Abstract
Echinococcus granulosus is an important zoonotic parasite globally causing cystic echinococcosis (CE) in humans and animals. In this study, prevalence of CE and variation of cox1 gene sequence were analyzed with isolates E. granulosus collected from different areas in northern Xinjiang, China. The survey showed that 3.5% of sheep and 4.1% of cattle were infected with CE. Fragment of cox1 was amplified from all the positive sheep and cattle samples by PCR. In addition, 26 positive samples across the 4 areas were included. The isolates were all E. granulosus sensu stricto (s.s.) containing 15 haplotypes (Hap1-15), and clustered into 2 genotypes, G1 (90.1%, 91/101) and G3 (9.9%, 10/101). Hap1 was the most common haplotype (48.5%, 49/101). Hap9 were found in humans samples, indicating that sheep and cattle reservoir human CE. It is indicate that E. granulosus may impact on control of CE in livestock and humans in the region.
-
Key words: Echinococcus granulosus sensu stricto, cox1, cystic echinococcosis, prevalence, gene, genotype, Xinjiang
INTRODUCTION
Cystic echinococcosis (CE) is a parasitic zoonosis caused by the metacestode of
Echinococcus granulosus sensu lato, which has recently been classified into at least 5 species based on their genetic variation [
1–
4]. Intermediate hosts (livestock and humans) are infected through the oral ingestion of eggs derived from feces of the definitive host, while the protoscoleces (PSCs) develop and grow into adult worms in the intestine of dogs/foxes once the liver or lungs of the intermediate hosts containing echinococcal cysts are uptaken by the definitive hosts [
5–
7].
The disease is highly endemic in Xinjiang, China; from 2004 to 2010, a total of 4,768 human echinococcosis cases were reported, which were accounting for 32.6% of total CE cases in China [
8]. In addition, it was reported that 9.8% of sheep, 8.4% of cattle, 6.8% of camels, and 4.3% of horses were infected with CE [
9]. In fact, the average number of annual operation cases was 960 (8,639/9 years) between 2005 and 2013, and the incidence rate of human CE cases was reported to be 4.4 cases per 100,000 inhabitants [
10,
11].
E. granulosus was considered a single species previously, but is now recognized as having extensive genetic diversity, with distinct strains/genotypes exhibiting differences in pathology. Mitochondrial DNA (mtDNA) sequencing has resulted in the recognition of 10 genotypes (G1-10) [
12] and their accurate identification in molecular epidemiological surveys of CE in different geographical settings and host assemblages. G1-G3 genotypes are also named the sheep (G1), the Tasmanian sheep (G2), and the buffalo (G3) strains, respectively [
12]. In China, the sheep strain is the predominant epidemic strain, and it also the majority strain in human in the world [
13,
14].
Given that Xinjiang has a variety of geographic landscapes and different suitable intermediate hosts, this may be the cause of the genetic variation in
E. granulosus sensu stricto (
s.s.) [
15–
17]. The few studies that have assessed
E. granulosus infections in humans in Xinjiang of China, with infection rates ranged from 0.3% to 3% [
11]. However, the genetic variation of
E. granulosus in Xinjiang is unclear. In the present study, we assessed the epidemiology of
E. granulosus in livestock and humans and identified the genetic variation of
E. granulosus in northern Xinjiang.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Sample collection
From May 2013 to May 2016, a total of 1,270 sheep and 759 cattle were inspected for cysts in their livers and lungs at 4 county slaughterhouses in northern Xinjiang. We also collected 26 echinococcal samples from CE patients in the region. Each single cyst of
E. granulosus s.s. was treated as an isolate. PSCs and/or germinal layers were collected from cysts and washed 10 times with phosphate-buffered saline (PBS) [
18] and stored at −20°C until genomic DNA extraction.
All the positive samples were selected for genotype identification. The genomic DNA (gDNA) of the isolates were extracted using the TIANamp Genomic DNA kit (Tiangen Boitech, Beijing, China) from approximately 30 mg of parasite tissue according to manufacturer’s instructions. DNA was eluted with 100 μl of water and stored at −20°C until used. The cox1 sequence gene fragment was amplified by PCR using the following pair of primers: Forward (5′-GTTTAGGGGCTGGTGTTGGT-3′) and Reverse (5′-CCGTCTTCACATCCAACCCA-3′). A 546 bp fragment was amplified in a 50 μl volume reaction containing 2 μl template (50–100 ng of gDNA), 25 μl mix (Tiangen Boitech), 1 μl of each primer at 10 μM, and 21 μl of water. The reaction was performed for 35 cycles. The pre-denaturation was done at 94°C for 3 min followed by 35 cycles of amplification with denaturation at 94°C for 30 sec, annealing at 56°C, and extension at 72°C for 1 min. The reaction was stopped after the final elongation at 72°C for 5 min. The PCR products were separated by electrophoresis on 1.2% agarose gels.
Sequencing of mtDNA and phylogenetic analysis
The PCR products of the targeted
cox1 gene fragment were purified from the DNA gel and subjected to sequencing by Tiangen Boitech. The sequences obtained were aligned using Clustal χ2 and BioEdit version 5 (
http://www.mbio.ncsu.edu/bioedit/bioedit.html/) and compared to the reference sequences from the GenBank database. All sequences were deposited in the GenBank database with access MH211191-MH211205. For more comprehensive analysis, sequences from
E. granulosus genotypes and other
Echinococcus species available in the GenBank were downloaded, and phylogenetic analysis was performed using MEGA 6.0. Phylogenetic trees were constructed using the neighbor-joining (NJ) method [Kimura’s 2-parameter distance analysis with a gamma shape parameter (a=0.5)]. The robustness of phylogenetic trees was tested by bootstrapping using 1000 replicates [
19]. A network of mtDNA haplotypes was illustrated by NETWORK 4.6.1.3 using statistical parsimony (
http://www.fluxusengineering.com/sharenet.htm).
The infection rates of E. granulosus s.s. were estimated as a percentage of positive samples with 95% confidence intervals (CI), and the prevalence in different regions was determined using IBM SPSS Statistics version 21.0 for Windows (IBM Corp., Armonk, New York, USA). The differences were considered significant when P<0.05 by Pearson’s Chi-Square test (χ2 test) analysis.
Ethics statement
The clinical research was conducted according to the principles expressed in the Declaration of Helsinki. The protocols for using surgically removed liver sections of CE patients (approval No. 20140228-15) were approved by the Ethics Committee of the First Affiliated Hospital of Xinjiang Medical University. All patients participating in the project were adults and provided written informed consent.
RESULTS
E. granulosus infection in different regions
The overall prevalence of
E. granulosus in sheep and cattle across 4 region level districts were 3.5% (44/1,270; 95% CI, 2.5–4.6) and 4.1% (31/759; 95% CI, 2.7–5.5) (
Table 1), respectively. There was no significant difference between sheep and cattle (χ
2=0.513,
P>0.05). The highest prevalence in sheep was found in Altai (9/196, 4.6%; 95% CI, 2.1–8.5). The lowest prevalence of sheep was in Urumqi (13/518, 2.5%; 95% CI, 1.2–3.9). There was no significant difference between the regions (χ
2=2.579,
P>0.05) (
Table 1). The highest prevalence in cattle was found in Tacheng (9/190, 4.7%; 95% CI, 1.7–7.8), followed by Altai (7/156, 4.5%; 95% CI, 1.8–9.0), Yili (10/250, 4.0%; 95% CI, 1.6–6.4) and Urumqi (5/163, 3.1%; 95% CI, 4.0–5.7), also, with no significant difference between the regions (χ
2=0.706,
P>0.05) (
Table 1). Sixteen positive samples from lungs and 59 from livers, no other organs were found
E. granulosus infection for sheep and cattle.
All the positive samples (n=101) were prepared for PCR for amplifying
cox1 gene fragment, including 44 from sheep, 31 from cattle and 26 from CE patients. Two genotypes (G1 and G3) were identified, and G1 (sheep strain) was the most common genotype (91/101, 90.1%) (
Table 2). Among these isolates, 90.1% (40/44) in sheep (
Table 1), 100% (31/31) in cattle (
Table 1), and 76.9% (20/26) in humans (
Table 2) were G1 genotype. While, G3 (buffalo strain) genotype was only found in sheep (4/44, 9.1%) (
Table 1) and humans (6/26, 23.1%) (
Table 2). Unique sequences have been deposited in the GenBank database under accession numbers MH211191 to MH211205.
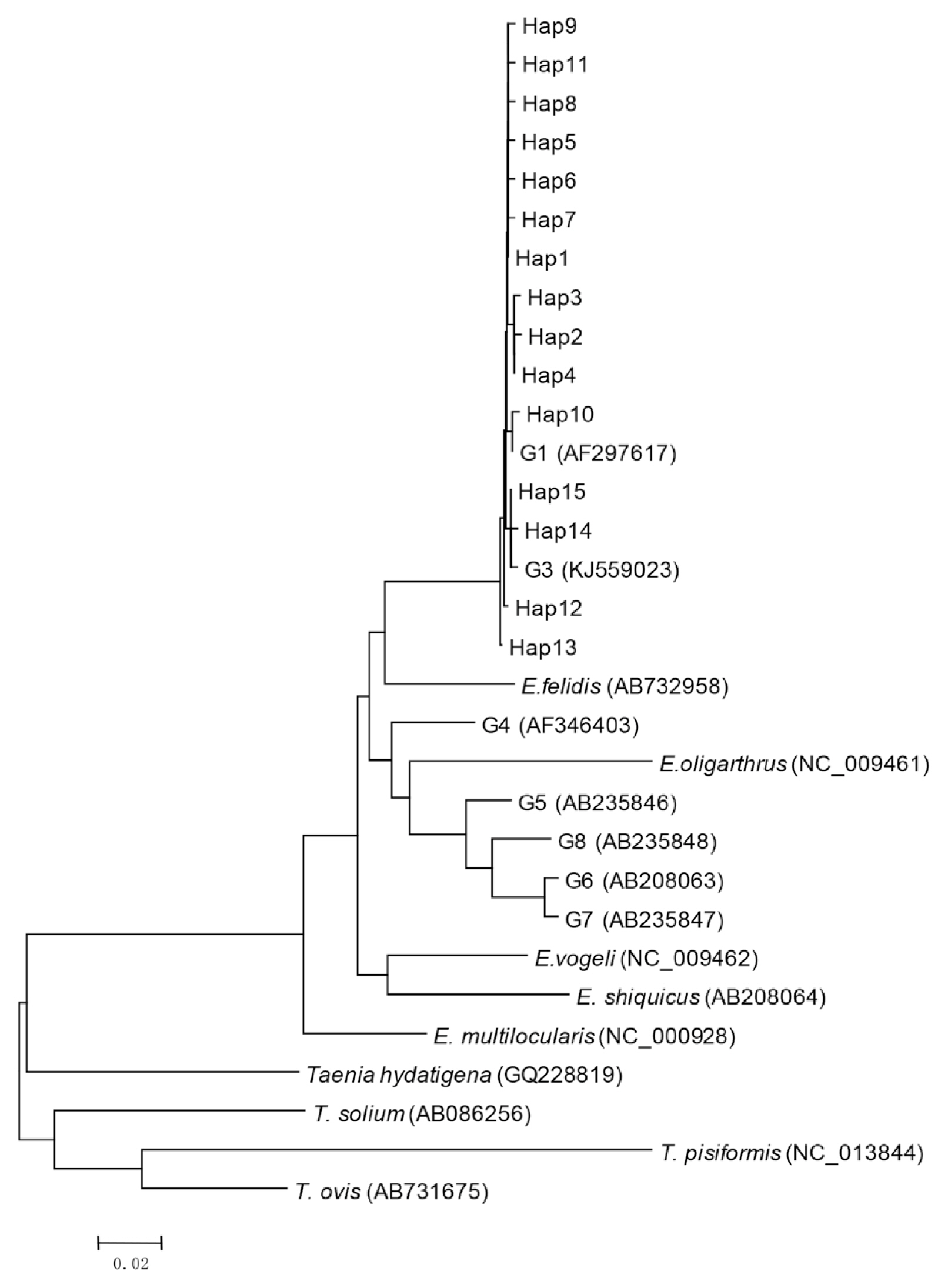
Bioinformatics analysis showed that 15 haplotypes, named Hap1 to Hap15, were identified. Hap1–13 belonged to G1 genotype, and Hap14 and Hap15 belonged to G3 genotype (
Fig. 1). Hap1 was the major haplotype accounting for 48.5% (49/101) of the isolates, including 29 from sheep (29/44, 65.9%), 11 from cattle (11/31, 35.5%), and 9 from humans (9/26, 34.6%) (
Table 3). Hap13 was the second most common haplotype, observed in 9 (8.9%) isolates including 3 sheep and 6 cattle (
Table 3). The other haplotypes (Hap2-12, Hap14, and Hap15) were found in 43 (42.6%) isolates. Hap5, Hap6, Hap12, and Hap15 were only found in humans (9.9%). In addition, Hap10 and Hap11 were only identified in cattle (8.9%).
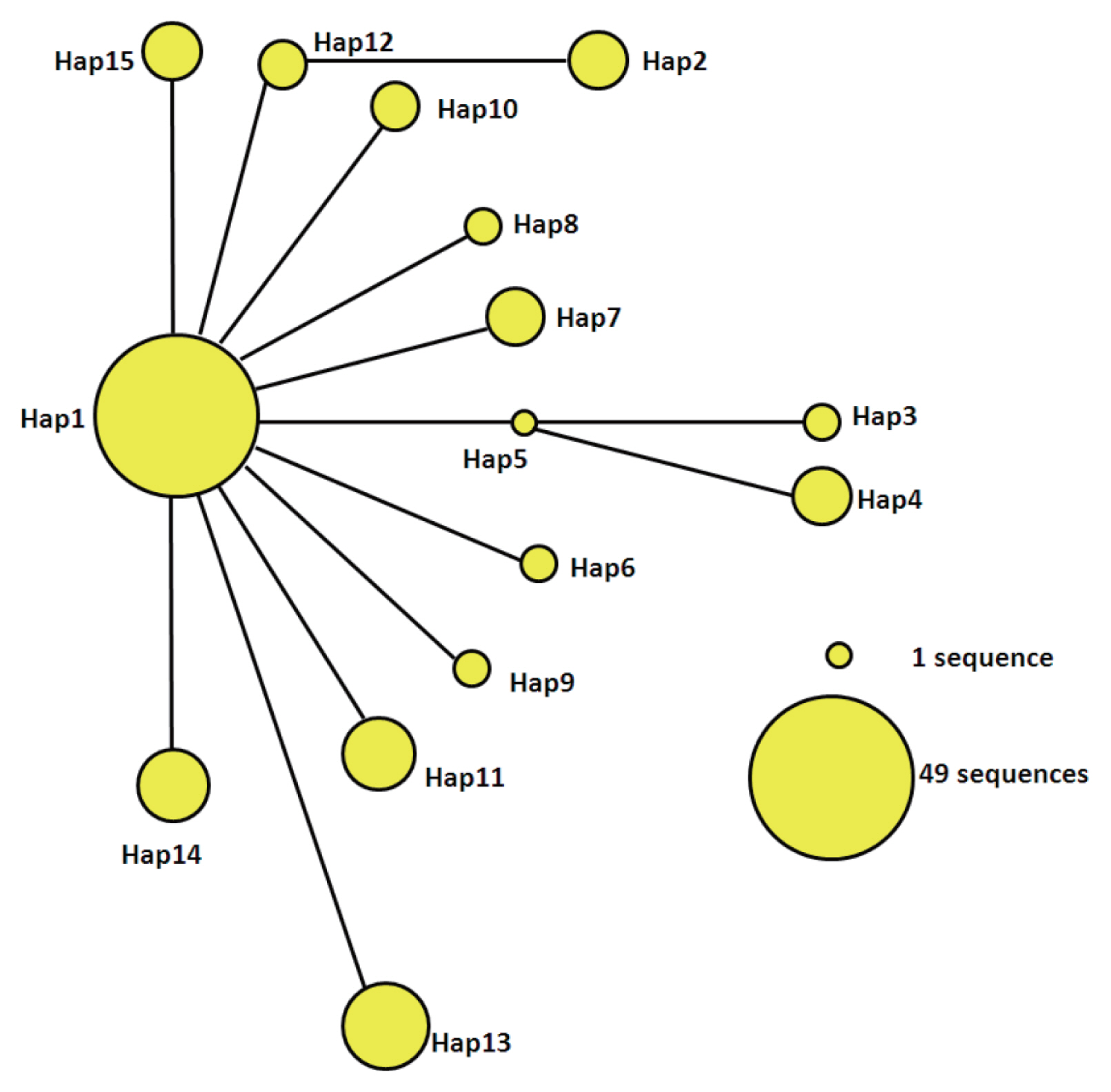
The statistical parsimony network of the mtDNA haplotypes is illustrated in
Fig. 2. Hap1 is the center of the network and other haplotypes are connected by Hap1. Among the participants in the network, Hap1 was the biggest group. All of the groups are a similar genetic distance from Hap2, Hap3, Hap4, and Hap13. Hap2 was closely related to Hap12 and far from Hap1. It is likely that Hap2 is a branch of Hap12, and Hap3 and Hap4 may be sub-branches of Hap5. At the same time, the sub-branches and branches had only one mutation. The network distance between Hap1 and Hap2, Hap3, and Hap4 equaled 2 mutational steps, suggesting that their genetic relatedness was weak.
DISCUSSION
E. granulosus is one of the serious parasites in the world, which affects human health and causes huge economic losses. The CE occurred in many parts of China in the 1990s, being present in at least 21 provinces, comprising 87% of its total territory with highly endemic areas in western China including Xinjiang, Gansu, Ningxia, Inner Mongolia, Qinghai, Tibet, and Sichuan provinces/autonomous regions [
11]. These surveys showed that 20–90% of sheep being infected with average of 56.8%. In this study, 4 regions were selected, and the infection rates ranged from 2.5% to 4.6% in sheep, which was significantly lower than the sheep infection (54%) in 1990’s by Liu et al. [
20] and (9.8%) in 2014 by Qingling et al. [
9] in Xinjiang. It showed that monthly dosing dogs with praziquantel (PZQ) has been used in counties in Xinjiang, which likely play a role in control of echinococcosis [
21] In addition, ongoing with the implementation of the National Prevention and Control of Echinococcosis (2010–2015) (China) [
22], almost all dogs were monthly treated by baited PZQ, which should play a key role in reduction of CE in sheep and cattle recently in northern Xinjiang. It may be limited in term of the true prevalence of CE for using animals from slaughterhouses, given that most (70–75%) of the sheep were less than 16 month-old and 25% of sheep were older than 5 year-old with a few of sheep aged between 3–4 years old (data unpublished). However, the survey for infection rates of sheep and cattle from slaughterhouses is a feasible and economic way to assess the prevalence of animals in the endemic regions [
22].
Statistical analysis indicates that cattle have a higher infection rate than sheep. This is because cattle are normally older than sheep at slaughterhouses. We checked in a slaughterhouse in winter time and found more than 80% were lamb. However, in the same slaughterhouse, the most cattle were over 2 years old. The age is a key factor impacting the prevalence between species of animals [
22].
CE was previously thought to be caused by
E. granulosus sensu lato which had 10 distinct strains/genotypes. However, recently this species has been classified into at least 9 species, including
E. granulosus sensu stricto,
E. granulosus sensu stricto (
s.s.) (the former ‘sheep strain’, G1-3),
E. equinus (horse strain, G4),
E. ortleppi (cattle strain, G5),
E. canadensis (camel strain, G6; pig strain, G7; cervid strain G8 and G10), and
E. felidis (lion strain) from
E. granulosus sensu lato [
23]. The variation is likely caused by broad geographical distribution and a wide range of intermediate hosts [
15,
24]. However, the diversity of
E. granulosus s.s. in Xinjiang is still unclear. In this study, all positive samples were sequenced successfully, we found that the
E. granulosus s.s. species is responsible for CE in Xinjiang based
cox1 sequence analysis. The present study showed that the G1 was the predominant genotype in Xinjiang. The G1 genotype (sheep strain) of
E. granulosus s.s. has been proved to be responsible for the majority of human CE cases in the world [
2,
15], Peru, China, Turkey [
25], Italy [
26] and Iran [
27], and sheep are often associated with its transmission [
27]. In this study, most sheep (90.1%) and human (76.9%) were infected with G1, which similar to Vural et al. [
25].
Previously studies found that G3 genotype was firstly detected in water buffalos [
28], and this genotype was also found in humans, sheep, and cattle [
25,
26,
29,
30]. Consistent with this report, we also found G3 genotype in sheep and humans. G1 is popular in most parts of the world except in India, where the G3 genotype predominates [
29]. The G3 genotype of
E. granulosus has been previously detected from cattle, buffalo, sheep, and human isolates from Italy [
26], Turkey [
25], India [
29], and Iran [
31]. Among the G3 genotype, in this study, only sheep and human were infected and we did not find cattle infected with G3, which is inconsistent with the results of the previous literatures, maybe the number of our samples is limited. However, to our knowledge, this is the first report showing that Xinjiang exists
E. granulosus G3 genotype.
The results showed that Hap1 was the most prevalent haplotype (49/101) in this study. The nucleotide sequence of this haplotype was identical to the most prevalent haplotype previously reported from Europe [
31], the Middle East [
32], South America [
33], and Siberia [
34], indicating Hap1 is the parental haplotype and most distributed. We found that the sequence of Hap13, which was the second most frequent haplotype in our samples (n=9), was 100% identical to the haplotype reported from Italy [
32,
35] and China (Qinghai Province) [
36]. Similarly, Hap14 was previously identified in China [
15,
37], and Hap15 in the Middle East [
32]. The other haplotypes (Hap2-Hap13), which were detected in 33 isolates in the present study, showed complete sequence homology with those previously reported from China [
15], the Middle East [
38], Argentina [
28], Iran [
39], and Eastern Europe [
31].
Among the 15 haplotypes of the 101
cox1 gene fragments, we found some haplotypes, such as Hap5, Hap6, Hap12, and Hap15 that only existed in human CE cases. The blast analysis showed that Hap12 and Hap15 are similar to reported sequences from Europe [
15], however there have been no previous reports of Hap5, Probably due to the small sample size, no cases of sheep infection were found.
The most sequences in the amplified region of cox1 had only one nucleotide replacement, showing a low genetic diversity, although Hap2, Hap3, Hap4, and Hap13 have 2 nucleotide substitutes. The phylogenetic tree and the haplotype network analysis also showed E. granulosus was relatively conserved [40].
In this study, 9 haplotypes of E. granulosus s.s. were identified in human CE cases, whereas, 4 haplotypes were only existed in humans, and 2 of these haplotypes are G3, indicating humans may have limit of haplotypes of E. granulosus and G3 may be more sensitive to human. We identified 6 haplotypes (Hap1, Hap2, Hap4, Hap7, Hap13, and Hap14) as the genotypes both in livestock and humans, indicating that human CE may come from sheep and cattle.
In summary, cystic echinococcosis is still endemic, but at low level in the northern Xinjiang, China compared with the endemic situation in the late of last century. With checking 1,270 sheep and 759 cattle in different areas of the region, 101 isolates of E. granulosus were isolated with 15 haplotypes identified. These contain 2 genotypes, G1 and G3 with G1 being predominant and infecting both humans and sheep/cattle.
Notes
-
CONFLICTS OF INTEREST
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 31560692). The authors would like to express their gratitude and appreciation to the staff working in the slaughterhouses and surgeons /doctors in the hospitals in Xinjiang for their assistance in collecting the samples for the study.
Fig. 1Phylogenetic tree of representative haplotypes Hap1-Hap15 of E. ranulosus from Xinjiang.
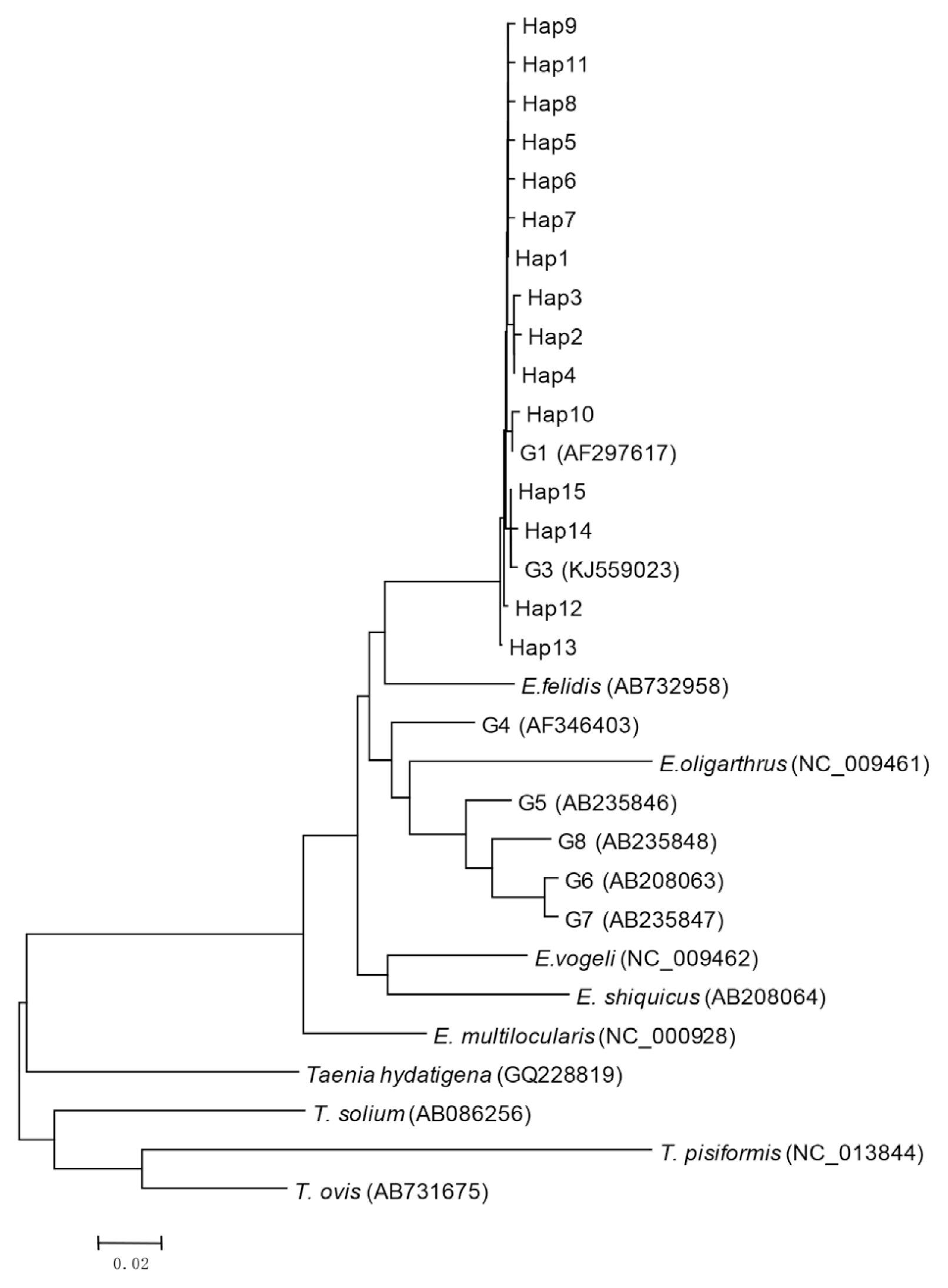
Fig. 2Parsimony network for cox1 combined with the sequences of E. granulosus s.s. from 15 haplotypes. The circular icon represents a haplotype containing identical sequences.
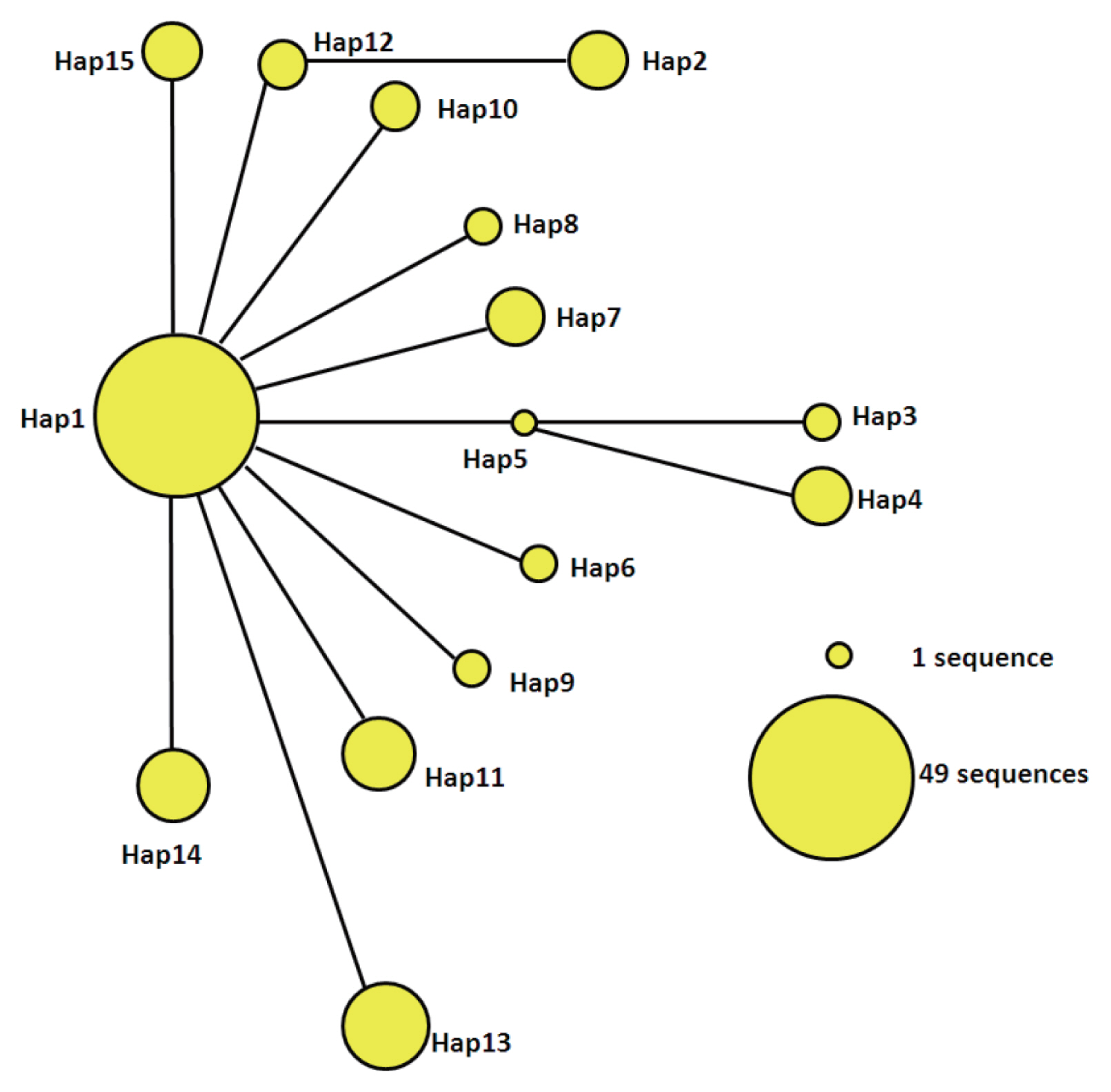
Table 1Prevalence of E. granulosus in sheep and cattle from different regions
Table 1
|
Region |
No. Samples |
No. Positive |
Infection rates (%) |
95% CI |
E. granulosus genotypes |
|
|
G1 (%) |
G3 (%) |
|
Sheep |
|
Urumqi |
518 |
13 |
2.5 |
1.2–3.9 |
12 (92.3) |
1 (7.7) |
|
Yili |
361 |
14 |
3.9 |
1.9–5.9 |
12 (85.7) |
2 (14.3) |
|
Tacheng |
195 |
8 |
4.1 |
1.8–8.0 |
7 (87.5) |
1 (12.5) |
|
Altai |
196 |
9 |
4.6 |
2.1–8.5 |
9 (100) |
0 (0) |
|
Total |
1,270 |
44 |
3.5 |
2.5–4.6 |
40 (90.1) |
4 (9.1) |
|
|
Cattle |
|
Urumqi |
163 |
5 |
3.1 |
4.0–5.7 |
5 (100) |
0 (0) |
|
Yili |
250 |
10 |
4.0 |
1.6–6.4 |
10 (100) |
0 (0) |
|
Tacheng |
190 |
9 |
4.7 |
1.7–7.8 |
9 (100) |
0 (0) |
|
Altai |
156 |
7 |
4.5 |
1.8–9.0 |
7 (100) |
0 (0) |
|
Total |
759 |
31 |
4.1 |
2.7–5.5 |
31 (100) |
0 (0) |
Table 2Prevalence and molecular characterization of E. granulosus in livestock and human from different regions
Table 2
|
Region |
Samples (%) |
Genotypes |
|
G1 (%) |
G3 (%) |
|
Urumqi |
26 (8)a
|
24 (92.3) |
2 (7.7) |
|
Yili |
30 (6)a
|
27 (90) |
3 (10) |
|
Tacheng |
23 (6)a
|
21 (91.3) |
2 (8.7) |
|
Altai |
22 (6)a
|
19 (86.3) |
3 (13.7) |
|
Total |
101 (26)a
|
91 (90.1) |
10 (9.9) |
Table 3 E. granulosus haplotypes characterized by partial cox1 sequence and used for phylogenetic analysis
Table 3
|
Haplotypes |
No. Host origin |
Region |
Accession No. (cox1) |
|
Hap1 |
Sheep (29), Cattle (11), Human (9) |
Urumqi (12), Yili (15), Tacheng (12), Altai (10) |
MH211191 |
|
Hap2 |
Sheep (2), Human 2) |
Urumqi (3), Altai (1) |
MH211192 |
|
Hap3 |
Cattle (2) |
Altai (2) |
MH211193 |
|
Hap4 |
Sheep (3), Human (1) |
Yili (3), Tacheng (1) |
MH211194 |
|
Hap5 |
Human (1) |
Tacheng (1) |
MH211195 |
|
Hap6 |
Human (2) |
Urumqi (2) |
MH211196 |
|
Hap7 |
Cattle (3), Human (1) |
Urumqi (2), Yili (2) |
MH211197 |
|
Hap8 |
Sheep (2) |
Tacheng (2) |
MH211198 |
|
Hap9 |
Sheep (2) |
Yili (2) |
MH211199 |
|
Hap10 |
Cattle (3) |
Urumqi (2), Altai (1) |
MH211200 |
|
Hap11 |
Cattle (6) |
Urumqi (3), Yili (1), Tacheng (1), Altai (1) |
MH211201 |
|
Hap12 |
Human (3) |
Yili (1), Tacheng (2) |
MH211202 |
|
Hap13 |
Sheep (3), Cattle (6) |
Urumqi (2), Yili (3), Tacheng (1), Altai (3) |
MH211203 |
|
Hap14 |
Sheep (4), Human (2) |
Urumqi (2), Yili (1), Tacheng (1), Altai (2) |
MH211204 |
|
Hap15 |
Human (4) |
Yili (2), Tacheng (1), Altai (1) |
MH211205 |
References
- 1. Addy F, Wassermann M, Kagendo D, Ebi D, Zeyhle E, Elmahdi IE, Umhang G, Casulli A, Harandi MF, Aschenborn O, Kern p, Mackenstedt U, Roming T. Genetic differentiation of the G6/7 cluster of Echinococcus canadensis based on mitochondrial marker genes. Int J Parasitol 2017;47:923-931.
- 2. Eckert J, Thompson RC. Historical Aspects of Echinococcosis. Adv Parasit 2017;95:1-64.
- 3. Beato S, Parreira R, Calado M, Grácio MA. Apparent dominance of the G1-G3 genetic cluster of Echinococcus granulosus strains in the central inland region of Portugal. Parasitol Int 2010;59:638-642.
- 4. Oudni-M’rad M, M’rad S, Ksia A, Lamiri R, Mekki M, Nouri A, Mezhoud H, Babba H. First molecular evidence of the simultaneous human infection with two species of Echinococcus granulosus sensu lato: Echinococcus granulosus sensu stricto and Echinococcus canadensis
. Parasitol Res 2016;115:1065-1069.
- 5. Otero-Abad B, Torgerson PR. A systematic review of the epidemiology of echinococcosis in domestic and wild animals. PLoS Negl Trop Dis 2013;7:e2249.
- 6. Lahmar S, Lahmar S, Boufana B, Bradshaw H, Craig PS. Screening for Echinococcus granulosus in dogs: Comparison between arecoline purgation, coproELISA and coproPCR with necropsy in pre-patent infections. Vet Parasitol 2007;144:287-292.
- 7. Zhang W, Ross AG, McManus DP. Mechanisms of Immunity in Hydatid Disease: Implications for Vaccine Development. J Immunol 2008;181:6679-6685.
- 8. Wang N, Xie Y, Liu T, Zhong X, Wang J, Hu D, Wang S, Gu X, Peng X, Yang G. The complete mitochondrial genome of G3 genotype of Echinococcus granulosus (Cestoda: Taeniidae). Mitochondrial DNA A DNA Mapp Seq Anal 2016;27:1701-1702.
- 9. Qingling M, Guanglei W, Jun Q, Xinquan Z, Tianli L, Xuemei S, Jinsheng Z, Huisheng W, Kuojun C, Chuangfu C. Prevalence of Hydatid Cysts in Livestock Animals in Xinjiang, China. Korean J Parasitol 2014;52:331-334.
- 10. Nakao M, Lavikainen A, Iwaki T, Haukisalmi V, Konyaev S, Oku Y, Okamoto M, Ito A. Molecular phylogeny of the genus Taenia (Cestoda: Taeniidae): Proposals for the resurrection of Hydatigera Lamarck, 1816 and the creation of a new genus Versteria. Int J Parasitol 2013;43:427-437.
- 11. Zhang W, Zhang Z, Wu W, Shi B, Li J, Zhou X, Wen H, McManus DP. Epidemiology and control of echinococcosis in central Asia, with particular reference to the People's Republic of China. Acta Trop 2015;141:235-243.
- 12. Bowles Josephine, Ba David, McManus Donald P. Genetic variants within the genus Echinococcus identified by mitochondrial DNA sequencing. Mol Biochem Parasitol 1992;54:165-174.
- 13. Ahmed ME, Eldigail MH, Elamin FM, Ali IA, Grobusch MP, Aradaib IE. Development and evaluation of real-time loop-mediated isothermal amplification assay for rapid detection of cystic echinococcosis. BMC Vet Res 2016;12:202.
- 14. Graichen DAS, Gottstein B, Matsumoto J, Müller N, Zanotto PMA, Ayala FJ, Haag KL. Expression and diversity of Echinococcus multilocularis AgB genes in secondarily infected mice: evaluating the influence of T-cell immune selection on antigenic variation. Gene 2007;392:98-105.
- 15. Nakao M, Li T, Han X, Ma X, Xiao N, Qiu J, Wang H, Yanagida T, Mamuti W, Wen H, Moro PL, Giraudoux P, Craig PS, Ito A. Genetic polymorphisms of Echinococcus tapeworms in China as determined by mitochondrial and nuclear DNA sequences. Int J Parasitol 2010;40:379-385.
- 16. Nakao M, Yanagida T, Konyaev S, Lavikainen A, Odnokurtsev VA, Zaikov VA, Ito A. Mitochondrial phylogeny of the genus Echinococcus (Cestoda: Taeniidae) with emphasis on relationships among Echinococcus canadensis genotypes. Parasitology 2013;140:1625-1636.
- 17. Wang K, Zhang X, Jin Z, Ma H, Teng Z, Wang L. Modeling and analysis of the transmission of Echinococcosis with application to Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region of China. J Theor Biol 2013;333:78-90.
- 18. Farhadi M, Fazaeli A, Haniloo A. Genetic characterization of livestock and human hydatid cyst isolates from northwest Iran, using the mitochondrial cox1 gene sequence. Parasitol Res 2015;114:4363-4370.
- 19. Rongsheng Mi XW, Huang Yan, Zhou Peng, Liu Yuxuan, Chen Yongjun, Chen Jun, Zhu Wei, Chen Zhaoguo. Prevalence and molecular characterization of Cryptosporidium in goats across four provincial level areas in China. PLoS One 2014;9:e111164.
- 20. Liu F, Che X, Chang Q. Prevalence of Hydatid Cysts in livestock in the Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region, PRC. Provo, USA. Brigham Young University Print Services; 1993, pp 177-189.
- 21. Zhang W, Zhang Z, Yimit T, Shi B, Aili H, Tulson G, You H, Li J, Gray DJ, McManus DP, Wang J. A Pilot Study for Control of Hyperendemic Cystic Hydatid Disease in China. PLoS Negl Trop Dis 2009;3:e534.
- 22. Yang S, Wu W, Tian T, Zhao J, Chen K, Wang Q, Feng Z. Prevalence of cystic echinococcosis in slaughtered sheep as an indicator to assess control progress in Emin County, Xinjiang, China. Korean J Parasitol 2015;53:355-359.
- 23. Romig T, Ebi D, Wassermann M. Taxonomy and molecular epidemiology of Echinococcus granulosus sensu lato. Vet Parasitol 2015;213:76-84.
- 24. Kamenetzky L, Gutierrez AM, Canova SG, Haag KL, Guarnera EA, Parra A, García GE, Rosenzvit MC. Several strains of Echinococcus granulosus infect livestock and humans in Argentina. Infect Genet Evol 2002;2:129-136.
- 25. Vural G, Baca AU, Gauci CG, Bagci O, Gicik Y, Lightowlers MW. Variability in the Echinococcus granulosus Cytochrome C oxidase 1 mitochondrial gene sequence from livestock in Turkey and a re-appraisal of the G1–3 genotype cluster. Vet Parasitol 2008;154:347-350.
- 26. Busi M, Šnábel V, Varcasia A, Garippa G, Perrone V, De Liberato C, D’Amelio S. Genetic variation within and between G1 and G3 genotypes of Echinococcus granulosus in Italy revealed by multilocus DNA sequencing. Vet Parasitol 2007;150:75-83.
- 27. Mahami Oskouei M, Ghabouli Mehrabani N, Miahipour A, Fallah E. Molecular characterization and sequence analysis of echinococcus granulosus, from sheep isolates in east azerbaijan province, northwest of iran. J Parasit Dis 2016;40:1-6.
- 28. Capuano F, Rinaldi L, Maurelli MP, Perugini AG, Veneziano V, Garippa G, Genchi C, Musella V, Cringoli G. Cystic echinococcosis in water buffaloes: epidemiological survey and molecular evidence of ovine (G1) and buffalo (G3) strains. Vet Parasitol 2006;137:262-268.
- 29. Sharma M, Sehgal R, Fomda BA, Malhotra A, Malla N. Molecular Characterization of Echinococcus granulosus Cysts in North Indian Patients: Identification of G1, G3, G5 and G6 Genotypes. PLoS Negl Trop Dis 2013;7:e2262.
- 30. Jia WZ, Yan HB, Guo AJ, Zhu XQ, Wang YC, Shi WG, Chen HT, Zhan F, Zhang SH, Fu BQ, Littlewood DT, Cai XP. Complete mitochondrial genomes of Taenia multiceps, T. hydatigena and T. pisiformis: additional molecular markers for a tapeworm genus of human and animal health significance. BMC Genomics 2010;11:447.
- 31. Casulli A, Manfredi MT, La Rosa G, Cerbo AR, Genchi C, Pozio E.
Echinococcus ortleppi and E. granulosus G1, G2 and G3 genotypes in Italian bovines. Vet Parasitol 2008;155:168-172.
- 32. Hassan ZI, Meerkhan AA, Boufana B, Hama AA, Ahmed BD, Mero WMS, Orsten S, Interisano M, Pozio E, Casulli A. Two haplotype clusters of Echinococcus granulosus sensu stricto in northern Iraq (Kurdistan region) support the hypothesis of a parasite cradle in the Middle East. Acta Trop 2017;172:201-207.
- 33. Laurimäe T, Kinkar L, Andresiuk V, Haag KL, Ponce-Gordo F, Acosta-Jamett G, Garate T, Gonzàlez LM, Saarma U. Genetic diversity and phylogeography of highly zoonotic Echinococcus granulosus genotype G1 in the Americas (Argentina, Brazil, Chile and Mexico) based on 8279bp of mtDNA. Infect Genet Evol 2016;45:290-296.
- 34. Konyaev SV, Yanagida T, Nakao M, Ingovatova GM, Shoykhet YN, Bondarev AY, Odnokurtsev VA, Loskutova KS, Lukmanova GI, Dokuchaev NE, Spiridonov S, Alshinecky MV, Sivkova TN, Andreyanov ON, Abramov SA, Krivopalov AV, Karpenko SV, Lopatina NV, Dupal TA, Sako Y, Ito A. Genetic diversity of Echinococcus spp. in Russia. Parasitology 2013;140:1637-1647.
- 35. Casulli A, Bart JM, Knapp J, La Rosa G, Dusher G, Gottstein B, Di Cerbo A, Manfredi MT, Genchi C, Piarroux R, Pozio E. Multi-locus microsatellite analysis supports the hypothesis of an autochthonous focus of Echinococcus multilocularis in northern Italy. Int J Parasitol 2009;39:837-842.
- 36. Ma J, Wang H, Lin G, Craig PS, Ito A, Cai Z, Zhang T, Han X, Ma X, Zhang J, Liu Y, Zhao Y, Wang Y. Molecular identification of Echinococcus species from eastern and southern Qinghai, China, based on the mitochondrial cox1 gene. Parasitol Res 2012;111:179-184.
- 37. Ma J, Wang H, Lin G, Zhao F, Li C, Zhang T, Ma X, Zhang Y, Hou Z, Cai H, Liu P, Wang Y. Surveillance of Echinococcus isolates from Qinghai, China. Vet Parasitol 2015;207:44-48.
- 38. Yanagida T, Mohammadzadeh T, Kamhawi S, Nakao M, Sadjjadi SM, Hijjawi N, Abdel-Hafez SK, Sako Y, Okamoto M, Ito A. Genetic polymorphisms of Echinococcus granulosus sensu stricto in the Middle East. Parasitol Int 2012;61:599-603.
- 39. Pour AA, Hosseini SH, Shayan P. The prevalence and fertility of hydatid cysts in buffaloes from Iran. J Helminthol 2012;86:373-377.