Abstract
This study was carried out to provide information on the taxonomic classification and analysis of mitochondrial genomes of Spirometra theileri. One strobila of S. theileri was collected from the intestine of an African leopard (Panthera pardus) in the Maswa Game Reserve, Tanzania. The complete mtDNA sequence of S. theileri was 13,685 bp encoding 36 genes including 12 protein genes, 22 tRNAs and 2 rRNAs with absence of atp8. Divergences of 12 protein-coding genes were as follow: 14.9% between S. theileri and S. erinaceieuropaei, 14.7% between S. theileri and S. decipiens, and 14.5% between S. theileri with S. ranarum. Divergences of 12 proteins of S. theileri and S. erinaceieuropaei ranged from 2.3% in cox1 to 15.7% in nad5, while S. theileri varied from S. decipiens and S. ranarum by 1.3% in cox1 to 15.7% in nad3. Phylogenetic relationship of S. theileri with eucestodes inferred using the maximum likelihood and Bayesian inferences exhibited identical tree topologies. A clade composed of S. decipiens and S. ranarum formed a sister species to S. erinaceieuropaei, and S. theileri formed a sister species to all species in this clade. Within the diphyllobothridean clade, Dibothriocephalus, Diphyllobothrium and Spirometra formed a monophyletic group, and sister genera were well supported.
-
Key words: Spirometra theileri, Panthera pardus, mitochondria, genome, Tanzania
INTRODUCTION
Spirometra species are intestinal tapeworms of feline and canine mammals belong to the family Diphyllobothriidae and to the order Diphyllobothridea (Pseudophyllidea). In the life cycle,
Spirometra species require 2 different intermediate hosts. The freshwater copepods are the first intermediate hosts. When the amphibians and reptiles consume the copepods, they become the second intermediate hosts [
1]. The procercoid occurs in the crustacean copepods, and the plerocercoid (sparganum) develops in amphibians, reptiles or mammals. Humans get infected by drinking natural water containing copepods or by consuming raw or undercooked second intermediate hosts [
2].
Spirometra theileri (Sparganum baxteri, Simboni 1907;
Diphyllobothrium theileri) was first reported with morphological description on adult
S. theileri collected from bush cat (
Leptailurus serval) and tiger cat (
Felis lybica) in East Africa [
3,
4]. The studies on the physiology and biology of
S. theileri were conducted using the plerocercoids obtained from the subcutaneous tissue of a warthog in Serengeti National Park, Tanzania [
5,
6]. The detailed morphological features of adult
S. theileri were studied from African mammals such as wild cat (
Felis lybica), serval (
Leptailurus serval), leopard (
Panthera pardus), lion (
Panthera leo), and jakal (
Canis aureus) [
7,
8].
The morphological descriptions of adult
S. theileri ranged from 35 to 40 cm long with 0.4 to 3.3 mm wide. The internal organs of
S. theileri consist of uterus in lobular forms of 3/4 complete coils of their inner mass, and the elliptical seminal vesicle with the average of 0.13 to 0.22 mm while the cirrus pouch measurement ranged from 0.3 to 0.19 mm [
4]. The major differentiating features between
S. pretoriensis and
S. theileri are uterus and cirrus pouch that the uterine loops of
S. theileri consists of 3–4.5 coils, and a cirrus pouch communicated through a short canal and much smaller vesicular seminis, while the uterus of
S. pretoriensis forms a single large loop, and the cirrus pouch possess a large vesicular seminis and muscular wall [
9]. The molecular identification of
S. theileri was carried out in African leopards and spotted hyenas in Tanzania [
10].
Spirometra theileri was reported by the molecular analysis of mitochondrial genes and morphological observations of adult tapeworms [
10]. Species identification of the genus
Spirometra tapeworms in Africa through reliable morphological and molecular characters remain controversial [
11,
12]. It was argued that the selective pressure and evolution constraints are among the factors demanding for more gene markers for proper classification [
13].
The mitochondrial DNA (mtDNA) information has been used for classification, phylogenetic reconstruction, taxonomic identification, and population genetics of the order diphyllobothridea [
14,
15]. Few
Spirometra species have been used for genetic variation, taxonomy, and phylogenetic studies by using mtDNA sequences such as cytochrome c oxidase subunit 1 and 3 (
cox1 and
cox3), NADH dehydrogenase subunit 1, 3, and 4 (
nad1,
nad3, and
nad4) [
16–
20]. Nevertheless, among the
Spirometra species recovered from various carnivorous mammals in Tanzania, there is no detailed molecular information, particularly in the whole mtDNA sequences on
Spirometra species.
This study was conducted to determine the complete mtDNA sequence and structure of S. theileri related to other Spirometra species. We described the phylogenetic affinity of Spirometra species with other cestodes based on the comparative phylogenetic analysis of the mitochondrial genome (mt genome) data.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Specimens and DNA sequencing
One strobila of S. theileri was obtained from the intestine of male African leopard (Panthera pardus) in the Maswa Game Reserve of Tanzania, in February 2012. The collected tapeworm was fixed in 70% ethanol until used for genomic DNA extraction. Total genomic DNA was extracted from a single proglottid using the DNeasy tissue kit (Qiagen, Valencia, California, USA).
The complete mt genome was PCR-amplified as 15 overlapping fragments using total genomic DNA [
16,
17,
21]. PCR and DNA sequencing were performed as described previously [
22].
The mt genome sequences were assembled, aligned, annotated using the Geneious 9.0 program. The mt genome sequence of
S. theileri was compared with
S. erinaceieuropaei (GenBank no. KJ599679),
S. decipiens (GenBank no. KJ599679), and
S. ranarum (MN259169). The 12 protein-coding genes were searched by comparing with mt gene sequences of 16 cestodes in the GenBank database. Flatworm mitochondrial genetic codes were used to translate the mitochondrial protein-coding genes. Twenty-two putative tRNA genes were identified using tRNAscan-SE. 2.0 [
23] and anticodon sequences. Two ribosomal RNAs (12S and 16S subunits) were determined by comparison with other rRNAs of cestodes. Putative stem-loop structures of non-coding mt regions were inferred using RNAdraw 1.1 program [
24].
The sequences of 12 protein-coding genes of
Taenia,
Echinococcus,
Hymenolepis,
Dibothriocephalus,
Dipylidium,
Hydatigera,
Moniezia,
Spirometra, were selected and 2 trematode sequences were set as an outgroup. The mt genome sequences used were as followings:
S. erinaceieuropaei (KJ599680),
S. decipiens (KJ599679),
S. ranarum (MN259169),
S. theileri (in this study),
D. latus (NC_008945),
D. nihonkaiense (NC_009463),
Dipylidium caninum (NC_021144),
Echinococcus granulosus (NC_008075),
E. multilocularis (NC_000928),
Hydatigera kamiyai (AB731761),
H. krepkogorski (NC_021142),
H. parva (NC_021141),
Hymenolepis diminuta (NC_002767),
H. nana (NC_029245),
Moniezia benedeni (NC_036218),
M. expansa (NC_036219),
Taenia solium (NC_004022),
T. saginata (NC_009938),
T. asiatica (NC_004826),
T. crassiceps (NC_002647),
T. crocutae (NC_024591),
T. hydatigena (FJ518620), and
T. regis (NC_024589). The mitochondrial 12 protein coding genes were analysed by jModelTest [
25]. The General Time Reversible model with gamma distribution and invariant sites (GTR+1+G) were selected as the best model of evolution for all elements and genes. Bayesian Inference (BI) were conducted by using Bayesian Evolutionary Analysis Sampling Trees version 2 (BEAST 2) [
26]. Bayesian was performed by Markov chain Monte Carlo (MCMC) ran for 10 million generations sampled at intervals of 1,000 generations. Phylogenetic trees were constructed using the mitochondrial 12 protein-coding gene DNA sequences of
Spirometra tapeworms by using ML and BI.
RESULTS
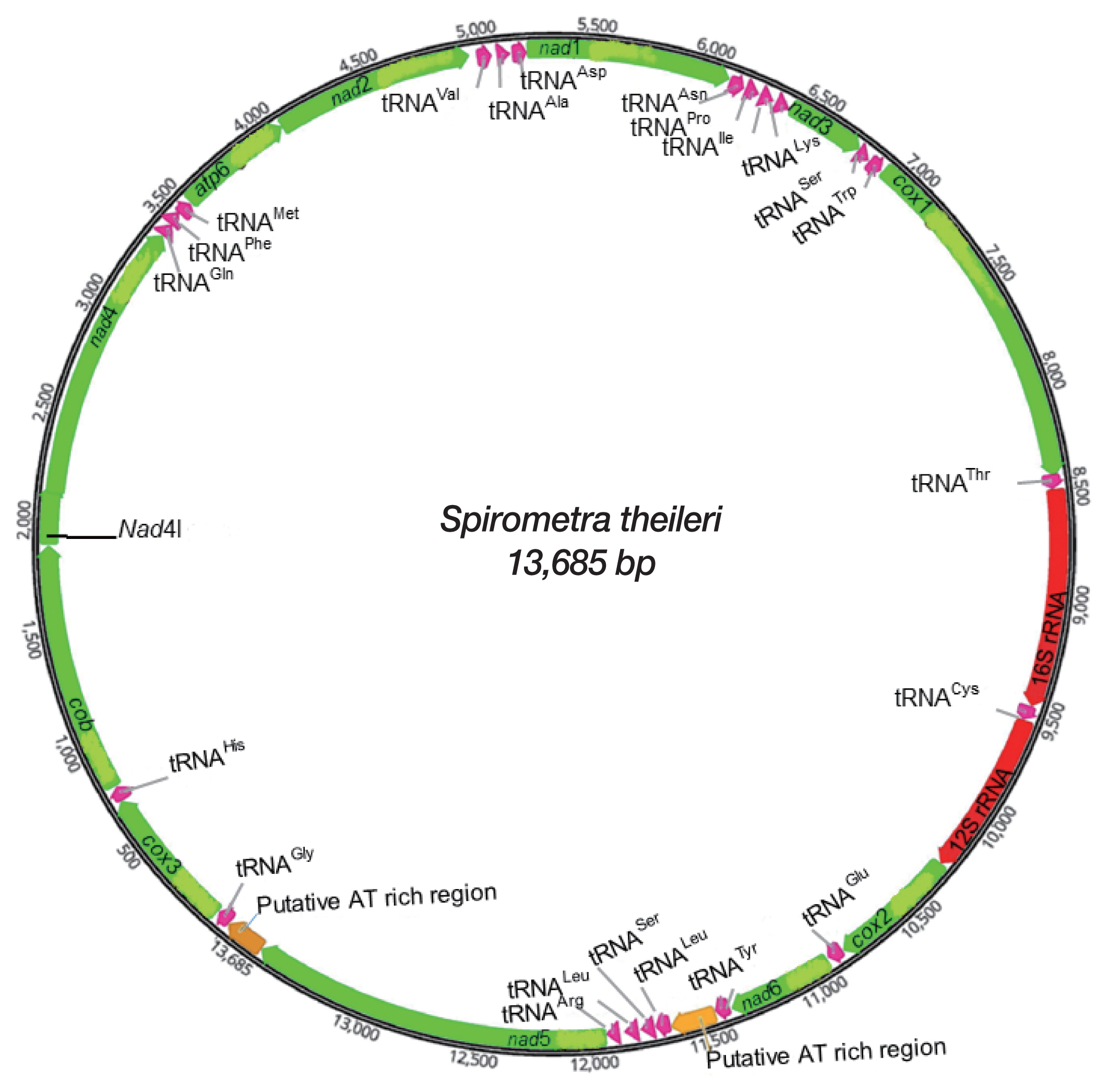
Gene content and organization of mitochondrial genome
A complete mtDNA sequence of
S. theileri revealed 13,685 bp in length (GenBank accession number MT274583), with 12 protein-coding genes, 22 tRNAs, and 2 rRNAs. An
atp8 gene was absent from this mt genome. All genes and elements were arranged in one direction, and at the same positions relative to loci in the cestode mt genomes (
Fig. 1). Mt genome of
S. theileri composed of 19.8% A, 45.9% T, 23.6% G, and 10.7% C. with the A-T content of 65.7% (
Table 1). Genes overlapping were revealed in mt genome of
S. theileri in
nad4L/
nad4 (40 bp),
trnQ/
trnF (4 bp),
trnQ/
trnM (4 bp), and
cox1/
trnT (10 bp) (
Table 2).
The 12 protein-coding genes constituted 10,086 bp in
S. theileri, and concealed 70% of the total
Spirometra mt genomes (
Table 1). The putative open reading frames of the 12 protein-coding genes in 4
Spirometra species start and end with complete codons. The ATG initiation codon of 4
Spirometra mt genome was used in 11 genes (
atp6,
cob,
cox1–3,
nad1,
nad2–4,
nad4L,
nad5, and
nad6), while the GTG initiation codon was used only in
cox3 gene. The TAG stop codon was used in 9 genes (
cob,
cox1,
cox3,
nad1–4,
nad4L, and
nad6) in
S. theileri, 7 genes (
cox1–3,
nad2–4, and
nad4L) in
S. erinaceieuropaei and 6 genes (
cox1,
cox3,
nad2,
Nad3,
nad4, and
nad4L) in
S. decipiens and
S. ranarum. The TAA stop codon was used in 3 genes (
atp6,
cox2, and
nad5) in
S. theileri, 5 genes (
atp6,
cob,
nad1,
nad5, and
nad6) in
S. erinaceieuropaei and for
S. decipiens and
S. ranarum, 6 genes were used such as
atp6,
cob,
cox2,
nad1,
nad5, and
nad6 (
Table 3). tRNAs most commonly used were tRNA
Leu(TTR, CTN) (15.3%), tRNA
Phe(TTY) (12.5%), tRNA
Val(GTN) (11.2%), tRNA
Ser (AGN,TCN) (9.6%) (
Table 3).
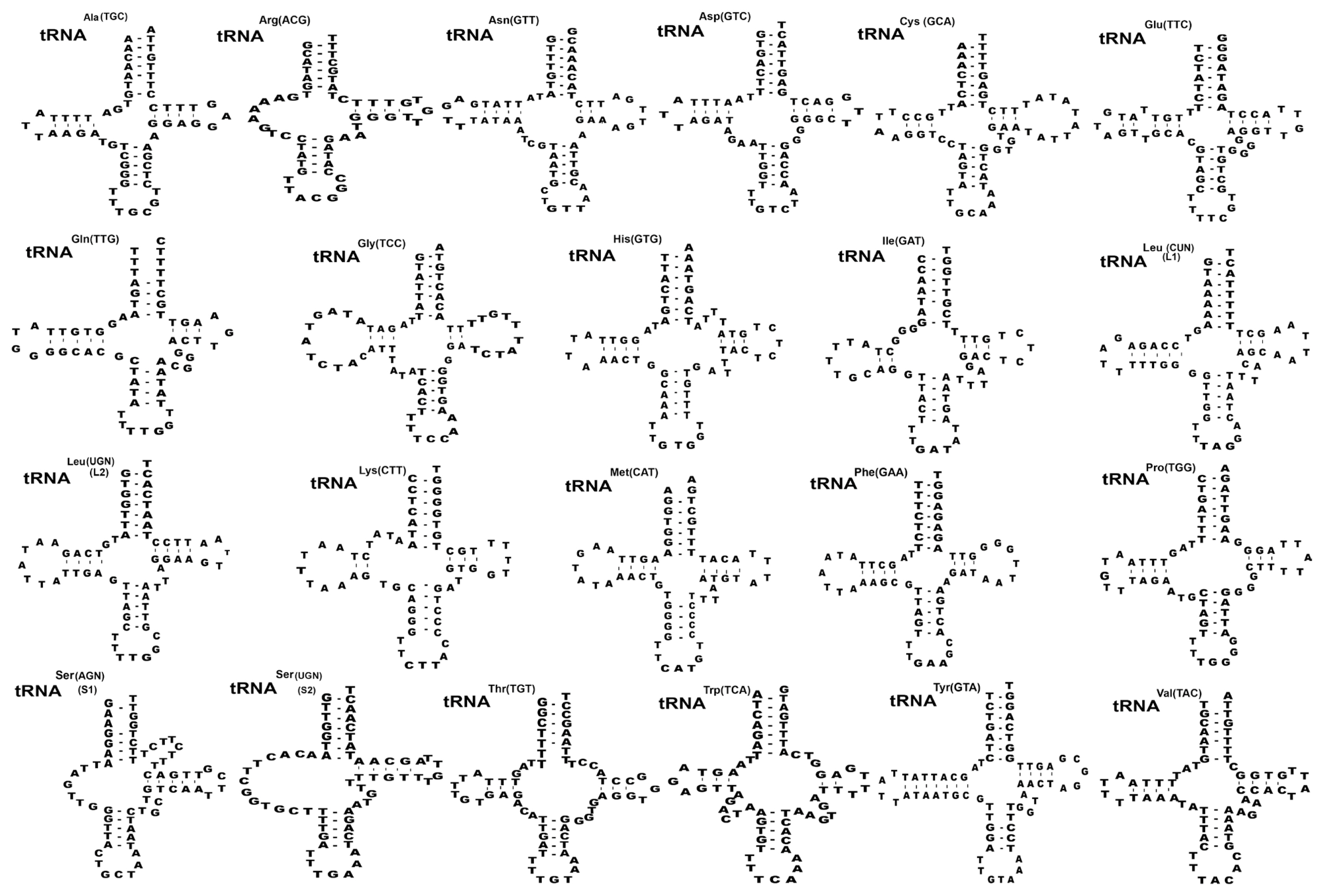
Twenty-two transfer RNAs were found in putative secondary structures ranging from 59 to 70 bp (
Fig. 2). Nineteen tRNAs had a typical cloverleaf shape with 4 arms such as aminoacyl acceptor arms, DHU arm, anticodon stems, and TΨC arms except in
trnR,
trnS1, and
trnS2 were replaced with 7–13 bp of unpaired loop in the DHU of
S. theileri slightly varied by 7–12 bp arms of unpaired loop in the DHU from other
Spirometra species. The aminoacyl acceptor arms consisted of 7 bp such as
trnC,
trnM,
trnQ,
trnR,
trnS1, and
trnT which contained 1–3 non-canonical base pairs. The anticodon stems of
trnY of 4
Spirometra species contained 5 bp with 2 non-canonical base pairs in stem structures. The TΨC arms of the 22 tRNAs in 4
Spirometra species consist of 2–5 bp, and a loop of 3–9 bp. The most prominent shapes of tRNAs were revealed in tRNA
ser(AGN) (S1) with unpaired Amino-Acyl arm, and tRNA
tyr(TCU) structure with 7bp paired in DHU arm found in
S. theileri varied from
S. erinaceieuropaei, and
S. decipiens (
Fig. 2). Two mitochondrial ribosomal subunits rrnL and rrnS were separated by
trnC in the 4
Spirometra species. The
rrnL and
rrnS were 968 bp and 730 bp long in
S. theileri: 967 bp and 733 bp long in
S. erinaceieuropaei, 973 bp and 730 bp long in
S. decipiens and
S. ranarum, respectively (
Table 3). The average nucleotide contents of the 16S rRNA and 12S rRNA in
S. theileri were 38.5% T, 12.6% C, 23.9% A, and 25.0% G with the A-T contents of 62.4%, different from the
S. erinaceieuropaei,
S. decipiens, and
S. ranarum (
Table 3).
Two non-coding regions in mt genome of 4
Spirometra species were predicted with the hairpin structures confined between
trnY and
trnL1 (NR1), and between
trnR and
nad5 (NR2). The length of NR1 was 200 bp long, and NR2 was 178 bp length with the average nucleotide contents of 34.2% A, 10.3% C, 20.5% G, and 35.1% T in
S. theileri (
Table 3).
The percentage pairwise comparison of the nucleotides and predicted amino acids composition of 4
Spirometra species were specified in
Table 4. The overall nucleotide sequence divergences of 12 protein-coding genes differed by 14.9% in
S. theileri and
S. erinaceieuropaei, 14.7% in
S. theileri and
S. decipiens and 14.5% in
S. theileri and
S. ranarum (
Table 4). Divergences of amino acids of 12 protein-coding genes of
S. theileri ranged from 1.3% to 2.3% in
cox1 and 15.7% in
nad3 and
nad5. The rRNA of
S. theileri differed with the range of 12.2% to 12.9% (rrnL) and 8.4% to 9.4% (rrnS) among the
Spirometra species (
Table 4).
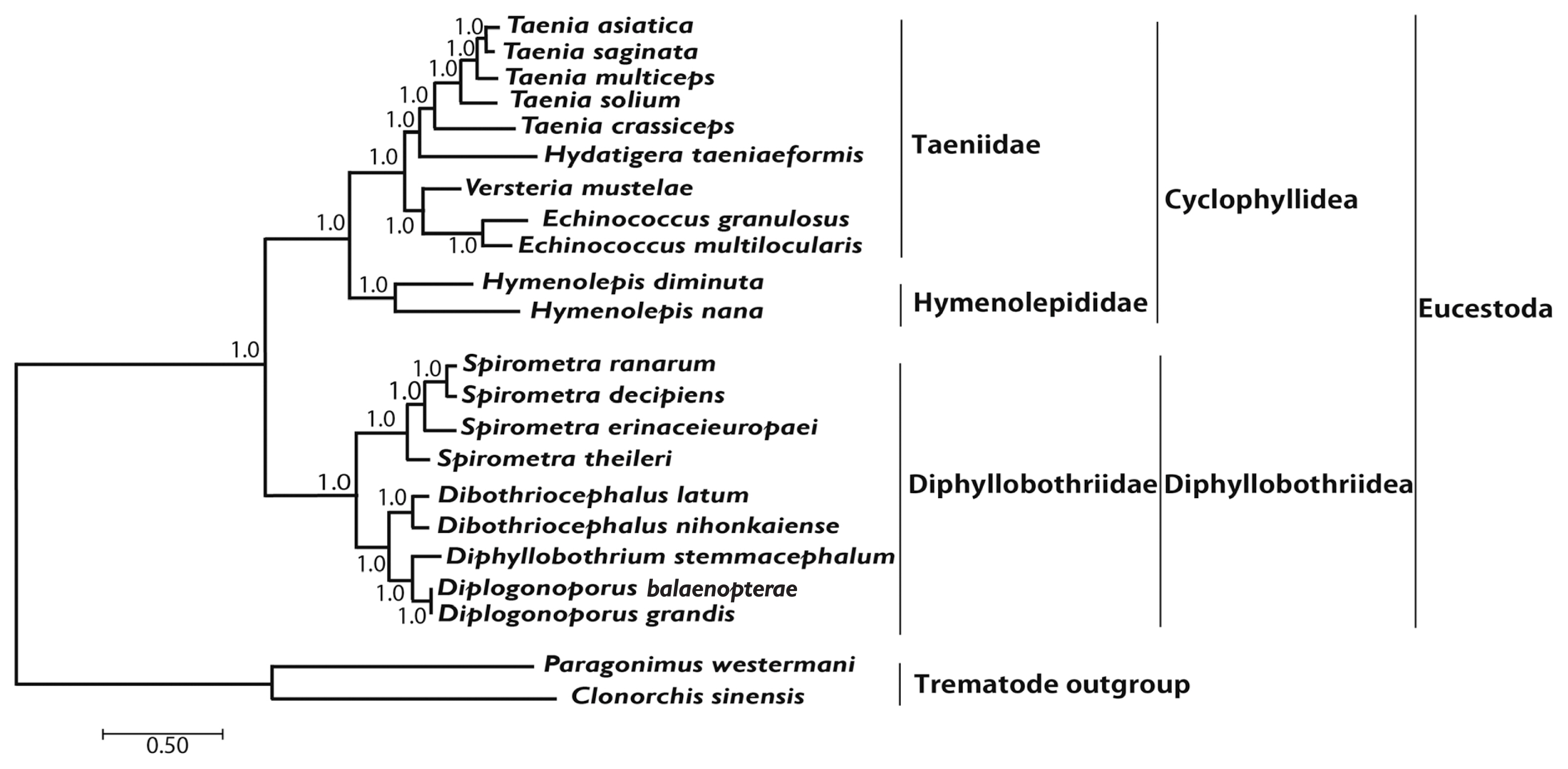
Phylogenetic analyses of 4
Spirometra species such as
S. theileri,
S. erinaceieuropaei,
S. decipiens, and
S. ranarum was performed using BI and ML based on concatenated amino acids sequences of 12 protein-coding genes from 20 cestodes, and 2 trematodes. An alignment set of 10,821 bp was used from 12 protein-coding genes loci of 22 taxa. Of the 2,896 (26.8%) identical sites and 67.7% pairwise identity showed in the set of the mtDNA sequences from ML analysis. A total of 4,019 amino acids lengths, 165 (4.1%) identical sites, and 37.3% pairwise identity was used phylogenetically informative under ML criterion. Phylogenetic relationships of diphyllobothridean cestodes among the eucestodes inferred using the BI and ML approaches exhibited identical tree topologies. A clade composed of
Dibothriocephalus latus and
D. nihonkaiense, formed the sister group to
Diphyllobothrium stemmacephalum,
Diplogonoporus balaenopterae, and
D. grandis. The sister group relationship of
Dibothriocephalus species and
Diphyllobothrium species supported by analyses of 12 protein-coding genes. A clade composed of
Spirometra decipiens and
S. ranarum, formed the sister species to
S. erinaceieuropaei, and
S. theileri formed the sister species to all species in this clade. Within the diphyllobothridean clade,
Dibothriocephalus,
Diphyllobothrium and
Spirometra formed a monophyletic group and sister genera are well supported (
Fig. 3).
DISCUSSION
Phylogenetic classification befitted an important feature in taxonomical studies over decades. In the present study, the whole mt genome of
S. theileri was sequenced and compared with
S. erinaceieuropaei,
S. decipiens and
S. ranarum. The molecular characteristics of the mt genome of
S. theileri were similar with other cestodes in gene arrangement, nucleotide composition, genetic code, and secondary structure of tRNA. The mt genomes of
Spirometra species reported to date are ranged from 13,643 bp to 13,685 bp in length such as 13,643 bp in
S. erinaceieuroapei (KJ599690) [
16], 13,641 bp in
S. decipiens (KJ599679) [
16], 13,644 bp in
S. ranarum (MN259169) [
17], and 13,685 bp in
S. theileri (MT274583, this study). The mt genome contains 12 protein-coding genes (lacking
atp8), 22 tRNAs, 2 rRNAs, and all genes and elements were transcribed in the same direction, which is a common feature of flatworm mtDNAs [
27]. The gene order in
S. theileri is identical with other
Spirometra species and the diphyllidean cestodes published to date, with the exception of
Hymenolepis diminuta in which the relative positions of
trn L1 and
trn S2 are switched [
28]. The nucleotide composition of the entire
S. theileri mt genome is biased towards A and T, and some genes overlapping were found in gene boundaries as often found in other metazoan mtDNAs. The start and termination codons of the 12 protein-coding genes were identified and compared with other cestodes mtDNAs. The genetic code of the Platyhelminthes mt genome has been investigated [
29]. The peculiarity in codon usage was observed in
Spirometra species like other cestode mt genomes. Of the 12 protein coding genes, the open reading frames inferred to initiation with ATG while the
cox3 uses GTG coding valine as an initiation codon, while the stop codon use TAG and TAA like in other metazoans. The predicted composition of amino acids encoded by high T and low C contents cause bias toward the use of T against C, which is common in Platyhelminthes. The most variable tRNAs structures are tRNA
tyr(TCU) and tRNA
ser(AGN) (S1). The tRNA
tyr(TCU) structure had 7 bp paired in DHU arm while unpaired Amino-Acyl arm in tRNA
ser(AGN) (S1) revealed in
S. theileri varied from S. erinaceieuroapei (KJ599690) and
S. decipiens (KJ599679).
The non-coding regions were found in a stem and loop structure of the NR1 and NR2 in
Spirometra species mtDNAs. These 2 non-coding areas have conserved secondary hairpin structures and are known to serve as the initiation site for second L-strand synthesis in other metazoan animal groups [
30]. These conserved sequence regions are also evident in the control regions for the most other cestodes mt genomes [
16].
The fact that genetic differences of 12 protein-coding genes between
S. theileri and other
Spirometra species differed by more than 14.5%, whereas the sequence differences for whole mtDNA sequences were more than 14.6% reveal that the
S. theileri is a valid species within the genus
Spirometra. The nucleotide sequence differences of 12 protein-coding genes in
S. decipiens and
S. ranarum was 1.5%, keeping it in the 0.0% to 2.4%. range. The degree of divergence in mtDNA sequence of the sister or congeneric species was estimated using the genetic distance of the
cob gene among mammalian group, and it was found that there is more than 2% sequence divergence for closely related species, while intraspecific divergences are greater than 2%, and more are less than 1% among amphibian, reptile, and avian host animals [
31]. However,
cox1 divergence among 13,320 species in 11 animal phyla ranged from 0.0% to 53.7%, while 79% of those species were greater than 8% sequence differences at the species taxonomy [
32]. In the current study, the sequence differences of
cox1,
cob,
nad2, and
nad4 genes between
S. decipiens and
S. ranarum were greater than 2% while other genes were less than 1.4% ranged from 0.0 to 1.4%, indicating that the
S. ranarum might be the inter or intra-species of
S. decipiens.
All haplotypes of Spirometra species were separated into 3 distinct clades in phylogenetic analyses based on ML and BI methods. Clade I was S. theileri, clade II was S. decipiens and S. ranarum and clade III was S. erinaceieuropaei. The ML and BI analyses supported monophyly of Spirometra species and identified the S. theileri, S. erinaceieuropaei and S. decipiens species as valid species.
In summary, this is the first study conducted revealing the complete mt genomes of Spirometra theileri recovered from African leopard in Tanzania. The use of mt genomes will solve the greater diversification of Spirometra species that can be used as an inference for evolutionary analysis. The information derived from the complete DNA sequences of the Spirometra species mt genomes will provide the knowledge of the mt genomics of parasitic cestodes, a source for molecular investigations and systematic studies of Spirometra species.
Notes
-
We have no conflict of interest related to this work.
ACKNOWLEDGMENT
This work was supported by the International Parasite Resource Bank and Inclusive Business Solution (IBS) project, Korea (No. 2020-0042).
Fig. 1Schematic representation of the mitochondrial genome of Spirometra theileri.
Fig. 2Inferred secondary structures of 22 mitochondrial tRNA from Spirometra theileri. Differences among the secondary tRNA structures of S. theileri in tRNAser(AGN) (S1) structure with an unpaired Amino-acyl arm and tRNAtyr(TUC) structure with 7 bp paired DHU arm found in S. theileri.
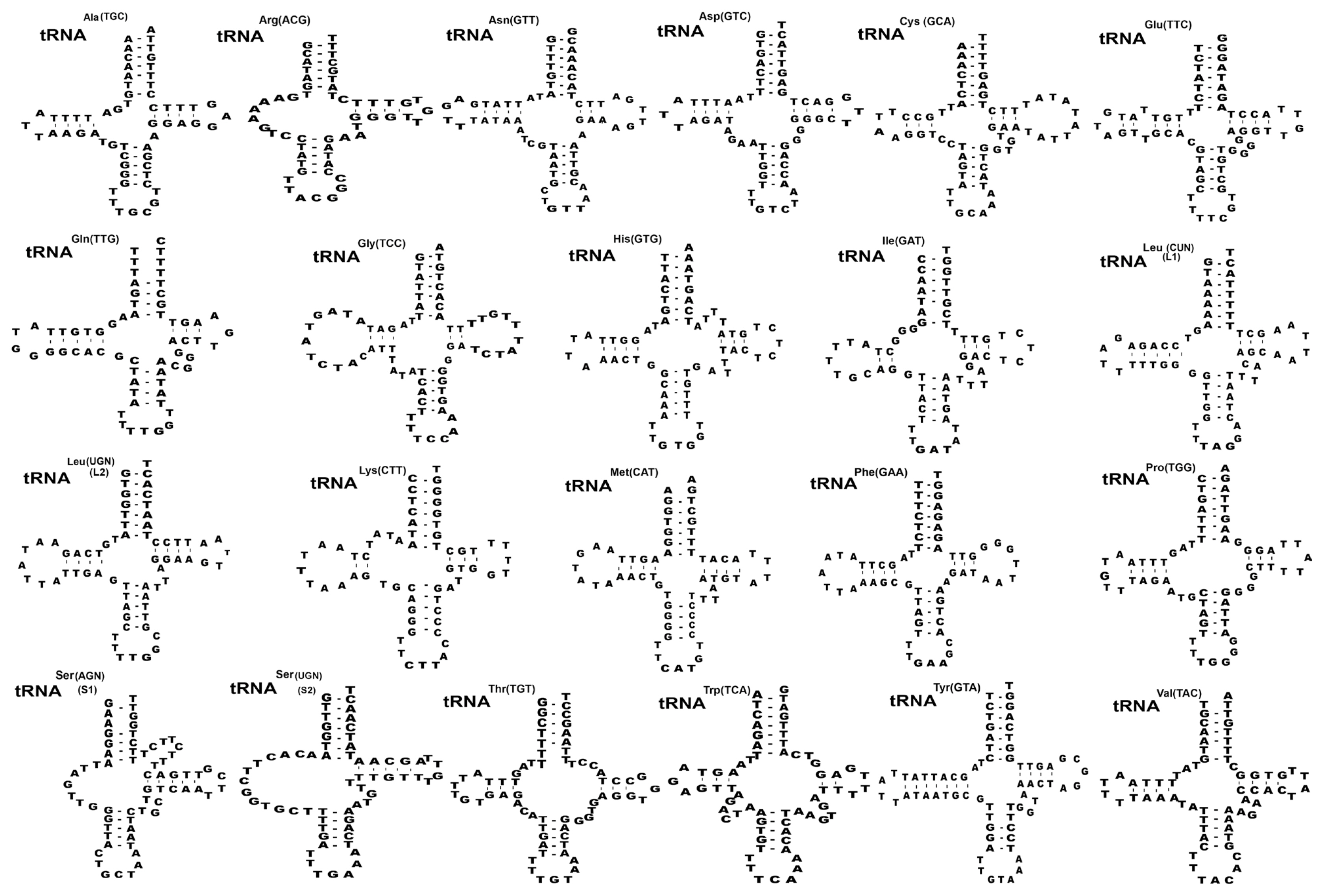
Fig. 3Phylogenetic relationship among eucestode species based on inferred nucleotide sequence data selected from 12 mitochondrial protein-coding gene loci for 22 platyhelminthes. The numbers above the branches represent bootstrap values for Bayesian inference and maximum likelihood.
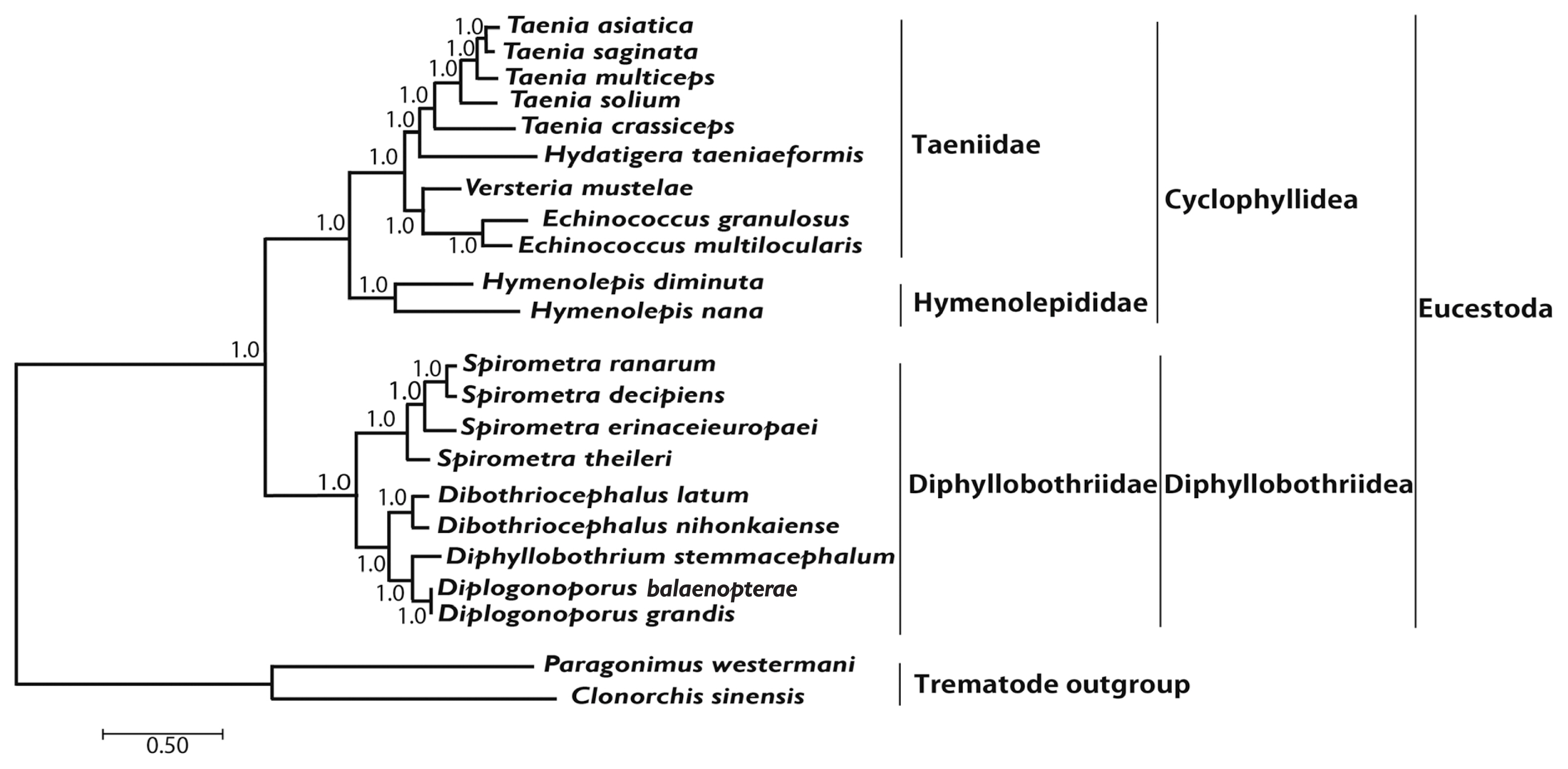
Table 1Nucleotide compositions of the complete mitochondrial genomes, protein-coding genes, and ribosomal RNA sequences of 4 Spirometra species
Table 1
|
Spp. |
Complete mtDNA sequence |
Protein-coding sequence |
rRNA sequence |
|
|
|
|
Length (bp) |
T % |
C % |
A % |
G % |
T+A % |
Length (bp) |
T % |
C % |
A % |
G % |
T+A % |
Length (bp) |
T % |
C % |
A % |
G % |
T+A % |
|
Sta
|
13,685 |
45.9 |
10.7 |
19.8 |
23.6 |
65.7 |
10,086 |
48.3 |
10.3 |
17.7 |
23.7 |
66.0 |
1,698 |
38.5 |
12.6 |
23.9 |
25.0 |
62.4 |
|
|
Seb
|
13,643 |
45.9 |
10.9 |
19.8 |
23.5 |
65.7 |
10,083 |
48.3 |
10.6 |
17.5 |
23.5 |
65.8 |
1,700 |
38.7 |
12.2 |
24.9 |
24.2 |
63.6 |
|
|
Sdc
|
13,641 |
46.0 |
11.0 |
20.3 |
22.6 |
66.3 |
10,086 |
48.6 |
10.6 |
18.3 |
22.5 |
66.9 |
1,703 |
37.6 |
12.9 |
25.1 |
24.4 |
62.7 |
|
|
Srd
|
13,644 |
45.8 |
11.2 |
20.4 |
22.6 |
66.2 |
10,067 |
66.2 |
10.7 |
17.9 |
23.9 |
65.3 |
1,702 |
38.1 |
12.5 |
25.0 |
24.3 |
63.1 |
Table 2Position and characteristics of the protein coding and non coding sequences in the mitochondrial genomes of Spirometra theileri, S. erinaceieuropaei, S. decipiens, and S. ranarum
Table 2
|
Gene or sequence |
Length of gene and sequence |
Codon used |
Position in genome (5′-3′) |
|
|
|
No. of nucleotide |
No. of amino acid |
Initiation |
Termination |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Sta
|
Seb
|
Sdc
|
Srd
|
Sta
|
Seb
|
Sdc
|
Srd
|
Sta
|
Seb
|
Sdc
|
Srd
|
Sta
|
Seb
|
Sdc
|
Srd
|
Sta
|
Seb
|
Sdc
|
Srd
|
|
trnG
|
68 |
67 |
67 |
67 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
1–68 |
1–67 |
1–67 |
1–67 |
|
|
cox3
|
651 |
651 |
651 |
651 |
216 |
216 |
216 |
216 |
GTG |
GTG |
GTG |
GTG |
TAG |
TAG |
TAG |
GTT |
72–714 |
71–721 |
71–721 |
71–713 |
|
|
trnH
|
69 |
70 |
69 |
69 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
713–781 |
712–781 |
712–780 |
714–782 |
|
|
cob
|
1,110 |
1,110 |
1,110 |
1,110 |
369 |
369 |
369 |
369 |
ATG |
ATG |
ATG |
ATG |
TAG |
TAA |
TAA |
TAA |
785–1,894 |
785–1894 |
784–1893 |
786–1895 |
|
|
nad4L
|
261 |
261 |
261 |
261 |
86 |
86 |
86 |
86 |
ATG |
ATG |
ATG |
ATG |
TAG |
TAG |
TAG |
TAG |
1,899–2,159 |
1,899–2,159 |
1,898–2,158 |
1,900–2,160 |
|
|
nad4
|
1,254 |
1,254 |
1,254 |
1,254 |
417 |
417 |
417 |
417 |
ATG |
ATG |
ATG |
ATG |
TAG |
TAG |
TAG |
TAG |
2,120–3,373 |
2,120–3,373 |
2,119–3,372 |
2,121–3,374 |
|
|
trnQ
|
63 |
64 |
64 |
64 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
3,374–3,436 |
3,374–3,437 |
3,373–3,436 |
3,375–3438 |
|
|
trnF
|
64 |
64 |
64 |
64 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
3,433–3,496 |
3,434–3,497 |
3,433–3,496 |
3,435–3498 |
|
|
trnM
|
68 |
68 |
68 |
68 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
3,493–3,560 |
3,494–3,561 |
3,493–3,560 |
3,495–3562 |
|
|
atp6
|
516 |
516 |
516 |
516 |
171 |
171 |
171 |
171 |
ATG |
ATG |
ATG |
ATG |
TAA |
TAA |
TAA |
TAA |
3,564–4,079 |
3,565–4,080 |
3,564–4,079 |
3,566–4,081 |
|
|
nad2
|
873 |
873 |
873 |
873 |
290 |
290 |
290 |
290 |
ATG |
ATG |
ATG |
ATG |
TAG |
TAG |
TAG |
TAG |
4,081–4,953 |
4,092–4,964 |
4,087–4,959 |
4,089–4,961 |
|
|
trnV
|
65 |
65 |
66 |
65 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
4,985–5,049 |
4,969–5,033 |
4,970–5,035 |
4,972–5,036 |
|
|
trnA
|
61 |
61 |
61 |
61 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
5,070–5,130 |
5,051–5,111 |
5,052–5,112 |
5,054–5,114 |
|
|
trnD
|
67 |
66 |
64 |
64 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
5,136–5,202 |
5,116–5,181 |
5,118–5,181 |
5,120–5,183 |
|
|
nad1
|
891 |
891 |
891 |
891 |
296 |
296 |
296 |
296 |
ATG |
ATG |
ATG |
ATG |
TAG |
TAA |
TAA |
TAA |
5,203–6,093 |
5,182–6,072 |
5,182–6,072 |
5,184–6,074 |
|
|
trnN
|
67 |
66 |
66 |
66 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
6,099–6,165 |
6,078–6,143 |
6,078–6,143 |
6,080–6,145 |
|
|
trnP
|
65 |
65 |
65 |
65 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
6,173–6,237 |
6,150–6,214 |
6,150–6,214 |
6,152–6,216 |
|
|
trnI
|
64 |
64 |
64 |
64 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
6,243–6,306 |
6,220–6,283 |
6,220–6,283 |
6,222–6,285 |
|
|
trnK
|
63 |
63 |
63 |
63 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
6,319–6,381 |
6,291–6,353 |
6,290–6,352 |
6,292–6,354 |
|
|
nad3
|
357 |
357 |
357 |
357 |
118 |
118 |
118 |
118 |
ATG |
ATG |
ATG |
ATG |
TAG |
TAG |
TAG |
TAT |
6,387–6,732 |
6,359–6,715 |
6,356–6,712 |
6,358–6,703 |
|
|
trnS1(CN)
|
59 |
59 |
59 |
59 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
6,733–6,798 |
6,705–6,763 |
6,702–6,760 |
6,704–6,762 |
|
|
trnW
|
66 |
65 |
66 |
66 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
6,801–6,866 |
6,773–6,837 |
6,763–6,828 |
6,765–6,830 |
|
|
cox1
|
1,566 |
1,566 |
1,566 |
1,566 |
521 |
521 |
521 |
521 |
ATG |
ATG |
ATG |
ATG |
TAG |
TAG |
TAG |
TAG |
6,874–8,439 |
6,845–8,410 |
6,836–8,401 |
6,838–8,403 |
|
|
trnT
|
69 |
69 |
70 |
70 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
8,430–8,498 |
8,401–8,469 |
8,392–8,461 |
8,394–8,463 |
|
|
rrnL
|
968 |
967 |
973 |
972 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
8,499–9,466 |
8,470–9,436 |
8,462–9,434 |
8,464–9,435 |
|
|
trnC
|
67 |
65 |
65 |
65 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
9,467–9,533 |
9,437–9,501 |
9,435–9,499 |
9,436–9,500 |
|
|
rrnS
|
730 |
733 |
730 |
730 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
9,534–10,263 |
9,502–10,234 |
9,500–10,229 |
9,501–10,230 |
|
|
cox2
|
570 |
570 |
570 |
570 |
189 |
189 |
189 |
189 |
ATG |
ATG |
ATG |
ATG |
TAA |
TAG |
TAA |
TAA |
10,264–10,833 |
10,235–10,804 |
10,230–10,799 |
10,231–10,800 |
|
|
trnE
|
70 |
65 |
65 |
65 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
10,839–10,908 |
10,810–10,874 |
10,805–10,869 |
10,806–10,870 |
|
|
nad6
|
468 |
465 |
468 |
468 |
155 |
154 |
155 |
155 |
ATG |
ATG |
ATG |
ATG |
TAG |
TAA |
TAA |
TAA |
10,913–11,380 |
10,879–11,343 |
10,874–11,341 |
10,875–11,342 |
|
|
trnY
|
68 |
68 |
68 |
68 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
11,387–11,454 |
11,350–11,417 |
11,348–11,415 |
11,349–11,416 |
|
|
NR1
|
200 |
201 |
204 |
205 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
11,455–11,654 |
11,418–11,618 |
11,416–11,619 |
11,417–11,621 |
|
|
trnL1(CUN
|
71 |
67 |
67 |
67 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
11,655–11,721 |
11,619–11,685 |
11,620–11,686 |
11,622–11,688 |
|
|
trnS2(UGN
|
65 |
66 |
66 |
65 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
11,724–11,788 |
11,688–11,753 |
11,689–11,754 |
11,691–11,755 |
|
|
trnL2(UUN
|
65 |
65 |
65 |
65 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
11,793–11,857 |
11,757–11,821 |
11,759–11,823 |
11,760–11,824 |
|
|
trnR
|
59 |
56 |
57 |
57 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
11,878–11,936 |
11,831–11,886 |
11,839–11,895 |
11,840–11,896 |
|
|
nad5
|
1,569 |
1,570 |
1,569 |
1,569 |
522 |
522 |
522 |
522 |
ATG |
ATG |
ATG |
ATG |
TAA |
TAA |
TAA |
TAA |
11,939–13,507 |
11,890–13,458 |
11,899–13,467 |
|
|
|
NR2
|
178 |
184 |
174 |
178 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
13,508–13,685 |
13,459–13,643 |
13,468–13,641 |
|
Table 3Codon usage in the 12 protein-coding genes of the mitochondrial genomes of Spirometra species
Table 3
|
NC |
AA |
Sta % |
Seb % |
Sdc % |
Srd % |
NC |
AA |
Sta % |
Seb % |
Sdc % |
Srd % |
|
TTT |
Phe |
11.7 |
11.9 |
11.5 |
11.8 |
TAT |
Tyr |
4.8 |
4.7 |
5.3 |
4.4 |
|
TTC |
Phe |
0.8 |
0.7 |
1 |
2.2 |
TAC |
Tyr |
1.2 |
1.2 |
0.7 |
0.8 |
|
TTA |
Leu |
4.7 |
5.6 |
6.2 |
4.6
|
TAA
|
*
|
0.1 |
0.1 |
0.2 |
1.6 |
|
TTG |
Leu |
6.9 |
6.7 |
5.7 |
3.4
|
TAG
|
*
|
0.2 |
0.2 |
0.2 |
1.8 |
|
CTT |
Leu |
1.9 |
1.7 |
2.2 |
2.6 |
CAT |
His |
1.4 |
1.3 |
1.1 |
0.9 |
|
CTC |
Leu |
0.2 |
0.2 |
0.1 |
0.6 |
CAC |
His |
0.1 |
0.3 |
0.4 |
0.3 |
|
CTA |
Leu |
0.7 |
0.6 |
0.7 |
1.2 |
CAA |
Gln |
0.1 |
0.1 |
0.1 |
0.5 |
|
CTG |
Leu |
0.9 |
0.8 |
0.8 |
1.3 |
CAG |
Gln |
0.4 |
0.5 |
0.5 |
0.6 |
|
ATT |
Ile |
3.8 |
4.2 |
4.2 |
5.2 |
AAT |
Asn |
1.5 |
1.5 |
1.6 |
1.3 |
|
ATC |
Ile |
0.4 |
0.5 |
0.4 |
0.7 |
AAC |
Asn |
0.3 |
0.3 |
0.2 |
0.5 |
|
ATA |
Ile |
2.2 |
1.9 |
2.2 |
2.1 |
AAA |
Asn |
1.0 |
0.9 |
1.1 |
0.8 |
|
ATG
|
Met |
2.3 |
2.4 |
2.4 |
1.7 |
AAG |
Lys |
1.4 |
1.4 |
1.4 |
0.9 |
|
GTT |
Val |
5.9 |
5.3 |
5.7 |
5.4 |
GAT |
Asp |
1.7 |
1.9 |
1.6 |
1.7 |
|
GTC |
Val |
0.5 |
0.7 |
0.5 |
0.6 |
GAC |
Asp |
0.4 |
0.1 |
0.4 |
0.5 |
|
GTA |
Val |
1.6 |
1.6 |
1.4 |
1.6 |
GAA |
Glu |
0.5 |
0.4 |
0.5 |
0.4 |
|
GTG
|
Val |
3.2 |
3.2 |
2.9 |
2.5 |
GAG |
Glu |
1.4 |
1.5 |
1.5 |
0.9 |
|
TCT |
Ser |
3.5 |
3.6 |
3.6 |
2.2 |
TGT |
Cys |
3.4 |
3.6 |
3.7 |
4.1 |
|
TCC |
Ser |
0.3 |
0.4 |
0.5 |
0.6 |
TGC |
Cys |
0.6 |
0.4 |
0.3 |
1.2 |
|
TCA |
Ser |
1.1 |
1.0 |
1.2 |
0.7 |
TGA |
Trp |
0.8 |
0.7 |
1.1 |
1.7 |
|
TCG |
Ser |
0.8 |
0.5 |
0.5 |
0.6 |
TGG |
Trp |
1.9 |
2.2 |
1.7 |
2.9 |
|
CCT |
Pro |
1.4 |
1.2 |
1.4 |
1.2 |
CGT |
Arg |
1.3 |
1.3 |
1.4 |
0.9 |
|
CCC |
Pro |
0.4 |
0.7 |
0.6 |
0.4 |
CGC |
Arg |
0.1 |
<0.1 |
<0.1 |
0.1 |
|
CCA |
Pro |
0.4 |
0.3 |
0.4 |
0.4 |
CGA |
Arg |
0.1 |
0.1 |
<0.1 |
0.3 |
|
CCG |
Pro |
0.4 |
0.3 |
0.2 |
0.5 |
CGG |
Arg |
0.1 |
0.2 |
0.2 |
0.7 |
|
ACT |
Thr |
2.0 |
2.0 |
2.1 |
1.3 |
AGT |
Ser |
2.8 |
2.4 |
2.9 |
2 |
|
ACC |
Thr |
0.2 |
0.4 |
0.5 |
0.3 |
AGC |
Ser |
0.2 |
0.5 |
0.3 |
0.3 |
|
ACA |
Thr |
0.6 |
0.4 |
0.3 |
0.4 |
AGA |
Ser |
0.6 |
0.7 |
0.4 |
0.5 |
|
ACG |
Thr |
0.4 |
0.6 |
0.5 |
0.3 |
AGG |
Ser |
0.3 |
0.8 |
0.5 |
0.8 |
|
GCT |
Ala |
1.9 |
2.1 |
1.9 |
0.9 |
GGT |
Gly |
4.4 |
4.5 |
4.3 |
2.9 |
|
GCC |
Ala |
0.2 |
0.5 |
0.6 |
0.2 |
GGC |
Gly |
0.3 |
0.4 |
0.3 |
0.6 |
|
GCA |
Ala |
0.3 |
0.2 |
0.4 |
0.2 |
GGA |
Gly |
0.6 |
0.6 |
0.8 |
0.5 |
|
GCG |
Ala |
0.5 |
0.3 |
0.2 |
0.3 |
GGG |
Gly |
2.6 |
2.4 |
2.5 |
2.5 |
Table 4Divergences of nucleotides and amino acids of the protein-coding genes
Table 4
|
|
Sta
|
Seb
|
Sdc
|
Srd
|
|
Sta
|
Seb
|
Sdc
|
Srd
|
|
Sta
|
Seb
|
Sdc
|
Srd
|
|
Sta
|
Seb
|
Sdc
|
Srd
|
|
cox1 |
|
|
|
|
cox2 |
|
|
|
|
cox3 |
|
|
|
|
cob
|
|
|
|
|
|
St |
|
- |
2.3 |
1.7 |
1.3 |
|
- |
4.2 |
5.3 |
5.3 |
|
- |
7.9 |
8.4 |
7.9 |
|
- |
5.7 |
5.4 |
5.7 |
|
Se |
|
10.1 |
- |
2.9 |
2.9 |
|
12.3 |
- |
3.2 |
3.2 |
|
13.8 |
- |
5.6 |
5.1 |
|
12.6 |
- |
4.1 |
3.8 |
|
Sd |
|
9.6 |
9.4 |
- |
0.4 |
|
13.2 |
10.4 |
- |
0.0 |
|
14.5 |
12.0 |
- |
0.9 |
|
12.9 |
10.9 |
- |
1.1 |
|
Sr |
|
9.8 |
8.8 |
2.2 |
- |
|
13.2 |
10.4 |
0.0 |
- |
|
14.0 |
12.7 |
1.4 |
- |
|
13.6 |
11.2 |
2.4 |
- |
|
|
atp6 |
|
|
|
|
nad1 |
|
|
|
|
nad2 |
|
|
|
|
nad3 |
|
|
|
|
|
St |
|
- |
8.7 |
11.6 |
10.5 |
|
- |
9.1 |
7.1 |
7.1 |
|
- |
14.1 |
12.8 |
12.8 |
|
- |
13.9 |
13.9 |
15.7 |
|
Se |
|
16.5 |
- |
8.2 |
8.2 |
|
12.0 |
- |
6.1 |
5.4 |
|
16.2 |
- |
8.6 |
7.6 |
|
17.6 |
- |
7.0 |
7.8 |
|
Sd |
|
17.2 |
13.4 |
- |
1.2 |
|
13.0 |
9.8 |
- |
0.7 |
|
16.3 |
13.7 |
- |
1.0 |
|
18.2 |
13.0 |
- |
0.9 |
|
Sr |
|
18.2 |
14.1 |
1.9 |
- |
|
12.6 |
10.0 |
2.1 |
- |
|
16.2 |
14.0 |
1.7 |
- |
|
18.8 |
13.6 |
1.7 |
- |
|
|
nad4 |
|
|
|
|
nad4L |
|
|
|
|
nad5 |
|
|
|
|
nad6 |
|
|
|
|
|
St |
|
- |
11.0 |
8.2 |
9.1 |
|
- |
5.8 |
3.5 |
4.7 |
|
- |
15.7 |
14.7 |
14.5 |
|
- |
16.2 |
9.7 |
9.7 |
|
Se |
|
15.8 |
- |
9.4 |
9.1 |
|
11.9 |
- |
2.3 |
2.3 |
|
21.2 |
- |
11.9 |
12.1 |
|
19.9 |
- |
14.8 |
14.8 |
|
Sd |
|
12.2 |
14.0 |
- |
1.4 |
|
12.3 |
11.9 |
- |
0.2 |
|
20.5 |
18.1 |
- |
0.8 |
|
15.8 |
18.8 |
- |
0.0 |
|
Sr |
|
13.2 |
13.7 |
2.6 |
- |
|
11.9 |
11.5 |
1.2 |
- |
|
20.5 |
18.1 |
1.4 |
- |
|
15.8 |
18.8 |
0.0 |
- |
References
- 1. Vitta A, Srisawangwong T, Sithithaworn P, Laha T, Tesana S. Laboratory production and maintenance of Spirometra erinacei spargana. Southeast Asian J Trop Med Public Health 2004;35:suppl. 280-283.
- 2. Li MW, Song HQ, Li C, Lin HY, Xie WT, Lin RQ, Zhu XQ. Sparganosis in mainland China. Int J Infect Dis 2011;15:154-156. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijid.2010.10.001
- 3. Baer JG. Contribution à la faune helminthologique Sud-Africaine. Note preliminaire. Ann. Parasitol Hum Comp 1924;2:237-247. (in French). https://doi.org/10.1051/parasite/1924023239
- 4. Baer JG. Contribution to the helminth fauna of South Africa. Mammalian cestodes. Union of South Africa. Department of Agriculture. 11th & 12th Reports of the Director of Veterinary Education and Research; 1926, pp 63-136.
- 5. Baer JG, Fain A. Cestodes. Report d’Exploration Parcs Nationaux de I’Upemba. Brussel, Belgium. Insitut des Parcs Nationaux du Congo Belge; 1955, p 36.
- 6. Opuni EK, Muller RL. Studies on Spirometra theileri (Baer, 1925) n. comb. 1. Identification and biology in the laboratory. J Helminthol 1974;48:15-23. https://doi.org/10.1017/S0022149X00022550
- 7. Graber M. Diphyllobothriosis and sparganosis in tropical Africa. Rev Elev Méd Vét Pays Trop 1981;34:303-311. (in French)..
- 8. Müller-Graf CD. A coprological survey of intestinal parasites of wild lions (Panthera leo) in the Serengeti and the Ngorongoro Crater, Tanzania, East Africa. J Parasitol 1995;8:812-814. https://doi.org/10.2307/3283987
- 9. Eom KS, Park H, Lee D, Choe S, Kang Y, Bia MM, Ndosi BA, Nath TC, Eamudomkarn C, Keyyu J, Fyumagwa R, Mduma S, Jeon HK. Identity of Spirometra theileri from a leopard (Panthera pardus) and spotted hyena (Crocuta crocuta) in Tanzania. Korean J Parasitol 2019;57:639-645. https://doi.org/10.3347/kjp.2019.57.6.639
- 10. Ndosi BA, Park H, Lee D, Choe S, Kang Y, Nath TC, Bia MM, Eamudomkarn C, Jeon HK, Eom KS. Morphological and molecular identification of Spirometra tapeworms (Cestoda: Diphyllobothriidae) from carnivorous mammals in the Serengeti and Selous ecosystems of Tanzania. Korean J Parasitol 2020;58:653-660. https://doi.org/10.3347/kjp.2020.58.6.653
- 11. Kavana N, Sonaimuthu P, Kasanga C, Kassuku A, Al-Mekhlafi HM, Fong MY, Khan MB, Mahmud R, Lau YL. Seroprevalence of sparganosis in rural communities of northern Tanzania. Am J Trop Med Hyg 2016;95:874-876. https://doi.org/10.4269/ajtmh.16-0211
- 12. Yamasaki H, Sanpool O, Rodpai R, Sadaow L, Laummaunwai P, Un M, Thanchomnang T, Laymanivong S, Aung WPP, Intapan PM, Maleewong W. Spirometra species from Asia: Genetic diversity and taxonomic challenges. Parasitol Int 2021;80:102181. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.parint.2020.102181
- 13. Avise JC. Molecular Markers, Natural History and Evolution. New York, USA. Chapman & Hall; 1994, pp 1-511.
- 14. Park JK, Kim KH, Kang S, Jeon HK, Kim JH, Littlewood DT, Eom KS. Characterization of the mitochondrial genome of Diphyllobothrium latum (Cestoda: Pseudophyllidea)-implications for the phylogeny of eucestodes. Parasitology 2007;134:749-759. https://doi.org/10.1017/S003118200600206X
- 15. Kim KH, Jeon HK, Kang S, Sultana T, Kim GJ, Eom KS, Park JK. Characterization of the complete mitochondrial genome of Diphyllobothrium nihonkaiense (Diphyllobothriidae: Cestoda), and development of molecular markers for differentiating fish tapeworms. Mol Cell 2007;3:379-390.
- 16. Eom KS, Park H, Lee D, Choe S, Kim KH, Jeon HK. Mitochondrial genome sequences of Spirometra erinaceieuropaei and S. decipiens (Cestoidea: Diphyllobothriidae). Korean J Parasitol 2015;53:455-463. https://doi.org/10.3347/kjp.2015.53.4.455
- 17. Jeon HK, Park H, Lee D, Choe S, Kang Y, Bia MM, Lee SH, Eom KS. Complete sequence of the mitochondrial genome of Spirometra ranarum: comparison with S. erinaceieuropaei and S. decipiens. Korean J Parasitol 2019;57:55-60. https://doi.org/10.3347/kjp.2019.57.1.55
- 18. Liu W, Zhao GH, Tan MY, Zeng DL, Wang KZ, Yuan ZG, Lin RQ, Zhu XQ, Liu Y. Survey of Spirometra erinaceieuropaei spargana infection in the frog Rana nigromaculata of the Hunan Province of China. Vet Parasitol 2010;173:152-156. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.vetpar.2010.06.005
- 19. Liu W, Liu GH, Li F, He DD, Wang T, Sheng XF, Zeng DL, Yang FF, Liu Y. Sequence variability in three mitochondrial DNA regions of Spirometra erinaceieuropaei spargana of human and animal health significance. J Helminthol 2012;86:271-275. https://doi.org/10.1017/S0022149X1100037X
- 20. Boonyasiri A, Cheunsuchon P, Suputtamongkol Y, Yamasaki H, Sanpool O, Maleewong W, Intapan PM. Nine human sparganosis cases in Thailand with molecular identification of causative parasite species. Am J Trop Med Hyg 2014;51:389-393. https://doi.org/10.4269/ajtmh.14-0178
- 21. Jeon HK, Lee KH, Kim KH, Hwang UW, Eom KS. Complete sequence and structure of the mitochondrial genome of the human tapeworm, Taenia asiatica (Platyhelminthes; Cestoda). Parasitol 2005;130:717-726. https://doi.org/10.1017/S0031182004007164
- 22. Jeon HK, Park H, Lee D, Choe S, Kim KH, Huh S, Sohn WM, Chai JY, Eom KS. Human infections with Spirometra decipiens plerocercoids identified by morphologic and genetic analyses in Korea. Korean J Parasitol 2015;53:299-305. https://doi.org/10.3347/kjp.2015.53.3.299
- 23. Lowe TM, Eddy SR. tRNAscan-SE: a program improved detection of transfer DNA genes in genomic sequence. Nuclei Acids Res 1997;25:955-964. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/25.5.955
- 24. Matzura O, Wennborg A. RNAdraw: an integrated program for RNA secondary structure calculation and analysis under 32-bit Microsoft Windows. Comput Appl Biosci 1996;12:247-249. https://doi.org/10.1093/bioinformatics/12.3.247
- 25. Posada D. jModelTest: Phylogenetic model averaging. Mol Biol Evol 2008;25:1253-1256. https://doi.org/10.1093/molbev/msn083
- 26. Suchard MA, Kitchen CMR, Sinsheimer JS, Weiss RE. Hierarchical phylogenetic models for analyzing multipartite sequence data. Syst Biol 2003;52:649-664. https://doi.org/10.1080/10635150390238879
- 27. Littlewood DTJ, Lockyer AE, Webster BL, Johnston DA, Le TH. The complete mitochondrial genomes of Schistosoma haematobium and Schistosoma spindale and the evolutionary history of mitochondrial genome changes among parasitic flatworms. Mol Phylogenet Evol 2006;39:452-467. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ympev.2005.12.012
- 28. Von Nickisch-Rosenegk M, Brown WM, Boore JL. Complete sequence of the mitochondrial genome of the tapeworm Hymenolepis diminuta: gene arrangements indicate that Platyhelminths and Eutrochozoans. Mol Biol Evol 2001;18:721-830. https://doi.org/10.1093/oxfordjournals.molbev.a003854
- 29. Garey JR, Wolstenholme DR. Paltyhelminth mitochondrial DNA: evidence for early evolutionary origin of a tRNAser(AGN) that contains a dihydrouridine arm replacement loop, and of serine-specifying AGA and AGG codons. J Mol Evol 1989;28:374-387. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02603072
- 30. Clary DO, Wolstenholme DR. Drosophila mitochondrial DNA: conserved sequences in the A+T rich region and supporting evidence for a secondary structure model of the small ribosomal RNA. J Mol Evol 1987;25:116-125. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02101753
- 31. Johns GC, Avise JC. A comparative summary of genetic distances in the vertebrates from the mitochondrial cytochrome b gene. Mol Bio Evol 1998;15:1481-1490. https://doi.org/10.1093/oxfordjournals.molbev.a025875
- 32. Herbert PDN, Ratnasingham S, deWaard JR. Barcoding animal life: cytochrome c oxidase subunit 1 divergences among closely related species. Proc Biol Sci 2003;270:suppl. 96-99. https://doi.org/10.1098/rsbl.2003.0025
 , Hansol Park1
, Hansol Park1 , Dongmin Lee1, Seongjun Choe1
, Dongmin Lee1, Seongjun Choe1 , Yeseul Kang1
, Yeseul Kang1 , Tilak Chandra Nath1,3
, Tilak Chandra Nath1,3 , Mohammed Mebarek Bia1, Chatanun Eamudomkarn4, Hyeong-Kyu Jeon1,*
, Mohammed Mebarek Bia1, Chatanun Eamudomkarn4, Hyeong-Kyu Jeon1,* , Keeseon S. Eom1,*
, Keeseon S. Eom1,*