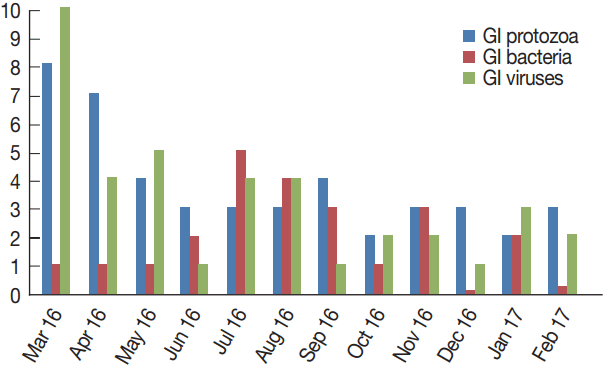Abstract
Infectious diarrhea is endemic in most developing countries. We aimed to investigate the protozoan, viral, and bacterial causes of acute diarrhea in Taif, Saudi Arabia. A cross-sectional prospective 1-year study was conducted on 163 diarrheal patients of various ages. Stool samples were collected, 1 per patient, and tested for 3 protozoa, 3 viruses, and 9 bacteria with the Luminex Gastrointestinal Pathogen Panel. Overall, 53.4% (87/163) of samples were positives (20.8% protozoa, 19.6% viruses, 2.8% bacteria, and 9.8% mixed). Rotavirus (19.6%), Giardia duodenalis (16.5%), and Cryptosporidium spp. (8.5%) were the mostly detected pathogens. Adenovirus 40/41 (4.2%), Salmonella (3%), Shiga toxin-producing Escherichia coli (3%), and Entamoeba histolytica (2.4%) were also detected. Norovirus GI/II, Vibrio cholerae, Yersinia enterocolitica, and Clostridium difficile toxin A/B were not detected in any patients. All pathogens were involved in coinfections except E. histolytica. Giardia (5.5%) and rotavirus (3%) were the most commonly detected in co-infections. Enterotoxigenic E. coli (2.4%), Campylobacter spp. (2.4%), E. coli 0157 (1.8%), and Shigella spp. (1.2%) were detected in patients only as co-infections. Infections were more in children 0–4 years, less in adults <40 years, and least >40 years, with statistically significant differences in risk across age groups observed with rotavirus (P<0.001), Giardia (P=0.006), and Cryptosporidium (P=0.036) infections. Lastly, infections were not significantly more in the spring. This report demonstrates the high burden of various enteropathogens in the setting. Further studies are needed to define the impact of these findings on the clinical course of the disease.
-
Key words: Giardia duodenalis, Entamoeba histolytica, Cryptosporidium, diarrhea, enteropathogen, co-infection, mono-infection, xTAG™ GPP
INTRODUCTION
Infectious diarrhea continues to be a worldwide public health problem. According to an estimate, around 2 billion episodes globally occur per year [
1]. Diarrhea is a leading cause of malnutrition and a second leading cause of death in children below the age of 5, killed 5.8 million children in 2015 [
2]. Diarrhea can be attributed to a variety of different gastrointestinal (GI) pathogens, including protozoa, viruses, and bacteria. The etiologic diagnosis of infectious diarrhea can be challenging due to 2 reasons. First, the clinical pictures of several infections are often similar, and making diagnosis, based on signs and symptoms, is difficult for physicians. Second, infections can be transmitted to humans via food or water, by person-to-person contact, exposure to animals, or acquired from the environment. Therefore, infection with multiple pathogen species could easily occur [
3]. In this case, detection of the concomitant pathogen or the secondary infection is of particular health importance. It could guide physicians to prescribe the most appropriate pathogen-specific medication and health authorities to prevent spread of infections.
Thus, prompt diagnosis of diarrhea should rely on laboratory tests that are subsequently performed based on a presumed etiology by the treating physicians. Nevertheless, the causative pathogen has been unrecognized in about 80% of cases [
4]. Indeed, this could be unfavorable for patient management and infection control. Rapid and accurate detection of the suspected GI pathogens in fecal specimens from patients with diarrhea can be also challenging for the microbiology laboratory. It often requires combinations of multiple diagnostic tests, including bacterial culture, antigen detection assay, in-house nucleic acid-based tests, and microscopy. These standard diagnostic test methods can be time-consuming, labor intensive, and exhibits distinct clinical performances [
5].
A few years ago, several molecular assays were developed, properly validated, received FDA-clearance, and had a growing popularity for the detection of multiple GI pathogens in human feces [
6–
9]. The Luminex® xTAG® Gastrointestinal Pathogen Panel (GPP) (Luminex Molecular Diagnostics, Toronto, Canada) was one of these assays. The xTAG GPP was designed to detect or rule out up to 15 pathogens causing diarrhea, in parallel, in 1 stool sample. The sensitivity of the assay has been reported to be higher than that of the conventional laboratory methods by 2 folds or more, according to earlier studies [
10,
11].
The microbiological etiology of diarrhea has been received much concern among researchers in many parts of the world, including Saudi Arabia [
12–
14]. However, most of the prior research has been focused on investigating a small range of pathogen species based on the combined use of various diagnostic methods.
In a cross-sectional study, we investigated a range of relevant enteric protozoan, viral, and bacterial pathogens in a population with community-acquired acute diarrheal episodes from Taif Province, Saudi Arabia using the xTAG GPP assay. Our main objective was to estimate the frequency of acute infectious diarrhea caused either by 1 pathogen or by multiple pathogens in the setting. The distribution of the detected infections according to patients’ ages, genders, and seasons were also investigated.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Study site and population
A cross-sectional study was undertaken from March 2016 through February 2017 in Taif region, western Saudi Arabia (
Fig. 1). This city is located around 2,000 m above the sea level. The city has desert weather, with hot summers and mild winters. All months see some rainfall, with more rain reported in the spring and late fall months. Patients of different ages, those have been attending 3 primary health centers seeking treatment for their acute diarrheal episodes, were invited to participate in our study.
Acute diarrheal episode was defined as passage of ≥3 loose bowels over a day for a period ≤2 weeks before interviewing. Those patients who presented with diarrhea of ≥2 weeks duration and those received anti-parasitic or antibiotic medications for their diarrhea episodes, 2 weeks prior to the meeting, were excluded from the study. Following these criteria, 163 patients were recruited in the current study.
Ethical considerations
Patients or their relatives were informed of the aim of the study and signed consent forms authorizing their voluntary participation. The regional ethics committee approved data collection, clinical samples collection, and analysis of the study results.
Sample collection and processing
A total of 163 fresh stool samples, 1 sample per each patient, were collected in screw-capped appropriate containers and delivered within 2 hr to the microbiology laboratory at the College of Applied Medical Sciences, Taif University, Saudi Arabia. Upon arrival, each stool sample was inspected for consistency and for the presence of mucous or blood, carefully coded, and immediately stored at −20°C. On a monthly base, frozen samples were transported in ice packs to Al Borg central reference laboratory for molecular diagnosis with the xTAG™ GPP assay.
Molecular testing with xTAG GPP
From a single fecal specimen, the GPP assay allows identification of 15 potential enteropathogens (types, genotypes, and toxin-production genes) frequently-associated with diarrhea. The sought-for GI pathogens included Cryptosporidium species (C. parvum and C. hominis) Entamoeba histolytica, Giardia duodenalis, Campylobacter species (C. jejuni, C. coli, and C. lari), Clostridium difficile toxin A/B, Escherichia coli O157, enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli (ETEC) LT/ST strains, Salmonella., Shiga-like-toxin producing E. coli (STEC) stx1/stx2 strains, Shigella species (S. boydii, S. sonnei, S. flexneri, and S. dysenteriae), Vibrio cholerae, Yersinia enterocolitica, adenovirus subtypes 40/41, norovirus genogroups I and II (GI/GII), and group-A rotavirus.
Samples preparation and nucleic acid purification
Samples were initially prepared with the VERSANT Sample Preparation 1.0 Reagents kit (Siemens Healthcare Diagnostics, Erlangen, Germany) following the manufacturer’s protocol. The crude nucleic acids were directly retrieved from 700 μl of the fecal suspension using the automated platform VERSANT kPCR Molecular System. The purified nucleic acid samples were collected in 100 μl elusion buffer, following the manufacturer’s instructions.
Multiplex PCR reaction set up
The xTAG GPP assay was performed according to the manufacturer’s recommendations (Luminex Molecular Diagnostics, Austin, Texas, USA). Briefly, 10 μl of the nucleic acids extract together with the target-specific tagged primers and the biotin-labeled primers were initially used to set up the multiplex reverse transcription PCR (RT-PCR). The PCR reactions were carried out in Biometra T3 Thermocycler (Biometra GmbH, Göt-tingen, Germany). Amplification of the target DNA results in PCR amplicons with molecular weights ranging from 58 to 293 bp.
Bead hybridization reactions
Aliquots of the xTAG bead mix, 20 μl each, were subjected to sonication, applied into a 96-well microtiter plate, and 5 μl of each PCR product was added into specified well. Subsequently, the xTAG 0.22 streptavidin, R-phycoerythrin conjugate (SAPE), was diluted with the xTAG reporter buffer, and 75 μl of the solution was added into each well.
Products detection and analysis
Following hybridization, the median fluorescence intensity was generated for each xTAG bead population using the Luminex 100/200 instrument pre-heated to 45°C. The data were analyzed using the xTAG Data Analysis Software for the GPP assay.
Data analysis
The xTAG GPP assay results were tabulated for statistical analysis. The GI pathogen prevalence rate was calculated in Microsoft Excel and stated as a percentage of positive samples in relation to the total number of sample tested. The chi-square test was used to test associations between age groups, gender, and GI pathogens positivity variables. For<5 values, Fisher’s exact chi-square test was used, and the P-value<0.05 was considered significant.
RESULTS
Overall results
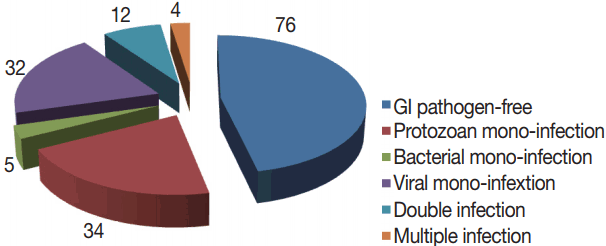
Total 163 patients were allocated in the current study; 91 were males and 72 were females. The age range was 0.5–60 years, with a mean age of 29.9±18.9 with the median age of 19. GI pathogens, 15 kinds, were looked-for in 1 stool sample collected from each participant with the xTAG GPP test. At least 1 enteropathogen was detected in 87 samples, with an estimated detection rate of 53.4%. Mono-infections were found in 71 (43.5%) samples and co-infections were identified in 16 (9.8%) samples. Moreover, co-infections included 12 (7.4%) samples presented as double infections and 4 (2.4%) samples were existed as triple infections (
Fig. 2).
Among the 87 diarrheal episodes that were proved infectious, 34 (20.8%) were protozoan mono-infections, 32 (19.6%) were viral mono-infections, 5 (2.8%) were sole bacterial infections, and 16 (9.8%) were mixed infections (
Fig. 2). Rotavirus (19.6%; n=32),
G. duodenalis (16.5%; n=27), and
Cryptosporidium spp., (8.5%; n=14), were the most commonly detected pathogens. Less frequently detected pathogens were adenovirus 40/41 (4.2%; n=7),
Salmonella (3%; n=5) and STEC (3%; n=5),
E. histolytica (2.5%; 4), ETEC (2.5%; 4),
Campylobacter spp., (2.5%; 4),
E. coli 0157 (1.8%; n=3), and
Shigella (1.2%; n=2). No sample was positive for norovirus genotypes I and II (GI/GII),
Vibrio cholerae,
Yersinia enterocolitica, or
Clostridium difficile toxin A/B (
Table 1).
All the detected pathogens were involved in co-infections except
E. histolytica. Moreover, both
G. duodenalis (5.5%; n=9) and rotavirus (3%; n=5) were the most predominant pathogens in co-infections.
Campylobacter spp. (2.4%; n=4),
ETEC (2.4%; n=4),
E. coli 0157 (1.8%; 3), and
Shigella spp., (1.2%; n=2) were detected in patients only as co-infections with other pathogens. Pathogens involved in co-infections were mentioned with their numbers in
Table 1.
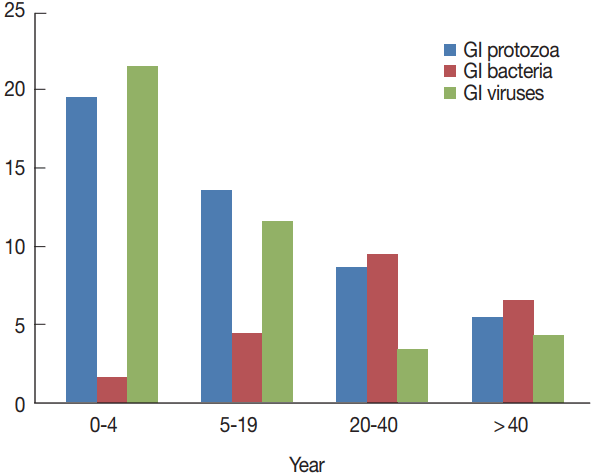
In general, infections were more in younger patients and in males, but no statistically significant difference observed between any of the 2 variables and the total number of pathogens detected (
P =0.93). Children under 4 years (n=36) were the most infected patients, particularly for protozoa and viruses (
Fig. 3). There were statistically significant differences among the distinct age groups and rotavirus infection (
P < 0.001),
Giardia infection (
P =0.006), and
Cryptosporidium infections (
P =0.036). On the contrary, bacterial infections were seen more prevalent in patients aged 20–40 years and to a lesser extent in patients above 40 years, with no statistical significant differences stated among the different age groups and any identified bacteria (
Table 1).
Table 2 shows the monthly distribution of the identified infection over 1 year period. Overall, infections occurred all the year around. Infections were dominant between March and August (70/107), including co-infections. GI protozoa were identified more in samples collected between March and June (22/45), the spring months in Saudi Arabia. Likewise, enteric viruses were detected more in samples collected during the same period (20/39), including co-infections. On the contrary, bacteria were identified more in samples collected in July and November (16/23), the summer months in the country. Lastly, none of the samples collected in December or October were positive for any enteric bacteria (
Fig. 4).
DISCUSSION
To the best of our knowledge, this is the first study, in Saudi Arabia, concerned with detection of multiple GI pathogens, commonly recognized to cause diarrhea in humans using the xTAG™ GPP assay. Also, this is the first report in the Taif region that studies, in an all-inclusive manner, the common viral, protozoan, and the bacterial etiologies of diarrhea.
One noteworthy finding in our study was the exceptionally high number of enteric pathogens detected in this setting. Pathogens were detected in 87 out of 163 patients, with an estimated prevalence rate of 53.4%, a prevalence has not been previously described in this setting. In other settings, variable estimates have been reported in the country. Fareid et al. [
15] identified enteric parasites in 50.4% and bacterial isolates in 88% of 160 schoolchildren presented with diarrhea based on conventional microscopy and stool cultures. Moreover, estimates of 34–46% have been reported for viral, bacterial, and parasitic causes of diarrhea in children less than 5 years [
16–
18]. However, the difference in populations, targeted and the methodologies adopted in these studies make the comparison problematic. With the xTAG GPP, Kahlau et al. [
10] have reported detection of enteropathogens, mostly not requested by the physician, with a frequency rate of 45% in a hospitalized population [
10]. Also, Albert et al. [
11] have reported that the xTAG GPP detected twice as many pathogens as the conventional assays in a study done in Kuwait.
Overall, young children were a most vulnerable group to infections in this setting, going with tremendous of reports in the literature. Moreover, infections were more in males than females, in the absolute numbers, consistent with a previous study [
19] and inconsistent with another [
20]. Identification of groups of patients most vulnerable to infections guides the health authorities for better disease management, infection control, and resource allocation.
Also in our study, we clearly demonstrated a variety of enteropathogens detected and displayed their proportions in the etiology of diarrhea in the population studied. Viral gastroenteritis was a leading cause of diarrhea, in line with the literature. Rotavirus was detected in 32 out of 163 (19.6%) patients studied. Again, little has been recently published regarding rotavirus infection in our setting. None the less, estimates of 4–46% have been reported for other populations [
21,
22]. The adenovirus was identified with a frequency rate of 4.2%, lower than an estimate (1.4%) has been reported by Tayeb et al. [
23] in other Saudi population [
23]. Interestingly, no cases for norovirus genotypes I and II (GI/GII) were identified, perhaps being most frequently a nosocomial infection [
24].
Coincided with several reports, viral gastroenteritis was predominant in children under 4 years, with a statistical significance observed (
P <0.001) for rotavirus infections. Moreover, infections were more in female than in male patients, but without statistical significance, consistent with an Australian survey [
20]. Although, viral infection was detected all the year around, the high positivity rate (59.3%) was displayed in the spring months, consistent with a Canadian report [
25].
Regarding protozoa, all the 3 protozoan parasites targeted were detected in patients.
Giardia was detected in 27 patients, with an estimated prevalence rate of 16.5%. In the same setting, a prevalence of 8.5–15% has been reported in 2 earlier studies [
26,
27].
Cryptosporidium infection was identified with an estimated prevalence of about 9%, minimally lower than an estimate, about 10%, described in an earlier study based on an in-house PCR [
13]. In developing countries, detection of this opportunistic protozoan in diarrheal patients has gained great concern reporting much higher estimates [
28]. Noteworthy was that both
Giardia and
Cryptosporidium have been widely recognized as common waterborne infections and found contaminating desalted water and ground water, 2 common drinking water resources in the country [
29]. On the contrary to the above protozoa,
E. histolytica was found only in 4 patients, with an estimated frequency of 2.4%. Frequencies of 6–18% have been displayed for
E. histolytica in other Saudi populations based on microscopic diagnosis [
30,
31]. Like other enteric pathogens, much higher estimates have been described for this protozoon in developing countries [
32]. Noteworthy, microscopic diagnosis of such unicellular parasite has been widely recognized insensitive and could not differentiate between
E. histolytica and the 2 other morphologically similar species, namely
E. dispar and
E. moshkovskii.
Regardless the type of protozoa, infection were most frequent in children 0–4 years, less in adult<40 years, and least frequent in patients >40 years. There was significant difference stated in risk of across age groups with
Giardia (
P =0.006) and
Cryptosporidium infections (
P =0.036). Furthermore,
Giardia infection was more in females, while
Cryptosporidium was more in males, but these differences were not statistically significant. Although protozoa were identified in patients throughout the year, infections especially with
Giardia and
Cryptosporidium were detected in a greatest number (20/45) in spring months, coinciding with an earlier report [
13].
Among the 9 bacteria studied,
Salmonella, STEC, ETEC, and
Campylobacter spp.,
E. coli 0157, and
Shigella were isolated, with an estimated prevalence rate of 10%. Estimates between 10% and 30% have been reported based on culture methods [
16,
18]. No cases for
Vibrio cholerae, Yersinia enterocolitica, or
Clostridium difficile toxin A/B were identified. Perhaps, measures taken by the health-authorities and increasing the awareness of the population about the importance of good food hygiene, after a period of foodborne diarrhea outbreaks, may be an explanation [
33].
C. difficile was like norovirus commonly acquired in hospitals [
34]. In contrast to the viral and protozoan infections, the enteric bacteria were identified more in teenagers and in males, with no statistical significance observed in risk across patients’ ages or genders with any of the bacterial isolates. Furthermore, more bacteria were detected in the summer months.
Also in this context, we clearly demonstrated the frequency of infections with multiple pathogens in patients with diarrhea. Co-infections were detected in 16 patients, with an estimated prevalence rate of 9.8%, comparable to estimates, 7.0–9.5%, documented, elsewhere [
7,
8]. Identical to several mono-infections detected, co-infection was identified more in children than other age groups and in males than females, but no significant statistical difference observed across both variables and the incidence of getting infected with multiple pathogens. Interestingly, all detected pathogens were found involved in mixed infections with except
E. histolytica. E. histolytica has been frequently co-infected with the other 2 morphologically similar species
E. dispar and
E. moshkovskii, not covered by the xTAG GPP assay [
35]. Both
G. duodenalis and rotavirus were the 2 pathogens most frequently detected in mixed infections.
Interestingly,
Campylobacter spp., ETEC,
E. coli 0517, and
Shigella spp. were identified in the studied population only as concomitant pathogens. Co-infections among enteric pathogens have been frequently described [
36–
38]. However, still there is a controversy regarding the clinical impact of concomitant infections on the diarrheal illness. Synergic effects of concomitant infections have been ruled out for rotavirus infection in a study and reported later in another [
39,
40].
Lastly, our study could be bounded by a number of factors. Some interesting data could be statistically biased by the relatively small number of positive samples. Moreover, non-inclusion of a control group in conjunction with patients did not help to clear the clinical impact of some findings. Lastly, pathogens commonly reported to cause diarrhea in the country like astrovirus, intestinal helminths, and other coccidian parasites, are not covered by the xTAG GPP assay and therefore, these enteric pathogens were not investigated in this study.
To conclude, in this report, we clearly demonstrated the high burden of pathogens causing diarrhea in the study setting. Giardia, rotavirus, and Cryptosporidium were the most dominant pathogens. Infections were frequent in children below 4 years. Furthermore, co-infections were identified with a relatively high frequency. Lastly, the methodology adopted in this study was proved useful for detection of multiple potential pathogens in this population. Further longitudinal case-control studies are needed to follow-up patients and define accurately the clinical impact of the identified pathogens on the diarrheal disease.
Notes
-
CONFLICT OF INTEREST
We have no conflict of interest related to this study.
ACKNOWLEDGMENT
This research was funded by Taif University, Saudi Arabia (grant no. 1-437-4949). The authors would like to thank Dr. Rizk A, Dr. Henawy I, and their colleagues for their great help while recruiting patients and collecting fecal samples.
Fig. 1Saudi Arabia map showing the location of Taif region and the nearby cities.

Fig. 2The results of xTAG GPP assay of 163 diarrheal stool samples.
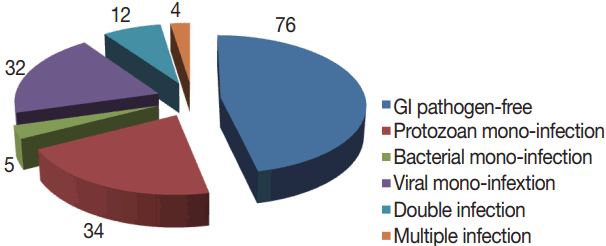
Fig. 3Distribution of gastrointestinal pathogens (mono-infections and co-infections) relative to the patients’ age groups.

Fig. 4Monthly distribution of the detected gastrointestinal pathogens.
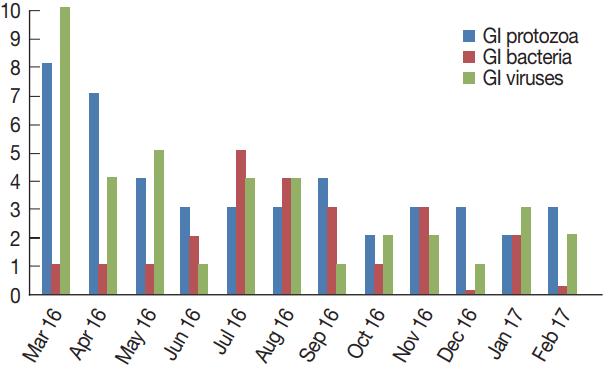
Table 1Distribution of GI pathogens (mono-infection and co-infections) relative to the patients’ age groups
Table 1
|
GI Pathogens |
Age (year) groups |
Total |
P-value |
|
|
0–4 (n=36) |
5–19 (n=40) |
20–40 (n=48) |
>40 (n=39) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Mono- |
Co- |
Mono- |
Co- |
Mono- |
Co- |
Mono- |
Co- |
Mono- |
Co- |
Total |
|
G. duodenalis
|
9 |
3 |
5 |
3 |
2 |
2 |
2 |
1 |
18 |
9 |
27 |
0.006 sig |
|
|
Cryptosporidium
|
6 |
1 |
4 |
0 |
1 |
1 |
1 |
0 |
12 |
2 |
14 |
0.036 sig |
|
|
E. histolytica
|
0 |
0 |
1 |
0 |
2 |
0 |
1 |
0 |
4 |
0 |
4 |
0.463 |
|
|
Salmonella
|
0 |
0 |
0 |
1 |
2 |
0 |
2 |
0 |
4 |
1 |
5 |
0.673 |
|
|
Shigella
|
0 |
0 |
0 |
1 |
0 |
1 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
2 |
2 |
0.273 |
|
|
E. coli 0157 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
2 |
0 |
1 |
0 |
3 |
3 |
0.173 |
|
|
STEC |
0 |
0 |
1 |
2 |
0 |
1 |
0 |
1 |
1 |
4 |
5 |
0.683 |
|
|
ETEC |
0 |
0 |
0 |
1 |
0 |
3 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
4 |
4 |
0.463 |
|
|
Campylobacter
|
0 |
1 |
0 |
2 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
1 |
0 |
4 |
4 |
0.653 |
|
|
Rotavirus |
16 |
3 |
7 |
1 |
1 |
1 |
3 |
0 |
27 |
5 |
32 |
<0.001 HS |
|
|
Adenovirus |
0 |
2 |
3 |
0 |
1 |
0 |
1 |
0 |
5 |
2 |
7 |
0.573 |
|
|
Total |
31 |
10 |
21 |
11 |
9 |
11 |
10 |
4 |
71 |
36a
|
107 |
0.930 |
Table 2The monthly distribution of the detected GI pathogens
Table 2
|
GI pathogen |
Study duration |
Total (163) |
|
|
2016 |
2017 |
|
|
|
Mar (14) |
Apr (13) |
May (13) |
Jun (14) |
Jul (12) |
Aug (14) |
Sep (13) |
Oct (11) |
Nov (15) |
Dec (14) |
Jan (14) |
Feb (16) |
|
G. duodenalis
|
5 |
4 |
3 |
1 |
1 |
1 |
3 |
2 |
2 |
1 |
2 |
2 |
27 |
|
|
Cryptosporidium spp. |
3 |
2 |
1 |
1 |
2 |
1 |
1 |
- |
1 |
1 |
- |
1 |
14 |
|
|
E. histolytica
|
- |
1 |
- |
1 |
- |
1 |
- |
- |
- |
1 |
- |
- |
4 |
|
|
Salmonella spp. |
1 |
- |
1 |
- |
2 |
- |
- |
1 |
- |
- |
- |
- |
5 |
|
|
Shigella spp. |
- |
- |
- |
- |
- |
2 |
- |
- |
- |
- |
- |
- |
2 |
|
|
E. coli 0157 |
- |
1 |
- |
1 |
- |
- |
- |
- |
- |
- |
1 |
- |
3 |
|
|
STEC |
- |
- |
- |
- |
2 |
|
2 |
- |
1 |
- |
- |
- |
5 |
|
|
ETEC |
- |
- |
- |
1 |
|
2 |
- |
- |
- |
- |
1 |
- |
4 |
|
|
Campylobacter spp. |
- |
- |
- |
- |
1 |
- |
1 |
- |
2 |
- |
- |
- |
4 |
|
|
Rotavirus |
9 |
4 |
2 |
1 |
4 |
3 |
1 |
2 |
1 |
1 |
3 |
1 |
32 |
|
|
Adenovirus |
1 |
- |
3 |
- |
- |
1 |
- |
- |
1 |
- |
- |
1 |
7 |
|
|
Total |
19 |
12 |
10 |
6 |
12 |
11 |
8 |
5 |
8 |
4 |
7 |
5 |
107a
|
References
- 1. Farthing M, Salam MA, Lindberg G, Dite P, Khalif I, Salazar-Lindo E, Ramakrishna BS, Goh KL, Thomson A, Khan AG, Krabshuis J, LeMair A. Acute diarrhea in adults and children: a global perspective. J Clin Gastroenterol 2013;47:12-20.
- 2. Wang H1, Liddell CA, Coates MM, Mooney MD, Levitz CE, Schumacher AE, Apfel H, Iannarone M, Phillips B, Lofgren KT, Sandar L, Dorrington RE, Rakovac I, Jacobs TA, Liang X, Zhou M6 Zhu J, Yang G, Wang Y, Liu S, Li Y, Ozgoren AA, Abera SF, Abubakar I, Achoki T, Adelekan A, Ademi Z, Alemu ZA, Allen PJ, AlMazroa MA, Alvarez E, Amankwaa AA, Amare AT, Ammar W, Anwari P, Cunningham SA, Asad MM, Assadi R, Banerjee A, Basu S, Bedi N, Bekele T, Bell ML, Bhutta Z, Blore JD, Basara BB, Boufous S, Breitborde N, Bruce NG, Bui LN, Carapetis JR, Cárdenas R, Carpenter DO, Caso V, Castro RE, Catalá-Lopéz F, Cavlin A, Che X, Chiang PP, Chowdhury R, Christophi CA, Chuang TW, Cirillo M, da Costa Leite I, Courville KJ, Dandona L, Dandona R, Davis A, Dayama A, Deribe K, Dharmaratne SD, Dherani MK, Dilmen U, Ding EL, Edmond KM, Ermakov SP, Farzadfar F, Fereshtehnejad SM, Fijabi DO, Foigt N, Forouzanfar MH, Garcia AC, Geleijnse JM, Gessner BD, Goginashvili K, Gona P, Goto A, Gouda HN, Green MA, Greenwell KF, Gugnani HC, Gupta R, Hamadeh RR, Hammami M, Harb HL, Hay S, Hedayati MT, Hosgood HD, Hoy DG, Idrisov BT, Islami F, Ismayilova S, Jha V, Jiang G, Jonas JB, Juel K, Kabagambe EK, Kazi DS, Kengne AP, Kereselidze M, Khader YS, Khalifa SE, Khang YH, Kim D, Kinfu Y, Kinge JM, Kokubo Y, Kosen S, Defo BK, Kumar GA, Kumar K, Kumar RB, Lai T, Lan Q, Larsson A, Lee JT, Leinsalu M, Lim SS, Lipshultz SE, Logroscino G, Lotufo PA, Lunevicius R, Lyons RA, Ma S, Mahdi AA, Marzan MB, Mashal MT, Mazorodze TT, McGrath JJ, Memish ZA, Mendoza W, Mensah GA, Meretoja A, Miller TR, Mills EJ, Mohammad KA, Mokdad AH, Monasta L, Montico M, Moore AR, Moschandreas J, Msemburi WT, Mueller UO, Muszynska MM, Naghavi M, Naidoo KS, Narayan KM, Nejjari C, Ng M, de Dieu Ngirabega J, Nieuwenhuijsen MJ, Nyakarahuka L, Ohkubo T, Omer SB, Caicedo AJ, Pillay-van Wyk V, Pope D, Pourmalek F, Prabhakaran D, Rahman SU, Rana SM, Reilly RQ, Rojas-Rueda D, Ronfani L, Rushton L, Saeedi MY, Salomon JA, Sampson U, Santos IS, Sawhney M, Schmidt JC, Shakh-Nazarova M, She J, Sheikhbahaei S, Shibuya K, Shin HH, Shishani K, Shiue I, Sigfusdottir ID, Singh JA, Skirbekk V, Sliwa K, Soshnikov SS, Sposato LA, Stathopoulou VK, Stroumpoulis K, Tabb KM, Talongwa RT, Teixeira CM, Terkawi AS, Thomson AJ, Thorne-Lyman AL, Toyoshima H, Dimbuene ZT, Uwaliraye P, Uzun SB, Vasankari TJ, Vasconcelos AM, Vlassov VV, Vollset SE, Waller S, Wan X, Weichenthal S, Weiderpass E, Weintraub RG, Westerman R, Wilkinson JD, Williams HC, Yang YC, Yentur GK, Yip P, Yonemoto N, Younis M, Yu C, Jin KY, El Sayed Zaki M, Zhu S, Vos T, Lopez AD, Murray CJ. Global, regional, and national levels of neonatal, infant, and under-5 mortality during 1990–2013: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2013. Lancet 2014;19:957-979.
- 3. Tang YW, Persing DH. Advances in the Clinical Microbiology of Enteric Infections. In Blaser MJ, Smith PD, Ravdin JI eds, Infections of the Gastrointestinal Tract. Lippincott Williams & Wilkins. Philadelphia, USA. 2002, pp 1185-1197.
- 4. Van Gilder T, Steiner TS, Thielman NM, Slutsker L, Tauxe RV, Hennessy T, Griffin PM, DuPont H, Sack RB, Tarr P, Neill M, Nachamkin I, Reller LB, Osterholm MT, Bennish ML, Pickering LK. Practice guidelines for the management of infectious diarrhea. Clin Infect Dis 2001;32:331-351.
- 5. Pawlowski SW, Warren CA, Guerrant R. Diagnosis and treatment of acute or persistent diarrhea. Gastroenterology 2009;136:1874-1886.
- 6. Dunbar SA, Zhang H, Tang YW. Advanced techniques for detection and identification of microbial agents of gastroenteritis. Clin Lab Med 2013;33:527-552.
- 7. Claas EC, Burnham CA, Mazzulli T, Templeton K, Topin F. Performance of the xTAG® gastrointestinal pathogen panel, a multiplex molecular assay for simultaneous detection of bacterial, viral, and parasitic causes of infectious gastroenteritis. J Microbiol Biotechnol 2013;23:1041-1045.
- 8. Mengelle C, Mansuy JM, Prere MF, Grouteau E, Claudet I, Kamar N, Huynh A, Plat G, Benard M, Marty N, Valentin A, Berry A, Izopet J. Simultaneous detection of gastrointestinal pathogens with a multiplex Luminex-based molecular assay in stool samples from diarrheic patients. Clin Microbiol Infect 2013;19:458-465.
- 9. Patel A, Navidad J, Bhattacharyya S. Site-specific clinical evaluation of the Luminex xTAG gastrointestinal pathogen panel for detection of infectious gastroenteritis in fecal specimens. J Clin Microbiol 2014;52:3068-3071.
- 10. Kahlau P, Malecki M, Schildgen V, Schulz C, Winterfeld I, Messler S, Mattner F, Schildgen O. Utility of two novel multiplexing assays for the detection of gastrointestinal pathogens–a first experience. Springerplus 2013;2:106.
- 11. Albert MJ, Rotimi VO, Iqbal J, Chehadeh W. Evaluation of the xTAG gastrointestinal pathogen panel assay for the detection of enteric pathogens in Kuwait. Med Princ Pract 2016;25:472-476.
- 12. Sterling CR, Adam RD. The Pathogenic Enteric Protozoa: Giardia, Entamoeba, Cryptosporidium and Cyclospora
. Kluwer Academic Publishers. Boston, USA. 2004.
- 13. Hawash Y, Dorgham LSh, Al-Hazmi AS, Al-Ghamdi MS. Prevalence of Cryptosporidium-associated diarrhea in a high altitude-community of Saudi Arabia detected by conventional and molecular methods. Korean J Parasitol 2014;52:479-485.
- 14. Hawash Y, Ghonaim MM, Al-Shehri SS. An improved PCR-RFLP assay for detection and genotyping of asymptomatic Giardia lamblia infection in a resource-poor setting. Korean J Parasitol 2016;54:1-8.
- 15. Fareid MA, Alshankyty IM, Amer OH. Prevalence of intestinal parasitic and bacterial pathogens in diarrhoeal and non-diarrhoeal school children’s at Hail, Saudi. N Y Sci J 2011;4:106-113.
- 16. Al Ayed MS, Asaad AM, Mahdi AA, Qureshi MA. Aetiology of acute gastroenteritis in children in Najran region, Saudi Arabia. J Health Specialties 2013;1:84.
- 17. Johargy A, Ghazi H, Mumenah A. Frequency of viral, bacterial and parasitic enteropathogens among young children with acute diarrhea in Saudi Arabia. J Pak Med Assoc 2010;60:456-459.
- 18. el-Sheikh SM, el-Assouli SM. Prevalence of viral, bacterial and parasitic enteropathogens among young children with acute diarrhoea in Jeddah, Saudi Arabia. J Health Popul Nutr 2001;1:25-30.
- 19. Nguyen TV, Le Van P, Le Huy C, Weintraub A. Diarrhea caused by rotavirus in children less than 5 years of age in Hanoi, Vietnam. J Clin Microbiol 2004;42:5745-5750.
- 20. Hall GV, Kirk MD, Ashbolt R, Stafford R, Lalor K. Frequency of infectious gastrointestinal illness in Australia, 2002: regional, seasonal and demographic variation. Epidemiol Infect 2006;134:111-118.
- 21. Khalil M, Azhar E, Kao M, Al-Kaiedi N, Alhani H, Al Olayan I, Pawinski R, Gopala K, Kandeil W, Anis S, Van Doorn LJ, DeAntonio R. Gastroenteritis attributable to rotavirus in hospitalized Saudi Arabian children in the period 2007–2008. Clin Epidemiol 2015;7:129-137.
- 22. Ahmed QMU. Rotavirus causing acute gastroenteritis infection in children at our hospital (eastern region of Saudi Arabia). Int J Immunol Stud 2014;2:55-60.
- 23. Tayeb HT, Dela Cruz DM, Al-Qahtani A, Al-Ahdal MN, Carter MJ. Enteric viruses in pediatric diarrhea in Saudi Arabia. J Med Virol 2008;80:1919-1929.
- 24. Pitz AM, Park GW, Lee D, Boissy YL, Vinjé J. Antimicrobial activity of bismuth subsalicylate on Clostridium difficile, Escherichia coli O157: H7, norovirus, and other common enteric pathogens. Gut Microbes 2015;6:93-100.
- 25. Pang XL, Preiksaitis JK, Lee BE. Enhanced enteric virus detection in sporadic gastroenteritis using a multi-target real-time PCR panel: a one-year study. J Med Virol 2014;86:1594-1601.
- 26. Shalaby I, Gherbawy Y, Banaja A. Molecular characterization of Giardia parasite isolated from stool samples collected from different hospitals in Taif City (Saudi Arabia). Trop Biomed 2011;28:487-496.
- 27. Hawash Y. Evaluation of an immunoassay-based algorithm for screening and identification of Giardia and Cryptosporidium antigens in human faecal specimens from Saudi Arabia. J Parasitol Res 2014;2014:213745.
- 28. Sow SO, Muhsen K, Nasrin D, Blackwelder WC, Wu Y, Farag TH, Panchalingam S, Sur D, Zaidi AK, Faruque AS, Saha D, Adegbola R, Alonso PL, Breiman RF, Bassat Q, Tamboura B, Sanogo D, Onwuchekwa U, Manna B, Ramamurthy T, Kanungo S, Ahmed S, Qureshi S, Quadri F, Hossain A, Das SK, Antonio M, Hossain MJ, Mandomando I, Nhampossa T, Acácio S, Omore R, Oundo JO, Ochieng JB, Mintz ED, O’Reilly CE, Berkeley LY, Livio S, Tennant SM, Sommerfelt H, Nataro JP, Ziv-Baran T, Robins-Browne RM, Mishcherkin V, Zhang J, Liu J, Houpt ER, Kotloff KL, Levine MM. The burden of Cryptosporidium diarrheal disease among children<24 months of age in moderate/high mortality regions of Sub-Saharan Africa and South Asia, utilizing data from the Global Enteric Multicenter Study (GEMS). PLoS Negl Trop Dis 2016;10:e0004729.
- 29. Hawash Y, Ghonaim M, Hussein Y, Alhazmi A, Alturkistani A. Identification of Giardia lamblia and the human infectious-species of Cryptosporidium in drinking water resources in Western Saudi Arabia by nested-PCR assays. Trop Biomed 2015;32:216-224.
- 30. Al Braiken FA, Amin A, Beeching NJ, Hommel M, Hart CA. Detection of Cryptosporidium amongst diarrhoeic and asymptomatic children in Jeddah, Saudi Arabia. Ann Trop Med Parasitol 2003;97:505-510.
- 31. Al-Braiken FA. Is intestinal parasitic infection still a public health concern among Saudi children? Saudi Med J 2008;29:1630-1635.
- 32. Kotloff KL, Nataro JP, Blackwelder WC, Nasrin D, Farag TH, Panchalingam S, Wu Y, Sow SO, Sur D, Breiman RF, Faruque AS, Zaidi AK, Saha D, Alonso PL, Tamboura B, Sanogo D, Onwuchekwa U, Manna B, Ramamurthy T, Kanungo S, Ochieng JB, Omore R, Oundo JO, Hossain A, Das SK, Ahmed S, Qureshi S, Quadri F, Adegbola RA, Antonio M, Hossain MJ, Akinsola A, Mandomando I, Nhampossa T, Acácio S, Biswas K, O’Reilly CE, Mintz ED, Berkeley LY, Muhsen K, Sommerfelt H, Robins-Browne RM, Levine MM. Burden and aetiology of diarrhoeal disease in infants and young children in developing countries (the Global Enteric Multicenter Study, GEMS): a prospective, case-control study. Lancet 2013;382:209-222.
- 33. Bakri M, Amin FAL, Saleh ALF, Saeed ALT, Nabag M, Harron M, Ismail KMK. Food hygiene in last ten years in Saudi Arabia: a review. EC Microbiol 2017;7:4-13.
- 34. Khanafer N, Vanhems P, Barbut F, Luxemburger C. Factors associated with Clostridium difficile infection: a nested case-control study in a three year prospective cohort. Anaerobe 2017;44:117-123.
- 35. Ali IK, Hossain MB, Roy S, Ayeh-Kumi PF, Petri Jr WA, Haque R, Clark CG.
Entamoeba moshkovskii infections in children in Bangladesh. Emerg Infect Dis 2003;9:580-584.
- 36. Moyo SJ, Kommedal Ø, Blomberg B, Hanevik K, Gjerde Tellevik M, Maselle SY, Langeland N. Comprehensive analysis of prevalence, epidemiological and clinical characteristics of mono-infections and co-infections in diarrhoeal diseases in children in Tanzania. Am J Epidemiol 2017;
- 37. Koh H, Baek SY, Shin JI, Chung KS, Jee YM. Coinfection of viral agents in Korean children with acute watery diarrhea. J Korean Med Sci 2008;23:937-940.
- 38. Varela G, Batthyány L, Bianco MN, Pérez W, Pardo L, Algorta G, Robino L, Suárez R, Navarro A, Pírez MC, Schelotto F. Entero-pathogens associated with acute diarrhea in children from households with high socioeconomic level in Uruguay. Int J Microbiol 2015;2015:592953.
- 39. Unicomb LE, Faruque SM, Malek MA, Faruque AS, Albert MJ. Demonstration of a lack of synergistic effect of rotavirus with other diarrheal pathogens on severity of diarrhea in children. J Clin Microbiol 1996;34:1340-1342.
- 40. Bhavnani D, Goldstick JE, Cevallos W, Trueba G, Eisenberg JN. Synergistic effects between rotavirus and co-infecting pathogens on diarrheal disease: evidence from a community-based study in northwestern Ecuador. Am J Epidemiol 2012;176:387-395.