Abstract
The ticks feed large amount of blood from their hosts and transmit pathogens to the victims. The salivary gland plays an important role in the blood feeding. When the female ticks are near engorgement, the salivary gland gradually loses its functions and begins to rapidly degenerate. In this study, data-independent acquisition quantitative proteomics was used to study changes in the phosphorylation modification of proteins during salivary gland degeneration in Haemaphysalis longicornis. In this quantitative study, 400 phosphorylated proteins and 850 phosphorylation modification sites were identified. Trough RNA interference experiments, we found that among the proteins with changes in phosphorylation, apoptosis-promoting Hippo protein played a role in salivary gland degeneration.
-
Key words: Tick, salivary gland, apoptosis, data-independent acquisition, RNA interference, Hippo
INTRODUCTION
The ticks are haematophagous ectoparasitic arthropods and have diverse hosts, including many species of mammals, birds, reptiles and amphibians. After being bitten by ticks, the host can develop erythema in part of the skin, oedema, and skin irritation. Tick bites can simultaneously transmit pathogens to the host, causing infection and directly affecting the health of livestock and humans [
1]. Several tick-borne pathogens are zoonotic and cause tick-transmitted diseases such as Lyme disease [
2], tick-borne encephalitis [
3], haemorrhagic fever [
4] and babesiosis [
5].
The salivary gland plays a pivotal role in blood feeding of the ticks. These glands regulate the water balance within the tick’s body and revert excess water from the host’s blood back to the host’s body [
6]. In addition, the salivary gland can secrete anticoagulatory proteins [
7], vasodilatory proteins [
8], immunomodulatory proteins [
9], and other substances that promote the rapid feeding of the host’s blood by ticks. Salivary gland development directly influences the blood-sucking ability and survival of ticks. Therefore, research on salivary gland development has great significance for better controlling the blood-sucking capability of ticks and thus their reproduction. It takes 5–10 days of continuous feeding on the host’s blood for female ticks to reach engorgement. During this period, the salivary gland continuously develops and improves in function [
10]. After engorgement, female ticks detach from the host’s body surface. The salivary gland begins to degenerate [
11], which is accompanied by acinar autolysis and the appearance of a large number of phagocytic vacuoles [
12]. Salivary gland degeneration proceeds under the regulation of hormones and multiple proteins, which constitutes a complex mechanism. One of the key factors in salivary gland degradation is the tick salivary gland degeneration factor (TSGDF). When female ticks reach engorgement, their abdominal skin stretches to release TSGDF for regulating salivary gland degeneration [
13]. TSGDF has been confirmed to be an ecdysteroid [
14]. In addition to hormones regulating salivary gland degeneration, some proteins also can promote degradation of salivary glands. For instance, the expression of caspase-1 rapidly increases during salivary gland degeneration, and the apoptosis of salivary gland cells is delayed after RNAi [
15].
We previously applied quantitative proteomics based on isobaric tags for relative and absolute quantitation (iTRAQ) to comprehensively analyse the patterns in protein expression levels during salivary gland degeneration [
16]. Changes in the expression levels of multiple proteins influenced salivary gland degeneration. Post-translational modifications of proteins can often determine protein function and regulate various life processes. Protein phosphorylation plays particularly an important regulatory role. To perform a more in-depth study of the molecular mechanisms of salivary gland degeneration, in this study, data-independent acquisition (DIA)-based quantitative proteomics was used to investigate the phosphorylation patterns of many proteins during salivary gland degeneration in
Haemaphysalis longicornis. Key regulatory proteins involved in this physiological mechanism were identified to gain insight into the mechanism underlying salivary gland degeneration.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Ethics statement
All experimental procedures were approved (Approval No. 165031) by the Animal Ethics Committee of Hebei Normal University.
Tick feeding
Haemaphysalis longicornis nymphs were collected from Zhangjiakou Xiaowutai Mountain National Nature Reserve in Hebei Province, PR China. The ticks were allowed to feed on the ears of New Zealand white rabbits (Female, 1.5 kg, Animal Experiment Center, Hebei Medical University). When not feeding, the ticks were cultured at 25±1°C and 75% relative humidity in artificial climate incubators.
Protein extraction
The time of natural detachment of engorged females tick from the host was recorded as 0 hr. The salivary glands were pulled out from the female ticks at 0, 12, 24, 36, and 48 hr post-engorgement. The salivary glands were then immediately placed in sterile PBS (0.01 M) containing NaF (0.05 M), Na3VO4 (0.01 M), and protease inhibitor cocktail (0.01 M) (Sigma, Roche, Mannheim, Germany). The salivary glands were immediately ground using what device. The homogenate was transferred into a 50 ml centrifuge tube and spun for 15 min at 4°C, 12,000×g, and the supernatant was transferred to a new tube. An equal volume of Tris-saturated phenol (pH 7.8) was added to the mixture, and vortexed for 5 min, followed by spinning for 15 min at 4°C, 12,000×g. Equal volume of 50 mM Tris-HCl (pH 8.0) was added and vortexed for 5 min and centrifuged at same condition. The organic phase was washed twice by the same method. After removing upper aqueous phase, the protein was precipitated by adding 5 volumes of 0.1 M ammonium acetate in methanol and stored at −20°C overnight. The mixture was centrifuged for 15 min at 4°C, 12,000×g, and the protein pellet at the bottom of the tube was further washed with methanol. The extracted proteins were lyophilised and frozen at −80°C for downstream experiments.
Protein digestion
The protein samples, 3 mg each, were reduced with 10 mM dithiothreitol at 37°C for 1 hr and alkylated with 20 mM iodoacetamide in the dark at 26°C with constant shaking for 30 min. The proteins were digested with trypsin (1:20 w/w, Promega, Madison, USA) at 37°C for 12 hr and supplemented with the same amount of enzyme 6 hr after the start of digestion. The digestion efficiency was monitored by LC-MS (Thermo Fisher Scientific, Waltham, Massachusetts, USA). The peptides were then desalted using a C18 solid-phase extraction column (Anpel, Shanghai, China), according to the manufacturer’s instruction.
Enrichment of Phosphopeptides
Enrichment of phosphopeptides was performed as previously described [
17]. Briefly, samples were trypsin digested then enriched for phosphopeptides using TiO
2 beads (GL Sciences, Tokyo, Japan). The enriched phosphopeptides were lyophilized and stored at −80°C until use.
The enriched phosphopeptide samples of each stage were mixed, and separated by high-pH RP-HPLC (e2695 Separation Module, Waters, Milford, Massachusetts, USA) by using Durashell-C18 column (5 μm particle size, 100 Å pore size, 4.6 mm×250 mm; Agela, California, USA) with solvent A (5 mM ammonium formate, pH 10.0) and solvent B (ACN with 5 mM ammonium formate, pH 10.0). The liquid phase separation gradient was 5% solvent B for 15 min, followed by 5–50% solvent B for 70 min, with a flow rate of 1 ml/min using a linear gradient. Fractions were collected at 1 min interval, combined into 10 groups, lyophilised and stored at −80°C until use.
Data-dependent acquisition (DDA) spectral library construction and analysis
Resuscitation was performed by adding 0.1% formic acid and indexed retention time (iRT) reagent (Biognosys, Zurich, Switzerland) to the lyophilized phosphorylated samples according to the manufacturer instructions. DDA analysis was carried out by ACQUITY UPLC M-Class system (Waters, Milford, USA) and Q Exactive HF mass spectrometer (Thermo Fisher Scientific, Waltham, Massachusetts, USA) Parameters for mass spectrometry identification were set as previously described [
17].
The above 10 groups DDA mass spectrometry identification results were combined for searching by Proteome Discoverer 2.2 (Thermo Fisher Scientific) to construct DDA spectral libraries. The database used for searching came from the
H. longicornis protein database derived from transcriptome sequences (NCBI GenBank accession number: GHLT00000000). To eliminate contamination, host
Oryctolagus cuniculus and human protein sequences were used as contaminating databases for proteomic search. Search parameters were as previously described [
17].
Phosphorylation samples were redissolved with 0.1% formic acid and iRT reagent. DIA spectral data were collected for each sample with setting parameters as previously described [
17]. The DIA data were analysed using Spectronaut software (version 11.0, Biognosys, Zurich, Switzerland). The default parameters were set for DIA data analysis.
An open source software GProX was used to conduct cluster analysis of the differentially expressed proteins with similar change patterns [
18]. Number of Clusters was set to 4, and a fixed regulation threshold (upper limit of 0.58 and lower limit of −0.58, corresponding to the original ratios of approximately 1.5 and 0.67, respectively) was used. A minimal membership for a plot was set as 0.5. Other parameters were set to default values. Gene ontology (GO) functional enrichment of the differentially expressed proteins was analysed using PANTHER classification system (
http://www.pantherdb.org/). Pathways associated with the differentially expressed proteins were identified using Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes (KEGG) database (
http://www.kegg.jp/kegg/).
An RNAi kit (Promega, Madison, USA) was used to synthesise double-stranded RNA (dsRNA) according to the manufacturer’s instructions. A Hippo-specific
H. longicornis nucleotide sequence 1,437–1,666 was selected for dsRNA synthesis. After the target mRNA was cloned and sequenced, the correct target cDNA sequences for RNAi were used for dsRNA synthesis. A primer pair used to synthesise dsRNA included T7 promoter sequence (underlined) as follows: 5′-
TAATACGACTCACTATAGGGTGGGTCACCTTCCTTGC-3′ and 5′-
TAATACGACTCACTATAGGAGATGAACAGCGTGTCCTTG-3′. Green fluorescent protein (GFP, accession number KX247384.1) dsRNA was synthesised as a control [
19]. Non-inoculated ticks were used as control. Forty female
H. longicornis were injected with 0.5–1 μl (4 μg/μl) of Hippo dsRNA and GFP dsRNA using a Hamilton syringe (33-gauge needle) in the lower right quadrant of the body [
20]. The engorged female ticks injected with Hippo dsRNA and GFP dsRNA, and ticks of other groups were maintained in a constant temperature and humidity incubator at 26°C.
Degree of mRNA knockdown was assayed using qRT-PCR. Total RNA of salivary glands of forty ticks were extracted using TRIzol Reagent (Invitrogen, Carlsbad, USA) [
21]. After treatment with DNase, cDNA was synthesised using a reverse transcription kit (Takara, Osaka, Japan). A primer pair used for qRT-PCR was as follows: 5′-GGCGGATTCAAAGCCAACG-3′ and 5′-CGCCTCCCGAGTTTGGTGT-3′. Gene expression silencing rate was compared between female ticks injected with Hippo-RNA targeting dsRNA and GFP control dsRNA. A fluorescence microscope (DVM6 digital microscope; Leica, Frankfurt, Germany) was used to observe morphological changes in the salivary gland. The changes of spawning amount after RNAi were measured in the ticks.
RESULTS
Phosphopeptides identified
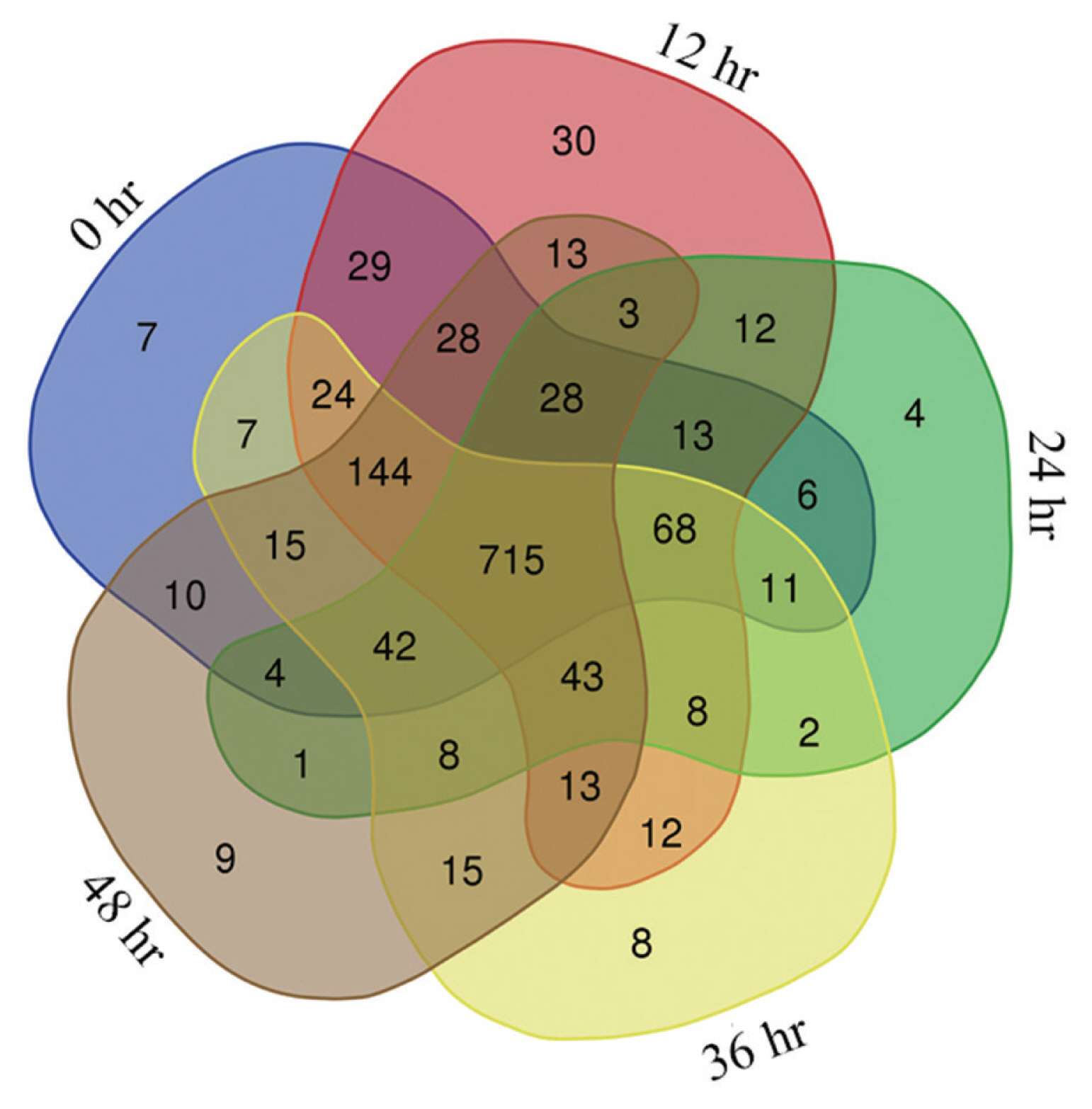
Phosphopeptides were identified as 1,394, 1,394, 1,392, 1,387, and 1,383 in the salivary glands of female ticks at 5 time points (0, 12, 24, 36, and 48 hr) after engorgement. The number of phosphopeptides identified with CV <20% among 4 replicates for each period was 1,151, 1,183, 968, 1,136, and 1,092, respectively. There were 715 phosphopeptides that occurred in all 5 stages (
Fig. 1), of which 633 phosphopeptides were annotated. The 715 phosphopeptides had 850 phosphorylation modification sites in total, 1 modification site in 558 peptides, 2 sites in 119 peptides and 3 sites in 8 peptides. By residue, 741 modifications occurred on serine residue, 98 on threonine residue, and 11 on tyrosine residue.
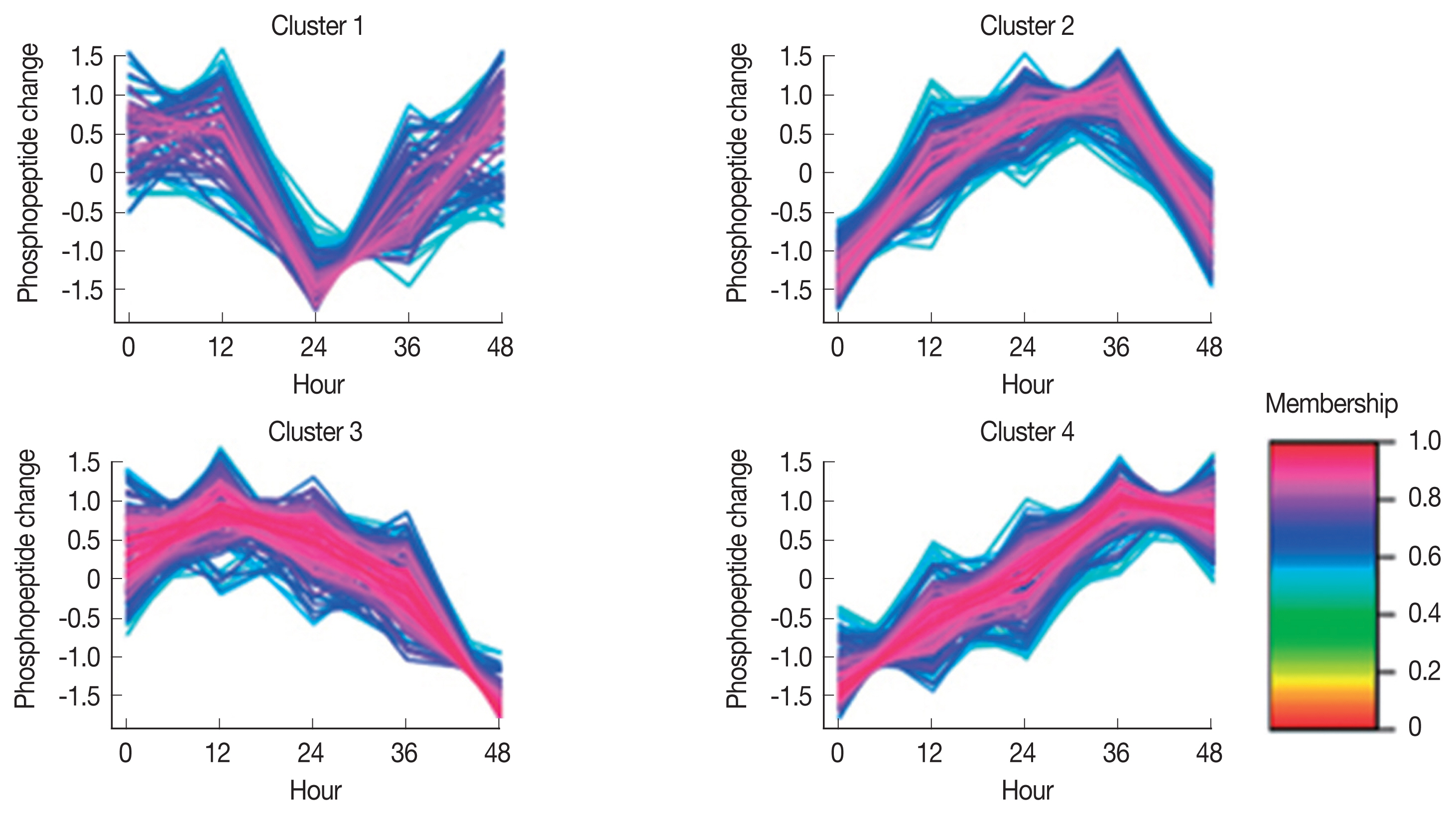
Pattern of differentially expressed phosphopeptides were grouped into 4 clusters (
Fig. 2). In Cluster 1 contained 95 phosphopeptides, level of phosphopeptide expression remained unchanged for 12 hr after engorgement, decreased at 24 hr and increased at 48 hr. Cluster 2 contained 163 phosphopeptides, and phosphopeptide level increased for 24 hr after engorgement, remained unchanged to 36 hr, and decreased at 48 hr. In Cluster 3 containeing 172 phosphopeptides, the level decreased for 48 hr after engorgement. In Cluster 4 containing 203 phosphopeptides, the level continuously increased for 48 hr after engorgement.
The 633 differentially expressed phosphopeptides were distributed among 400 phosphorylated proteins, there were 8 GO terms enriched in molecular function. The proportion of binding and catalytic activity terms was relatively large (47.5% and 38.0%, respectively). There were 11 GO terms enriched in biological process. The proportion of cellular process and metabolic process terms was relatively large (33.7% and 24.2%, respectively). There were 6 GO terms enriched in cellular component. The proportion of cell and organelle terms was relatively large (45.3% and 36.6%, respectively).
Up-regulated proteins in 12 hr were enriched in 6 molecular function terms, and the proportion of binding term was relatively large (50.0%). There were 11 enriched terms for biological process, and the proportion of cellular process term were relatively large (30.7%). There were 10 enriched terms for cellular component, and the proportions of cell part and cell terms were relatively large (21.8% and 21.8%, respectively). Down-regulated proteins in 12 hr were enriched in 3 molecular function terms, and the proportion of binding term was relatively large (66.7%). There were 8 enriched terms for biological process, and the proportion of cellular process term were relatively large (23.5%). There were 5 enriched terms for cellular component, and the proportions of cell part and cell terms were relatively large (29.4% and 29.4%, respectively).
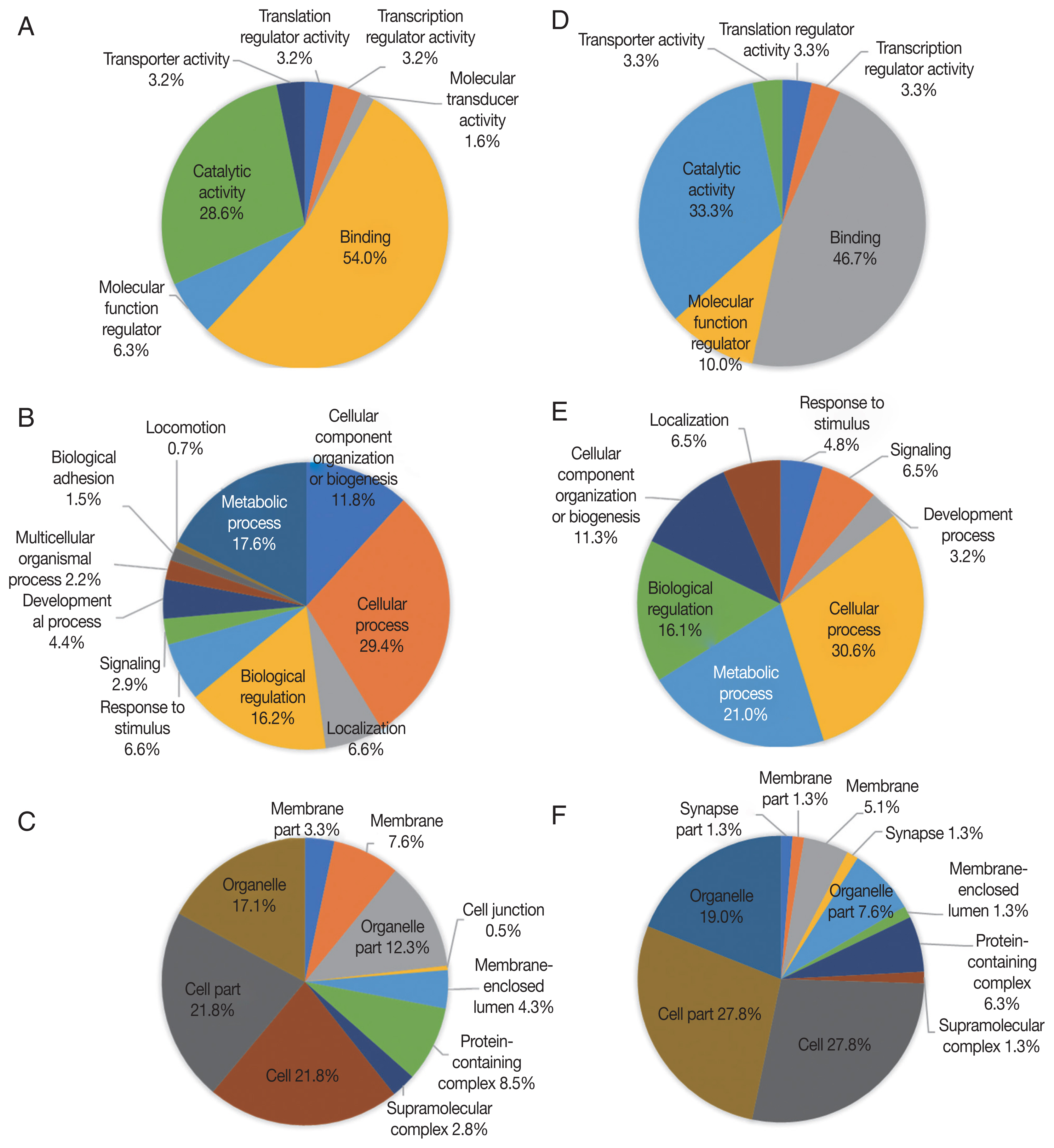
Up-regulated proteins in 24 hr were enriched in 7 molecular function terms, and the proportion of binding term was relatively large (54.0%) (
Fig. 3A). There were 11 enriched terms for biological process, and the proportion of cellular process term were relatively large (29.4%) (
Fig. 3B). There were 10 enriched terms for cellular component, and the proportions of cell part and cell terms were relatively large (21.8% and 21.8%, respectively) (
Fig. 3C). Down-regulated proteins in 24 hr were enriched in 6 molecular function terms, and the proportion of binding term was relatively large (46.7%) (
Fig. 3D). There were 8 enriched terms for biological process, and the proportion of cellular process term were relatively large (30.6%) (
Fig. 3E). There were 11 enriched terms for cellular component, and the proportions of cell part and cell terms were relatively large (27.8% and 27.8%, respectively) (
Fig. 3F).
Up-regulated proteins in 36 hr were enriched in 7 molecular function terms, and the proportion of binding term was relatively large (50.0%). There were 11 enriched terms for biological process, and the proportion of cellular process term were relatively large (29.6%). There were 10 enriched terms for cellular component, and the proportions of cell part and cell terms were relatively large (22.8% and 22.8%, respectively). Down-regulated proteins in 36 hr were enriched in 6 molecular function terms, and the proportion of binding term was relatively large (60.7%). There were 8 enriched terms for biological process, and the proportion of cellular process term were relatively large (31.4%). There were 11 enriched terms for cellular component, and the proportions of cell part and cell terms were relatively large (25.6% and 25.6%, respectively).
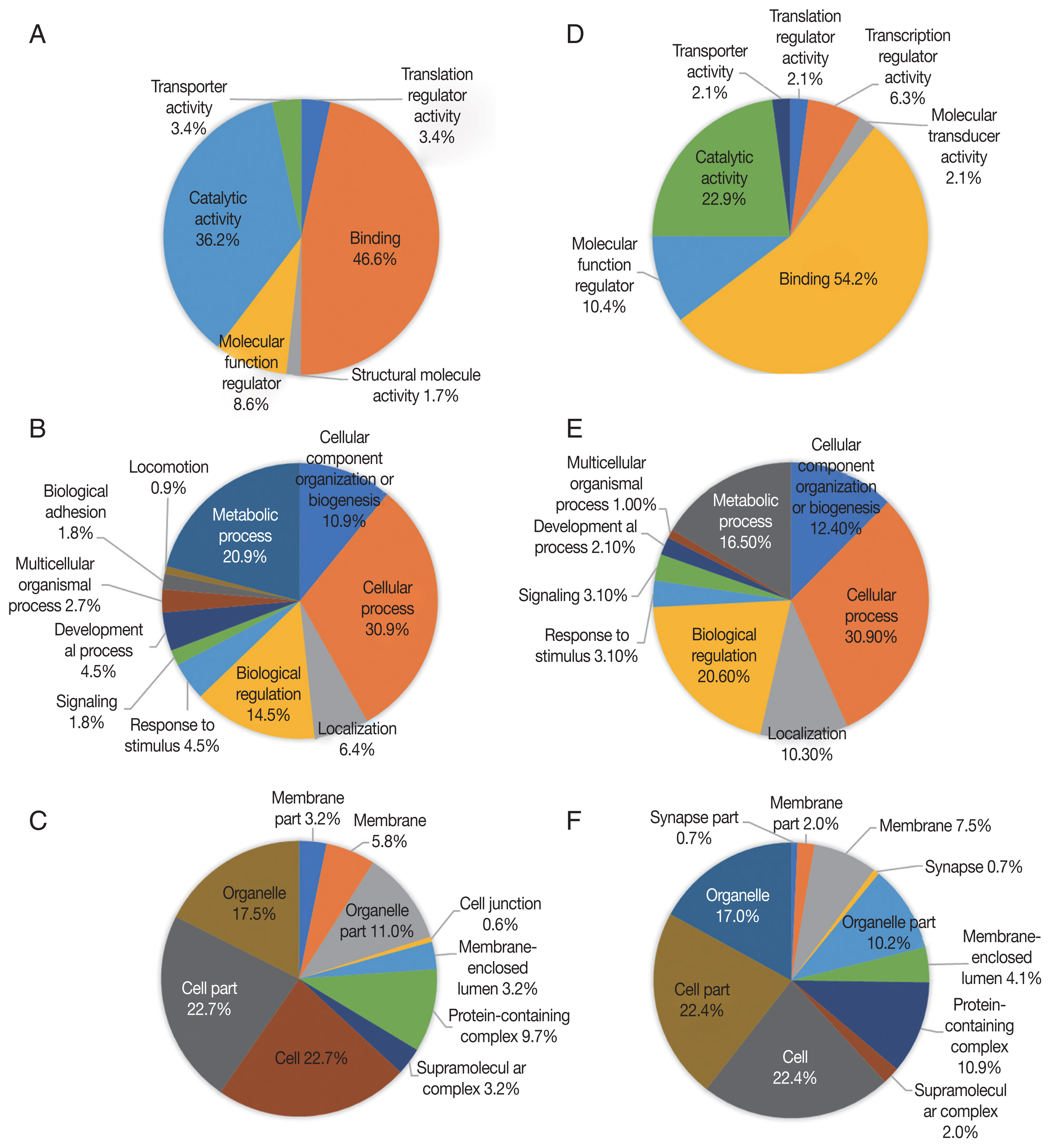
Up-regulated proteins in 48 hr were enriched in 6 molecular function terms, and the proportion of binding term was relatively large (46.6%) (
Fig. 4A). There were 11 enriched terms for biological process, and the proportion of cellular process term were relatively large (30.9%) (
Fig. 4B). There were 10 enriched terms for cellular component, and the proportions of cell part and cell terms were relatively large (22.7% and 22.7%, respectively) (
Fig. 4C). Down-regulated proteins in 48 hr were enriched in 7 molecular function terms, and the proportion of binding term was relatively large (54.2%) (
Fig. 4D). There were 9 enriched terms for biological process, and the proportion of cellular process term were relatively large (30.9%) (
Fig. 4E). There were 11 enriched terms for cellular component, and the proportions of cell part and cell terms were relatively large (22.4% and 22.4%, respectively) (
Fig. 4F).
The phosphorylated proteins on Cluster 1 were mainly involved in the metabolic pathway. Proteins in Cluster 2 were involved in endocytosis, RNA transport signalling pathways, metabolic pathways, tight junctions, and the Hippo signalling pathway. The proteins in Cluster 3 were mainly involved in the regulation of endocytosis, cAMP signalling, and P14K-AKT signalling. The phosphoryled proteins in Cluster 4 were involved in apoptosis and the Hippo signalling pathway. This finding indicated that some proteins activated the apoptosis pathway and facilitated salivary gland degeneration.
RNAi of the Hippo gene
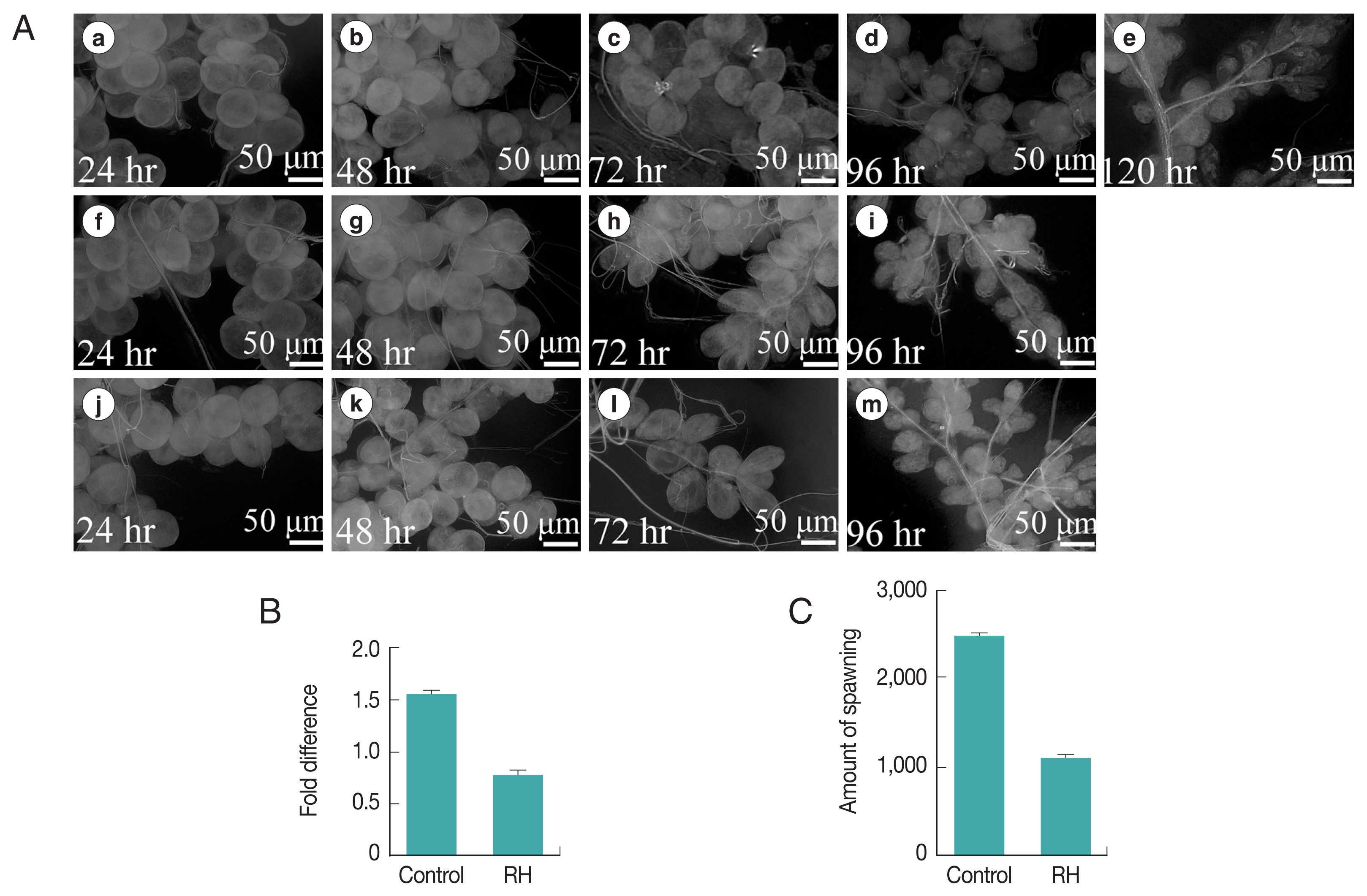
When dsRNA of the Hippo gene was injected into engorged female ticks, the interference efficiency was verified by qRT-PCR. When Hippo mRNA was knocked down, the salivary gland phenotype showed significant changes. Compared with
H. longicornis in the control group, whose salivary gland completely degenerated 120 hr after engorgement, salivary gland degeneration in ticks with Hippo mRNA knockdown was slower and still not complete at that time point (
Fig. 5A). After Hippo was knocked down, the results indicated that silencing rate of mRNA in the salivary glands of female ticks injected with Hippo dsRNA was 49.3% (
Fig. 5B). In addition, the spawning time of female ticks was significantly shortened, approximately shortened 5.3±1.0 days. The egg production was significantly reduced (
Fig. 5C).
DISCUSSION
During salivary gland degeneration in
H. longicornis, the expression levels of many proteins changes significantly [
16]. During this process, the post-translational modification of various proteins is also altered. In particular, changes in phosphorylation play an important role in regulating salivary gland degeneration in ticks. Based on the expression level patterns of the phosphopeptides, the proteins corresponding to these phosphopeptides were classified into 4 different Clusters for a more systematic analysis of the causes of changes in phosphorylation, we discussed some of the phosphorylation proteins that have changed (
Table 1).
The extent of phosphorylated proteins in Cluster 4 increased during salivary gland degeneration. Some phosphorylated proteins involved in apoptosis were classified into this Cluster, including Hippo and death domain-associated protein (Daxx). Hippo is mainly involved in the Hippo signalling pathway, which is found in
Caenorhabditis elegans [
22],
Drosophila melanogaster [
23], and mammals [
24]. In particular, studies of
Drosophila have found that the main functions of Hippo are the inhibition of cell proliferation and the promotion of apoptosis [
25]. The Hippo signalling pathway is composed of a core kinase cascade. Hippo is a member of the Ste-20 protein kinase family, and once it is phosphorylated, the transcriptional activator Yorkie (Yki) is inactivated through a series of cascade reactions [
26]. Hippo can bind to and phosphorylate the protein Salvador (Sav) [
27]. In this study, the phosphorylation of Hippo increased during salivary gland degeneration in female ticks, which is likely a major cause of salivary gland cell apoptosis. The continued increase in Hippo phosphorylation activated a certain downstream protein, which initiated its pro-apoptotic function, thereby promoting the apoptosis of salivary gland cells [
28]. In the RNAi experiment, the Hippo gene in engorged female ticks was knocked down. The interference results showed that Hippo knockdown could delay salivary gland degeneration, which further confirmed the pro-apoptotic function of Hippo in salivary gland degeneration in ticks.
Daxx is a highly phosphorylated multifunctional protein that can perform different biological functions responding to various stimuli [
29]. Daxx is a key protein in the FasL/Fas-mediated apoptosis pathway. Through phosphorylating Daxx, homeodomain-interacting protein kinases (HIPKs) activate Daxx, which in turn promotes the translocation of Daxx from the nucleus to the cytoplasm [
30]. Once translocated to the cytoplasm, Daxx binds to Fas-associated death domain and then activates and binds to apoptosis signal-regulating kinase 1 (ASK1). This is followed by a further phosphorylation of ASK1 and activation of Jun N-terminal kinase (JNK). JNK directly or indirectly inhibits the expression of growth factors such as Bcl-2, ultimately leading to apoptosis [
31]. Homologous proteins of Daxx are present in
Drosophila and other arthropods [
32]. However, the presence of Daxx protein and its functions in ticks has not been reported. In this study, the level of Daxx phosphorylation continuously increased during salivary gland degeneration in female ticks. Such a change is suggested as one of the major causes of salivary gland cell apoptosis.
Phosphorylation of the proteins in Cluster 3 decreased during salivary gland degeneration, under phosphorylation, majority of peptides were downregulated, indicating that the degree of phosphorylation of most proteins was decreased following salivary gland degeneration. Cluster 3 included cell division cycle 37 protein (CDC37), Dynamin, engulfment and cell motility 1 (ELMO1) and more. CDC37 has been shown to be an essential protein for regulating protein kinase activity and stability in different stages of the cell cycle [
33]. Casein kinase II (CK2) is activated by phosphorylating CDC37, which in turn promotes the binding of CDC37 and HSP90 and further regulates the functions of aurora kinase B [
33]. Aurora kinase B is a member of the aurora kinase family, which is an important regulator of mitosis, participating in many processes that regulate mitosis [
34]. During salivary gland degeneration in female ticks, apoptosis or autophagy occurs and almost no cells are produced; as the normal replication of cells is no longer necessary, CDC37 is no longer needed and its extent of phosphorylation and vitality is decreased.
Dynamin is a GTPase that participates in many cell activities, including endocytosis, intracellular membrane transport, actin remodelling, and migration [
35]. Dynamin forms a protein complex with tyrosine phosphatase (PTP-PEST), which inhibits phosphatase activity, increases the phosphorylation level and activates dynamin [
36]. Irrespective of rapid or slow endocytosis, the process of vesicles detaching from the plasma membrane requires the scission of dynamin. When vesicles are formed, dynamin forms a spiral aggregate in vesicles and the neck region of the plasma membrane. The aggregation undergoes structural changes during GTP hydrolysis, and the spiral longitudinal stretching eventually breaks the vesicles from the neck region [
37]. Studies have found that the absence of dynamin in
Drosophila leads to the dysfunction of lysosomes and autophagy [
38]. In the current study, the level of dynamin phosphorylation decreased during salivary gland degeneration in female ticks, indicating that dynamin viability gradually declined.
ELMO1 is a relatively conserved protein that is mainly involved in the migration of phagocytic cells and the phagocytosis of dead cells [
39]. In the chemokine signalling pathway, the protein HCK SH3 in the Src kinase family binded to ELMO1, phosphorylating and activating ELMO1. This allows phagocytic cells to quickly recognise, phagocytose, and digest dead cells [
40]. Homologous proteins of ELMO1 are present in arthropods and participate in the phagocytosis of dead cells and promote cell migration [
41]. A large number of cells die during salivary gland degeneration, and very few new cells are produced during the degeneration process. As replication of the cells is no more necessary, ELMO1 is no longer needed, and its extent of phosphorylation and vitality decreases during salivary gland degeneration in the female ticks.
Notes
-
CONFLICT OF INTEREST
The authors declare there are no conflict of interests.
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS
This work was supported by the Natural Science Foundation for Excellent Youth Scholars of Hebei Province of China (Nos. C2017205135). The Open Funds of the State Key Laboratory of Veterinary Etiological Biology, Lanzhou Veterinary Research Institute, Chinese Academy of Agricultural Sciences (Nos. SKLVEB2018KFKT007), and the Medical Science Research Project of Hebei Province of China (Nos. 20190036).
Fig. 1Phosphopeptides in female H. longicornis engorged salivary glands at 0, 12, 24, 36, and 48 hr.
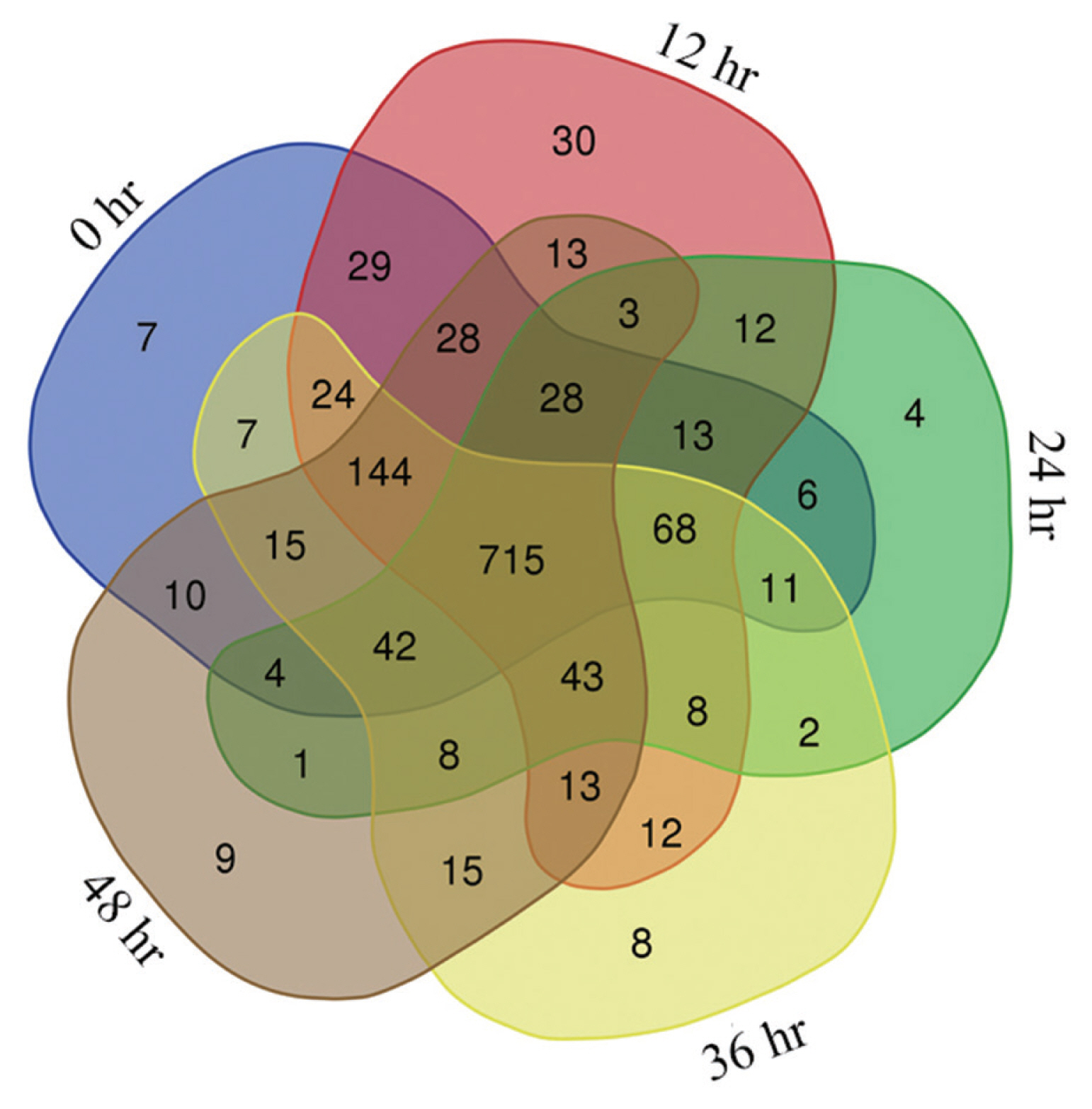
Fig. 2Clusters of differentially phosphorylated peptides in the salivary glands of engorged H. longicornis females.

Fig. 3GO analysis of 24 hr differentially expressed phosphorylated proteins during salivary gland degeneration in female H. longicornis. The percentages of proteins assigned to the different terms are shown. (A–C) up-regulated phosphorylated proteins. (D–F) down-regulated phosphorylated proteins. (A) molecular function; (B) biological process; (C) cellular component; (D) molecular function; (E) biological process; (F) cellular component.
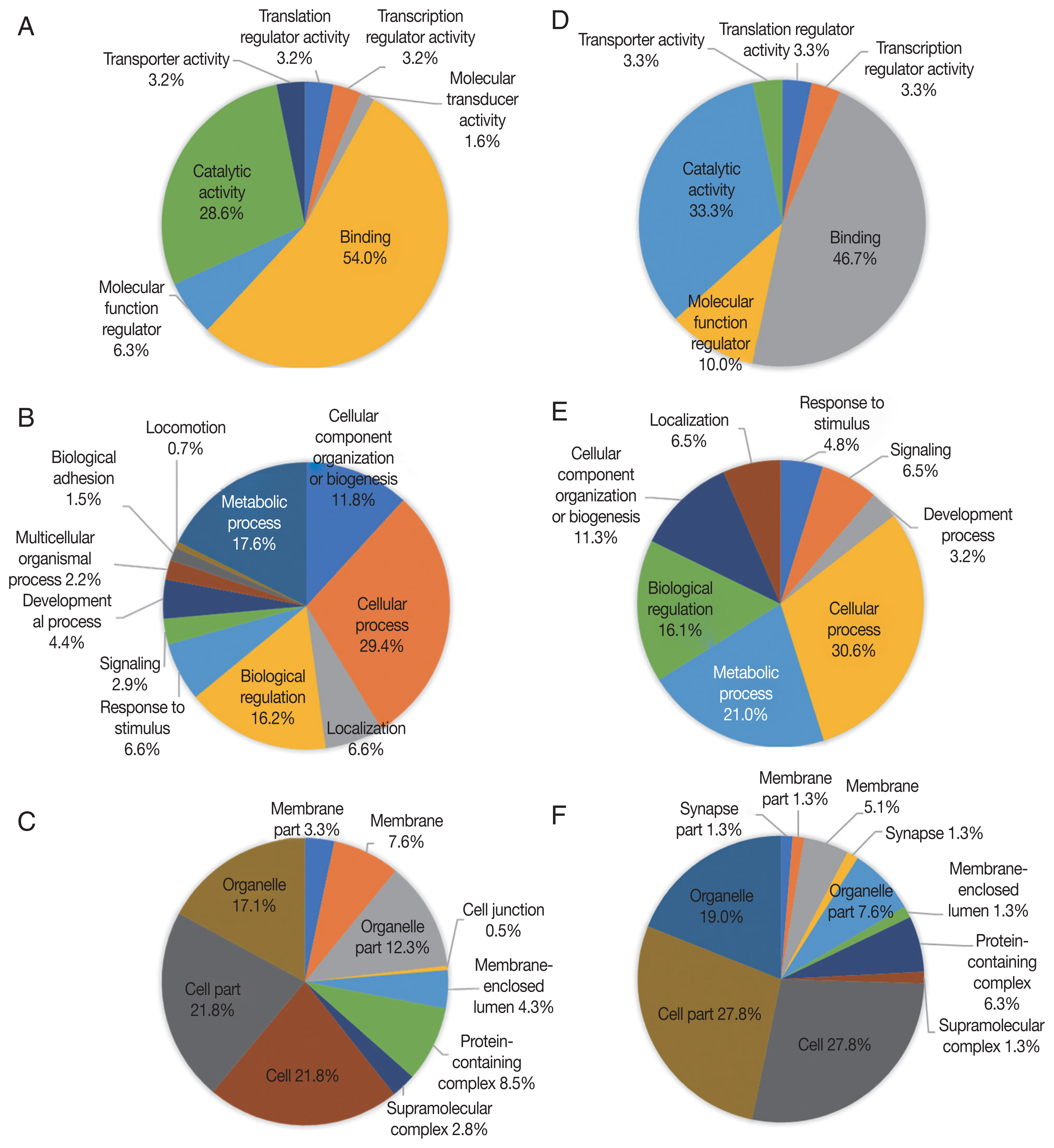
Fig. 4GO analysis of 48 hr differentially expressed phosphorylated proteins during salivary gland degeneration in female H. longicornis. The percentages of proteins assigned to the different terms are shown. (A–C) Up-regulated phosphorylated proteins. (D–F) Down-regulated phosphorylated proteins. (A) molecular function; (B) biological process; (C) cellular component; (D) molecular function; (E) biological process; (F) cellular component.
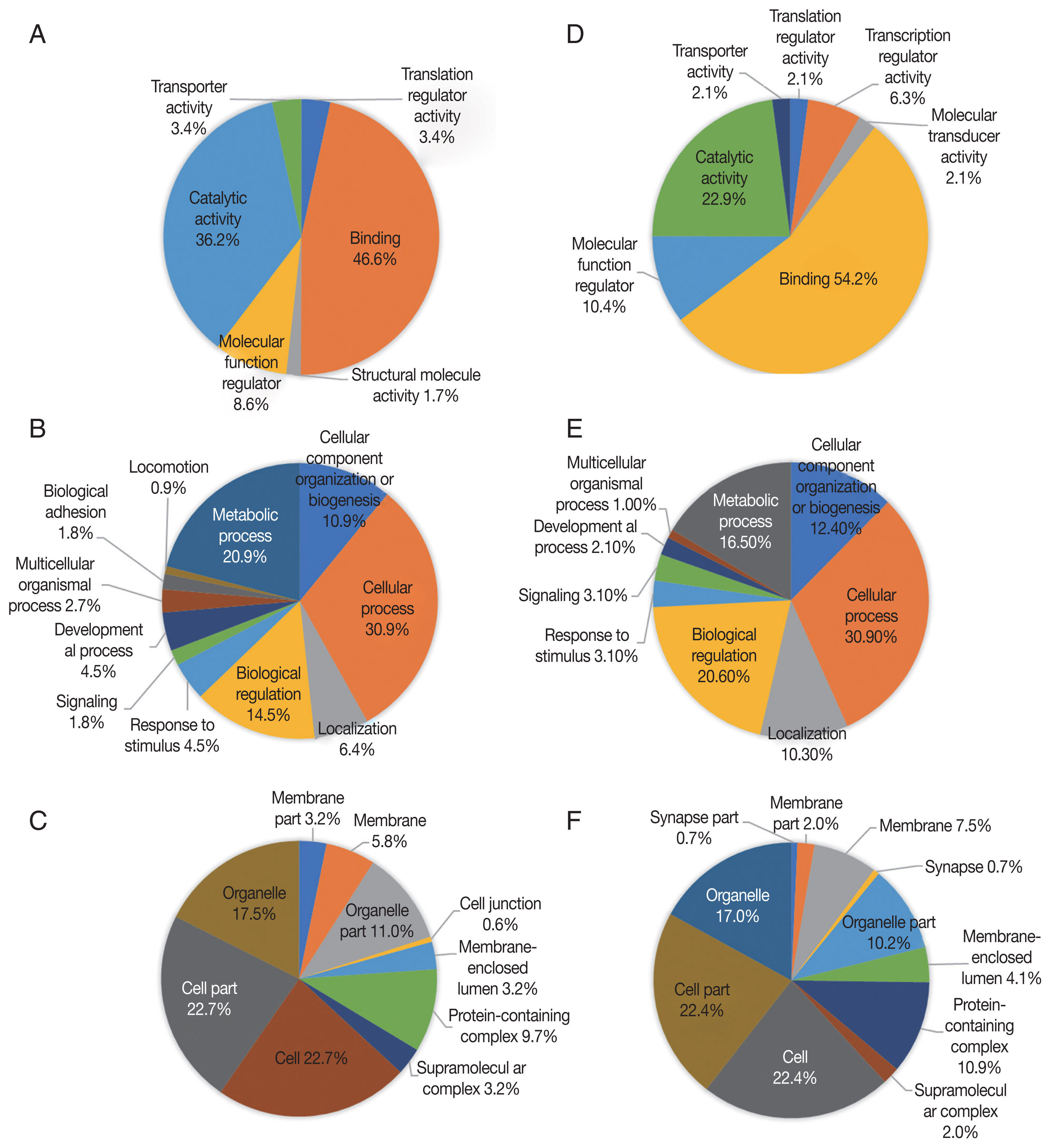
Fig. 5(A) Phenotypic change of salivary glands after RNAi targeting Hippo mRNA in the engorged females. Upper raw (a–e), Hippo dsRNA injected; middle raw (f–i), Normal control; lower raw (j–m): GFP dsRNA injected. (B) Silencing of gene expression. (C) Inhibition of spawning amount by H. longicornis females after RNAi. RH: RNAi Hippo.
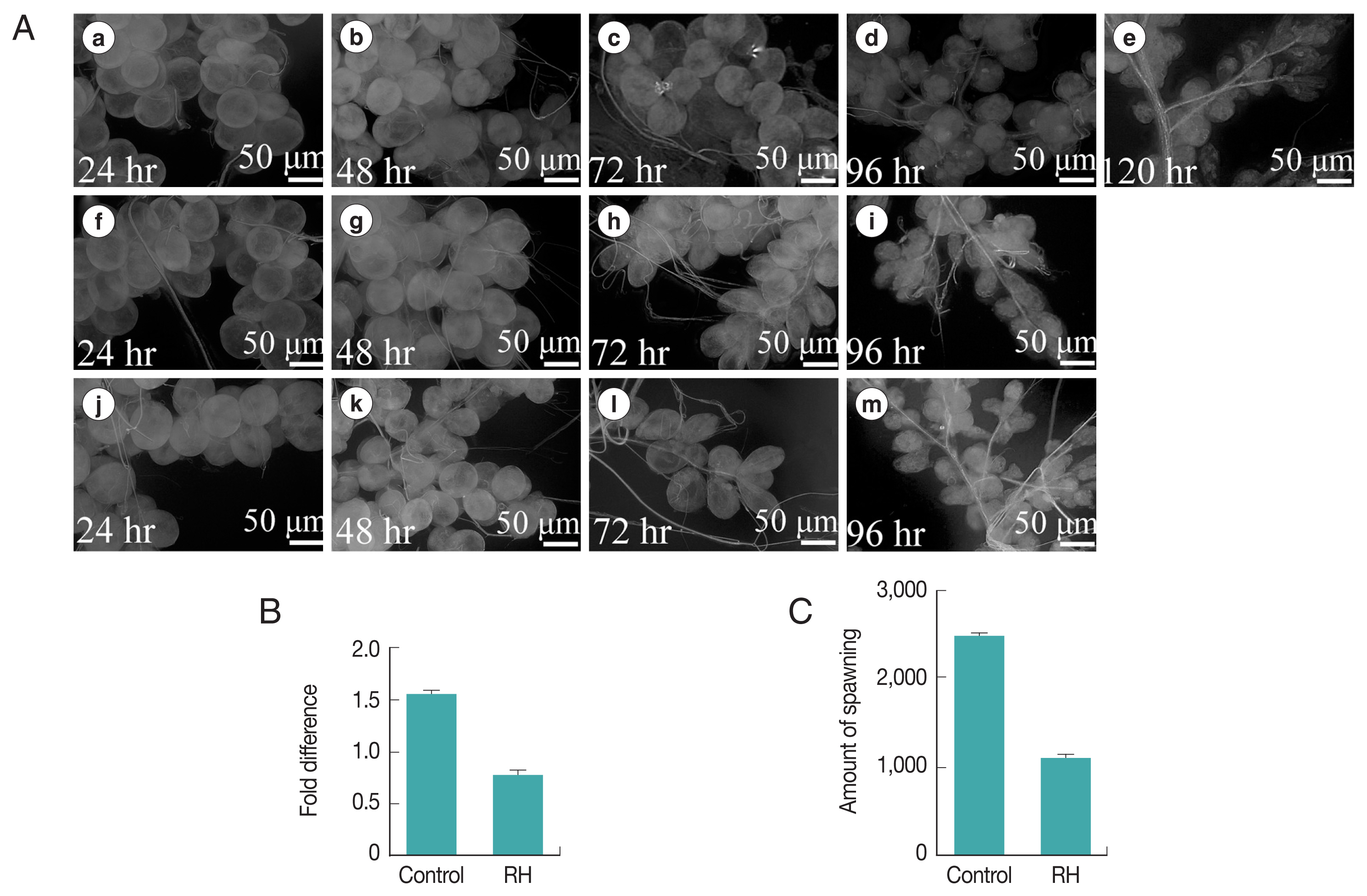
Table 1Proteins differentially phosphorylated and involved in Hippo, Apoptosis, RNA transport, cAMP and other important pathways during salivary glands degradation in female Haemophisalis longicormins
Table 1
|
Protein name |
GI number |
Description |
Phosphopeptide and site |
KEGG pathway |
|
Hippo ↑ |
241701230 |
Serine/threonine protein kinase |
RGS[+80]TGEAFLDDDEVDAGTMVK |
Hippo signaling pathway |
|
Daxx ↑ |
1316145131 |
Death domain-associated protein |
EQAIVIS[+80]DDEGPEER |
Apoptosis signalling pathway |
|
CDC37 ↓ |
241747021 |
Cell division cycle protein 37 |
TIEVSDDEDET[+80]HPNIDTPSLFR
TIEVS[+80]DDEDETHPNIDTPSLFR |
P13K-AKT signalling pathway |
|
ELMO1 ↓ |
241722888 |
Engulfment and cell motility protein 1 |
LLDTEGVDIPES[+80]PPPIPK |
Chemokine signaling pathway |
|
Dynamin ↓ |
242000334 |
Dynamin |
MQPPDSPRPAPPS[+80]PGGPR
MQPPDS[+80]PRPAPPS[+80]PGGPR |
Phospholipase D signaling pathway |
|
HSP40 ↑ |
241844830 |
Heat shock protein |
DVS[+80]LDGMDADPFFAR |
Protein processing in endoplasmic reticulum |
|
PIK3C2A ↑ |
241738280 |
Phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase class |
S[+80]KSPVVDKPASTTNSQVR |
Phosphatidylinositol signaling system |
|
PAIP1 ↑ |
241779579 |
Polyadenylate-binding protein |
TSS[+80]HSSSPSAGPAEDSLPILCGPDGVPISR |
RNA transport signaling pathway |
|
SNX32 ↓ |
241742597 |
Sorting nexin |
S[+80]NPEPNPPK |
Endocytosis signaling pathway |
|
PDE10A ↓ |
241601372 |
Cyclic nucleotide phosphodiesterase |
SLCHTNS[+80]LTTLPK |
cAMP signaling pathway |
References
- 1. Gondard M, Cabezas-Cruz A, Charles RA, Vayssier-Taussat M, Albina E, Moutailler S. Ticks and tick-borne pathogens of the caribbean: current understanding and future directions for more comprehensive surveillance. Front Cell Infect Microbiol 2017;7:490.
- 2. Narasimhan S, Schuijt TJ, Abraham NM, Rajeevan N, Coumou J, Graham M, Robson A, Wu MJ, Daffre S, Hovius JW, Fikrig E. Modulation of the tick gut milieu by a secreted tick protein favors Borrelia burgdorferi colonization. Nat Commun 2017;8:184.
- 3. Sun RX, Lai SJ, Yang Y, Li XL, Liu K, Yao HW, Zhou H, Li Y, Wang LP, Mu D, Yin WW, Fang LQ, Yu HJ, Cao WC. Mapping the distribution of tick-borne encephalitis in mainland China. Ticks Tick Borne Dis 2017;8:631-639.
- 4. Papa A, Tsergouli K, Tsioka K, Mirazimi A. Crimean-congo hemorrhagic fever: tick-host-virus interactions. Front Cell Infect Microbiol 2017;7:213.
- 5. Davies S, Abdullah S, Helps C, Tasker S, Newbury H, Wall R. Prevalence of ticks and tick-borne pathogens: Babesia and Borrelia species in ticks infesting cats of Great Britain. Vet Parasitol 2017;244:129-135.
- 6. Martins LA, Malossi CD, Galletti MFBM, Ribeiro JM, Fujita A, Esteves E, Costa FB, Labruna MB, Daffre S, Fogaça AC. The transcriptome of the salivary glands of Amblyomma aureolatum reveals the antimicrobial peptide microplusin as an important factor for the tick protection against Rickettsia rickettsii infection. Front Physiol 2019;10:529.
- 7. Hajdušek O, Síma R, Ayllón N, Jalovecká M, Perner J, de la Fuente J, Kopáček P. Interaction of the tick immune system with transmitted pathogens. Front Cell Infect Microbiol 2013;3:26.
- 8. Kotál J, Langhansová H, Lieskovská J, Andersen JF, Francischetti IM, Chavakis T, Kopecký J, Pedra JH, Kotsyfakis M, Chmelař J. Modulation of host immunity by tick saliva. J Proteomics 2015;128:58-68.
- 9. Kaufman W. The influence of various factors on fluid secretion by in vitro salivary glands of ixodid ticks. J Exp Biol 1976;64:727-742.
- 10. Ullah SA, Kaufman WR. Salivary gland degeneration and ovary development in the Rocky Mountain wood tick, Dermacentor andersoni Stiles (Acari: Ixodidae). II. Determination of the ‘critical weight’. Ticks Tick-borne Dis 2014;5:516-522.
- 11. Harris RA, Kaufman WR. Neural involvement in the control of salivary gland degeneration in the ixodid tick Amblyomma hebraeum
. J Exp Biol 1984;109:281-290.
- 12. Tirloni L, Islam MS, Kim TK, Diedrich JK, Yates JR 3rd, Pinto AF, Mulenga A, You MJ, Da Silva Vaz I Jr. Saliva from nymph and adult females of Haemaphysalis longicornis: a proteomic study. Parasites Vector 2015;8:338.
- 13. Harris RA, Kaufman WR. Hormonal control of salivary gland degeneration in the ixodid tick Amblyomma hebraeum
. J Insect Physiol 1981;27:241-248.
- 14. Harris RA, Kaufman WR. Ecdysteroids: possible candidates for the hormone which triggers salivary gland degeneration in the ixodid tick Amblyomma hebraeum
. Experientia 1985;41:740-742.
- 15. Yu X, Zhou Y, Cao J, Zhang H, Gong H, Zhou J. Caspase-1 participates in apoptosis of salivary glands in Rhipicephalus haemaphysaloides
. Parasit Vectors 2017;10:225.
- 16. Wang H, Zhang X, Wang X, Zhang B, Wang M, Yang X, Han X, Wang R, Ren S, Hu Y, Liu J. Comprehensive analysis of the global protein changes that occur during salivary gland degeneration in female ixodid ticks Haemaphysalis longicornis
. Front Physiol 2019;9:1943.
- 17. Hawkins LJ, Wang M, Zhang B, Xiao Q, Wang H, Storey KB. Glucose and urea metabolic enzymes are differentially phosphorylated during freezing, anoxia, and dehydration exposures in a freeze tolerant frog. Comp Biochem Physiol Part D Genomics Proteomics 2019;30:1-13.
- 18. Rigbolt KT, Vanselow JT, Blagoev B. GProX, a user-friendly platform for bioinformatics analysis and visualization of quantitative proteomics data. Mol Cell Proteomics 2011;10:O110.007450.
- 19. Gong H, Umemiya R, Zhou J, Liao M, Zhang H, Jia H, Nishikawa Y, Xuan X, Fujisaki K. Blocking the secretion of saliva by silencing the HlYkt6, gene in the tick Haemaphysalis longicornis
. Insect Biochem Mol Biol 2009;39:372-381.
- 20. Kocan KM, Zivkovic Z, Blouin EF, Naranjo V, Almazán C, Mitra R, de la Fuente J. Silencing of genes involved in Anaplasma marginale-tick interactions affects the pathogen developmental cycle in Dermacentor variabilis
. BMC Dev Biol 2009;9:1-11.
- 21. Ren S, Zhang B, Xue X, Wang S, Zhao H, Zhang X, Wang M, Xiao Q, Wang H, Liu J. Salivary gland proteome analysis of developing adult female Haemaphysalis longicornis ticks: molecular motor and TCA cycle-related proteins play an important role throughout development. Parasit Vectors 2019;12:613.
- 22. Feng G, Zhu Z, Li WJ, Lin Q, Chai Y, Dong MQ, Ou G. Hippo kinases maintain polarity during directional cell migration in Caenorhabditis elegans. EMBO J 2017;3:334-345.
- 23. Varelas X. The Hippo pathway effectors TAZ and YAP in development, homeostasis and disease. Development 2017;141:1614-1626.
- 24. Dong Y, Du X, Ye J, Han M, Xu T, Zhuang Y, Tao W. A cell-intrinsic role for Mst1 in regulating thymocyte egress. J Immunol 2009;183:3865-3872.
- 25. Ura S, Masuyama N, Graves JD, Gotoh Y. MST1-JNK promotes apoptosis via caspase-dependent and independent pathways. Genes Cells 2001;6:519-530.
- 26. Meng Z, Moroishi T, Guan KL. Mechanisms of Hippo pathway regulation. Gene Dev 2016;30:1-17.
- 27. Wu S, Huang J, Dong J, Pan D. Hippo encodes a Ste-20 family protein kinase that restricts cell proliferation and promotes apoptosis in conjunction with salvador and warts. Cell 2003;114:445-456.
- 28. Zheng Y, Wang W, Liu B, Deng H, Uster E, Pan D. Identification of Happyhour/MAP4K as alternative Hpo/Mst-like kinases in the Hippo kinase cascade. Dev Cell 2015;34:642-655.
- 29. Niu YL, Li C, Zhang GY. Blocking Daxx trafficking attenuates neuronal cell death following ischemia/reperfusion in rat hippocampus CA1 region. Arch Biochem Biophys 2011;515:89-98.
- 30. Ecsedy JA, Michaelson JS, Leder P. Homeodomain-interacting protein kinase 1 modulates Daxx localization, phosphorylation, and transcriptional activity. Mol Cell Biol 2003;23:950-960.
- 31. Yang X, Khosravi-Far R, Chang HY, Baltimore D. Daxx, a novel Fas-binding protein that activates JNK and apoptosis. Cell 1997;89:1067-1076.
- 32. Fromental-Ramain C, Ramain P, Hamiche A. The Drosophila DAXX-like protein (DLP) cooperates with ASF1 for H3. 3 deposition and heterochromatin formation. Mol Cell Biol 2017;37:e00597-16.
- 33. Lange BM, Rebollo E, Herold A, González C. Cdc37 is essential for chromosome segregation and cytokinesis in higher eukaryotes. EMBO J 2002;21:5364-5374.
- 34. Miyata Y, Nishida E. CK2 controls multiple protein kinases by phosphorylating a kinase-targeting molecular chaperone, Cdc37. Mol Cell Biol 2004;24:4065-4074.
- 35. Hinshaw JE. Dynamin and its role in membrane fission. Annu Rev Cell Dev Bi 2000;16:483-519.
- 36. Eleniste PP, Huang S, Wayakanon K, Largura HW, Bruzzaniti A. Osteoblast differentiation and migration are regulated by dynamin GTPase activity. Int J Biochem Cell Biol 2014;46:9-18.
- 37. Praefcke GJ, McMahon HT. The dynamin superfamily: universal membrane tubulation and fission molecules? Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 2004;5:133-147.
- 38. Fang X, Zhou J, Liu W, Duan X, Gala U, Sandoval H, Tong C. Dynamin regulates autophagy by modulating lysosomal function. J Genet Genomics 2016;43:77-86.
- 39. Yokoyama N, deBakker CD, Zappacosta F, Huddleston MJ, Annan RS, Ravichandran KS, Miller WT. Identification of tyrosine residues on ELMO1 that are phosphorylated by the Src-family kinase Hck. Biochemistry 2005;44:8841-8849.
- 40. Elliott MR, Zheng S, Park D, Woodson RI, Reardon MA, Juncadella IJ, Kinchen JM, Zhang J, Lysiak JJ, Ravichandran KS. Unexpected requirement for ELMO1 in clearance of apoptotic germ cells in vivo. Nature 2010;467:333-337.
- 41. Van Goethem E, Silva EA, Xiao H, Franc NC. The Drosophila TRPP cation channel, PKD2 and Dmel/Ced-12 act in genetically distinct pathways during apoptotic cell clearance. PLoS One 2012;7:e31488.