Abstract
Macrophages play a key role in chronic inflammation, and are the most abundant immune cells in the tumor microenvironment. We investigated whether an interaction between inflamed prostate cancer cells stimulated with Trichomonas vaginalis and macrophages stimulates the proliferation of the cancer cells. Conditioned medium was prepared from T. vaginalis-infected (TCM) and uninfected (CM) mouse prostate cancer (PCa) cell line (TRAMP-C2 cells). Thereafter conditioned medium was prepared from macrophages (J774A.1 cell line) after incubation with CM (MCM) or TCM (MTCM). When TRAMP-C2 cells were stimulated with T. vaginalis, protein and mRNA levels of CXCL1 and CCL2 increased, and migration of macrophages toward TCM was more extensive than towards CM. Macrophages stimulated with TCM produced higher levels of CCL2, IL-6, TNF-α, their mRNAs than macrophages stimulated with CM. MTCM stimulated the proliferation and invasiveness of TRAMP-C2 cells as well as the expression of cytokine receptors (CCR2, GP130, CXCR2). Importantly, blocking of each cytokine receptors with anti-cytokine receptor antibody significantly reduced the proliferation and invasiveness of TRAMP-C2 cells. We conclude that inflammatory mediators released by TRAMP-C2 cells in response to infection by T. vaginalis stimulate the migration and activation of macrophages and the activated macrophages stimulate the proliferation and invasiveness of the TRAMP-C2 cells via cytokine-cytokine receptor binding. Our results therefore suggested that macrophages contribute to the exacerbation of PCa due to inflammation of prostate cancer cells reacted with T. vaginalis.
-
Key words: Trichomonas vaginalis, macrophage, inflammation, prostate cancer, cytokine, chemokine, receptor
INTRODUCTION
Trichomoniasis is considered the most prevalent nonviral sexually-transmitted infection worldwide, affecting individuals of all ages, ethnicities, and socioeconomic groups [
1,
2].
Trichomonas vaginalis infection in men is asymptomatic or causes only mild symptoms [
3]. For this reason, persistent infection with
T. vaginalis has been hypothesized to cause chronic inflammation [
4]. In addition,
T. vaginalis had been detected in the prostate urethra, lumen, submucosal layer and stroma by immunoperoxidase staining, indicating that
T. vaginalis could invade prostate tissue [
5].
We showed previously that seropositivity for
T. vaginalis in the patients with prostate disease was 19.7% (benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH) 18.7%, prostate cancer (PCa) 22.7%), which was significantly higher than the 1.7% (
P=0.001) in the healthy group [
6]. These results suggest that patients with prostate tumors have been exposed to
T. vaginalis at a 10-fold higher rate than normal men.
Cytokines and chemokines are known to play important roles in cancer progression and metastasis [
7]. Recently, we confirmed that when prostate cancer cells are infected with
T. vaginalis, cytokines produced in the inflammatory response bind to the cytokine receptors on the cancer cells, thus stimulating proliferation of the cancer cells. Therefore, it has been suggested that cytokines contribute to the
T. vaginalis-induced exacerbation of PCa [
8].
Macrophages play a key role in chronic inflammation and are the most abundant immune cells in the tumor microenvironment, so-called tumor-associated macrophages (TAMs) [
9]. TAMs play crucial roles in the survival, proliferation and metastasis of cancer cells [
10].
This study was performed to determine whether macrophages activated by prostate cancer cells inflamed by T. vaginalis infection are involved in the proliferation of prostate cancer cells.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Parasite and cell lines
Trichomonas vaginalis isolate T016 was grown in trypticase-yeast extract-maltose medium supplemented with 10% heat-inactivated horse serum (Life Technologies, Carlsbad, California, USA). The mouse prostate cancer cell line (TRAMP-C2 cells) was a gift from Prof. Jung Han Yoon Park (Hallym University) and were grown in Dulbecco’s Modified Eagle’s Medium (DMEM; GE Healthcare Life Sciences, Logan, Utah, USA) containing penicillin and streptomycin (WelGENE, Gyeongsan, Korea) supplemented with 10% fetal bovine serum (FBS; GE Healthcare Life Sciences) in a 5% CO
2 humidified incubator at 37°C [
11]. The mouse macrophage cell line (J774A.1 cells) was purchased from the Korean Cell Line Bank (KCLB, Seoul, Korea) and cultured in DMEM containing 1% penicillin and streptomycin plus 10% FBS. All cell lines were maintained in a 5% CO
2 humidified incubator at 37°C.
Preparation of conditioned media and treatments
For conditioned medium preparation, TRAMP-C2 cells (2×10
5 cells/well) were seeded in 24-well plates for 24 hr. The medium was changed to serum-free medium, and the cells were incubated with (TCM) or without live
T. vaginalis (CM) in a ratio of 1:1 for 6 hr. Conditioned medium was collected, filtered through a 0.2 μm filters to remove cell debris, and stored at −20°C until use [
12].
The J774A.1 cells (2×105 cells/well) were seeded in 24-well plates in DMEM medium for stabilization. After 24 hr, the cells were incubated with 10% TCM or 10% CM for 6 hr, and supernatants were collected and stored in the same way, yielding conditioned media MTCM and MCM, respectively. Final concentration of the conditioned media was adjusted to 10% with cell culture medium.
Measurement of cytokine level
Chemokine (C-X-C motif) ligand 1 (CXCL1) and chemokine (C-C motif) ligand 2 (CCL2) levels produced by the TRAMP-C2 cells stimulated with live T. vaginalis were measured in cell culture medium using the mouse CXCL1 ELISA DuoSet (R&D System, Minneapolis, Minnesota, USA) and CCL2 ELISA set (BD, Bioscience Pharmingen, San Diego, California, USA). The concentrations of CCL2, IL-6, and TNF-α produced by the J774A.1 cells treated with TCM or CM for 6 hr were determined with mouse CCL2 ELISA set (BD), mouse IL6 ELISA DuoSet (R&D) and mouse TNF-α ELISA kits (R&D), respectively.
Macrophage chemotaxis assay
Chemotaxis was assessed in 24-well plates fitted with 5 mm pore polycarbonate membrane inserts [
13]. Briefly, the lower wells were filled with 350 ml of conditioned medium or DMEM, and polycarbonate membrane inserts were placed over the lower wells. For adhesion of the cells, the filters were pretreated with human plasma fibronectin (100 μg/ml) overnight at 4°C, and air-dried for 30 min. The upper wells were filled with 200 ml of macrophages (2×10
5 cells/well) in serum-free medium, and the plates were incubated for 24 hr at 37°C. After incubation, cells that did not migrate through the pores were wiped off the membranes with cotton swabs. The cells that had migrated to the underside of the membrane were fixed in methanol and stained with Giemsa solution, and the cells in 5 randomly-selected fields per membrane were counted under a light microscope. The chemotactic index was calculated from the number of cells relative to the control.
To measure cell proliferation, a wound healing assay was used. For this assay, the TRAMP-C2 cells reached confluence were wounded by scraping across the surface of the well with a sterile micropipette tip. The cells were washed immediately and incubated in 10% conditioned medium for 24 hr. Before and after incubation, at least 10 different fields of the wounded area of each sample were photographed with an inverted microscope (Leica, Wetzler, Germany) [
11].
Invasiveness of TRAMP-C2 cells was investigated using 24-well plates with 8 μm pore polycarbonate membrane inserts pre-coated with matrigel (200–300 μg/ml, SigmaAldrich, St Louis, Missouri, USA) for 2 hr at 37°C. The matrigel matrix layer was not allowed to dry out before use. Conditioned media (350 μl each; MTCM, MCM, TCM or CM) were used as chemoattractant in the lower chamber, and TRAMP-C2 cells (2×105 cells/well) were seeded in the upper chamber. The plates were incubated at 37°C for 24 hr. The invaded cells were fixed in methanol for 10 min and stained with Giemsa solution for 20 min. The cells in 5 randomly selected fields per membrane were counted under a light microscope. Invasiveness was calculated from the number of cells relative to the control.
To investigate the effects of CXCL1, CCL2, IL-6 on the proliferation and invasiveness of TRAMP-C2 cells, anti-CXCR2 antibody (Abcam, Cambridge, UK) for the CXCL1 receptor, or anti-CCR2 antibody (Abcam) for the CCL2 receptor and anti-GP130 antibody (Cell Signaling Technology, Danvers, Massachusetts, USA) for the IL-6 receptor, were added to the cells before adding the conditioned media. The plates were incubated at 37°C for 24 hr and analyzed by wound healing and invasiveness assays.
Quantitative real-time PCR (Q-PCR) for cytokine mRNAs
The mRNA level of the inflammatory cytokines (CXCL1, CCL2, IL-6 or TNF-α) in the TRAMP-C2 cells incubated with
T. vaginalis, and in the macrophages co-incubated with TCM or CM was measured by Q-PCR. The cells were seeded at 2×10
6 cells/well on 24-well plates and incubated with
T. vaginalis (2×10
6 cells/well) for 30 min. The following procedures were performed as previously described [
11,
12]. Total RNA was extracted from cells using Trizol reagent (Favorgen Biotech Corp, Kaohsiung, Taiwan) and the cDNA was used as template for subsequent PCR amplification using gene-specific primers. CXCL1; 5′-CAC CCA AAC CGA AGT CAT AG-3′, 5′-AAG CCA GCG TTC ACC AGA-3′, CCL2; 5′-GCT ACA AGA GGA TCA CCA GC-3′, 5′-TGT CTG GAC CCA TTC CTT CT-3′, IL-6; 5′-CCA CTT CAC AAG TCG GAG GCT TA-3′, 5′-CCA CTT CAC AAG TCG GAG GCT TA-3′, TNF-α; 5′-TGG GAC AGT GAC CTG GAC TGT-3′, 5′-TTC GGA AAG CCC ATT TGA GT-3′, GAPDH; 5′-AAT ACG GCT ACA GCA ACA GG-3′, 5′-TTG GGA TAG GGC CTC TCT TG-3′. For quantitative real-time PCR, target mRNAs were amplified using LightCycler 480 SYBR Green I Master (Roche Life Science, Mannheim, Germany) and analyzed with LightCycler 480 Software (Roche Life Science). PCR thermal cycles were: 45 cycles at 95°C for 5 min, 95°C for 10 sec, 60°C for 10 sec and 72°C for 10 sec.
To observe expression of cytokine receptors (CCR2, GP130, CXCR2) on the surface of prostate cancer cell, we used an immunofluorescence assay [
12]. The TRAMP-C2 cells were seeded at 2×10
5 cells/well on sterile cover glasses in 12-well plates and cultured in complete medium. After overnight incubation, the medium was replaced with MCM or MTCM, and the cells were cultured at 37°C for 24 hr. They were washed, fixed with 4% paraformaldehyde for 10 min at room temperature and blocked with 0.1% normal goat serum for 1 hr. The cover glasses were incubated with anti-cytokine antibody overnight at 4°C, washed and incubated with Alexa 594-labelled goat anti-rabbit lgG (Invitrogen, Carlsbad, California, USA) at 37°C for 1 hr. The cells were mounted in Vectashield mounting medium (Vector Laboratories, Burlingame, California, USA) with DAPI to visualize nuclei. Fluorescence was measured with a fluorescence microscope (Leica, Wetzlar, Germany).
Statistical analyses were performed with SPSS (version 21, IBM, Chicago, Illinois, USA). The Mann-Whitney U test was used to compare results, and 2-tailed P-values<0.05 were considered statistically significant. All data are expressed as mean± SEM of 3 or 4 independent measurements.
RESULTS
Migration and activation of macrophages induced by conditioned medium from inflamed TRAMP-2 cells stimulated with T. vaginalis
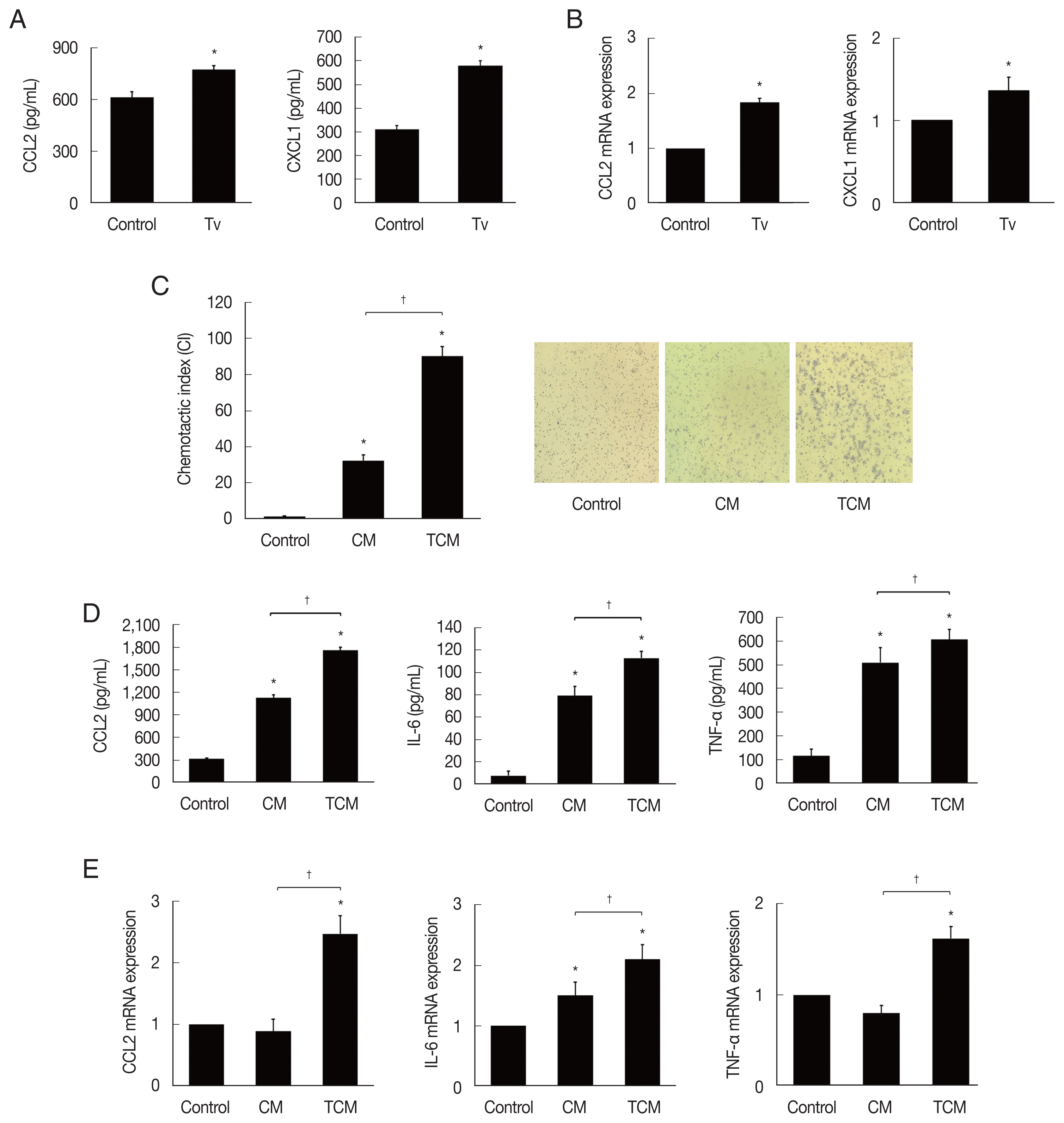
We first examined chemokines produced by TRAMP-C2 cells treated with
T. vaginalis (1:1) for 6 hr. The TRAMP-C2 cells released CCL2 and CXCL1. Chemokine production was significantly increased in comparison with cells incubated without
T. vaginalis (
P<0.05;
Fig. 1A). When TRAMP-C2 cells were stimulated with live
T. vaginalis (1:1) for 30 min, the chemokine mRNAs were also significantly upregulated in comparison to the control (
Fig. 1B).
Chemotaxis of J774A.1 cells induced by TCM was significantly greater than that induced by CM or DMEM medium. These results suggest that TCM containing CCL2 and CXCL1 has a role in the recruitment of J774A.1 cells (
P<0.05;
Fig. 1C).
We examined whether the macrophages displayed an inflammatory reaction in response to TCM. When the macrophages were stimulated with TCM, they released CCL2, IL-6 and TNF-α, and their mRNAs increased (
P<0.05;
Fig. 1D, E). This result confirmed that cytokine production increased in inflamed macrophages exposed to TCM.
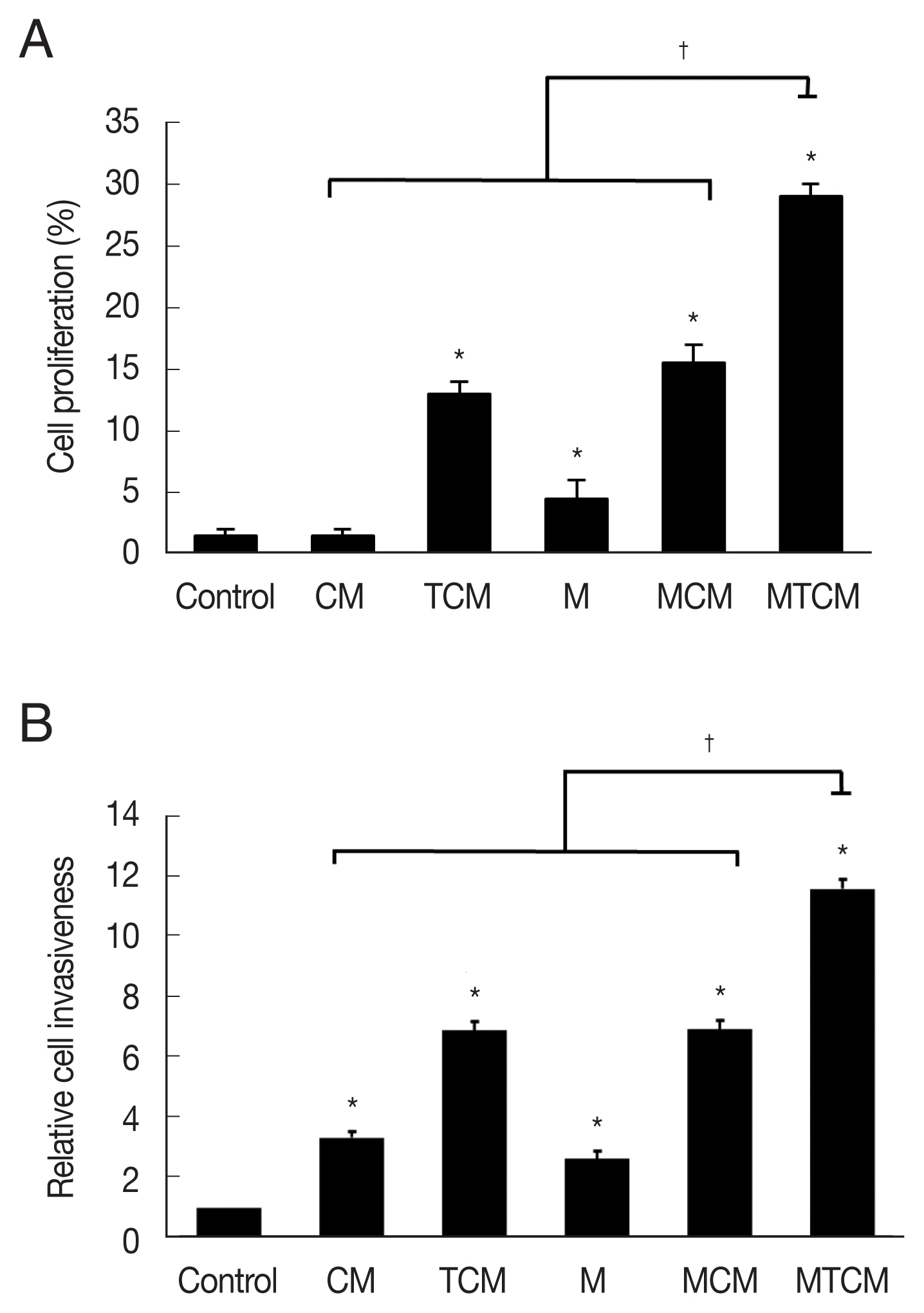
The MTCM containing higher levels of cytokines than the other conditioned media (CM, TCM, MCM) stimulated wound healing of TRAMP-2 cells (
P<0.05;
Fig. 2A), indicating that MTCM stimulated the proliferation of PCa cells. In a matrigel invasiveness assay, MTCM stimulated the invasiveness of TRAMP-C2 cells more than CM, TCM, MCM (
Fig. 2B).
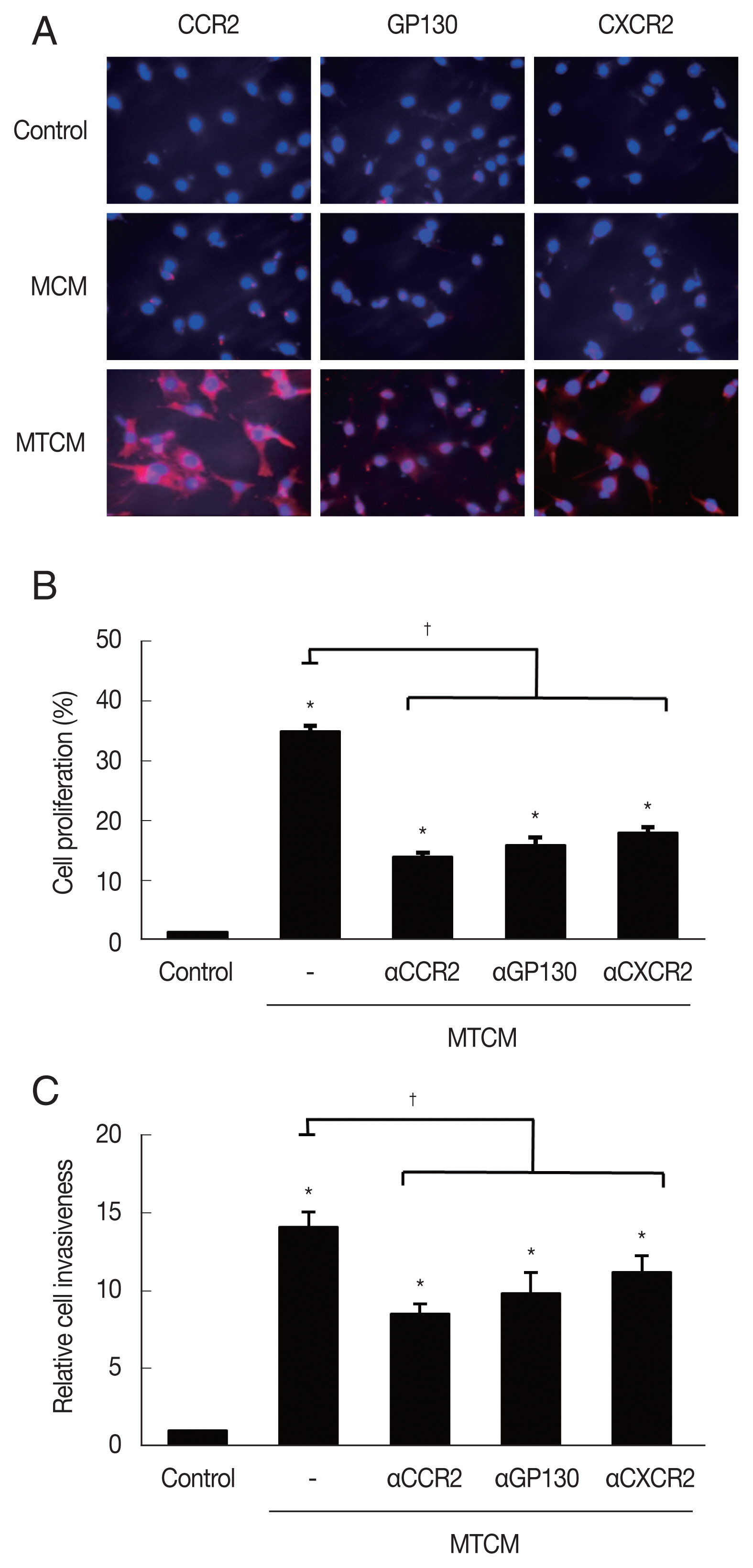
MTCM increased the expression of cytokine receptors CCR2, GP130 and CXCR2 as observed by fluorescence microscopy (
Fig. 3A). To see whether the cytokine receptors were implicated in the increased proliferation and invasiveness of TRAMP-C2 cells, the effects of anti-cytokine receptor antibodies (anti-CXCR2, -CCR2, -GP130 antibody) were examined. These antibodies reduced the effects of the MTCM in proliferation and invasiveness of TRAMP-C2 cells (
Fig. 3B, C). Therefore, cytokine-cytokine receptor signaling pathways were found involved in the proliferation and invasiveness of TRAMP-C2 cell.
DISCUSSION
Macrophages are present in all tissues under homeostatic physiological conditions [
14,
15]. In general, macrophages in cancers are double-edged swords exerting pro- and anti-tumor effects depending on the balance between a number of signals, including cytokines, chemokines, antibodies and myeloid checkpoints [
16]. Macrophages are a major component of the leukocyte infiltrate present in widely different amounts in all tumors [
17,
18]. The TAMs have served as a paradigm for leukocytes and inflammatory mediators present in the tumor context, and play a dominant role as orchestrators of cancer-related inflammation.
Cytokines and chemokines are known to be involved in tumor progression and metastasis [
7]; Cytokine/chemokines impact tumorigenesis by either directly regulating tumor cell growth, invasiveness, and metastasis or indirectly, by exerting modulatory effects on stromal cells and immune cells, promotion of metastatic niches, as well as inducing angiogenesis in the cancer microenvironment [
19–
21].
The purpose of this study was to investigate the role of macrophages in PCa cell proliferation in response to infection with T. vaginalis, which is thought to cause chronic prostate infection. We found that when PCa cells were reacted with T. vaginalis, inflammatory mediators including CCL2 induced macrophage migration, and activated macrophages induced increased expression of CCR2, GP130, and CXCR2 in the PCa cells, thereby stimulating their proliferation.
CCL2, which is present in TCM, belongs to the CC family of chemokines, and is a ligand for CCR2. It is a well-known chemoattractant for macrophages and has been found to be involved in the metastasis of various cancer types. Prostate cancer cells express substantial levels of CCL2, which has both autocrine and paracrine functions [
22]. The CCL2/CCR2 axis is known to play a role in the growth of prostate cancers, since inhibition of CCL2 activity with neutralizing antibodies or knocking down CCR2 abrogates tumor invasiveness and decreases the overall tumor burden [
23,
24]. Similarly, the use of CCR2 antibodies in this study significantly reduced the stimulation of proliferation and invasiveness of PCa cells by MTCM containing CCL2.
IL-6 is a pleiotropic pro-inflammatory cytokine which has been shown to be involved in prostate tumorigenesis and to act via both autocrine and paracrine mechanisms. It has been found to play roles in epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT), angiogenesis, and bone remodeling [
10]. There are several reports of the pathological effect of IL-6 produced during
T. vaginalis infection of prostate cells; Sutcliffe et al. [
4] suggested that chronic, latent
T. vaginalis infection of prostate tissue up-regulates the signaling cascade leading to prostate carcinogenesis by inducing production of IL-6 via transcriptional activation of the STAT3-PIM1-HMGA1 cascade. Our previous findings suggest that prostate epithelial cells incubated with
T. vaginalis cause IL-6 production to increase by activating various signaling molecules such as TLR2/4, ROS, MAPKs, AP-1, NF-κB and JAK2/STAT3, and inducing EMT via NF-κB and JAK/STAT3 [
25]. Also, IL-6 produced in response to
T. vaginalis infection of prostate cells has an important effect on the tumor microenvironment by promoting progression of PCa cells following induction of M2 macrophage polarization [
13]. In the present study, we observed that when we blocked the increased expression of the IL-6 receptor on PCa cells treated with MTCM with anti-GP130 antibody, the proliferation and invasiveness of the PCa cells were significantly reduced. Therefore, IL-6 may be involved in the proliferation of PCa cells via binding of GP130.
The CXCL1 contained in TCM attracts several immune cell types, especially neutrophils and other non-hematopoietic cells, to the site of injury or infection and plays an important role in regulation of immune and inflammatory responses. CXCL1 has a potentially similar role to IL-8/CXCL8 [
10]. It is reported to be upregulated in prostate cancer [
26]. It promotes prostate cell EMT, migration, and invasiveness via the AKT/NF-κB axis [
27]. Lu et al. [
28] recently reported that CXCL1 triggers EMT, migration, and prostate tumor progression via the CXCL1-LCN2 paracrine axis. A role of CXCL1 in osteoclast development has also been identified. In metastatic prostate cancer, the maturation of osteoclasts is accelerated following CXCL1 stimulation, and this effect is blocked upon treatment with neutralizing antibodies against CXCL1 [
29]. In this study, the expression of CXCL1 mRNA (data not shown) and CXCR2 was increased in PCa cells exposed to MTCM. In addition, PCa cell proliferation was reduced by treatment with anti-CXCR2 antibody, indicating that the CXCL1-CXCR2 signal is involved in the proliferation of PCa cells.
This study has some limitations. In the experiment on the expression of the cytokine receptor on the surface of PCa cells treated with MTCM, no results for an isotype control antibody could be presented. This control needs to be performed in future experiments
Taken together, our findings suggest that PCa cells produce chemokines when inflamed by T. vaginalis infection, and that this induces the migration and activation of macrophages. Also, crosstalk with these macrophages promotes the proliferation and invasiveness of PCa cells through cytokine-cytokine receptor signaling.
Notes
-
There are no conflicts of interest related to this study.
ACKNOWLEDGMENT
The data that support the findings of this study are available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.
Fig. 1Production of cytokines and their mRNAs by TRAMP-C2 cells stimulated with T. vaginalis, and by macrophages stimulated with CM or TCM. (A) Cytokines and (B) mRNA by TRAMP-C2 cells incubated with live T. vaginalis (Tv). (C) Migration of macrophages to CM and TCM. Relative to DMEM medium. (D) Production of CCL2, IL-6 & TNF-α, and (E) their mRNAs by macrophages stimulated with CM or TCM. Control, DMEM medium. *P<0.05 versus control, †P<0.05 versus TCM.

Fig. 2Proliferation and invasiveness of prostate cancer cell line (TRAMP-C2 cells) stimulated with MTCM. (A) Proliferation examined by wound healing assay. (B) Invasiveness examined by matrigel invasiveness assay. Control, DMEM medium. M, supernatant of macrophages alone. *P<0.05 versus control, †P<0.05 versus MTCM.

Fig. 3Expression of cytokine receptors and effect of anti-cytokine receptor antibody on the proliferation and invasiveness of TRAMP-C2 cells stimulated with MTCM. (A) Cytokine receptor expression observed by fluorescence microscopy. Cell nuclei were stained in blue and cytokine receptors in red. Control, DMEM medium. (B) Proliferation and (C) invasiveness of TRAMP-C2 cells pretreated with anti-cytokine receptor antibodies were measured by wound healing and matrigel invasiveness assays, respectively. *P<0.05 versus control, †P<0.05 versus MTCM.

References
- 1. Conrad MD, Gorman AW, Schillinger JA, Fiori PL, Arroyo R, Malla N, Dubey ML, Gonzalez J, Blank S, Secor WE, Carlton JM. Extensive genetic diversity, unique population structure and evidence of genetic exchange in the sexually transmitted parasite Trichomonas vaginalis. PLoS Negl Trop Dis 2012;6:e1573. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pntd.0001573
- 2. Chetty R, Mabaso N, Abbai N. Genotypic variation in Trichomonas vaginalis detected in South African pregnant women. Infect Dis Obstet Gynecol 2020;2020:1687427. https://doi.org/10.1155/2020/1687427
- 3. Abdolrasouli A, Amin A, Baharsefat M, Roushan A, Mofidi S. Persistent urethritis and prostatitis due to Trichomonas vaginalis: a case report. Can J Infect Dis Med Microbiol 2007;18:308-310. https://doi.org/10.1155/2007/196046
- 4. Sutcliffe S, Neace C, Magnuson NS, Reeves R, Alderete JF. Trichomonosis, a common curable STI, and prostate carcinogenesis - a proposed molecular mechanism. PLoS Pathog 2012;8:e1002801. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.ppat.1002801
- 5. Gardner WA Jr, Culberson DE, Bennett BD. Trichomonas vaginalis in the prostate gland. Arch Pathol Lab Med 1986;110:430-432.
- 6. Kim JH, Moon HS, Kim KS, Hwang HS, Ryu JS, Park SY. Comparison of seropositivity to Trichomonas vaginalis between men with prostatic tumor and normal men. Korean J Parasitol 2019;57:21-25. http://doi.org/10.3347/kjp.2019.57.1.21
- 7. Adekoya TO, Richardson RM. Cytokines and chemokines as mediators of prostate cancer metastasis. Int J Mol Sci 2020;21:4449. http://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21124449
- 8. Kim SS, Kim KS, Han IH, Kim Y, Bang SS, Kim JH, Kim YS, Choi SY, Ryu JS. Proliferation of mouse prostate cancer cells inflamed by Trichomonas vaginalis. Korean J Parasitol 2021;59:547-556. http://doi.org/10.3347/kjp.2021.59.6.547
- 9. Schoppmann SF, Birner P, Stockl J, Kalt R, Ullrich R, Caucig C, Kriehuber E, Nagy K, Alitalo K, Kerjaschki D. Tumor-associated macrophages express lymphatic endothelial growth factors and are related to peritumoral lymphangiogenesis. Am J Pathol 2002;161:947-956. http://doi.org/10.1016/S0002-9440(10)64255-1
- 10. Lissbrant IF, Stattin P, Wikstrom P, Damber JE, Egevad L, Bergh A. Tumor associated macrophages in human prostate cancer: relation to clinicopathological variables and survival. Int J Oncol 2000;17:445-451. http://doi.org/10.3892/ijo.17.3.445
- 11. Chung HY, Kim JH, Han IH, Ryu JS. Polarization of M2 macrophages by interaction between prostate cancer cells treated with Trichomonas vaginalis and adipocytes. Korean J Parasitol 2020;58:217-227. http://doi.org/10.3347/kjp.2020.58.3.217
- 12. Kim JH, Han IH, Shin SJ, Park SY, Chung HY, Ryu JS. Signaling role of adipocyte leptin in prostate cell proliferation induced by Trichomonas vaginalis. Korean J Parasitol 2021;59:235-249. http://doi.org/10.3347/kjp.2021.59.3.235
- 13. Han IH, Song HO, Ryu JS. IL-6 produced by prostate epithelial cells stimulated with Trichomonas vaginalis promotes proliferation of prostate cancer cells by inducing M2 polarization of THP-1-derived macrophages. PLoS Negl Trop Dis 2020;14:e0008126. http://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pntd.0008126
- 14. Gordon S, Taylor PR. Monocyte and macrophage heterogeneity. Nat Rev Immunol 2005;5:953-964. http://www.doi.org/10.1038/nri1733
- 15. Ginhoux F, Guilliams M. Tissue-resident macrophage ontogeny and homeostasis. Immunity 2016;44:439-449. http://www.doi.org/10.1016/j.immuni.2016.02.024
- 16. Locati M, Curtale G, Alberto Mantovani A. Diversity, mechanisms and significance of macrophage plasticity. Annu Rev Pathol 2020;15:123-147. http://www.doi.org/10.1146/annurev-pathmechdis-012418-012718
- 17. Mantovani A, Marchesi F, Malesci A, Laghi L, Allavena P. Tumor-associated macrophages as treatment targets in oncology. Nat Rev Clin Oncol 2017;14:399-416. http://www.doi.org/10.1038/nrclinonc.2016.217
- 18. Noy R, Pollard JW. Tumor-associated macrophages: from mechanisms to therapy. Immunity 2014;41:49-61. http://doi:10.1016/j.immuni.2014.06.010.
- 19. Dranoff G. Cytokines in cancer pathogenesis and cancer therapy. Nat Rev Cancer 2004;4:11-22. http://www.doi.org/10.1038/nrc1252
- 20. Chow MT, Luster AD. Chemokines in cancer. Cancer Immunol Res 2014;2:1125-1131. http://doi:10.1158/2326-6066.CIR-14-0160.
- 21. Nagarsheth N, Wicha MS, Zou W. Chemokines in the cancer microenvironment and their relevance in cancer immunotherapy. Nat Rev Immunol 2017;17:559-572. http://www.doi.org/10.1038/nri.2017.49
- 22. Lu Y, Cai Z, Galson DL, Xiao G, Liu Y, George DE, Melhem MF, Yao Z, Zhang J. Monocyte chemotactic protein-1 (MCP-1) acts as a paracrine and autocrine factor for prostate cancer growth and invasion. Prostate 2006;66:1311-1318. http://www.doi.org/10.1002/pros.20464
- 23. Lu Y, Chen Q, Corey E, Xie W, Fan J, Mizokami A, Zhang J. Activation of MCP-1/CCR2 axis promotes prostate cancer growth in bone. Clin Exp Metastasis 2009;26:161-169. http://www.doi.org/10.1007/s10585-008-9226-7
- 24. Loberg RD, Day LL, Harwood J, Ying C, St John LN, Giles R, Neeley CK, Pienta KJ. CCL2 is a potent regulator of prostate cancer cell migration and proliferation. Neoplasia 2006;8:578-586. http://www.doi.org/10.1593/neo.06280
- 25. Han IH, Kim JH, Kim SS, Ahn MH, Ryu JS. Signalling pathways associated with IL-6 production and epithelial-mesenchymal transition induction in prostate epithelial cells stimulated with Trichomonas vaginalis. Parasite Immunol 2016;38:678-687. http://www.doi.org/10.1111/pim.12357
- 26. Miyake M, Lawton A, Goodison S, Urquidi V, Rosser CJ. Chemokine (C-X-C motif) ligand 1 (CXCL1) protein expression is increased in high-grade prostate cancer. Pathol Res Pract 2014;210:74-78. http://doi:10.1016/j.prp.2013.08.013.
- 27. Kuo PL, Shen KH, Hung SH, Hsu YL. CXCL1/GROα increases cell migration and invasion of prostate cancer by decreasing fibulin-1 expression through NF-κB/HDAC1 epigenetic regulation. Carcinogenesis 2012;33:2477-2487. http://www.doi.org/10.1093/carcin/bgs299
- 28. Lu Y, Dong B, Xu F, Xu Y, Pan J, Song J, Zhang J, Huang Y, Xue W. CXCL1-LCN2 paracrine axis promotes progression of prostate cancer via the Src activation and epithelial-mesenchymal transition. Cell Commun Signal 2019;17:118. http://www.doi.org/10.1186/s12964-019-0434-3
- 29. Hardaway AL, Herroon MK, Rajagurubandara E, Podgorski I. Marrow adipocyte-derived CXCL1 and CXCL2 contribute to osteolysis in metastatic prostate cancer. Clin Exp Metastasis 2015;32:353-368. http://www.doi.org/10.1007/s10585-015-9714-5