Abstract
The aim of this study was to identify antigens for a vaccine or drug target to control rabbit coccidiosis. A combination of 2-dimensional electrophoresis, immunoblotting, and mass spectrometric analysis were used to identify novel antigens from the sporozoites of Eimeria stiedae. Protein spots were recognized by the sera of New Zealand rabbits infected artificially with E. stiedae. The proteins were characterized by matrix-assisted laser desorption ionization time of flight mass spectrometry (MALDI-TOF/TOF-MS) analysis in combination with bioinformatics. Approximately 868 protein spots were detected by silver-staining, and a total of 41 immunoreactive protein spots were recognized by anti-E. stiedae sera. Finally, 23 protein spots were successfully identified. The proteins such as heat shock protein 70 and aspartyl protease may have potential as immunodiagnostic or vaccine antigens. The immunoreactive proteins were found to possess a wide range of biological functions. This study is the first to report the proteins recognized by sera of infected rabbits with E. stiedae, which might be helpful in identifying potential targets for vaccine development to control rabbit coccidiosis.
-
Key words: Eimeria stiedae, rabbit, sporozoite, immunoproteomics, vaccine target
INTRODUCTION
Rabbit as an animal model have been widely used for experimental researches. Coccidiosis is one of the most important diseases in rabbit breeding, which is a highly contagious infection and caused by several species of
Eimeria [
1].
Eimeria stiedae is one of the most pathogenic species in domestic rabbits [
2].
E. stiedae parasitizes the bile duct epithelial cells which causes severe liver coccidiosis, resulting in enormous economic losses [
3]. General clinical symptoms include reduced food consumption, slow growth, diarrhea, and even death of a large number of rabbits [
4,
5].
Because no vaccines are yet available, the control of rabbit coccidiosis is primarily based on careful management combined with prophylactic medication in feed or water [
6]. However, the present methods for the control of rabbit coccidiosis face the problems of the rise of drug resistance, high cost of new drug development, and societal pressure against use of the chemicals [
7–
9]. These have prompted the development of new control strategies against rabbit coccidiosis, and an efficient vaccine that can prevent rabbit coccidiosis is urgently needed. Recent efforts are therefore directed towards the development of recombinant vaccines against coccidiosis [
10–
12].
Immunoproteomic analysis is a powerful technique for high-throughput detection to identify novel potential antigens [
13]. This methodology had been applied to identify immunoreactive antigens in parasites such as
Toxoplasma gondii, Neospora caninum, Haemonchus contortus, and
Brugia malayi [
14–
19]. Nevertheless, very few studies of coccidian infection in rabbits have been done, and most were restricted only to histopathology, biochemistry, and treatment of hepatic coccidiosis due to
E. stiedae [
20–
22]. In the present study, we first used an immunoproteomics approach to identify potential immunoreactive proteins of
E. stiedae. The results might be helpful in identifying potential new vaccine candidates or drug targets to control rabbit coccidiosis.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Collections of parasites and immmue sera
Oocysts of E. stiedae (Jiangsu strain) were propagated and maintained by passage through coccidian-free New Zealand rabbits in the Laboratory Animal Center of Nantong University, Nantong, China. Oocysts were purified from the livers of infected rabbits by floating in sucrose solution and were enumerated by hemocytometer. All animal experiments were performed in compliance with the Institutional Animal Care and Use Committee of Nantong University and national regulations and policies (no. 20150605–001).
Twelve 6-week-old healthy New Zealand rabbits, weighing 1–1.5 kg were used. Six New Zealand rabbits reared coccidian-free were orally infected with individual doses of 1×104 sporulated oocysts of E. stiedae. The rabbits were challenged 3 times at 2-week intervals with 5,000 sporulated oocysts per rabbit. Blood samples were obtained from rabbits by cardiac puncture 2 weeks after the last infection. Sera were collected from the samples, aliquoted, and stored at −80°C until used. Six unchallenged rabbits were reared in the same condition. All rabbits were fed ad libitum and free water. A cycle of 12-hr light and 12-hr dark was used throughout the experiment.
Preparation of protein extracts and 2-dimensional gel electrophoresis (2-DE)
Sporozoites of
E. stiedae were purified from sporulated oocysts, and soluble proteins were prepared as described previously [
13,
18]. Briefly, the sporulated oocysts were sonicated in an ice box, and the pellet was resuspended in a lysis buffer. Sporozoites were excysted and then purified on a cotton column (2 cm) to eliminate encysted sporocysts and oocysts. The sporozoite pellet was then concentrated and purified with the ReadyPrep 2-D Cleanup Kit (Bio-Rad, Hercules, California, USA). Protein concentration was determined by the Bradford method using Bio-Rad protein assay (Bio-Rad). Samples of aliquots were stored at −80°C until use.
The purified proteins (200 μg) were separated by isoelectric focusing (IEF) on non-linear IPG strips (pH 3–10; 13 cm) (GE Healthcare, Little Chalfont, UK). The IEF was carried out under the following step: 500 V for 1 hr, 1,000 V for 1 hr, then 8,000 V for 10 hr to reach a total of 60,000 Vh. After completion of IEF, the second dimensional separation was carried in 12.5% polyacrylamide gel using the Multiphor system (Amersham Biosciences, Amersham, UK). Gels were fixed overnight in a fixing solution and stained by the silver-staining method. Each sample was repeated 3 times.
Immunoblot analysis and in-gel digestion
Immunoblot analysis and in-gel digestion was performed by a semi-dry transfer system as previously described [
19]. Briefly, the membranes were blocked with 5% W/V skim milk in 0.05% Tween-20 PBS, incubated with anti-
E. stiedae serum of rabbit diluted 1:500 in blocking buffer and then horseradish peroxidase-conjugated goat anti-rabbit antibody (BioRad) diluted at 1:2,500. The immunoreactive proteins were visualized and analyzed by autoradiography using enhanced chemiluminescence reagent (Pierce Biotechnology, Rockford, Illinois, USA) and ImageMaster 2D Platinum software (Version 7.0, Amersham Bioscience, Swiss Institute of Bioinformatics, Geneva, Switzerland). Normal rabbit serum was used to test another blotting membrane as a negative control. Western blot analysis was repeated 3 times. The immunogenic spots were selected, and in-gel digestion was performed with trypsin.
In-gel digestion products were sent to Shanghai Applied Protein Technology Co. Ltd. for analysis by MALDI-TOF/TOF-MS (ABI Voyager DE Pro, Applied Biosystems). Sequences of identified proteins were submitted to a BLAST server (
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/BLAST/) for a homology search. GO analysis for characterized proteins based on BLAST results was carried out using Blast2GO version 2.7.2. The identified proteins were categorized through a InterProsan InterProScan software. The results were subjected to analyze by GO categories using the Web Gene Ontology Annotation Plotting (WEGO,
http://wego.genomics.org.cn/cgi-bin/wego/index.pl).
RESULTS
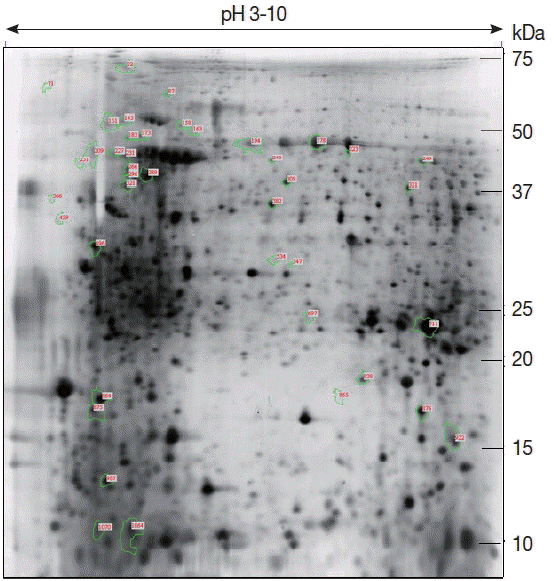
2-DE profiles of E. stiedae sporozoites
Proteins from the sporozoites of
E. stiedae were separated by 2-DE to find immunogenic proteins. The protein profiles of
E. stiedae sporozoites extracts were well represented by 2-DE separations across a pH 3–10 gradient. About 868 protein spots were obtained on the 2-DE maps constructed with silver-stained gels and analyzed by ImageMaster 2D Platinum software (
Fig. 1).
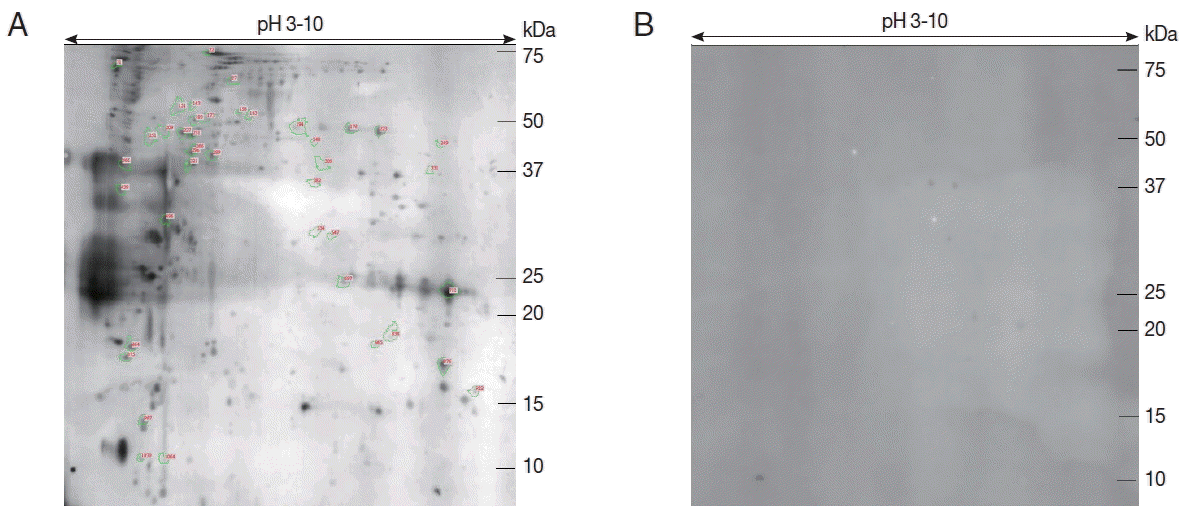
To evaluate the immunity of
E. stiedae sporozoite proteins, western blot assay was conducted with anti-
E. stiedae sera obtained from infected rabbits. Approximately 291 spots were shown on western blot maps of the sporozoites of
E. stiedae (
Fig. 2A), whereas none were detected on the negative-control sera (
Fig. 2B).
Forty-one protein spots were shown to be highly matched to those from the sporozoites of
E. stiedae in the preparative 2-DE (
Fig. 2A). The parameters, including the probability score for the match, isoelectric point (pI), molecular weight (MW), and the number of peptide matches, were used for confident protein identification.
The results displayed that spots 227, 248, 289, and 321 were identified as heat shock protein of
Eimeria. The spot 178 was identified as a merozoite surface protein of Plasmodium. The spot 158 was identified as an ATP-dependent RNA helicase of
Eimeria brunetti, and the spot 309 was identified as an eukaryotic aspartyl protease of
Eimeria maxima. The spot 249 was identified as the SICA antigen of
Plasmodium knowlesi. Two proteins (spot 987 and 1070) were identified as prefolding subunit 6 of
Hammondia hammondi. Several spots were identified as hypothetical proteins of
Toxoplasma, Eimeria, and
Plasmodium. Two spots (838 and 865) were identified as homologous proteins (sperm-tail PG-rich repeat protein and repeat-containing protein) to other protozoan parasites (
Tetrahymena thermophila and
Stylonychia lemnae). In total, 23 protein spots were successfully identified by MALDI-TOF/TOF-MS (
Table 1).
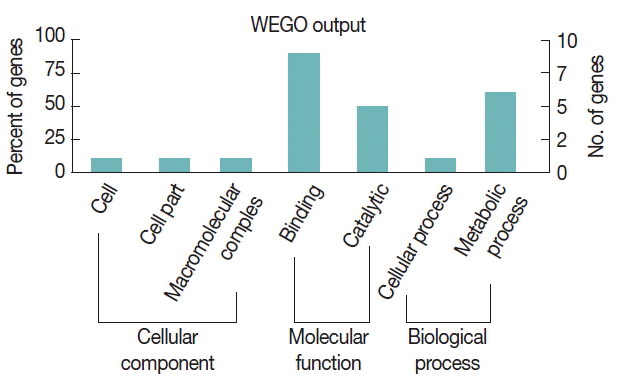
To further study the biological functions of the 23 immunoreactive proteins, GO annotation was carried out. Annotated relevant parasite proteins from the NCBI database were analyzed by Blast2GO based on BLASTP search. Proteins identified in this study were further categorized by their cellular component, molecular function, and biological process using WEGO. These proteins were classified into 2 categories, including cellular process and metabolic process, based on their biological process. A large proportion of proteins were categorized in binding related to the molecular function (
Fig. 3).
DISCUSSION
The rabbit (
Oryctolagus cuniculus) is a valuable animal species widely used for biomedical research purposes, meat, and fur production [
23]. However, coccidiosis is common in rabbits and considered a severe problem leading to a large economic loss. Duszynski and Couch [
24] reported that the rate of coccidiosis infection ranged from 64% to 100% in the world. According to a report, China is the largest rabbit-producing country, which produced approximately 700 million of rabbit in 2013 and the year-over-year percentage increase was about 2% [
25]. Previous reports showed that the infection rate of coccidia in the surveyed experimental rabbits was up to 100% in China [
26].
In order to overcome the above-mentioned drawbacks of the current methods to control coccidiosis, researches have focused on novel strategies based on recombinant vaccination as a potential alternative method of coccidiosis control [
27,
28]. Characterization of specific antigens of
Eimeria is a pivotal step in development of a recombinant coccidial vaccine. In recent years, employing a combination of 2-DE, immunoblotting, and mass spectrometric analysis has proved to be a powerful approach to identify novel antigens [
29]. Right now, there is a wide array of immunogenic antigens from
E. tenella sporozoites and merozoites characterized by an immunoproteomics method [
30,
31].
E. tenella antigens, such as sporozoite antigen, immunoglobulin heavy chain protein, heat shock protein 70 (HSP70), pyruvate kinase, enoloase, eimepsine, and lactate dehydrogenase were identified as immunogenic antigens [
18,
19].
To our knowledge, there were few reports on rabbit coccidiosis, especially those focused on identification of novel antigens of
E. stiedae. In this study, we report for the first time an immunoproteomic analysis of sporozoite proteins of
E. stiedae from infected rabbits. Using immunoproteomic analysis, a total of 41 immunoreactive protein spots were recognized by anti-
E. stiedae sera of infected rabbits, and 23 protein spots were successfully identified by MALDI-TOF/TOF-MS. Of the 23 analyzed spots, 7 proteins belonged to the family Eimeriidae. Four spots (spot 248, 289, 227, and 321) were identified as HSP70 of
Eimeria, 2 of which were at similar Mr and pI values as their orthologues in
Eimeria praecox, while the other 2 were from
Eimeia necatrix and
E. brunetti. HSP70 is considered to be from a predominant HSP family and plays a key regulatory role in parasite development and pathogenesis [
32]. It is a highly abundant protein in apicomplexan parasites and is often detected in proteomics studies [
33,
34]. Liu et al. [
19] reported that a protein matching HSP70 of
Eimeria acervulina was identified by immunoproteomic analysis from a second-generation merozoites of
E. tenella. In this study, HSP70 was detected by sera from rabbits infected with
E. stiedae, implying that it could be a potential vaccine or drug target for
E. stiedae.
In the present study, several other proteins common to all parasites were also distinguished. Among them, 2 particular enzymes were detected, a 50 kDa aspartyl protease called eimepsin in
Eimeria (gi557184952) and an ATP-dependent RNA helicase (gi557242052). The aspartyl protease was identified from the spot 309. The exact function of this enzyme is still unknown, but previous studies have shown that aspartyl protease is produced in large quantities during sporulation of
Eimeria oocysts and could be involved in invasion of host cells by free parasitic stages [
35]. Aspartyl protease was also detected in
E. tenella sporozoites in a previous study [
18]. The other enzyme, ATP-dependent RNA helicase was identified from the spot 158, which are implicated in all aspects of cellular RNA metabolism and promote unwinding of RNA during splicing and translation [
13]. This protease has previously been reported to exist in
Eimeria bovis and
Schistosoma japonicum by proteomic analysis [
36]. Spots 183, 547, 71, and 331 were identified as hypothetical proteins of
T. gondii with unknown function not described previously at the protein level. Another 6 hypothetical proteins also showed immunoreactivity to
E. stiedae positive antisera. The biological characteristics of these proteins remain to be identified.
Notes
-
CONFLICT OF INTEREST
We have no conflict of interest related to this work.
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (grant no. 31301926) and the Natural Science Foundation of Jiangsu Province of China (grant no. BK20130388). We thank Shanghai Applied Protein Technology Co. Ltd. for technological support.
Fig. 1Separation of proteins extracted from sporozoites of E. stiedae by 2-DE. Isoelectrofocusing was performed using a pH 3–10 strip. SDS-PAGE was carried out on a 12.5% gel and then stained by the silver-staining method.

Fig. 2Immunoblot analysis of sporozoite proteins of E. stiedae using anti-E. stiedae sera (A). Protein spots selected for further analysis are numbered. Immunoblot analysis of sporozoite proteins of E. stiedae using normal rabbit serum (B).
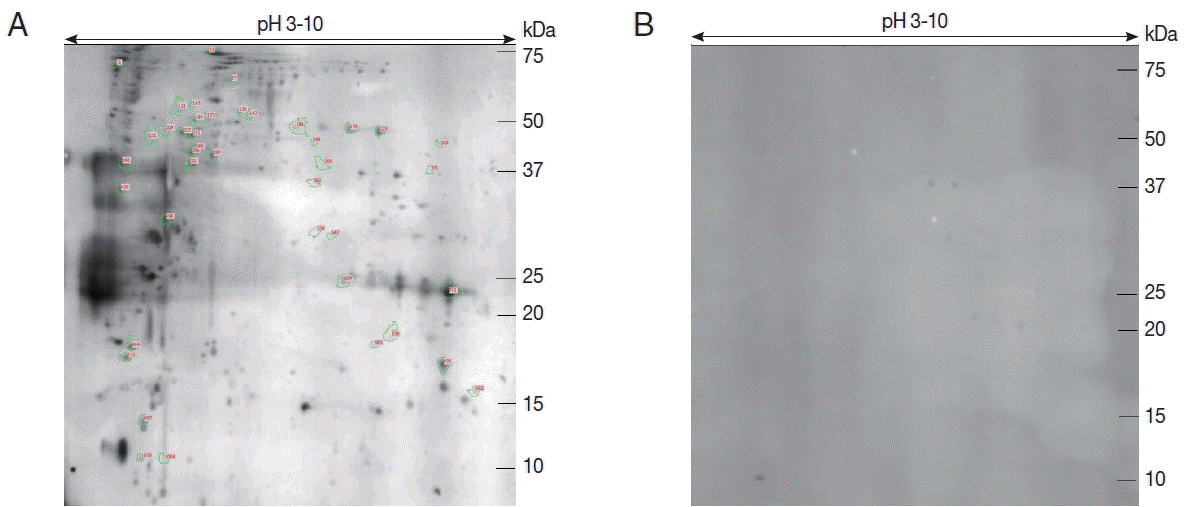
Fig. 3Gene ontology (GO) categories of sporozoite proteins of E. stiedae recognized by anti-E. stiedae sera. The proteins were categorized into cellular component, molecular function and biological process by Web Gene Ontology Annotation Plot (WEGO) according to the information.
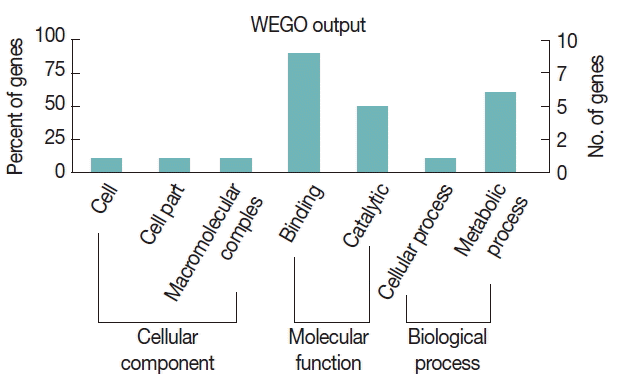
Table 1Characterization of the sporozoites proteins of Eimeria stiedae by MALDI-TOF/TOF-MS and searched using ‘Mascot’ server
Table 1
|
Spot no.a
|
Database ID no.b
|
Protein name |
Species |
Mascot score |
Sequence coverage (%)c
|
TheorecticalMr/pId
|
No. matched peptidese
|
|
22 |
gi557167540 |
Hypothetical protein |
E. maxima
|
68 |
62 |
13792.4/8.69 |
9 |
|
71 |
gi672286816 |
Hypothetical protein |
Toxoplasma gondii
|
77 |
15 |
484744.8/5.47 |
67 |
|
87 |
gi672195787 |
Hypothetical protein |
Plasmodium inui San Antonio
|
77 |
21 |
217806.5/5.41 |
44 |
|
143 |
gi657007322 |
Hypothetical protein |
Plasmodium vinckei
|
73 |
30 |
130388.4/5.89 |
34 |
|
158 |
gi557242052 |
ATP-dependent RNA helicase |
E. brunetti
|
71 |
25 |
76923/9.39 |
20 |
|
163 |
gi586742367 |
Hypothetical protein |
Tetrahymena thermophila
|
74 |
25 |
110789.1/9.16 |
26 |
|
178 |
gi525346891 |
Merozoite surface protein 3 |
Plasmodium cynomolgi
|
73 |
25 |
99198.5/4.83 |
25 |
|
183 |
gi672571227 |
Hypothetical protein |
Toxoplasma gondii
|
105 |
15 |
634071.3/5.3 |
84 |
|
227 |
gi557145360 |
Heat shock protein 70 |
E. praecox
|
129 |
21 |
56177.9/4.98 |
11 |
|
248 |
gi557243846 |
Heat shock protein |
E. necatrix
|
350 |
24 |
70417.6/5.27 |
13 |
|
249 |
gi194247223 |
SICA antigen |
Plasmodium knowlesi
|
72 |
18 |
223865.4/8.45 |
42 |
|
289 |
gi557234094 |
Heat shock protein 70 |
E. brunetti
|
94 |
19 |
77762.2/5.46 |
14 |
|
309 |
gi557184952 |
Eukaryotic aspartyl protease |
E. maxima
|
248 |
19 |
43543.9/5.76 |
7 |
|
321 |
gi557145360 |
Heat shock protein 70 |
E. praecox
|
97 |
14 |
56177.9/4.98 |
7 |
|
331 |
gi672292023 |
Hypothetical protein |
Toxoplasma gondii
|
78 |
36 |
48417.1/10.72 |
18 |
|
534 |
gi657011465 |
Hypothetical protein |
Plasmodium vinckei
|
67 |
33 |
60032.6/9.37 |
21 |
|
547 |
gi672569086 |
Hypothetical protein |
Toxoplasma gondii
|
82 |
13 |
634453.7/5.3 |
77 |
|
838 |
gi586737227 |
Sperm-tail PG-rich repeat protein |
Tetrahymena thermophila
|
72 |
51 |
32719.3/9.87 |
16 |
|
865 |
gi678337729 |
Ankyrin repeat-containing protein |
Stylonychia lemnae
|
71 |
26 |
103391.2/8.46 |
24 |
|
864 |
gi675218855 |
Conserved protein |
Plasmodium chabaudi
|
74 |
19 |
224685.5/8.44 |
39 |
|
875 |
gi325117235 |
Hypothetical protein |
Neospora caninum
|
73 |
19 |
208965.7/9.67 |
33 |
|
987 |
gi661337512 |
Prefoldin subunit 6 |
Hammondia hammondi
|
78 |
77 |
14489.4/7.82 |
14 |
|
1070 |
gi661337512 |
Prefoldin subunit 6 |
Hammondia hammondi
|
68 |
77 |
14489.4/7.82 |
13 |
References
- 1. Vadlejch J, Knízková I, Makovcová K, Kunc P, Jankovská I, Janda K, Borkovcová M, Langrová I. Thermal profile of rabbits infected with Eimeria intestinalis. Vet Parasitol 2010;171:343-345.
- 2. Abu-Akkada SS, Oda SS, Ashmawy KI. Garlic and hepatic coccidiosis: prophylaxis or treatment? Trop Anim Health Prod 2010;42:1337-1343.
- 3. Peeters JE, Geeroms R, Halen P. Evolution of coccidial infection in commercial and domestic rabbits between 1982 and 1986. Vet Parasitol 1988;29:327-331.
- 4. Joyner LP, Catchpole J, Berrett S. Eimeria stiedae in rabbits: the demonstration of responses to chemotherapy. Res Vet Sci 1983;34:64-67.
- 5. Peeters JE, Geeroms R. Efficacy of toltrazuril against intestinal and hepatic coccidiosis in rabbits. Vet Parasitol 1986;22:21-35.
- 6. Yan W, Wang W, Wang T, Suo X, Qian W, Wang S, Fan D. Simultaneous identification of three highly pathogenic Eimeria species in rabbits using a multiplex PCR diagnostic assay based on ITS1–5.8S rRNA-ITS2 fragments. Vet Parasitol 2013;193:284-288.
- 7. Martin AG, Danforth HD, Barta JR, Fernando MA. Analysis of immunological cross-protection and sensitivities to anticoccidial drugs among five geographical and temporal strains of Eimeria maxima. Int J Parasitol 1997;27:527-533.
- 8. Vermeulen AN. Progress in recombinant vaccine development against coccidiosis: a review and prospects into the next millennium. Int J Parasitol 1998;28:1121-1130.
- 9. Hanada S, Omata Y, Umemoto Y, Kobayashi Y, Furuoka H, Matsui T, Maeda R, Saito A. Relationship between liver disorders and protection against Eimeria stiedai infection in rabbits immunized with soluble antigens from the bile of infected rabbits. Vet Parasitol 2003;111:261-266.
- 10. Abdel Megeed KN, Abuel Ezz NM, Abdel-Rahman EH. Protective effect of Eimeria stiedae coproantigen against hepatic coccidiosis in rabbits. J Egypt Soc Parasitol 2005;35:581-595.
- 11. Song H, Yan R, Xu L, Song X, Shah MAA, Zhu H, Li X. Efficacy of DNA vaccines carrying Eimeria acervulina lactate dehydrogenase antigen gene against coccidiosis. Exp Parasitol 2010;126:224-231.
- 12. Hanada S, Umemoto Y, Omata Y, Koyama T, Nishiyama K, Kobayashi Y, Furuoka H, Matsui T, Maeda R, Saito A. Eimeria stiedae merozoite 49-kDa soluble antigen induces protection against infection. J Parasitol 2003;89:613-617.
- 13. Hong Y, Peng J, Jiang W, Fu Z, Liu J, Shi Y, Li X, Li J. Proteomic analysis of Schistosoma japonicum schistosomulum proteins that are differentially expressed among hosts differing in their susceptibility to the infection. Mol Cell Proteomics 2011;10:M110.006098.
- 14. Lee EG, Kim JH, Shin YS, Shin GW, Kim YH, Kim GS, Kim DY, Jung TS, Suh MD. Two-dimensional gel electrophoresis and immunoblot analysis of Neospora caninum tachyzoites. J Vet Sci 2004;5:139-145.
- 15. Yan F, Xu L, Liu L, Yan R, Song X, Li X. Immunoproteomic analysis of whole proteins from male and female adult Haemonchus contortus. Vet J 2010;185:174-179.
- 16. Sun XM, Ji YS, Elashram SA, Lu ZM, Liu XY, Suo X. Identification of antigenic proteins of Toxoplasma gondii RH strain recognized by human immunoglobulin G using immunoproteomics. J Proteomcs 2012;77:423-432.
- 17. Wongkamchai S, Chiangjong W, Sinchaikul S, Chen ST, Choochote W, Thongboonker V. Identification of Brugia malayi immunogens by an immunoproteomics approach. J Proteomics 2011;74:1607-1613.
- 18. de Venevelles P, Chich JF, Faigle W, Loew D, Labbé M, Girard-Misguich F, Péry P. Towards a reference map of Eimeria tenella sporozoite proteins by two-dimensional electrophoresis and mass spectrometry. Int J Parasitol 2004;34:1321-1331.
- 19. Liu L, Xu L, Yan F, Yan R, Song X, Li X. Immunoproteomic analysis of the second-generation merozoite proteins of Eimeria tenella. Vet Parasitol 2009;164:173-182.
- 20. Watanabe H, Koyama T, Omata Y, Uzuka Y, Tanabe S, Sarashina T, Maeda R, Saito A. Trail antigen in Eimeria stiedae sporozoites associated with a thrombospondin-related motif and the entry of cultured cells. Vet Parasitol 2001;99:287-295.
- 21. Çam Y, Atasever A, Eraslan G, Kibar M, Atalay O, Beyaz L, Inci A, Liman BC. Eimeria stiedae: experimental infection in rabbits and the effect of treatment with toltrazuril and ivermectin. Exp Parasitol 2008;119:164-172.
- 22. Oliveira UC, Fraga JS, Licois D, Pakandl M, Gruber A. Development of molecular assays for the identification of the 11 Eimeria species of the domestic rabbit (Oryctolagus cuniculus). Vet Parasitol 2011;176:275-280.
- 23. Bhat TK, Jithendran KP, Kurade NP. Rabbit coccidiosis and its control: a review. World Rabbit Sci 1996;4:37-41.
- 24. Duszynski DW, Couch L. The Biology and Identification of the Coccidia (Apicomplexa) of Rabbits of the World. San Diego, California, USA. Academic Press; 2013, pp 4-5.
- 25. Dalle Zotte A, Szendro Z. The role of rabbit meat as functional food. Meat Sci 2011;88:319-331.
- 26. Song HY, Zhu SX, Liu C, Shao YX. A survey of Eimeria infections in experimental rabbits in Jiangsu Province. Prog Vet Med 2012;33:88-91.
- 27. Xu Q, Song X, Xu L, Yan R, Shah MA, Li X. Vaccination of chickens with a chimeric DNA vaccine encoding Eimeria tenella TA4 and chicken IL-2 induces protective immunity against coccidiosis. Vet Parasitol 2008;156:319-323.
- 28. Song H, Qiu B, Yan R, Xu L, Song X, Li X. The protective efficacy of chimeric SO7/IL-2 DNA vaccine against coccidiosis in chickens. Res Vet Sci 2013;94:562-567.
- 29. Kositanont U, Saetun P, Krittanai C, Doungchawee G, Tribuddharat C, Thongboonkerd V. Application of immunoproteomics to leptospirosis: towards clinical diagnostics and vaccine discovery. Proteomics Clin Appl 2007;1:400-409.
- 30. Shirley MW. The genome of Eimeria spp., with special reference to Eimeria tenella—a coccidium from the chicken. Int J Parasitol 2000;30:485-493.
- 31. Williams RB, Catchpole J. A new protocol for a challenge test to assess the efficacy of live anticoccidial vaccines for chickens. Vaccine 2000;18:1178-1185.
- 32. De Jong-Brink M. How schistosomes profit from the stress responses they elicit in their hosts. Adv Parasitol 1995;35:177-256.
- 33. Cohen AM, Rumpel K, Coombs GH, Wastling JM. Characterisation of global protein expression by two-dimensional electrophoresis and mass spectrometry: proteomics of Toxoplasma gondii. Int J Parasitol 2002;32:39-51.
- 34. Marugán-Hernández V, Alvarez-García G, Risco-Castillo V, Regidor-Cerrillo J, Ortega-Mora LM. Identification of Neospora caninum proteins regulated during the differentiation process from tachyzoite to bradyzoite stage by DIGE. Proteomics 2010;10:1740-1750.
- 35. Jean L, Péry P, Dunn P, Bumstead J, Billington K, Ryan R, Tomley F. Genomic organisation and developmentally regulated expression of an apicomplexan aspartyl proteinase. Gene 2001;262:129-136.
- 36. Lutz K, Schmitt S, Linder M, Hermosilla C, Zahner H, Taubert A. Eimeria bovis-induced modulation of the host cell proteome at the meront I stage. Mol Biochem Parasitol 2011;175:1-9.