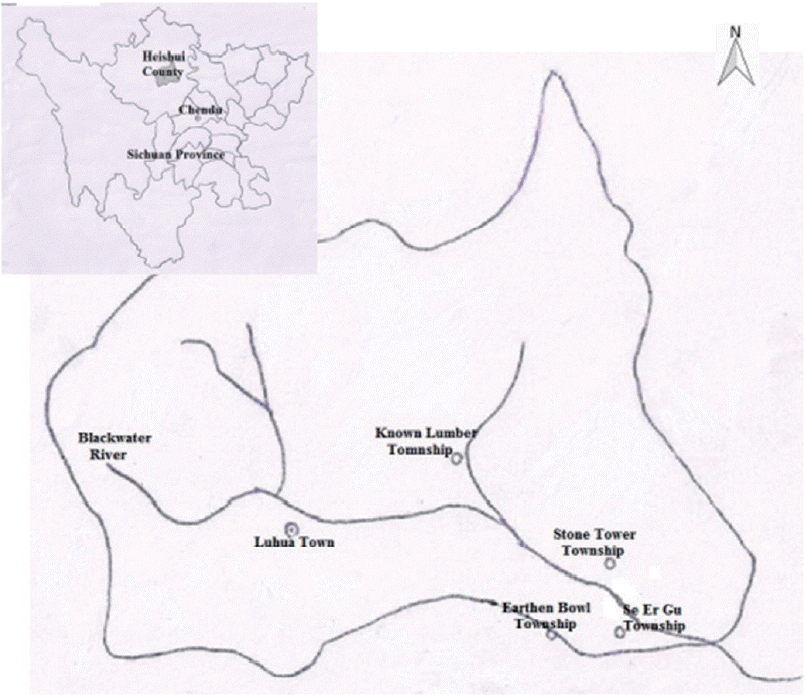
Fig. 2Agarose gel electrophoresis of kDNA PCR. Lane M, DNA marker; lane 1, positive control PCR product with primer RV1–RV2; lane 2, positive control PCR product with primer K13A–K13B; lanes 3, 5, 7,9, blood samples PCR products with primer RV1–RV2; lanes 4, 6, 8, 10, blood samples PCR products with primer K13A–K13B; lane 11, negative control PCR product with primer RV1–RV2; lane 12, negative control PCR product with primer K13A–K13B.
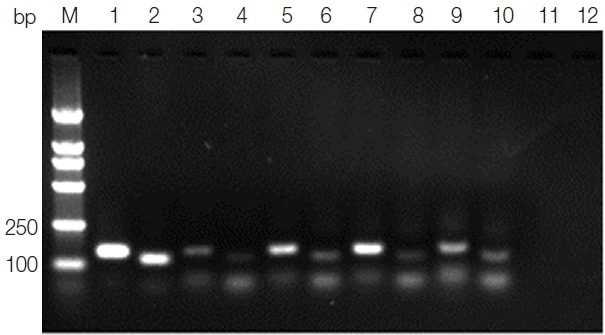
Table 1
Leishmania infection among dogs by test method
Table 1
|
Districts |
No. of dogs examined |
No. of ELISA positives |
ELISA (%) |
No. of PCR positives |
PCR |
P-value between ELISA and PCR |
No. of ELISA and PCR positives |
|
Known Lumber Township |
40 |
7 |
17.5 |
11 |
27.5 |
0.422 |
4 |
|
Earthen Bowl Township |
30 |
6 |
20.0 |
8 |
26.7 |
0.761 |
2 |
|
Se Er Gu Township |
20 |
5 |
25.0 |
6 |
30.0 |
1.000 |
2 |
|
Stone Tower Township |
15 |
3 |
20.0 |
5 |
33.3 |
0.682 |
0 |
|
Total |
105 |
21 |
20.0 |
30 |
28.6 |
0.198 |
8 |
References
- 1. Wang JY, Cui G, Chen HT, Zhou XN, Gao CH, Yang YT. Current epidemiological profile and features of visceral leishmaniasis in People’s Republic of China. Parasit Vectors 2012;5:31.
- 2. Zhang FN, Xiao N, Chen YL. Prevalent trends and control strategy of leishmaniasis in Sichuan province in 2004–2008. Chin Trop Med 2009;9:1836-1838.
- 3. Zhang FN, Zhang LP, Zhang YZ. Analysis on risk factors of leishmaniasis in quake stricken endemic areas in Sichuan. J Prev Med Infect 2010;6:433-437.
- 4. Zhang FN, Li GR, Lei Y, Chen YL. Analysis on leishmaniasis in Sichuan province from 1984 to 2005. J Pathog Biol 2007;2:79-80.
- 5. Gramiccia M, Gradoni L. The current status of zoonotic leishmaniasis and approaches to disease control. Int J Parasitol 2005;35:1169-1180.
- 6. Moshfe A, Mohebali M, Edrissian G, Zarei Z, Akhoundi B, Kazemi B, Jamshidi S, Mahmoodi M. Canine visceral leishmaniasis: asymptomatic infected dogs as a source of L. infantum infection. Acta Trop 2009;112:101-105.
- 7. Zhao GH, Yin K, Zhong WX, Cui Y, Wang HF. Development and application of rapid molecular method for detection of asymptomatic infection of Leishmania. Zhongguo Xue Xi Chong Bing Fang Zhi Za Zhi 2015;27:45-48. 52.
- 8. Wang JY, Ha Y, Gao CH, Wang Y, Yang YT, Chen HT. The prevalence of canine Leishmania infantum infection in western China detected by PCR and serological tests. Parasit Vectors 2011;4:69.
- 9. Bhang DH, Choi US, Kim HJ, Cho KO, Shin SS, Youn HJ, Hwang CY, Youn HY. An autochthonous case of canine visceral leishmaniasis in Korea. Korean J Parasitol 2013;51:545-549.
- 10. Martín-Sánchez J, Pineda JA, Morillas-Márquez F, García-García JA, Acedo C, Macías J. Detection of Leishmania infantum kinetoplast DNA in peripheral blood from asymptomatic individuals at risk for parenterally transmitted infections: relationship between polymerase chain reaction results and other Leishmania infection markers. Am J Trop Med Hyg 2004;70:545-548.
- 11. Scarlata F, Vitale F, Saporito L, Reale S, Vecchi VL, Giordano S, Infurnari L, Occhipinti F, Titone L. Asymptomatic Leishmania infantum/chagasi infection in blood donors of western Sicily. Tran R Soc Trop Med Hyg 2008;102:394-396.
- 12. Fukutani KF, Figueiredo V, Celes FS, Cristal JR, Barral A, Barral-Netto M, de Oliveira CI. Serological survey of Leishmania infection in blood donors in Salvador, Northeastern Brazil. BMC Infect Dis 2014;14:422.
- 13. Hamarsheh O, Nasereddin A, Damaj S, Sawalha S, Al-Jawabreh H, Azmi K, Amro A, Ereqat S, Abdeen Z, Al-Jawabreh A. Serological and molecular survey of Leishmania parasites in apparently healthy dogs in the West Bank, Palestine. Parasit Vectors 2012;5:183.
- 14. Otranto D, Paradies P, de Caprariis D, Stanneck D, Testini G, Grimm F, Deplazes P, Capelli G. Toward diagnosing Leishmania infantum infection in asymptomatic dogs in an area where leishmaniasis is endemic. Clin Vaccine Immunol 2009;16:337-343.
- 15. Solano-Gallego L, Morell P, Arboix M, Alberola J, Ferrer L. Prevalence of Leishmania infantum infection in dogs living in an area of canine leishmaniasis endemicity using PCR on several tissues and serology. J Clin Microbiol 2001;39:560-563.
- 16. de Ferreira EC, de Lana M, Carneiro M, Reis AB, Paes DV, da Silva ES, Schallig H, Gontijo CM. Comparison of serological assays for the diagnosis of canine visceral leishmaniasis in animals presenting different clinical manifestations. Vet Parasitol 2007;146:235-241.
- 17. Porrozzi R, Santos da Costa MV, Teva A, Falqueto A, Ferreira AL, dos Santos CD, Fernandes AP, Gazzinelli RT, Campos-Neto A, Grimadi G Jr. Comparative evaluation of enzyme-linked immunosorbent assays based on crude and recombinant leishmanial antigens for serodiagnosis of symptomatic and asymptomatic Leishmania infantum visceral infections in dogs. Clin Vaccine Immunol 2007;14:544-548.
- 18. Silva LA, Romero HD, Fagundes A, Nehme N, Fernandes O, Rodrigues V, Costa RT, Prata A. Use of the polymerase chain reaction for the diagnosis of asymptomatic Leishmania infection in a visceral leishmaniasis-endemic area. Rev Inst Med Trop Sao Paulo 2013;55:101-104.
- 19. Costa CH, Gomes RB, Silva MR, Garcez LM, Ramos PK, Santos RS, Shaw JJ, David JR, Maguire JH. Competence of human host as a reservoir for Leishmania chagasi. J Infect Dis 2000;182:997-1000.
- 20. Moreno EC, Gonçalves AV, Chaves AV, Melo MN, Lambertucci JR, Andrade AS, Negrão-Corrêa D, de Figueiredo Antunes CM, Carneiro M. Inaccuracy of enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay using soluble and recombinant antigens to detect asymptomatic infection by Leishmania infantum. PLoS Negl Trop Dis 2009;3:e536.
- 21. Lun ZR, Fang Y, Wang CJ, Brun R. Trypanosomiasis of domestic animals in China. Parasitol Today 1993;9:41-45.
- 22. Lachaud L, Marchergui-Hammami S, Chabbert E, Dereure J, Dedet JP, Bastien P. Comparison of six PCR methods using peripheral blood for detection of canine visceral leishmaniasis. J Clin Microbiol 2002;40:210-215.
- 23. Costa CH, Stewart JM, Gomes RB, Garcez LM, Ramos PK, Bozza M, Satoskar A, Dissanayake S, Santos RS, Silva MR, Shaw JJ, David JR, Maguire JH. A symptomatic human carriers of Leishmania chagasi. Am J Trop Med Hyg 2002;66:334-337.
- 24. Wang JY, Ha Y, Gao CH, Wang Y, Yang YT, Chen HT. The prevalence of canine Leishmania infantum infection in western China detected by PCR and serological tests. Parasit Vectors 2011;4:69.
- 25. Wang JY, Chen SB, Gao CH, Jin CF, Feng Y, Zhang CJ, He HX, Yang CM, Yang YT, Bao YF. Survey on the Leishmania infantum asymptomatic infection in dogs in Wenxian county of Gansu province. Chin J Zoonoses 2006;22:734-737.
- 26. Dantas-Torres F, Brandao-Filho SP. Visceral leishmaniasis in Brazil: revisiting paradigms of epidemiology and control. Rev Inst Med Trop Sao Paulo 2006;48:151-156.
- 27. Otranto D, Paradies P, de Caprariis D, Stanneck D, Testini G, Grimm F, Deplazes P, Capelli G. Toward diagnosing Leishmania infantum infection in asymptomatic dogs in an area where leishmaniasis is endemic. Clin Vaccine Immunol 2009;16:337-343.