Abstract
Strains of Toxoplasma gondii in Brazil are highly genetically diverse compared to strains from North America and Europe. Dogs are epidemiologically important because they act as sentinels for T. gondii infections in humans and are good indicators of environmental contamination. The aim of this study was to isolate and genetically characterize T. gondii strains from tissues of naturally infected Brazilian dogs. For this study, 21 blood samples were collected from dogs at the Zoonosis Control Centers of Ilhéus and Itabuna cities, Bahia, Brazil. The sera were examined for T. gondii antibodies using the indirect hemagglutination test. Brains and hearts of seropositive dogs were bioassayed in mice to isolate and characterize T. gondii parasites by PCR-RFLP using 10 genetic markers (SAG1, newSAG2, SAG3, BTUB, c22-8, c29-2, GRA6, PK1, APICO, and L358). However, T. gondii was isolated from only 4 (57.1%) dogs, designated TgDgBr6, 13, 17, and 21. All strains were virulent, causing clinical changes (rough hair coat, lethargy, and abdominal distention) and the death of all mice within 8–20 days after inoculation. Genetic analysis of these 4 T. gondii isolates revealed 4 distinct genotypes with different clonal lineage combinations (types I, II, and III) and 2 atypical alleles. Using PCR-RFLP with several markers, this study contributes to evaluations of the genetic diversity of strains circulating in Brazil.
-
Key words: Toxoplasma gondii, dog, genotype, toxoplasmosis, Brazil
INTRODUCTION
Toxoplasma gondii is a parasite able to infect all warm-blooded animals, including humans, birds, and marine mammals, as well as other marine life, such as bivalve mollusks [
1–
3]. It is the cause of a worldwide endemic zoonosis known as toxoplasmosis, which has major implications for public health. Although infections with this parasite are usually asymptomatic, toxoplasmosis affects thousands of people every year, causing symptoms, such as eye problems that persist throughout life. Long-term sequelae in congenitally affected children and serious complications, even death, in immunosuppressed patients have been reported [
4,
5].
Canids are generally asymptomatic; however, they are highly susceptible to this parasite and are exposed to the same sources of infection as humans and other animals. Therefore, they are epidemiologically important because they are sentinels of
T. gondii infection for humans and are good indicators of environmental contamination. This is especially true in urban areas, where dogs usually circulate freely and are highly exposed to sources of parasite infection [
4,
6,
7].
Brazil has a high prevalence of
T. gondii infection in animals and humans, with prevalences ranging from 50 to 80% in the adult population [
8]. Studies on the genetic variability of
T. gondii isolates by PCR with restriction fragment length polymorphism (PCR-RFLP) using various multilocus markers have shown the variety of parasite genotypes in Brazil and worldwide [
4,
9,
10]. In Brazil, new genotypes of
T. gondii are frequently identified in various animal species, including dogs, suggesting extremely high genetic diversity of the parasite in human and animal populations in the country [
11–
14]. This genetic diversity indicates an unusual population structure or recombination of the protozoan.
T. gondii isolates from Brazil are biologically and genetically different from isolates obtained in North America, Europe, and Africa, which have typical clonal cell lines (types I, II, and III) with low evidence of recombination [
9,
10].
Furthermore,
T. gondii infections in Brazil tend to be more severe than infections in countries with typical clonal cell structures. This pathogenicity of
T. gondii in Brazil may be associated with atypical strains arising from frequent sexual recombination of the parasite [
15]. Recombination is believed to affect the virulence of the parasite, based on severe cases of toxoplasmosis associated with
T. gondii infections in immunocompetent humans [
4].
This study aimed to isolate and genetically characterize T. gondii strains derived from naturally infected dogs using PCR-RFLP with 10 markers, PCR, and sequencing, as well as to assess the pathogenicity of isolates in albino mice.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Animals and serological test
For this study, blood and tissue samples (brain and heart) were collected from a total of 21 dogs from the CCZ in the cities of Ilhéus and Itabuna in Bahia State, Brazil, from August 2013 to March 2014. Samples, collected after the animals were euthanized, for other reasons, in the CCZ, were taken to the Veterinary Parasitology Laboratory of the Veterinary Hospital for processing.
Blood was collected in tubes without anticoagulant and then centrifuged at 1,465 g for 10 min at 25°C to obtain serum. Antibodies against
T. gondii were detected by hemagglutination inhibition (HAI) using an Immuno-HAI Toxoplasmosis Kit (Wama Diagnóstica, São Paulo, Brazil) with a cutoff of 1:16, according to the manufacturer’s instructions [
16]. The heart and brain from each dog were placed individually into clean plastic bags containing saline solution (0.9% NaCl) and an antibiotic solution (1,000 IU of penicillin G potassium and 100 μg of streptomycin/ml of PBS) and refrigerated for the biological assay was completed. This project was approved by the Ethics Committee on Animal Use (protocol no. 016/2011).
Brains and hearts of seropositive dogs were processed in the Veterinary Parasitology Laboratory of the Veterinary Hospital of UESC for use in the biological assay. The organs were homogenized individually in a minimum amount of PBS. The digestion procedure was based on procedures reported previously [
17], with some modifications. One dose of 1 ml of the product from this peptic digestion was inoculated intraperitoneally into individual Swiss Webster mice. Three mice were inoculated per sample, with 3 for the brain and 3 for the heart homogenate. The mice were observed for 42 days, and during this period we assessed the virulence of the parasite by recording mortality in these animals.
Initially, 50–100 mg specimens were obtained from each stored mouse organ (spleens, livers, hearts, lungs, and brains). These specimens were macerated with a mortar and a pestle in liquid nitrogen to prepare for DNA extraction. For the extraction, we used an Easy-DNA Kit (Invitrogen, Carlsbad, California, USA) with protocol number 3 from the kit.
PCR detection of T. gondii
To amplify a 529-bp fragment of
T. gondii DNA, we performed PCR using Tox4 forward (CGCTGCAGGGAGGAAGACGAAAGTTG) and Tox5 reverse (CGCTGCAGACACAGTGCATCTGGATT) primers [
18].
Each PCR sample contained 50 μl, with 5 μl of the extracted DNA and 45 μl of a mixture containing 0.5 μM each primer, 0.1 mM each dNTP (Invitrogen), 5 μl of a 1×PCR buffer, 1.25 mM MgCl2, and 1.5 U Taq DNA polymerase (Invitrogen). The final reaction volume was completed with ultra-pure DNAse and RNAse-free water. Amplifications were performed for 35 cycles in a Veriti thermal cycler (Applied Biosystems, Foster City, California, USA) with the following conditions: 1 denaturation cycle of 7 min at 94°C, followed by 33 cycles of denaturation for 1 min at 94°C, annealing for 1 min at 55°C, and extension for 1 min at 72°C. Cycle 35 consisted of a final extension time of 10 min at 72°C. PCR products were subjected to 2% agarose gel electrophoresis, stained with SYBR® Safe DNA Gel Stain, and visualized using an L-Pix imaging system (Loccus Biotechnology, São Paulo, Brazil). A positive control (DNA from the RH strain of T. gondii) and a negative control (ultrapure water) were included in each PCR reaction.
Multilocus PCR-RFLP
DNA extracted and PCR amplified from the tissue of all infected mice and the control strain were analyzed using a multilocus PCR-RFLP technique with the following genetic markers: SAG1, new SAG2, SAG3, BTUB, c22-8, c29-2, GRA6, L358, PK1, and APICO, as described in [
19].
In the first step of this assay, DNA was amplified by nested-PCR (nPCR) using external primers (primary reaction) for each marker. This amplification was performed in a final volume of 50 μl for each sample, with a mixture containing 5 μl of a 1×PCR buffer, 1.5 mM MgCl2, 0.2 mM each dNTP (Invitrogen), 10 pM each primer, 2.5 U Taq DNA polymerase (Invitrogen), and 5.0 μL of extracted DNA. The final reaction volume was completed with ultra-pure DNAse and RNAse-free water. The primary PCR reaction consisted of 35 cycles with an initial denaturation step at 94°C for 5 min, denaturation at 94°C for 1 min, annealing at 58°C for 1 min, and extension at 72°C. Cycle 35 consisted of a 10-min extension at 72°C.
PCR products from the first reaction (1.5 μl for each sample) were used for nested-PCR amplifications (35 cycles) with internal primers (second reaction) for each marker. This secondary reaction consisted of the same temperatures and times as used in the first reaction; however, the annealing temperature depended on the specific marker targeted, and a final volume of 45 μl was used for each sample reaction.
To reveal the RFLP digestion pattern, 7 μl of nPCR products was added to 8 μl of a mixture containing NEB reaction buffer, 0.1 mg/ml BSA, and 1 unit of restriction enzyme. Enzymatic digestion products from each PCR were subjected to agarose gel electrophoresis, stained with SYBR® Safe DNA Gel Stain, and visualized using an imager with ultraviolet light (L-Pix image system, Loccus Biotechnology). A positive control (DNA from the RH, PTG e CTG strain of
T. gondii) and a negative control (ultrapure water) were included in each PCR reaction [
19]. DNA banding patterns of the isolates were compared with those of verified genotypes in ToxoDB (
http://toxodb.org/toxo/).
Triplicate PCR samples were purified with a PureLink® Genomic DNA kit (Invitrogen) and sent to Ludwig Biotec (Rio Grande do Sul, Brazil) for sequencing of 10 genetic markers (SAG1, new SAG2, SAG3, BTUB, c22-8, c29-2, GRA6, L358, PK1, and APICO). Sequencing was performed on an ABI PRISM 3100 Genetic Analyzer (Applied Biosystems) in both directions. As a positive control, the
T. gondii RH strain nPCR product was sequenced in both directions in duplicate. The chromatograms were analyzed using Phred software. The multilocus sequences were assembled into contigs using the CAP3 program, aligned with ClustalW (version 1.83), manually corrected using the BioEdit Sequence Alignment Editor, and compared with the sequences of the following 10
T. gondii reference strains available in the NCBI database (
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/bioproject/): GT1, ME49, VEG, FOU, MAS, VAND, RUB, p89, TgCATBr5 and TgCATBr9.
Sequences of
T. gondii isolates from the same geographical origin, with sequences of 8 isolates from pigs [
11], 3 isolates from sheep [
13], and 3 isolates from porcupines (
Chaetomys subspinosus) [
20], all from the southern region of Bahia State, Brazil. The RH strain of
T. gondii was used as a positive control. APICO sequences were aligned with the complete apicoplast genome of
T. gondii (U87145.2). All sequences were also compared with those available in the ToxoDB database using the BLASTn program.
Phylogenetic analysis was performed using MEGA software version 5, using the neighbor-joining algorithm, with distances calculated by the Nei-Tajima method. The stability of the topology was evaluated by bootstrapping with 1000 repetitions. Sequences from all isolates mentioned above were included in the phylogenetic analysis. The Tajima D test was used to analyze polymorphisms in the nucleotide sequences, based on the number of differences in pairs and the number of segregating polymorphic sites. All positions with less than 95% coverage were eliminated from the analysis.
RESULTS
Serological analysis of 21 samples from dogs showed that 7 (33.3%) were positive for anti-T. gondii antibodies. In the biological assay of organs from seropositive animals, it was possible to isolate 4 strains of the parasite. All were virulent in mice, causing clinical changes such as rough hair coat, lethargy, distended abdomens, and death 8–20 days after infection. Furthermore, tachyzoites were observed in the peritoneal fluid of all positive mice. Based on inoculations of brain and heart tissue from 14 animals, the parasite was found present in 7 organs: 4 hearts and 3 brains.
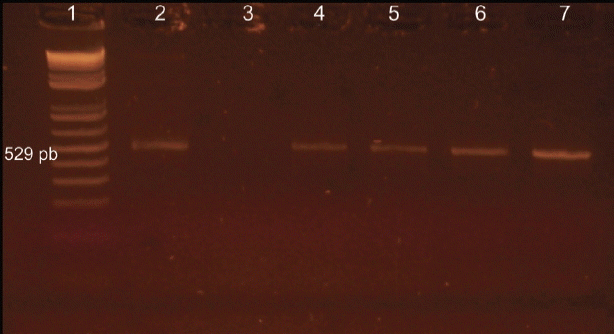
PCR using Tox4 and Tox5 primers on tissue samples from inoculated mice identified 4 (57.1%) dogs positive for
T. gondii (
Fig. 1), with 57.1% (4/7) of PCR positives detected in mice inoculated with hearts and 42.8% (3/7) with brains of infected dogs (
Table 1). These same samples were also positive in the nested-PCR using 10 pairs of primers (external and internal).
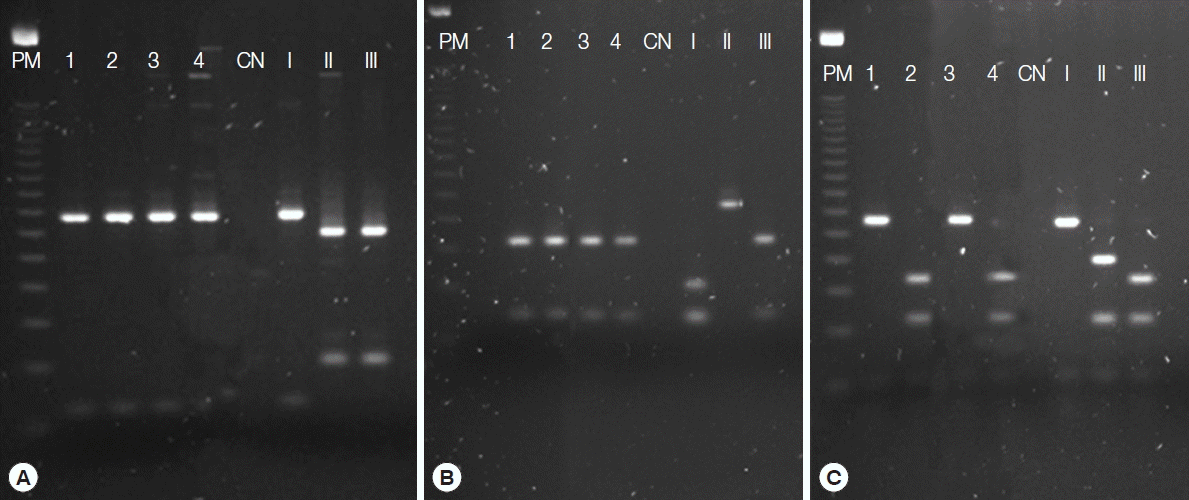
Genotyping of the 4 isolates by PCR-RFLP using 10 markers indicated 4 genotypes (
Fig. 2) with different combinations of clonal cell strains (types I, II, and III). Two of these genotypes showed atypical alleles (u-1) at the c22-8 locus. In all genotypes, we observed atypical alleles (u-2) at the PK1 locus. These isolates were designated TgDgBA6, 13, 17, and 21, with Tg for
T. gondii, Dg for dogs, and BA for Bahia, and the number identifying the dog positive for parasite DNA (
Table 2).
These isolates were considered unique genotypes in ToxoDB because they were not classified among the clonal cell genotypes (type I, II, or III) or the principal Brazilian clonal cell genotypes (BrI, BrII, BrIII, and BrIV) defined in [
9]. Furthermore, they showed no similarity with any other described genotypes from animals or humans in Brazil or worldwide.
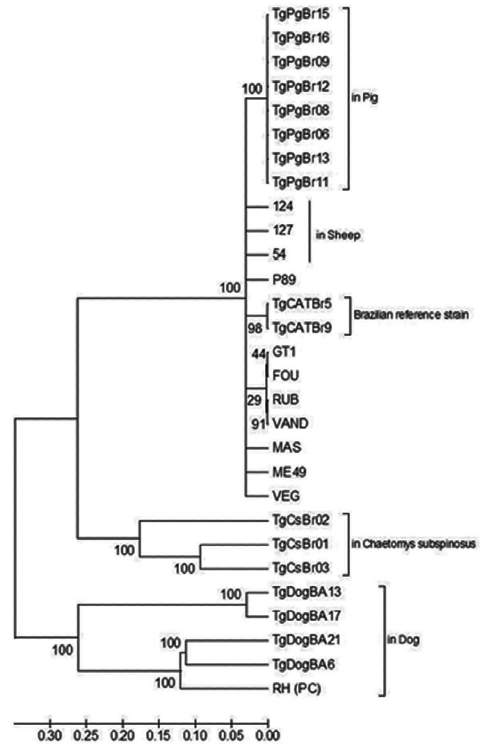
Phylogenetic analysis of DNA sequences using the neighbor-joining method indicated distinct clustering of the Bahian
T. gondii, with samples from this study (TgDogBA6, 13, 17, and 21) grouped on the same branch as the monophyletic RH strain (Type 1) with 100% bootstrap support (
Fig. 3). The Tajima
D test was used to analyze 29 nucleotide sequences with 3,666 bases aligned and 3,459 segregation sites. All positions with gaps and missing data were discarded. The analysis revealed neutrality (D=2.679661).
DISCUSSION
In this study, 7 seropositive animals were found. Three animals considered positive by serology were negative by bioassay and by PCR, which emphasizes the importance of biological assays to identify samples with viable parasites and greatly enhance the detection of
T. gondii DNA by PCR of samples from inoculated mice [
21].
Four isolates of
T. gondii were obtained from 7 samples of each tissue (brain and heart) from dogs, with a higher proportion of isolates, 57.1% (4/7), obtained from dog hearts than from brains (42.8%, 3/7). Several studies that have obtained
T. gondii isolates from various animals have used myocardium tissue as the primary sample for this procedure [
12,
22,
23]. Similar to other studies, we used the bioassay in mice to assess the virulence of these isolates in conjunction with the identification of genotypes [
6,
23,
24]. The virulence of an isolate can be determined by parasite-mouse interactions, and this virulence can be correlated with the genotype of that isolate [
9,
25].
Molecular analysis by multilocus PCR-RFLP with 10 markers of the 4 isolates from dogs suggests high genetic diversity in the population of circulating
T. gondii in the Bahia microregion. This can be compared with genotyping results of isolates from dogs in other countries such as Egypt [
24], where only 3 genotypes and a mixed infection were detected in 22 isolates from stray dogs. Despite the small number of isolates obtained in this study, 4 distinct genotypes with recombinant features or atypical loci were detected.
There was no similarity between the genotypes found in this study and those of
T. gondii isolates from Brazilian dogs in previous reports [
9,
26,
27]. There was also no resemblance to the genotypes identified in the reports [
11,
13], which genotyped isolates from swine and sheep, respectively, in the same Bahia microregion as surveyed in this study (
Table 2). This reinforces the fact that
T. gondii in Brazil is far more genetically diverse than
T. gondii in other countries. It does not exhibit the clonality or show a predominant genotype, even genotypes considered Brazilian clonal (BrI, BrII, BrIII, and BrIV), which have expanded into different regions of the country, observed by some researchers [
9,
14]. In addition, no genotypes observed in this study were previously reported among animal or human isolates from other regions of Brazil or the rest of the world, and they are considered unique by ToxoDB.
In 2008, Pena et al. [
9] showed that despite the fact that the markers used for RFLP were developed based on DNA from clonal cell lines (I, II, and III), they are capable of detecting atypical alleles (u-1, u-2) in the SAG1, new SAG2, c22-8, c29-2, and PK1 loci. In this study, an atypical allele, u-1, was identified in the c22-8 locus of 2 genotypes (TgDgBA 17 and 21), and another, u-2, was identified in the PK1 locus in all genotypes (TgDgBA 6, 13, 17, and 21).
Both the PCR-RFLP technique (
Table 2) and multilocus sequencing (
Fig. 1) were used to differentiate the isolates from the other, confirming the high genetic diversity of
T. gondii in the Bahian microregion. This is even more evident in the phylogenetic analysis, in which the isolates from this study grouped separately from other genotypes (
Fig. 1). The Tajima
D test revealed neutrality, i.e., high nucleotide diversity and an excess of intermediate frequency variants among the
T. gondii strains used in this analysis. The high genetic diversity of
T. gondii strains suggest that recombinant genotypes are common and widespread, likely as a result of the high rate of sexual recombination of these parasites [
17].
Analysis of DNA sequences is fundamental to evaluating parasite polymorphism and to comparing isolates to others from around the world, as accomplished in this study. Further, it eliminates the potential bias of some clonal cell markers, which may underestimate the actual genetic diversity of the parasite in RFLP analyses. Because this agent is widely distributed and has a sexual phase during the part of its life cycle spent in cats, and because Brazil has both domestic and wild cat populations, we believe that
T. gondii exhibits a panmictic evolutionary pattern, with
T. gondii subject to frequent recombination by gene exchange, preventing the existence of stable genotypes [
28].
All strains found in this study were virulent to mice, since all infected mice showed clinical signs of acute toxoplasmosis followed by death within 30 days of inoculation, similar to findings reported previously [
9,
29], and 100% mortality in mice within 4 weeks of infection. The virulence observed in this study may be related to the fact that most of the isolates in this study had type I alleles at more than 1 locus. These alleles are considered highly virulent, resulting in death of infected mice [
14,
30]. Furthermore, the presence of atypical alleles can affect the phenotype of recombinant strains, resulting in greater virulence. A recombinant may have new virulence mechanisms, resulting in a new genotype that exhibits greater pathogenicity in mice, and more severe cases of toxoplasmosis in immunocompetent individuals, also causing emerging diseases with its expansion [
30].
T. gondii population in Brazil is probably dependent on a high rate of environmental contamination with sporulated oocysts, resulting in intermediate host infections, and consequently, in increased opportunities for genetic recombination of this agent in domestic and wild cats living in Brazil. However, because of contamination from environmental and/or from dietary sources, we believe that the genotypes found in dogs in this study may also be circulating in humans, since they share sources of infection and live in close proximity to another.
Notes
-
CONFLICT OF INTEREST
We have no conflict of interest related to this work.
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS
The authors would like to thank the Foundation for the Support of Research of the Bahia State (FAPESB, grant no. PNE0003/2011) and the Coordination for higher Education Staff Development (CAPES, grant no. AUX-PE-PARASITOLOGIA-1267/2011) for the financial support.
Fig. 1Resolution on agarose gel of the products from PCR with specific primers for Toxoplasma gondii. Lane 1, molecular weight, 100-bp DNA ladder; lane 2, positive control; lanes 3, negative control; lane 4–7, positive animals.
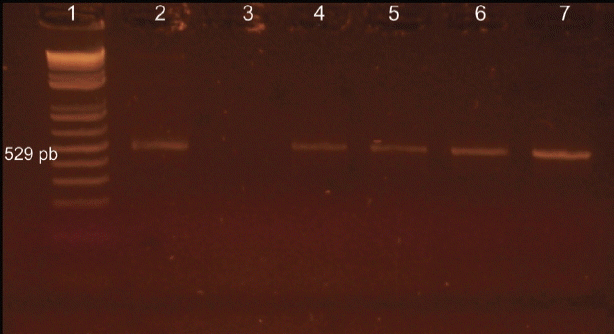
Fig. 2Resolution on agarose gel of the products from nested-PCR with genomic genetic markers SAG1 (A), SAG3 (B), and L358 (C) for Toxoplasma gondii. PM, molecular weight, 100-bp DNA ladder; 1–4, positive samples; CN, negative control; I, positive control type I (RH strain); II, positive control type II (PTG strain); III, positive control type III (CTG strain).
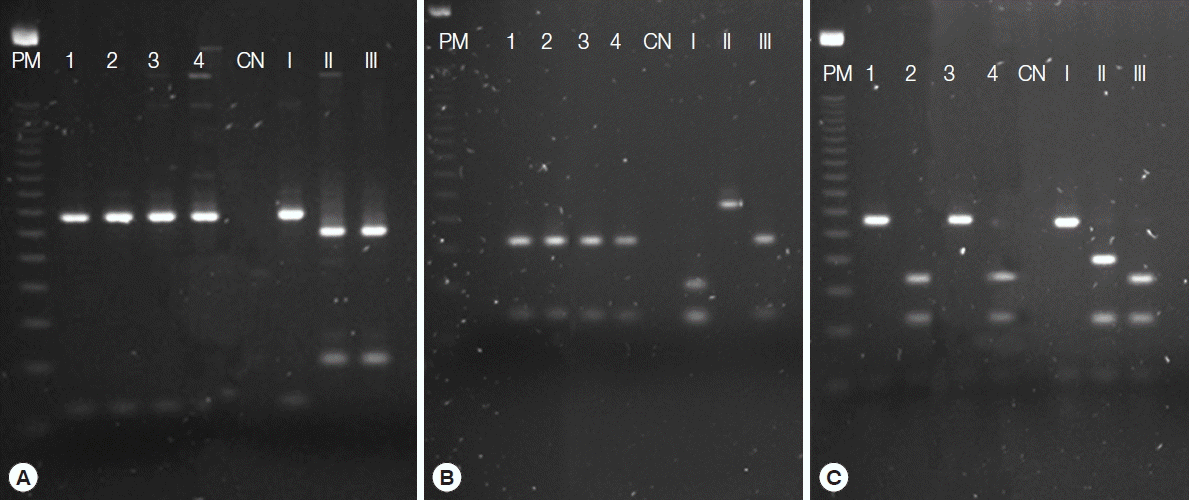
Fig. 3Phylogram of Toxoplasma gondii strains as determined by multilocus sequence analysis using 10 genomic genetic markers (SAG1, SAG2 novo, SAG3, BTUB, c22-8, c29-2, GRA6, L358, PK1, and APICO). The tree was constructed using the neighbor-joining method after bootstrapping with 1,000 repetitions. The distances were computed using the Tajima-Nei method. Strains from dogs (of this study), sheep and pigs from Bahia State of Brazil, and the Brazilian reference strains were highlighted. RH strain was used as positive control (PC) of the sequencing reaction.
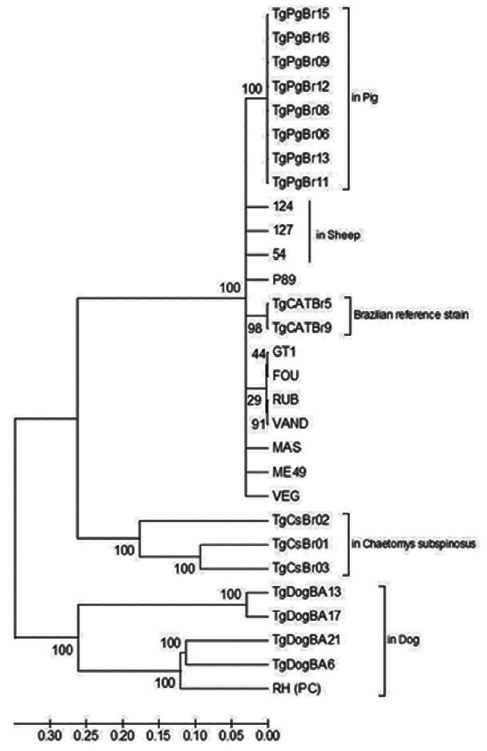
Table 1
Toxoplasma gondii detection in naturally infected dog samples by PCR associated with bioassay
Table 1
|
Seropositive dogs (no.) |
Bioassay PCR |
|
|
Brain inoculation |
Heart inoculation |
|
|
|
Lung |
Spleen |
Liver |
Heart |
Brain |
Lung |
Spleen |
Liver |
Heart |
Brain |
|
5 |
0a/3b
|
0/3 |
0/3 |
0/3 |
0/3 |
0/3 |
0/3 |
0/3 |
0/3 |
0/3 |
|
|
6 |
0/3 |
0/3 |
0/3 |
0/3 |
0/3 |
3/3 |
3/3 |
3/3 |
3/3 |
3/3 |
|
|
8 |
0/3 |
0/3 |
0/3 |
0/3 |
0/3 |
0/3 |
0/3 |
0/3 |
0/3 |
0/3 |
|
|
13 |
3/3 |
2/3 |
3/3 |
3/3 |
3/3 |
3/3 |
3/3 |
3/3 |
3/3 |
2/3 |
|
|
16 |
0/3 |
0/3 |
0/3 |
0/3 |
0/3 |
0/3 |
0/3 |
0/3 |
0/3 |
0/3 |
|
|
17 |
3/3 |
3/3 |
3/3 |
3/3 |
3/3 |
3/3 |
2/3 |
3/3 |
2/3 |
2/3 |
|
|
21 |
3/3 |
3/3 |
3/3 |
3/3 |
3/3 |
3/3 |
3/3 |
3/3 |
3/3 |
3/3 |
|
|
SUBTOTAL (A) |
3/7 (42.8%) |
3/7 (42.8%) |
3/7 (42.8%) |
3/7 (42.8%) |
3/7 (42.8%) |
4/7 (57.1%) |
4/7 (57.1%) |
4/7 (57.1%) |
4/7 (57.1%) |
4/7 (57.1%) |
|
|
SUBTOTAL (B) |
3/7 (42.8%) |
4/7 (57,1%) |
|
|
TOTAL (A + B) |
7/14 (50.0%) |
Table 2Different multi-locus genotypes of Toxoplasma gondii isolates by PCR-RFLP from Bahia, Brazil
Table 2
|
Isolated |
Virulent |
Genetic Markers |
Genotypeb
|
References |
|
|
SAG1 |
SAG2 |
SAG3 |
BTUB |
c22-8 |
c29-2 |
GRA6 |
L358 |
APICO |
PK1 |
|
TgDgBA 6 |
Virulent |
I |
III |
III |
I |
I |
II |
III |
I |
I |
u-2a
|
Unique |
Present paper (dogs) |
|
TgDgBA 13 |
Virulent |
I |
III |
III |
II |
I |
II |
III |
III |
I |
u-2 |
Unique |
|
TgDgBA 17 |
Virulent |
I |
II |
III |
II |
u-1 |
II |
III |
I |
I |
u-2 |
Unique |
|
TgDgBA 21 |
Virulent |
I |
I |
III |
I |
u-1 |
II |
III |
III |
I |
u-2 |
Unique |
|
|
TgPgBr 06, 08, 11, 12, 14, 15 |
- |
I |
I |
III |
III |
I |
NA |
NA |
NA |
III |
I |
5 |
Bezerra et al. [11]b (swine) |
|
TgPgBr7 |
- |
I |
I |
III |
III |
u-1 |
NA |
NA |
NA |
III |
NA |
6 |
|
TgPgBr9 |
- |
I |
I |
III |
II |
I |
NA |
NA |
NA |
III |
I |
7 |
|
TgPgBr10 |
- |
u-1a
|
I |
III |
III |
III |
NA |
NA |
NA |
III |
I |
8 |
|
TgPgBr13 |
- |
I |
I |
III |
I |
III |
NA |
NA |
NA |
III |
u-1 |
9 |
|
TgPgBr16 |
- |
I |
I |
III |
I |
I |
NA |
NA |
NA |
III |
I |
10 |
|
|
#54 |
- |
I |
I |
I |
III |
III |
u-1 |
III |
u-1 |
III |
u-1 |
54 |
Maciel et al. [13] (sheep) |
|
#124 |
- |
I |
I |
I |
III |
III |
u-1 |
III |
u-1 |
III |
u-1 |
124 |
|
#127 |
- |
I |
I |
I |
III |
III |
u-1 |
III |
u-1 |
III |
u-1 |
127 |
References
- 1. Dubey JP, Beattie CP. Toxoplasmosis of Animals and Man. Florida, USA. CRC; 1988, pp 1-220.
- 2. Dubey JP, Zarnke R, Thomas NJ, Wong SK, Van Bonn W, Briggs M, Davis JW, Ewing R, Mense M, Kwok OC, Romand S, Thulliez P. Toxoplasma gondii, Neospora caninum, Sarcocystis neurona, and Sarcocystis canis-like infections in marine mammals. Vet Parasitol 2003;116:275-296.
- 3. Ribeiro LA, Santos LK, Brito PA Jr, Maciel BM, Da Silva AV, Albuquerque GR. Detection of Toxoplasma gondii DNA in Brazilian oysters (Crassostrea rhizophorae). Genet Mol Res 2015;14:4658-4665.
- 4. Dubey JP, Lago EG, Gennari SM, Su C, Jones JL. Toxoplasmosis in humans and animals in Brazil: high prevalence, high burden of disease and epidemiology. Parasitology 2012;139:1375-1424.
- 5. Dubey JP. Toxoplasmosis-a waterborne zoonosis. Vet Parasitol 2004;126:57-72.
- 6. da Silva RC, de Lima VY, Tanaka EM, da Silva AV, de Souza LC, Langoni H. Risk factors and presence of antibodies to Toxoplasma gondii in dogs from the coast of São Paulo State, Brazil. Pesq Vet Bras 2010;30:161-166.
- 7. Yan C, Fu LL, Yue CL, Tang RX, Liu YS, Lv L, Shi N, Zeng P, Zhang P, Wang DH, Zhou DH, Zhu XQ, Zheng KY. Stray dogs as indicators of Toxoplasma gondii distributed in the environment: the first report across an urban-rural gradient in China. Parasit Vectors 2012;5:5.
- 8. Bahia-Oliveira LM1, Jones JL, Azevedo-Silva J, Alves CC, Oréfice F, Addiss DG. Highly endemic, waterborne toxoplasmosis in north Rio de Janeiro state, Brazil. Emerg Infect Dis 2003;9:55-62.
- 9. Pena HF, Gennari SM, Dubey JP, Su C. Population structure and mouse-virulence of Toxoplasma gondii in Brazil. Int J Parasitol 2008;38:561-569.
- 10. Su C, Khan A, Zhou P, Majumdar D, Ajzenberg D, Dardé ML, Zhu XQ, Ajioka JW, Rosenthal BM, Dubey JP, Sibley LD. Globally diverse Toxoplasma gondii isolates comprise six major clades originating from a small number of distinct ancestral lineages. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2012;109:5844-5849.
- 11. Bezerra RA, Carvalho FS, Guimarães LA, Rocha DS, Maciel BM, Wenceslau AA, Lopes CW, Albuquerque GR. Genetic characterization of Toxoplasma gondii isolates from pigs intendend for human consumption in Brazil. Vet Parasitol 2012;189:153-161.
- 12. Clementino-Andrade MM, Pinheiro BV, Cunha MM, Carneiro AC, Andrade Neto VF, Vitor RW. New genotypes of Toxoplasma gondii obtained from farm animals in Northeast Brazil. Res Vet Sci 2013;94:587-589.
- 13. Maciel BM, Moura RL, Carvalho FS, Costa EA, Albuquerque GR. Identification and genetic characterization of a new Brazilian genotype of Toxoplasma gondii from sheep intended for human consumption. Parasitol Int 2014;6:567-570.
- 14. Silva LA, Andrade RO, Carneiro AC, Vitor RW. Overlapping Toxoplasma gondii genotypes circulating in domestic animals and humans in shoutheastern Brazil. PLoS One 2014;9:1-7.
- 15. Ajzenberg D, Bañuls AL, Su C, Dumètre A, Demar M, Carme B, Dardé ML. Genetic diversity, clonality and sexuality in Toxoplasma gondii. Int J Parasitol 2004;34:1185-1196.
- 16. Carlos RSA, Albuquerque GR, Bezerra RA, Sicupira PML, Munhoz AD, Lopes CWG. Ocorrência de anticorpos anti-Toxoplasma gondii e principais fatores de risco associados à infecção canina na região de Ilhéus-Itabuna, estado da Bahia. Rev Bras Med Vet 2010;32:115-121. (in Portuguese).
- 17. Dubey JP. Refinement of pepsin digestion method for isolation of Toxoplasma gondii from infected tissues. Vet Parasitol 1998;74:75-77.
- 18. Homan WL, Vercammen M, De Braekeleer J, Verschueren H. Identification of a 200 to 300 fold repetitive 529 pb DNA fragment in Toxoplasma gondii, and its use for diagnostic and quantitative PCR. Int J Parasitol 2000;30:69-75.
- 19. Su C, Shwab EK, Zhou P, Zhu XQ, Dubey JP. Moving towards an integrated approach to molecular detection and identification of Toxoplasma gondii. Parasitology 2010;137:1-11.
- 20. Bezerra RA, Giné GA, Maciel BM, Gaiotto FA, Albuquerque GR. Identification and genetic characterization of Toxoplasma gondii in free-ranging bristle-spined porcupine (Chaetomys subspinosus), a threatened arboreal mammal from the Brazilian Atlantic Forest. Parasit Vectors 2015;8:277.
- 21. Bezerra RA, Carvalho FS, Guimarães LA, Rocha DS, Silva FL, Wenceslau AA, Albuquerque GR. Comparison of methods for detection of Toxoplasma gondii in tissues of naturally exposed pigs. Parasitol Res 2012;110:509-514.
- 22. Dubey JP, Hill DE, Rozeboom DW, Rajendaran C, Choudhary S, Ferreira LR, Kwok OC, Su C. High prevalence and genotypes of Toxoplasma gondii isolated from organic pigs in northern USA. Vet Parasitol 2012;188:14-18.
- 23. Dubey JP, Rajendran C, Ferreira LR, Martins J, Kwok OC, Hill DE, Villena I, Zhou H, Su C, Jones JL. High prevalence and genotypes of Toxoplasma gondii isolated from goats, from a retail meat store, destined for human consumption in the USA. Int J Parasitol 2011;41:827-833.
- 24. El Behairy AM, Choudhary S, Ferreira LR, Kwok OC, Hilali M, Su C, Dubey JP. Genetic characterization of viable Toxoplasma gondii isolates from stray dogs from Giza, Egypt. Vet Parasitol 2013;193:25-29.
- 25. Dubremetz JF, Lebrun M. Virulence factors of Toxoplasma gondii. Microbes Infect 2012;14:1403-1410.
- 26. Dubey JP, Gennari SM, Sundar N, Vianna MC, Bandini LM, Yai LE, Kwok OC, Su C. Diverse and atypical genotypes identified in Toxoplasma gondii from dogs in São Paulo, Brazil. J Parasitol 2007;93:60-64.
- 27. Langoni H, Matteucci G, Medici B, Camossi LG, Richini-Pereira VB, Silva RC. Detection and molecular analysis of Toxoplasma gondii and Neospora caninum from dogs with neurological disorders. Rev Soc Bras Med Trop 2012;45:365-368.
- 28. Soares RM. Caracterização molecular de Toxoplasma gondii. Rev Bras Parasitol Vet 2004;13:17-19. (in Portuguese).
- 29. da Silva AV, da Silva RC, Zamprogna TO, Lucas TM. Toxoplasma gondii in swine with emphasis in Brazilian contribution. Sci Med 2010;20:120-130.
- 30. Dardé ML. Toxoplasma gondii, “new” genotypes and virulence. Parasite 2008;15:366-371.