Abstract
Free-living amoebas (FLAs) can cause severe disease in humans and animals when they become infected. However, there are no accurate survey reports on the prevalence of FLAs in Korea. In this study, we collected 163 tap water samples from buildings, apartments, and restrooms of highway service areas in 7 Korean provinces with high population density. All these buildings and facilities have water storage tanks in common. The survey was separated into categories of buildings, apartments, and highway service areas. Five hundred milliliters of tap water from each building was collected and filtered with 0.2 μm pore filter paper. The filters were incubated in agar plates with heated E. coli at 25°C. After axenization, genomic DNA was collected from each FLA, and species classification was performed using partial 18S-rDNA PCR-sequencing analysis. We found that 12.9% of tap water from buildings with storage tanks in Korea was contaminated with FLAs. The highway service areas had the highest contamination rate at 33.3%. All of the FLAs, except one, were genetically similar to Vermamoeba vermiformis (Hartmannella vermiformis). The remaining FLA (KFA21) was very similar to Acanthamoeba lugdunensis (KA/E26). Although cases of human infection by V. vermiformis are very rare, we must pay attention to the fact that one-third of tap water supplies in highway service areas have been contaminated.
-
Key words: Vermamoeba vermiformis, free-living amoeba, tap water of storage tank, 18S-rDNA sequencing
Free-living amoebas (FLAs) are ubiquitous protozoa akin to bacteria, fungi, and algae. FLAs are found all around us, including in dust, seawater, soil, the atmosphere, and lakes [
1]. FLAs are classified as several species. Of these species,
Balamuthia, Naegleria, Sappinia, Vermamoeba (formerly
Hartmannella), and
Acanthamoeba have been reported to infect humans and animals [
2]. The symptoms of the infections varied by individual case and FLA species [
3]. In the case of
Naegleria infection in humans, encephalitis, such as primary amebic meningoencephalitis, has been observed.
Acanthamoeba, Vermamoeba, Sappinia, and
Balamuthia infections have primarily been observed in the eyes, a condition known as amebic keratitis [
4–
8]. In recent studies,
Acanthamoeba has also been observed as one of the potential allergens leading to airway inflammation through intranasal infection [
9]. The tap water for many public facilities as well as large residential and office buildings is stored in storage tanks and supplied through individual water pipes when needed for activities such as drinking, washing, and cooking [
10]. These water storage tanks can be easily contaminated by external pollutants in the air. In addition, special circumstances, such as flooding and heavy rains, can cause wastewater to flow backward from basement water tanks to the rooftop water tanks, resulting in extreme contamination of the tap water [
11]. For this reason, 79% of USA and 89% of UK household tap water samples have been reported to contain FLAs [
11,
12]. In this study, we investigated the FLA contamination rate in the tap water supplies of office buildings, apartments, and restrooms of highway service areas in South Korea. FLA contamination rates and genetic classification of species were investigated. A total of 163 tap water samples was collected using water sample bottles (MEDI-LAND, Seoul, Korea) from 37 apartments, 102 office buildings, and 24 highway service areas. Each 500 ml sample of tap water was filfered through 0.2 μm pore filter (Adventec MFS, California, USA). The exposed filters were placed upside down on 1.5% of agar plates, which were smeared with heated
Escherichia coli and then incubated at 25°C. After one week, trophozoites or cysts of FLAs were detected under a microscope. A single cyst of each FLA was moved to a new
E. coli treated agar plate under a microscope and then observed for additional growth of FLAs without any contamination. A piece of an agar plate with many FLA cysts was treated with 0.1N HCl for 24 hr for axenization. The agar plate was incubated according to previous reports [
13]. Each FLA was named as KFA (Korean Free-living Amoeba) followed by a number (according to the detection order). To identify the genetic level of the FLAs, genomic DNA was extracted according to manufacturer protocols (Qiagen, Valencia, California, USA). Genetic analyses were performed with 18S-rDNA partial sequences of the FLAs. The primer sequences for 18S-rDNA were 5′-TTT GAA TTC GCT CCA ATA GCG TAT ATT AA-3′ and 5′-TTT GAA TTC AGA AAG AGC TAT CAA TCT GT-3′. Phylogenetic analyses were performed with FLA isolates and 2 reference sequences (
A. lugdunensis KA/E26 EF140627 and
V. vermiformis CRIB-06 DQ123623) using the MEGA6 program.
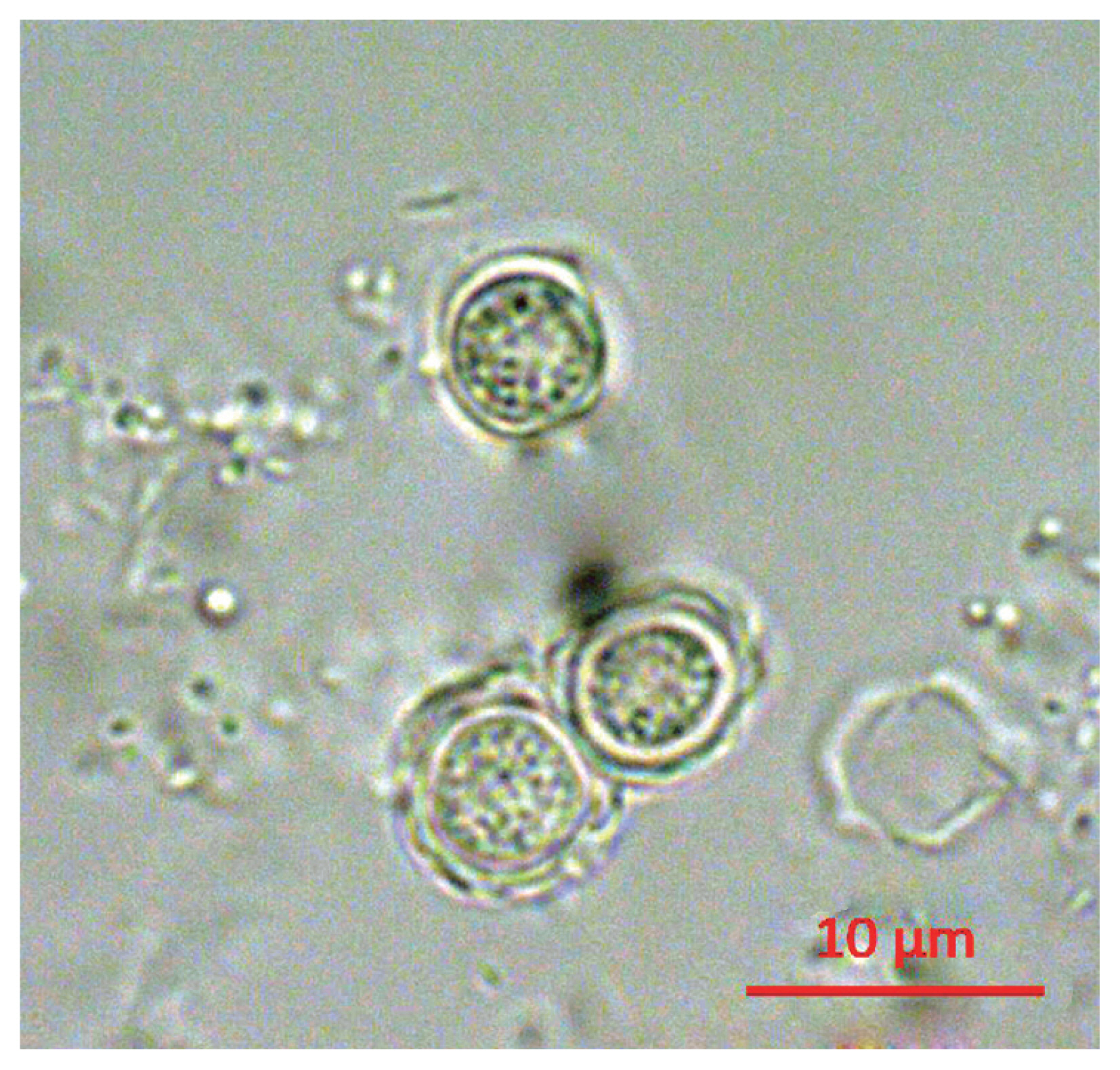
Following the analyses, we found that 21 out of 163 (12.9%) tap water samples were contaminated with FLAs. The shapes of the cysts were very similar each other; the size of cysts were belong to 5–25 μm and they have 2 layers of membranes commonly (
Fig. 1). FLAs were detected in 4 samples from apartments (10.8%), 9 samples from office buildings (8.8%), and 8 samples from highway service areas (33.3%) (
Table 1). The observed FLA contamination rate was higher for highway service areas than apartments and office buildings. In order to determine the FLA contamination rate by region, we divided the FLA contaminated tap water samples into 8 regions (
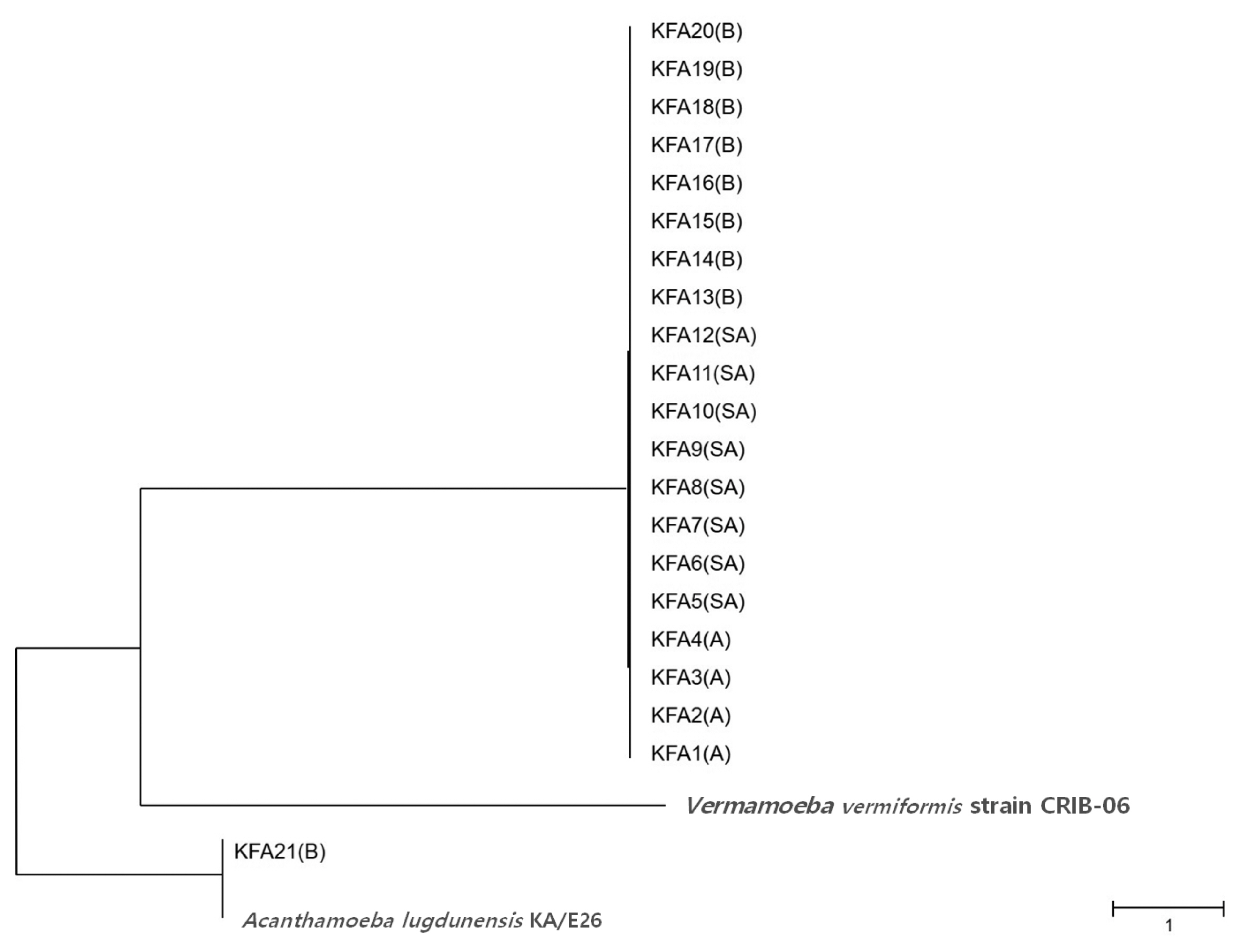
Table 2). FLA contamination was the highest in the Gyeongbuk region (north of Gyeongsang province), including Daegu (25.8%). In the Gyeongnam region (south of Gyeongsang province), which includes Busan and Ulsan, an FLA contamination rate of 16.1% was observed. In order to identify species, we isolated all FLAs from the contaminated tap water samples and ultimately collected 21 different FLAs. The genetic variation in the 21 different FLAs was analyzed using 18S-rDNA sequencing. We found that 20 of the FLAs were genetically similar to
V. vermiformis. The remaining FLA was genetically similar to
A. lugdunensis KA/E26 (
Fig. 2).
FLAs are distributed in the components of many of our environments, such as dust, wastewater, sea water, soil, river, and the atmosphere, along with many other pollutants [
14,
15]. FLAs belonging to the
Acanthamoeba, Balamuthia, and
Naegleria species are important causes of numerous diseases in humans and animals. They infect a host through cyst formation before developing trophozoites and reproducing by mitosis [
16]. They can enter the eyes, skin, lungs, and brain, resulting in severe pain. FLAs also live in contact lenses and eyewash solutions, and they have the potential to induce amebic keratitis [
17,
18]. Recently, with increasing interest in personal beauty, the utilization of contact lenses has increased. At the same time, the number of amebic keratitis patients in the U.K increased to 59 million as of 2016 [
19]. In addition to amebic keratitis,
Acanthamoeba has also been found to cause allergic airway inflammation in a recent study [
9]. The isolated FLAs in this study were genetically related to
V. vermiformis and
A. lugdunensis KA/E26.
A. lugdunensis KA/E26 has already been investigated, revealing genetic similarity to
A. lugdunensis L3A and
A. lugdunensis KA/E2. Numerous genetic isoforms of KA/E2 have been isolated from water, lens cases, and human eyes in Korea [
13,
20–
23]. These genetic isoforms have been reported as a pathogen of amebic keratitis and potential allergen leading to airway inflammation [
24]. Many studies in various countries have investigated FLA contamination rates [
25]. For example, in the U.S., 79% of household tap water samples were contaminated with FLAs [
11]. Likewise, in the U.K., 89% of household water samples contained FLAs [
11,
12]. In our study results, 33.3% of tap water samples from highway service areas were contaminated with FLAs. Although
Acanthamoeba was not detected in any samples,
Vermamoeba also has potential pathogenicity to humans [
26]. Furthermore, because the life cycle of the 2 FLAs (
Vermamoeba and
Acanthamoeba) are very similar,
Acanthamoeba could become more prevalent if we do not carefully maintain the storage water tanks.
In conclusion, we found that 12.9% of tap water in buildings with water storage tanks was contaminated with FLAs. Thus, it is necessary to determine the exact FLA contamination rate and establish regulatory policies for minimizing FLA contamination of tap water in South Korea.
Notes
-
CONFLICT OF INTEREST
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS
This work was supported by a 2-Year Research Grant of Pusan National University.
Fig. 1Morphology of cyst of KFA 2.
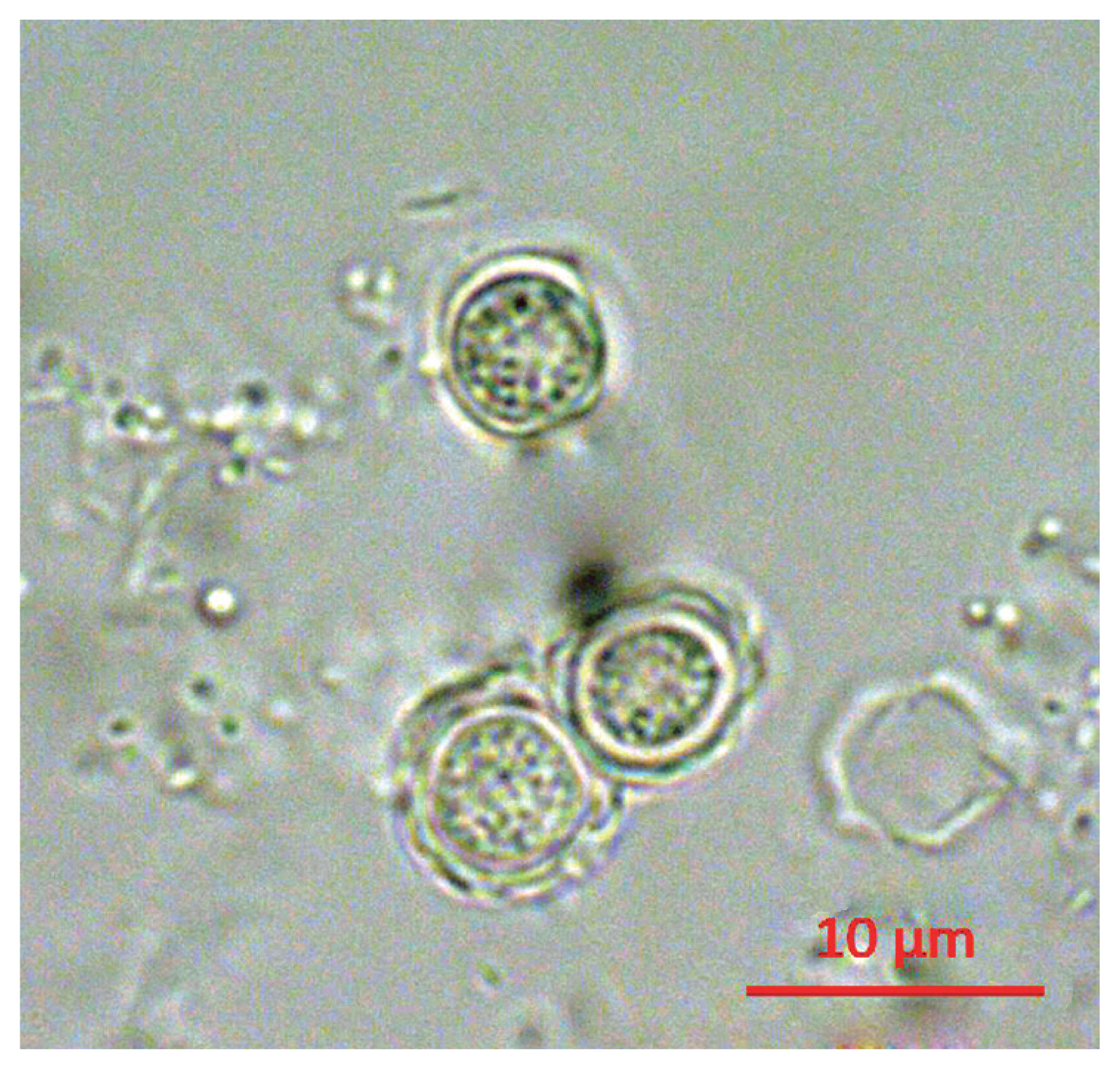
Fig. 2Phylogenetic tree of 21 KFA isolates in Korea. Phylogenetic classifications were analyzed using 18S-rDNA with the MEGA6 program, the neighbor-joining method, and bootstrap analysis (1,000 replicates) based on the ClustalW algorithm. SA, service area; A, apartment; B, building. GenBanK acc. No.: A. lugdunensis KA/E26, EF140627; V. vermiformis CRIB-06, DQ123623. No. of KFA1 – KFA21 were assigned to MT071758 – MT071778.
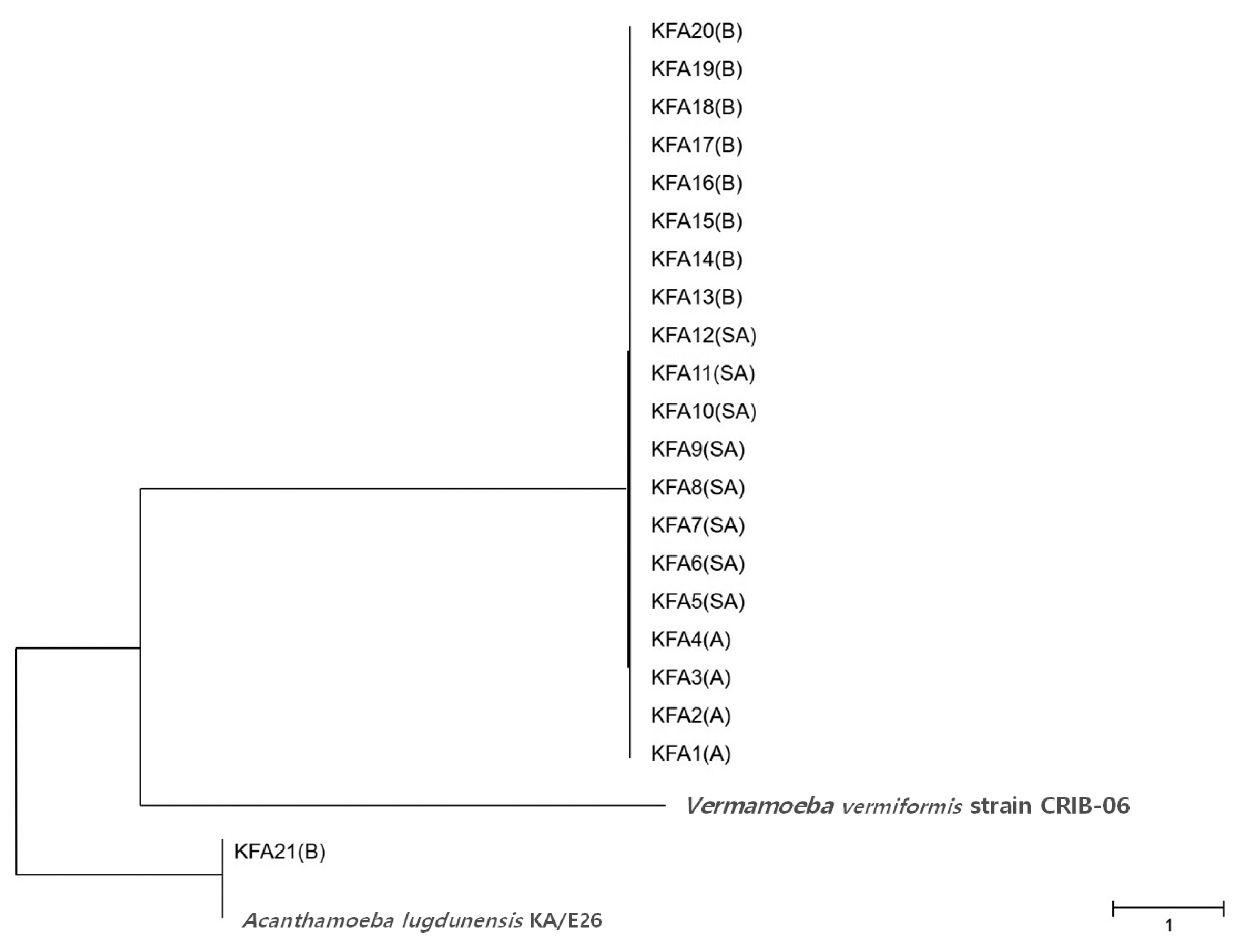
Table 1FLA contamination rate by building type
Table 1
|
Building type |
No. of samples |
FLA detected samples (%) |
|
Apartment |
37 |
4 (10.8) |
|
Office building |
102 |
9 (8.8) |
|
Highway service area |
24 |
8 (33.3) |
|
Total |
163 |
21 (12.9) |
Table 2Regional FLA contamination rate
Table 2
|
Region |
No. of samples |
FLA detected samples (%) |
|
Incheon, Seoul, Gyeonggi |
42 |
2 (4.8) |
|
Daejun, Chungchung |
15 |
1 (6.7) |
|
Jeonnam, Jeonbuk |
10 |
0 (0.0) |
|
Daegu, Gyeongbuk |
31 |
8 (25.8) |
|
Busan, Ulsan, Gyeongnam |
62 |
10 (16.1) |
|
Gangwon |
1 |
0 (0.0) |
|
Jeju |
2 |
0 (0.0) |
|
Total |
163 |
21 (12.9) |
References
- 1. Greub G, Raoult D. Microorganisms resistant to free-living amoebae. Clin Microbiol Rev 2004;17:413-433.
- 2. Schuster FL, Visvesvara GS. Free-living amoebae as opportunistic and non-opportunistic pathogens of humans and animals. Int J Parasitol 2004;34:1001-1027.
- 3. Martinez AJ. Free-Living Amoebas: natural history, prevention, diagnosis, pathology and treatment of disease. Boca Raton, USA. CRC Press. 1985.
- 4. Aitken D, Hay J, Kinnear FB, Kirkness CM, Lee WR, Seal DV. Amebic keratitis in a wearer of disposable contact lenses due to a mixed Vahlkampfia and Hartmannella infection. Ophthalmology 1996;103:485-494.
- 5. Grace E, Asbill S, Virga K. Naegleria fowleri: pathogenesis, diagnosis, and treatment options. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 2015;59:6677-6681.
- 6. Niyyati M, Lorenzo-Morales J, Rezaeian M, Martin-Navarro CM, Haghi AM, Maciver SK, Valladares B. Isolation of Balamuthia mandrillaris from urban dust, free of known infectious involvement. Parasitol Res 2009;106:279-281.
- 7. Qvarnstrom Y, da Silva AJ, Schuster FL, Gelman BB, Visvesvara GS. Molecular confirmation of Sappinia pedata as a causative agent of amoebic encephalitis. J Infect Dis 2009;199:1139-1142.
- 8. Stehr-Green JK, Bailey TM, Visvesvara GS. The epidemiology of Acanthamoeba keratitis in the United States. Am J Ophthalmol 1989;107:331-336.
- 9. Park MK, Cho MK, Kang SA, Park HK, Kim DH, Yu HS.
Acanthamoeba protease activity promotes allergic airway inflammation via protease-activated receptor 2. PLoS One 2014;9:e92726.
- 10. National Research Council. Drinking Water and Health. 4:Washington DC, USA. The National Academies Press. 1982.
- 11. Kilvington S, Gray T, Dart J, Morlet N, Beeching JR, Frazer DG, Matheson M.
Acanthamoeba keratitis: the role of domestic tap water contamination in the United Kingdom. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 2004;45:165-169.
- 12. Marciano-Cabral F, Jamerson M, Kaneshiro ES. Free-living amoebae, Legionella and Mycobacterium in tap water supplied by a municipal drinking water utility in the USA. J Water Health 2010;8:71-82.
- 13. Lee SJ, Jeong HJ, Lee JE, Lee JS, Xuan YH, Kong HH, Chung DI, Ock MS, Yu HS. Molecular characterization of Acanthamoeba isolated from amebic keratitis related to orthokeratology lens overnight wear. Korean J Parasitol 2006;44:313-320.
- 14. Visvesvara GS, Moura H, Schuster FL. Pathogenic and opportunistic free-living amoebae: Acanthamoeba spp., Balamuthia mandrillaris, Naegleria fowleri, and Sappinia diploidea
. FEMS Immunol Med Microbiol 2007;50:1-26.
- 15. Kang H, Sohn HJ, Seo GE, Seong GS, Ham AJ, Park AY, Jung SY, Lee SE, Cho SH, Shin HJ. Molecular detection of free-living amoebae from Namhangang (southern Han River) in Korea. Sci Rep 2020;10:335.
- 16. Corliss JO, Esser SC. Comments on the role of the cyst in the life cycle and survival of free-living protozoa. Trans Am Microsc Soc 1974;93:578-593.
- 17. Trabelsi H, Dendana F, Sellami A, Sellami H, Cheikhrouhou F, Neji S, Makni F, Ayadi A. Pathogenic free-living amoebae: epidemiology and clinical review. Pathol Biol (Paris) 2012;60:399-405.
- 18. Castrillón JC, Orozco LP.
Acanthamoeba spp. as opportunistic pathogens parasites. Rev Chilena Infectol 2013;30:147-155. (in Spanish).
- 19. Carnt NP, Hoffman JM, Verma S, Hau S, Radford CFP, Minassian DC, Dart JKG.
Acanthamoeba keratitis: confirmation of the UK outbreak and a prospective case-control study identifying contributing risk factors. Br J Ophthalmol 2018;102:1621-1628.
- 20. Jeong HJ, Yu HS. The role of domestic tap water in Acanthamoeba contamination in contact lens storage cases in Korea. Korean J Parasitol 2005;43:47-50.
- 21. Kong HH, Shin JY, Yu HS, Kim J, Hahn TW, Hahn YH, Chung DI. Mitochondrial DNA restriction fragment length polymorphism (RFLP) and 18S small-subunit ribosomal DNA PCR-RFLP analyses of Acanthamoeba isolated from contact lens storage cases of residents in southwestern Korea. J Clin Microbiol 2002;40:1199-1206.
- 22. Yu HS, Choi KH, Kim HK, Kong HH, Chung DI. Genetic analyses of Acanthamoeba isolates from contact lens storage cases of students in Seoul, Korea. Korean J Parasitol 2001;39:161-170.
- 23. Yu HS, Kong HH, Kim SY, Hahn YH, Hahn TW, Chung DI. Laboratory investigation of Acanthamoeba lugdunensis from patients with keratitis. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 2004;45:1418-1426.
- 24. Schaumberg DA, Snow KK, Dana MR. The epidemic of Acanthamoeba keratitis: where do we stand? Cornea 1998;17:3-10.
- 25. Rodríguez-Zaragoza S. Ecology of free-living amoebae. Crit Rev Microbiol 1994;20:225-241.
- 26. Scheid PL, Lâm TT, Sinsch U, Balczun C.
Vermamoeba vermiformis as etiological agent of a painful ulcer close to the eye. Parasitol Res 2019;118:1999-2004.
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by

- A socioenvironmental approach to the nosogenic potential of freshwaters with presence of thermotolerant free-living amoebae in Costa Rica
Johan Alvarado-Ocampo, Juan José Romero Zúñiga, Julián Castro, Frida Chaves Monge, Marco Ruiz Campos, Alexa Bustamante Cortés, Elizabeth Abrahams Sandí, Lissette Retana Moreira
Frontiers in Public Health.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Presence and diversity of free-living amoebae and their potential application as water quality indicators
Areum Choi, Ji Won Seong, Jeong Hyun Kim, Jun Young Lee, Hyun Jae Cho, Shin Ae Kang, Mi Kyung Park, Mi Jin Jeong, Seo Yeong Choi, Yu Jin Jeong, Hak Sun Yu
Parasites, Hosts and Diseases.2024; 62(2): 180. CrossRef - A Narrative Review of Acanthamoeba Isolates in Malaysia: Challenges in Infection Management and Natural Therapeutic Advancements
Mohammad Wisman Abdul Hamid, Roslaini Bin Abd Majid, Victor Fiezal Knight Victor Ernest, Nik Noorul Shakira Mohamed Shakrin, Firdaus Mohamad Hamzah, Mainul Haque
Cureus.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Proper Management for Rigid Gas Permeable Contact and Orthokeratology Lens
Kyu Young Shim, Jong Hwa Jun
Annals of Optometry and Contact Lens.2023; 22(1): 7. CrossRef - Well water sources simultaneous contamination with Cryptosporidium and Acanthamoeba in East-Southeast Asia and Acanthamoeba spp. in biofilms in the Philippines
Frederick R. Masangkay, Giovanni D. Milanez, Joseph D. Dionisio, Luzelle Anne G.-L. Ormita, Abel V. Alvarez, Panagiotis Karanis
Science of The Total Environment.2022; 837: 155752. CrossRef - Recognition of Cell Wall Mannosylated Components as a Conserved Feature for Fungal Entrance, Adaptation and Survival Within Trophozoites of Acanthamoeba castellanii and Murine Macrophages
Marina da Silva Ferreira, Susana Ruiz Mendoza, Diego de Souza Gonçalves, Claudia Rodríguez-de la Noval, Leandro Honorato, Leonardo Nimrichter, Luís Felipe Costa Ramos, Fábio C. S. Nogueira, Gilberto B. Domont, José Mauro Peralta, Allan J. Guimarães
Frontiers in Cellular and Infection Microbiology.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Free-living amoebae in an oil refinery wastewater treatment facility
Saeid Andalib, Hanieh Mohammad Rahimi, Maryam Niyyati, Farzaneh Shalileh, Sara Nemati, Soheila Rouhani, Mohammad Reza Zali, Hamed Mirjalali, Panagiotis Karanis
Science of The Total Environment.2022; 839: 156301. CrossRef - Free-Living Amoeba Vermamoeba vermiformis Induces Allergic Airway Inflammation
Da-In Lee, Sung Hee Park, Shin-Ae Kang, Do Hyun Kim, Sun Hyun Kim, So Yeon Song, Sang Eun Lee, Hak Sun Yu
The Korean Journal of Parasitology.2022; 60(4): 229. CrossRef - The increasing importance of Vermamoebavermiformis
Ruqaiyyah Siddiqui, Zinb Makhlouf, Naveed Ahmed Khan
Journal of Eukaryotic Microbiology.2021;[Epub] CrossRef