Abstract
Ticks are the vectors of various pathogens, threatening human health and animal production across the globe. Here, for the first time we detected Ricketssia spp., Borrelia spp. and protozoan in ticks from Poyang Lake region in Jiangxi Province of eastern China. In 3 habitat categories and on 12 host species, 311 ticks from 11 species were collected. Haemaphysalis longicornis was the predominant species, accounting for 55.63%, followed by Rhipicephalus microplus, Haemaphysalis flava and Ixodes granulatus. Of the collected ticks, 7.07% were positive for tick-borne pathogens, and H. longicornis and H. flava were found to be co-infected with Ricketssia spp. and protozoan. H. flava was the most detected positive for tick-borne pathogens, whereas H. longicornis had the lowest infection rate, and the difference in infection rates between tick species was significant (χ2=61.24, P<0.001). Furthermore, adult ticks demonstrated remarkably greater infection rate than immature ticks (χ2=10.12, P=0.018), meanwhile ticks on Erinaceidae showed significantly higher positivity than ticks collected on other host species (χ2=108.44, P<0.001). Genetic fragment sequencing and analyses showed at least 4 pathogen species presence in ticks, namely Borrelia yangtzensis, Rickettsia slovaca or Rickettsia raoultii related genospecies, Babesia vogeli and Hepatozoon canis or Hepatozoon felis related genospecies. The finding indicates that the abundant ticks can carry diverse pathogens in Poyang Lake region, and pathogen infection is highly related to species, vertebrate hosts and life stages of ticks.
-
Key words: Tick-borne pathogens (TBPs), tick, epidemiology, risk factors, Poyang Lake region
INTRODUCTIOIN
Ticks, a group of specialized obligate hemophagous ectoparasites, parasitize abundant host species and are the vectors of wide range of pathogens of veterinary and public health importance [
1–
6]. Recently, they are considered to occupy the second place after mosquitoes as vectors of human infectious diseases in the world. As of May 31 2015, there were at least 5,568 cases of human tick-borne diseases reported around China, including large number of patients with Lyme diseases and newly emerging severe fever with thrombocytopenia syndrome [
1].
China has the complex distributions and the great diversity of tick species because of its diverse ecological habitats. Ticks in China were reported to be carriers of various human pathogens including protozoans and bacterium like
Borrelia spp. and
Richettsia spp. [
1,
7,
8]. Poyang Lake region, belonging to Jiangxi (a province of southeastern China), has already recorded sporadic human tick-borne diseases and at least 13 tick species. Our previous work detected some tick-borne pathogens in a few kinds of hosts, such as rodents and dogs in Poyang Lake region [
4–
6]. However, knowledge on tick-borne pathogens in tick vectors in this region is limited. Therefore, in this study we showed evidence to illustrate the distribution of pathogens comprising
Borrelia spp.,
Rickettsia spp., and protozoa in tick vectors from Poyang Lake region in Jiangxi, and elucidated its relation with tick species, developmental stage, host and vegetation. The results will be a basis for future epidemiological studies and risk assessment of human tick-borne pathogens in Poyang Lake region.
MATERIAL AND METHODS
Study area
The study had been conducted for 3 years (2013–2015) in Poyang Lake region of Jiangxi Province, southeastern China, which has altitudes higher than 35 m and lower than 190 m above sea level. This area experiences a subtropical climate with over than 1,000 mm of annual rainfall, −10°C of maximum low temperature and 40°C of maximum high temperature. Temperatures usually vary from 10 to 37°C between May and October when tick populations are active. Types of vegetation cover include mixed broadleaf and coniferous woodland and grassland (
Table 1). We selected 12 counties in Poyang lake region as investigation sites (
Table 1).
Ticks in vegetation covers were collected by flagging or dragging both at ground level and over and through the vegetation with a cotton cloth (100×60 cm). Each site was visited at least 3 times to cover all of 3 categories of habitats (grassland, woodland, and shrubs). Each habitat category was selected to cover a 900-m
2 area with many animal trails and tracks. Ticks were removed from the cotton cloth every 2 minutes. Ticks parasitizing hosts were collected from 24 villages and 12 wild animal markets. In villages, domestic animals and fowls were restricted by owners for sampling. In markets, wild animal bodies were employed for tick collection. Rodentia around villages were trapped using peanut baited rodent traps for tick examination. All the procedures were carried out according to ethical guidelines for the use of animal samples permitted by Obihiro University of Agriculture and Veterinary Medicine (Animal experiment access num: 28–100). The information regarding all of the collected specimens, including their location, vegetation type, host, number of ticks collected from the body of each animal and the date of collection, were recorded. Ticks were collected from the entire body of each host into separate sample bottle containing 70% ethanol. Standard taxonomic keys were used to morphologically identify adults [
9]. Larvae and nymphs were identified individually based on molecular methods [
10]. The specimens were kept in 70% ethanol and used for further molecular identification and detection of tickborne pathogens.
Tick specimens immersed in 70% ethanol were air dried, and then rinsed in sterile water for 3 times. After rinsed in sterile phosphate-buffered saline, ticks were dried on sterile filter paper in a biosafety hood, and individually ground in sterile tubes. DNA was extracted using the QIAamp Tissue Kit (QIAGEN, Hilden, Germany) according to the manufacturer’s instructions. The genomic DNA was stored at 4°C until used as a template in PCR assays.
Pathogen identification
A total of 3 groups of pathogens were assayed:
Borrelia spp.,
Rickettsia spp. and protozoa. A conventional PCR was performed with a set of primers (forward: 5′-ACATATTCAGATGCAGACAGAGGT-3′, reverse: 5′-GCAATCATAGCCATTGCAGATTGT-3′) designed to amplify the 665-bp flagellin gene of
Borrelia spp. For citrate synthase encoding gene (
gltA), a primer set of primer 1 (5′-GCAAGTATCGGTGAGGATGTAAT-3′) and primer 2 (5′-GCTTCCTTAAAATTCAATAAATCAGGAT-3′) was used and expected to yield a 401-bp fragment depending on the
Rickettsia spp. For amplification of 209–214 bp fragment of 18S ribosomal RNA (rRNA) in the protozoa, a set of primers (forward: 5′-GCATTTAGCGATGGACCATTCAAG-3′, reverse: 5′-CCTGTATTGTTATTTCTTGTCACTACCTC-3′) was designed for PCR. PCR reagents were used as recommended by the manufacturer (Takara Bio Inc., Dalian, China). The amplification for
flagellin gene included 5 min pre-denaturation at 94°C followed by 30 cycles of denaturation at 94°C for 30 sec, annealing at 60°C for 30 sec and extension at 72°C for 1 min, and final extension at 72°C for 7 min. The amplifications for 18S rRNA gene in the protozoa and
gltA gene in the
Rickettsia spp. were performed under the same conditions as
flagellin gene except the extension at 72°C for 45 sec for the protozoa and the annealing at 50°C for 30 sec. Positive samples were sequenced to identify potential microbial species with a resemblance to known species based on by an online software (
http://www.bioinformatics.org/sms2/ident_sim.html).
All obtained sequences were assembled and edited by using SeqMan software. We compared them with sequences in the GenBank database. We performed multiple sequence alignments by using the ClustalX program. Phylogenetic trees were constructed by using the Neighbor-Joining (NJ) algorithm in the MEGA v.7.0.26 software. Support for the tree nodes was calculated with 1,000 bootstrap replicates.
Data analyses
All the raw data were collated in Excel spreadsheets. The differences in infection rates of ticks at species levels, at developmental stages, on hosts, in habitat categories, and the difference in infection rates of ticks collected in vegetation covers and on hosts were evaluated using Chi square (
http://quantpsy.org). In the 2×2 case of the chi-square test of independence, if expected frequencies is less than 5, Yates’ correction is employed [
11].
RESULTS
Tick samples
A total of 311 ticks belonging to 5 genera and 11 species were collected from 5 species of domestic animals (
Canis familiaris, Capra aegagrus hircus, Bos spp.,
Bubalus bubalis, and
Equus ferus), 5 species of wild animals (
Lepus sinensis, Erinaceidae,
Apodemus agrarius, Rattus norvegicus, Rattus rattoides), a species of bird (
Phasianus colchicus) and a species of chicken (
Gallus gallus domesticus), in 2 kinds of vegetation types from 12 locations in Poyang Lake region (
Table 1).
L. sinensis harbored abundant ticks such as
Haemaphysalis longicornis, Ixodes acuminatus, Ixodes sinensis and
Rhipicephalus haemaphysaloides, with the third highest tick population density of 3.77 ticks per a host. Hosts with the first highest and second highest tick loads were Erinaceidae (4.33 ticks per host) and
Bos spp. (4.31 ticks per host), respectively. Other hosts with higher tick abundance were
B. bubalis and
C. aegagrus hircus, harboring 3 tick species. Sixty-seven female (14.79%) and 102 male (30.87%) adult ticks were obtained. Sixty-seven larvae and 102 nymphs accounted for 21.54% and 32.80% of the total number of ticks collected respectively. Of the 11 tick species collected, 3 species belonged to the genus
Haemaphysalis, 3 species belonged to the genus
Rhipicephalus, 3 species belonged to
Ixodes, 1 species belonged to
Dermacentor, and 1 other species belonged to the genus
Amblyomma. The most abundant species was
H. longicornis (55.63%), found in a kind of vegetation cover and infesting the most diverse host species (7 species). Three other common species included
H. flava,
R. microplus and
I. granulatus (
Tables 2,
3).
Protozoa,
Borrelia spp. and
Rickettsia spp. were detected in 4 tick species. Overall, 7.07% of ticks were tested positive for at least 1 pathogen. In detail, 2.31% of
H. longicornis were detected positive for
Rickettsia spp., or/and Protozoa, 18.75% of
I. granulatus for
Borrelia spp., 52.38% of
H. flava for protozoa or/and
Rickettsia spp. and 5.19% of
R. microplus for protozoa. Infection rate in
H. flava was significantly greater than that in
H. longicornis (χ
2=61.24,
P < 0.001). Coinfection with protozoa and
Rickettsia were found in
H. longicornis and
H. flava, with coinfection rate of 0.58% and 47.62%, respectively. There was no positive samples found in 7 tick species (
H. phasiana, I. acuminatus, R. sanguineus, R. haemaphysaloides, I. sinensis, A. testudinarium and
D. auratus) (
Table 3).
The overall prevalence of pathogens in larvae, nymphs, male, and female ticks were 1.49%, 2.94%, 10.87%, and 13.54%, respectively. There was major difference in the prevalence of these pathogens between immatures (larvae and nymphs) and matures (males and females) (χ
2=10.12,
P =0.018). However, there was no significant difference in prevalence of these pathogens in ticks among host species and vegetation, although the positive rate of pathogens in ticks collected from hosts was approximately 2 times more than that collected by flagging over vegetation (χ
2=0.44,
P =0.51). Prevalence of these pathogens in ticks collected from
Canis familiaris, C. aegagrus hircus, Muridae and Erinaceidae were 4.65%, 11.43%, 18.75%, and 84.62%, respectively, and ticks on Erinaceidae were at significantly higher risk for pathogen infection compared to ticks on other hosts (χ
2=108.44,
P < 0.001). There was no positive ticks found on other host species. Prevalence of these pathogens in ticks in grasslands and woodland were 2.08% and 0, respectively, and there was on significant difference (χ
2=1.37,
P =0.24) (
Table 4).
Further sequencing and sequence alignment showed that 1
Borrelia species (
Borrelia yangtzensis), 2 protozoan species (
Babesia vogeli and
Hepatozoon canis or
Hepatozoon felis related geospecies), and 1
Rickettsia species (
Rickettsia slovaca or
Rickettsia raoultii related genospecies) were successfully sequenced from 4 tick species. The 665-base pair sequence of
Borrelia spp. flagellin gene (MG717513) yielded in the study was 99.21–99.37% identical to other 2 sequences of MG717514 and MG717515 produced in the study. When compared to other fragments deposited in GenBank, MG717513 showed 98.73–98.89% identity to
B. yangtzensis (EU135599, EU135601, and EU135602), 98.57–98.73% identity to
Borrelia valaisiana (AB022134 and AB022135), and 95.25% identity to
Borrelia burgdorferi sensu lato (X75202, X63413, and D63364). Therefore, 3 individuals of
Borrelia spp. in the study were identified as
B. yangtzensis or
B. yangtzensis-related species. In
Rickettsia spp., the 401 base-pair sequence of
gltA gene (MG717516) obtained in a
H. longicornis tick collected in grassland was 100% identical to the sequences of
gltA gene isolated from 2
H. longicornis ticks (MG717517 and MG717523) on
C. familiaris and 10
H. flava ticks on Erinaceidae (MG717518-MG717522, MG717524-MG717528), and 96.26% identical to the sequence in a
H. flava tick on Erinaceidae (MG717529) (
Table 5;
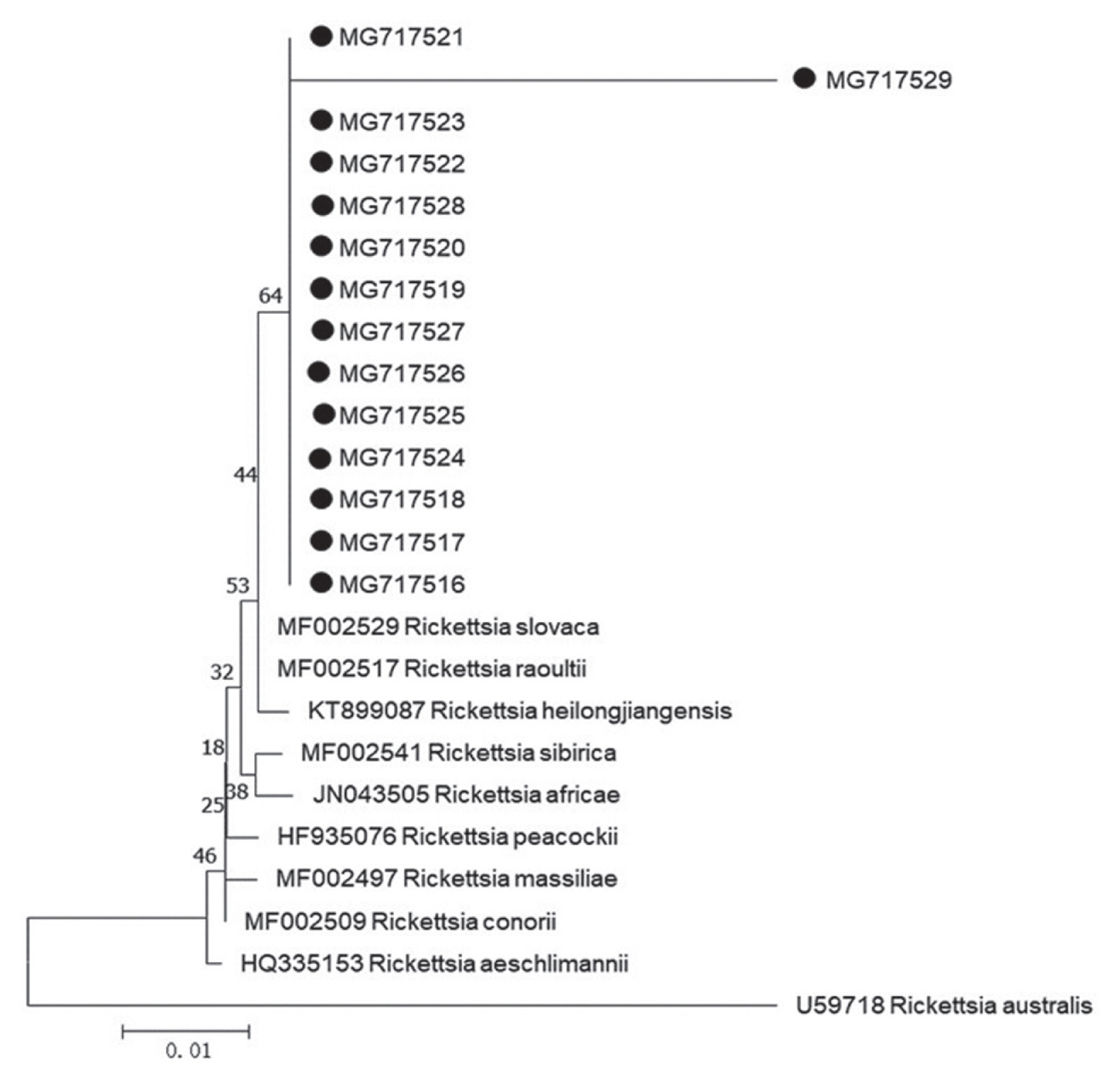
Fig. 1). Our 13 sequences (MG717516-MG717528) showed 99.75% identity to the sequences of
R. raoultii (MF002517) and
R. slovaca (MF002529) deposited in GenBank, in addition, 1 remaining sequence (MG717529) presented 96.01% identity to
R. raoultii and
R. slovaca. The
Rickettsia spp. pathogens in the study were identified as
R. raoultii or
R. slovaca related genospecies. Of 15 protozoa-positive specimens for amplification of 209–214 base-pair 18S ribosomal RNA by means of PCR method, 2 specimens were successfully sequenced (
Table 5). The closest matches of 209 base-pair 18S ribosomal RNA of protozoa in our study were
B. vogeli isolated in dogs from Jiangsu, China (MG586235, 100%), Serbia (KY747491, 100%), and Argentina (KY290978, 99%), and in
R. sanguineus from India (MG050159, 100%) and from Australia (MG758132, 100%), in
Haemaphysalis concinna from Czech Republic (KX8 57477, 100%). The 214 base-pair 18S ribosomal RNA of protozoa (MG675579) isolated in
H. longicornis from grassland in the study showed 94.86% to
H. canis (MG917719 and MG209594) and
H. felis (KU232308), 92.99% identity to
Hepatozoon ursi (KU232308), hence we proposed the protozoan as
H. canis or
H. felis related genospecies.
R. slovaca or
R. raoultii related genospecies was most frequently identified (14 times, 3 from the tick
H. longicornis, 11 times from the tick
H. flava), followed by
B. yangtzensis (triple from
I. granulatus). The other 2 protozoan species were detected only once. Twenty one of the 33 detections of pathogens were on
H. flava collected from Erinaceidae (
Table 5).
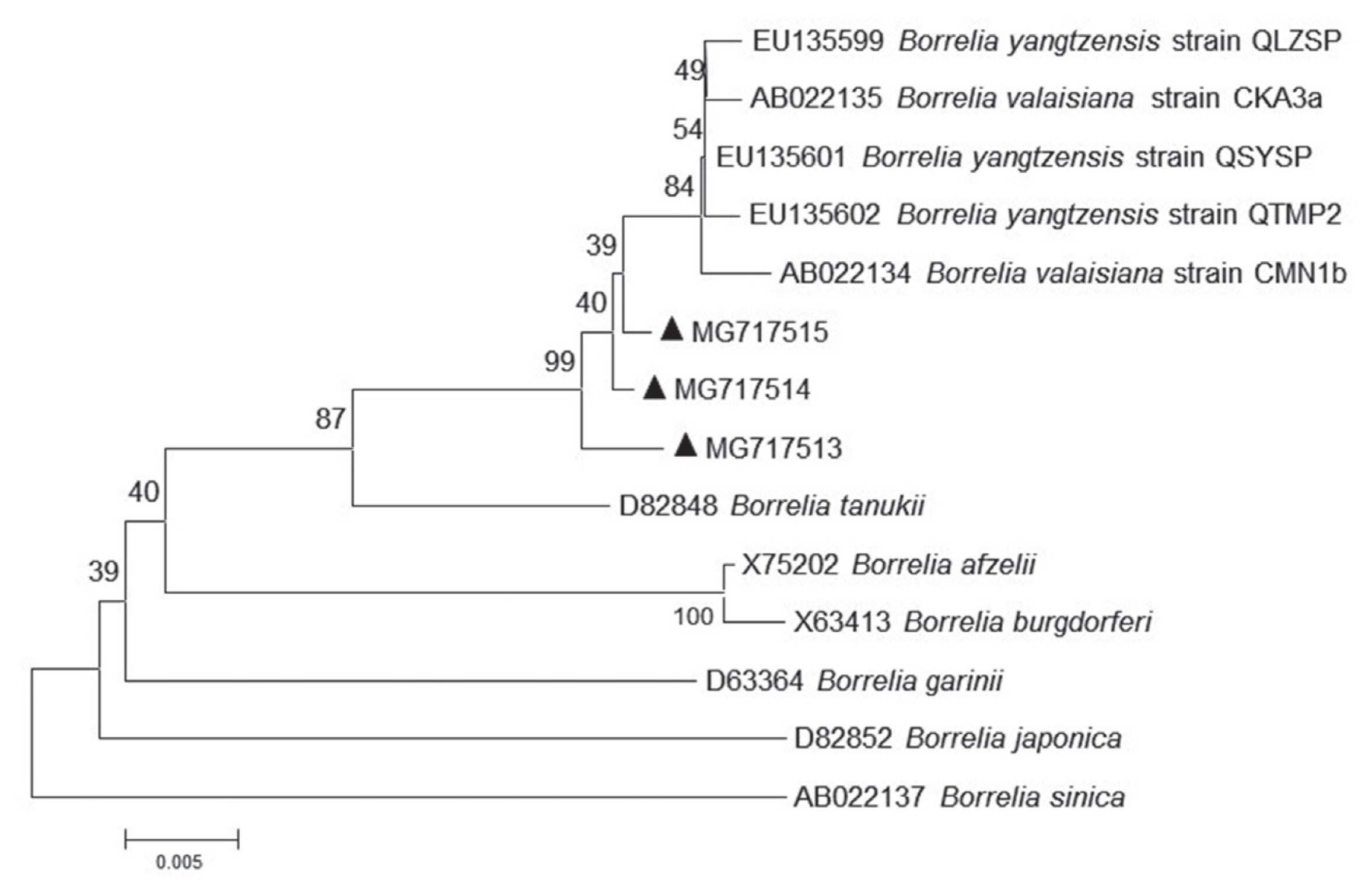
For phylogenetic analyses, 3 sequences of
B. yangtzensis flagellin gene obtained from
I. granulatus belonged to the same cluster where they shared with the strain QLZSP, QSYSP, and QTMP2 of
B. yangtzensis and strain CKA3a and CMN1b of
B. valaisiana (
Table 5;
Fig. 2). The sequences of
R. raoultii or
R. slovaca related
Rickettsia spp. (MG717516-MG7175129) were clustered with those of
R. raoultii (MF002517) and
R. slovaca (MF002529) (
Fig. 2).
DISCUSSION
In Poyang Lake region, the common animals and birds with potential for tick parasitism and easy to contact human were
C. familiaris, C. aegagrus hircus, A. agrarius, R. norvegicus, G. gallus domesticus, and
L. sinensis, accounting for over 90% of hosts captured. Rodents like
A. agrarius and
R. norvegicus were trapped with large number, but a few ticks were found, whereas
B. yangtzensis was occasionally detected in ticks removed from the rodents.
B. yangtzensis, a
Borrelia species in the
B. burgdorferi complex was originally discovered in Chinese Yangtze River Valley region in 2015, and it was reported in
H. longicornis and
I. granulatus ticks from small mammals in China and isolated in rodents or shrews in Japan [
12]. However,
B. yangtzensis was not detected in
H. longicornis albeit greater than 50% ticks collected in the study were
H. longicornis. The reason, we guessed, might be that
H. longicornis was not an efficient vectors of
B. yangtzensis, hence the pathogen was rarely presented in the ticks. Poyang Lake region belongs to part of Yangtze River Valley region, and has similar distribution pattern of ticks and tick related small mammals to other parts of Yangtze River Valley region, therefore
B. yangtzensis can also be found in
I. granulatus collected in rodents in our study. The sequences of
flagellin gene in
B. yangtzensis in the study showed higher identity to
B. valaisiana than to other known Lyme Borreliosis group spirochaete species, which was in agreement with the previous study [
12].
Despite some
L. sinensis were majorly tick infested, pathogens were not found in those ticks. We had 3 Erinaceidae hosts, and found diverse pathogens like
R. slovoca or
R. raoultiilike genospcies and
Babesia spp. in attached ticks with high infection rate. Ticks on Erinaceidae might serve as vectors within Erinaceidae populations in this region, thus readily leading to high infection rate. This increases the chance that ticks transport pathogens from a natural hedgehog cycle to other hosts, including humans [
13].
C. familiaris, usually functioning as a guard dog and a pet in investigated sites, were closely related to human, furthermore, some ticks on dogs in our study were positive for
R. slovoca or
R. raoultii related genospcies which is likely considered as human pathogen. Dogs, incidental hosts for the agent of spotted fever group, can become infected by a bite of ixodid ticks, and then transmit the pathogens to human [
14]. Therefore, people should avoid contact with such dogs and ticks.
In this study, 11 tick species were collected, with
H. longicornis acting as the predominant species, and other common ticks included
H. flava,
R. microplus and
I. granulatus. These common tick species were also reported in other subtropical regions of China like Zhejiang and Hubei [
15]. Our findings indicated that
H. flava and
H. longicornis were the ticks frequently detected positive for presence of
R. raoultii or
R. slovoca related genospecies.
R. raoultii and
R. slovoca were reported as human pathogenic agents [
3,
16,
17]. Previous researches showed that
R. raoultii had been reported in northern regions of China [
3,
7], and
R. slovaca recorded in Europe and Xinjiang, China [
7,
16,
17]. Although natural infection with tick-borne pathogens occurs [
1], other tick species like
R. sanguineus, R. haemaphysaloides, I. sinensis, and
A. testudinarium were tested negative for
Borrelia spp.,
Rickettsia spp. and protozoa infection in our study. The possible reason might be because of a few numbers of ticks collected and thus decreasing the probability of pathogen detection.
Compared to immature ticks, mature ticks tended to pathogen infection, furthermore, we found that females had comparable positivity rate with males. In contrast, a study conducted in Europe showed higher pathogen infection rate in immatures than matures [
18]. Our study demonstrated that relatively high infection rate were determined in adult ticks collected from hedgehogs. The result suggests hedgehogs functioning as important pathogen reservoirs, and corresponds with a previous indication that several species of birds played a role as Lyme disease spirochetal reservoirs infective to ticks [
18]. Therefore, in some cases, positivity rate is not depended by tick developmental stage but by which reservoir hosts that ticks attach to. For vegetation types, grassland sheltered more ticks than woodland and shrubs, and there were some ticks infected with
R. slovaca or
R. raoultii related genospecies in grassland. However, non-infected ticks were found in woodland, in contrast to more than 6 tick-borne pathogens infection in ticks from French suburban woodland [
19]. Workers and visitors for travelling in the field should pay more attention to questing ticks in grassland in prevention of occurrence of tick-borne diseases. In addition, people in this region should keep a distance from hosts with tick infestation, especially the hosts with high risk for human tick-borne pathogens including hedgehogs, dogs and rodents.
Notes
-
CONFLICT OF INTEREST
The authors declare that there are no conflicts of interest.
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS
This study was supported financially by Jiangxi Provincial Department of Science and Technology (grant number 2016 BBG70005); Nanchang Science and Technology Bureau (Hong Scientific Research Program [2016] No. 96 Item 77); and the Health and Family Planning Commission of Jiangxi Province (grant number 20162007). The sponsors have no role in study design; in the collection, analysis and interpretation of data; in the writing of the report; and in the decision to submit the article for publication. The authors thank Rongman Xu, Yi Sun, and Ze Chen for morphological identification of tick species, and also wish to acknowledge the contribution of Yuanping Deng (the director of Anyi Center for Disease Control and Prevention), for technical assistance during the collection of samples. Weiqing Zheng was partially supported by Sasakawa Medical Fellowship through Japan-China Medical Association.
Fig. 1Phylogenetic tree of Rickettsia spp. based on gltA gene. The trees were calculated by the neighbor-joining method using MEGA v.7.0.26 software. Values of the bootstrap support of the particular branching calculated for 1,000 replicated are indicated at the nodes. The variant sequences obtained from GenBank are designated by accession number and species. Rickettsia australis is used as outgroup. (●) denotes sequences of R. slovaca or R. raoultii related genospecies obtained in the study.
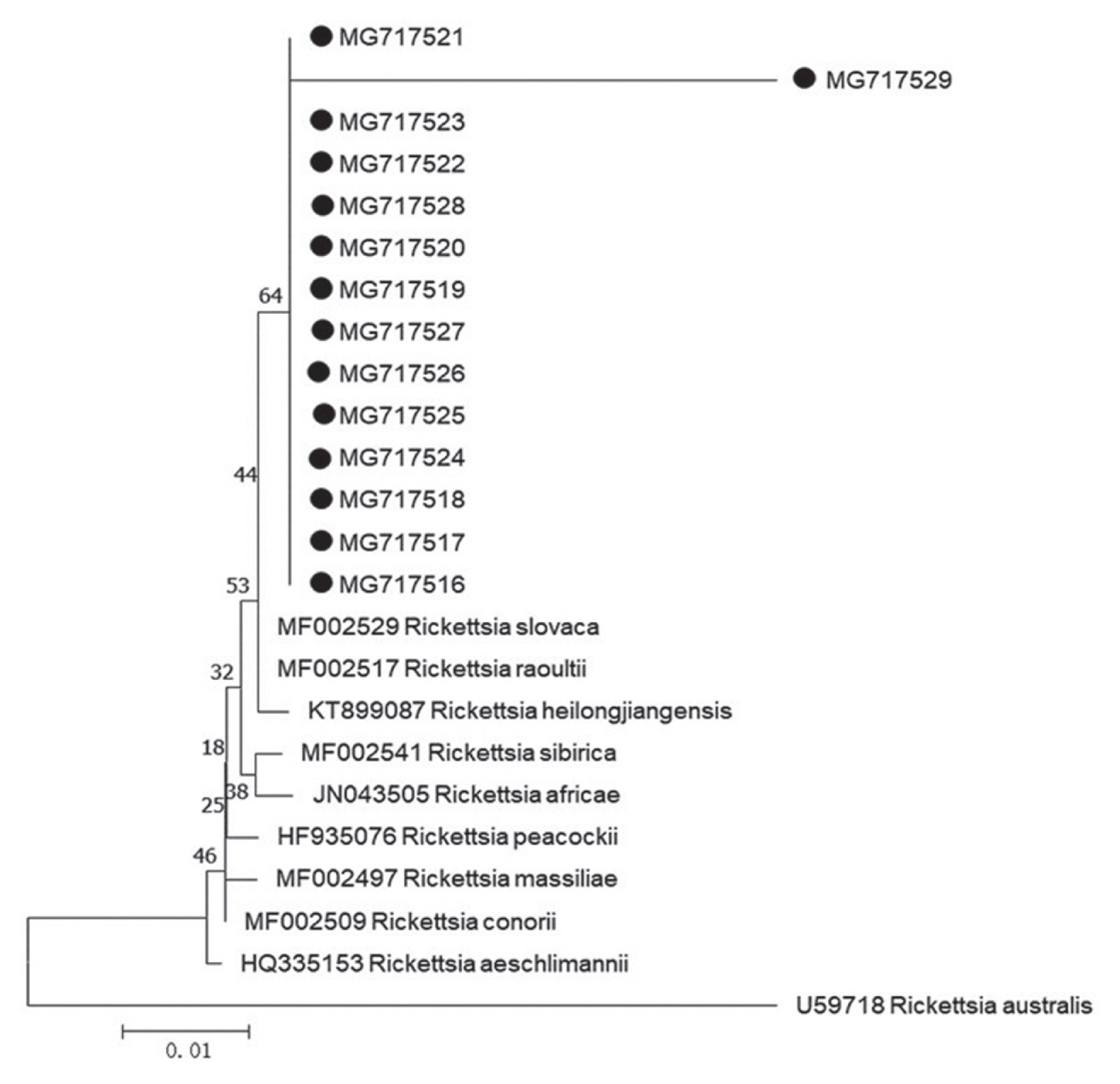
Fig. 2Molecular phylogenetic tree of the Borrelia agent. The aligned nucleotide sequence of flagellin gene was subjected to analysis. Bootstrap 1,000 replicates are showed at the nodes. Scale bars indicate nucleotide substitutions per sites. Borrelia sinica is used as outgroups. (▲) prior to accession numbers are the sequences in the study.
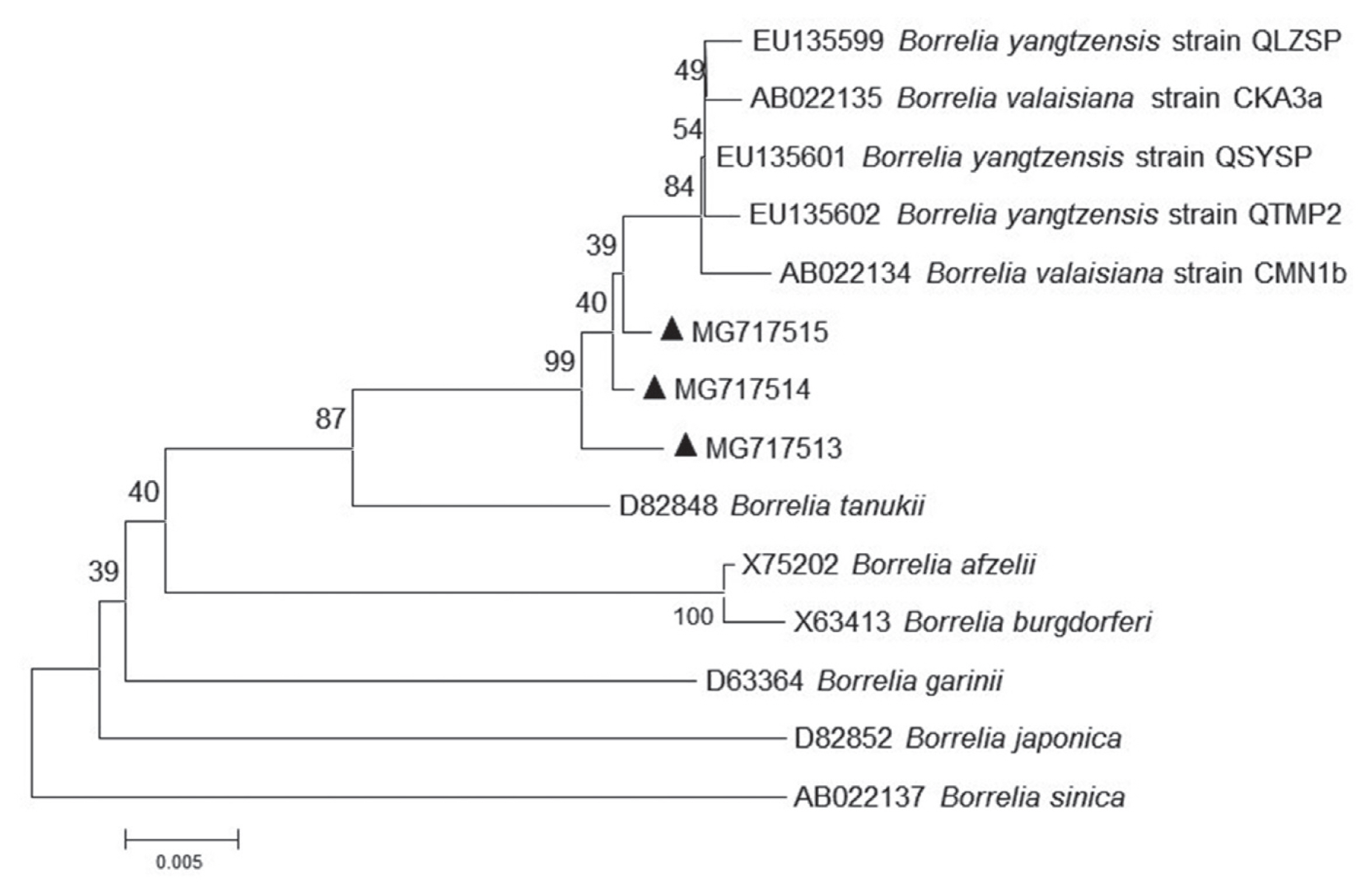
Table 1Location and vegetation type of 12 plots sampled in this study
Table 1
|
Location |
Geographic coordinates |
Vegetation type |
Year surveyed |
|
Anyi |
N 28.6173°, W 115.5423° |
G, S, W |
2014, 2015 |
|
Wanli |
N 28.8400°, W 115.7589° |
W |
2014 |
|
Xinjian |
N 28.9800°, W 115.9154° |
G |
2014 |
|
Qingyunpu |
N 28.6389°, W 115.9127° |
G |
2013, 2014 |
|
Duchang |
N 29.2542°, W 116.1946° |
W |
2015 |
|
Hukou |
N 29.7469°, W 116.2330° |
W |
2015 |
|
Wuning |
N 29.2574°, W 115.0986° |
G, S |
2015 |
|
Poyang |
N 29.0000°, W 116.6730° |
G |
2015 |
|
Wannian |
N 28.6899°, W 116.9728° |
W |
2015 |
|
Wuyuan |
N 29.2709°, W 117.75793° |
G, S, W |
2015 |
|
Yichun city |
N 27.5914°, W 114.3252° |
G, S, W |
2015 |
|
Xingan |
N 27.7327°, W 115.3791° |
G, S, W |
2015 |
Table 2Summary of species and number of ticks collected from hosts and by flagging over vegetation cover
Table 2
|
Vegetation covers/Animal hosts |
Tick species |
No. of ticks collected |
Densitya
|
|
|
L |
N |
A |
|
Woodland (a=800 m2) |
Haemaphysalis longicornis
|
0 |
0 |
2M |
0.0038 |
|
Dermacentor auratus
|
0 |
0 |
1M |
|
|
|
Grassland (a=800 m2) |
H. longicornis
|
3 |
34 |
5M6F |
0.06 |
|
|
Subtotal (a=1,600 m2) |
-
|
3 |
34 |
8M6F |
0.032 |
|
|
Canis familiaris (n=24) |
H. longicornis
|
0 |
5 |
4M25F |
1.79 |
|
R. sanguineus
|
0 |
0 |
1M8F |
|
|
|
Capra aegagrus hircus (n=44) |
H. longicornis
|
0 |
2 |
0 |
0.80 |
|
Haemaphysalis flava
|
2 |
2 |
3M1F |
|
|
Rhipicephalus microplus
|
0 |
8 |
6M11F |
|
|
|
Bos spp. (n=13) |
H. longicornis
|
1 |
8 |
0 |
4.31 |
|
R. microplus
|
0 |
20 |
8M19F |
|
|
|
Bubalus bubalis (n=7) |
H. longicornis
|
0 |
0 |
1F |
1 |
|
R. microplus
|
0 |
0 |
5F |
|
|
Amblyomma testudinarium
|
0 |
0 |
1F |
|
|
|
Phasianus colchicus (n=5) |
Haemaphysalis phasiana
|
0 |
5 |
0 |
1 |
|
|
Lepus sinensis (n=22) |
H. longicornis
|
57 |
12 |
5M1F |
3.77 |
|
Ixodes acuminatus
|
0 |
0 |
1F |
|
|
Ixodes sinensis
|
0 |
0 |
2M2F |
|
|
Rhipicephalus haemaphysaloides
|
3 |
0 |
0 |
|
|
|
Erinaceidae (n=3) |
H. flava
|
0 |
1 |
3M9F |
4.33 |
|
|
Apodemus agrarius (n=206) |
Ixodes granulatus
|
0 |
0 |
1M4F |
0.02 |
|
|
Rattus norvegicus (n=95) |
I. granulatus
|
0 |
0 |
3M1F |
0.04 |
|
|
Rattus rattoides (n=8) |
I. granulatus
|
0 |
5 |
2M |
0.88 |
|
|
Equus ferus (n=6) |
H. longicornis
|
0 |
0 |
1F |
0.17 |
|
|
Gallus gallus domesticus (n=30) |
H. longicornis
|
1 |
0 |
0 |
0.03 |
|
|
Subtotal (n=463) |
-
|
64 |
68 |
38M90F |
0.56 |
|
|
Total (n=463; a=1,600 m2) |
-
|
67 |
102 |
46M96F |
- |
Table 3Pathogen infection rates in ticks collected in Poyang Lake region
Table 3
|
Tick species (number collected) |
Borrelia
|
Rickettsia
|
Protozoa |
Protozoa+Rickettsia
|
Infection rate (%) |
χ2
|
P-value |
|
Haemaphysalis longicornis (n=173) |
0 |
4 (2.31) |
1 (0.58) |
1 (0.58) |
4 (2.31) |
61.24 |
<0.001 |
|
Ixodes granulatus (n=16) |
3 (18.75) |
0 |
0 |
0 |
3 (18.75) |
|
|
|
Haemaphysalis flava (n=21) |
0 |
11 (52.38) |
10 (47.62) |
10 (47.62) |
11 (52.38) |
|
|
|
Rhipicephalus microplus (n=77) |
0 |
0 |
4 (5.19) |
0 |
4 (5.19) |
|
|
|
Haemaphysalis phasiana (n=5) |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
|
|
|
|
Ixodes acuminatus (n=1) |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
|
|
|
|
Rhipicephalus sanguineus (n=9) |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
|
|
|
|
Rhipicephalus haemaphysaloides (n=3) |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
|
|
|
|
Ixodes sinensis (n=4) |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
|
|
|
|
Amblyomma testudinarium (n=1) |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
|
|
|
|
Dermacentor auratus (n=1) |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
|
|
|
Table 4Comparison of difference of collected ticks and positive rates of pathogens among ticks by life stage, host species and vegetation type
Table 4
|
Group |
|
Sampled ticks |
Positive ticks |
χ2
|
P-value |
|
|
No. |
% |
|
Life stage |
Larvae |
67 |
1 |
1.49 |
10.12 |
0.018 |
|
Nymph |
102 |
3 |
2.94 |
|
|
|
Male |
46 |
5 |
10.87 |
|
|
|
Female |
96 |
13 |
13.54 |
|
|
|
|
Vegetation type |
Grassland |
48 |
2 |
4.17 |
1.37 |
0.24 |
|
woodland |
3 |
0 |
0.00 |
|
|
|
|
Host |
Muridae |
16 |
3 |
18.75 |
108.44 |
<0.001 |
|
Canis familiaris
|
43 |
2 |
4.65 |
|
|
|
Capra aegagrus hircus
|
35 |
4 |
11.43 |
|
|
|
Lepus sinensis
|
83 |
0 |
0.00 |
|
|
|
Erinaceidae |
13 |
11 |
84.62 |
|
|
|
Bubalus bubalis
|
7 |
0 |
0.00 |
|
|
|
Bos spp. |
56 |
0 |
0.00 |
|
|
|
Phasianus colchicus
|
5 |
0 |
0.00 |
|
|
|
|
Vegetation vs host |
Vegetation |
51 |
2 |
3.92 |
0.44 |
0.51 |
|
Host |
260 |
20 |
7.69 |
|
|
Table 5Pathogens in ticks collected from different hosts in different locations
Table 5
|
Pathogens |
|
Ticks species (No. positive) |
Host species |
Sampling site |
GenBank accession No. |
|
Borrelia
|
B. yangtzensis
|
I. granulatus (1♂1♀) |
R. norvegicus
|
Anyi |
MG717514-MG717515 |
|
I. granulatus (1N) |
R. rattoides
|
Anyi |
MG717513 |
|
|
Rickettsia
|
R. raoultii or R. slovaca related genospecies |
H. longicornis (2♀) |
Canis familiaris
|
Xinjian, Poyang |
MG717517, MG717523 |
|
H. longicornis (1♀) |
Grassland |
Qingyunpu |
MG717516 |
|
H. flava (1N3♂1♀) |
Erinaceidae |
Hukou |
MG717518-MG717522 |
|
H. flava (1♂5♀) |
Erinaceidae |
Hukou |
MG717524-MG717529 |
|
Rickettsia sp. |
H. longicornis (1L) |
Grassland |
Qingyunpu |
- |
|
|
Protozoa |
Babesia vogeli
|
H. flava (1♂) |
Erinaceidae |
Hukou |
MG675580 |
|
Babesia sp. |
H. flava (9♀) |
Erinaceidae |
Hukou |
- |
|
R. microplus (1N3♀) |
Capra aegagrus hircus
|
Yichun |
- |
|
Hepatozoon canis or Hepatozoon felis related genospecies |
H. longicornis (1♀) |
Grassland |
Qingyunpu |
MG675579 |
References
- 1. Fang LQ, Liu K, Li XL, Liang S, Yang Y, Yao HW, Sun RX, Sun Y, Chen WJ, Zuo SQ, Ma MJ, Li H, Jiang JF, Liu W, Yang XF, Gray GC, Krause PJ, Cao WC. Emerging tick-borne infections in mainland China: an increasing public health threat. Lancet Infect Dis 2015;15:1467-1479.
- 2. Saito K, Ito T, Asashima N, Ohno M, Nagai R, Fujita H, Koizumi N, Takano A, Watanabe H, Kawabata H. Borrelia valaisiana infection in a Japanese man associated with traveling to foreign countries. Am J Trop Med Hyg 2007;77:1124-1127.
- 3. Li H, Zhang PH, Huang Y, Du J, Cui N, Yang ZD, Tang F, Fu FX, Li XM, Cui XM, Fan YD, Xing B, Li XK, Tong YG, Cao WC, Liu W. Isolation and identification of Rickettsia raoultii in human cases: a surveillance study in three medical centers in China. Clin Infect Dis 2018;66:1109-1115.
- 4. Zheng WQ, Chen HY, Liu MM, Adjou Moumouni PF, Efstratiou A, Liu ZB, Xuan XN. First evidence of Mycoplasma haemocanis in China. Trop Biomed 2017;34:983-990.
- 5. Zheng WQ, Liu Y, Tao H, Li Z, Xuan X, Liu X, Adjou Moumouni PF, Wu Y, Liu W, Chen H. First molecular evidence of Anaplasma phagocytophilum in rodent population of Nanchang, China. Jpn J Infect Dis 2018;71:129-133.
- 6. Zheng W, Liu M, Adjou Moumouni PF, Liu X, Efstratiou A, Liu Z, Liu Y, Tao H, Guo H, Wang G, Gao Y, Li Z, Ringo AE, Jirapattharasate C, Chen H, Xuan X. First molecular detection of tick-borne pathogens in dogs from Jiangxi, China. J Vet Med Sci 2017;79:248-254.
- 7. Han R, Yang J, Niu Q, Liu Z, Chen Z, Kan W, Hu G, Liu G, Luo J, Yin H. Molecular prevalence of spotted fever group rickettsiae in ticks from Qinghai Province, northwestern China. Infect Genet Evol 2018;57:1-7.
- 8. Takada N, Masuzawa T, Ishiguro F, Fujita H, Kudeken M, Mitani H, Fukunaga M, Tsuchiya K, Yano Y, Ma XH. Lyme disease Borrelia spp. in ticks and rodents from northwestern China. Appl Environ Microbiol 2001;67:5161-5165.
- 9. Teng GF. Chinese Economic Insect Archive, Ixodidae. Beijing, China. Science Press. 1978, pp 1-174.
- 10. Lv J, Wu S, Zhang Y, Chen Y, Feng C, Yuan X, Jia G, Deng J, Wang C, Wang Q, Mei L, Lin X. Assessment of four DNA fragments (COI, 16S rDNA, ITS2, 12S rDNA) for species identification of the Ixodida (Acari: Ixodida). Parasit Vectors 2014;7:93.
- 11. Preacher KJ. Calculation for the chi-square test: An interactive calculation tool for chi-square tests of goodness of fit and independence [Computer software]; Available from: http://quantpsy.org/2001.
- 12. Margos G, Chu CY, Takano A, Jiang BG, Liu W, Kurtenbach K, Masuzawa T, Fingerle V, Cao WC, Kawabata H. Borrelia yangtzensis sp. nov., a rodent-associated species in Asia, is related to Borrelia valaisiana. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 2015;65:3836-3840.
- 13. Skuballa J, Petney T, Pfäffle M, Taraschewski H. Molecular detection of Anaplasma phagocytophilum in the European hedgehog (Erinaceus europaeus) and its ticks. Vector Borne Zoonotic Dis 2010;10:1055-1057.
- 14. Nicholson WL, Allen KE, McQuiston JH, Breitschwerdt EB, Little SE. The increasing recognition of rickettsial pathogens in dogs and people. Trends Parasitol 2010;26:205-212.
- 15. Lu X, Lin XD, Wang JB, Qin XC, Tian JH, Guo WP, Fan FN, Shao R, Xu J, Zhang YZ. Molecular survey of hard ticks in endemic areas of tick-borne diseases in China. Ticks Tick Borne Dis 2013;4:288-296.
- 16. Gouriet F, Rolain JM, Raoult D. Rickettsia slovaca Infection, France. Emerg Infect Dis 2006;12:521-523.
- 17. de Sousa R, Pereira BI, Nazareth C, Cabral S, Ventura C, Crespo P, Marques N, da Cunha S. Rickettsia slovaca infection in humans, Portugal. Emerg Infect Dis 2013;19:1627-1629.
- 18. Olsén B, Jaenson TG, Bergström S. Prevalence of Borrelia burgdorferi sensu lato-infected ticks on migrating birds. Appl Environ Microbiol 1995;61:3082-3087.
- 19. Reis C, Cote M, Paul RE, Bonnet S. Questing ticks in suburban forest are infected by at least six tick-borne pathogens. Vector Borne Zoonotic Dis 2011;11:907-916.