Abstract
Ticks can transmit pathogenic bacteria, protozoa, and viruses to humans and animals. In this study, we investigated the microbiomes of Haemaphysalis longicornis according to sex and life stages. The Shannon index was significantly higher for nymphs than adult ticks. Principal coordinates analysis showed that the microbiome composition of female adult and male adult ticks were different. Notably, Coxiella-like bacterium (AB001519), known as a tick symbiont, was found in all nymphs and female adult ticks, but only one out of 4 male adult ticks had Coxiella-like bacterium (AB001519). In addition, Rickettsia rickettsii, Coxiella burnetii, and Anaplasma bovis were detected in this study.
-
Key words: Haemaphysalis longicornis, Rickettsia, Coxiella, microbiome, vector-borne disease
INTRODUCTION
Ticks can transmit pathogenic bacteria, protozoa, viruses that cause great suffering and potentially fatal diseases in humans worldwide [
1]. Ticks also cause considerable losses to the livestock industry by causing irritation and blood loss to their hosts, thus decreasing the leather quality and at the same time acting as vectors of many pathogens [
2].
Haemaphysalis longicornis has been reported in Australia, New Zealand, New Caledonia, Fiji, Japan, Korea, Northeastern China, USSR, and USA [
3–
6].
The bacterial pathogens transmitted by
Haemaphysalis spp. are
Rickettsia spp.,
Ehrlichia spp.,
Anaplasma spp.,
Francisella spp.,
Coxiella spp., and
Borrelia spp. which cause the following diseases, respectively: Rocky Mountain spotted fever, Siberian or North Asian typhus, Japanese spotted fever, and Australian spotted fever; human monocytic ehrlichiosis and canine ehrlichiosis; human granulocytic anaplasmosis, and bovine anaplasmosis; tularemia; Q fever; and Lyme disease and tick-borne relapsing fever [
7]. The parasites transmitted by
Haemaphysalis spp. are
Theileria spp.,
Babesia spp., and
Hepatozoon spp. which likewise cause the following diseases, respectively: tropical theileriosis and sheep theilerosis; cattle, dog, and sheep babesiosis; and hepatozoonosis [
7].
Despite the importance of H. longicornis as an important pathogen vector, little is known regarding its microbiome. In this study, we employed high-throughput sequencing of the V3–V4 hypervariable regions of the 16S rRNA gene to investigate the bacterial abundance and diversity between the nymph stage and the adult developmental stages of H. longicornis to evaluate the changes in the bacterial abundance and the maintenance of the bacterial community throughout the life cycle of the tick.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Tick collection and identification
Ticks were collected within a radius of 50 m from vegetation (geographical location: 37.323366/129.233736) by flagging in Samcheok, Gangwon-do Province, Korea, in June 2020. Species identification of the collected ticks was performed by examination under a dissecting microscope, according to Yamaguti et al. [
8]. Among the 140
H. longicornis obtained, 11 nymphs, 3 female adults, and 4 male adults were randomly selected for microbiome study.
The surface of each tick was sterilized using alcohol before DNA extraction. DNA was extracted from individual ticks using a NucleoSpin DNA Insect kit (Macherey–Nagel, Düren, Germany) according to the manufacturer’s instructions.
High-throughput sequencing of 16S rRNA gene amplicons
The V3–V4 region of the 16S rRNA gene was amplified by PCR using the following bacterial universal primer pair: forward primer, 5′-TCGTCGGCAGCGTCAGATGTGTATAAGAGACAGCCTACGGGNGGCWGCAG-3′ and reverse primer, 5′-GTCTCGTGGGCTCGGAGATGTGTATAAGAGACAGGACTACHVGGGTATCTAATCC-3′ [
9]. A limited-cycle amplification step was performed to add multiplexing indices and Illumina sequencing adapters. The libraries were normalized, pooled, and sequenced using the MiSeq platform (600 cycles, Illumina MiSeq V3 cartridge; Illumina, San Diego, California, USA) according to the manufacturer’s instructions.
Bioinformatic analyses were performed as described by Kim et al. [
9]. Raw reads were processed through a quality check, and low-quality (Q <25) reads were filtered using Trimmomatic 0.32 [
10]. Paired-end sequence data were then merged using PandaSeq [
11]. Primers were trimmed using the ChunLab in-house program (ChunLab, Inc., Seoul, Korea), applying a similarity cut-off of 0.8. Sequences were denoised using the Mothur pre-clustering program, which merges sequences and extracts unique sequences, allowing up to 2 differences between sequences [
12]. The EzBioCloud database [
13] was used for taxonomic assignment using BLAST 2.2.22 [
14], and pairwise alignments were generated to calculate similarity [
15]. The UCHIME algorithm and non-chimeric 16S rRNA database from EzBioCloud were used to detect chimeric sequences for reads with a best hit similarity rate of <97% [
16]. Sequence data were then clustered using CD-Hit and UCLUST [
17,
18]. All of the abovementioned analyses were performed with EzBioCloud, a commercially available ChunLab bioinformatics cloud platform for microbiome research (
https://www.ezbiocloud.net/). The reads were normalized to 10,000 to perform the analyses. We computed the Shannon index [
19], unweighted pair group method with arithmetic mean (UPGMA) clustering [
20], and principal coordinates analysis (PCoA) [
21] based on the generalized UniFrac distance [
22]. We used the Kruskal–Wallis test to test for differences in the number of operational taxonomic units (OTUs) and used the Shannon index to compare microbiome diversity between the 2 age groups. We used linear discriminant analysis effect size (LEfSe) analysis to identify significantly different taxa [
23]. Swarm plot was created by the beeswarm package in R software (version 4.0.5).
RESULTS
For
H. longicornis nymph, female adult, and male adult ticks, the average reads assigned to bacteria were 35,622, 59,365, and 51,859, respectively (
Supplementary Table S1). The number of OTUs, which reflects species richness, was not significantly different between the groups (
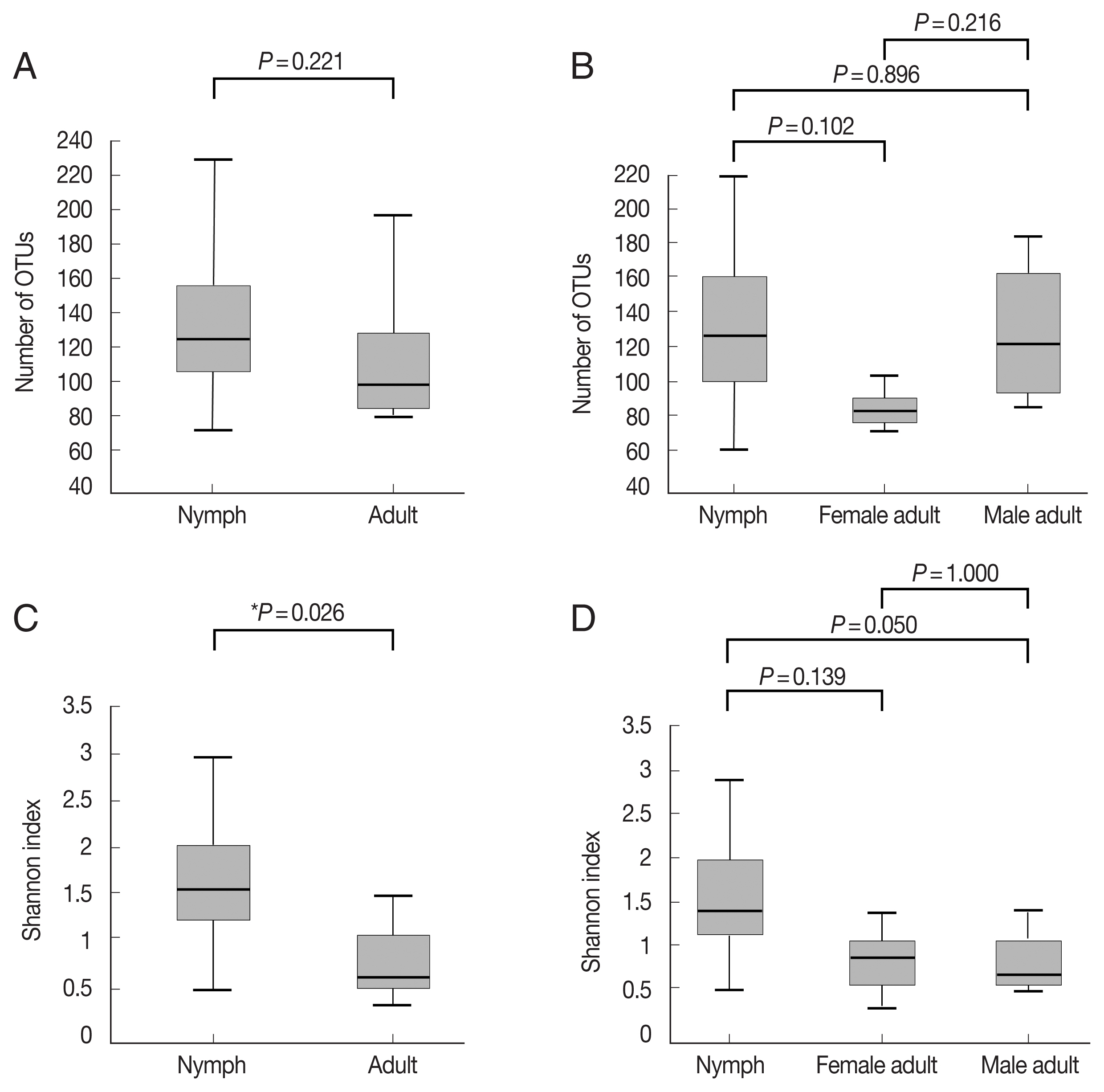
Fig. 1A, B;
Supplementary Table S1). The Shannon index, which reflects species diversity, was significantly higher for nymphs (n=11) than the adult ticks (both males and females, n=7;
P=0.026;
Fig. 1C). However, it did not differ significantly among the 3 groups, and the average Shannon indices were 1.55, 0.83, and 0.78 for nymphs (n=11), female adults (n=3), and male adult (n=4) ticks, respectively (
Fig. 1D;
Supplementary Table S1).
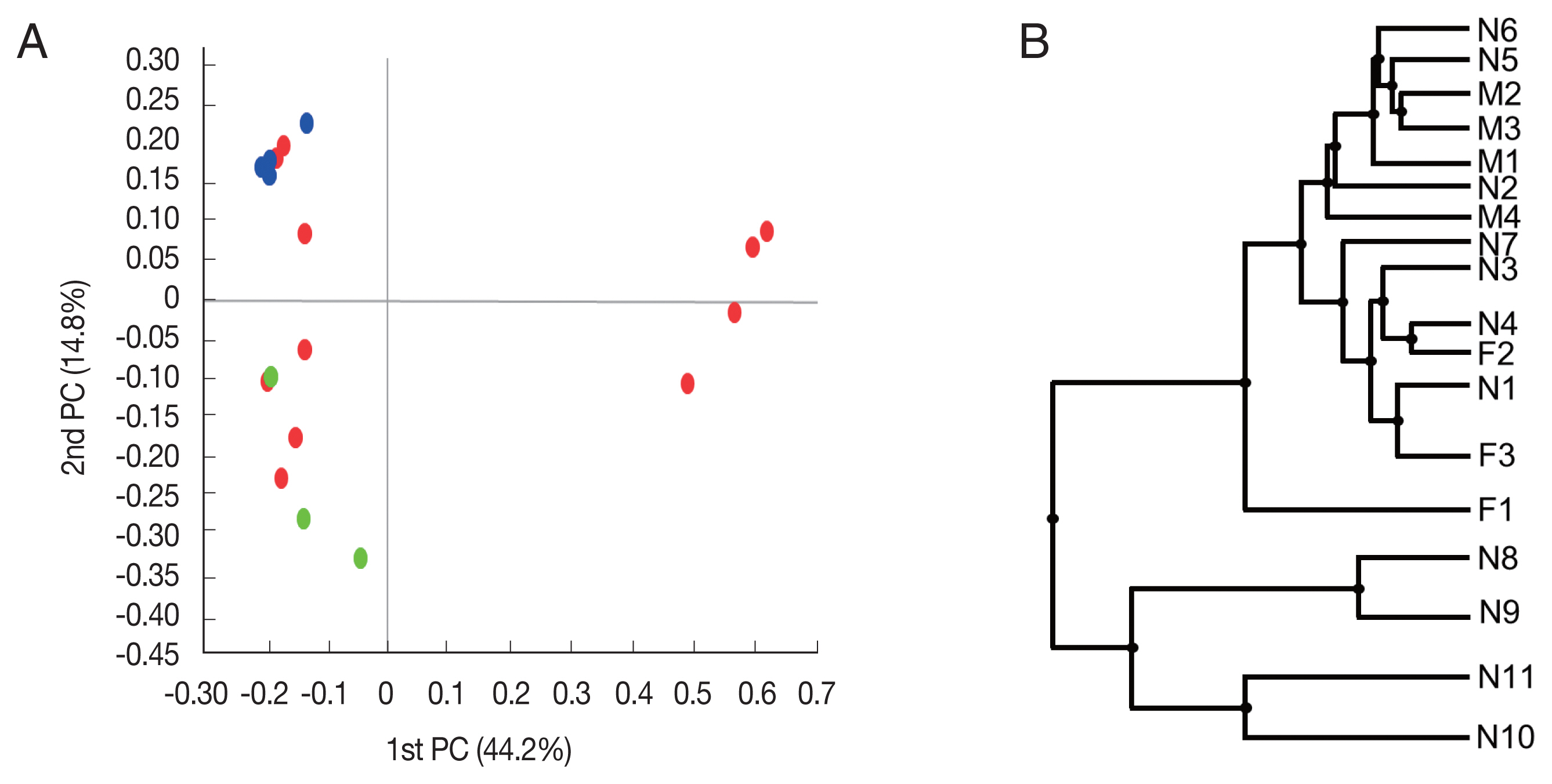
Beta diversity was analyzed to show the difference in bacterial composition between the samples. First, the PCoA result showed that the samples of the male adult group and those of the female adult group clustered well (
Fig. 2A), suggesting that the bacterial composition of the 2 groups was different. In contrast, nymph samples were relatively scattered in the plot versus the other groups. Similarly, in UPGMA clustering, the male adult and female adult samples were clustered closely among their groups than the nymph samples.
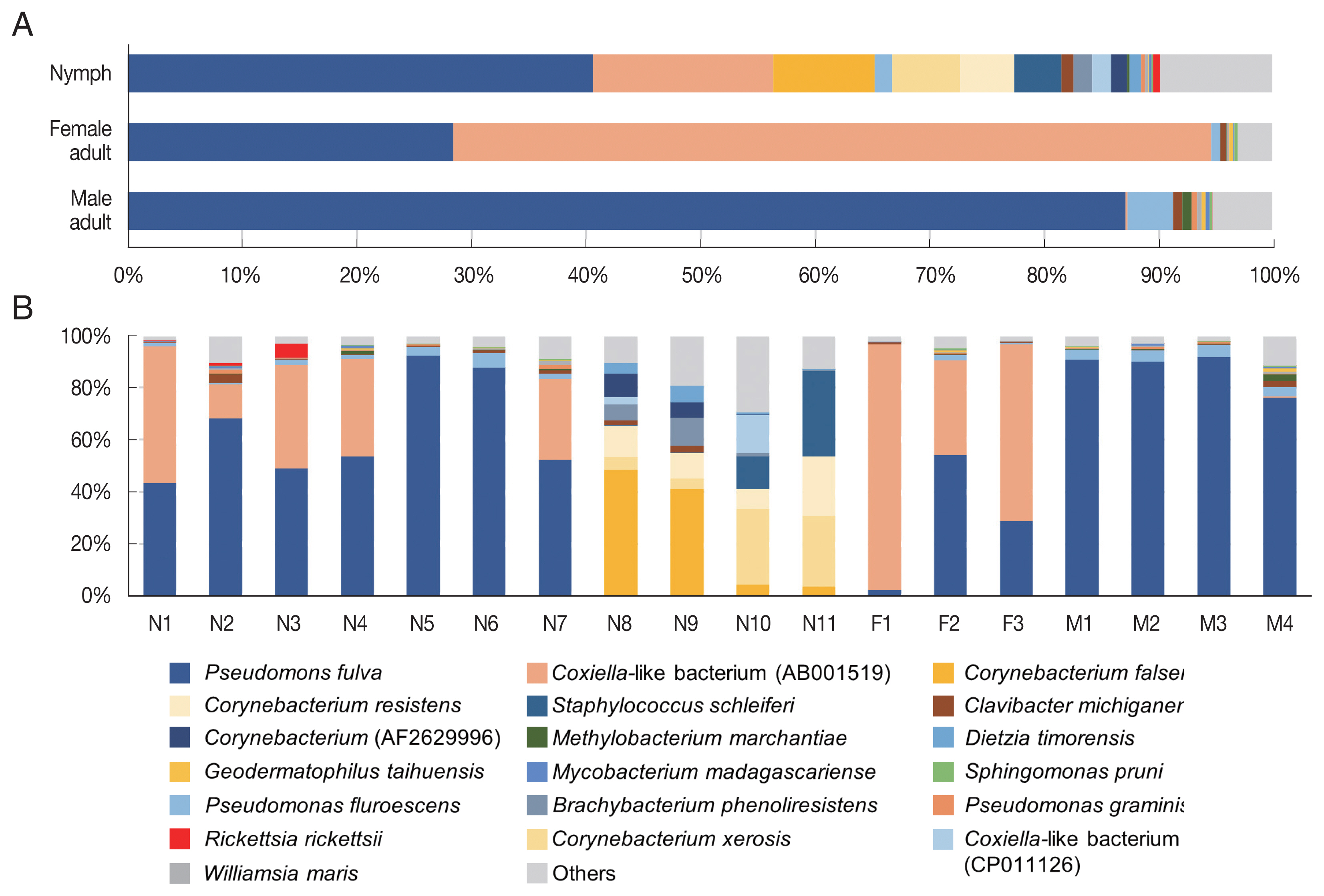
In the composition, the most predominant bacterial species was
Pseudomonas fulva, which was found in all ticks evaluated in this study with an average relative abundance of 48.9% (
Fig. 3A, B). The second most abundant species was
Coxiella-like bacterium (AB001519), a known tick endosymbiont [
24], with an average relative abundance of 20.7% (
Fig. 3A).
Coxiella-like bacterium (AB001519) was found in all nymphs and female adult ticks although some nymph samples showed very few reads for this species (
Fig. 3B;
Supplementary Table S2). In contrast, among the 4 male adult tick samples,
Coxiella-like bacterium (AB001519) was found in only one sample with 0.7% relative abundance (
Fig. 3B). Relative abundance of
Corynebacterium spp., including
C. falsenii,
C. xerosis, and
C. resistens was more than 40% in 4 nymphs (N8, N9, N10, and N11) but it was not detected in other samples (
Fig. 3B).
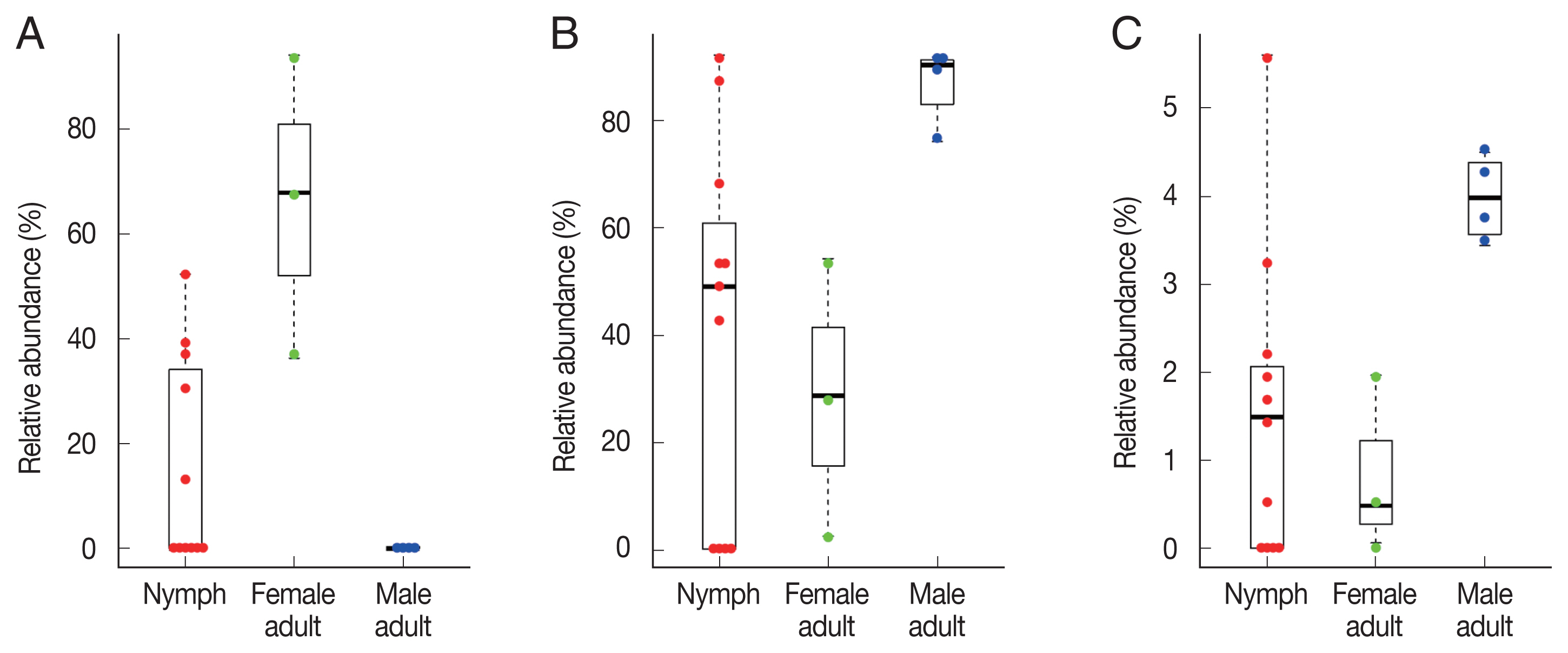
To identify significant differences in bacterial abundance between the nymph, female adult, and female adult ticks, we performed LEfSe analysis. The LDA scores for
Coxiella-like bacterium (AB001519) was 4.88 and its average relative abundance was 66.4% in female adult ticks, 15.7% in nymphs, and 0.2% in male adult ticks (
Table 1;
Fig. 4A). The LDA score for
P. fulva was 4.79 and its relative abundance was the highest in male adult ticks (86.9%,
Fig. 4B). The LDA score for
P. fluorescens was 3.51 and its relative abundance was the highest in male adult ticks (4.0%,
Fig. 4C).
Known pathogenic species were also identified.
Rickettsia rickettsii was detected in 3 nymphs and 3 male adult ticks and
Coxiella burnetii was detected in 4 nymphs (
Supplementary Table S2). In addition,
Anaplasma bovis, which infects ruminants, was found in one nymph (
Supplementary Table S2).
Ehrlichia spp.,
Francisella spp., and
Borrelia spp. were not detected in this study.
DISCUSSION
H. longicornis is the most common tick species in the grass in Korea. According to previous studies, out of 7,973 ticks collected from farms in Korea, 7,758 (97.3%) were identified as
H. longicornis [
25,
26].
H. longicornis is also known as a transmitter of several pathogens such as
Rickettsia spp., Anaplasmataceae,
Borrelia spp.,
Babesia spp.,
Francisella spp.,
Bratonella spp.,
Coxiella spp., and severe fever with thrombocytopenia syndrome virus [
27].
In this study, we investigated the differences in the microbiomes of
H. longicornis nymphs, female adults, and male adults. The Shannon index was significantly higher for nymphs than the adult ticks (
Fig. 1C). This suggests that nymphs harbor a more diverse bacterial community compared to adult ticks. In 6 species of ticks, including
Haemaphysalis leporispalustris, microbiome richness and diversity were highest in the larval stage and eventually decreased in subsequent life stages; this result is in concordance with our findings [
28]. Life-stage related differences in the microbiome of
H. longicornis indicate that the tick loses most of the bacteria present in the early developmental stages and then reestablishes the bacterial community after molting [
29,
30].
Coxiella spp. is known as an endosymbiont essential for the survival and reproduction of hard ticks [
26,
31].
Coxiella-like bacteria are a large group of yet-to-be-isolated and characterized bacteria phylogenetically close to the causative agent of Q fever,
C. burnetii [
32]. These
Coxiella-like bacteria are maternally inherited endosymbionts, highly prevalent in tick populations, and engaged in mutualistic interactions with their arthropod hosts [
33]. In our study, the relative abundance of
Coxiella-like bacterium (AB001519) was significantly different among nymphs, female adult, and male adult ticks. An average of 66.4% of female adult ticks and all nymphs and female adult ticks were found to have
Coxiella-like bacterium (AB 001519). In contrast, only one tick out of 4 male adult ticks had
Coxiella-like bacterium (AB001519), and its relative abundance was only 0.7%.
Coxiella-like bacterium (AB001519) may be playing an important role in the development and reproduction of
H. longicornis especially for female adult and during the nymph stage. Since
Coxiella-like bacterium (AB001519) is almost eliminated in male adult ticks, there may be no role for this bacterium in male adult ticks; likewise, this bacterium may be transmitted vertically from mother tick to offspring. In addition, at least one strain of
Pseudomonas was identified in each tick in this study.
Pseudomonas spp. were frequently detected in ticks in other studies, indicating that it may have a symbiotic association with ticks [
34,
35].
Among the 18 tick samples in this study,
R. rickettsii was found in 6,
C. burnetii in 4, and
A. bovis in 1, although further investigation is necessary to determine the pathogenicity of the isolated strains.
R. rickettsii is the causative agent of Rocky Mountain spotted fever, one of the most virulent human infections [
36]. Using molecular assays, several spotted fever-causing
Rickettsia spp., including
R. japonica,
R. conorii,
R. akari,
R. felis,
R. rickettsii and unclassified
Rickettsia spp., have been detected in humans, ticks, and mites [
37–
39].
C. burnetii is an obligate intracellular bacterial pathogen causing Q fever that is manifested by pneumonia, fever, and granulomatous hepatitis. The reservoir of
C. burnetii includes mammals, birds, and arthropods such as ticks [
40]. Domestic animals represent the most frequent source of human
C. burnetii infection [
40]. The number of human Q fever cases in Korea has been rapidly increasing since 2015 [
41]. Several studies have investigated
C. burnetii infection in dairy cattle in Korea [
42].
A. bovis can be transmitted by ticks to cattle, sheep, goats, and other domestic ruminants [
43].
A. bovis causes fever, anemia, drowsiness, convulsions, weight loss, and enlargement of lymph nodes in cattle [
44]. Recently,
A. bovis was also detected in Korean spotted deer (
Cervus nippon) [
45], Korean water deer (
Hydropotes inermis) [
46], and
H. longicornis in Korea [
47,
48].
A limitation of this study was that we did not investigate the microbiome of H. longicornis in its larval stage. A single larva is not sufficient for the effective extraction of DNA, which is required to further perform high-throughput sequencing. However, the strength of this study was that we were able to investigate the microbiome of the individual ticks without pooling their DNA samples. In addition, ticks were collected from a relatively small location and at a single time point. Further similar studies on a larger number of ticks collected from various locations and at multiple time points are required.
In conclusion, in this metagenomics study on H. longicornis, different microbiome patterns were found among nymphs, female adult ticks, and male adult ticks. Coxiella-like bacterium (AB001519) was found in all nymphs and female adult ticks, but rarely in male adult ticks. In addition, several potential pathogens were found such as R. rickettsii, C. burnetii, and A. bovis.
Supplementary Information
Notes
-
The authors have no competing interests to be declared.
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS
This study was supported by a National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF) grant funded by the Korean Government (MEST; numbers NRF-2019R1A2B5B01069843, 2020R1I1A2074562).
Raw sequence data are available in NCBI GenBank under Bioproject PRJNA733831.
Fig. 1Alpha diversities of the microbiomes of Haemaphysalis longicornis. (A) The number of OTUs (species richness) in nymph (n=11) and adult tick (n=7) groups. (B) The number of OTUs in nymph (n=11), female adult tick (n=3), and male adult tick (n=4) groups. (C) The Shannon index in nymph and adult tick groups. (D) The Shannon index in nymph, female adult tick, and male adult tick groups. The boxplots indicate the minimum, first quartile, second quartile (median), third quartile, and maximum values.
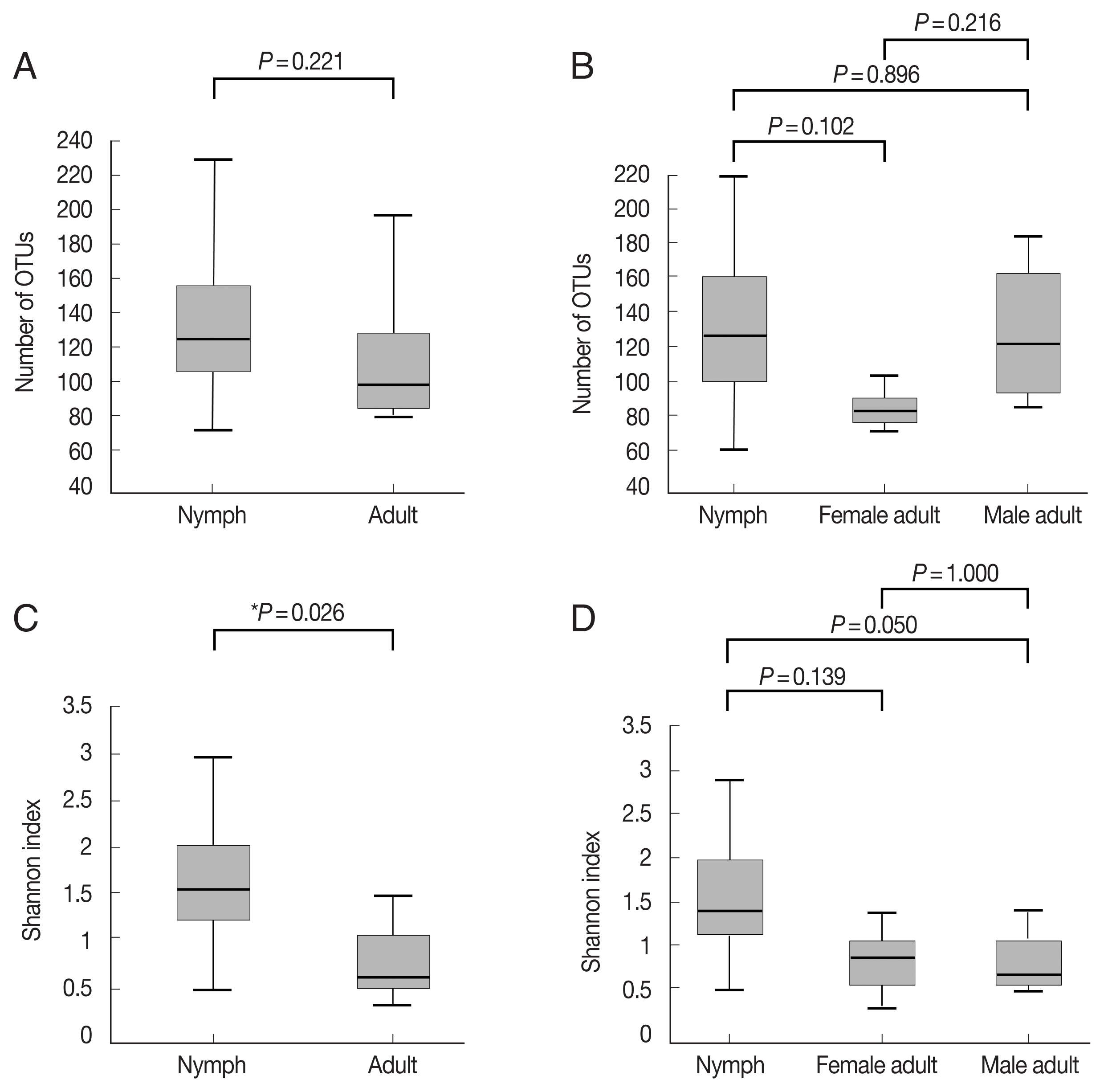
Fig. 2Beta diversities of the microbiomes of Haemaphysalis longicornis. (A) Principal coordinates (PC) depicting differences in the taxonomic compositions of the bacterial communities. Nymph (red), female (green), and male adults (blue). (B) Unweighted pair group method with arithmetic mean (UPGMA) clustering. N1–N11 represent nymphs, F1–F3 represent female adult ticks, and M1–M4 represent male adult ticks.
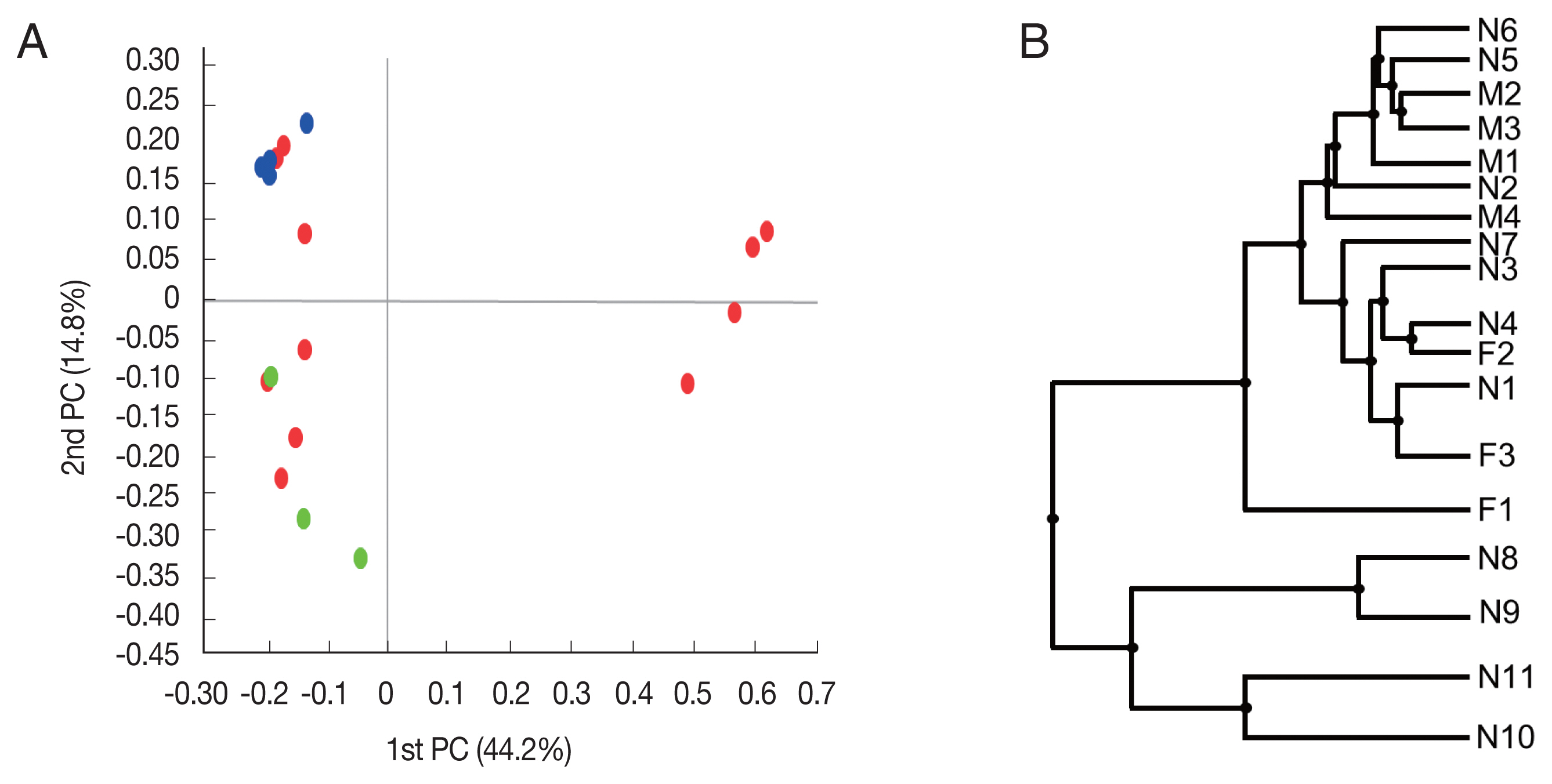
Fig. 3Microbiome composition at species level in Haemaphysalis longicornis. (A) Average microbiome composition in the ticks. (B) Individual microbiome composition of the nymph (N1–N11), female (F1–F3), and male (M1–M4) ticks.
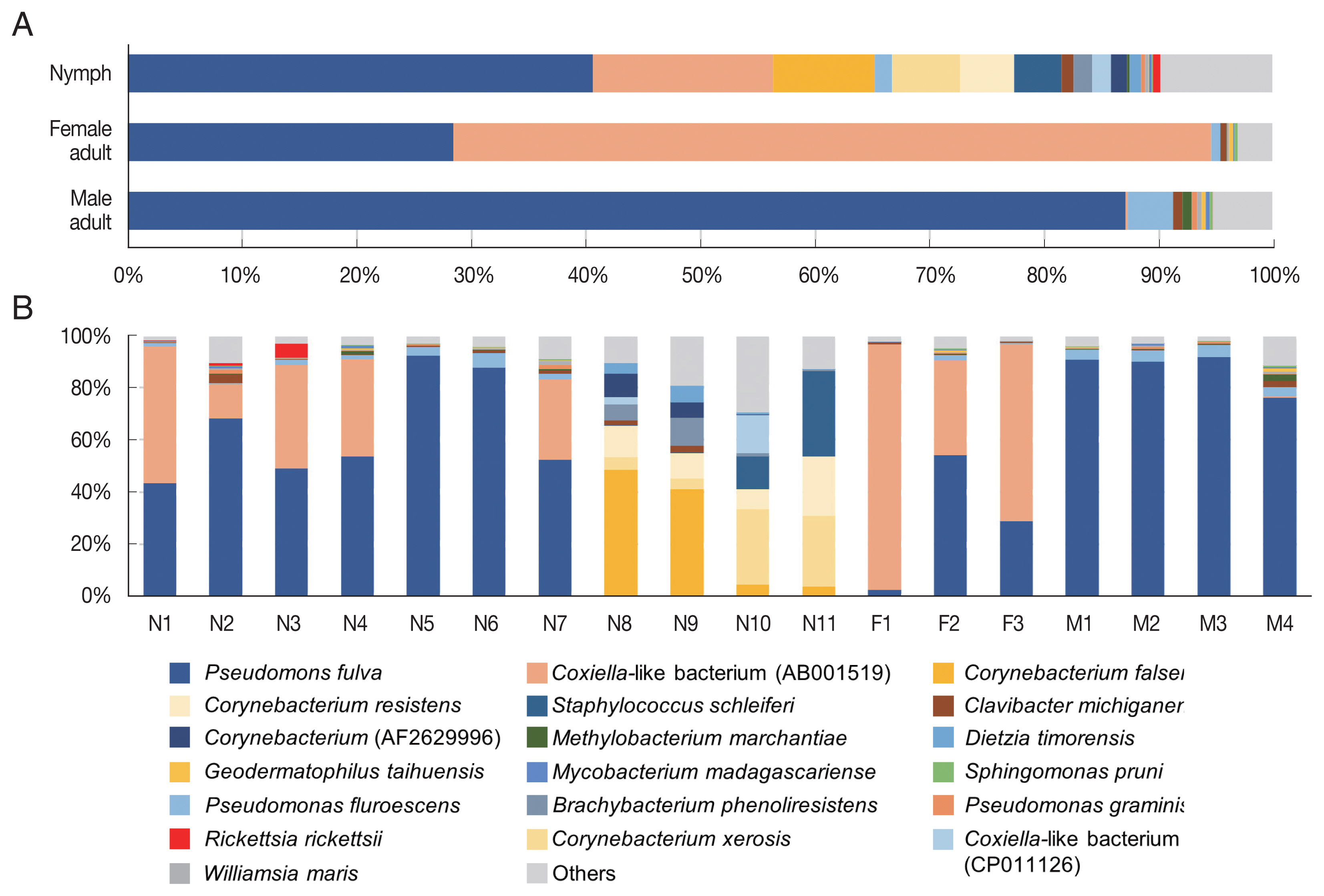
Fig. 4Swarm plots of the relative abundance in Haemaphysalis longicornis. (A) Coxiella-like bacterium (AB001519). (B) Pseudomonas fulva. (C) Pseudomonas fluorescens.
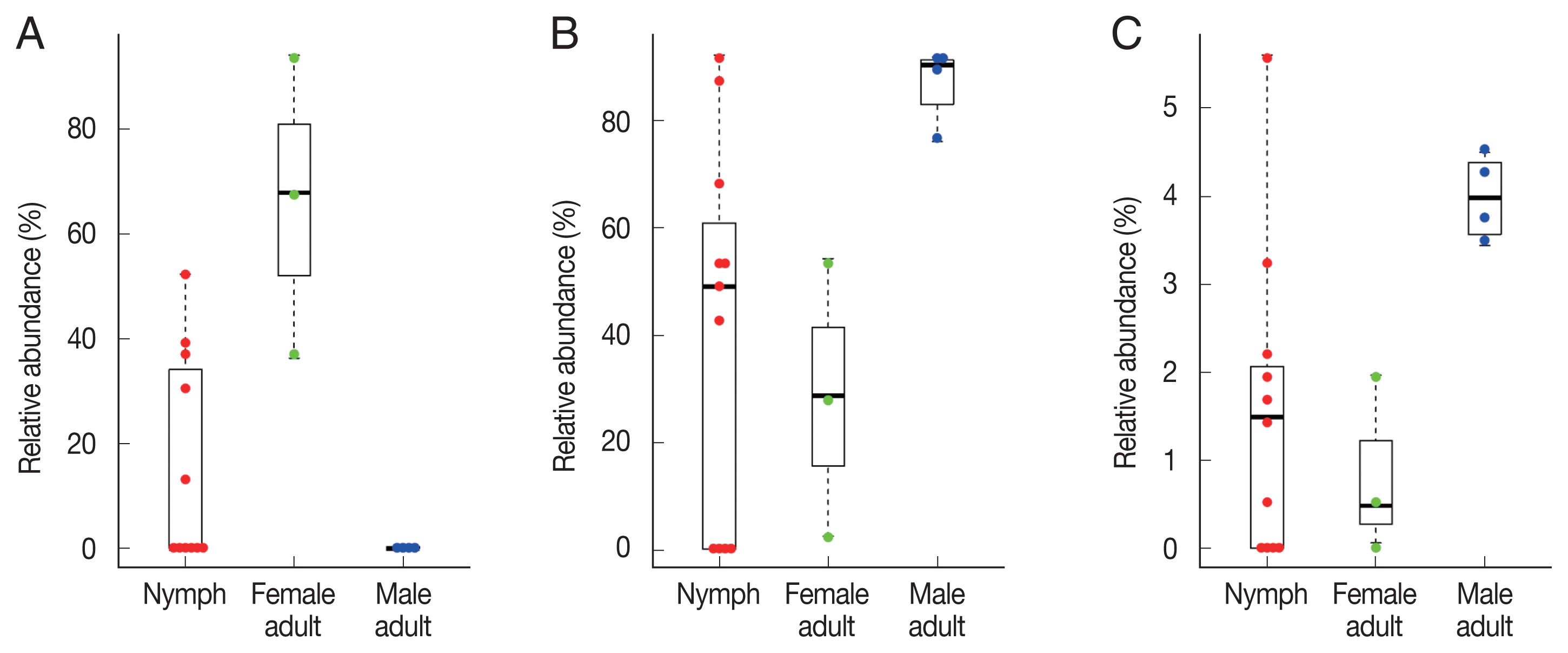
Table 1Linear discriminant effect size analysis on differentially abundant bacterial taxa between Haemaphysalis longicornis nymph, female and male ticks
Table 1
|
Taxon name |
Taxon rank |
LDA effect size |
P-value |
Relative abundance in female adult (%) |
Relative abundance in male adult (%) |
Relative abundance in nymph (%) |
|
Coxiella-like bacterium (AB001519) |
Species |
4.88 |
0.016 |
66.4 |
0.2 |
15.7 |
|
Pseudomonas fulva
|
Species |
4.79 |
0.049 |
28.1 |
86.9 |
40.6 |
|
Pseudomonas fluorescens
|
Species |
3.51 |
0.037 |
0.90 |
4.0 |
1.5 |
|
Coxiella
|
Genus |
4.94 |
0.008 |
66.4 |
0.2 |
17.9 |
|
Pseudomonas
|
Genus |
4.83 |
0.038 |
29.2 |
91.8 |
42.9 |
|
Coxiellaceae |
Family |
4.94 |
0.008 |
66.4 |
0.2 |
17.9 |
|
Pseudomonadaceae |
Family |
4.83 |
0.038 |
29.2 |
91.8 |
42.9 |
|
Legionellales |
Order |
4.94 |
0.008 |
66.4 |
0.2 |
17.9 |
|
Pseudomonadales |
Order |
4.83 |
0.038 |
29.2 |
91.8 |
43.0 |
References
- 1. Jongejan F, Uilenberg G. The global importance of ticks. Parasitology 2004;129(suppl):3-14. https://doi.org/10.1017/s0031182004005967
- 2. Roy BC, Estrada-Peña A, Krücken J, Rehman A, Ard Menzo Nijhof AM. Morphological and phylogenetic analyses of Rhipicephalus microplus ticks from Bangladesh, Pakistan and Myanmar. Ticks Tick Borne Dis 2018;9:1069-1079. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ttbdis.2018.03.035
- 3. Wormser GP, Mckenna D, Piedmonte N, Vinci V, Egizi AM, Backenson B, Falco RC. First recognized human bite in the United States by the Asian Longhorned Tick, Haemaphysalis longicornis. Clin Infect Dis 2020;70:314-316. https://doi.org/10.1093/cid/ciz449
- 4. Bickerton M, Toledo A. Multiple pruritic tick bites by Asian Longhorned tick larvae (Haemaphysalis longicornis). Int J Acarol 2020;46:373-376. https://doi.org/10.1080/01647954.2020.1805004
- 5. Hoogstraal H, Roberts FH, Kohls GM, Tipton VJ. Review of Haemaphysalis (Kaiseriana) longicornis Neumann (resurrected) of Australia, New Zealand, New Caledonia, Fiji, Japan, Korea, and Northeastern China and USSR, and its parthenogenetic and bisexual populations (Ixodoidea, Ixodidae). J Parasitol 1968;54:1197-1213. https://doi.org/10.2307/3276992
- 6. White SA, Bevins SN, Ruder MG, Shaw D, Vigil SL, Randall A, Deliberto TJ, Dominguez K, Thompson AT, Mertins JW, Alfred JT, Yabsley MJ. Surveys for ticks on wildlife hosts and in the environment at Asian longhorned tick (Haemaphysalis longicornis)-positive sites in Virginia and New Jersey, 2018. Transbound Emerg dis 2021;68:605-614. https://doi.org/10.1111/tbed.13722
- 7. de la Fuente J, Estrada-Pena A, Venzal JM, Kocan KM, Sonenshine DE. Overview: Ticks as vectors of pathogens that cause disease in humans and animals. Front Biosci 2008;13:6938-6946. https://doi.org/10.2741/3200
- 8. Yamaguti N, Tipton VJ, Keegan HL, Toshioka H. Ticks of Japan, Korea, and the Ryukyu islands. Brigham Young Univ Sci Bull Bio Ser 1971;15:1-227. https://doi.org/10.5962/bhl.part.25691
- 9. Kim JY, Kim EM, Yi MH, Lee JY, Lee SW, Hwang YJ, Yong DE, Sohn WM, Yong TS. Chinese liver fluke Clonorchis sinensis infection changes the gut microbiome and increases probiotic Lactobacillus in mice. Parasitol Res 2019;118:693-699. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00436-018-6179-x
- 10. Bolger AM, Lohse M, Usadel . Trimmomatic: a flexible trimmer for Illumina sequence data. Bioinformatics 2014;30:2114-2120. https://doi.org/10.1093/bioinformatics/btu170
- 11. Masella AP, Bartram AK, Truszkowski JM, Brown DG, Neufeld JD. PANDAseq: paired-end assembler for illumina sequences. BMC bioinformatics 2012;13:31. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2105-13-31
- 12. Schloss PD, Westcott SL, Ryabin T, Hall JR, Hartmann M, Hollister EB, Lesniewski RA, Oakley BB, Parks DH, Robinson CJ, Sahl JW, Stres B, Thallinger GG, Van Horn DJ, Weber CF. Introducing mothur: open-source, platform-independent, community supported software for describing and comparing microbial communities. Appl Environ Microbiol 2009;75:7537-7541. https://doi.org/10.1128/AEM.01541-09
- 13. Yoon SH, Ha SM, Kwon SJ, Lim JM, Kim YS, Seo HS, Chun JS. Introducing EzBioCloud: a taxonomically united database of 16S rRNA gene sequences and whole-genome assemblies. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 2017;67:1613-1617. https://doi.org/10.1099/ijsem.0.001755
- 14. Altschul SF, Gish W, Miller W, Myers EW, Lipman DJ. Basic local alignment search tool. J Mol Biol 1990;215:403-410. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0022-2836(05)80360-2
- 15. Myers EW, Miller W. Optimal alignments in linear space. Comput Appl Biosci 1988;4:11-17. https://doi.org/10.1093/bioinformatics/4.1.11
- 16. Edgar RC, Haas BJ, Clemente JC, Quince C, Knight R. UCHIME improves sensitivity and speed of chimera detection. Bioinformatics 2011;27:2194-2200. https://doi.org/10.1093/bioinformatics/btr381
- 17. Edgar RC. Search and clustering orders of magnitude faster than BLAST. Bioinformatics 2010;26:2460-2461. https://doi.org/10.1093/bioinformatics/btq461
- 18. Fu L, Niu B, Zhu Z, Wu S, Li W. CD-HIT: accelerated for clustering the next-generation sequencing data. Bioinformatics 2012;28:3150-3152. https://doi.org/10.1093/bioinformatics/bts565
- 19. Shannon C, Petigara N, Seshasai S. A mathematical theory of communication. Bell Syst Tech J 1948;27:379-423. https://doi.org/10.1002/j.1538-7305.1948.tb01338.x
- 20. Sneath PHA, Sokal RR. Numerical Taxonomy—the Principles and Practice of Numerical Classification. San Francisco, USA. W. H. Freeman; 1973, https://doi.org/10.2307/2412767
- 21. Gower JC. Some distance properties of latent root and vector methods used in multivariate analysis. Biometrika 1966;53:325-338. https://doi.org/10.1093/biomet/53.3-4.325
- 22. Lozupone C, Knight R. UniFrac: a new phylogenetic method for comparing microbial communities. Appl Environ Microbiol 2005;71:8228-8235. https://doi.org/10.1128/AEM.71.12.8228-8235.2005
- 23. Segata N, Izard J, Waldron L, Gevers D, Miropolsky L, Garrett WS, Huttenhower C. Metagenomic biomarker discovery and explanation. Genome Biol 2011;12:R60. https://doi.org/10.1186/gb-2011-12-6-r60
- 24. Zhong Jianmin. Coxiella-like endosymbionts. Adv Exp Med Biol 2012;984:365-379. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-94-007-4315-1_18
- 25. Chae JB, Cho YS, Cho YK, Kang JG, Shin NS, Chae JS. Epidemiological Investigation of Tick Species from Near Domestic Animal Farms and Cattle, Goat, and Wild Boar in Korea. Korean J Parasitol 2019;57:319-324. https://doi.org/10.3347/kjp.2019.57.3.319
- 26. Lee JH, Park HS, Jang WJ, Koh SE, Park TK, Kang SS, Kim BJ, Kook YH, Park KH, Lee SH. Identification of the Coxiella sp. detected from Haemaphysalis longicornis ticks in Korea. Microbiol Immunol 2004;48:125-130. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1348-0421.2004.tb03498.x
- 27. Rosenberg R, Lindsey NP, Fischer M, Gregory CJ, Hinckley AF, Mead PS, Paz-Bailey G, Waterman SH, Drexler NA, Kersh GJ, Hooks H, Partridge SK, Visser SN, Beard CB, Petersen LR. Vital signs: trends in reported vectorborne disease cases - United States and Territories, 2004–2016. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep 2018;67:496-501. https://doi.org/10.15585/mmwr.mm6717e1
- 28. Chicana B, Couper LI, Kwan JY, Tahiraj E, Swei A. Comparative Microbiome Profiles of Sympatric Tick Species from the Far-Western United States. Insects 2019;10:353. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects10100353
- 29. Ruiling Z, Zhendong H, Guangfu Y, Zhong Z. Characterization of the bacterial community in Haemaphysalis longicornis (Acari: Ixodidae) throughout developmental stages. Exp Appl Acarol 2019;77:173-186. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10493-019-00339-7
- 30. Zolnik CP, Prill RJ, Falco RC, Daniels TJ, Kolokotronis SO. Microbiome changes through ontogeny of a tick pathogen vector. Mol Ecol 2016;25:4963-4977. https://doi.org/10.1111/mec.13832
- 31. Zhong J, Jasinskas A, Barbour AG. Antibiotic treatment of the tick vector Amblyomma americanum reduced reproductive fitness. PLoS One 2007;2:e405. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0000405
- 32. Rahal M, Medkour H, Diarra AZ, Bitam I, Parola , Mediannikov O. Molecular identification and evaluation of Coxiella-like endosymbionts genetic diversity carried by cattle ticks in Algeria. Ticks Tick Borne Dis 2020;11:101493. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ttbdis.2020.101493
- 33. Duron O. The IS1111 insertion sequence used for detection of Coxiella burnetii is widespread in Coxiella-like endosymbionts of ticks. FEMS Microbiol Lett; 2015. 362:fnv132 https://doi.org/10.1093/femsle/fnv132
- 34. Murrell A, Dobson SJ, Yang X, Lacey E, Barker SC. A survey of bacterial diversity in ticks, lice and fleas from Australia. Parasitol Res 2003;89:326-334. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00436-002-0722-4
- 35. Rudolf I, Mendel J, Šikutová S, Svec P, Masaríková J, Nováková D, Bunková L, Sedlácek I, Hubálek Z. 16S rRNA gene-based identification of cultured bacterial flora from host-seeking Ixodes ricinus, dermacentor reticulatus and haemaphysalis concinna ticks, vectors of vertebrate pathogens. Folia Microbiol (Praha) 2009;54:419-428. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12223-009-0059-9
- 36. Ammerman NC, Beier-Sexton M, Azad AF. Laboratory maintenance of Rickettsia rickettsii. Curr Protoc Microbiol 2008;11:3A.5.1-3A.5.21. https://doi.org/10.1002/9780471729259.mc03a05s11
- 37. Choi YJ, Jang WJ, Kim JH, Ryu JS, Lee SH, Park KH, Paik HS, Koh YS, Choi MS, Kim IS. Spotted fever group and typhus group rickettsioses in humans, South Korea. Emerg Infect Dis 2005;11:237-244. https://doi.org/10.3201/eid1102.040603
- 38. Lee JH, Park HS, Jung KD, Jang WJ, Koh SE, Kang SS, Lee IY, Lee WJ, Kim BJ, Kook YH, Park KH, Lee SH. Identification of spotted fever group rickettsiae detected from Haemaphysalis longicornis in Korea. Microbiol Immunol 2003;47:301-304. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1348-0421.2003.tb03399.x
- 39. Choi YJ, Lee EM, Park JM, Lee KM, Han SH, Kim JK, Lee SH, Song HJ, Choi MS, Kim IS, Park KH, Jang WJ. Molecular detection of various rickettsiae in mites (Acari: trombiculidae) in southern Jeolla Province, Korea. Microbiol Immunol 2007;51:307-312. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1348-0421.2007.tb03912.x
- 40. Maurin M, Raoult D. Q fever. Clin Microbiol Rev 1999;12:518-553. https://doi.org/10.1128/CMR.12.4.518
- 41. Lee SH, Lee JH, Park SD, Lee HK, Hwang SD, Jeong HW, Heo JY, Lee YS. Isolation of Coxiella burnetii in patients with nonspecific febrile illness in South Korea. BMC Infect Dis 2020;20:421. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12879-020-05130-3
- 42. Ouh IO, Seo MG, Do JC, Kim IK, Cho MH, Kwak DM. Seroprevalence of Coxiella burnetii in bulk-tank milk and dairy cattle in Gyeongbuk province, Korea. Korean J Vet Serv 2013;36:243-248. (in Korean). https://doi.org/10.7853/kjvs.2013.36.4.243
- 43. Ooshiro M, Zakimi S, Matsukawa Y, Katagiri Y, Inokuma H. Detection of Anaplasma bovis and Anaplasma phagocytophilum from cattle on Yonaguni Island, Okinawa, Japan. Vet Parasitol 2008;154:360-364. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.vetpar.2008.03.028
- 44. Harrison A, Bastos AD, Medger K, Bennett NC. Eastern rock sengis as reservoir hosts of Anaplasma bovis in South Africa. Ticks Tick Borne Dis 2013;4:503-505. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ttbdis.2013.06.007
- 45. Lee M, Yu D, Yoon J, Li Y, Lee J, Park J. Natural co-infection of Ehrlichia chaffeensis and Anaplasma bovis in a deer in South Korea. J Vet Med Sci 2009;71:101-103. https://doi.org/10.1292/jvms.71.101
- 46. Kang JG, Ko S, Kim YJ, Yang HJ, Lee H, Shin NS, Choi KS, Chae JS. New genetic variants of Anaplasma phagocytophilum and Anaplasma bovis from Korean water deer (Hydropotes inermis argyropus). Vector Borne Zoonotic Dis 2011;11:929-938. https://doi.org/10.1089/vbz.2010.0214
- 47. Lee MJ, Chae JS. Molecular detection of Ehrlichia chaffeensis and Anaplasma bovis in the salivary glands from Haemaphysalis longicornis ticks. Vector Borne Zoonotic Dis 2010;10:411-413. http://doi.org/10.1089/vbz.2008.0215
- 48. Doan HT, Noh JH, Choe SE, Yoo MS, Kim YH, Reddy KE, Quyen DV, Nguyen LT, Nguyen TT, Kweon CH, Jung SC, Chang KY, Kang SW. Molecular detection and phylogenetic analysis of Anaplasma bovis from Haemaphysalis longicornis feeding on grazing cattle in Korea. Vet Parasitol 2013;196:478-481. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.vetpar.2013.03.025
 , Ju Yeong Kim1,†, Myung-hee Yi1, In-Yong Lee1, Dongeun Yong2, Bo-Young Jeon3, Tai-Soon Yong1,*
, Ju Yeong Kim1,†, Myung-hee Yi1, In-Yong Lee1, Dongeun Yong2, Bo-Young Jeon3, Tai-Soon Yong1,*