Abstract
The cysts of Sarcocystis grueneri were detected and characterized from the cardiac muscles of the Korean water deer (Hydropotes inermis argyropus). Of the 38 heart muscle samples examined by light microscopy, 10 were found infected with the cysts of Sarcocystis sp. The cysts appeared oval to spherical shape and measured 110–380 μm in length and 90–170 μm in width. A phylogenetic tree of the 18S rRNA sequences (1.5 kb) revealed a close relationship of the infected cysts to genus Sarcocystis. The 18S rRNA sequence of the infected cysts showed 100% identity to S. grueneri and 97% to S. capracanis. Here, we first report the S. grueneri infections in the Korean water deer.
-
Key words: Sarcocystis grueneri, Korean water deer, 18S rRNA
INTRODUCTION
The genus
Sarcocystis is recognized in the phylum Apicomplexa that can cause mortality of many animals and impact animal community diversity. These parasites typically infect both intermediate and definitive host animals. Intermediate host animals include herbivores and omnivorous animals that can be infected when ingesting oocysts in the feces of the definitive host animals. In turn, carnivorous animals of definitive hosts are infected when they consume the intermediate host prey infected by
Sarcocystis [
1–
3].
The cysts of
Sarcocystis species were prevalent in the cervid and in the bovid. These mammals play as the intermediate hosts in life cycle of the parasites. Recently, several species of
Sarcocystis has been found in diverse cervid species [
3–
10]. Thus, it has been suggested that the host rage of
Sarcocystis parasites could be broader than the known animal species [
11].
The infection surveys of the
Sarcocystis parasites among a domestic cattle population in the Republic of Korea (ROK) reveal the considerably higher infection prevalence of the parasites, especially in the old aged cattle population and also the studies found that dog is the main definitive host animal of the parasite [
12–
16]. In addition,
Sarcocystis grueneri were found in a red deer and
Sarcocystis tenella in Korean native goats [
17,
18]. The water deer (
Hydropotes inermis) is a small deer seemingly more similar to a musk deer than a true deer and is the only species of genus
Hydropotes which belongs to family Cervidae. There are 2 subspecies: The Chinese Water Deer (
H. inermis inermis) and the Korean Water Deer (
H. inermis argyropus) [
19,
20]. In the ROK, the Korean water deer is one of the widely distributed animals and overpopulated in some regions of the ROK [
21]. There is no report on
Sarcocystis infection in wild Korean water deer in the ROK. Our study first detected and characterized the infection of
S. grueneri in wild Korean water deer in the ROK.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Sample collection and histological study
The cardiac muscle samples were collected from 38 wild Korean water deer (male 23, female 15) at the wild animal rescue centers in Gangwon-do, Gyeonggi-do, Chungcheongbuk-do, and Daejeon city (
Table 1) in 2004–2012. The divisions of heart were fixed in 10% neutral buffered formalin, embedded in paraffin, sectioned at 4 μm, and stained with hematoxylin and eosin for screening by light microscopy (LM).
Fresh positive myocardium tissues were examined in order that genomic DNA was extracted with frozen after collection and stored at −20°C before examination immediately upon thawing. With tissue cutting of 0.05 g to 0.25 g, both 10 positive samples and 1 negative sample (confirmed by LM) were placed in 1.5 ml microcentrifuge tubes containing with PBS (pH 7.4).
Genomic DNA extraction was carried out using DNeasy Blood & Tissue Kits (Qiagen, Hilden, Germany) according to the manufacturer’s instructions. DNA was eluted in 30 μl of buffer (10 mM Tris-Cl, pH 8.5) yielding 33.2 ng of the average concentration were measured by Nano spectrophotometer (Nano Photometer, Implen, Munich, Germany). Loads of overlapping region between members of the Sarcocystidae covering 18S rRNA gene were amplified by the polymerase chain reaction (PCR) using primer 18S 2L (F)-GGATAACCGTGGTAATTCTATG and 18S 1H (R)-TATCCCCATCACGATGCATAC [
22]. One reaction mixture contained the genomic DNA of 33.2 ng (1 μl/reaction), HiPi PCR PreMix (Elpis Biotech. Inc., Daejeon, Korea)-
Taq polymerase in 250 mM Tris-HCl (pH 9.0) of 1 unit, 80 mM (NH
4)
2SO
4, 10% DMSO, 8.75 mM MgCl
2, 0.05% bromophenol blue, 12% glycerol, and the oligonucleotide primers (10 pmol each/ reaction of 1 μl), RNase-free water to add to final composition. Reactions were started at 95°C for 3 min, followed by 35 cycles of 94°C for 40 sec, 55°C for 45 sec or 1 min, and 72°C for 1 min 30 sec, with final incubation at 72°C for 5 min. The PCR products have been analyzed by electrophoresis of 1.2% agarose gel. The 1,500 bp amplicon of the both species examined proved to be difficult to sequence directly from PCR products; the region was cloned for specific sequences.
The purified PCR amplicons were cloned into the pGEM
®-T Easy Vector (Promega, Madison, Wisconsin, USA). Plasmid DNA were purified and sequenced using an automatic sequencer (ABI 3730xl DNA Analyzer, Applied Biosystems, Foster City, California, USA). The achieved sequences were compared with phylogenetic analyses on the SSU rRNA gene from
Sarcocystis species sequenced as well as with other registered sequences of
Sarcocystis spp. from intermediate hosts, retrieved from Gen-Bank using BLAST program (
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/BLAST). A score of sequences were aligned by the Align IR (Ver 2.0;
http://biosupport.licor.com/support), Clustal X (Ver 2.0;
www.clustal.org), and MEGA 4 [
23], respectively. Using the neighbor-joining (NJ) (Kimura 2-parameter distance model) methods was based on a guide tree as pairwise and multiple alignment parameters. The final alignment was comprised of a score of sequences with 39 taxa (
Table 2).
RESULTS
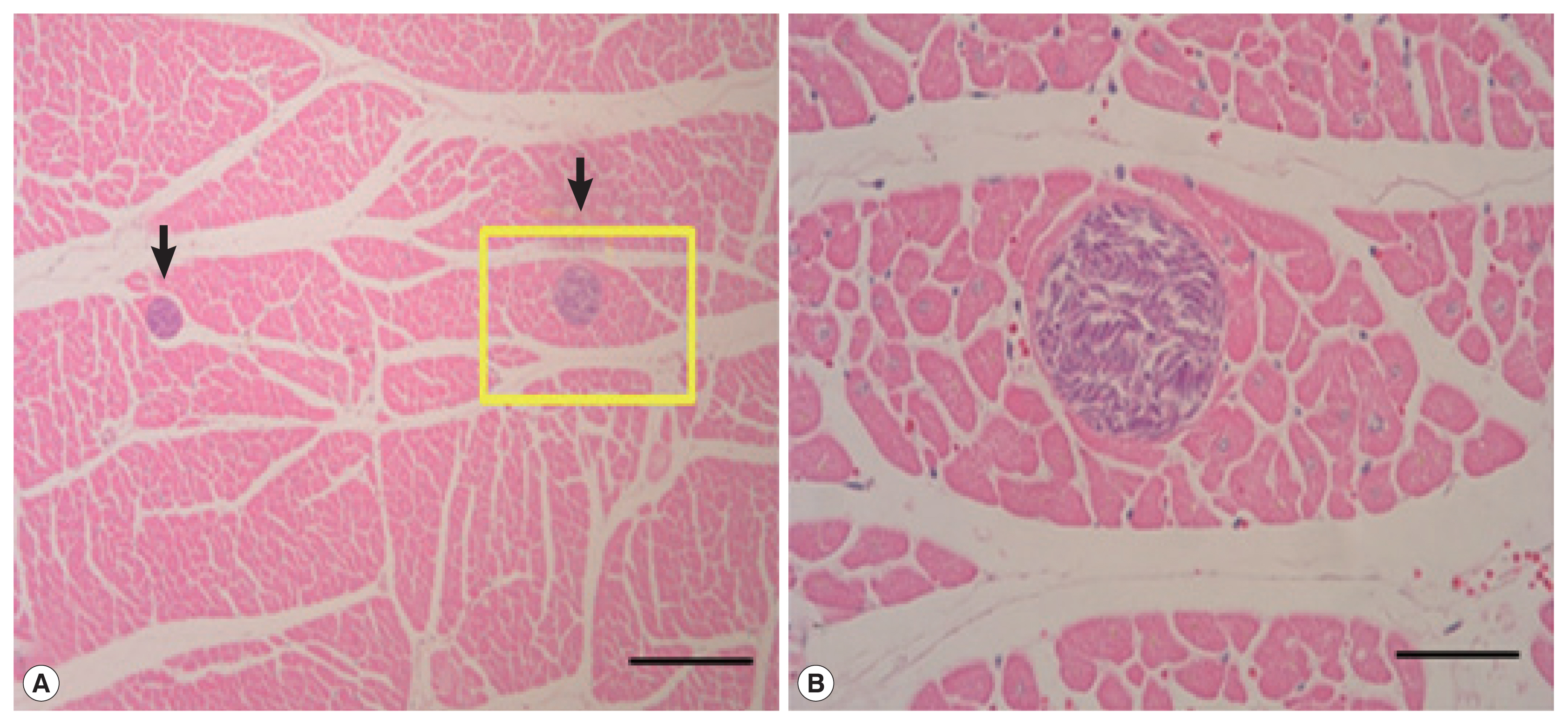
Sarcocysts were not found in the liver or lungs (n=38), but detected from 10 heart muscle samples. All cysts were located in sarcoplasm of myocardium surrounded by thin and smooth cyst wall. All of the sarcocysts were filled with bradyzoites (
Fig. 1). The cysts appeared oval to spherical shape, 110–380 μm long and 90–170 μm wide under LM. The prevalence of
Sarcocystis was 26.3% (
Table 1). Although it appears that these parasites were the species of
S. grueneri, the further molecular identification of these parasites is required.
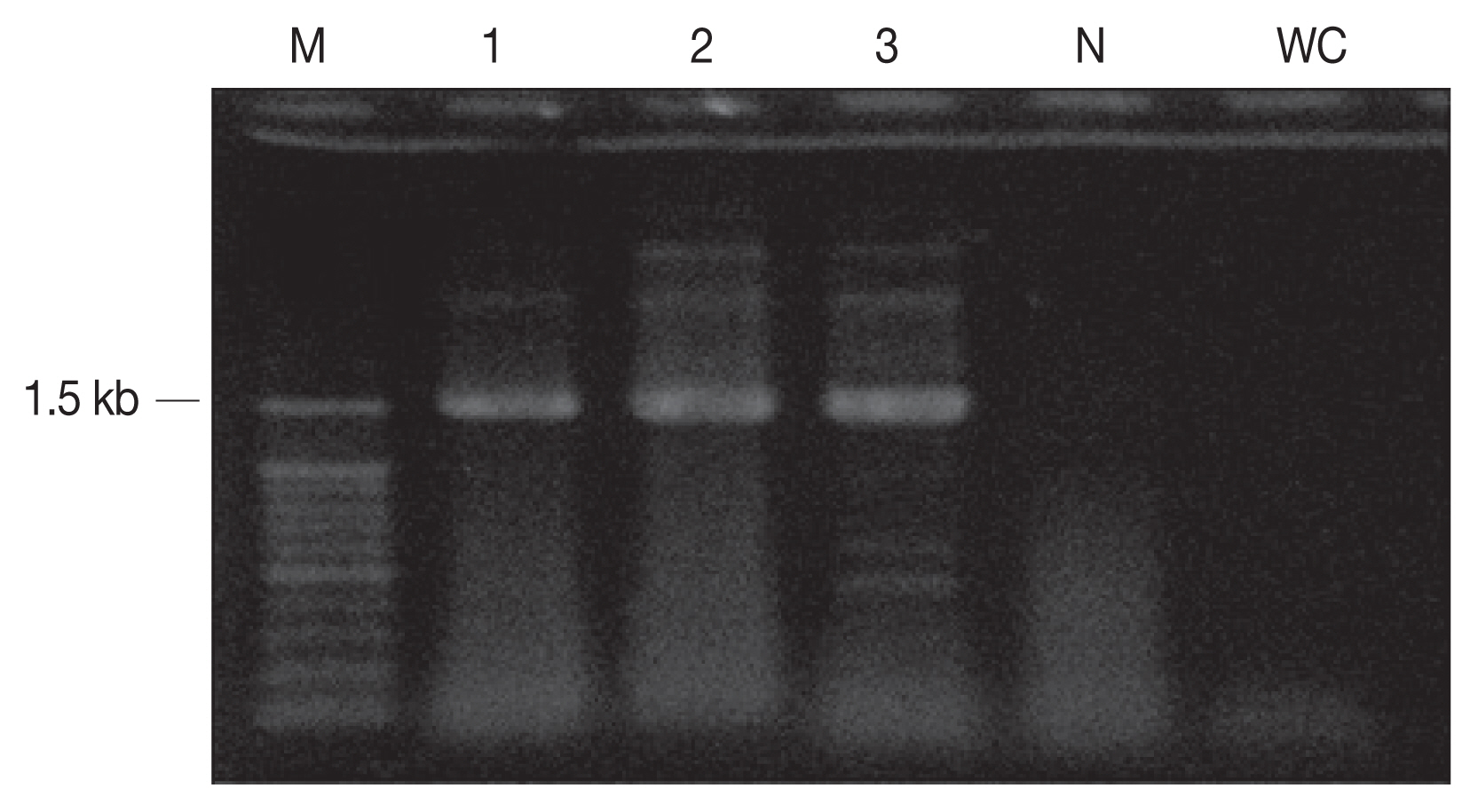
The cyst samples were amplified using the primers of 18S rRNA and revealed 1.5 kb fragment (
Fig. 2) which was a close analogue of
S. grueneri found in reindeer (
Rangifer tarandus tarandus) [
5]. One sequence as a representative of was deposited in GenBank (accession number KC556825). The sample sequences were compared with complete 18S rRNA sequences from other 39 taxa of genus
Sarcocystis (
Table 2). The 18S rRNA sequence is proposed as a standard gene for the phylogenetic analysis among the species within the protozoa phyla, which is hence used for species identification in this study [
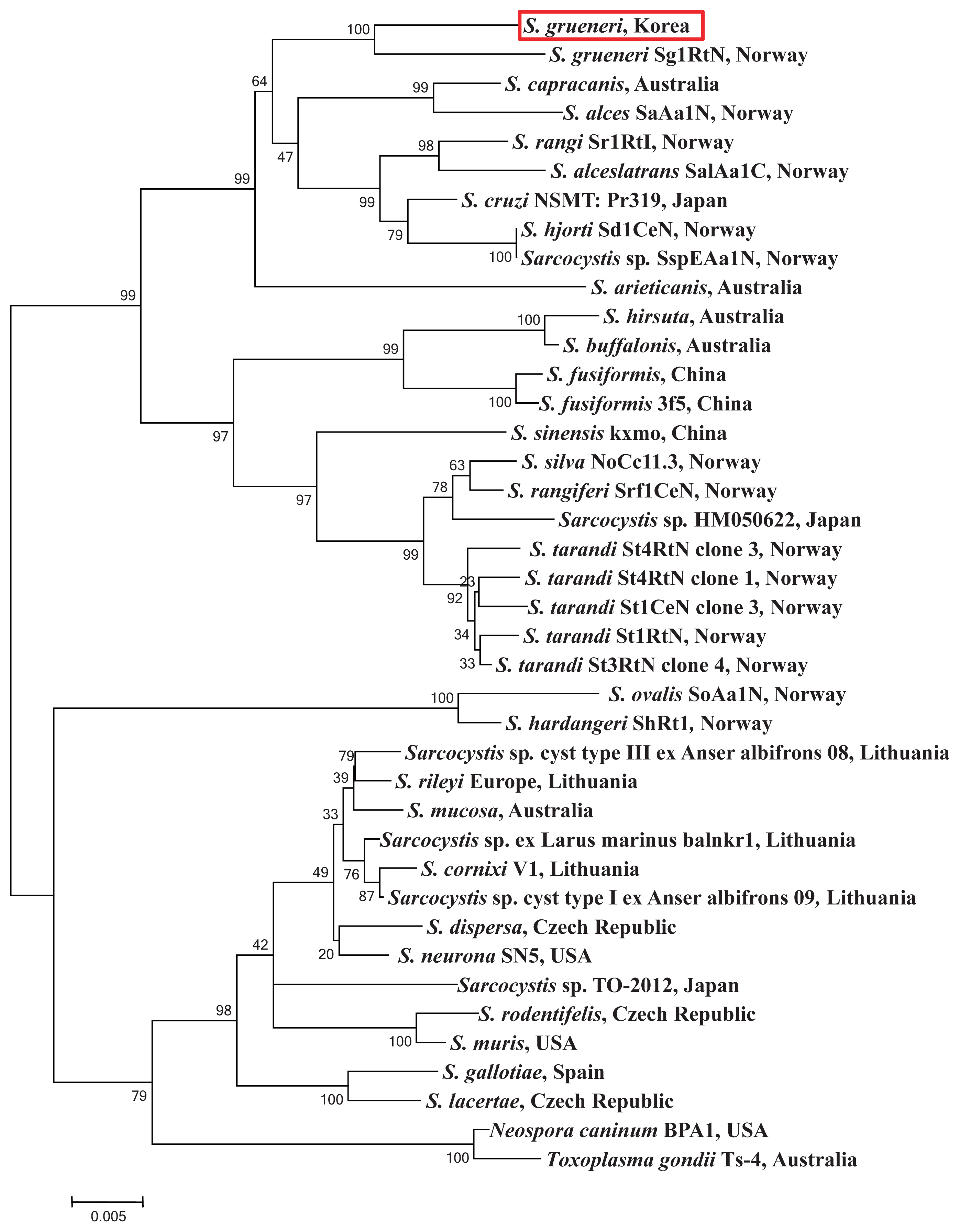
24]. The sequence identified between the cyst samples showed 100% homology with
S. grueneri and 97% with
S. capracanis. In addition, both 53% AT base construction and low level of sequence variations were consistently shown in the phylogenetic analysis (
Fig. 3).
DISCUSSION
In previous study, the cysts of
S. grueneri were found in the heart muscles, which indicate the specific organ tropism of the parasite [
10]. Similar to the previous study, a cervid animal may be infected in heart muscle by similar
Sarcocystis species. The Korean water deer may serve as an intermediate host with a similar level of high specificity and prevalence as observed in other studies [
9]. For instance, 98.0% of the sister species of a cervid animal in Germany were infected with
Sarcocystis parasites [
25,
26]. Thus, it appears that the infection of
Sarcocystis species is quite common to many species of a cervid animal. Although the Korean water deer is widely distributed in ROK, it has not been extensively studies until recent years especially in infection study of the parasite of
Sarcocystis species. In this study, we found that the infection rate of the
Sarcocystis parasites was 26.3% (10 out of 38 samples of the Korean water deer). Among the 38 collection sites in the ROK, 6 infection muscles (15.8%) were detected in the provinces of Gangwon, Gyeonggi, and Chungcheongbuk-do, and 4 infection samples in Daejeon city (10.5%), respectively. Furthermore, identification of the parasite that is collected from the Korean water deer was examined by molecular method. In previous study, molecular technique could identify a single species of the parasite from the host animal tissues and distinguish individual species from other parasites of
Sarcocystis species [
5]. For more accurate morphometry for the species identification of the parasites, the electron microscope has been used and successfully reported key morphological features in several parasites. For instance, the cyst of
S. grueneri collected from rein deer are morphologically similar to the cysts collected from either the host animal roe deer (
Capreolus capreolus) or red deer (
Cervus elaphus) in the protrusion of the cyst wall [
8,
27].
The general phylogenetic trend of Sarcocystinae has already explained other former studies [
22,
24,
28,
29]. In our study, the fundamental composition did not change by including
Sarcocystis species from a similar intermediate host. Phylogenetic topology of bootstraps of 1,000 described the 2 species highly similar and their branch length very close from the sequences of 18S rRNA gene in
S. grueneri (Genbank accession number EF056010). Thus, the results of phylogenetic analysis indicate that our sample is in the clade of a sister taxa including
S. capracanis,
S. alces, S. rangi, and
S. alceslatrans. Furthermore, these species also share the similar intermediate host animal in the family Cervidae except for
S. capracanis (
Fig. 3).
In addition, it has been known that the parasites of
Sarcocystis species infect both animal hosts such as intermediate host and definitive host, especially in the stage of sporocyst and oocyst. Interestingly, in previous study, it has been shown that humans are susceptible to the infection of sarcocysts [
30]. This infection could be caused by water contaminated with feces from the other animal hosts or food washed with unsanitary water [
31]. Other unknown animals including human could be a potential target for the infection of
Sarcocystis parasites. In this context, the DNA sequences of 18S rRNA gene related to
Sarcocystis parasites presented in this study can promote further development of needed diagnostics to prevent a potential infection of
Sarcocystis parasite in wild animals and humans.
Notes
-
CONFLICT OF INTEREST
We have no conflict of interest related to this work.
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS
This work was carried out with the support of the Cooperative Research Program for Agriculture Science & Technology Development (project no. PJ01197804), Rural Development Administration, Republic of Korea.
Fig. 1(A) Photos of sarcocysts (arrows) in the cardiac muscle of the Korean water deer. Tissue reactions by the sarcocysts were not recognizable. Scale bar=200 μm. (B) Higher magnification of a sarcocyst in A (rectangle), showing many bradyzoites in the cyst. Scale bar=50 μm. H–E stain.

Fig. 2PCR amplicons (1.5 kb) of sarcocysts inform the cardiac muscle. M, 100 bp DNA ladder; N, negative control; WC, water control (negative control).

Fig. 3Phylogram of 18S rRNA sequences from Sarcocystis spp. with evolutionary relationships of 39 taxa. Bootstrap values (> 50%) based on 1,000 replications are shown. The S. grueneri detected in this study is red-boxed.

Table 1Prevalence of Sarcocystis from Korean water deer in the Republic of Korea
Table 1
|
Locality and no. of samples |
No. positive (%) |
|
Gangwon-do (n=21) |
6 (28.6) |
|
Daejeon-si (city) (n=14) |
4 (28.6) |
|
Chungcheongbuk-do (n=2) |
0 (0.0) |
|
Gyeonggi-do (n=1) |
0 (0.0) |
|
Total (n=38) |
10 (26.3) |
Table 2Sequence analyzed of the Sarcocystis species used in 18S rRNA genes and GenBank accession no.
Table 2
|
Taxon name/Strain |
GenBank accession no. |
Intermediate host |
|
S. alces, SaAa1N |
EU282018 |
Moose (Alces alces) |
|
S. alceslatrans, SalAa1C |
EU282033 |
Moose (Alces alces) |
|
S. arieticanis
|
L24382 |
Sheep (Ovis aries) |
|
S. buffalonis
|
AF017121 |
Water buffalo (Bubalus bubalis) |
|
S. capracanis
|
L76472 |
Goat (Capra aegagrus hircus) |
|
S. cornixi, V1 |
EU553478 |
Hooded crow (Corvus cornix) |
|
S. cruzi, NSMT: Pr319 |
AB682782 |
Water buffalo (Bubalus bubalis), Cattle (Bos taurus) |
|
S. dispersa
|
AF120115 |
Mouse (Mus musculus) |
|
S. fusiformis, 3f5 |
AF176927 |
Water buffalo (Bubalus bubalis) |
|
S. fusiformis
|
U03071 |
Water buffalo (Bubalus bubalis) |
|
S. gallotiae
|
AY015112 |
Lizard (Gallotia galloti) |
|
S. grueneri, Sg1RtN |
EF056010 |
Reindeer (Rangifer tarandus) |
|
S. hardangeri, ShRt1I |
EF467654 |
Moose (Alces alces) |
|
S. hirsuta
|
AF017122 |
Cattle (Bos taurus) |
|
S. hjorti, Sd1CeN |
GQ250990 |
Red deer (Cervus elaphus) |
|
S. lacertae
|
AY015113 |
Common wall Lizard (Podarcis muralis) |
|
S. mucosa
|
AF109679 |
Rat (Rattus norvegicus) |
|
S. muris
|
M64244 |
Mouse (Mus musculus) |
|
S. neurona, SN5 |
U07812 |
Brown-headed cowbirds (Molothrus ater) |
|
S. ovalis, SoAa1N |
EU282019 |
Moose (Alces alces) |
|
S. rangi, Sr1RtI |
EF467655 |
Reindeer (Rangifer tarandus) |
|
S. rangiferi, Srf1CeN clone 2 |
GQ251022 |
Red deer (Cervus elaphus) |
|
S. rileyi, Europe |
HM185742 |
Mallard duck (Anas platyrhynchos) |
|
S. rodentifelis
|
AY015111 |
Reindeer (Rangifer tarandus) |
|
S. silva, NoCc11.3 |
JN226125 |
Roe deer (Capreolus capreolus) |
|
S. sinensis, kxmo |
AF266959 |
Water buffalo (Bubalus bubalis), Cattle (Bos taurus) |
|
S. tarandi, St1RtN |
EF056017 |
Red deer (Cervus elaphus) |
|
S. tarandi, St4RtN clone 3 |
GQ250974 |
Red deer (Cervus elaphus) |
|
S. tarandi, St1CeN clone 3 |
GQ251013 |
Red deer (Cervus elaphus) |
|
S. tarandi, St4RtN clone 1 |
GQ250972 |
Red deer (Cervus elaphus) |
|
S. tarandi, St3RtN clone 4 |
GQ250970 |
Red deer (Cervus elaphus) |
|
Sarcocystis sp. TO-2012 |
AB691780 |
Ryukyu Rat (Diplothrix legata) |
|
Sarcocystis sp. cyst type I ex) Anser albifrons
|
EU502869 |
Mallard duck (Anas platyrhynchos) |
|
Sarcocystis sp. cyst type III ex) Anser albifrons
|
EU502868 |
Hooded crow (Corvus cornix) |
|
Sarcocystis sp. ex) Larus marinus
|
JQ733508 |
Black-backed gull (Larus marinus) |
|
Sarcocystis sp. HM050622 |
AB257156 |
Sika deer (Cervus nippon yesoensis) |
|
Sarcocystis sp. SspEAa1N |
EU282017 |
Moose (Alces alces) |
|
Neospora caninum
|
U17345 |
Cattle (Bos taurus) |
|
Toxoplasma gondii
|
U00458 |
Vertebrates |
References
- 1. Dubey JP. A review of Sarcocystis of domestic animals and of other coccidia of cats and dogs. J Am Vet Med Assoc 1976;169:1061-1078.
- 2. Fayer R. Production of Sarcocystis cruzi sporocysts by dogs fed experimentally infected and naturally infected beef. J Parasitol 1977;63:1072-1075.
- 3. Dubey JP, Speer CA, Epling GP. Sarcocystosis in newborn calves fed Sarcocystis cruzi sporocysts from coyotes. Am J Vet Res 1982;43:2147-2164.
- 4. Colwell DD, Mahrt JL. Ultrastructure of the cyst wall and merozoites of Sarcocystis from moose (Alces alces) in Alberta, Canada. Z Parasitenkd 1981;65:317-329.
- 5. Dahlgren SS, Gjerde B. Genetic characterisation of six Sarcocystis species from reindeer (Rangifer tarandus tarandus) in Norway based on the small subunit rRNA gene. Vet Parasitol 2007;146:204-213.
- 6. Dahlgren SS, Gjerde B.
Sarcocystis in Norwegian roe deer (Capreolus capreolus): molecular and morphological identification of Sarcocystis oviformis n. sp. and Sarcocystis gracilis and their phylogenetic relationship with other Sarcocystis species. Parasitol Res 2009;104:993-1003.
- 7. Dubey JP. Coyote as a final host for Sarcocystis species of goats, sheep, cattle, elk, bison and moose in Montana. Am J Vet Res 1980;41:1227-1229.
- 8. Entzeroth R, Chobotar B, Scholtyseck E. Ultrastructure of Sarcocystis sp. from the muscle of a white-tailed deer (Odocoileus virginianus). Z Parasitenkd 1982;68:33-38.
- 9. Entzeroth R, Chobotar B, Scholtyseck E, Neméseri L. Light and electron microscope study of Sarcocystis sp. from the fallow deer (Cervus dama). Z Parasitenkd 1985;71:33-39.
- 10. Kutkienė L. Investigations of red deer (Cervus elaphus) Sarcocystis species composition in Lithuania. Acta Zool Litu 2003;13:390-395.
- 11. Atkinson CT, Wright SD, Telford SR, McLaughlin GS, Forrester DJ, Roelke ME, McCown JW. Morphology, prevalence, and distribution of Sarcocystis spp. in white tailed deer (Odocoileus virginianus) from Florida. J Wildl D 1993;29:73-84.
- 12. Kang YB, Kim SH, Wee SH. A survey of Sarcocystis infections in slaughtered cattle in Korea. Korean J Vet Res 1988;28:387-390. (in Korean).
- 13. Jang H, Kang YB, Wee SH, Choi SH. Survey of Sarcocystis infections in cattle in Korea. Res Rept RDA(V) 1990;32:32-37. (in Korean).
- 14. Yang JH, Kang YB, Wee SH, Lee ST, Kim KS. Prevalence of Sarcocystis infections in the slaughtered cattle in Cheju. Korean J Vet Res 1990;30:507-510. (in Korean).
- 15. Park YJ, Kim JS, Joeung DS, Sin MK, Kim KS, Kim TJ. A survey of Sarcocystis infections in the slaughtered cattle and identification of Sarcocystis cruzi
. Korean J Vet Publ Hlth 1994;18:251-259. (in Korean).
- 16. Wee SW, Shin SS. Experimental induction of two-host life cycle of Sarcocystis cruzi between dogs and Korean native cattle. Korean J Parasitol 2001;39:227-232. (in Korean).
- 17. Son WY, Kim NS, Ryu SY, Kim HC, Rhee JH, Cho JG, Park BK. Ultrastructure of Sarcocystis grueneri-like sarcocysts from cardiac muscle of red deer (Cervus elaphus) in Korea. J Vet Clin 2009;26:595-599.
- 18. Hong EJ, Sim C, Chae JS, Kim HC, Park J, Choi KS, Yu DH, Park CH, Yoo JG, Park BK. Ultrastructural and molecular identification of Sarcocystis tenella (Protozoa, Apicomplexa) in naturally infected Korean native goats. Veterinarni Medicina 2016;61:374-381.
- 19. Allen GM. Mammals of China and Mongolia. Natural history of central Asia. American Museum of Natural History; New York. 1940, 11:pp 1126-1261.
- 20. Valerius G. Deer of the World: Their Evolution, Behaviour, and Ecology. Pennsylvania, USA. Stackpole books; 1998, pp 26-28.
- 21. Cooke A, Farrell L. Chinese water deer. Mammal society; 1998, p 30.
- 22. Yang ZQ, Zuo YX, Yao YG, Chen XW, Yang GC, Zhang YP. Analysis of the 18S rRNA genes of Sarcocystis species suggests that the morphologically similar organisms from cattle and water buffalo should be considered the same species. Mol Biochem Parasitol 2001;115:283-288.
- 23. Tamura K, Dudley J, Nei M, Kumar S. MEGA4: Molecular Evolutionary Genetics Analysis (MEGA) software version 4.0. Mol Biol Evol 2007;24:1596-1599.
- 24. Morrison DA, Bornstein S, Thebo P, Wernery U, Kinne J, Mattsson JG. The current status of the small subunit rRNA phylogeny of the coccidia (Sporozoa). Int J Parasitol 2004;34:501-514.
- 25. Erber M, Boch J, Barth D.
Sarcosporidia strains in the roe deer. Berl Munch Tierarztl Wochenschr 1978;91:482-486. (in German).
- 26. Partenheimer-Hannemann C. Untersuchung zum Vorkommen von Sarkosporidien bei Reh-und Rotwild im Raum Bitburg-Prüm area (Rheinland-Pfalz). Inaugural-Dissertation. Hannover: Tierärztliche Hochschule Hannover; 1991.
- 27. Speer CA, Dubey JP.
Sarcocystis wapiti sp. nov. from the North American wapiti (Cervus elaphus). Can J Zool 1982;60:881-888.
- 28. Slapeta JR, Kyselová I, Richardson AO, Modrý D, Lukes J. Phylogeny and sequence variability of the Sarcocystis singaporensis Zaman and Colley, (1975) 1976 ssrDNA. Parasitol Res 2002;88:810-815.
- 29. Tenter AM, Johnson AM. Phylogeny of the tissue cyst-forming coccidia. Adv Parasitol 1997;39:69-139.
- 30. Heydorn AO. Sarkosporidieninfiziertes Fleisch als mögliche Krankheitsursache für den Menschen. Arch Lebensmittelhyg 1977;28:27-31. (in German).
- 31. Fayer R.
Sarcocystis spp. in human infections. Clin Microbiol Rev 2004;17:894-902.