Abstract
Plasmodium vivax is usually considered morbidity in endemic areas of Asia, Central and South America, and some part of Africa. In Thailand, previous studies indicated the genetic diversity of P. vivax in malaria-endemic regions such as the western part of Thailand bordering with Myanmar. The objective of the study is to investigate the genetic diversity of P. vivax circulating in Southern Thailand by using 3 antigenic markers and 8 microsatellite markers. Dried blood spots were collected from Chumphon, Phang Nga, Ranong and, Surat Thani provinces of Thailand. By PCR, 3 distinct sizes of PvMSP3α, 2 sizes of PvMSP3β and 2 sizes of PvMSP1 F2 were detected based on the length of PCR products, respectively. PCR/RFLP analyses of these antigen genes revealed high levels of genetic diversity. The genotyping of 8 microsatellite loci showed high genetic diversity as indicated by high alleles per locus and high expected heterozygosity (HE). The genotyping markers also showed multiple-clones of infection. Mixed genotypes were detected in 4.8% of PvMSP3α, 29.1% in PvMSP3β and 55.3% of microsatellite markers. These results showed that there was high genetic diversity of P. vivax isolated from Southern Thailand, indicating that the genetic diversity of P. vivax in this region was comparable to those observed other areas of Thailand.
-
Key words: Plasmodium vivax, malaria, genetic diversity, antigenic marker, microsatellite marker
INTRODUCTION
Malaria remains one of the significant global health problems. Despite enormous control efforts over many decades, about 40% of the world’s population who lives in more than 140 countries are at risk of malaria [
1]. South-East Asia suffers the highest burden for
Plasmodium vivax. 74% of the
P. vivax cases are in South-East Asia followed by 11% in Eastern Mediterranean Region, and 10% African Region, respectively [
2]. In Thailand,
P. vivax is the most prevalent and accounts for 80% of the total infection [
3]. Unlike
P. falciparum,
P. vivax has a unique dormant stage that can cause relapse in weeks or months after the initial infection. These latent hypnozoites complicate the ability to classify as re-infection or recurrent infection and could cause treatment failure due to the relapse of hypnozoites. This phenomenon contributes to the parasite resistance to standard antimalarial regimens, especially the emergence of chloroquine resistance [
4] and the use of primaquine, an anti-hypnozoite drug against
P. vivax relapse, especially in glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase deficiency patients [
5]. Furthermore,
P. vivax infected only reticulocytes [
6] and represented only in the blood circulation about 0.5–2% [
7]. At present, cultivation of
P. vivax is challenging to maintain in vitro, resulting in a limitation on molecular research. Only blood samples from
P. vivax infected patients are the source for molecular studies. Multiple clone infections are often observed with
P. vivax infection, which are caused by a single mosquito bite carrying a mixture of parasites or different mosquitoes bite each taking a single clone [
8–
10]. The multiple parasitic she infection usually poses a higher risk of treatment failure [
11]. Hence, understanding the genetic diversity of parasite populations would reveal their population dynamics and epidemiology in different regions which could help in assessment of the effectiveness of malaria control.
PCR/RFLP technique is a reliable genotyping method for large-scale genetic analysis of
P. vivax even though the technique demands time-consuming investigation of restriction fragments. The most polymorphic markers frequently used for PCR/RFLP analysis of
P. vivax are members of Merozoite surface protein (MSP) genes,
MSP1, MSP3α, and
MSP3β. On the contrary, sequencing usually offers higher resolution at the nucleotide sequence level, but it is not applicable for multiple-clone of infections. Recently, microsatellite analysis is the method for detection of size polymorphism using capillary electrophoresis and subsequent analysis by software such as GeneMapper or GeneMarker. This method uses highly polymorphic and reliable markers for analysis of
P. vivax population [
12–
16] owning to its capability to detect differences among closely related species of
P. vivax [
17–
19].
The detailed knowledge of the genetic diversity of
P. vivax is essential for the understanding of the dynamics of malaria disease transmission in this region. The high genetic diversity of
P. vivax population has been reported in the Thai–Myanmar border [
20,
21]. However, little is known about the genetic diversity of
P. vivax circulating strains in endemic areas of Southern Thailand. This study evaluates the genetic diversity of
P. vivax isolated from Southern Thailand using 3 merozoite surface genes markers;
MSP1 F2,
MSP3α, and
MSP3β genes, and highly polymorphic 8 microsatellite markers; Pv1.501, Pv3.27, Pv6.34, Pv8.504, Pv14.297, Pv3.502, Pv11.162, and MS1.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Study sites and blood collection
One hundred and forty-seven patients who attended malaria clinics of the Office of Disease Prevention and Control 11, Thailand, from 2012 to 2015 were involved in this study.
Fig. 1 shows sample collecting sites and the number of samples collected from each area.
P. vivax infected individuals were treated with 25 mg/kg chloroquine and 0.5 mg/kg primaquine for 14 days as the first-line drugs according to the treatment protocol of the Ministry of Public Health, Thailand. Approximately 80 μl of blood that had been microscopically confirmed for
P. vivax infection was collected by finger-prick and spotted on 3M filter paper, (Whatman International Ltd., Maidstone, UK) and let the blood spots air dry at room temperature before keeping in a plastic zip bag. This study was approved by the Ethics Committee of Faculty of Medicine, Prince of Songkla University (REC57-0077-19-2). Written informed consent was obtained from all the participants.
P. vivax DNA from dried blood spot was extracted by QIAamp DNA Mini Kit (Qiagen, Hilden, Germany) following the manufacturer’s instruction. The final volume of the DNA solution was eluted in volume of 100 μl. Nested PCR was used to confirm human malaria species based on the small subunit (SSU) 18S ribosomal RNA (18S rRNA) gene as described by the previous study [
22].
Plasmodium vivax genotyping
Amplification of
P. vivax MSP3α, MSP3β, and
MSP1 F2 genes were performed as previously described [
13,
16,
23]. The final reaction volume of 20 μl PCR comprised 0.2 μl of each primer, 10×of PCR buffer, 0.2 mM of deoxynucleotides (dNTPs), 1 mM of MgCl
2 and 0.5 unit of
Taq DNA polymerase (Invitrogen, Carlsbad, California, USA). Primers for PCR amplification are shown in
Table 1. Two μl of genomic DNA was added in the first round PCR and 1.5 μl of the primary PCR product was used in the second round of PCR. The concentration of MgCl
2 for
PvMSP3 genes amplification was 2.5 mM and for
PvMSP1 F2 gene was 1 mM. Ten μl of the amplified PCR product was mixed with 2 μl of loading buffer and applied to 1.8% agarose gel.
Genotyping P. vivax antigenic markers were done by nested PCR/RFLP assays using restriction enzyme HhaI, PstI and, AluI (NEB Inc., Beverly, Massachusetts, USA), respectively. Five μl of the final product was applied to 2% agarose gel electrophoresis. The size of the amplified fragments was estimated by comparison with a 100 bp ladder marker set.
Microsatellite markers containing 8 polymorphic markers, i.e., Pv1.501, Pv3.27, Pv6.34, Pv8.504, Pv14.297, Pv3.502, Pv11.162, and MS1 were analyzed using the methods as described previously [
18,
24]. The microsatellite primers are summarized in
Table 1. Two μL of genomic DNA were used as a template for the first PCR amplification, and 1 μl of the primary amplification product was carried out as a template for the secondary amplification. ABI 3130 Genetic Analyzer and GeneMapper
® software version 4.0 (Applied Biosystems, Foster City, California, USA) was used to measure an allele in each locus compared to LIZ-500 size standards. The multiplicity of infection (MOI) of a given isolate was measured by calculating the number of different alleles at each of the 8 loci. Single infections were those with only 1 peak per locus in electropherogram in any of the genotyped loci, while multiple-clone infections were defined as more than one peak at each locus and the height of minor peak was at least 1/3 of the height of the predominant allele present for each locus [
25]. The genetic diversity was measured using the frequency of the predominated allele at each locus to calculate i) the mean number of alleles (
A), which were calculated from all detected alleles at each locus divided by the total number of samples, and ii) the expected heterozygosity (
HE) at a given locus, which
HE=[n/(n–1)][1-∑pi
2], where “n” is the number of samples and pi is the frequency of the i
th allele.
HE ranges between 0 and 1; a value close to 1 indicated high genetic diversity levels in the population [
10]. Both parameters were computed using version 2.9.3 of FSTAT software [
26]. Multilocus linkage disequilibrium (LD) was calculated using a standardized index of association (
ISA) [
27,
28]. Only the dominant alleles were considered to verify linkage. This test compares the variance (
VD) of the number of alleles shared between all pairs of haplotypes observed in the population (
D) with the variance expected under random association of alleles (
VE) as follows:
ISA=(
VD/
VE-1) (
r-1), where
r is the number of loci analyzed. The analysis was performed using the LIAN 3.7 software [
29].
RESULTS
Out of the 147 microscopically confirmed P. vivax cases recruited from various regions of Southern Thailand, nested PCR results indicated that 130 were mono-P. vivax infection, 4 were mono-P. falciparum, 3 were mixed infection of P. vivax and P. falciparum, and 10 samples were unable to be amplified due to minimal quantities of parasite DNA. Total of 130 P. vivax samples were isolated from 4 provinces: 50 from Chumphon, 7 from Phang Nga, 58 from Ranong, and 15 from Surat Thani, respectively.
Characterization of Pvmsp1 F2, Pvmsp3α and Pvmsp3β
PvMSP3α gene of
P. vivax was successfully amplified in 62 out of 130 samples (47.70%) (Chumphon=21/50, Phang Nga=5/7, Ranong=35/58, and Surat Thani=1/15). Three different allele-types were detected in different allele sizes of 1.9, 1.5, and 1.1 kb which were categorized as types A, B, and C, respectively. These 3 genetic types have been recognized as a previously described study [
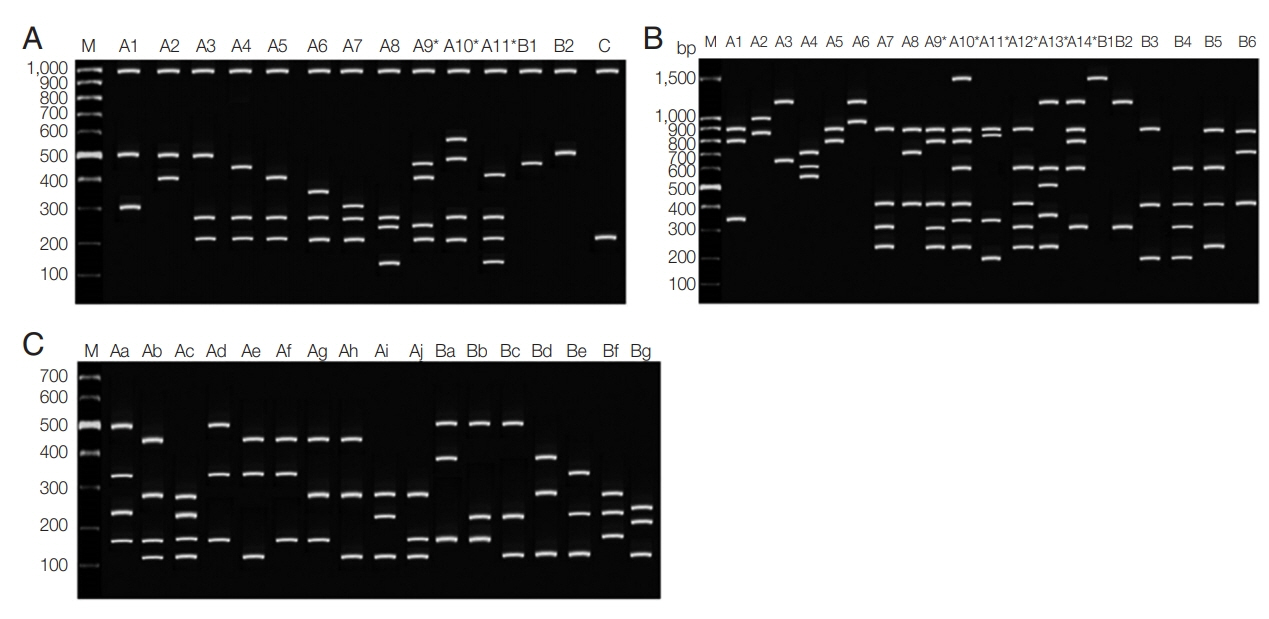
38]. Type A which corresponded to the sequence of the Belem strain and types B and C were the deletions close to the N-terminus of the central alanine-rich domain. In this report, 49/62 (79%) was found in type A, 3/62 (3.3%) was type B, and type C was 11/62 (17.7%), respectively. No mixed genotypes were identified. After
HhaI digestion, the conservation of the large fragment was seen (1,000 bp) and fragments less than 100 bp was not disregarded [
23]. In this study, a total of 14 patterns were found with DNA fragment sizes between 150–600 bp (
Fig. 2A). There were 11 haplotypes of type A (A1–A11), 2 haplotypes of type B (B1–B2), and one variant of type C. The highest frequency was 16% observed with haplotype A3 (fragment size 500/280/210 bp). Mixed genotypes were found in 3 isolates (4.8%) including allele type A9–A11 when the summed size of the restriction amplicon exceeded the size of the PCR products. The frequencies of each pattern are shown in
Table 2.
For
PvMSP3β gene, 60/130 (46.15%) of the samples were successfully amplified (Chumphon=17/50, Phang Nga=3/7, Ranong=35/58, Surat Thani=1/15). The alleles differed radically into 2 types: type A showed size polymorphism with ~1.7–2.2 kb, which corresponds to the insertions of sequences in the central Ala-rich domain of the gene. Another type was the amplicon size ~1.4–1.5 kb, which categorized as type B. This type is considered to be concordant with the Belem reference strain [
16]. The PCR products of
PvMSP3β showed type A in 43/60 (71.67%) and 16/60 of type B (26.67%). Another one isolate (1.67%) was considered a mixed infection because more than one PCR products of different sizes were observed. After digestion with
PstI restriction enzyme, a total of 20 restriction patterns with DNA fragment sizes between 150–1,500 bp were found from 55/60 samples (
Table 3;
Fig. 2B). Among them, alleles A1 (900+800+350) was the most frequent (16.4%). Mixed infection was detected in 16 isolates (29.1%), including allele type A9–A14.
PvMSP1 F2 gene could be amplified from 67/130 (51.54%) samples (Chumphon=29/50, Phang Nga=2/7, Ranong =27/58 and Surat Thani=9/15). Two distinct size variants were type A (1,150 bp) and type B (1,090 bp). These 2 classified types were based on the polymorphic in size of 100 Thai
P. vivax isolates which described in the previous study [
13]. After
AluI restriction enzyme digestion, PCR/RFLP revealed distinct 17 patterns with fragments containing between 140–500 bp (
Fig. 2C). The allele frequencies of
PvMSP1 F2 gene are shown in
Table 4. No mixed genotyped was noticed.
Microsatellite genotyping of P. vivax
Eight microsatellite loci of
P. vivax were successfully genotyped from 103/130 (79.2%) samples, (38/55 from Chumphon, 4/7 from Phang Nga, 46/58 from Ranong and 15/15 from Surat Thani). The microsatellite characteristics of the 8 microsatellite loci used in
P. vivax genotyping are described in
Table 5. A total of 102 different alleles, included predominate and minor peaks, were observed in all the samples and markers. The predominant alleles data set at each locus were used to calculate the genetic diversity with an average
HE=0.82 (SD=±0.14) for all 8 microsatellite markers. Only Pv11.162 was the least polymorphic markers (
HE=0.49). The average number of alleles (
A) was 12.25 (SD=±6.2), ranged from 5 (locus MS1) to 24 (locus 3.27). The average number of distinct alleles per locus values were calculated from all detected alleles at each locus and divided by the total number of samples amplified was 1.12 (SD=±0.12). A total of 103 samples, these were 46 samples (Chumphon=16/38, Phang Nga=2/2, Ranong=24/46, and Surat Thani=4/15) determined to have single clone
P. vivax infection and the 57 samples determined to have multiple clone
P. vivax infections. The highest multiple clone infections were found in loci Pv1.501 (30/95 samples) and Pv3.27 (25/100 samples), while Pv 3.502, Pv6.34 and 11.162 were found multiple clone infections in 8/99, 7/97 and 7/94 samples, respectively. Among the 3 loci include Pv8.504, Pv14.297 and MS1 were the lowest multiple clone infections with 4/100, 3/102 and 2/47 samples, respectively. Multiple of allele sizes at 8 loci in this study are described in
Table 6.
The number of alleles (
A) among the 4 sites was significantly different at
P<0.05 by ANOVA (
Table 7). The overall mean expected heterozygosity (
HE) was 0.77±SE 0.01 (rang 0.75 to 0.79), and the average number of alleles (
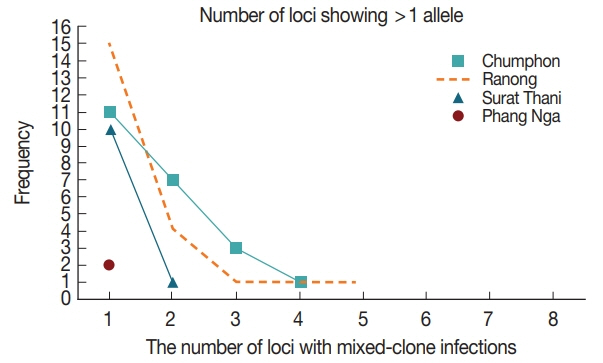
A) was 6.6 alleles± SD 3.07 (range 2.8 to 9.2). Multiple-clone infections were found from 57 (55.3%) samples resulting in MOI of 1.63. Up to 5 different markers were detected from one patient in Ranong province (
Fig. 3). Significant LD was observed in every province (Chumphon -
IAS=0.0385,
P<0.000, Phang Nga -
IAS=0.1235,
P<0.001, Ranong -
IAS=0.2488,
P<0.0001 and Surat Thani -
IAS=0.4442,
P<0.0001) suggesting inbreeding of the parasites.
DISCUSSION
Over the last 4 decades, the prevalence of
P. vivax in Thailand has been rising from 20% to 50% of all malarial cases [
30]. Two main mechanisms have been proposed to explain the phenomena: (i) a competitive suppression between species during co-infection within the human host [
31–
33]; and (ii) a difference in vector competence and capacity for
P. falciparum and
P. vivax by mosquito vector species [
34–
36]. This study aimed to analyze the genetic diversity of
P. vivax in the Southern part of Thailand, mainly focusing on the high malaria prevalent provinces such as Chumphon, Ranong, Surat Thani, and Phang Nga. The genetic characterization of the parasite populations was analyzed using the single-copy genes;
PvMSP1 F2,
PvMSP3α,
PvMSP3β and 8 polymorphic microsatellite markers. Several previous studies have used this type of genetic markers to study the genetic diversity in endemic malaria transmission [
13,
15,
18,
19,
23]. The limitation of this study was that there was an insufficient amount of DNA template in the samples owing to a small volume (80 μl) of the collected blood sample. Nevertheless, we successfully amplified about 63% of the samples.
Three distinct sizes of PCR products for
PvMSP3α were detected for 3 different allelic variants. They were 1.9 kb (Type A), 1.5 kb (Type B) and 1.1 kb (Type C). The results were concordant with allele observed in India, Papua New Guinea, Western Thailand, Afghanistan, and Pakistan [
37–
40], while the different band size of approximately 0.75 kb or 300 bp was reported in Pakistan [
41]. Genotyping
PvMSP3α marker also showed mixed genotypes. This was concordant with the previous reports from Papua New Guinea, Western of Thailand, Iran, Pakistan, India and French Guiana where a significant degree of mixed genotype was observed between 2–36% [
23,
38–
40,
42,
43].
PvMSP3β gene in the present study had produced 2 categories, Type A (1.7–2.2 kb) and Type B (1.4–1.5 kb). The finding was similar to those observed along the Thailand–Myanmar border, the Thailand–Cambodia border and area of North-West Frontier Province (NWFP) of Pakistan [
44,
45], Anhui and Guizhou provinces of Chinese [
16], and India [
46]. The extra allele type ~0.65 kb (Type C) was previously reported in Mae Sod, Thailand [
16]. Our study showed that Type A (1.7–2.2 kb) was the highest frequency of vivax malaria circulating in Southern Thailand. Similarly, the report from Anhui, Hainan, Yunnan, and Myanmar [
23] also indicated a higher prevalence of Type A alleles. Type B (1.4–1.5 kb) was found as 60.4% of
P. vivax populations of Western Thailand and 85% of India [
46] whereas from Chinese Bengbu and Guangxi samples, both A and B types were equally prevalent [
23]. Mixed infection with
PvMSP3β was detected in one sample (1.67%) from Ranong which was genotyped by PCR. The PCR/RFLP of
PstI analysis further revealed the presence of 16 mixed alleles (29.1%) in type A genotype, isolated from 10 Ranong and 2 Phang Nga provinces. Previously, the mixed infection was reported as 4% in Thailand–Myanmar border and the Thailand–Cambodia border [
45], 20.5% in Western Thailand [
37] and 5.6% in China [
16].
For
PvMSP1 Fragment 2 genotyping, 2 sizes differences were found: Type A (1,150 bp) and Type B (1,090 bp). The result was identical to the previous studies [
13,
21]. Size polymorphisms could distinguish a total of 17 distinct genotypes after digesting with
AluI (
Table 3), and no mixed infection was observed whereas report from
P. vivax genotyping from endemic regions of Thailand showed 12 patterns and 12.5% with multiple genotypes [
21]. This would indicate that the various clones of infection could occur in the same host but one time of mosquito biting would transfer distinct clones into hosts [
21]. The overall number of alleles
(A) for 8 markers was 12.6 in this study, and it was significantly different among the 4 sites, at
P<0.05 by ANOVA test (
Table 5). The result of the number of alleles (
A) in this study was concordant with the other studies from Asia [
18–
20,
47,
48]. High
HE values were observed in
P. vivax isolates from Southern Thailand (0.87) (
Table 4) whereas the isolates from South Korea was 0.43 [
47] indicating the high genetic diversity of
P. vivax in Southern Thailand. Multiple clone infection was found for 55.3% (57/103) in the 4 study areas, particularly in Surat Thani, Chumphon, Phang Nga and Ranong, respectively. However, this result would reflect sample sizes from these regions (
Table 5). The multiplicity of infection of this study was 1.63 which also agreed with the findings from previous reports [
18,
19,
49].
In this study, genotyping the P. vivax from 4 malaria-endemic provinces of Southern Thailand using 3 merozoite surface protein genes PvMSP3α, PvMSP3β, PvMSP1 F2 genes, and 8 microsatellite markers revealed 14 RFLP patterns of PvMSP3α, 20 of PvMSP3β, and 17 of PvMSP1 F2. Mixed genotypes were present in 4.8% of PvMSP3α and 29.1% of PvMSP3β genes. High HE values were also observed. 55.3% of samples carried more than one P. vivax parasite infection. However, immune selection could interfere with the data interpretation of PCR/RFLP on antigenic marker loci. These results revealed high genetic diversity P. vivax isolates from Southern Thailand. The information would help in understanding the epidemiology of P. vivax parasites and controlling and elimination of the malaria parasite in Southern Thailand.
Notes
-
CONFLICT OF INTEREST
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS
The authors would like to thank the staffs of Malaria Clinics of the Office of Disease Prevention and Control 11, Thailand. The present work was supported by Prince of Songkla University, Thailand (Grant No. MET570512S).
Fig. 1Map of the study sites in Southern Thailand.
Fig. 2Restriction fragment length polymorphism patterns of Plasmodium vivax. (A) PvMSP3α after PCR/RFLP using HhaI enzyme. (B) PvMSP3β after PCR/RFLP using PstI enzyme. (C) PvMSP1 F2 after PCR/RFLP using AluI enzyme. M represented 100-bp marker.
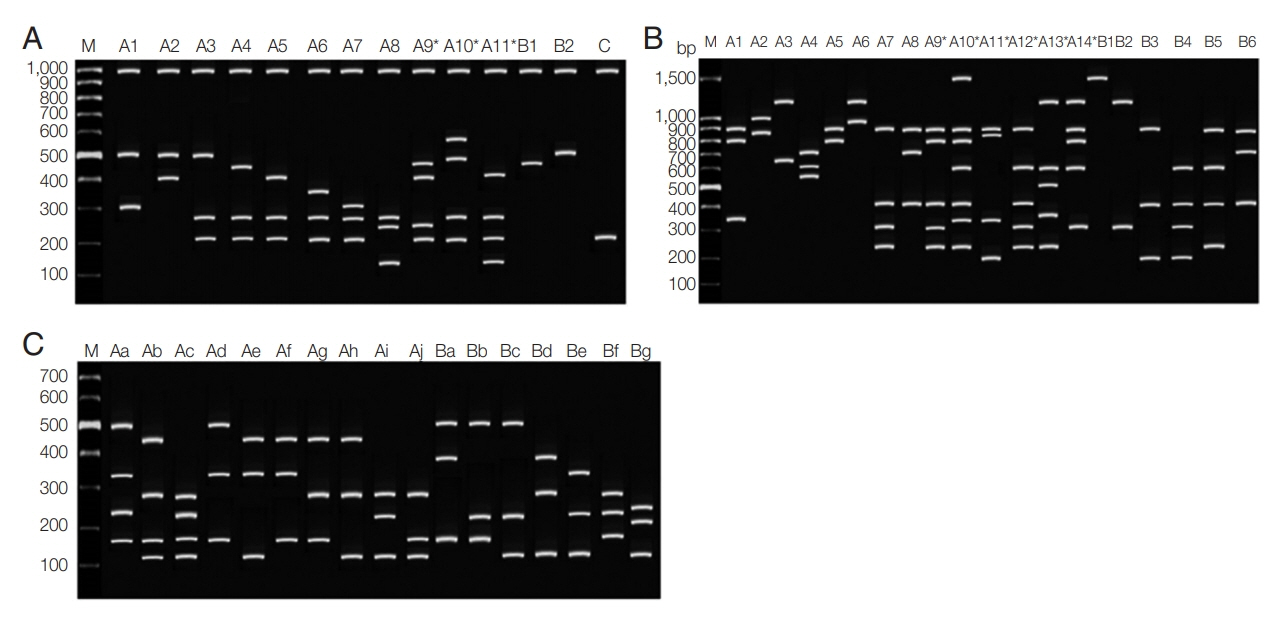
Fig. 3Frequency distribution of the number of loci with mixed-clone infections isolated from Southern Thailand. Fifty-seven multiple-clone infections were detected for Chumphon, Ranong, Surat Thani and Phang Nga provinces, respectively.
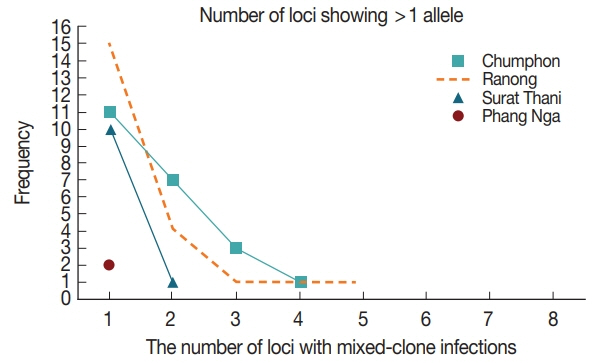
Table 1Primer sequences for Plasmodium vivax genotyping
Table 1
|
Gene |
Primer |
Sequence (5′→3′) |
Reference |
|
Merozoite surface protein gene markers |
|
PvMSP3α (N1) |
3α-OF |
CAGCAGACACCATTTAAGG |
Bruce et al., 1999 [23] |
|
3α-OR |
CCGTTTGTTGATTAGTTGC |
|
|
PvMSP3α (N2) |
3α-NF |
GACCAGTGTGATACCATTAAC |
|
|
3α-NR |
ATACTGGTTCTTCGTCTTCAGG |
|
|
PvMSP3β (N1) |
3β-OF |
GGTATTCTTCGCAACACTC |
Yang et al., 2006 [16] |
|
3β-OR |
GCTTCTGATGTTATTTCCAG |
|
|
PvMSP3β (N2) |
3β-NF |
CGAGGGGCGAAATTGTAAACC |
|
|
3β-NR |
GCTGCTTCTTTTGCAAAGG |
|
|
PvMSP1 F2 (N1) |
VM1-O2F |
GATGGAAAGCAACCGAAGAAGGGAAT |
Imwong et al., 2005 [13] |
|
VM1-O2R |
AGCTTGTACTTTCCATAGTGGTCCAG |
|
|
PvMSP1 F2 (N2) |
VM1-N2F |
AAAATCGAGAGCATGATCGCCACTGAGAAG |
|
|
|
Microsatellite markers |
|
Pv1.501 |
Forward |
TCCTGTAACTCCTGCTCTGT |
Imwong et al., 2007 [18] |
|
motif: GGTGAGA |
Reverse |
CTTACTTCTACGTGCCCACT |
|
|
Forward, s-n |
6FAM-AATTGTAGTTCAGCCCATTG |
|
|
Pv3.27 |
Forward |
AAGCTGCACTGAATTATGCT |
|
|
motif: AAAC |
Reverse |
TTCCAAATGTATGTGCAGTC |
|
|
Forward, s-n |
6FAM-AGCACAAGCATATGCAAAA |
|
|
Pv3.502 |
Forward |
CCATGGACAACGGGTTAG |
|
|
motif: AACGGATG |
Reverse |
TCCTACTCAGGGGGAATACT |
|
|
Forward, s-n |
HEX-GTGGACCGATGGACCTAT |
|
|
Pv6.34 |
Forward |
CAAATCATGGTAGCCTCCTA |
|
|
motif: AC |
Reverse |
GCTATGCATGTGTGGATGT |
|
|
Forward, s-n |
6FAM-TTAAGCTTCTGCATGCTCTT |
|
|
Pv8.504 |
Forward |
AAAAGACTAGGCAGTTGACG |
|
|
motif: TGACCAA |
Reverse |
AGTGTGTGTAGTGGGTGGAG |
|
|
Forward, s-n |
HEX-TCTTCTCGTTCTCCTTTTCTG |
|
|
Pv14.297 |
Forward |
TGACATCTTTCAAATATTCCTTT |
|
|
motif: AAG |
Reverse |
TGAAAAATGTTCCGCTACTT |
|
|
Forward, s-n |
HEX-TACACCCTTTAGGTCCTCGT |
|
|
Pv11.162 |
Forward |
GTAGGAACACGCCACGTT |
|
|
motif: ATAC |
Reverse |
TAAATGACACTTTGGCTTCC |
|
|
Forward, s-n |
HEX-TTTGTTAGGAGATCCGTCTG |
|
|
MS1 |
Forward |
6-FAM TCAACTGTTGGAAGGGCAAT |
Karunaweera et al., 2007 [24] |
|
motif: GAA |
Reverse |
ctgtcttTTGCTGCGTTTTTGTTTCTG |
|
Table 2Frequencies of each allelic fragment pattern of PvMSP3α gene in 62 isolates of Plasmodium vivax from Southern Thailand as identified by PCR/RFLP after digested with HhaI restriction enzyme
Table 2
|
Genotype (kb) |
Allele type |
HhaI restriction fragments (bp) |
No. of samples of each Province |
Total No. of samples |
Frequency (%) |
|
|
Chumphon |
Phang Nga |
Ranong |
Surat Thani |
|
A (~1.9) |
A1 |
1,000+500+300 |
2 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
2 |
3.23 |
|
A2 |
1,000+500+400 |
0 |
0 |
2 |
0 |
2 |
3.23 |
|
A3 |
1,000+500+280+210 |
1 |
0 |
9 |
0 |
10 |
16.13 |
|
A4 |
1,000+450+280+210 |
1 |
1 |
7 |
0 |
9 |
14.53 |
|
A5 |
1,000+400+280+210 |
5 |
0 |
3 |
0 |
8 |
12.9 |
|
A6 |
1,000+350+280+210 |
2 |
1 |
3 |
1 |
6 |
9.68 |
|
A7 |
1,000+300+280+200 |
0 |
0 |
3 |
0 |
4 |
6.45 |
|
A8 |
1,000+300+250+150 |
1 |
2 |
2 |
0 |
5 |
8.06 |
|
A9*
|
1,000+450+400+250+200 |
0 |
0 |
1 |
0 |
1 |
1.61 |
|
A10*
|
1,000+550+480+280+200 |
0 |
0 |
1 |
0 |
1 |
1.61 |
|
A11*
|
1,000+400+280+210+150 |
1 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
1 |
1.61 |
|
|
B (~1.5) |
B1 |
1,000+500 |
0 |
0 |
1 |
0 |
1 |
1.61 |
|
B2 |
1,000+500 |
0 |
0 |
1 |
0 |
1 |
1.61 |
|
|
C (~1.1) |
C1 |
1,000+200 |
8 |
1 |
2 |
0 |
11 |
17.74 |
|
|
Total |
|
|
21 |
5 |
35 |
1 |
62 |
100 |
Table 3Frequencies of each allelic fragment pattern of PvMSP3β gene in 55 isolates of Plasmodium vivax from Southern Thailand as identified by PCR/RFLP after digested with PstI restriction enzyme
Table 3
|
Genotype (kb) |
Allele type |
PstI restriction fragment (bp) |
No. of samples of each Province |
Total No. of sample |
Frequency (%) |
|
|
Chumphon |
Phang Nga |
Ranong |
Surat Thani |
|
A (~1.7–2.2) |
A1 |
900+800+350 |
4 |
0 |
5 |
0 |
9 |
16.36 |
|
A2 |
1,000+850 |
2 |
0 |
3 |
0 |
5 |
9.09 |
|
A3 |
1,200+650 |
4 |
0 |
1 |
1 |
6 |
10.91 |
|
A4 |
700+600+550 |
1 |
0 |
2 |
0 |
3 |
5.45 |
|
A5 |
900+800 |
0 |
0 |
1 |
0 |
1 |
1.82 |
|
A6 |
1,200+980 |
0 |
1 |
0 |
0 |
1 |
1.82 |
|
A7 |
900+400+300+250 |
0 |
0 |
1 |
0 |
1 |
1.82 |
|
A8 |
900+700+400 |
0 |
0 |
1 |
0 |
1 |
1.82 |
|
A9*
|
900+800+400+300+250 |
0 |
0 |
4 |
0 |
4 |
7.27 |
|
A10*
|
1,500+900+800+600+400+350+250 |
0 |
0 |
1 |
0 |
1 |
1.82 |
|
A11*
|
900+850+350+150 |
0 |
0 |
3 |
0 |
3 |
5.45 |
|
A12*
|
900+600+400+300+250 |
1 |
0 |
1 |
0 |
2 |
3.64 |
|
A13*
|
1,200+600+500+380+200 |
0 |
1 |
0 |
0 |
1 |
1.82 |
|
A14*
|
1,200+900+800+600+300 |
0 |
1 |
1 |
0 |
2 |
3.64 |
|
|
B (~1.4–1.5) |
B1 |
1,500 |
2 |
0 |
4 |
0 |
6 |
10.91 |
|
B2 |
1,200+300 |
0 |
0 |
1 |
0 |
1 |
1.82 |
|
B3 |
900+400+200 |
0 |
0 |
1 |
0 |
1 |
1.82 |
|
B4 |
600+400+300+200 |
0 |
0 |
1 |
0 |
1 |
1.82 |
|
B5 |
900+600+400+250 |
0 |
0 |
3 |
0 |
3 |
5.45 |
|
B6*
|
900+700+400 |
3 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
3 |
5.45 |
|
|
Total |
|
|
17 |
3 |
34 |
1 |
55 |
100 |
Table 4Frequencies of each allelic fragment pattern of PvMSP1 F2 gene in 67 isolates of Plasmodium vivax from Southern Thailand as identified by PCR/RFLP after digested with AluI restriction enzyme
Table 4
|
Genotype (kb) |
Allele type |
AluI restriction fragment (bp) |
No. of samples of each Province |
Total No. of sample |
Frequency (%) |
|
|
Chumphon |
Phang Nga |
Ranong |
Surat Thani |
|
A |
Aa |
170+230+320+450 |
1 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
1 |
1.49 |
|
Ab |
140+170+280+450 |
1 |
0 |
2 |
4 |
7 |
10.45 |
|
Ac |
140+170+230+280 |
1 |
0 |
1 |
0 |
2 |
2.99 |
|
Ad |
170+320+500 |
2 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
2 |
2.99 |
|
1,150 pb |
Ae |
140+320+480 |
0 |
0 |
4 |
0 |
4 |
5.97 |
|
Af |
170+320+480 |
3 |
0 |
0 |
2 |
5 |
7.45 |
|
Ag |
170+280+480 |
0 |
1 |
0 |
1 |
2 |
2.99 |
|
Ah |
140+280+480 |
3 |
1 |
5 |
0 |
9 |
13.42 |
|
Ai |
140+230+280 |
7 |
0 |
3 |
0 |
10 |
14.92 |
|
Aj |
140+170+280 |
0 |
0 |
1 |
0 |
1 |
1.49 |
|
|
B |
Ba |
170+380+500 |
1 |
0 |
2 |
0 |
3 |
4.48 |
|
Bb |
170+230+500 |
0 |
0 |
2 |
0 |
2 |
2.99 |
|
Bc |
140+230+500 |
0 |
0 |
3 |
1 |
4 |
5.97 |
|
1,090 pb |
Bd |
140+280+380 |
4 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
4 |
5.97 |
|
Be |
140+230+320 |
1 |
0 |
1 |
0 |
2 |
2.99 |
|
Bf |
170+230+280 |
0 |
0 |
2 |
1 |
3 |
4.48 |
|
Bg |
140+210+240 |
5 |
0 |
1 |
0 |
6 |
8.96 |
|
|
Total |
|
|
29 |
2 |
27 |
9 |
67 |
100 |
Table 5All microsatellite fragment sizes and allele frequency of Plasmodium vivax isolates from Southern Thailand
Table 5
|
Marker (size, bp) |
Microsatellite analysis |
|
|
Pv1.501 (76–195) |
Pv 3.27 (85–240) |
Pv 3.502 (128–265) |
Pv 6.34 (136–200) |
Pv 8.504 (191–317) |
Pv 11.162 (172–228) |
Pv 14.297 (180–229) |
MS1 (228–246) |
|
Samples amplified |
95 |
100 |
99 |
97 |
100 |
94 |
102 |
47 |
|
|
All detected alleles |
128 |
125 |
109 |
104 |
104 |
97 |
109 |
49 |
|
|
Microsatellite fragmentsa (%) |
76 (0.8) |
92 (12.6) |
134 (2.8) |
134 (1.9) |
198 (9.5) |
176 (1.0) |
180 (6.4) |
225 (12.2) |
|
83 (5.4) |
96 (3.1) |
142 (4.6) |
136 (1.0) |
205 (10.5) |
180 (70.1) |
183 (2.8) |
228 (36.7) |
|
90 (10.8) |
100 (5.5) |
150 (27.5) |
138 (3.8) |
212 (21.9) |
184 (16.5) |
186 (9.2) |
231 (22.4) |
|
97 (16.2) |
104 (7.9) |
158 (8.3) |
140 (4.8) |
219 (26.7) |
188 (4.1) |
189 (12.8) |
234 (10.2) |
|
104 (14.6) |
108 (5.5) |
166 (15.6) |
142 (22.1) |
226 (6.7) |
192 (3.1) |
192 (22.0) |
237 (2.0) |
|
111 (13.1) |
112 (7.1) |
174 (9.2) |
144 (6.7) |
233 (8.6) |
196 (5.2) |
195 (35.8) |
240 (16.3) |
|
118 (6.9) |
116 (6.3) |
182 (3.7) |
146 (11.5) |
247 (2.9) |
|
198 (10.1) |
|
|
125 (3.1) |
120 (4.7) |
190 (0.9) |
148 (12.5) |
254 (3.8) |
|
201 (0.9) |
|
|
132 (7.7) |
124 (1.6) |
198 (12.8) |
150 (3.8) |
261 (1.0) |
|
|
|
|
139 (4.6) |
128 (3.1) |
206 (7.3) |
152 (10.6) |
268 (2.9) |
|
|
|
|
146 (4.6) |
132 (8.7) |
222 (1.8) |
154 (5.8) |
275 (2.9) |
|
|
|
|
153 (4.6) |
136 (7.9) |
246 (5.5) |
156 (4.8) |
289 (2.9) |
|
|
|
|
160 (1.5) |
144 (2.4) |
|
158 (4.8) |
|
|
|
|
|
160 (1.5) |
148 (0.8) |
|
160 (1.0) |
|
|
|
|
|
167 (1.5) |
152 (1.6) |
|
166 (3.8) |
|
|
|
|
|
181 (1.5) |
156 (2.4) |
|
198 (1.0) |
|
|
|
|
|
188 (1.5) |
160 (3.1) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
164 (2.4) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
176 (0.8) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
188 (0.8) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
204 (0.8) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
208 (0.8) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
212 (0.8) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
236 (2.4) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
240 (7.1) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
No. of alleles (A) |
15 |
24 |
12 |
16 |
12 |
6 |
8 |
5 |
|
|
No. of alleles per locus |
1.35 |
1.25 |
1.1 |
1.07 |
1.04 |
1.03 |
1.07 |
1.04 |
|
|
HE
|
0.897 |
0.938 |
0.87 |
0.896 |
0.859 |
0.494 |
0.804 |
0.768 |
Table 6Multiple of allele sizes at eight loci from Plasmodium vivax isolates from Southern Thailand
Table 6
|
Marker (size, bp) |
Microsatellite analysis |
|
|
Pv1.501 (76–195) |
Pv 3.27 (85–240) |
Pv 3.502 (128–265) |
Pv 6.34 (136–200) |
Pv 8.504 (191–317) |
Pv 11.162 (172–228) |
Pv 14.297 (180–229) |
MS1 (228–246) |
|
No. of multiple alleles at each locus |
30 |
25 |
8 |
7 |
4 |
7 |
3 |
2 |
|
|
Multiple of allele sizes at particular locus (%) |
97/132 (6.7) |
96/132 (4) |
150/166 (50) |
140/146 (14.3) |
205/212/219 (25) |
186/189 (14.3) |
180/188 (33.4) |
227/230 (50) |
|
97/118 (3.3) |
96/104 (4) |
150/166/174 (12.5) |
142/150 (14.3) |
205/212 (25) |
189/192 (14.3) |
180/196 (33.3) |
227/236 (50) |
|
90/97 (13.3) |
92/132/152 (4) |
150/166/198 (12.5) |
142/158 (14.3) |
212/219 (25) |
189/195 (14.3) |
180/184 (33.3) |
|
|
90/118 (3.3) |
92/132 (8) |
166/174 (12.5) |
144/148 (14.3) |
212/247 (25) |
192/198 (14.3) |
|
|
|
90/111/132 (3.3) |
100/156 (4) |
166/198 (12.5) |
146/158 (28.6) |
|
186/195 (14.3) |
|
|
|
90/111 (23.3) |
100/108 (4) |
|
148/154 (14.3) |
|
180/195 (14.3) |
|
|
|
83/76 (3.3) |
104/132 (4) |
|
|
|
183/192 (14.3) |
|
|
|
83/104 (3.3) |
108/100 (4) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
167/188 (3.3) |
108/112 (4) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
139/160 (3.3) |
108/112 (4) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
132/153 (6.7) |
108/188 (4) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
125/146 (3.3) |
112/236 (4) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
125/139 (3.3) |
116/120 (4) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
111/132 (3.3) |
116/132 (4) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
111/104 (3.3) |
116/144 (4) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
104/125 (3.3) |
116/160 (4) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
104/111/132 (3.3) |
116/240 (4) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
104/111/118 (3.3) |
120/128/132 (4) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
104/111 (3.3) |
124/132 (4) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
160/208 (4) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
132/240 (8) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
236/240 (8) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Table 7The genetic diversity based on eight microsatellite markers of Plasmodium vivax isolated from four different provinces of Southern Thailand
Table 7
|
Genetic diversity |
Province |
P-value*
|
Chumphon
n=38 |
Phang Nga
n=4 |
Ranong
n=46 |
Surat Thani
n=15 |
Mean |
|
No. of alleles |
9.2 |
2.8 |
9 |
5.4 |
6.6 |
<0.05*
|
|
HI
|
0.769 |
0.771 |
0.785 |
0.757 |
0.771 |
0.935 |
|
Multiple-clone infections, % (isolated) |
58% (22/38) |
50% (2/4) |
48% (22/46) |
73% (11/15) |
57.25 |
0.104 |
|
MOI**
|
1.67 |
1.5 |
1.53 |
1.8 |
1.63 |
0.408 |
References
- 1. World Health Organization. World Malaria Report 2016. Geneva, Switzerland. World Health Organization; 2016.
- 2. World Health Organization. World Malaria Report 2015. Geneva, Switzerland. World Health Organization; 2015.
- 3. Wongsrichanalai C, Meshnick SR. Declining artesunate-mefloquine efficacy against falciparum malaria on the Cambodia-Thailand border. Emerg Infect Dis 2008;14:716-719.
- 4. Rijken MJ, Boel ME, Russell B, Imwong M, Leimanis ML, Phyo AP, Muehlenbachs A, Lindegardh N, McGready R, Rénia L, Snounou G, Singhasivanon P, Nosten F. Chloroquine resistant vivax malaria in a pregnant woman on the western border of Thailand. Malar J 2011;10:113.
- 5. Howes RE, Piel FB, Patil AP, Nyangiri OA, Gething PW, Dewi M, Hogg MM, Battle KE, Padilla CD, Baird JK, Hay SI. G6PD deficiency prevalence and estimates of affected populations in malaria endemic countries: a geostatistical model-based map. PLoS Med 2012;9:e1001339.
- 6. Kitchen SF. The infection of reticulocytes by Plasmodium vivax
. Am J Trop Med Hyg 1938;18:347-359.
- 7. Mons BCJ, van der Star W, van der Kaay HJ. Erythrocytic schizogony and invasion of Plasmodium vivax in vitro. Int J Parasitol 1988;18:307-311.
- 8. Orjuela-Sanchez P, Sá JM, Brandi MC, Rodrigues PT, Bastos MS, Amaratunga C, Duong S, Fairhurst RM, Ferreira MU. Higher microsatellite diversity in Plasmodium vivax than in sympatric Plasmodium falciparum populations in Pursat, Western Cambodia. Exp Parasitol 2013;134:318-326.
- 9. Ferreira MU, Karunaweera ND, da Silva-Nunes M, da Silva NS, Wirth DF, Hartl DL. Population structure and transmission dynamics of Plasmodium vivax in rural Amazonia. J Infect Dis 2007;195:1218-1226.
- 10. Gunawardena S, Karunaweera ND, Ferreira MU, Phone-Kyaw M, Pollack RJ, Alifrangis M, Rajakaruna RS, Konradsen F, Amerasinghe PH, Schousboe ML, Galappaththy GN, Abeyasinghe RR, Hartl DL, Wirth DF. Geographic structure of Plasmodium vivax: microsatellite analysis of parasite populations from Sri Lanka, Myanmar, and Ethiopia. Am J Trop Med Hyg 2010;82:235-242.
- 11. Lee SA, Yeka A, Nsobya SL, Dokomajilar C, Rosenthal PJ, Talisuna A, Dorsey G. Complexity of Plasmodium falciparum infections and antimalarial drug efficacy at 7 sites in Uganda. J Infect Dis 2006;193:1160-1163.
- 12. Zakeri S, Barjesteh H, Djadid ND. Merozoite surface protein-3alpha is a reliable marker for population genetic analysis of Plasmodium vivax
. Malar J 2006;5:53.
- 13. Imwong M, Pukrittayakamee S, Gruner AC, Renia L, Letourneur F, Looareesuwan S, White NJ, Snounou G. Practical PCR genotyping protocols for Plasmodium vivax using Pvcs and Pvmsp1
. Malar J 2005;4:20.
- 14. Kim JR, Imwong M, Nandy A, Chotivanich K, Nontprasert A, Tonomsing N, Maji A, Addy M, Day NPJ, White NJ, Pukrittayakamee S. Genetic diversity of Plasmodium vivax in Kolkata, India. Malar J 2006;5:71.
- 15. Rayner JC, Huber CS, Feldman D, Ingravallo P, Galinski MR, Barnwell JW.
Plasmodium vivax merozoite surface protein PvMSP-3 beta is radically polymorphic through mutation and large insertions and deletions. Infect Genet Evol 2004;4:309-319.
- 16. Yang Z, Miao J, Huang Y, Li X, Putaporntip C, Jongwutiwes S, Gao Q, Udomsangpetch R, Sattabongkot J, Cui L. Genetic structures of geographically distinct Plasmodium vivax populations assessed by PCR/RFLP analysis of the merozoite surface protein 3beta gene. Acta Trop 2006;100:205-212.
- 17. Gomez JC, McNamara DT, Bockarie MJ, Baird JK, Carlton JM, Zimmerman PA. Identification of a polymorphic Plasmodium vivax microsatellite marker. Am J Trop Med Hyg 2003;69:377-379.
- 18. Imwong M, Nair S, Pukrittayakamee S, Sudimack D, Williams JT, Mayxay M, Newton PN, Kim JR, Nandy A, Osorio L, Carlton JM, White NJ, Day NP, Anderson TJ. Contrasting genetic structure in Plasmodium vivax populations from Asia and South America. Int J Parasitol 2007;37:1013-1022.
- 19. Thanapongpichat S, McGready R, Luxemburger C, Day NP, White NJ, Nosten F, Snounou G, Imwong M. Microsatellite genotyping of Plasmodium vivax infections and their relapses in pregnant and non-pregnant patients on the Thai-Myanmar border. Malar J 2013;12:275.
- 20. Kittichai V, Koepfli C, Nguitragool W, Sattabongkot J, Cui L. Substantial population structure of Plasmodium vivax in Thailand facilitates identification of the sources of residual transmission. PLoS Negl Trop Dis 2017;11:e0005930.
- 21. Kosaisavee V, Hastings I, Craig A, Lek-Uthai U. The genetic polymorphism of Plasmodium vivax genes in endemic regions of Thailand. Asian Pac J Trop Med 2011;4:931-936.
- 22. Snounou G, Viriyakosol S, Zhu XP, Jarra W, Pinheiro L, do Rosario VE, Thaithong S, Brown KN. High sensitivity of detection of human malaria parasites by the use of nested polymerase chain reaction. Mol Biochem Parasitol 1993;61:315-320.
- 23. Bruce MC, Galinski MR, Barnwell JW, Snounou G, Day KP. Polymorphism at the merozoite surface protein-3alpha locus of Plasmodium vivax: global and local diversity. Am J Trop Med Hyg 1999;61:518-525.
- 24. Karunaweera ND, Ferreira MU, Hartl DL, Wirth DF. Fourteen polymorphic microsatellite DNA markers for the human malaria parasite Plasmodium vivax
. Mol Ecol Notes 2007;7:172-175.
- 25. Anderson TJ, Su XZ, Bockarie M, Lagog M, Day KP. Twelve microsatellite markers for characterization of Plasmodium falciparum from finger-prick blood samples. Parasitology 1999;119:113-125.
- 26. Goudet J. Fstat version 1.2: a computer program to calculate F-statistics. J Heredity 86:485-486.
- 27. Hudson RR. Analytical results concerning linkage disequilibrium in models with genetic transformation and conjugation. J Evol Biol 1994;7:535-548.
- 28. Smith JM, Smith NH, Rourke M, Spratt BG. How clonal are bacteria? Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 1993;90:4384.
- 29. Haubold B, Hudson RR. LIAN 3.0: detecting linkage disequilibrium in multilocus data. Bioinformatics 2000;16:847-849.
- 30. Sattabongkot J, Tsuboi T, Zollner GE, Sirichaisinthop J, Cui L.
Plasmodium vivax transmission: chances for control? Trends Parasitol 2004;20:192-198.
- 31. Boyd MF, Kitchen SF. Simultaneous Inoculation with Plasmodium vivax and Plasmodium falciparum
. Am J Trop Med Hyg 1937;17:855-861.
- 32. Boyd MF, Kitchen SF. Vernal vivax activity in persons simultaneously inoculated with Plasmodium vivax and Plasmodium falciparum
. Am J Trop Med Hyg 1938;18:505-514.
- 33. James SP. Some general results of a study of induced malaria in England. Trans R Soc Trop Med Hyg 1931;24:477-525.
- 34. Nigatu W, Abebe M, Dejene A.
Plasmodium vivax and P. falciparum epidemiology in Gambella, south-west Ethiopia. Trop Med Parasitol 1992;43:181-185.
- 35. Somboon P, Suwonkerd W, Lines JD. Susceptibility of Thai zoophilic Anophelines and suspected malaria vectors to local strains of human malaria parasites. Southeast Asian J Trop Med Public Health 1994;25:766-770.
- 36. Limrat D, Rojruthai B, Apiwathnasorn C, Samung Y, Prommongkol S. Anopheles barbirostris/campestris as a probable vector of malaria in Aranyaprathet, Sa Kaeo Province. Southeast Asian J Trop Med Public Health 2001;32:739-744.
- 37. Rayner JC, Corredor V, Feldman D, Ingravallo P, Iderabdullah F, Galinski MR, Barnwell JW. Extensive polymorphism in the plasmodium vivax merozoite surface coat protein MSP-3alpha is limited to specific domains. Parasitology 2002;125:393-405.
- 38. Cui L, Mascorro CN, Fan Q, Rzomp KA, Khuntirat B, Zhou G, Chen H, Yan G, Sattabongkot J. Genetic diversity and multiple infections of Plasmodium vivax malaria in Western Thailand. Am J Trop Med Hyg 2003;68:613-619.
- 39. Zakeri S, Safi N, Afsharpad M, Butt W, Ghasemi F, Mehrizi AA, Atta H, Zamani G, Djadid ND. Genetic structure of Plasmodium vivax isolates from two malaria endemic areas in Afghanistan. Acta Trop 2010;113:12-19.
- 40. Zakeri S, Raeisi A, Afsharpad M, Kakar Q, Ghasemi F, Atta H, Zamani G, Memon MS, Salehi M, Djadid ND. Molecular characterization of Plasmodium vivax clinical isolates in Pakistan and Iran using pvmsp-1, pvmsp-3alpha and pvcsp genes as molecular markers. Parasitol Int 2010;59:15-21.
- 41. Cui L, Escalante AA, Imwong M, Snounou G. The genetic diversity of Plasmodium vivax populations. Trends Parasitol 2003;19:220-226.
- 42. Prajapati SK, Joshi H, Valecha N.
Plasmodium vivax merozoite surface protein-3 alpha: a high-resolution marker for genetic diversity studies. J Vector Borne Dis 2010;47:85-90.
- 43. Véron V, Legrand E, Yrinesi J, Volney B, Simon S, Carme B. Genetic diversity of msp3alpha and msp1_b5 markers of Plasmodium vivax in French Guiana. Malar J 2009;8:40.
- 44. Khatoon L, Baliraine FN, Bonizzoni M, Malik SA, Yan G. Genetic structure of Plasmodium vivax and Plasmodium falciparum in the Bannu district of Pakistan. Malar J 2010;9:112.
- 45. Rungsihirunrat K, Chaijaroenkul W, Siripoon N, Seugorn A, Na-Bangchang K. Genotyping of polymorphic marker (MSP3alpha and MSP3beta) genes of Plasmodium vivax field isolates from malaria endemic of Thailand. Trop Med Int Health 2011;16:794-801.
- 46. Gupta P, Pande V, Eapen A, Singh V. Genotyping of MSP3β gene in Indian Plasmodium vivax
. J Vector Borne Dis 2013;50:197-201.
- 47. Iwagami MFM, Hwang SY, Kim SH, Kho WG, Kano S. Population structure and transmission dynamics of Plasmodium vivax in the Republic of Korea based on microsatellite DNA analysis. PLoS Negl Trop Dis 2012;6:e1592.
- 48. Menegon M, Bardají A, Martínez-Espinosa F, Bôtto-Menezes C, Ome-Kaius M, Mueller I, Betuela I, Arévalo-Herrera M, Kochar S, Kochar SK, Jaju P, Hans D, Chitnis C, Padilla N, Castellanos ME10, Ortiz L, Sanz S, Piqueras M, Desai M, Mayor A, Del Portillo H, Menéndez C, Severini C. Microsatellite Genotyping of Plasmodium vivax Isolates from Pregnant Women in Four Malaria Endemic Countries. PLoS One 2016;11:e0152447.
- 49. Havryliuk T, Ferreira MU. A closer look at multiple-clone Plasmodium vivax infections: detection methods, prevalence and consequences. Mem Inst Oswaldo Cruz 2009;104:67-73.