Abstract
In most developing countries, Dientamoeba fragilis infection is an obscure protozoan infection. We aimed to determine a frequency and clinical importance of D. fragilis infection in Taif, Saudi Arabia. A 1-year case control study included patients with gastrointestinal (cases, n=114) or non-gastrointestinal symptoms (controls, n=90). The fecal samples were examined with the classical parasitological methods for intestinal protozoa, and by real time PCR for D. fragilis. The infection by D. fragilis was detected in 5.8% by PCR and in 4.4% patients by microscopy. The infection was identified more in control group (n=9) than in cases (n=3); a sole infection in 11 patients and mixed with Giardia in 1 patient. The other enteric parasites detected were Blastocystis sp. (8.3%), Giardia sp. (5.3%), Cryptosporidium sp. (2.9%), Entamoeba histolytica (1.4%), Entamoeba coli (0.9%) and Hymenolepis nana (0.4%). Our results tend to reinforce the need to increase awareness of D. fragilis infection in Saudi Arabia.
-
Key words: Dientamoeba fragilis, diagnosis, microscopy, PCR, Saudi Arabia
INTRODUCTION
Dientamoeba fragilis is a single-celled protozoan parasite of the human gut. Infection may also be able to affect non-human primates and pigs.
D. fragilis has emerged as a neglected cosmopolitan intestinal protozoa [
1]. A prevalence of 0–82% has been recorded for the infection worldwide [
2]. Most of these figures come from countries with high incomes. On the contrary, the prevalence of this infection in low-income countries is not well known [
3]. The infection’s transmission and pathogenicity of
D. fragilis remain a subject of an ongoing debate [
4]. Fecal-oral transmission and infection along with pinworm eggs have often been suggested [
5]. The parasite is often retrieved from patients with gastrointestinal symptoms [
6]. Abdominal pain or cramps and diarrhea are common symptoms for
Dientamoeba infection [
7]. Other symptoms such as nausea, vomiting, anorexia, fever and eosinophilia have been also reported [
8,
9].
The classical parasitological methods (wet mount preparations and stool concentration techniques) make it difficult to detect
D. fragilis in feces. Permanently staining methods or cultivation procedures are often required to achieve a correct parasitological diagnosis. This fact confirms that the nucleic acid-based assays have been the diagnostic method of choice for
D. fragilis in feces [
10].
In Saudi Arabia, infections with intestinal parasites pose a public health problem. Nonetheless, the diagnosis of these infections is largely done by microscopic examination of patients feces [
11–
13]. This strategy eventually led to numerous protozoan infections being overlooked, including
D. fragilis. In this study, we aimed to assess incidence and clinical significance of
D. fragilis infection in a clinic, Saudi Arabia.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Ethical statements
This study got an approval (No: 41-710-0023) from the ethical committee of Applied Medical Sciences College at Al-Taif University. Recruitment of patients and collection of samples was carried out on a voluntary basis. Participants were given the research information and asked to sign a written consent form.
Study population
Patients visiting a primary health care clinic in Taif, Saudi Arabia, were invited to participate in a case-control study in 2018. Cases were chosen from patients with symptoms of enteric infections such as nausea, vomiting, urgency, loss of appetite, passage of bloody stool, passage of mucoid stool, and/or abdominal pain. Controls were selected from patients with non-gastrointestinal problems. Patients who have recently received anti-parasitic drugs and who have refused to provide fecal samples were excluded from this study.
Data collection
A questionnaire with specific demographic variables (age, gender, residence, recent travel to tropics and contact with infected household member) and clinical symptoms (diarrhea, abdominal pain or cramp, fever, nausea or vomiting, blood in stool or mucous in stool) was used in this study.
Parasitological examination
Stool samples (1 per patient) were obtained from all participants on the day of the interview or shortly afterwards. Fresh feces (within half an hour of collection) were microscopically screened for intestinal protozoa and instantly fixed; 1 part in 10% formalin and 1 part in 70% ethanol. Properly labeled preserved specimens were transported to the Medical Laboratory at Taif University’s College of Applied Medical Sciences. Smear preparations from formalin-fixed specimens were permanently stained inside the laboratory with iron-haematoxylin, Ziehl-Neelsen and trichrome stain, as mentioned elsewhere [
14,
15]. The ethanol-fixed specimens were kept at −20°C for
Dientamoeba DNA detecting PCR.
The ethanol preserved frozen feces were used for DNA extraction. Total genomic DNA was extracted and purified from stool specimen sediment (~200 mg) with QIAamp DNA Stool minikit (Qiagen, Hilden, Germany) following an amended manufacturer protocol [
16]. Using a
Dientamoeba fragilis-specific PCR, the fecal-recovered DNA was amplified and analyzed. The amplification reaction was initiated by a set of 1 pair of published primers (forward primer Df-124F: 5′-CAACGGATGTCTTGGCTCTTTA-3′, reverse primer Df-221R 5′-TGCATTCAAAGATCGAACTTATCAC-3′ and a TaqMan probe Df-172revT 5′-CAATTCTAGCCGCTTAT-3′ targeting 98 bp of 5.8 small subunits of the ribosomal RNA gene. The primers and the probe were synthesized by the VH Bio (Gateshead, UK). The reaction set up and thermal cycles were conducted in LightCycler (Roche Diagnostics Corporation, Mannheim, Germany). GoTaq Hot Start Polymerase (Promega) and other PCR reagents were used in amplification reactions with final concentrations closely similar to a published previous protocol [
17].
In order to evaluate the qualitative variables of the study participants, the chi-square and Fisher’s exact test, on the Social Science Statistics website (
https:/www.socscistatistics.com/) were implemented.
P-value less than 0.05 was considered statistically significant. With aid of the MedCalc statistical software website (
https:/www.medcalc.org/calc/diagnostictest.php), diagnostic performance of the permanently stain smear microscopy was calculated. The sensitivity, specificity, positive predictive value and negative predictive value of the permanently stained smear microscopy was calculated in comparison to the RT-PCR test’s results as a nominated gold standard.
RESULTS
We recruited 114 patients with gastrointestinal complaints (cases) and 90 patients with non-gastrointestinal complaints (controls) during the study period (
Table 1). All matching conditions were met between cases and controls. The patients were presented with abdominal pain/cramp 39.2%, diarrhea 50% and nausea or vomiting 7.3%. Of the 204 samples tested, 50% showed diarrhea, 12.7% containing mucus and 4.9% bloody feces.
Dientamoeba fragilis trophozoites (
Fig. 1) were detected from the stained smears of 9 patients, with a total prevalence of 4.4%. The RT- PCR detected
D. fragilis DNA from 12 patients, 3 from cases and 9 from controls. Three fecal specimens found positive for the parasite DNA by the RT- PCR were missed by the microscopic examination. RT-PCR found all the microscopically positive samples. Taking the RT-PCR test results as a nominated gold standard, the sensitivity, specificity, negative and positive predictive values of the permanently stained smear microscopic examination were 75%, 100%, 98.4%, and 100%, respectively. Common symptoms associated with
D. fragilis infection were abdominal pain 100%, diarrhea 66.6%, and vomiting 33.3%. All the
D. fragilis-positive patients had chronic diarrhea and loose stool (
Supplementary Table S1).
The history of recent contact to a family member with gastrointestinal symptom(s) was reported less in cases than in controls, with observed significant difference (P<0.05). The infection was described in all age groups, but more patients in age category ≤19-year-old (10.8%). There was no statistically significant difference between cases and controls regarding D. fragilis positivity in all age groups. D. fragilis was described in 11 patients as a mono-parasitic infection and in 1 patient as coinfection with Giardia spp. This patient was an 11-year-old male child who had diarrhea for more than 2 weeks.
Other enteric parasites were detected (
Table 2) from 31 cases and 4 controls with 17.1% total prevalence rate. There was significant difference between cases and controls for the enteric parasites’ positivity, (
P<0.01). The enteric parasites included 8.3%
Blastocystis sp., 5.3%
Giardia sp., 2.9%
Cryptosporidium sp., 1.4%
Entamoeba histolytica, 0.9%
Entamoeba coli, and 0.4%
Hymenolepis nana. A significant difference regarding the positivity rates between cases and controls was observed for
Blastocystis sp.,
Giardia and
Cryptosporidium sp. Polyparasitism was reported in 5 cases (
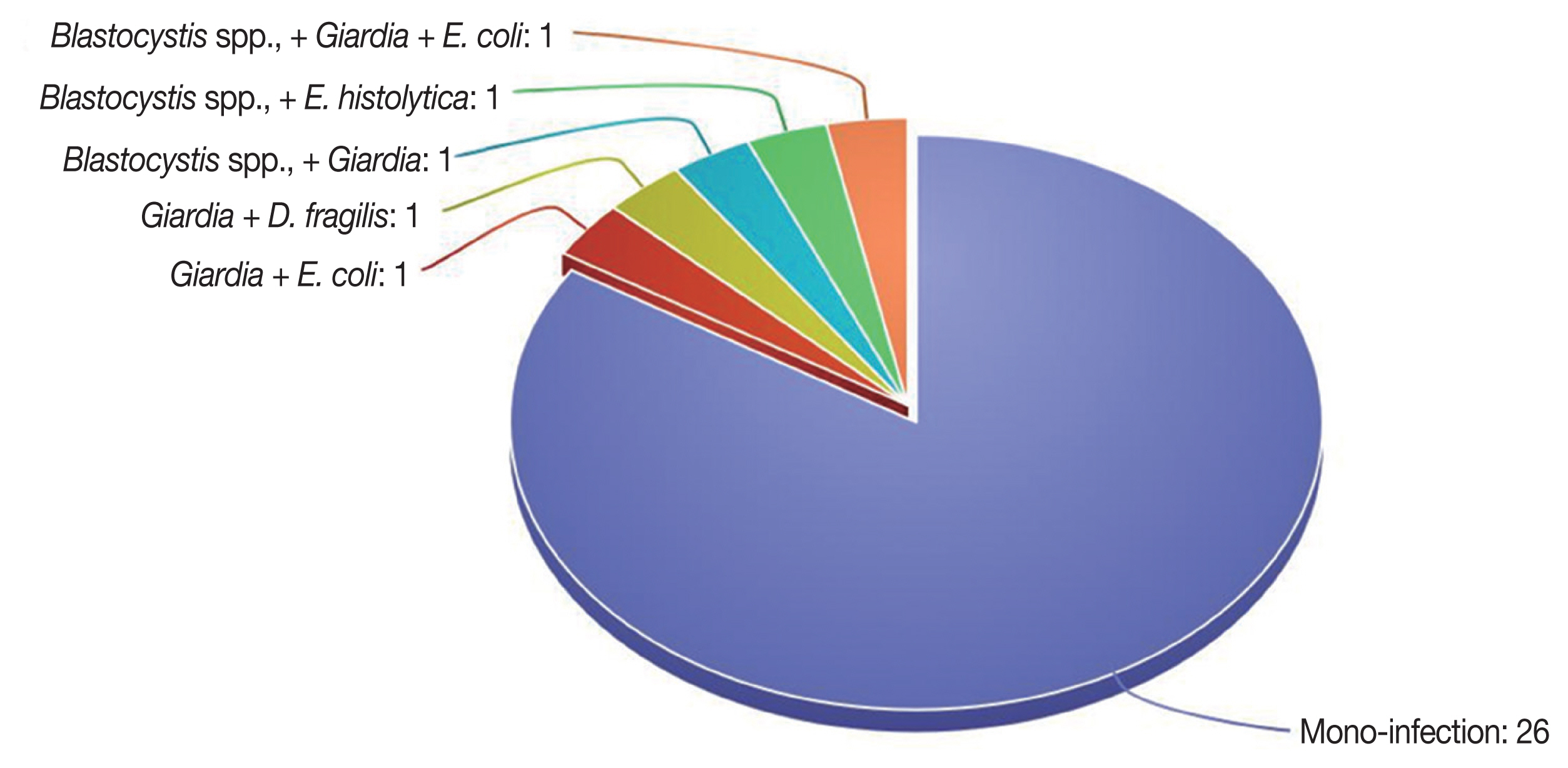
Fig. 2).
DISCUSSION
The D. fragilis infection is an unsolved issue in most developing countries and needs more focus. This was the first case-control study investigating the occurrence and the clinical significance of infection among a population from Saudi Arabia. A strength point, considered in our case-control study, was related to selection of the controls. We selected the control subjects from those attending a health care center with non-gastrointestinal symptoms to be representative for the same population as in cases to avoid selection bias. Another strength point considered in our study was related to the methodology adopted for D. fragilis detection. In this study, besides microscopy, we used a RT-PCR with sufficient sensitivity and specificity to enhance the detectability of the parasite in patients’ feces.
In the current study,
D. fragilis was second to
Blastocystis spp. Infection was detected with the RT-PCR at an estimated frequency rate of 5.8%. In Saudi Arabia, an estimate 0.2–0.6% of
D. fragilis infection was described [
18,
19]. Wakid has identified the infection in food processing workers based on microscopic examination of permanently stain fecal smears. Microscopy was thought to be a less effective detection method for
D. fragilis and often underestimated the frequency of the parasite, compared to the molecular diagnostic methods [
20–
22]. According to a recent study, there was an annual increase of 28% in the detection of
D. fragilis infection after implementation of a fecal PCR in diagnosis. The RT-PCR used in our research was superior to permanently stain smear microscopy for diagnosis of
D. fragilis in human [
23,
24]. Despite its high diagnostic sensitivity, due to high cost, many clinical laboratories, particularly those in poor countries, still hesitate to use PCR to detect
D. fragilis in human feces. In this case, it is recommended to search for this protozoan infection through microscopic examination of permanently stained fecal smears by well-trained experts.
The occurrence and clinical importance of
Dientamoeba infection in symptomatic and non-symptomatic individuals have been investigated in few case-control studies. The infection has been less frequently reported in patients with digestive symptoms than in asymptomatic individuals. In Holland, it was reported
D. fragilis infection in 25.7% of symptomatic cases and 37.3% of asymptomatic control subjects [
25]. In Denmark, the infection was 23% in patients and 35% in asymptomatic control subjects [
26]. Here, in our research, we significantly identified
D. fragilis in 2.6% of symptomatic cases and 10% of asymptomatic controls, coinciding with the above findings. The occurrence of high prevalence of
D. fragilis in asymptomatic carriers was a surprising finding in our research. Such a finding raises the degree of uncertainty surrounding the pathogenic potential of the parasite in the population. In comparison to our results, there were also significantly higher prevalence rates (>20 percent) in several regions of the world, including countries from Europe, Middle East, and South America [
27–
29].
The common symptoms associated with
D. fragilis infection were diarrhea, abdominal pain and vomiting, in agreement with the literature [
30–
33]. None of the
Dientamoeba-positive patients, in our study, gave history of fever or reported blood or mucous in feces. The targeted population, method of detection used, infection severity, accompanying infections, and protozoan genotypes may affect the outcomes of infections in each study. In a recent study investigating the genetic diversity of
Dientamoeba clinical isolates recovered from patients with irritable bowel syndrome, 4 distinct parasite subtypes have been identified, each type has been associated with different clinical presentations.
It was astonishing to us that concurrent infection with
Giardia sp. was only 1 case.
Dientamoeba/
Giardia mixed infection was documented 7.1% from 1 population [
33] and 9% from another [
22] in disagreement with our study. Enteropathogens/
D. fragilis coinfection was registered in 58% of a study population [
35] and in 23% of another [
22]. It is worth mentioning that the
Blastocystis sp. has been the most common protozoan parasite cohabiting
Dientamoeba infection [
36]. Nonetheless, 1 recent report found that almost half of patients with dientamoebiasis was coinfected with
Entamoeba histolytica/dispar [
37]. Evidence about
Dientamoeba infection acquisition along with pinworm infection have been reported [
38], but still remains controversial. Enteropathogens other than the intestinal parasites like the enteroviruses and enteric bacteria were not sought for in the current survey study. These microbes could not be excluded as possible cohabiting pathogens with
D. fragilis. One could not relate any symptoms to
D. fragilis infection alone. In present study, colonization of
D. fragilis was more common in patients aged 5–19 years [
22]. Children of daycare-age or school-age and adults aged 30–40 years were 2 main age categories infected with
D. fragilis [
28].
In Saudi Arabia,
Blastocystis sp.,
Giardia sp. and
Cryptosporidium sp., were frequently detected.
E. histolytica,
E. coli and
Hymenolepis nana were identified in few cases. The above parasitic infections were reported prevalent in Saudi communities [
11,
12,
39].
In conclusion, our results tend to reinforce the need for increased awareness of D. fragilis infection in Saudi Arabia. The study described frequent D. fragilis infections in the asymptomatic controls, with reported RT-PCR superiority over microscopy in parasite’s detection.
Notes
-
CONFLICT OF INTEREST
The authors declare no conflict of interest related to this study.
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS
Authors would like to thank patients, health personnel, and technicians for their support and cooperation in this research work. The current study was supported by a special fund given from the Deanship of Scientific Research, Taif University, Saudi Arabia (Grant or Award Number 1-439-6081).
Supplementary Materials
Supplementary Table S1.
The demographic factors and clinical features of Dientamoeba-positives cases and controls
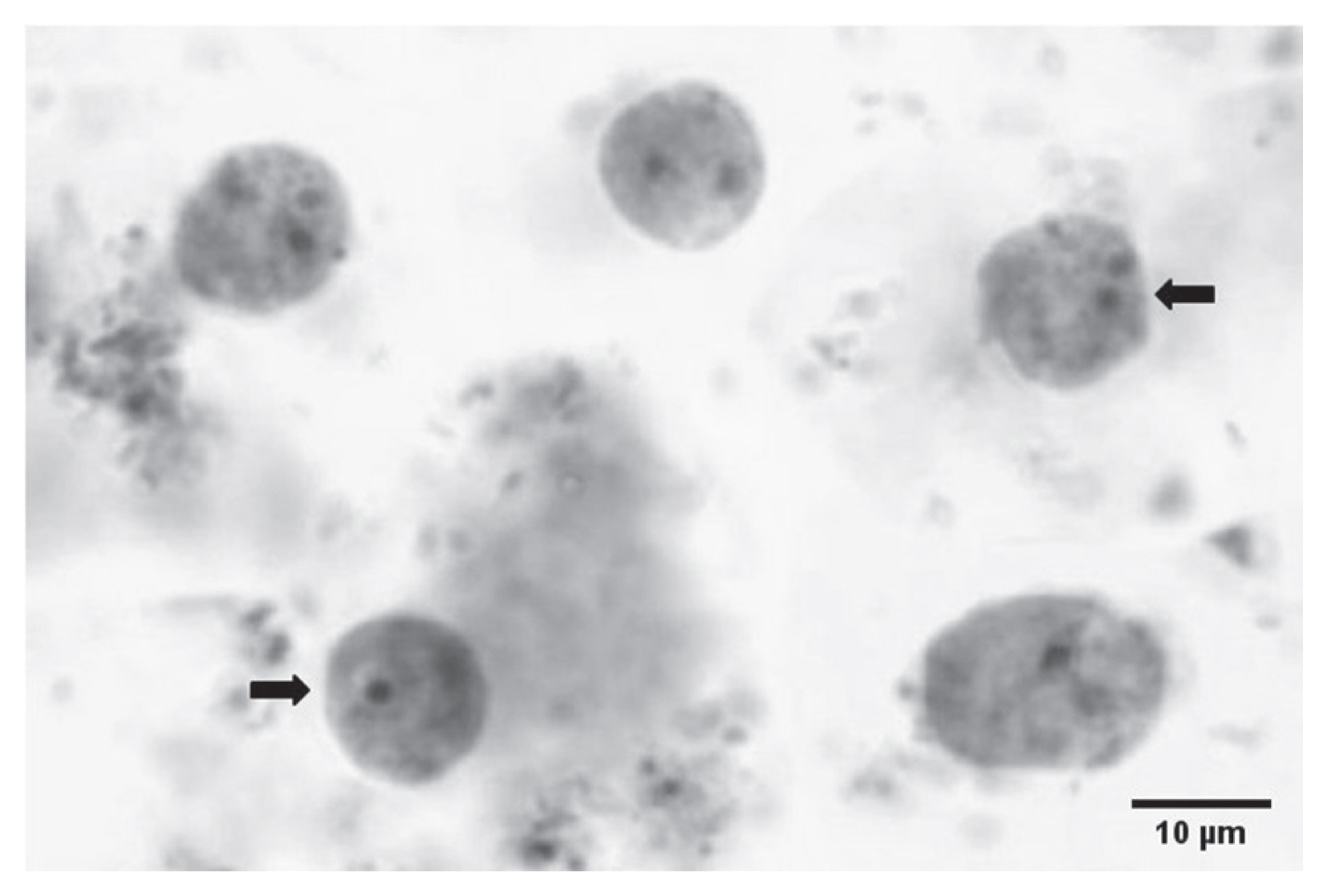
Fig. 1Microscopic image for Dientamoeba fragilis pleomorphic trophozoites in formalin-fixed iron-haematoxylin-stained fecal smear. Trophozoite having one nucleus and another with 2 nuclei (arrow).

Fig. 2A diagram showing polyparasitism of the positive infections.
Table 1Demographic factors and clinical features of 204 cases and 90 controls
Table 1
|
Character |
No. (%) |
No. (%) |
P-value |
|
Age (yr) |
|
<5 |
18 (15.7) |
14 (15.5) |
0.963 |
|
5–19 |
25 (21.9) |
17 (18.8) |
0.593 |
|
20–50 |
39 (34.2) |
31 (34.4) |
0.972 |
|
>50 |
32 (28.0) |
28 (31.1) |
0.635 |
|
|
Gender: Male/Female |
54/60 |
43/47 |
0.953 |
|
|
Travel to tropics: Yes/no |
53/61 |
13/77 |
<0.001*
|
|
|
Residence: Rural/urban |
47/67 |
21/69 |
0.007*
|
|
|
Household member with GI complaint: Yes/no |
41/73 |
7/83 |
<0.001*
|
|
|
Abdominal pain/cramp: Yes/no |
80/34 |
NA |
NA |
|
|
Diarrhea: Yes/no |
102/12 |
NA |
NA |
|
|
Diarrhea: Acute/chronic |
73/29 |
NA |
NA |
|
|
Loose stool: Yes/no |
11/103 |
NA |
NA |
|
|
Watery stool: Yes/no |
43/71 |
NA |
NA |
|
|
Nausea or vomiting: Yes/no |
15/99 |
NA |
NA |
|
|
Blood in stool: Yes/no |
10/104 |
NA |
NA |
|
|
Mucous in stool: Yes/no |
26/88 |
NA |
NA |
|
|
Fever: Yes/no |
16/98 |
NA |
NA |
Table 2Other enteric parasites detected from feces
Table 2
|
Other Parasite |
No. in case |
No. in control |
Prevalence (%) |
P-value |
|
Blastocystis spp. |
15a
|
2 |
8.3 |
0.004*
|
|
Giardia lamblia
|
10b
|
1 |
5.3 |
0.024*
|
|
Cryptosporidium spp. |
6 |
0 |
2.9 |
0.027*
|
|
Entamoebae histolytica
|
2 |
1 |
1.47 |
0.704 |
|
Entamoeba coli
|
2c
|
0 |
0.98 |
0.206 |
|
Hymenolepis nana
|
1 |
0 |
0.49 |
0.373 |
|
Total |
31d
|
4 |
17.1 |
0.008*
|
References
- 1. Chan D, Barratt J, Roberts T, Phillips O, Šlapeta J, Ryan U, Marriott D, Harkness J, Ellis J, Stark D. Detection of Dientamoeba fragilis in animal faeces using species-specific real-time PCR assay. Vet Parasitol 2016;227:42-47.
- 2. Garcia LS.
Dientamoeba fragilis, one of the neglected intestinal Protozoa. J Clin Microbiol 2016;54:2243-2250.
- 3. Cacciò SM. Molecular epidemiology of Dientamoeba fragilis
. Acta trop 2018;184:73-77.
- 4. Wong ZW, Faulder K, Robinson JL. Does Dientamoeba fragilis cause diarrhea? A systematic review. Parasitol Res 2018;117:971-980.
- 5. Clark CG, Röser D, Stensvold CR. Transmission of Dientamoeba fragilis: pinworm or cysts? Trends Parasitol 2014;30:136-140.
- 6. Ögren J, Dienus O, Löfgren S, Einemo IM, Iveroth P, Matussek A.
Dientamoeba fragilis prevalence coincides with gastrointestinal symptoms in children less than 11 years old in Sweden. Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis 2015;34:1995-1998.
- 7. Intra J, Sarto C, Besana S, Tiberti N, Brambilla P. The importance of considering the neglected intestinal protozoan parasite Dientamoeba fragilis
. J Med Microbiol 2019;68:890-892.
- 8. van Gestel RS, Kusters JG, Monkelbaan JF. A clinical guideline on Dientamoeba fragilis infections. Parasitol 2019;146:1131-1139.
- 9. Menéndez C, Fernández-Suarez J, Ribeiro JA, Rodríguez-Pérez M, Vázquez F, Gonzalez-Sotorrios N, Rodríguez-Guardado A. Epidemiological and clinical characteristics of Dientamoeba fragilis infection. Enferm Infecc Microbiol Clin 2019;37:290-295.
- 10. Hamidi N, Meamar AR, Akhlaghi L, Rampisheh Z, Razmjou E.
Dientamoeba fragilis diagnosis by fecal screening: relative effectiveness of traditional techniques and molecular methods. J Infect Dev Ctries 2018;12:52-59.
- 11. Zaglool DA, Khodari YA, Gazzaz ZJ, Dhafar KO, Shaker HA, Farooq MU. Prevalence of intestinal parasites among patients of Al-Noor specialist hospital, Makkah, Saudi Arabia. Oman Med J 2011;26:182-185.
- 12. Hassen Amer O, Ashankyty IM, Haouas NA. Prevalence of intestinal parasite infections among patients in local public hospitals of Hail, Northwestern Saudi Arabia. Asian Pac J Trop Med 2016;9:44-48.
- 13. Taha HA, Soliman MI, Banjar SAN. Intestinal parasitic infections among expatriate workers in Al-Madina Al-Munawarah, Kingdom of Saudi Arabia. Trop Biomed 2013;30:78-88.
- 14. McHardy IH, Wu M, Shimizu-Cohen R, Couturier MR, Humphries RM. Detection of intestinal protozoa in the clinical laboratory. J Clin Microbiol 2014;52:712-720.
- 15. Windsor JJ, Rafay AM. Laboratory detection of Dientamoeba fragilis
. Br J Biomed Sci 1997;54:223-224.
- 16. Hawash Y. DNA extraction from protozoan oocysts/cysts in feces for diagnostic PCR. Korean J Parasitol 2014;52:263-271.
- 17. Verweij JJ, Mulder B, Poell B, van Middelkoop D, Brienen EA, van Lieshout L. Real-time PCR for the detection of Dientamoeba fragilis in fecal samples. Mol Cell Probes 2007;21:400-404.
- 18. Wakid MH, Azhar EI, Zafar TA. Intestinal parasitic infection among food handlers in the holy city of Makkah during Hajj season, Hegira. JKAU Med Sci 2009;16:39-52.
- 19. Wakid MH. Distribution of intestinal parasites among food handlers in Jeddah, Saudi Arabia. J Parasit Dis 2006;30:146-152.
- 20. Calderaro A, Gorrini C, Montecchini S, Peruzzi S, Piccolo G, Rossi S, Gargiulo F, Manca N, Dettori G, Chezzi C. Evaluation of a real-time polymerase chain reaction assay for the detection of Dientamoeba fragilis
. Diagn Microbiol Infect Dis 2010;67:239-245.
- 21. Stark D, Barratt J, Roberts T, Marriott D, Harkness J, Ellis J. Comparison of microscopy, two xenic culture techniques, conventional and real-time PCR for the detection of Dientamoeba fragilis in clinical stool samples. Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis 2010;29:411-416.
- 22. Pietilä JP, Meri T, Siikamäki H, Tyyni E, Kerttula AM, Pakarinen L, Jokiranta TS, Kantele A.
Dientamoeba fragilis - the most common intestinal protozoan in the Helsinki Metropolitan Area, Finland, 2007 to 2017. Euro Surveill 2019;24:1800546.
- 23. Stark D, Beebe N, Marriott D, Ellis J, Harkness J. Evaluation of three diagnostic methods, including real-time PCR, for detection of Dientamoeba fragilis in stool specimens. J Clin Microbiol 2006;44:232-235.
- 24. Bruijnesteijn van Coppenraet LE, Wallinga JA, Ruijs GJ, Bruins MJ, Verweij JJ. Parasitological diagnosis combining an internally controlled real-time PCR assay for the detection of four protozoa in stool samples with a testing algorithm for microscopy. Clin Microbiol Infect 2009;15:869-874.
- 25. Bruijnesteijn van Coppenraet LE, Dullaert-de Boer M, Ruijs GJ, van der Reijden WA, van der Zanden AG, Weel JF, Schuurs TA. Case–control comparison of bacterial and protozoan microorganisms associated with gastroenteritis: application of molecular detection. Clin Microbiol Infect 2015;21:592.e9-592.19.
- 26. Krogsgaard LR, Engsbro AL, Stensvold CR, Nielsen HV, Bytzer P. The prevalence of intestinal parasites is not greater among individuals with irritable bowel syndrome: a population-based case-control study. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol 2015;13:507-513.
- 27. Osman M, El Safadi D, Cian A, Benamrouz S, Nourrisson C, Poirier P, Pereira B, Razakandrainibe R, Pinon A, Lambert C, Wawrzyniak I, Dabboussi F, Delbac F, Favennec L, Hamze M, Viscogliosi E, Certad G. Prevalence and risk factors for intestinal protozoan infections with Cryptosporidium, Giardia, Blastocystis and Dientamoeba among schoolchildren in Tripoli, Lebanon. PLoS Negl Trop Dis 2016;10:e0004496.
- 28. Gijsbers CF, Benninga MA, Büller HA. Clinical and laboratory findings in 220 children with recurrent abdominal pain. Acta Paediatr 2011;100:1028-1032.
- 29. Röser D, Simonsen J, Nielsen HV, Stensvold CR, Mølbak K.
Dientamoeba fragilis in Denmark: epidemiological experience derived from four years of routine real-time PCR. Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis 2013;32:1303-1310.
- 30. Stensvold CR, van der Giezen M. Associations between gut microbiota and common luminal intestinal parasites. Trends Parasitol 2018;34:369-377.
- 31. Aykur M, Kurt CC, Erdogan DD, Avcı CB, Vardar R, Aydemir S, Girginkardeşler N, Gündüz C, Dagci H. Investigation of Dientamoeba fragilis prevalence and evaluation of sociodemographic and clinical features in patients with gastrointestinal symptoms. Acta Parasitol 2019;64:162-170.
- 32. Banik GR, Barratt JL, Marriott D, Harkness J, Ellis JT, Stark D. A case-controlled study of Dientamoeba fragilis infections in children. Parasitol 2011;138:819-823.
- 33. Al-Hindi AI, Shammala BM.
Dientamoeba fragilis in Gaza Strip: a neglected protozoan parasite. Iran J Parasitol 2013;8:249-255.
- 34. Hussein EM, Al-Mohammed HI, Hussein AM. Genetic diversity of Dientamoeba fragilis isolates of irritable bowel syndrome patients by high-resolution melting-curve (HRM) analysis. Parasitol Res 2009;105:1053-1060.
- 35. Sarafraz S, Farajnia S, Jamali J, Khodabakhsh F, Khanipour F. Detection of Dientamoeba fragilis among diarrheal patients referred to Tabriz health care centers by nested PCR. Trop Biomed 2013;30:113-118.
- 36. Stensvold CR, Lewis HC, Hammerum AM, Porsbo LJ, Nielsen SS, Olsen KE, Arendrup MC, Nielsen HV, Mølbak K.
Blastocystis: unravelling potential risk factors and clinical significance of a common but neglected parasite. Epidemiol Infect 2009;137:1655-1663.
- 37. Stark D, Barratt J, Roberts T, Marriott D, Harkness J, Ellis J. A review of the clinical presentation of dientamoebiasis. Am J Trop Med Hyg 2010;82:614-619.
- 38. Ögren J, Dienus O, Löfgren S, Iveroth P, Matussek A.
Dientamoeba fragilis DNA detection in Enterobius vermicularis eggs. Pathog Dis 2013;69:157-158.
- 39. Al-Mohammed HI, Amin TT, Aboulmagd E, Hablus HR, Zaza BO. Prevalence of intestinal parasitic infections and its relationship with socio–demographics and hygienic habits among male primary schoolchildren in Al–Ahsa, Saudi Arabia. Asian Pac J Trop Med 2010;3:906-912.