Abstract
Our objective was to investigate whether inflammatory microenvironment induced by Trichomonas vaginalis infection can stimulate proliferation of prostate cancer (PCa) cells in vitro and in vivo mouse experiments. The production of CXCL1 and CCL2 increased when cells of the mouse PCa cells (TRAMP-C2 cell line) were infected with live T. vaginalis. T. vaginalis-conditioned medium (TCM) prepared from co-culture of PCa cells and T. vaginalis increased PCa cells migration, proliferation and invasion. The cytokine receptors (CXCR2, CCR2, gp130) were expressed higher on the PCa cells treated with TCM. Pretreatment of PCa cells with antibodies to these cytokine receptors significantly reduced the proliferation, mobility and invasiveness of PCa cells, indicating that TCM has its effect through cytokine-cytokine receptor signaling. In C57BL/6 mice, the prostates injected with T. vaginalis mixed PCa cells were larger than those injected with PCa cells alone after 4 weeks. Expression of epithelial-mesenchymal transition markers and cyclin D1 in the prostate tissue injected with T. vaginalis mixed PCa cells increased than those of PCa cells alone. Collectively, it was suggested that inflammatory reactions by T. vaginalis-stimulated PCa cells increase the proliferation and invasion of PCa cells through cytokine-cytokine receptor signaling pathways.
-
Key words: Trichomonas vaginalis, inflammation, cancer, cytokine, chemokine, receptor
INTRODUCTION
Trichomoniasis is the most common curable sexually-transmitted infection (STI). Each year the pathogen causes an estimated 276.4 million new cases worldwide [
1,
2].
Trichomonas vaginalis has been detected in the urine of patients with prostatitis, and in the prostate tissue of patients with benign prostatic hyperplasia and prostate cancer [
3–
6]. Most
T. vaginalis-infected men are asymptomatic and can remain undiagnosed and untreated, and this has been thought to result in chronic persistent prostatic infection [
2,
7]. To date, there are few studies investigating the association between
T. vaginalis infection and risk of prostate cancer [
8–
10]. Although conflicting results have been obtained regarding
T. vaginalis serostatus and prostate cancer, recent evidence does not support such an association. However, the frequently chronic course of the infection in men has been reported to make it possible for the parasite to ascend to the prostate and establish a site of inflammation that may lead to aggravation of prostate cancer [
11]. In addition, chronic inflammation has been reported to be a causative factor in a variety of cancers, and chronic prostatitis is associated with prostate cancer [
12,
13].
Infection with the Gram-negative anaerobe
Porphyromonas gingivalis increases the invasiveness of oral cancer cells in vitro [
14], and inflammation of the prostate induced by urethral instillation of bacteria (
E. coli) accelerates prostate cancer progression in mice [
15].
Mycoplasma hyorhinis promotes the migration and invasiveness of gastric cancer cells by activating the NLRP3 inflammasome [
16], and
T. vaginalis macrophage migration inhibitory factor (
T. vaginalis MIF) increases the in vitro growth and invasiveness of benign and malignant prostate cells [
17]. However, it is not known whether the proliferation of prostate cancer (PCa) cells is stimulated by infecting them with live
T. vaginalis. Cytokines and chemokines are of key importance involved in tumor growth and metastasis. Similarly in prostate cancer, many cytokines including IL-6, C-C motif chemokine ligand 2 (CCL2) and C-X-C motif chemokine ligand 1 (CXCL1) exert modulatory roles in prostate cancer metastasis [
18].
The aim of this study was to investigate whether the inflammatory microenvironment including cytokines and chemokines induced by infecting PCa cells with T. vaginalis affects their multiplication in vitro, and in in vivo mouse experiments. Our findings suggest that T. vaginalis stimulates the growth of PCa cells by inducing an inflammatory response of the PCa cells in vitro and in vivo mouse experiments.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Ethics statement
All animal experimental protocols have been reviewed and approved by the Institutional Animal Care and Use Committee of Hanyang University under protocol number (HY-IACUC-2016-0159A). All animal experiments were handled in accordance with Korean Food and Drug Administration guidelines.
Cell culture
Trichomonas vaginalis (
T. vaginalis, T016 isolate), TRAMP-C2 cell line (established from a prostate tumor of a TRAMP mouse) were cultured as described in our previous study. All the cells were incubated in 5% CO
2 at 37°C [
19].
Preparation of conditioned media
To investigate the effect of the culture supernatant (conditioned medium) of TRAMP-C2 cells infected with
T. vaginalis on the proliferation and invasiveness of PCa cells, conditioned medium of TRAMP-C2 cells stimulated with
T. vaginalis was prepared [
20]. TRAMP-C2 cells were seeded 2×10
5 cells/well in DMEM medium in 24-well plates. After 24 hr, the cells were changed to serum-free medium, cultured for another 24 hr for stabilization, and incubated with or without live
T. vaginalis in a ratio of 1: 1 for 6 hr. Thereafter the supernatants were collected and filtered through 0.2 μm pore filters, and frozen in aliquots. Supernatants of TRAMP-C2 cells incubated with or without
T. vaginalis were named
T. vaginalis-conditioned medium (TCM) and conditioned medium (CM), respectively. The final concentrations of conditioned media used in various assays were adjusted to 10–50% with cell culture medium.
TRAMP-C2 cells were seeded at 2×105 cells/well on 24-well plates with or without trichomonads (2×106 cells/well). After 6 hr, the supernatant was collected and stored at −20°C. The cytokines were measured with ELISA kits (BD Biosciences, San Jose, California, USA) according to the manufacturer’s instructions.
Measurement of reactive oxygen species (ROS)
Intracellular ROS were measured by spectrofluorometer using 2′,7′-dichlorofluorescein diacetate (DCF-DA, Molecular Probes, Eugene, Oregon, USA) [
21]. Briefly, TRAMP-C2 cells with or without diphenyleneiodonium (DPI, Sigma Aldrich, Missouri, USA) pretreatment were co-cultured with
Trichomonas vaginalis secretory product (TvSP).
To prepare TvSP, live trichomonads (1×107) on the logarithmic growth phase were washed once with Hank’s balanced salt solution (HBSS), resuspended in 1 ml HBSS, and incubated for 1 hr at 37°C. Culture supernatant was centrifuged for 10 min at 14,000 rpm and filtered through of filters with 0.22 μm pore size. The cells were washed and stained with 30 μm DCF-DA for 1 hr at 37°C. Intracellular ROS were determined with a spectrofluorometer (VICTOR X, Perkin-Elmer, Waltham, Massachusetts, USA) at excitation and emission wavelengths of 485 and 530 nm, respectively.
Quantitative real-time PCR (Q-PCR)
Expression of inflammatory cytokine mRNA (CXCL1, CCL2, IL-6) by TRAMP-C2 cells incubated with
T. vaginalis was measured by Q-PCR. The cells were seeded at 2×10
5 cells/well on 24-well plates and coincubated with
T. vaginalis for 30 min. Following process was performed as previously described [
21,
22]. Relative gene expression was assessed with the LightCycler 480 Software (Roche, Mannheim, Germany) and presented as fold-difference. GAPDH was used as internal controls.
The primers for mouse CXCL1 were; 5′-CAC CCA AAC CGA AGT CAT AG-3′forward and 5′-AAG CCA GCG TTC ACC AGA-3′reverse, mouse CCL2; 5′-GCT ACA AGA GGA TCA CCA GC-3′ forward and 5′-TGT CTG GAC CCA TTC CTT CT-3′ reverse, mouse IL-6; 5′-CCA CTT CAC AAG TCG GAG GCT TA-3′ forward and 5′-CCA CTT CAC AAG TCG GAG GCT TA-3′ reverse, mouse GAPDH; 5′-AAT ACG GCT ACA GCA ACA GG-3′ forward and 5′-TTG GGA TAG GGC CTC TCT TG-3′ reverse.
Proliferation, wound healing, and invasion assays
To examine the effects of conditioned medium on the growth of mouse prostate cancer cells, the CCK-8 assay for proliferation measurement, and wound healing assay for migration were performed as previously described [
20,
22]. The sizes of the wounded areas were calculated using ImageJ software. The invasiveness of TRAMP-C2 cells treated with conditioned medium was tested according to the protocol described in our previous report [
20].
To observe expression of CXCR2, CCR2, and GP130 on the cell surface of TRAMP-C2 cells treated with DMEM, CM, or TCM (10%), immunofluorescence was used as previously described [
20,
22]. Fluorescence was measured with a confocal microscope (Las software, Leica, Wetzlar, Germany).
To investigate the effects of CXCL1, CCL2, IL-6 on the proliferation, migration and invasion of mouse prostate cancer cells, anti-CXCR2 antibody for the CXCL1 receptor, or anti-CCR2 antibody for the CCL2 receptor and anti-GP130 antibody for the IL-6 receptor were added to the cells before adding the conditioned media, and the plates were incubated for 48 hr (proliferation) or 24 hr (migration & invasiveness) [
20,
22]. After incubation, cell proliferation, migration and invasiveness were analyzed by CCK, wound healing, and invasion assays, respectively.
To test whether inflammatory microenvironment induced by
T. vaginalis infection can stimulate proliferation of PCa cells in vivo experiments, TRAMP-C2 cells and
T. vaginalis injection into the mouse prostate was performed as previously described [
23]. 17 weeks male C57BL/6 mice were maintained under semi specific pathogen free condition.TRAMP-C2 cells (2×10
6 cells suspended in 100 μl matrigel/PBS) with or without
T. vaginalis (4×10
5 cells suspended in 100 μl TRAMP-C2 cell with matrigel/PBS) were injected into prostate of the mouse by 30-gauge needle. After 4 weeks, all animals were killed by CO
2 exposure (at 21 weeks old). The tumors were removed en bloc with the seminal vesicles, weighed, and photographed. They were then fixed in 4% paraformaldehyde and embedded. All the mice work was performed by a urologist.
Immunohistochemistry assay were performed as previously described [
24]. Primary antibodies were anti-cyclin D1 (phospho S90) antibody (1:500; Abcam, Cambridge, Massachusetts, USA), anti-E-cadherin antibody (1:250, mouse monoclonal, Cell signaling Technology, Danvers, Massachusetts, USA) and anti-N-cadherin antibody (1:500, rabbit polyclonal, Abcam). 3,3′-Diaminobenzidine tetrahydrochloride was used as chromogen, and sections were counterstained with hematoxylin. Digital microscope images were obtained by capturing the most representative sections using a camera linked to an Olympus light microscope. The immunostaining was reviewed by the 2 pathologists blinded to the study design. Staining was quantified by estimating staining intensity and the percentage of stained tumor cells. Staining intensity was scored according to the following scale: 0 (negative), 1 (weak), 2 (intermediate), and 3 (strong). Immunoreactivity for cyclin D1 was evaluated as the percentage of positive tumor cells with discrete nuclear staining. E-cadherin and N-cadherin immunoreactivity was observed in the cytoplasm of tumor cells and quantified with the following formula (H-score). H-score=1×(% of 1+cells)+ 2×(% of 2+cells)+3×(% of 3+cells).
Statistical analyses were performed using SPSS Statistics, version 21 (IBM, Chicago, Illinois, USA). The Mann-Whitney U test was used to assess the significance of differences, and P-values<0.05 were considered statistically significant. The data are expressed as means±SDs of 3 to 4 independent experiments.
RESULTS
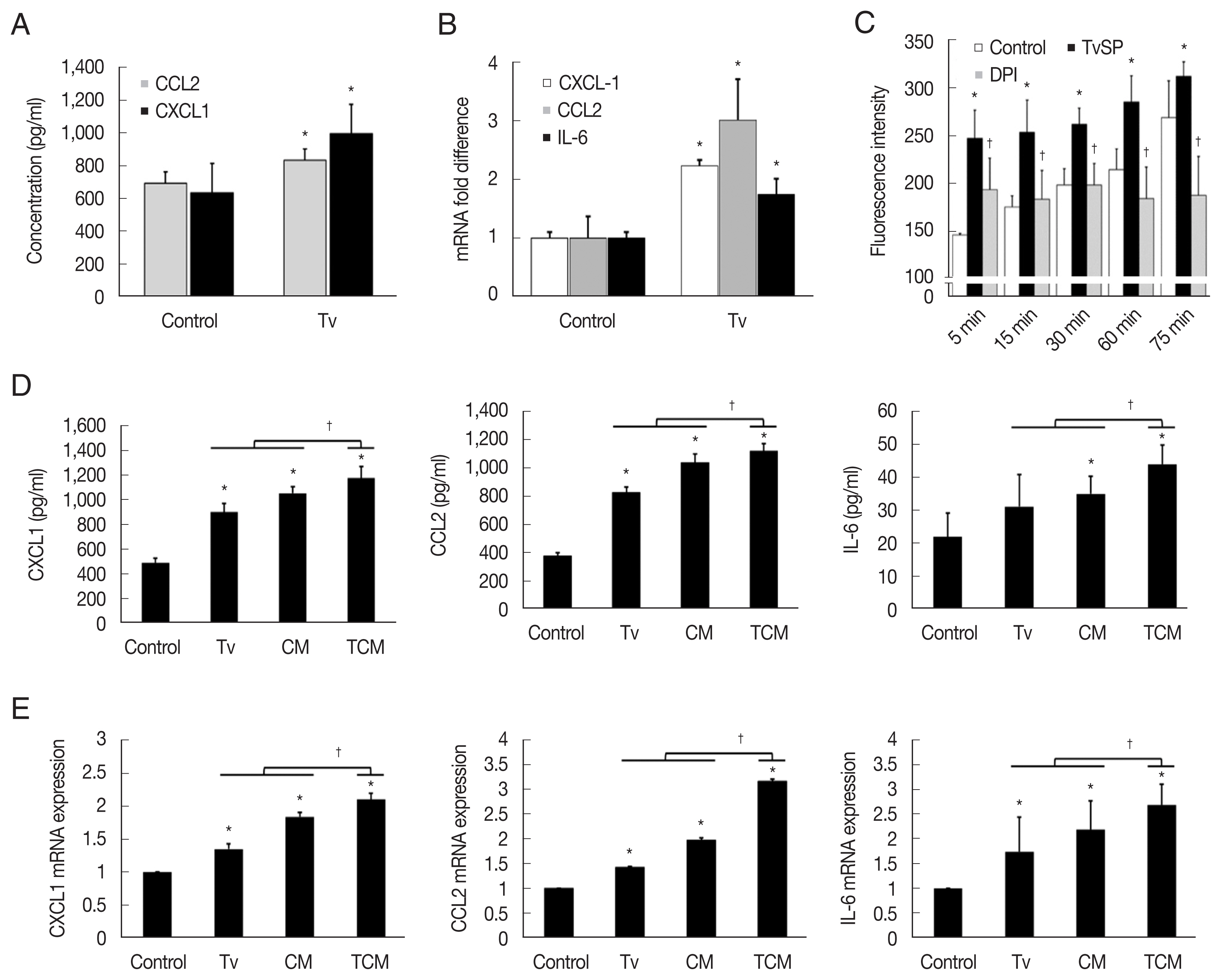
Inflammatory response of TRAMP cells stimulated with T. vaginalis
TRAMP-C2 cells stimulated with
T. vaginalis (1:1) produced CXCL1 and CCL2 within 6 hr, and CXCL1, CCL2 and IL-6 mRNA levels increased 2–3-fold within 1 hr (
Fig. 1A, B). Although IL-6 production was not measured by ELISA, IL-6 mRNA was measured by Q-PCR. Then, to see whether TCM was more effective than
T. vaginalis, TRAMP cells were incubated with
T. vaginalis, CM or TCM for 6 hr. TRAMP cells stimulated with TCM produced more CXCL1, CCL2, and IL-6 than those treated with CM or
T. vaginalis (
P<0.05), as well as higher levels of the transcripts for these cytokines (
P<0.05;
Fig. 1D, E).
For ROS measurement, we used TvSP because live
T. vaginalis might interfere with the detection of fluorescence. When TRAMP-C2 cells were incubated with TvSP, ROS production increased in a time-dependent manner, and pretreatment with DPI, an NADPH oxidase inhibitor, significantly reduced the production of ROS, suggesting that the ROS were generated by NADPH oxidase. We conclude that
T. vaginalis infection induces TRAMP cells to produce cytokines and ROS (
Fig. 1C).
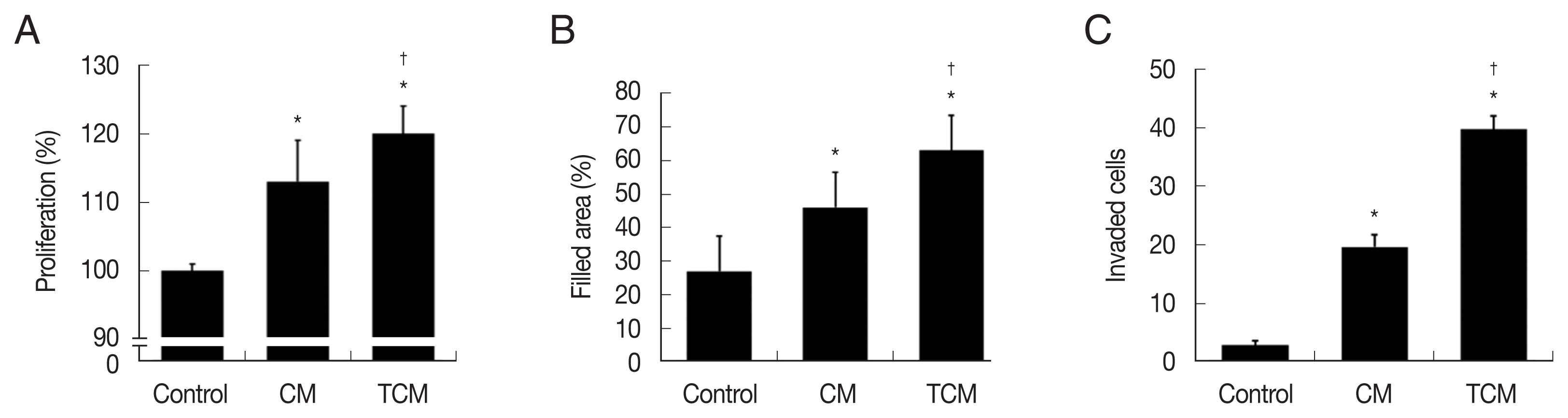
We investigated whether the interaction between prostate cancer cells and
T. vaginalis affected the proliferation of the cancer cells. TRAMP-C2 cells proliferation was indeed stimulated by TCM, and to a lesser extent by CM (
Fig. 2A). Migration of the prostate cancer cells was measured by the wound-healing assay. As shown in
Fig. 2B, TRAMP-C2 cells treated with TCM migrated more rapidly than cells treated with CM, and even more rapidly than control cells, and similar results were obtained in the invasiveness assay (
Fig. 2C).
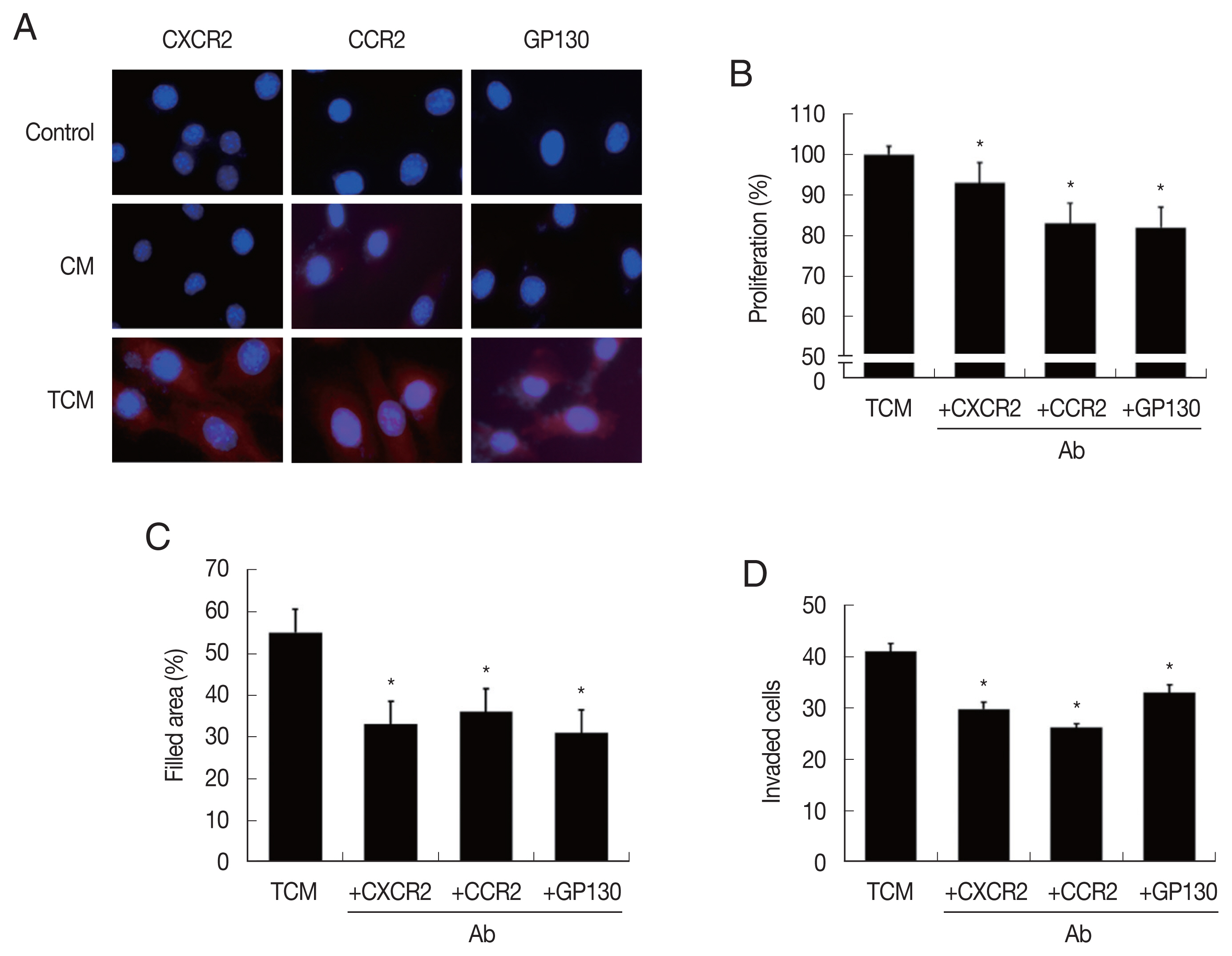
In order to confirm that CM and TCM induce the expression of cytokine receptors in prostate cancer cells, PCa were incubated in CM or TCM for 6 hr and cytokine receptor expressions were measured. TCM, and to a lesser extent, CM, increased the expression of CXCR2 (for CXCL1), CCR2(CCL2) and GP130 (IL-6), as observed by fluorescence microscopy (
Fig. 3A). To see whether the cytokine receptors were implicated in the increased proliferation, migration and invasiveness of PCa cells, the effects of anti-cytokine receptor antibodies (anti-CXCR2, -CCR2, -GP130 antibody) were examined. These antibodies reduced the effects of the TCM in proliferation, migration and invasiveness of PCa cells (
Fig. 3B–D). Therefore, cytokine-cytokine receptor signaling pathways were found involved in the proliferation, migration and invasiveness of TRAMP-C2 cell.
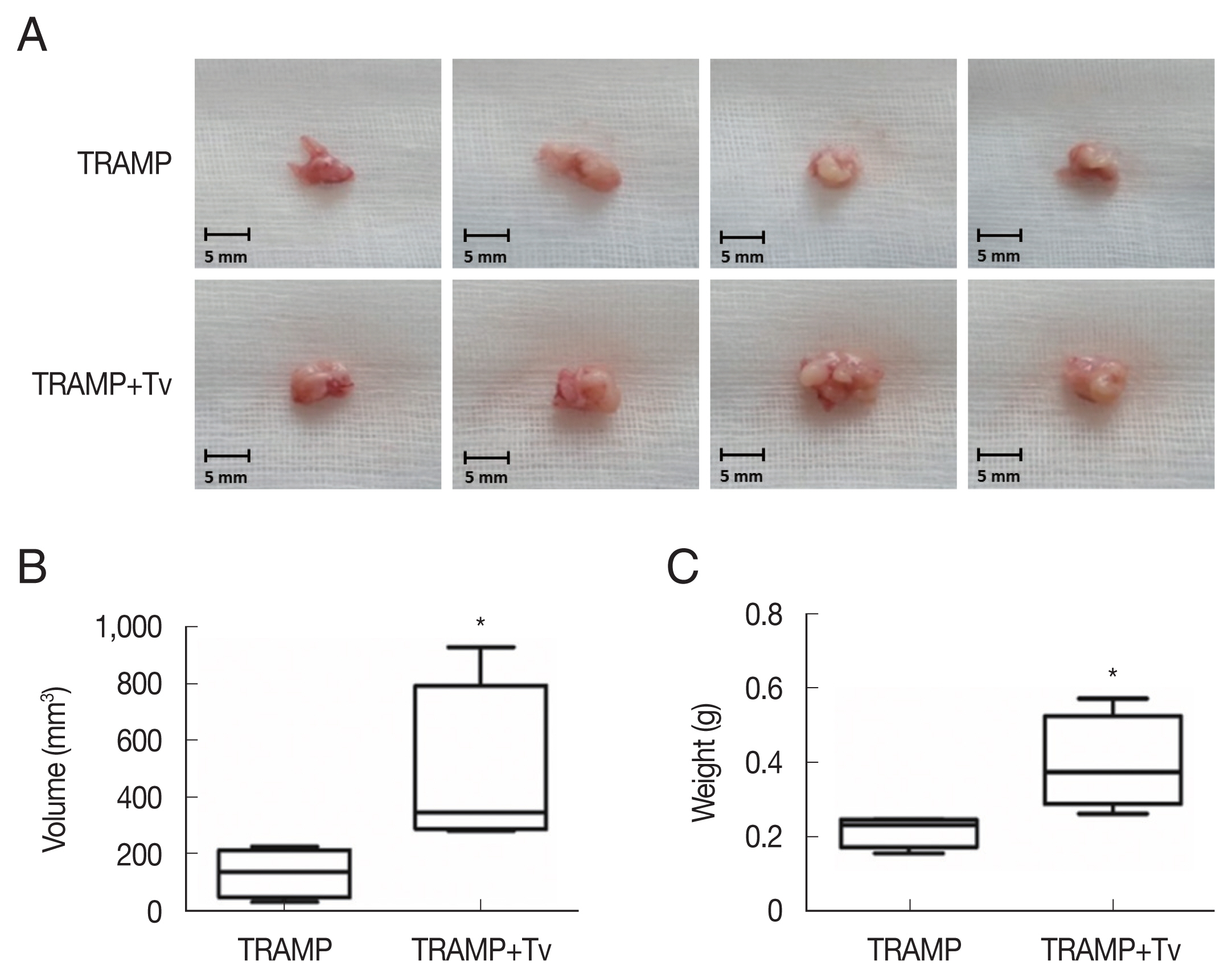
The PCa cells mixed with
T. vaginalis formed substantially larger prostate cancers compared with those injected without
T. vaginalis after 4 weeks (
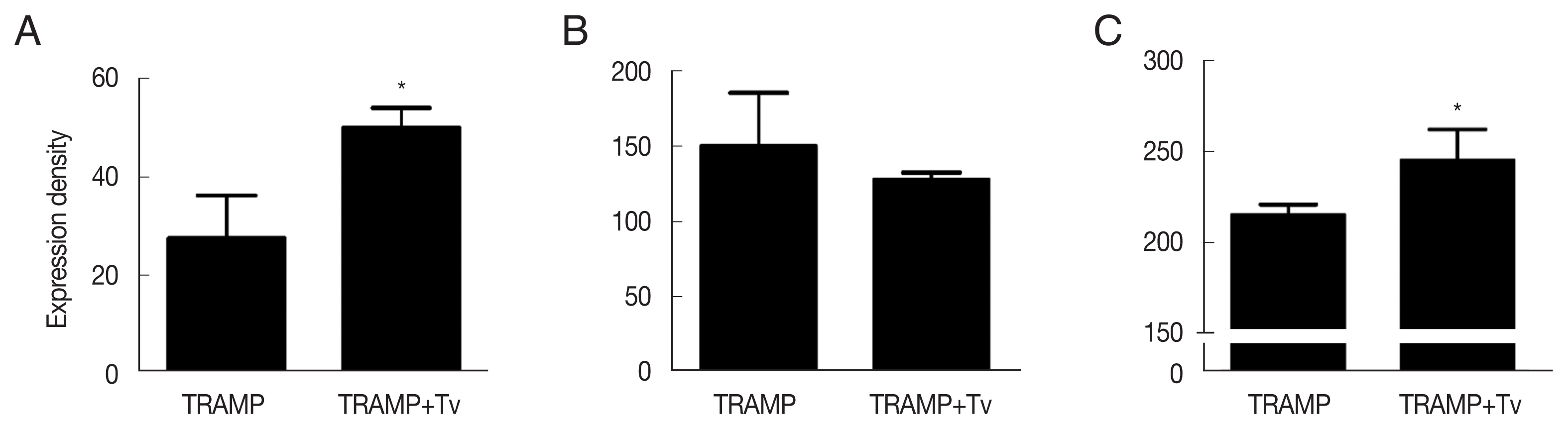
Fig. 4). Cyclin D1, a regulator of cell cycle progression, was higher in the cancer structures formed after co-injection of
T. vaginalis (
P<0.05;
Fig. 5A). EMT known to contribute to the growth of cancers was more extensive when
T. vaginalis was injected along with the TRAMP-C2 cells, by demonstrating decreased expression of E-cadherin (an epithelial cell marker) and increased expression of N-cadherin (a mesenchymal cell marker) in the tumors formed by those cells (
Fig. 5B, C).
DISCUSSION
Infection is recognized as a major cause of cancer worldwide. About 2 million of the 12.7 million new cancer cases that occurred in 2008, were attributable to infections. For example,
Helicobacter pylori, hepatitis B and C viruses, and human papilloma viruses were responsible for 1.9 million cases, mainly gastric, liver, and cervical cancers [
25]. About 20% of cancer deaths worldwide are attributable to chronic infection and/or inflammation [
26]. Shacter and Weitzman [
12] have argued that chronic inflammation is a causative factor in a number of cancers. Acute inflammation evokes host defense against infection, whereas chronic inflammation can predispose the host to a variety of chronic illnesses, including cancer [
26].
Hanahan and Weinberg [
27] proposed a model to define the 6 properties that a cancer acquires; They include sustaining proliferative signaling, evading growth suppressors, resisting cell death, enabling replicative immortality, inducing angiogenesis, and activating invasion and metastasis. Mantovani [
28] and Mantovani et al. [
29] added an additional hallmark, the inflammatory microenvironment, to these 6 properties and suggests that cancer-related inflammation promotes genetic instability.
It was reported that more than 2/3 of men had histological evidence of chronic prostate inflammation [
30], despite of the fact that less than 10% of these men reported symptoms of prostatitis. In the same context, most of
T. vaginalis-infected men are asymptomatic and can remain undiagnosed and untreated. This has been hypothesized to result in chronic persistent prostatic infections [
2,
7]. Inflammation is expected to alter the prostatic microenvironment in multiple ways that may facilitate cancer initiation or progression [
31]. However, there is no investigation on the aggressiveness of prostate cancers formed by PCa cells infected with
T. vaginalis. In the current study, we have shown for the first time that the inflammatory response by PCa cells stimulated with
T. vaginalis increases the proliferation and invasiveness of these cells.
An advantage of this study is that we also showed that live T. vaginalis stimulated the multiplication of the prostate cancer cells when they were injected into mice and also increased the expression of cyclin D1and the EMT marker.
Chemokines and their receptors play many roles in cancer development although their primary role is controlling the trafficking of leukocytes during inflammatory responses. In the present study we showed that chemokines (CXCL1, CCL2) contained in TCM stimulated the proliferation and invasiveness of TRAMP cells by binding to their receptors (CXCR2, CCR2) since pretreatment with anti-CXCR2 & anti-CCR2 antibodies significantly reduced the effects of TCM.
In
Fig. 1D and E, the conditional medium increased cytokine production more than the
T. vaginalis. The conditioned medium of TRAMP cells includes secretory factors derived from cancer cells. Alkaline phosphatase, MMP-3 and epidermal growth factor receptor were reported as secretory factors derived from cancer cells in PCa [
32–
34]. Therefore, it is inferred that various inflammatory factors secreted from TRAMP cells increased cytokine production by stimulating cancer cells
CXCL1 (also known as growth-regulated oncogene-alpha) is a secreted growth factor that interacts with the G-protein-coupled receptor CXCR2 and plays a key role in inflammation, and as a chemoattractant for neutrophils. CXCL1 and its receptor CXCR2 are linked to metastatic potential [
35]. CXCL1 is overexpressed in gastric, colon and skin cancers [
36,
37]. The level of CXCL1 is higher in prostate cancers than in benign control tissue, and tumors with higher Gleason scores have higher CXCL1 levels [
38]. These findings support a role for CXCL1 in prostate tumor initiation and progression.
In the present study, when TRAMP-C2 cells were infected with live
T. vaginalis, the production of CXCL1 and CCL2 by the PCa cells increased. In addition, CCL2 is reported to acts as a paracrine and autocrine factor for prostate cancer growth and invasiveness, and CCR2 expression correlated with Gleason score and clinical pathologic stages. Also, activation of the CCL2/CCR2 axis promoted PCa growth in bone [
39,
40]. In this context, our data suggest that CCL2 stimulates PCa cells growth by binding to the CCR2 receptor.
Since IL-6 serum levels are elevated in patients with untreated metastatic or castration-resistant prostate cancers, it is thought to be a key mediator in several steps of prostate cancer development: initiation of prostate tumorigenesis, stimulation of tumor growth, induction of aggressive growth, promotion of tumor metastasis and resistance to chemotherapy [
41]. Also, IL-6/IL-6R is believed to be key signaling elements in prostate cancer development [
42]. In line with the above reports, in our study TRAMP cells grew faster when incubated with TCM and produced elevated levels of IL-6 & IL-6R (gp130), while anti-gp130 Ab reduced the growth and invasiveness of the TRAMP cells.
It is well known that an impaired “oxidant-anti-oxidant” balance causes DNA damage and may result in cell death and/or in the generation of mutations leading to increased expression of oncogenes and inactivation of tumor-suppressor genes [
43]. Reactive oxygen and nitrogen species are reported to be involved in the development and progression of several human cancers such as breast, prostate, colorectal, and gastric cancers [
44]. In this connection we showed that TRAMP-C2 cells produced higher levels of ROS when treated with TvSP, and the ROS appeared to be produced by NADPH oxidase. The increased ROS may contribute to growth of the PCa cells.
Cyclin D1 is the regulatory subunit of the cyclin-dependent kinases Cdk4/6, which are positive regulators of cell proliferation [
45,
46]. Cyclin D1 has been linked to tumor invasiveness and metastasis in clinical studies. Overexpression of cyclin D1 is associated with metastasis of prostate cancer to bone [
47]. Recently cytoplasmic cyclin was found mainly associated with the invasive capability of tumor cells [
45]. We noted that injection with
T. vaginalis along with TRAMP cells led to increased expression of cyclin D1 in prostate cancer tissue.
Initiation of EMT is considered the first step leading to cancer metastasis, and contributing to the poor prognosis of cancer patient. EMT occurs by breakdown of cell-to-cell or cell-to-extracellular matrix (ECM) adhesion in the polarized lining of epithelia, and the loss of E-cadherin of is responsible for the collapse of intercellular mechanical communication. In contrast, key mesenchymal markers become highly enriched during EMT [
48], and in our study prostate tissue injected with TRAMP cells mixed with
T. vaginalis contained reduced epithelial marker (E-cadherin) and increased mesenchymal marker (N-cadherin).
In conclusion, this study showed that inflammatory reactions by T. vaginalis-stimulated PCa cells increased the proliferation and invasion of these cells through cytokine-cytokine receptor signals. Our findings suggest that T. vaginalis stimulates the growth of PCa cells by inducing an inflammatory response of the PCa cells in vitro and in vivo mouse model.
Notes
-
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS
This research was supported by a National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF) grant funded by the Korean Government (MSIP) (NRF-2017R1A2B4002072).
The data that support the findings of this study are available from the corrresponding author upon reasonable request and the experiments complied with the current laws of this country.
Fig. 1Expression of cytokines and their mRNA by TRAMP-C2 cells stimulated with T. vaginalis, CM and TCM. (A, B) TRAMP-C2 cells were incubated with live T. vaginalis for 6 hrs. (C) ROS production by TRAMP-C2 cells incubated with T. vaginalis secretory products (TvSP). (D, E) Production of CXCL1, CCL2 & IL-6 by TRAMP-C2 cells stimulated with T. vaginalis, CM or TCM was measured by ELISAs and real-time PCR, respectively. Control, DMEM medium. *P<0.05 versus control, †P<0.05 versus TCM or versus TvSP in Fig. 1C.

Fig. 2Proliferation, migration, and invasiveness of prostate cancer cells stimulated with TCM. (A) Proliferation, (B) migration and (C) invasiveness were examined by the CCK8 assay, wound healing assay and matrigel invasiveness assay, respectively. Control, DMEM medium. *P<0.05 versus control, †P<0.05 versus CM.

Fig. 3Expression of cytokine receptors in TRAMP-C2 cells stimulated with TCM, and effect of cytokine receptor Ab on proliferation, migration and invasiveness of TRAMP-C2 cell treated with TCM. (A) Cytokine receptor expression. Cell nuclei in blue and cytokine receptors in red. Control, DMEM medium. (B) Proliferation, (C) migration and (D) invasiveness of TRAMP-C2 cells pretreated with anti-cytokine receptor Ab were measured by CCK8 assay, wound healing and matrigel invasiveness assays, respectively. *P<0.05 versus untreated TCM.

Fig. 4
Trichomonas vaginalis promotes prostate tumor growth in the mice injected with TRAMP-C2 cells after 4 weeks. (A) Prostates of the mice. (B) Volumes and (C) weights of the prostates of mice. *P<0.05 versus TRAMP alone. Bar=5 mm.

Fig. 5Expression of cyclin D1 and epithelial-mesenchymal transition markers in the TRAMP cells co-injected with T. vaginalis. (A) Cyclin D1. (B) E-cadherin. (C) N-cadherin. *P<0.05 versus TRAMP alone.

References
- 1. World Health Organization. Report on Global Sexually Transmitted Infection Surveillance [internet]; Geneva, Switzerland: World Health Organization; 2018. Arailable from: https://www.who.int/reproductivehealth/publications/stis-surveillance-2018/en
- 2. Menezes CB, Frasson AP, Tasca T. Trichomoniasis - are we giving the deserved attention to the most common non-viral sexually transmitted disease worldwide? Microb Cell 2016;3:404-419. https://doi.org/10.15698/mic2016.09.526
- 3. Škerka V, Schönwald S, Krhen I, Leo M, Ante B, Nataša-Šterk K, Vladimira K, Adriana V. Aetiology of chronic prostatitis. Int J Antimicrob Agents 2002;19:471-474. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0924-8579(02)00087-0
- 4. Lee JJ, Moon HS, Lee TY, Hwang HS, Ahn MH, Ryu JS. PCR for diagnosis of male Trichomonas vaginalis infection with chronic prostatitis and urethritis. Korean J Parasitol 2012;50:157-159. https://doi.org/10.3347/kjp.2012.50.2.157
- 5. Mitteregger D, Aberle SW, Makristathis A, Walochnik J, Brozek W, Marberger M, Kramer G. High detection rate of Trichomonas vaginalis in benign hyperplastic prostatic tissue. Med Microbiol Immunol 2012;201:113-116. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00430-011-0205-2
- 6. Gardner WA Jr, Culberson DE, Bennett BD. Trichomonas vaginalis in the prostate gland. Arch Pathol Lab Med 1986;110:430-432.
- 7. Sutcliffe S, Neace C, Magnuson NS, Reeves R, Alderete JF. Trichomonosis, a common curable STI, and prostate carcinogenesis - a proposed molecular mechanism. PLoS Pathog; 2012. 8e1002801 https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.ppat.1002801
- 8. Stark JR, Judson G, Alderete JF, Mundodi V, Kucknoor AS, Giovannucci EL, Platz EA, Sutcliffe S, Fall K, Kurth T, Ma J, Stampfer MJ, Mucci LA. Prospective study of Trichomonas vaginalis infection and prostate cancer incidence and mortality: Physicians’ Health Study. J Natl Cancer Inst 2009;101:1406-1411. https://doi.org/10.1093/jnci/djp306
- 9. Sutcliffe S, Giovannucci E, Alderete JF, Chang T, Gaydos CA, Zenilman JM, De Marzo AM, Willett WC, Platz EA. Plasma antibodies against Trichomonas vaginalis and subsequent risk of prostate cancer. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev 2006;15:939-945. https://doi.org/10.1158/1055-9965.EPI-05-0781
- 10. Sutcliffe S, Alderete JF, Till C, Goodman PJ, Hsing AW, Zenilman JM, De Marzo AM, Platz EA. Trichomonosis and subsequent risk of prostate cancer in the Prostate Cancer Prevention Trial. Int J Cancer 2009;124:2082-2087. https://doi.org/10.1002/ijc.24144
- 11. Caini S, Gandini S, Dudas M, Bremer V, Severi E, Gherasim A. Sexually transmitted infections and prostate cancer risk: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Cancer Epidemiol 2014;38:329-338. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.canep.2014.06.002
- 12. Shacter E, Weitzman SA. Chronic inflammation and cancer. Oncology 2002;16:217-226.
- 13. Kamp DW, Shacter E, Weitzman SA. Chronic inflammation and cancer: the role of the mitochondria. Oncology 2011;25:400-410.
- 14. Ha NH, Park DG, Woo BH, Kim DJ, Choi JI, Park BS, Kim YD, Lee JH, Park HT. Porphyromonas gingivalis increases the invasiveness of oral cancer cells by upregulating IL-8 and MMPs. Cytokine 2016;86:64-72. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cyto.2016.07.013
- 15. Simons BW, Durham NM, Bruno TC, Grosso JF, Schaeffer AJ, Ross AE, Hurley PJ, Berman DM, Drake CG, Thumbikat P, Schaeffer EM. A human prostatic bacterial isolate alters the prostatic microenvironment and accelerates prostate cancer progression. J Pathol 2015;235:478-489. https://doi.org/10.1002/path.4472
- 16. Xu Y, Li H, Chen W, Yao X, Xing Y, Wang X, Zhong J, Meng G. Mycoplasma hyorhinis activates the NLRP3 inflammasome and promotes migration and invasiveness of gastric cancer cells. PLoS One 2013;8:e77955. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0077955
- 17. Twu O, Dessi D, Vu A, Mercer F, Stevens GC, de Miguel N, Rappelli P, Cocco AR, Clubb RT, Fiori PL, Johnson PJ. Trichomonas vaginalis homolog of macrophage migration inhibitory factor induces prostate cell growth, invasiveness, and inflammatory responses. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2014;111:8179-8184. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1321884111
- 18. Adekoya TO, Richardson RM. Cytokines and Chemokines as Mediators of Prostate Cancer Metastasis. Int J Mol Sci 2020;23:4449. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21124449
- 19. Chung HY, Kim JH, Han IH, Ryu JS. Polarization of M2 macrophages by interaction between prostate cancer cells treated with Trichomonas vaginalis and adipocytes. Korean J Parasitol 2020;58:217-227. https://doi.org/10.3347/kjp.2020.58.3.217
- 20. Kim JH, Kim SS, Han IH, Sim S, Ahn MH, Ryu JS. Proliferation of prostate stromal cell induced by benign prostatic hyperplasia epithelial cell stimulated with Trichomonas vaginalis via crosstalk with mast cell. Prostate 2016;76:1431-1444. https://doi.org/10.1002/pros.23227
- 21. Han IH, Kim JH, Kim SS, Ahn MH, Ryu JS. Signalling pathways associated with IL-6 production and epithelial-mesenchymal transition induction in prostate epithelial cells stimulated with Trichomonas vaginalis. Parasite Immunol 2016;38:678-687. https://doi.org/10.1111/pim.12357
- 22. Kim JH, Han IH, Shin SJ, Park SY, Chung HY, Ryu JS. Signaling role of adipocyte leptin in prostate cell proliferation induced by Trichomonas vaginalis. Korean J Parasitol 2021;59:235-249. https://doi.org/10.3347/kjp.2021.59.3.235
- 23. Somers KD, Brown RR, Holterman DA, Yousefieh N, Glass WF, Wright GL jr, Schellhammer PF, Qian J, Ciavarra RP. Orthotopic treatment model of prostate cancer and metastasis in the immunocompetent mouse: efficacy of flt3 ligand immunotherapy. Int J Cancer 2003;107:773-780. https://doi.org/10.1002/ijc.11464
- 24. Jang SM, Han H, Jun YJ, Jang SH, Min KW, Sim J, Ahn HI, Lee KH, Jang KS, Paik SS. Clinicopathological significance of CADM4 expression, and its correlation with expression of E-cadherin and Ki-67 in colorectal adenocarcinomas. J Clin Pathol 2012;65:902-906. https://doi.org/10.1136/jclinpath-2012-200730
- 25. de Martel C, Ferlay J, Franceschi S, Vignat J, Bray F, Forman D, Plummer DM. Global burden of cancers attributable to infections in 2008: a review and synthetic analysis. Lancet Oncol 2012;13:607-615. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1470-2045(12)70137-7
- 26. Aggarwal BB, Vijayalekshmi RV, Sung B. Targeting inflammatory pathways for prevention and therapy of cancer: short-term friend, longterm foe. Clin Cancer Res 2009;15:425-430. https://doi.org/10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-08-0149
- 27. Hanahan D, Weinberg RA. The hallmarks of cancer. Cell 2000;100:50-70. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0092-8674(00)81683-9
- 28. Mantovani A. Cancer: inflaming metastasis. Nature 2009;457:36-37. https://doi.org/10.1038/457036b
- 29. Mantovani A, Garlanda C, Allavavena P. Molecular pathways and targets in cancer-related inflammation. Ann Med 2010;42:161-170. https://doi.org/10.3109/07853890903405753
- 30. Nickel JC, Roehrborn CG, O’Leary MP, Bostwick DG, Somerville MC, Rittmaster RS. The relationship between prostate inflammation and lower urinary tract symptoms: examination of baseline data from the REDUCE trial. Eur Urol 2008;54:1379-1384. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eururo.2007.11.026
- 31. de Marzo AM, Platz EA, Sutcliffe S, Xu J, Gronberg H, Drake CG, Nakai Y, Isaacs WB, Nelson WG. Inflammation in prostate carcinogenesis. Nat Rev Cancer 2007;7:256-269. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrc2090
- 32. Frieling JS, Li T, Tauro M, Lynch CC. Prostate cancer-derived MMP-3 controls intrinsic cell growth and extrinsic angiogenesis. Neoplasia 2020;22:511-521. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neo.2020.08.004
- 33. Rao SR, Snaith AE, D Marino D, Cheng X, Lwin ST, Orriss IR, Hamdy FC, Edwards CM. Tumour-derived alkaline phosphatase regulates tumour growth, epithelial plasticity and disease-free survival in metastatic prostate cancer. Br J Cancer 2017;116:227-236. https://doi.org/10.1038/bjc.2016.402
- 34. Kharmate G, Hosseini-Beheshti E, Caradec J, Chin MY, Tomlinson Guns ES. Epidermal growth factor receptor in prostate cancer derived exosomes. PLoS One 2016;11:e0154967. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0154967
- 35. Cheng WL, Wang CS, Huang YH, Tsai MM, Liang Y, Lin KH. Overexpression of CXCL1 and its receptor CXCR2 promote tumor invasiveness in gastric cancer. Ann Oncol 2011;22:2267-2276. https://doi.org/10.1093/annonc/mdq739
- 36. Verbeke H, Struyf S, Laureys G, Van Damme J. The expression and role of CXC chemokines in colorectal cancer. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev 2011;22:345-358. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cytogfr.2011.09.002
- 37. Dhawan P, Richmond A. Role of CXCL1 in tumorigenesis of melanoma. J Leukoc Biol 2002;72:9-18.
- 38. Miyake M, Lawton A, Goodison S, Urquidi V, Rosser CJ. Chemokine (C-X-C motif) ligand 1 (CXCL1) protein expression is increased in high-grade prostate cancer. Pathol Res Pract 2014;210:74-78. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.prp.2013.08.013
- 39. Lu Y, Cai Z, Xiao G, Liu Y, Keller ET, Yao Z, Zhang J. CCR2 expression correlates with prostate cancer progression. J Cell Biochem 2007;101:676-685. https://doi.org/10.1002/jcb.21220
- 40. Lu Y, Chen Q, Corey E, Xie W, Fan J, Mizokami A, Zhang J. Activation of MCP-1/CCR2 axis promotes prostate cancer growth in bone. Clin Exp Metastasis 2009;26:161-169. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10585-008-9226-7
- 41. Nguyen DP, Li J, Tewari AK. Inflammation and prostate cancer: the role of interleukin 6 (IL-6). BJU Int 2014;113:986-992. https://doi.org/10.1111/bju.12452
- 42. Azevedo A, Cunha V, Teixeira AL, Medeiros R. IL-6/IL-6R as a potential key signaling pathway in prostate cancer development. World J Clin Oncol 2011;2:384-396. https://doi.org/10.5306/wjco.v2.i12.384
- 43. Porta C, Riboldi E, Sica A. Mechanisms linking pathogens-associated inflammation and cancer. Cancer Lett 2011;305:250-262. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.canlet.2010.10.012
- 44. Kruk J, Aboul-Enein HY. Reactive Oxygen and Nitrogen Species in carcinogenesis: implications of oxidative stress on the progression and development of several cancer types. Mini Rev Med Chem 2017;17:904-919. https://doi.org/10.2174/1389557517666170228115324
- 45. Fusté NP, Castelblanco E, Felip I, Santacana M, Fernandes-Hernanadez R, Gatius S, Pedraza N, Pallares J, Cemeli T, Valls J, Rarres M, Ferrezuelo F, Dolcet X, Matias-Guiu X, Gari E. Characterization of cytoplasmic cyclin D1 as a marker of invasiveness in cancer. Oncotarget 2016;7:26979-26991. https://doi.org/10.18632/oncotarget.8876
- 46. Kato J, Matsushime H, Hiebert SW, Ewen ME, Sherr CJ. Direct binding of cyclin D to the retinoblastoma gene product (pRb) and pRb phosphorylation by the cyclin D-dependent kinase CDK4. Genes Dev 1993;7:331-342. https://doi.org/10.1101/gad.7.3.331
- 47. Li Z, Wang C, Jiao X, Lu Y, Fu M, Quong AA, Dye C, Yang J, Dai M, Zhang X, Li A, Burbelo P, Stanley ER, Pestell RG. Cyclin D1 regulates cellular migration through the inhibition of thrombospondin 1 and ROCK signaling. Mol Cell Biol 2006;26:4240-4256. https://doi.org/10.1128/MCB.02124-05
- 48. Lo UG, Lee CF, Lee MS, Hsieh JT. The role and mechanism of epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition in prostate cancer progression. Int J Mol Sci 2017;18:2079. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms18102079