Abstract
Pathogenic Acanthamoeba spp. cause granulomatous amoebic encephalitis and keratitis. Acanthamoeba keratitis (AK) is a rare but serious ocular infection that can result in permanent visual impairment or blindness. However, pathogenic factors of AK remain unclear and treatment for AK is arduous. Expression levels of proteins secreted into extracellular space were compared between A. castellanii pathogenic (ACP) and non-pathogenic strains. Two-dimensional polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis revealed 123 differentially expressed proteins, including 34 increased proteins, 7 qualitative increased proteins, 65 decreased proteins, and 17 qualitative decreased proteins in ACP strain. Twenty protein spots with greater than 5-fold increase in ACP strain were analyzed by liquid chromatography triple quadrupole mass spectrometry. These proteins showed similarity each to inosine-uridine preferring nucleoside hydrolase, carboxylesterase, oxygen-dependent choline dehydrogenase, periplasmic-binding protein proteinases and hypothetical proteins. These proteins expressed higher in ACP may provide some information to understand pathogenicity of Acanthamoeba.
-
Key words: Acanthamoeba castellanii, secretory product
INTRODUCTION
Acanthamoeba is an opportunistic pathogen capable of causing granulomatous encephalitis and keratitis [
1].
Acanthamoeba keratitis (AK) is a rare disease. However, the incidence of AK has gradually increased because
Acanthamoeba has a wide-spread distribution in the environment while contact lens use is increasing [
2,
3]. AK is a painful corneal infection that may lead to vision loss or enucleation [
4]. The first critical step in the pathogenesis of infection is its adhesion to the surface of host tissues. It is known that mannose binding protein can mediate the adhesion of
Acanthamoeba to the surface of cornea [
5]. Serine and cysteine proteolytic activities of
Acanthamoeba could play important roles in infections [
6]. However, information regarding the mechanism of pathogenic
Acanthamoeba for adhesion, tissue invasion, and infection is limited.
Proteins secreted into extracellular space as potential targets for treatment and diagnosis of amoebiasis have been reported [
7,
8]. During infection, ES proteins released by
Entamoeba histolytica trophozoites are involved in the invasion into colonic mucosa of the host [
8]. A unique cysteine protease in ES products of pathogenic strain of
E. histolytica has been cloned [
7]. Arginine deiminase, ornithine carbamoyl transferase, and enolase have been identified from secreted proteins of
Giardia intestinalis as immunodominant antigens [
9]. During contact with human vaginal epithelial cells,
Trichomonas vaginalis releases 19 major proteins, including cysteine proteases [
10].
In pathogenic strain of
Acanthamoeba, extracellular serine proteases have been identified as virulence factors [
11]. A secretory protease of
A. castellanii can degrade immunoglobulin A (IgA), IgG, and IgM [
12]. Recently, proteomic analysis of secreted proteins by
Acanthamoeba for non-pathogenic strain ATCC 30010 and clinically pathogenic isolates has been performed [
13], revealing 44 secreted proteins, including 10 consensus secretory proteins and 34 strain specific secretory proteins. However, definite virulence factors of pathogenic
Acanthamoeba have not been found yet. More detailed information about pathogenic strains is needed.
To gain more information on virulence factors of Acanthamoeba infection, the objective of this study was to compare the levels of proteins secreted into extracellular space between pathogenic ATCC 30011 strain and non-pathogenic ATCC 30868 strain of Acanthamoeba. Differentially expressed proteins were identified, focusing on highly expressed proteins in pathogenic Acanthamoeba.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Cultivation of Acanthamoeba and isolation of secreted proteins
Acanthamoeba castellanii non-pathogenic (ACNP) strain (ATCC 30011) and Acanthamoeba castellanii pathogenic (ACP) strain (ATCC 30868) were obtained from the American Type Culture Collection, and cultured axenically in PYG medium (20 g/L proteose peptone, 1 g/L yeast extract, 0.1 M glucose, 4 mM MgSO4, 0.4 mM CaCl2, 3.4 mM sodium citrate, 0.05 mM Fe(NH4)2(SO4)2, 2.5 mM Na2HPO4, and 2.5 mM KH2PO4) at 25°C. Cultured media were harvested after cultivation for 7 days.
Sample preparation and 2-dimensional gel electrophoresis
Sample preparation and 2-dimensional gel electrophoresis (2-DE) were performed as described by Bahk et al. [
14]. The cell culture medium (700 ml) was first passed through Amicon Ultra-15 Centrifugal Filter Unit (Merck KGaA, Darmstadt, Germany) at 5,000 g. The harvested samples were suspended in 7 M urea, 2 M thiourea, 4% (w/v) CHAPS, 2.5% (w/v) dithiothreitol (DTT) and protease inhibitor cocktail (Roche Molecular Biochemicals, Indianapolis, Indiana). The lysates were homogenized and centrifuged at 15,000 g for 20 min and suitably stored at −80°C. Protein concentration was determined by the Bradford method (Bio-Rad, Hercules, California, USA). For 2-DE analysis, pH 4–7 immobilized pH gradient (IPG) strips (GE Healthcare Life Sciences, Pittsburgh, Pennsylvania) were rehydrated in swelling buffer containing 7 M urea, 2 M thiourea, 2.5% (w/v) DTT, and 4% (w/v) CHAPS. The protein lysates (600 μg) were loaded into the rehydrated IPG strips using an IPGphor III (GE Healthcare Life Sciences, Pittsburgh, Pennsylvania) and the 2-DE separation was performed on 10% sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gels (SDS-PAGE). After fixation for 1 hr in 40% (v/v) methanol containing 5% (v/v) phosphoric acid, the gels were stained with Colloidal Coomassie Blue G-250 (ProteomeTech, Seoul, Korea). The gels were destained using deionized water and images were acquired with image scanner (Bio-Rad, Hercules, California). Image analysis was carried out using ImageMasterTM 2D Platinum software (Amersham Biosciences, Hercules, California). For comparison of protein spots, more than 25 spots in all gels were correspondingly landmarked and normalized.
Protein spots were excised from SDS-PAGE gels and in-gel digested with trypsin [
14]. In brief, the gel pieces were washed for 1 hr at room temperature in 25 mM ammonium bicarbonate buffer, pH 7.8, containing 50% (v/v) acetonitrile. Following dehydration in a centrifugal vacuum concentrator for 10 min, gel pieces were rehydrated in 0.05% trypsin solution (Promega, Madison, Wisconsin). After incubation in 25 mM ammonium bicarbonate buffer, pH 7.8, at 37°C overnight, the tryptic peptides were extracted with 5 μl of 0.5% formic acid containing 50% (v/v) acetonitril for 40 min with mild sonication. The extracted solution was concentrated using a centrifugal vacuum concentrator. Prior to mass spectrometric analysis, the peptide solution was desalted using a reversed-phase column [
15].
LC–MS/MS analysis was performed through an agilent 1,100 series nano-LC and LTQ-mass spectrometer (Thermo Electron, San Jose, California). The capillary column used for LC–MS/ MS analysis (150 mm×0.075 mm) was obtained from Proxeon (Odense M, Denmark) and slurry packed in house with 5 μm, 100 Å pore size Magic C18 stationary phase (Michrom Bioresources, Auburn, California). The mobile phase A for the LC separation was 0.1% formic acid in deionized water and the mobile phase B was 0.1% formic acid in acetonitrile. The chromatography gradient was set up to give a linear increase from 6% B to 50% B for 22 min, from 50% B to 95% B for 5 min, and from 95% B to 6% B for 13 min. The flow rate was 0.4 μl/min. For tandem mass spectrometry, mass spectra were acquired using data-dependent acquisition with full mass scan (350–1,800 m/z) followed by MS/MS scans. Each MS/MS scan acquired was an average of one microscans on the LTQ. The temperature of the ion transfer tube was controlled at 200°C and the spray was 1.5–2.0 kV. The normalized collision energy was set at 35% for MS/MS. The individual spectra from MS/ MS were processed using the SEQUEST software (Thermo Quest, San Jose, California) and the generated peak lists were used to query in house database using the MASCOT program (Matrix Science Ltd., London, UK). We set the modifications of methionine, cysteine, methylation of arginine, and phosphorylation of serine, threonine, and tyrosine for MS analysis and tolerance of peptide mass was 10 ppm. MS/MS ion mass tolerance was 0.8 Da, allowance of missed cleavage was 1, and charge states (+2 and +3) were taken into account for data analysis. We took only significant hits as defined by MASCOT probability analysis. MS/MS spectra were subjected to batch de novo sequencing by PepNovo program, and candidate peptide sequences were used for subsequent MS BLAST searches.
RESULTS
Comparison of proteins secreted into extracellular space of non-pathogenic and pathogenic strain of A. castellanii
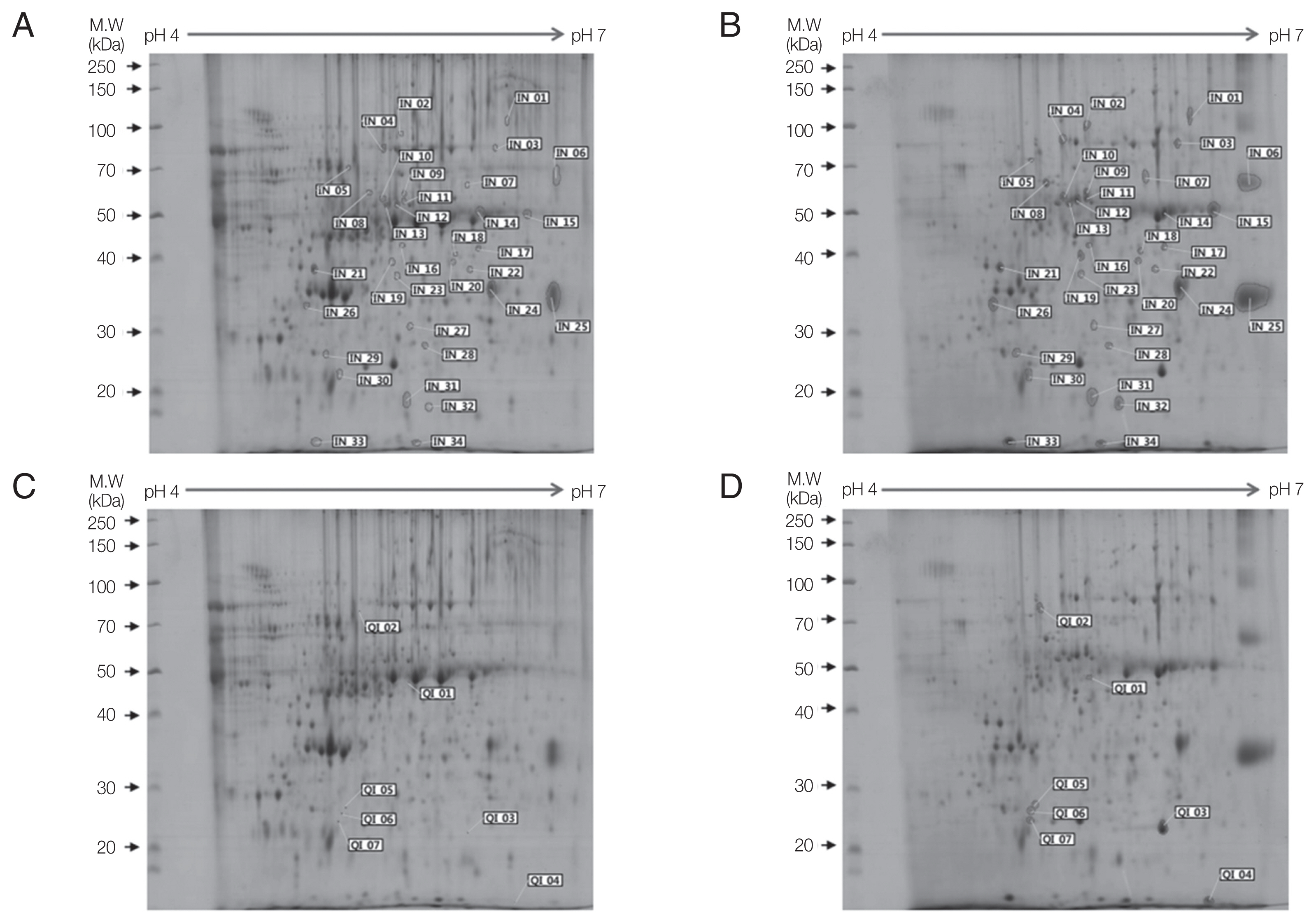
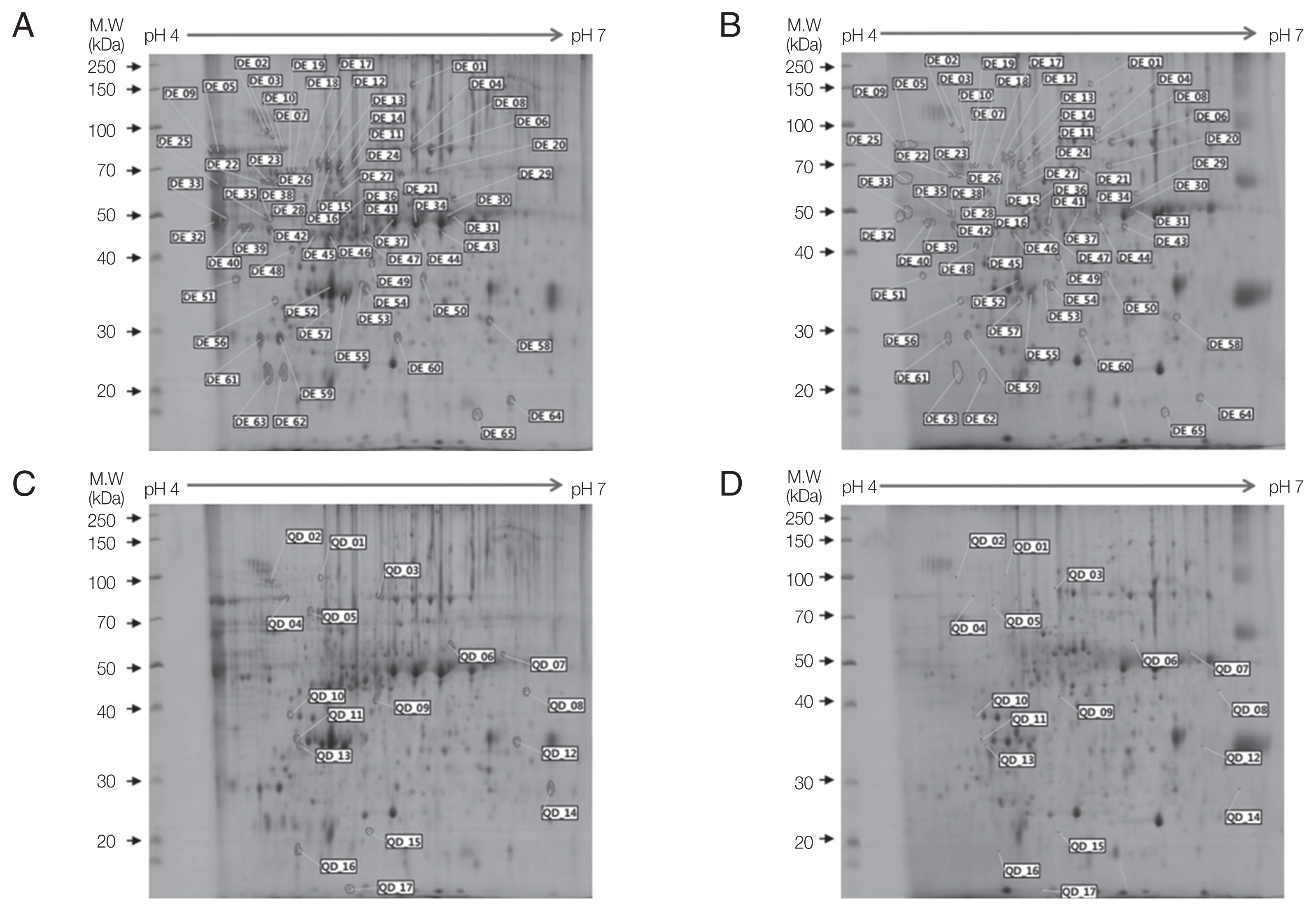
In 2-DE gels, excretory-secretory (ES) products harvested from culture media after cultivation for 7 days showed more protein spots than those after 3 days or 5 days of culture. For 2-DE analysis, broad-range pH gradients (pH 3–10) and narrow range pH gradient (pH 4–7) strips were used for ES proteins of Acanthamoeba. Protein spots were determined to be weakly acidic as they were concentrated along the center of the broad-range pH gradient (pH 3–10) strip. Narrow range pH gradient (pH 4–7) strip provided enhanced resolution as these protein spots were evenly distributed throughout the strip. ES proteins of ACNP and ACP strians were evaluated by pH 4–7 strip and 10% SDS-PAGE. Compared to the ACNP strain, the ACP strain showed 123 differentially expressed proteins, where 34 proteins increased (IN), 7 proteins qualitatively increased (QI), 65 proteins decreased (DE), and 17 proteins qualitatively decreased (QD). IN refers to proteins that are present in ACNP but significantly increased in ACP. QI refers to proteins that are absent in ACNP but expressed in ACP. DE refers to proteins that are expressed in ACNP, but decreased in ACP. Finally, QD refers to proteins that are not expressed in ACP but expressed in ACNP.
Proteins up-regulated in the pathogenic A. castellanii
Proteins down-regulated in the pathogenic A. castellanii
Proteins highly expressed in pathogenic A. castellanii
Among 41 up-regulated protein spots, 13 proteins with more than 5-fold higher expression and 7 qualitative increase proteins were selected for protein identification. To identify these highly expressed ES proteins in ACP strain, 20 protein spots were analyzed by LC–MS/MS. Results of the mass spectrometer and database search for 20 highly expressed protein spots are summarized in
Table 1. Nine out of 20 protein spots were related to
Acanthamoeba (
Table 1). Hypothetical protein ACA_279470 (IN02, IN11, and QI02) contained a periplasmic- binding protein domain. One protein spot (IN15) showed similarity with inosine uridine preferring nucleoside hydrolase. Another spot (IN01) showed similarity with carboxylesterase of
A. castellanii. Protein spots of IN08 and QI06 were similar to oxygen-dependent choline dehydrogenase of
Rhizoctonia solani. Unfortunately, IN06, IN18, and IN32 were hypothetical proteins.
DISCUSSION
To search for pathogenic factors of
Acanthamoeba, ES proteins of
A. castellanii non-pathogenic (ACNP) strain and
A. castellanii pathogenic (ACP) strain were compared by 2-dimensional polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. Observation of distinct protein spots revealed 123 differentially expressed proteins, including 41 up-regulated proteins and 82 down-regulated proteins in ACP strain compared to those in the ACNP strain. Twenty protein spots highly expressed in ACP strain were isolated from gels for identification (
Table 1). All 20 spots were identified, nine were related to
Acanthamoeba database.
Among these protein spots, 3 spots (IN02, IN11, and QI02) were identified as hypothetical protein of
Acanthamoeba (
Table 1). The aforementioned IN02, IN11, and QI02 included periplasmic binding protein region. Periplasmic binding proteins (PBPs) are nonenzymatic receptors that bacteria can use to sense small molecules and transport them into the cytoplasm [
16]. Most PBPs participate in the transport of solute molecules into the cytoplasm via ATP-binding cassette transporters [
17]. Most Gram-negative bacteria are thought to employ periplasmic- binding-protein-dependent transport. Periplasmic chaperone in
Camphylobacter jejuni is involved in its invasion to cultured human epithelial cells [
18].
One protein spot highly expressed in the ACP strain (IN01) showed similarity with carboxylesterase superfamily protein of
A. castellanii Neff (
Table 1). Carboxylesterases are widely distributed in nature. Carboxylates are conjugated by other enzymes to increase solubility and eventually excreted. A cell wall-associated carboxylesterase has been reported to be required for virulence of
Mycobacterium tuberculosis [
19].
Another protein spot highly expressed in the ACP strain (IN15) showed similarity with inosine-uridine preferring nucleoside hydrolase of
Acanthamoeba (
Table 1). Inosine-uridine preferring nucleoside hydrolase is an enzyme that catalyses the hydrolysis of commonly occuring purine and pyrimidine nucleosides into ribose and associated base. This enzyme is important for parasitic organisms known to be deficient in de novo synthesis of purines to salvage host purine nucleosides.
Plasmodium falciparum is a purine auxotroph. It salvages host cell purines for synthesis of cofactors and nucleic acids [
20].
Two protein spots in ACP strain (IN08 and QI06) showed similarity with oxygen-dependent choline dehydrogenase of
Rhizoctonia solani (
Table 1). Choline dehydrogenase is an enzyme catalyzing the dehydrogenation of choline to betaine aldehyde. Choline dehydrogenase plays a dual role (choline conversion and mitophagy) in the membrane of mitochondria [
21].
To date, biochemical and kinetic properties of proteins highly expressed in ACP have been poorly characterized. We cloned 6 cDNAs, which encodes highly expressed proteins in the ACP (periplasmic binding protein, carboxyl esterase, inosine uridine preferring nucleoside hydrolase, chorismate mutase, adenylyl cyclase assosciated protein, and prokumamolisin). We plan on identifying characteristics associated with pathotoxicity for these proteins, and develop rapid and sensitive diagnostic methods.
Characterization of highly expressed secretory proteins in pathogenic Acanthamoeba will provide better understanding about its pathogenesis. It might lead to early diagnosis and treatment for Acanthamoeba infections.
Notes
-
CONFLICT OF INTEREST
The authors declare that there are no conflicts of interest.
Supplementary materials
Supplementary Table S2. Image analysis of proteins qualitatively increased (QI) in ACP strain
kjp-56-6-553-suppl.pdf
Supplementary Table S4. Image analysis of proteins qualitatively decreased (QD) in ACP strain
kjp-56-6-553-suppl.pdf
ACKNOWLEDGMENT
This research was supported by Basic Science Research Program through the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF) funded by the Ministry of Education (grant number: 2016R1D1A1B03933863).
Fig. 1Two-dimensional gel electrophoresis of up-regulated proteins in
A. castellanii. Comparison of ES proteins between ACNP strain (A, C) and ACP strain (B, D) revealed 34 proteins with increased expression (B) and 7 proteins demonstrating qualitative increase (D) in the ACP strain. Numbers in Fig. 1 represents spot identification numbers listed in
Supplementary Tables S1 and
S2.

Fig. 2Two-dimensional gel electrophoresis of down-regulated proteins in
A. castellanii. Comparision of ES proteins between ACNP strain (A, C) and ACP strain (B, D) showed 65 decreased proteins (B) and 17 qualitatively decreased proteins (D) in the ACP strain. Numbers in Fig. 2 represents spot identification numbers listed in
Supplementary Tables S3 and
S4.

Table 1Proteins up-regulated 5-times or more in ACP strain
Table 1
|
Group ID |
Description |
Score |
Mass (kDa) |
|
IN01 |
carboxylesterase superfamily protein [Acanthamoeba castellanii Neff] |
65 |
57.9 |
|
IN02 |
hypothetical protein ACA1_279470 [Acanthamoeba castellanii Neff] |
82 |
63.1 |
|
IN03 |
ALB protein [Bos taurus] |
81 |
71.2 |
|
IN06 |
hypothetical protein ACA1_362140 [Acanthamoeba castellanii Neff] |
100 |
25.3 |
|
IN07 |
ALB protein [Bos taurus] |
65 |
71.2 |
|
IN08 |
oxygen-dependent choline dehydrogenase [Rhizoctonia solani] |
45 |
70.0 |
|
IN11 |
hypothetical protein ACA1_279470 [Acanthamoeba castellanii Neff] |
154 |
63.1 |
|
IN15 |
inosine uridine preferring nucleoside hydrolase family protein [Acanthamoeba castellanii Neff] |
74 |
38.0 |
|
IN16 |
hypothetical protein BBAD15_g11018 [Beauveria bassiana D1–5] |
17 |
60.8 |
|
IN18 |
hypothetical protein ACA1_052470 [Acanthamoeba castellanii Neff] |
54 |
38.7 |
|
IN26 |
adaptor protein complex AP-3 delta subunit [Sphaerulina musiva SO2202] |
19 |
116.4 |
|
IN32 |
hypothetical protein ACA1_132680 [Acanthamoeba castellanii Neff] |
50 |
19.6 |
|
IN33 |
hypothetical protein I79_015947 [Cricetulus griseus] |
26 |
14.3 |
|
QI01 |
prokumamolisin, activation domain containing protein [Acanthamoeba castellanii Neff] |
50 |
63.6 |
|
QI02 |
hypothetical protein ACA1_279470 [Acanthamoeba castellanii Neff] |
64 |
63.1 |
|
QI03 |
RIKEN cDNA 4732456N10, partial [Mus musculus] |
108 |
59.3 |
|
QI04 |
hypothetical protein PB105628.00.0, partial [Plasmodium berghei] |
26 |
4.9 |
|
QI05 |
hypothetical protein BCV71DRAFT_164154, partial [Rhizopus microsporus] |
37 |
17.1 |
|
QI06 |
oxygen-dependent choline dehydrogenase [Rhizoctonia solani] |
45 |
66.9 |
|
QI07 |
odorant-binding protein 19c [Drosophila pseudoobscura pseudoobscura] |
21 |
19.9 |
References
- 1. Marciano-Cabral F, Cabral G. Acanthamoeba spp. as agents of disease in humans. Clin Microbiol Rev 2003;16:273-307.
- 2. Jones DB, Visvesvara GS, Robinson NM. Acanthamoeba polyphaga keratitis and Acenthamoeba uveitis associated with fatal meningo-encephalitis. Trans Ophthalmol Soc UK 1975;95:221-232.
- 3. Verani JR, Lorick SA, Yoder JS, Beach MJ, Braden CR, Roberts JM, Conover CS, Chen S, McConnell KA, Chang DC, Park BJ, Jones DB, Visvesvara GS, Roy SL. National outbreak of Acanthamoeba keratitis associated with use of a contact lens solution, United States. Emerg Infect Dis 2009;15:1236-1242.
- 4. Awwad ST, Petroll WM, McCulley JP, Cavanagh HD. Updates in Acanthamoeba keratitis. Eye Contact Lens 2007;33:1-8.
- 5. Garate M, Marchant J, Cubillos I, Cao Z, Khan NA, Panjwani N. In vitro pathogenicity of Acanthamoeba is associated with the expression of the mannose-binding protein. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 2006;47:1056-1062.
- 6. de Serrano-Luna JJ, Cervantes-Sandoval I, Calderón J, Navarro-García F, Tsutsumi V, Shibayama M. Protease activities of Acanthamoeba polyphaga and Acanthamoeba castellanii. Can J Microbiol 2006;52:16-23.
- 7. Reed S, Bouvier J, Pollack AS, Engel JC, Brown M, Hirata K, Que X, Eakin A, Hagblom P, Gillin F. Cloning of a virulence factor of Entamoeba histolytica. Pathogenic strains possess a unique cysteine proteinase gene. J Clin Invest 1993;91:1532-1540.
- 8. Moncada D, Keller K, Chadee K. Entamoeba histolytica-secreted products degrade colonic mucin oligosaccharides. Infect Immun 2005;73:3790-3793.
- 9. Ringqvist E, Palm JE, Skarin H, Hehl AB, Weiland M, Davids BJ, Reiner DS, Griffiths WJ, Eckmann L, Gillin FD, Svärd SG. Release of metabolic enzymes by Giardia in response to interaction with intestinal epithelial cells. Mol Biochem Parasitol 2008;159:85-91.
- 10. Kucknoor AS, Mundodi V, Alderete JF. The proteins secreted by Trichomonas vaginalis and vaginal epithelial cell response to secreted and episomally expressed AP65. Cell Microbiol 2007;9:2586-2597.
- 11. Lorenzo-Morales J, Ortega-Rivas A, Foronda P, Abreu-Acosta N, Ballart D, Martínez E, Valladares B. RNA interference (RNAi) for the silencing of extracellular serine proteases genes in Acanthamoeba: molecular analysis and effect on pathogenecity. Mol Biochem Parasitol 2005;144:10-15.
- 12. Na BK, Cho JH, Song CY, Kim TS. Degradation of immunoglobulins, protease inhibitors and interleukin-1 by a secretory proteinase of Acanthamoeba castellanii. Korean J Parasitol 2002;40:93-99.
- 13. Huang JM, Lin WC, Li SC, Shih MH, Chan WC, Shin JW, Huang FC. Comparative proteomic analysis of extracellular secreted proteins expressed by two pathogenic Acanthamoeba castellanii clinical isolates and a non-pathogenic ATCC strain. Exp Parasitol 2016;166:60-67.
- 14. Bahk YY, Kim SA, Kim JS, Euh HJ, Bai GH, Cho SN, Kim YS. Antigens secreted from Mycobacterium tuberculosis: identification by proteomics approach and test for diagnostic marker. Proteomics 2004;4:3299-3307.
- 15. Gobom J, Nordhoff E, Mirgorodskaya E, Ekman R, Roepstorff P. Sample purification and preparation technique based on nano-scale reversed-phase columns for the sensitive analysis of complex peptide mixtures by matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization mass spectrometry. J Mass Spectrom 1999;34:105-116.
- 16. Quiocho FA. Atomic structures of periplasmic binding proteins and the high-affinity active transport systems in bacteria. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci 1990;326:341-351.
- 17. Tam R, Saier MH Jr. Structural, functional, and evolutionary relationships among extracellular solute-binding receptors of bacteria. Microbiol Rev 1993;57:320-346.
- 18. Kervella M, Pagès JM, Pei Z, Grollier G, Blaser MJ, Fauchère JL. Isolation and characterization of two Campylobacter glycine-extracted proteins that bind to HeLa cell membranes. Infect Immun 1993;61:3440-3448.
- 19. Lun S, Bishai WR. Characterization of a novel cell wall-anchored protein with carboxylesterase activity required for virulence in Mycobacterium tuberculosis. J Biol Chem 2007;282:18348-18356.
- 20. Hyde JE. Targeting purine and pyrimidine metabolism in human apicomplexan parasites. Curr Drug Targets 2007;8:31-47.
- 21. Park S, Choi SG, Yoo SM, Son JH, Jung YK. Choline dehydrogenase interacts with SQSTM1/p62 to recruit LC3 and stimulate mitophagy. Autophagy 2014;10:1906-1920.