Abstract
Angiostrongylus cantonensis invades the central nervous system (CNS) of humans to induce eosinophilic meningitis and meningoencephalitis and leads to persistent headache, cognitive dysfunction, and ataxic gait. Infected mice (nonpermissive host), admittedly, suffer more serious pathological injuries than rats (permissive host). However, the pathological basis of these manifestations is incompletely elucidated. In this study, the behavioral test, histological and immunohistochemical techniques, and analysis of apoptotic gene expression, especially caspase-3, were conducted. The movement and motor coordination were investigated at week 2 post infection (PI) and week 3 PI in mice and rats, respectively. The cognitive impairs could be found in mice at week 2 PI but not in rats. The plaque-like lesion, perivascular cuffing of inflammatory cells, and dilated vessels within the cerebral cortex and hippocampus were more serious in mice than in rats at week 3 PI. Transcriptomic analysis showed activated extrinsic apoptotic pathway through increased expression of TNFR1 and caspase-8 in mice CNS. Immunohistochemical and double-labeling for NeuN and caspase-3 indicated the dramatically increased expression of caspase-3 in neuron of the cerebral cortex and hippocampus in mice but not in rats. Furthermore, western-blotting results showed high expression of cleaved caspase-3 proteins in mice but relatively low expression in rats. Thus, extrinsic apoptotic pathway participated in neuronal apoptosis might be the pathological basis of distinct behavioral dysfunctions in rodents with A. cantonensis infection. It provides the evidences of a primary molecular mechanism for the behavioral dysfunction and paves the ways to clinical diagnosis and therapy for A. cantonensis infection.
-
Key words: Angiostrongylus cantonensis, eosinophilic meningitis, meningoencephalitis, apoptosis
INTRODUCTION
Angiostrongyliasis is caused by the rat lung worm,
Angiostrongylus cantonensis, a kind of nematode that was first identified and reported by Chen at 1935 in wild rats in the vicinity of Canton in China [
1]. Humans accidentally acquire infection with this nematode either by eating poorly cooked intermediate hosts (freshwater snails and slug) or carrier hosts (land crabs and freshwater shrimps) or by consuming the contaminated vegetables containing third-stage larvae [
2–
7]. The definitive hosts of
A. cantonensis are divided into permissive (rat) and nonpermissive hosts (mice, guinea pigs, rabbits, rhesus monkeys, and humans) based on whether the worms invade the lung and eventually attain sexual maturity. In the permissive host, the worms can migrate to lungs without causing severe eosinophilic meningitis. But in nonpermissive hosts, larvae generally fail to migrate to the lungs and terminate their development at a young adult worm stage dwelling in CNS until death, which can cause meningitis or meningoencephalitis characterized by obviously increasing eosinophil infiltrations [
8,
9].
Clinical exploration revealed that
A. cantonensis invading human CNS caused eosinophilic meningitis and meningoencephalitis, and resulted in a serial of neurological symptoms, including persistent headache, paresthesia or hyperesthesia, nuchal rigidity, seizure, cognitive dysfunction, ataxic gait, and even unconsciousness [
10–
18]. These neurological symptoms were also identified in animals with
A. cantonensis infection, which obviously presented lessening of the spontaneous activity and dysfunction for symmetry, balance and coordination of movements in infected rodents [
19–
21]. Further comparison of the pathological injuries indicated that eosinophilic response and tissue damage were more serious in nonpermissive hosts than in permissive hosts [
22–
27]. However, the potential molecular mechanism of the behavioral dysfunctions and neuronal injuries with
A. cantonensis infection are still incompletely known.
To primary exploration of the molecular mechanismof pathological basis of the behavioral dysfunctions, the behavioral test, classical histological and immunohistochemical techniques, and transcriptomic analysis were conducted. Moreover, we mainly focused on the time points at 2, 3 and week 4 PI because the larvae are first detected in the cranial cavity of rodents at week 2 PI and their number peaked at week 3 PI. Thus, this study will provide the evidences for further research on pathological mechanism and the potential direction for clinical therapy.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Experimental animals
Healthy female Sprague-Dawley (SD) rats and BALB/c mice aged between 6 and 8 weeks were supplied from the Center of Animal Experiments of Sun Yat-sen University, Guangzhou, P. R. China (SYSU, ZSSOM; permit no: 2016-122). All animals were housed in a specific pathogen-free environment, and the procedures done were strictly followed the Guide for the Care and Use of Experimental Animals of the National Institutes of Health, China. Both mice and rats were randomly divided into 4 groups (10 animals per group) as the control, week 2 PI, week 3 PI, and week 4 PI, and for each rat, 100 of the third-stage larvae (L3) of
A. cantonensis were used to infect mice by the gavage method and 20 for each mouse according to our previous study [
27].
The L3 larvae of
A. cantonensis were obtained from
Biomphalaria glabrata, the intermediate host maintained in our laboratory for the life cycle of
A. cantonensis. L3 larvae of
A. cantonensis were harvested using the method described by Chen and Lai [
28] and Lan and Lai [
29]. Briefly,
B. glabrata were homogenized and digested in a pepsin-HCl solution (pH 2.0, 500 IU pepsin/g tissue) at 37°C for 2 hr. The L3 larvae in the sediment were identified and collected.
The balance beam task followed the modified version of Shear et al. [
30] and Chan et al. [
31]. Experimental rodents were trained to travel from the end of a narrow-suspended beam into a dark goal box. The number of foot slips and the time of completing trial were recorded by 2 observers. A foot slip was defined as a paw descending below the surface of the beam. The record of foot slips and time was started when the front paws crossed the starting position and ended once the nose of the experimental rodents entered the dark goal box. Animals were tested 3 times daily, for 3 consecutive days at week 2, 3, and 4 PI. If the animal fell from the beam, or took more than 3 min, the task was recorded as incompletion.
Grip strength [
30,
32,
33] was measured by recording the time when the experimental rodents were able to hold onto a steel wire suspended 50 cm above a thick foam cushion. Grip strength test was performed 3 times per day for 3 consecutive days at week 2, 3, and 4 PI.
In Morris water maze task (MWMT), following the protocol described previously [
34,
35], the experimental rodents were released (not dropped) into the water in 4 random starting positions (N, S, E, and W) with the faces to the tank wall. Trial was started at the moment that the rodents were released and stopped when they reached the platform hidden beneath the surface of the water. Each trial limited 2 min for rats and 1 min for mice. The experimental rodents were guided to the platform when they could not find it within time limit and were allowed to stay on it for 30 sec before the next swim. All swimming tracks were recorded by computer tracking program (Ethovision Software, Noldus, Wageningen, The Netherlands).
Given 4 trails daily, rodents were trained for 3 consecutive days at week 2, 3, and 4 PI and 1 probe trial (2-min for rats and 1-min for mice) were given after 24 hr following the last acquisition trail. Latencies (spatial learning) and percentage of time stay in the target quadrant compared with the other quadrants (probe trial) were measured.
Transcriptomic data analysis
In our previous study, RNA libraries were constructed from mouse brain tissues collected on day 2 PI and week 1, 2, and 3 PI, after total RNA was extracted using Trizol reagent (Invitrogen, Carlsbad, California, USA). Similarly, the samples from the control mice were collected on the 21st day PI, and the samples were frozen in liquid nitrogen. The overall flow of RNA library construction and deep sequencing had been shown in our previous study [
36].
The raw data was processed with a bioinformatics’ pipeline of filter low quality tags, trim adaptor, clean reads mapping to the Mus musculus genome using TopHat, Refseq genes expression analysis using cufflinks, annotate and classify RNAs into different categories. Expression patterns of apoptotic genes in the apoptotic pathways were analyzed in mice brain with A. cantonensis infection.
Histochemistry examination of neuronal injury
Animals were anesthetized with chloral hydrate (350 mg/kg) and perfused transcardially with 300 ml of 0.9% sodium chloride and then 400 ml of 4% paraformaldehyde (in 0.1 M phosphate buffer PB, pH 7.4). The brains of the control and week 2, 3, and 4 PI animals were collected, used for pathological examinations, postfixed in 4% paraformaldehyde (in 0.1 MPB, pH 7.4) overnight, successively immersed in 10%, 20%, 30% sucrose solution with PB until the tissue sank, and then sliced in 30 μm thick coronal sections on a semiconductor freezing microtome (Leica, Bensheim, Germany). The sections were stained with hematoxylin and eosin (HE) according to the conventional staining methods [
37].
Brain sections were pretreated with 0.3% H2O2 in 0.01M PBS at 37°C for 30 min. To process for conventional immunohistochemical staining, series of sections were incubated for 48 hr at 4°C with primary antibody: neuronal nuclei (a neuronal marker, mouse anti-NeuN 1:500 Chemicon, Temecula, California, USA), glial fibrillary acidic protein (an astrocyte marker, mouse anti-GFAP 1:500 Chemicon), ionized calcium binding adapter molecule 1 (a microglia and macrophage maker, rabbit anti-Iba1 1:500) and caspase-3 (a marker of apoptotic signal, rabbit anti-caspase-3 1:250), separately. After rinsing 3 times with PBS, sections were incubated with secondary antibody: anti-mouse IgG or anti-rabbit IgG (1:100, Sigma, St. Louis, Missouri) for 3 hr, respectively, and then with the corresponding mouse or rabbit PAP complex (1:200, Sigma) at room temperature for 2 hr. The DAB-peroxidase reaction (0.05% in 0.01 M PBS, pH 7.4, Sigma) was performed for 2–8 min and mounted onto gelatin-coated slides, dried, dehydrated, cleared with xylene, and covered with neutral balsam.
For immunofluorescence staining, the brain sections were incubated with rabbit anti-ECP (eosinophil cationic protein, a basic protein located in the eosinophil primary matrix, 1: 200, Invitrogen), mouse anti-NeuN, and rabbit anti-Caspase-3, respectively. Each sections were washed 3 times for 5 min in PBS and followed by 2 hr incubation with the secondary antibody: Alexa 594-conjugated goat anti-rabbit IgG (1: 300, Invitrogen) or Alexa 594-conjugated goat anti-mouse IgG (1:300, Invitrogen) at room temperature. After washing with PBS, the sections were mounted on gelatin-coated slides, cover slipped with antifade medium (Electron Microscopy Sciences, Hatfield, Pennsylvania, USA) and observed under the fluorescence microscope (Carl Zeiss, Jena, Germany).
Western blotting of caspase-3 expression
Cold PBS-washed different brain tissues were collected and then blended with Bullet Blender (Next Advance, Inc. New York, USA) lysing in precooled cell lysis buffer. The mixtures were kept cool on ice for 30 min. The supernatants were recollected, after centrifuged at 12,000 rpm for 5 min at 4°C, for total protein content assay. Quantitative 30 μg of protein were inactivated and then resolved by 10% SDS-PAGE and transferred to polyvinylidene fluoride membranes, which were then blocked in 5% skim milk for other 2 hr followed by blocking with the rabbit anti-caspase-3 antibody or rabbit anti-cleaved-caspase-3 antibody (1: 200,) at 4°C overnight. Thereafter, the membranes were washed 3 times with PBST and incubated with HRP-conjugated goat anti-rabbit IgG secondary antibody (1:500) at room temperature for 90 min. Washed 3 times with PBST, the membranes were followed by detection with chemiluminescence and quantified using ChemiDoc Touch System (BioRad, Hercules, California, USA). The immunoreactive bands were normalized with respect to β-actin.
Statistical analysis
The statistical analysis of differences between groups was performed by using the Student’s t-tests with Prism 6.0 (GraphPad Software, San Diego, California, USA), and data were presented as means±SD. P<0.05 was considered as significant.
RESULTS
Worsened motor dysfunction of mice induced by A. cantonensis infection
Comparison of larval and neuronal injuries in both rodents showed that the percentage of larvae in the cerebrum was significantly higher in rats than in mice. In contrast, the percentage of larvae in the brainstem was significantly higher in mice than in rats. The percentage of larval distribution in the cerebellum was significantly higher in mice than in rats at week 2 and 3 PI. Besides, the recovery rate at week 3 PI was apparently higher compared to other infection stages (
Supplementary Table 1).
Behavioral changes of rats and mice with
A. cantonensis infection were detected to evaluate the neuronal injury. The results of balance-beam task showed that movement and motor coordination functions were damaged in both
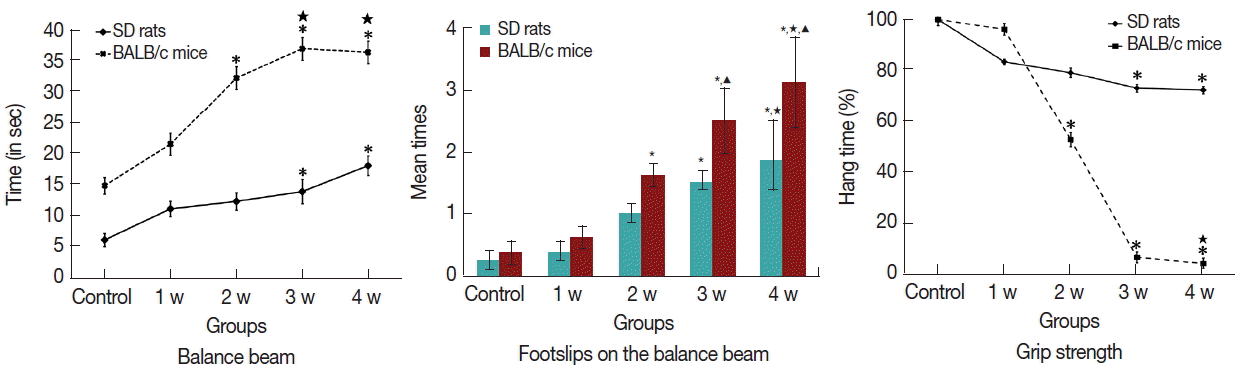
A. cantonensis-infected rats and mice. The infected rats and mice needed longer time to complete the task than the control after week 2 and 3 PI, respectively (
Fig. 1A;
Supplementary Table 2). Similarly, the times of foot slip were significantly increased in the infected rats and mice after week 2 and 3 PI, respectively (
Fig. 1B;
Supplementary Table 3). The results of grip strength task showed no significant difference in the rats and mice at the week 1 PI, but the hang time slightly decreased in rats after week 3 PI, and dramatically decreased in mice after week 2 PI (
Fig. 1C;
Supplementary Table 4). Thus, mice were earlier than rats to reveal the behavioral dysfunction; moreover, mice had the higher intensity of behavioral dysfunction than in rats.
Assessments of cognitive impairments are the typical method to evaluate the neuronal injury of rodents with
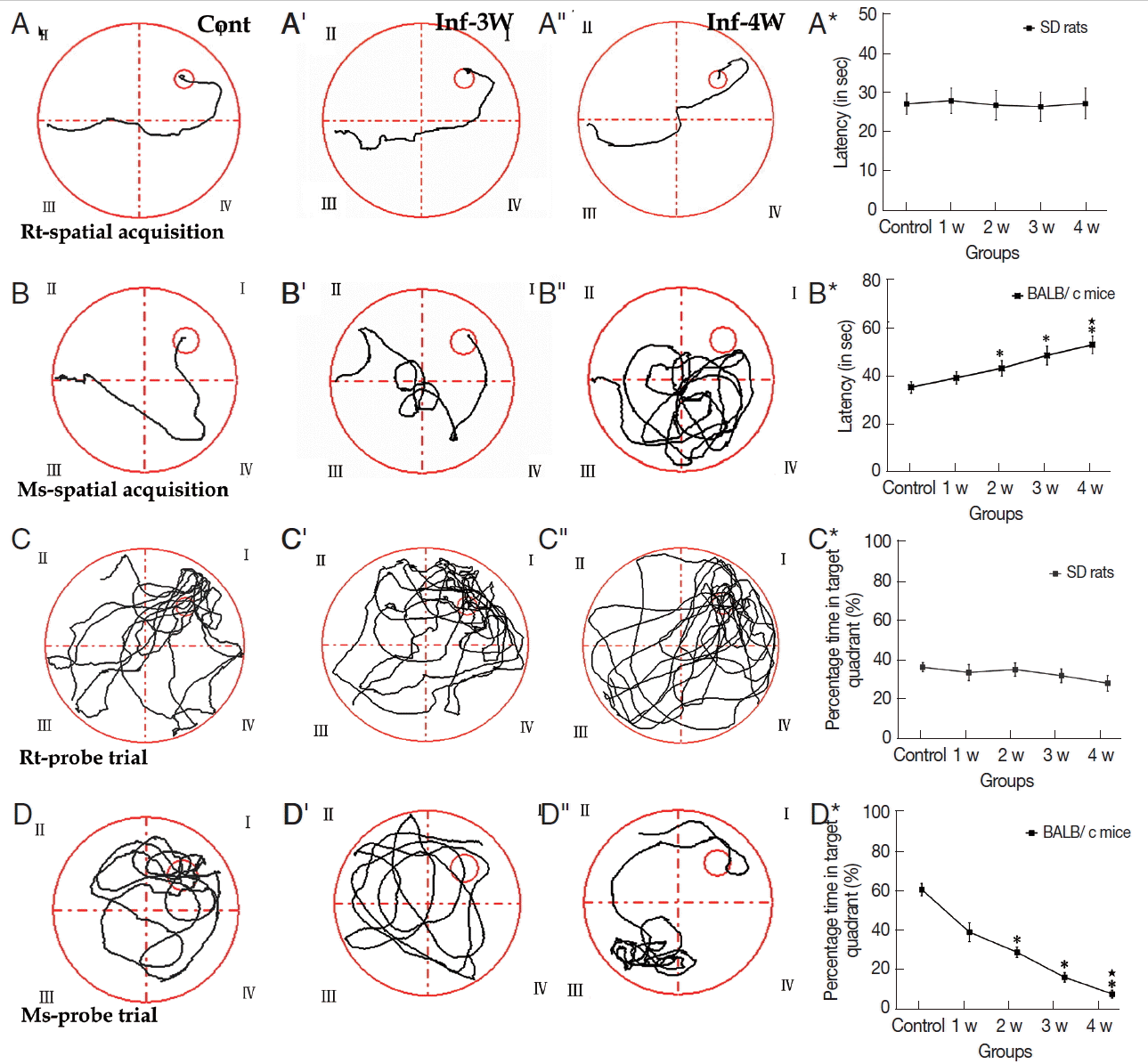
A. cantonensis infection. MWMT experimental data showed that no significant difference was observed in both tests of spatial learning and memory ability in rats (
Fig. 2A-A*;
Supplementary Table 5). In the spatial learning task, however, cognitive impairments became more serious compared to the control in the infectious course, and the infected mice needed more time to locate the hidden platform than the controls after week 2 PI (
Fig. 2B-B*;
Supplementary Table 5). In the percentage of time spent in the target quadrant of probe trail task, no significant change was observed in rats (
Fig. 2C-C*;
Supplementary Table 6), but the infected mice had lower levels compared with the control, and the lowest level appeared at week 4 PI (
Fig. 2D-D*;
Supplementary Table 6). Thus, cognitive impairments in mice, including sense, motor, learning, and memory, was more serious than in rats with
A. cantonensis infection. The behavioral dysfunctions are consistent to the pathological injuries of the specific functional regions of the brain, including the cortex (sense and motor) and hippocampus (learning and memory). Therefore, our further experiments focused on these 2 regions in both rodents with
A. cantonensis infection.
The pathological characters in the brain tissue of the cerebral cortex (sense and motor) and hippocampus (learning and memory) were carefully investigated at week 3 PI because serious behavioral dysfunctions could be found in rats at week 3 PI. The results showed that dilated vessels and perivascular cuffing of inflammatory cells were mainly observed in the cerebral cortex and hippocampus of mice and rats. Thus, pathological injuries in both regions were consistent to the behavioral dysfunctions in both rodents with
A. cantonensis infection. In detail, plaque-like lesions were clearly observed near the dilated vessels in the cerebral cortex and hippocampus of both rodents with
A. cantonensis infection (
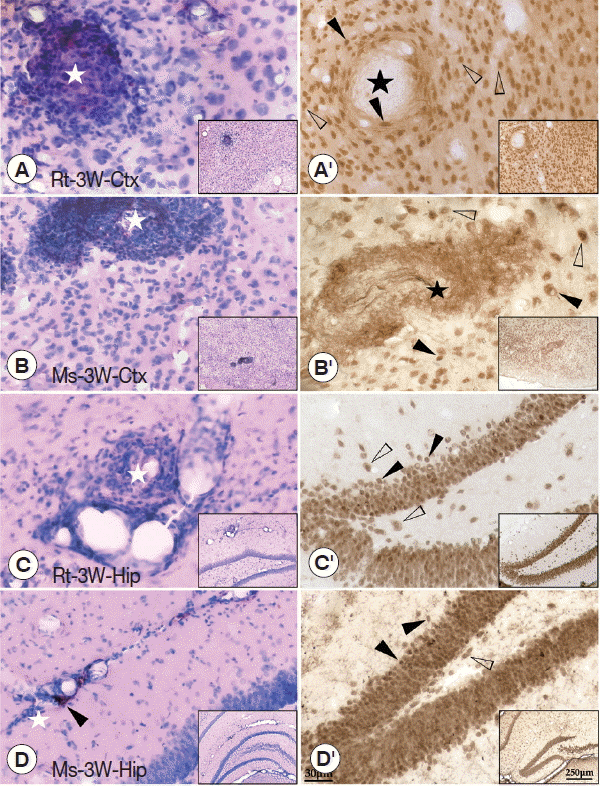
Fig. 3A–D). Immunohistochemical staining of NeuN showed that plaque-like lesions in the cerebral cortex were intensive with loss of neurons in the core (black star) (
Fig. 3A′, 3B′). However, in the hippocampus, the blebbing in neurons, nucleus condensing (pyknosis), and cell shrinkage (loss of endochylema) (black arrowheads) could be found along with the hippocampal dentate gyrus and CA1 area (
Fig. 3C′, 3D′), suggesting that the neuronal injuries accompanied with cell apoptosis in the hippocampus. Thus, the molecular mechanism of pathological damages between cerebral cortex and hippocampus might be different.
We further investigated expression patterns of the genes in the apoptosis pathways to explore the mechanisms of serious neuronal injuries in mice with
A. cantonensis infection. In mammals, neuronal apoptosis is one of the typical reasons of pathogenesis of memory loss and cognitive impairment. Neuronal apoptosis can be initiated by 2 dominant pathways: (i) intrinsic pathway, which is triggered by cellular stress and the subsequent Bcl-2-stimulated the release of mitochondrial cytochrome c that is related to caspase-9 and Apaf-1 activation; (ii) extrinsic pathway, which can be initiated by ligation of death receptors followed by activation of caspase-8. Both of these pathways converge to programmed cell death that is arisen from the cleavage of caspase-7 and 3 [
38–
40].
Gene expression profiles in both apoptosis pathways were listed in
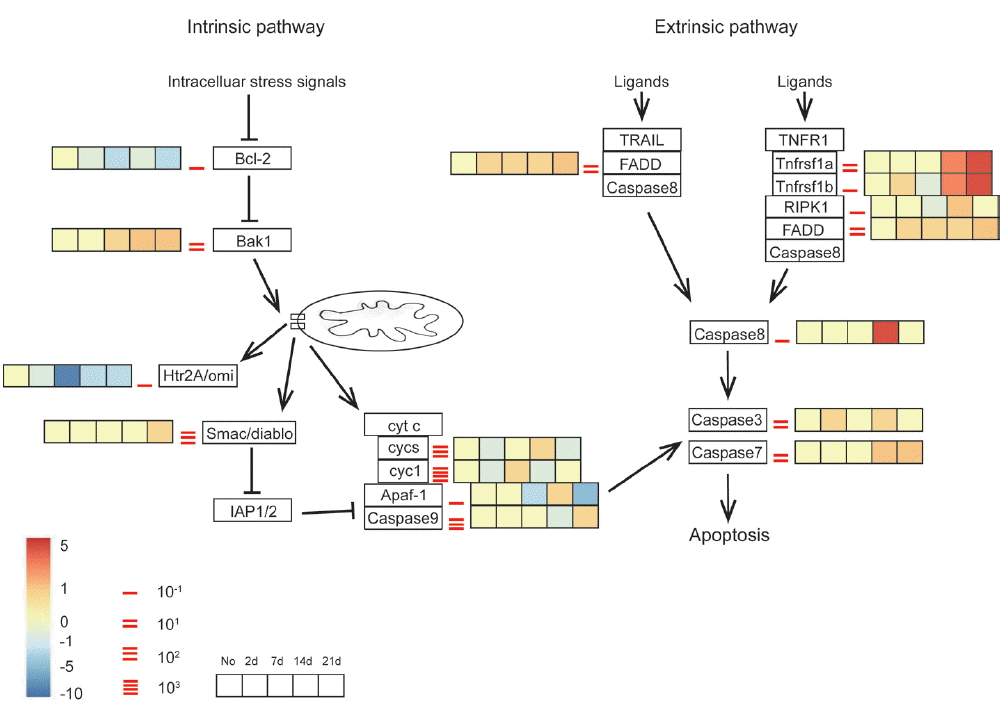
Fig. 4. Data of extrinsic pathway suggested that the extrinsic apoptotic pathway was strongly activated in
A. cantonensis-infected mice through TNFR1a and TNFR1b at week 2 PI, followed by the increased expression level of the RIPK1, FADD, and caspase-8. Furthermore, caspase-3 and 7 were also slightly up-regulated across all time points in the brain tissue, with moderately higher expression at day 2 and week 2 and 3 PI, respectively. The intrinsic pathway was consisted with anti-apoptosis mediator, Bcl-2, and downstream mediator, Bak1. Both of these 2 checkpoint genes promoted apoptosis at time point almost immediately post-infected (day 2 PI) and throughout the course of the study. Although the up-regulated Bak1 induced the discordant alternations of the downstream genes, such as cytochrome
c (cyt
c, in our dataset, called cycs and cyct), Apaf-1, caspase-9, that were unable to rule out use of these genes as efforts to modulate with respect to apoptosis. Thus, it suggested that neuronal apoptosis by extrinsic pathway was activated in mice in response to
A. cantonensis infection.
To further understand the apoptotic effects of the main pathological loci in the brain, immunohistochemistry of caspase-3 in the cerebral cortex and hippocampus was conducted. Caspase-3 positive cells (considered to be apoptotic cells) were detected at the cerebral cortex and hippocampus of both
A. cantonensis-infected rodents. In the cerebral cortex, caspase-3 positive cells appeared in the center of plaque-like lesions and limited in that local region, but in the hippocampus, caspase-3 positive cells were widely visible at dentate gyrus and CA1 area (
Fig. 5A-A′, B-B′). The results of double labeling for caspase-3 and NeuN showed that only a few neurons were labeled for caspase-3 at the rat cerebral cortex and hippocampus (
Fig. 5C-C″, D-D″). However, numerous neurons (NeuN+) labeled for caspase-3 were detected in the mouse cerebral cortex (in plaque-like lesions) and hippocampus (especially in dentate gyrus and CA1 area) at week 3 PI (
Fig. 5E-E″, F-F″). The results of both rodents showed that the density of caspase-3 positive cells of cerebral cortex and hippocampus in mice was dramatically higher than in rats at week 3 PI.
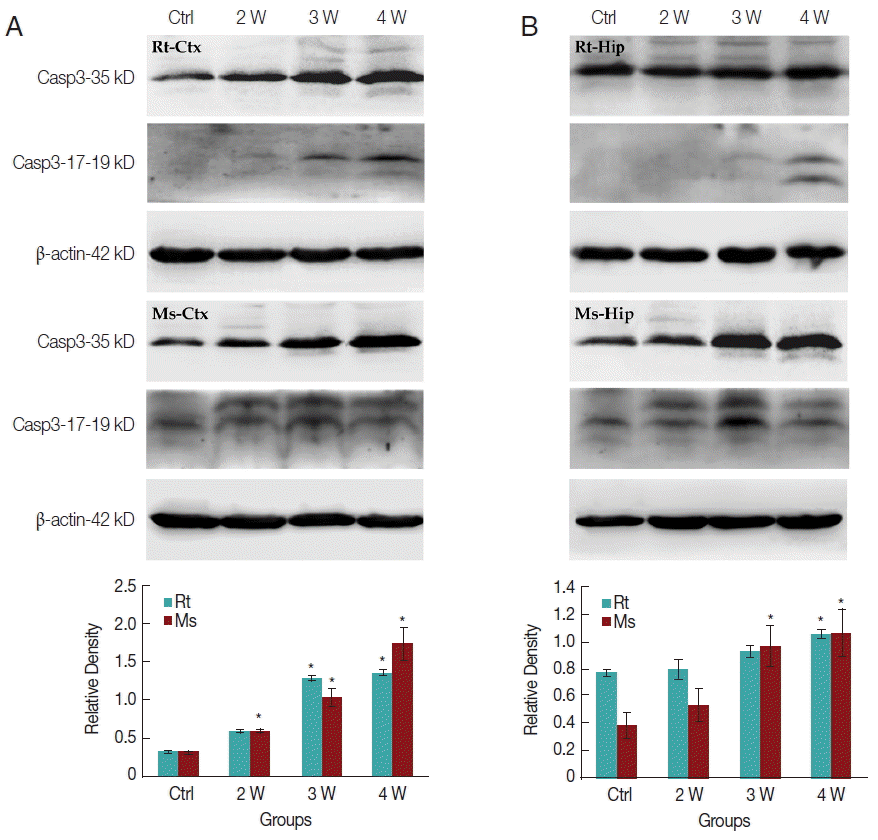
In caspase-3 dependent apoptotic pathway, the 35 kDa caspase-3 protein will be divided into 2 fragments of 17 and 19 kDa cleaved-caspase-3 protein to execute the final apoptosis. In the present study, only slightly increased caspase-3 expression in transcriptomic data could be observed. Western-blotting was further used to elucidate the expression level of caspase-3 and cleaved-caspase-3 in the cerebral cortex and hippocampus, respectively. Caspase-3 expression level was increased in the rat cerebral cortex after week 3 PI but in mice after week 2 PI (
Fig. 6A). In the hippocampus, caspase-3 expression level was significantly increased in rat at week 4 PI but in mice after week 3 PI (
Fig. 6B). The cleaved-caspase-3 expression level appeared slightly in the rat cerebral cortex after week 3 PI but significantly in mouse after week 2 PI (
Fig. 6A). The cleaved-caspase-3 expression level also increased slightly in the rat hippocampus after week 4 PI but significantly in mouse after week 2 PI (
Fig. 6B). In total, the mice cerebral cortex and hippocampus had the higher levels of caspase-3 and cleaved-caspase-3 than rats. The apoptotic effects through caspase-3 cascade pathway were significantly activated in the mice cerebral cortex and hippocampus than in the corresponding loci of rats.
DISCUSSION
Clinical exploration and animal investigation confirmed that
A. cantonensis invading CNS caused the neurological symptoms with behavioral dysfunctions [
10–
16]. In this study, we clearly elucidated that rats and mice presented dysfunctions of movement, motor coordination, and cognition, and we further primarily explored the molecular mechanisms from the perspective of cell apoptosis by pathological observations and analysis of gene expression patterns in the apoptosis pathway. It provides reasonable explanations for the neurological symptoms in clinical patients and the behavioral disorders in animals infected with
A. cantonensis.
Our previous study showed that the larvae were located within the subarachnoid space and cerebral ventricle at the early stage of infection, but in the brain parenchyma, at the late stage of infection [
27]. The data from autopsies also revealed that numerous worms were presented in the subarachnoid spaces over the frontal cortex, pons, tip of the temporal lobes, and paraventricular areas of the lateral ventricle [
41–
43]. Detailed comparison of larvae distribution and size, and neurological damages in rats and mice with
A. cantonensis infection showed that higher percentage of larvae in the rat cerebrum and higher percentage of larvae in the mice brainstem. The results further confirmed that the recovery of worms were dominant in the hippocampus of the mice, but the worms were mainly found in the cortex of the rats (
Supplementary Table 7). It suggested that distinct distribution of the larvae might be related to the distinct neurological damages and symptoms in both rodents.
The major pathological damages in human CNS induced by
A. cantonensis infection include; (1) meningitis with a predominance of eosinophils and plasma cells; (2) multiple microcavities, tortuous tracks, and microscopic hemorrhage surrounded by inflammatory cells and neuron lesions in the brain and spinal cord parenchyma; (3) granulomatous response to the dead worms; (4) nonspecific vascular reactions, thrombosis, and aneurysm formation [
42,
44]. In
A. cantonensis-infected mammalian brains (permissive host rats and nonpermissive hosts, including mice, rabbits, and guinea pigs), similar pathological changes were also found in CNS [
23,
24,
28,
29,
45,
46]. In this study, plaque-like lesions also showed in various regions in infected animals. These regions, especially the cortex and hippocampus, execute the functions of the sense, motor, learning, and memory. The histopathologic investigations also indicated that the plaque-like lesions were infiltrated by numerous eosinophils, with neurons lost in the lesion core in the cortex (sense and motor) and hippocampus (learning and memory). Thus, it is suggested that the worm distribution caused the damages in the corresponding regions, leading to functional impairments. Similar results have been reported in
Toxoplasma gondii infected mice which revealed reduced exploratory activity according to the climbing and rearing, showing more exposed part of the OF arena, smaller preference for the central, and less grooming behavior, which were related to the presence of cysts both in the amygdala and hippocampus [
47]. Another study showed that a high density of lesions, such as the recruited immune cells and the presence of activated resident glia accompanied by limited alterations of neuronal connectivity abnormalities, was observed within the somatosensory cortex (SSC). Altered fiber density indicated a reduction in spine density and dendritic arbor in the SSC and hippocampus [
48]. Moreover, a previous study demonstrated that double immunofluorescent staining of NeuN and caspase-3 resulted into the neuronal apoptosis during
T. gondii infection [
49]. Therefore, the investigations in this study of immunohistochemical staining and double-labeling for NeuN and caspase-3 showed that numerous apoptotic neurons were widely distributed in the hippocampal dentate gyrus and CA1 compared to the nidus limited in a local region in the cortex, which might be one of the explanations for behavioral dysfunctions in animals and neurological symptoms in clinical patients.
Memory loss and cognitive impairment are always closely correlated with neuronal apoptosis. In our study, the dramatically increased TNFR1 and caspase-8 expression in the brain tissue was observed in mice with
A. cantonensis infection. In the extrinsic pathway, TNFR1 plays an important role by recruiting the cytosolic adaptor FADD and RIPK1, which are associated with caspase-8 in a variety of immune and parenchymal tissues [
50]. Furthermore, it is TNFR1 that induces extrinsic apoptosis through RIPK1 and caspase-8 in Yersinia-induced cell death of murine macrophages [
51]. Furthermore, cleaved-caspase-3 expression level was significantly increased in the cortex and hippocampus in mice but not in rats, indicating that neuronal apoptosis by TNFR1 and caspase-8 pathway might be the key molecular mechanism to induce the neuronal injury with
A. cantonensis infection. These results were consistent to the distinct extent of the behavioral dysfunction in mice and rats.
In summary, all these recovery rate, pathologic evidences in the cerebral cortex and hippocampus, and activated extracellular caspase-dependent apoptosis pathway in mice and rats indicated that mice (nonpermissive host) experienced more serious pathological injuries with the caspase-dependent neuronal cell apoptosis than rats (permissive host). The neurological symptoms in clinical infected patients can be explained using the behavioral disorders in our experimental model. The results of mice with A. cantonensis infection will be important for clinical diagnosis and therapy. It also provides evidence that neuroprotection should be considered for the patients with A. cantonensis infection.
Notes
-
ETHICS STATEMENT
All procedures of the animals were carried out according to the guidelines of the Association for Assessment and Accreditation of Laboratory Animal Care International. Our protocols followed institutional ethical guidelines that were approved by the Ethics Committee of ZSSOM on Laboratory Animal Care, Sun Yat-sen University, Guangzhou, P. R. China (SYSU, ZSSOM; permit no: 2016-122).
-
CONFLICT OF INTEREST
We have no conflict of interest related with this study.
Supplementary materials
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS
This research was supported by the National Key R & D Program of China (no. 2016YFC1200500 and 2016YFC1202003), Natural Science Foundation of Guangdong Province (no. 2015 A030310093), and National Science Foundation of China, P. R. China (nos. 81471288, 31070941).
Fig. 1Comparison of balance beam, foot slip, and grip strength for the infected rats and mice in balance-beam tasks. (A) Comparative analysis of completion time for balance-beam task of infected rats and mice. (B) Comparative analysis of foot slip for experimental rats and mice on completing the balance-beam task. (C) Comparative analysis of hang time for grip strength task of infected rats and mice. *: comparison between infection groups and control group, P<0.05. ★: comparison among the different infectious stages, P<0.05.▲: comparison between rats and mice, P<0.05.

Fig. 2MWMT of rats and mice at different time points. (A-A″, B-B″) The tracks of spatial learning in MWMT for rats and mice, respectively. (C-C″, D-D″) The tracks of probe trail for rats and mice in MWMT, respectively. Bar-graphs B* and D* show the comparative analysis of the MWMT, from which the significant declines of spatial learning and memory abilities in infected mice are shown compared with the controls. *: comparison between the infectious groups and the control group, P<0.05.★: comparison among the different infectious stages, P<0.05.

Fig. 3HE and immunohistochemical staining of the cerebral cortex and hippocampus of infected rats and mice. (A, B) HE staining of the cerebral cortex showing the plaque-like lesion and infiltration of inflammatory cells (white star), perivascular cuffing of inflammatory cells. (C, D) HE staining of the hippocampus showing the dilated vessels (black arrowheads), plaque-like lesion, and infiltration of inflammatory cells (white star). (A′, B′) Immunohistochemical staining for NeuN in the cerebral cortex showing loss of neurons (black star). (C′, D′) Immunohistochemical staining for NeuN in the hippocampus showing the blebbing in neurons, nucleus condensing, and cell shrinkage (black arrowheads) compared with normal neuron (white arrowheads). The magnification of the images saw the scale at their right bottom. Ctx: cortex; Hip: hippocampus.

Fig. 4Transcriptomic analysis of expression pattern of the apoptotic pathways in infected mouse brain in different time points. Key genes of interest corresponding to the apoptosis profiling are divided into intrinsic and extrinsic pathways. Different time points of transcriptomic expression pattern in infected mouse brain are shown in the gradient heat map from blue (−10 fold) to red (5 fold) with baseline from 10–1 to 103.

Fig. 5Immunohistochemistry for caspase-3 and double-labeling for NeuN and caspase-3 in cerebral cortex and hippocampus of the infected rats and mice. (A-A′, B-B′) Caspase-3 positive cells (black arrowheads) shown in the cerebral cortex and hippocampus of rats (A and B) and mice (A′ and B′) (star means the plaque-like lesions). (C-C″ to F-F″) The double-labeling for NeuN and caspase-3 in the hippocampus and cerebral cortex of rats and mice (white arrowhead means neurons labeled by caspase-3). Ctx: cortex; Hip: hippocampus.

Fig. 6Protein expression levels of caspase-3 and cleaved-caspase-3 in the cerebral cortex and hippocampus of the infected rats and mice. Relative density shows the caspase-3 expression level in rats and mice with A. cantonensis. β-actin acted as the control. *P<0.05.

References
- 1. Chen HT. Un nouveau nematode pulmonaire, Pulmonem A. cantonensis n.g., n. sp. des rats de Canton. Ann Parasitol Hum Comp 1935;13:312-317.
- 2. Jin EH, Ma Q, Ma DQ, He W, Ji AP, Yin CH. Magnetic resonance imaging of eosinophilic meningoencephalitis caused by Angiostrongylus cantonensis following eating freshwater snails. Chin Med J 2008;121:67-72.
- 3. Kliks MM, Kroenke K, Hardman JM. Eosinophilic radiculomyeloencephalitis: an angiostrongyliasis outbreak in American Samoa related to ingestion of Achatina fulica snails. Am J Trop Med Hyg 1982;31:1114-1122.
- 4. Noda S, Uchikawa R, Matayoshi S, Watanabe Y, Sato A. Observations on the transmission of Angiostrongylus cantonensis from snail to rodent. J Helminthol 1987;61:241-246.
- 5. Slom TJ, Cortese MM, Gerber SI, Jones RC, Holtz TH, Lopez AS, Zambrano CH, Sufit RL, Sakolvaree Y, Chaicumpa W, Herwaldt BL, Johnson S. An outbreak of eosinophilic meningitis caused by Angiostrongylus cantonensis in travelers returning from the Caribbean. N Engl J Med 2002;346:668-675.
- 6. Thiengo SC, Maldonado A, Mota EM, Torres EJL, Caldeira R, Carvalho OS, Oliveira APM, Simoes RO, Fernandez MA, Lanfredi RM. The giant African snail Achatina fulica as natural intermediate host of Angiostrongylus cantonensis in Pernambuco, northeast Brazil. Acta Trop 2010;115:194-199.
- 7. Tsai HC, Lee SS, Huang CK, Yen CM, Chen ER, Liu YC. Outbreak of eosinophilic meningitis associated with drinking raw vegetable juice in southern Taiwan. Am J Trop Med Hyg 2004;71:222-226.
- 8. Alicata JE, Jindrak K. Angiostrongylosis in the Pacific and Southeast Asia. Illinois, USA. Charles C. Thomas; 1970.
- 9. John DT. The biology of Angiostrongylus cantonensis in the white mice. Dis Abstr Int 1971;31:6431.
- 10. Rosen L, Chappell R, Laqueur GL, Wallace GD, Weinstein PP. Eosinophilic meningoencephalitis caused by a metastrongylid lung-worm of rats. JAMA 1962;179:620-624.
- 11. Alicata JE. Biology and distribution of the rat lungworm, Angiostrongylus cantonensis, and its relationship to eosinophilic meningoencephalitis and other neurological disorders of man and animals. Adv Parasitol 1965;3:223-248.
- 12. Punyagupta S, Juttijudata P, Bunnag T. Eosinophilic meningitis in Thailand. Clinical studies of 484 typical cases probably caused by Angiostrongylus cantonensis. Am J Trop Med Hyg 1975;24:921-931.
- 13. Yii CY. Clinical observations on eosinophilic meningitis and meningoencephalitis caused by Angiostrongylus cantonensis on Taiwan. Am J Trop Med Hyg 1976;25:233-249.
- 14. Pien FD, Pien BC. Angiostrongylus cantonensis eosinophilic meningitis. Int J Infect Dis 1999;3:161-163.
- 15. Kuberski T, Wallace GD. Clinical manifestations of eosinophilic memingitis due to Angiostrongylus cantonensis. Neurology 1979;29:1566-1570.
- 16. Tsai HC, Liu YC, Kunin CM, Lee SS, Chen YS, Lin HH, Tsai TH, Lin WR, Huang CK, Yen MY, Yen CM. Eosinophilic meningitis caused by Angiostrongylus cantonensis: report of 17 cases. Am J Med 2001;111:109-114.
- 17. Clouston PD, Corbett AJ, Pryor DS, Garrick R. Eosinophilic meningitis: cause of a chronic pain syndrome. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 1990;53:778-781.
- 18. Lo Re V 3rd, Gluckman SJ. Eosinophilic meningitis due to Angiostrongylus cantonensis in a returned traveler: case report and review of the literature. Clin Infect Dis 2001;33:e112-e115.
- 19. John DT, Martinez AJ. Animal model of human disease. Central nervous system infection with the nematode Angiostrongylus cantonenis. Animal model: eosinophilic meningoencephalitis in mice infected with Angiostrongylus cantonensis. Am J Pathol 1975;80:345-348.
- 20. Perez O, Capron M, Lastre M, Venge P, Khalife J, Capron A. Angiostrongylus cantonensis: role of eosinophils in the neurotoxic syndrome (Gordon-like phenomenon). Exp Parasitol 1989;68:403-413.
- 21. He HJ, Lv ZY, Li ZY, Zhang LY, Liao Q, Zheng HQ, Su WY, Rao SQ, Yu XB, Wu ZD. Efficacy of combined treatment with albendazole and baicalein against eosinophilic meningitis induced by Angiostrongylus cantonensis in mice. J Helminthol 2011;85:92-99.
- 22. Gardiner CH, Wells S, Gutter AE, Fitzgerald L, Anderson DC, Harris RK, Nichols DK. Eosinophilic meningoencephalitis due to Angiostrongylus cantonensis as the cause of death in captive non-human primates. Am J Trop Med Hyg 1990;42:70-74.
- 23. Ishida K, Yoshimura K. Eosinophil responses of permissive and nonpermissive hosts to the young adult worms of Angiostrongylus cantonensis. Z Parasitenkd 1986;72:661-671.
- 24. Ishida K, Yoshimura K. Differences in responses of rat- and guinea-pig-eosinophils to eosinophil chemotactic factors derived from Angiostrongylus cantonensis. Parasite Immunol 1990;12:269-283.
- 25. Wang JJ, Lee JD, Chang JH, Chung LY, Chen ER, Yen CM. The susceptibility of five stains mice to infections with Angiostrongylus cantonensis. Kaohsiung J Med Sci 1995;11:599-603.
- 26. Yoshimura K, Sugaya H, Kawamura K, Kumagai M. Ultrastructural and morphometric analyses of eosinophils from the cerebrospinal fluid of the mouse and guinea-pig infected with Angiostrongylus cantonensis. Parasite Immunol 1988;10:411-423.
- 27. OuYang L, Wei J, Wu Z, Zeng X, Li Y, Jia Y, Ma Y, Zhan M, Lei W. Differences of larval development and pathological changes in permissive and nonpermissive rodent hosts for Angiostrongylus cantonensis infection. Parasitol Res 2012;111:1547-1557.
- 28. Chen KM, Lai SC. Biochemical and pathological evaluation of albendazole/thalidomide co-therapy against eosinophilic meningitis or meningoencephalitis induced by Angiostrongylus cantonensis. J Antimicrob Chemother 2007;59:264-276.
- 29. Lan KP, Lai SC. Differences of proteolytic enzymes and pathological changes in permissive and nonpermissive animal hosts for Angiostrongylus cantonensis infection. Vet Parasitol 2009;165:265-272.
- 30. Shear DA, Dong J, Gundy CD, Haik-Creguer KL, Dunbar GL. Comparison of intrastriatal injections of quinolinic acid and 3-nitropropionic acid for use in animal models of Huntington’s disease. Prog Neuropsychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry 1998;22:1217-1240.
- 31. Chan CC, Khodarahmi K, Liu J, Sutherland D, Oschipok LW, Steeves JD, Tetzlaff W. Dose-dependent beneficial and detrimental effects of ROCK inhibitor Y27632 on axonal sprouting and functional recovery after rat spinal cord injury. Exp Neurol 2005;196:352-364.
- 32. Crawley JN. Behavioral phenotyping of transgenic and knockout mice: experimental design and evaluation of general health, sensory functions, motor abilities, and specific behavioral tests. Brain Res 1999;835:18-26.
- 33. Sun L, Lam WP, Wong YW, Lam LH, Tang HC, Wai MS, Mak YT, Pan F, Yew DT. Permanent deficits in brain functions caused by long-term ketamine treatment in mice. Hum Exp Toxicol 2011;30:1287-1296.
- 34. D’Hooge R, De Deyn PP. Applications of the Morris water maze in the study of learning and memory. Brain Res Brain Res Rev 2001;36:60-90.
- 35. Vorhees CV, Williams MT. Morris water maze: procedures for assessing spatial and related forms of learning and memory. Nat Protoc 2006;1:848-858.
- 36. Yu L, Wu X, Wei J, Liao Q, Xu L, Luo S, Zeng X, Zhao Y, Lv Z, Wu Z. Preliminary expression profile of cytokines in brain tissue of BALB/c mice with Angiostrongylus cantonensis infection. Parasit Vectors 2015;8:328.
- 37. Voogd J, Feirabend HKP. Classic Methods in Neurobiology. 2:New York, USA. Plenum; 1981, pp 301-365.
- 38. Bratton SB, Salvesen GS. Regulation of the Apaf-1-caspase-9 apoptosome. J Cell Sci 2010;123:3209-3214.
- 39. Stoka V, Turk B, Schendel SL, Kim TH, Cirman T, Snipas SJ, Ellerby LM, Bredesen D, Freeze H, Abrahamson M, Bromme D, Krajewski S, Reed JC, Yin XM, Turk V, Salvesen GS. Lysosomal protease pathways to apoptosis. Cleavage of bid, not pro-caspases, is the most likely route. J Biol Chem 2001;276:3149-3157.
- 40. Zakeri Z, Lockshin RA. Cell death: history and future. Adv Exp Med Biol 2008;615:1-11.
- 41. Kanpittaya J, Jitpimolmard S, Tiamkao S, Mairiang E. MR findings of eosinophilic meningoencephalitis attributed to Angiostrongylus cantonensis. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 2000;21:1090-1094.
- 42. Lindo JF, Escoffery CT, Reid B, Codrington G, Cunningham-Myrie C, Eberhard ML. Fatal autochthonous eosinophilic meningitis in a Jamaican child caused by Angiostrongylus cantonensis. Am J Trop Med Hyg 2004;70:425-428.
- 43. Tangchai P, Nye SW, Beaver PC. Eosinophilic meningoencephalitis caused by angiostrongyliasis in Thailand. Autopsy report. Am J Trop Med Hyg 1967;16:454-461.
- 44. Nye SW, Tangchai P, Sundarakiti S, Punyagupta S. Lesions of the brain in eosinophilic meningitis. Arch Pathol 1970;89:9-19.
- 45. Tseng YK, Tu WC, Lee HH, Chen KM, Chou HL, Lai SC. Ultrastructural localization of matrix metalloproteinase-9 in eosinophils from the cerebrospinal fluid of mice with eosinophilic meningitis caused by Angiostrongylus cantonensis. Ann Trop Med Parasitol 2004;98:831-841.
- 46. Wang LC, Jung SM, Chen CC, Wong HF, Wan DP, Wan YL. Pathological changes in the brains of rabbits experimentally infected with Angiostrongylus cantonensis after albendazole treatment: histopathological and magnetic resonance imaging studies. J Antimicrob Chemother 2006;57:294-300.
- 47. Gatkowska J, Wieczorek M, Dziadek B, Dzitko K, Dlugonska H. Behavioral changes in mice caused by Toxoplasma gondii invasion of brain. Parasitol Res 2012;111:53-58.
- 48. Parlog A, Harsan LA, Zagrebelsky M, Weller M, von Elverfeldt D, Mawrin C, Korte M, Dunay IR. Chronic murine toxoplasmosis is defined by subtle changes in neuronal connectivity. Dis Model Mech 2014;7:459-469.
- 49. Zhang YH, Chen H, Chen Y, Wang L, Cai YH, Li M, Wen HQ, Du J, An R, Luo QL, Wang XL, Lun ZR, Xu YH, Shen JL. Activated microglia contribute to neuronal apoptosis in Toxoplasmic encephalitis. Parasit Vectors 2014;7:372.
- 50. Brenner D, Blaser H, Mak TW. Regulation of tumour necrosis factor signalling: live or let die. Nat Rev Immunol 2015;15:362-374.
- 51. Peterson LW, Philip NH, Dillon CP, Bertin J, Gough PJ, Green DR, Brodsky IE. Cell-Extrinsic TNF Collaborates with TRIF Signaling To Promote Yersinia-Induced Apoptosis. J Immunol 2016;197:4110-4117.