Abstract
When free-ranging birds are accidentally killed or die, there may be greater potential for their associated ticks to detach, seek alternate hosts, and become established. We examined 711 carcasses of 95 avian species for ticks at a stopover island of migratory birds in the Republic of Korea where only Ixodes nipponensis and I. persulcatus were previously reported from local mammals and vegetation. A total of 16 ticks, I. turdus and Haemaphysalis flava, were collected from 8 fresh carcasses belonging to 5 avian species. Despite their known abundance on migratory birds and mainland Korea, these species had not colonized the isolated insular ecosystem possibly due to the low abundance and diversity of local hosts. The results imply that increasing human impact, such as the anthropogenic mortality of migratory birds and the introduction of non-native mammalian hosts, will increase the potential invasion and colonization risk of ticks. This finding also suggests that tick surveillance consisting of fresh carcasses of dead migratory birds may provide additional information, often ignored in surveillance of ticks on live birds, for the potential introduction of non-native ticks and associated pathogens affecting animal and human health.
-
Key words: Carcass, non-native tick, migratory bird, surveillance
Ticks belonging to the family Ixodidae are common bird ectoparasites that are vectors of a number of zoonotic pathogens, e.g.,
Rickettsia,
Bartonella,
Anaplasma, and
Ehrlichia spp. and tick-borne encephalitis virus, that impact wild and domestic animal/bird and human health [
1–
7]. Birds have been strongly implicated as transport hosts of ticks from their breeding and wintering grounds during their spring and fall migrations [
3–
5,
8–
13]. Recent climatic changes have altered migratory patterns of birds [
14,
15]. The timing of altered migratory routes have resulted in birds passing through areas not previously traversed, which may result in the transport and introduction of ticks and associated pathogens into previously non-native areas [
14].
Previous monitoring of migratory bird ticks and associated pathogens were generally conducted by capturing and examining live migratory birds [
1,
3–
7,
11]. Recently killed birds due to window collision or those died from exhaustion due to the extended flight or diseases acquired at their breeding and wintering grounds were not considered. Ticks may frequently remain on their avian hosts for several days, which is often greater than the host’s stopover period. Therefore, the occurrence of ticks on live migratory birds at stopover sites is not necessarily linked to the introduction of the ticks along their migratory routes. Conversely, ticks on fresh migratory bird carcasses at stopover sites represent the potential for the introduction of non-native ticks and their associated pathogens from the host site of origin due to detachment and search for alternate hosts. This study aimed to provide an understanding of the potential for the introduction of native and non-native ticks and their associated pathogens from fresh avian carcasses recovered at a migratory bird stopover site.
Ticks were examined and collected from migratory bird carcasses recovered at Hong-do 1-gu village on Hong Island (Hong-do) (N 34° 41′, E 125° 11′), Shinan-gun, Jeonnam Province, in the Republic of Korea (hereafter Korea). Hong Island is located 115 km southwest of the Korean Peninsula and is a primary stopover site for migratory birds originating from their wintering grounds in the subtropical and tropical Pacific Region or breeding grounds in the northern latitude such as Siberia [
5,
16]. Only 10 of >320 avian species are residents on Hong Island [
16], whereas the majority are non-breeding groups traversing Hong Island on their route to their breeding (spring migration) and wintering (fall) grounds. Therefore, Hong Island is a key stopover site for migratory birds crossing the Yellow Sea, not a breeding area of resident birds, in Korea. On the other hand, the terrestrial mammalian fauna is very poor because of its geographic isolation from mainland Korea and China. The Brown Rat (
Rattus norvegicus) was the only known terrestrial mammal in the 1960s [
17], and 2 more species (Ussuri White-toothed Shrew
Crocidura lasiura and Greater Horseshoe
Bat Rhinolophus ferrumequinum) were reported in 2008 [
18]. There are currently a small number of human-introduced mammals such as domestic dogs (
Canis lupus familiaris), domestic and feral cats (
Felis catus), and Siberian Weasels (
Mustela sibirica).
Fresh carcasses of migratory birds were collected daily at the study site from January 2008 through October 2009. Birds were identified to species and the cause (s) of mortality determined (e.g., window collision, attacks by mammal predators, and dehydration or exhaustion resulting from the long flight). We stored each dead bird in a plastic zip lock bag for 1 hr before examination and collected ticks released from the carcass. Then we examined the bird carcass for ticks and removed the remaining ticks using fine forceps and placed them in 2-ml and 4-ml cryovials containing 70% ethanol [
5,
7,
13]. Ticks were provided to Force Health Protection&Preventive Medicine (FHP&PM), 65th Medical Brigade/MEDDAC-Korea, Seoul, Korea, where they were identified to species using standard keys [
19,
20]. This tick surveillance on bird carcasses was conducted concurrently with the surveillance on live migratory birds on Hong Island [
5].
To understand the local native tick fauna on Hong Island, tick surveillance of local mammals using Havahart live animal traps (81.3 cm×25.4 cm×30.5 cm; Woodstream Corp., Lititz, Pennsylvania, USA) were set out from April 2008 through March 2010. We examined 54 cats (
Felis catus) and 9 Siberian weasels, and a total of 22 cats (40.7%) and one weasel (11.1%) were infested with ticks. Ticks were similarly removed using fine forceps and provided to the FHP&PM where they were identified to species.
Ixodes nipponensis Kitaoka and Saito (50 adults from 21 cats) and
Ixodes persulcatus Schulze (2 adults from 1 cat) were collected from the cats, while only
I. nipponensis (2 adults) was collected from 1 weasel (
Fig. 1). Additionally, tick surveillance was conducted using tick drags, a 1.0 m×1.5 m flannel cloth attached to a wooden dowel dragged over open grassland vegetation and forested ground cover for questing ticks [
21], during August 2008 and 2009. While no ticks were collected by tick drag, one blood-fed adult
I. nipponensis was collected from vegetation along a village roadside in March 2010. During the same period, the shrews and rats killed by cats and road accidents or found dead by poisoning were also examined, but no ticks were detected. Live birds were not used in this study, and all trapping and collection efforts were approved and implemented by the Korea National Park Service and local government (Shinan County Office).
A total of 711 dead birds belonging to 61 genera and 95 species were collected and examined for ticks. No ticks were observed from carcasses of resident birds, e.g., Peregrine Falcon (
Falco peregrinus) (1), Great Tit (
Parus major) (1), Varied Tits (
P. varius) (6), and Brown-eared Bulbuls (
Hypsipetes amaurotis) (2). However, ticks were collected from the head region of 8 carcasses (1.1%) of 5 migratory bird species, Scaly Thrushes (
Zoothera aurea) (3), Pale Thrushes (
Turdus pallidus) (2), Thick-billed Shrike (
Lanius tigrinus) (1), Black-faced Bunting (
Emberiza spodocephala) (1), and the Japanese White-eye (
Zosterops japonicus) (1) (
Fig. 1). Four of the species were true migratory species, while the Japanese White-eye, a partial migrant, is not a true resident in the study area [
16]. From the bird carcasses, a total of 16 live ticks were collected and identified as
Ixodes turdus Nakatsuji (13) and
Haemaphysalis flava Neumann (3) based on their morphology (
Table 1;
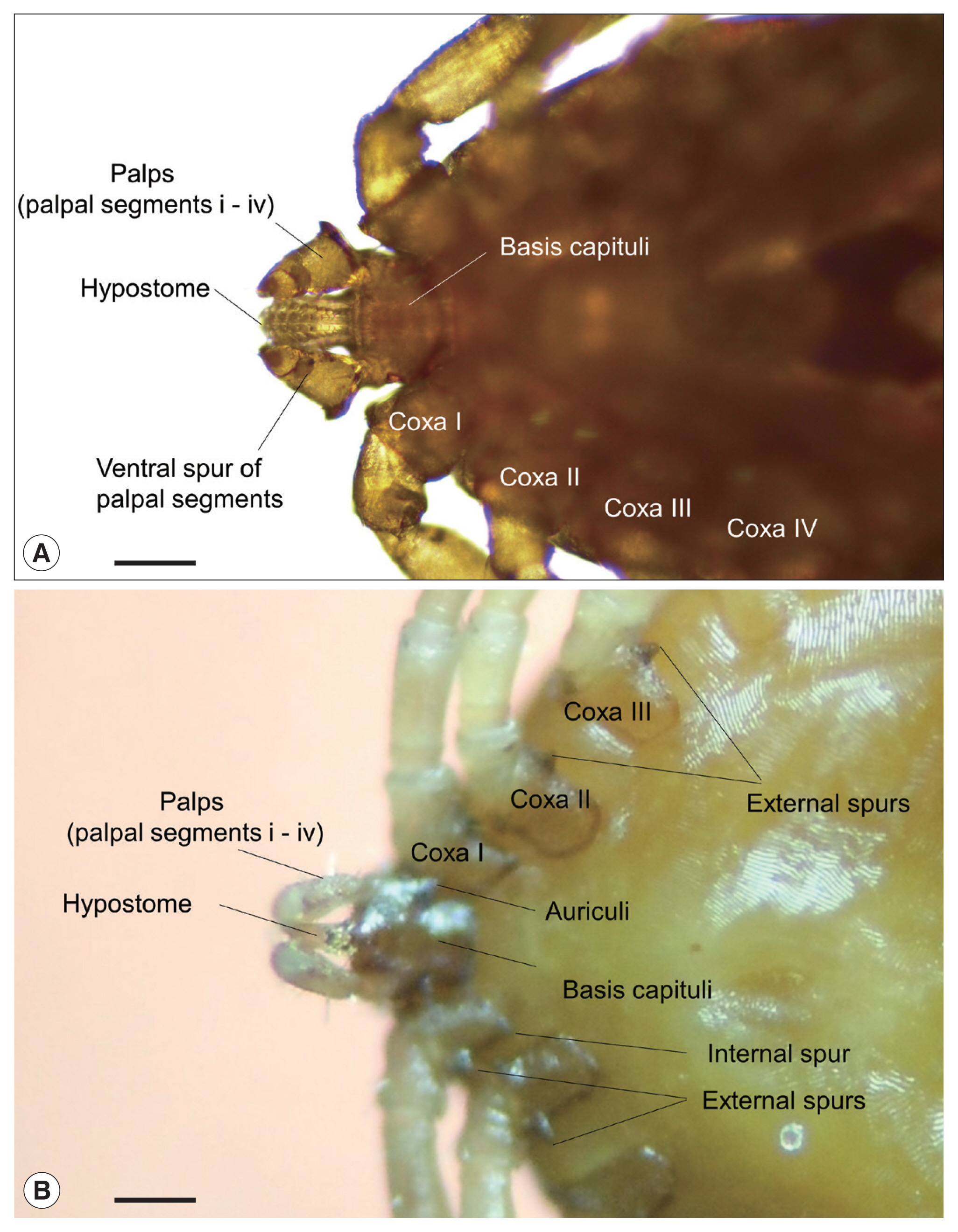
Fig. 2). Both species represented typical morphological features of their genera;
H. flava had relatively short palps and a triangular capitulum, while
I. turdus showed a more prolonged capitulum due to elongated palps [
20]. In particular, the nymphs of
I. turdus had well-projected auriculae and well-developed external spurs on their coxae (
Fig. 2B) while those of
I. nipponensis have less prominent and blunt ones. Nymphs of
H. flava are similar to those of
H. longicornis commonly collected on the mainland, but the ventral spurs of palpal segments III were much shorter and blunt along with less prominent spurs on their coxae (
Fig. 2A).
Tick surveillance, conducted concurreltly on live birds in the study area, also revealed that both
I. turdus and
H. flava were the most commonly observed ticks on migratory birds [
5]. However, despite such an abundance of immature
I. turdus and
H. flava on live migratory birds in the study area [
5], we did not find any evidence of their colonization on the island. Their ecology and hosts for different life stages are not well described and still in debate, but
I. turdus is a probable bird tick in all life stages with few exceptional records on rodents [
22], and
H. flava occurs on birds during their immature stages but their adults are found primarily on medium to large mammalian hosts [
23]. Therefore, their absence or non-establishment in the study area probably resulted from the low diversity and abundance of their suitable avian and especially mammalian hosts in a remote and isolated insular environment.
Although tick drags of vegetation and ground cover were unsuccessful in collecting ticks, evidence suggests that at least 2 species,
I. nipponensis and
I. persulcatus collected from local mammals and their habitats, are well established and colonized on the island.
I. nipponensis are common and widely distributed ticks among many Korean mammals, including Siberian weasels, and while
I. persulcatus is less commonly collected, it has been collected from cats on mainland Korea [
24,
25]. Most of the poor mammal fauna on the island (cats, weasels, dogs, and even possibly shrews) seem to be both intentionally and accidentally introduced by human colonization to the insular environment. Therefore, these colonized ticks might have been introduced together with the introduction of their preferred mammalian hosts (cats and weasels). Otherwise, these ticks at least benefited from the human-introduced mammals after possible and occasional influx events by migratory birds, because the nymphs of
I. nipponensis, which were rare but clearly found in live migratory birds [
5], could feed on local mammalian hosts to continue their life stages in the study area.
In this study, unlike the previous tick and tick-borne disease surveillance programs that only examined live avian hosts for ectoparasites [
1,
3–
7,
11], we examined ticks from carcasses of migratory birds on Hong Island that were killed or died of anthropogenic or natural causes on a stopover island and subsequently found unreported ticks from local fauna on the site. Our data provide the first direct evidence of tick release and influx from freshly killed birds to local environments. Our result suggests that migratory birds can serve as potential hosts for the introduction of non-native ticks, either during extended stays or as a result of death on stopover islands. Since time differences between the death of migratory avian hosts and the recovery of their carcasses influence the detection rate of ticks, infestation rates were lower (1.1%) when compared to a similar study for ticks collected from live captured migratory birds at the same study island (2.4%) [
5], 3 stopover islands (2.0%) [
7], and Jeju Island (7.95%) [
13] in Korea. Differences in the tick prevalence may imply that many undetected ticks in this study may have already detached and released into the local area from avian carcasses before collection and examination.
The possible introduction of the 2 non-native ticks to the island is closely linked with the potential introduction of non-native and emerging pathogens: e.g.,
Rickettsia japonica and
Borrelia spp. in
H. flava [
7,
26] and
Anaplasma,
Bartonella, and
Borrelia spp. in
I. turdus [
6,
26,
27]. While zoonotic pathogens are frequently identified from ticks attached to live migratory birds, the occurrence and establishment of these ticks on stopover islands during bird migrations may not occur as frequently as from dead birds, because live host birds may depart the areas before the ticks detach [
8,
9]. Most ticks observed on avian hosts were larvae and nymphs that often remained on their hosts for 2 to 4 days [
28]. However, there is no definitive information on how long the ticks remained on migratory birds in East Asia under different climatic conditions, life stages, and tick and host fauna as well as how long each species of migratory birds stays on a stopover island. Although we cannot completely rule out the possibility that the nymphs and larvae detaching from the bird carcasses originated inside the study area, our surveillance efforts on local tick fauna in vegetation and mammals suggested a little chance of local infestation of
I. turdus and
H. flava. All these questions remain to be solved through future field and experimental studies. Nevertheless, the opportunity for the introduction and establishment of non-native tick species increases when ticks detach from freshly-killed bird carcasses in search of new avian hosts or alternate hosts, e.g., cats, rodents, weasels, or non-migratory birds.
The findings of this study provide 2 implications. First, accidental death tolls of migratory birds by human-induced mortality may pose additional risks for the introduction and influx of ticks into local environments. Every year in the Republic of Korea, about 7,800,000 birds are suspected to be accidentally killed by collision with man-made transparent structures (such as roadside transparent noise barriers and building windows), and a significant part of the death toll is likely from migratory birds (Korean Ministry of Environment, unpublished data). The human-induced bird mortality (64.5%) was much higher than the natural mortality of migratory birds (24.2%) in this study area [
29]. Therefore, negative human impact on biodiversity may increase public health concerns on the emergence of non-native ticks and tick-borne diseases. Secondly, questing new hosts after an accidental tick introduction, survival in local environments, and subsequent tick colonization may be affected by locally available host densities. As human-induced changes in host distribution and diversity increase, the risk of invasion and colonization of non-native ticks will also increase.
Non-native species denotes a species that are intentionally or accidentally introduced outside of their natural range boundaries in a biogeographical context, rather than their political or jurisdictional boundaries [
30]. Therefore, even though
I. turdus and
H. flava are native ticks in mainland Korea, they were non-native species introduced by the accidental death of migratory birds to a naïve insular environment and may become invasive species when their introduction does or is likely to cause harm to human and animal health [
30]. The transport and invasion of ticks, blood-sucking ectoparasites, and zoonotic pathogens by birds along their migratory route becomes an important health concern, especially as evidence of recent climate change and altered migratory patterns may result in the introduction of non-native ectoparasites and associated pathogens not present on their previous migratory routes [
3,
4,
11,
12,
14]. However, along with the lack of information on the ecology of ticks, the detailed process and possible roles of migratory birds in the invasion and colonization of non-native ticks across physical and ecological barriers are still unclear. More organized and systematic monitoring of migratory birds, whether alive or freshly killed, combined with active tick surveillance efforts may bridge this knowledge gap over a human-dominated landscape in the era of human-induced climate change and biodiversity loss.
Notes
-
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS
We thank the members of the Bird Research Center (previously Migratory Birds Center), Korea National Park Service, who assisted with bird banding, bird counting, and carcass collecting activities in the study area. This research was supported by the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF 2018R1D1A1B07050135 awarded to CYC, 2019R1I1A1A01063760 awarded to HYN) grants funded by the Korean Government (Ministry of Education). This work was also supported, in part, by the Armed Forces Health Surveillance Division, Global Emerging Infections Surveillance (AFHSD-GEIS), Silver Spring, Maryland, USA (ProMIS ID #P0131_20_ME_03). None of the authors of this paper has a financial or personal relationship with other people or organizations that could inappropriately influence or bias the content of the paper. Authors (HCK, TAK) as employees of the U.S. Government, conducted the work as part of their official duties. Title 17 U.S.C. § 105 provides that ‘Copyright protection under this title is not available for any work of the United States Government’ Title 17 U.S.C § 101 defines a U.S. Government work as a work prepared by an employee of the U.S. Government as part of the person’s official duties. The opinions expressed herein are those of the authors and are not to be construed as official or reflecting the views of the US Department of the Army, Department of Defense, or the US Government.
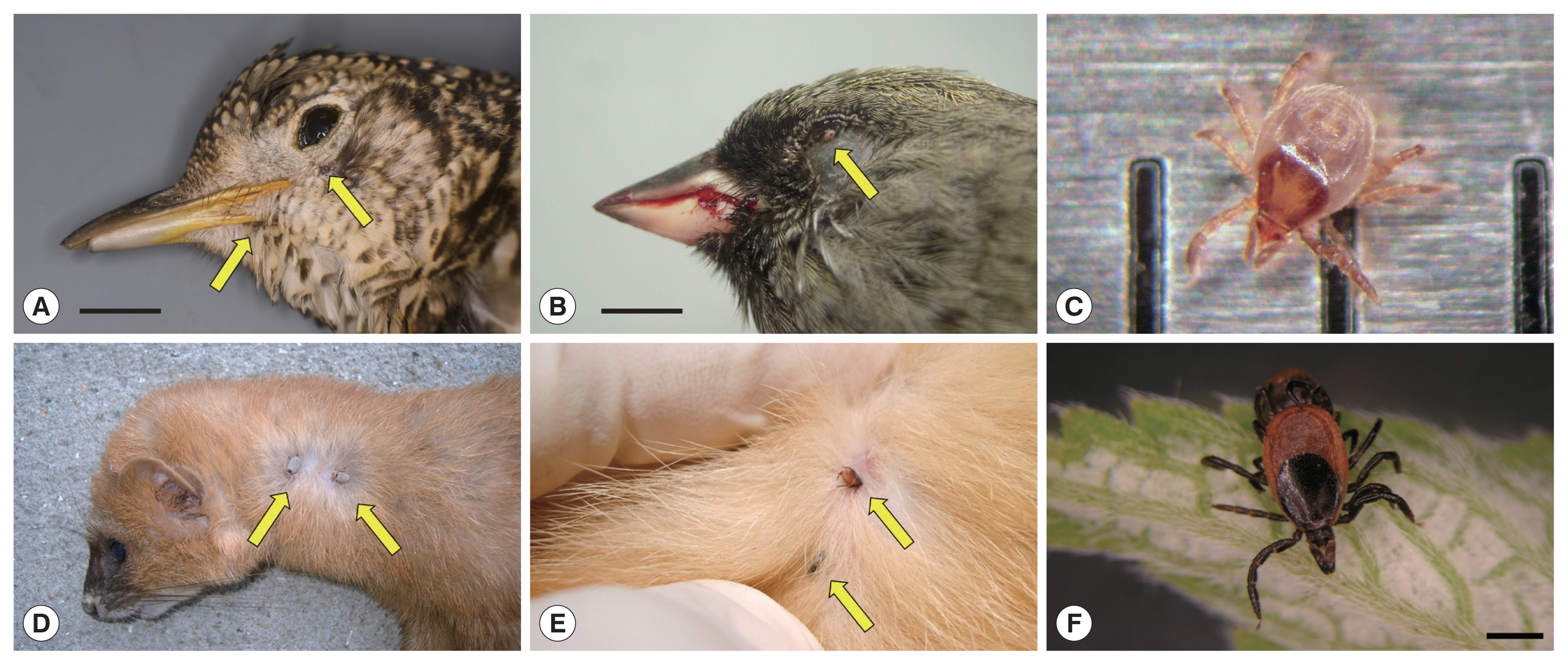
Fig. 1Ticks on fresh carcasses of migratory birds accidentally killed by window collision (upper panels) and live terrestrial mammals (lower panels) on Hong Island, Shinan County in the Republic of Korea. (A) Scaly Thrush (Zoothera aurea) with 2 Ixodes turdus ticks on its gape and chin; horizontal bar: 1.5 cm. (B) Male Black-faced Bunting (Emberiza spodocephala) with one I. turdus on its lower eyelid; note the blood on the bill due to head trauma from collision; horizontal bar: 0.5 cm. (C) An active I. turdus nymph escaped from a dead Scaly Thrush; the distance between 2 consecutive vertical bars is 1 mm. (D) Siberian Weasel (Mustela sibirica) with 2 adult I. niponnesis. (E,F) Two adult I. nipponensis found on and collected from a feral cat (Felis catus); horizontal bar: 1 mm.
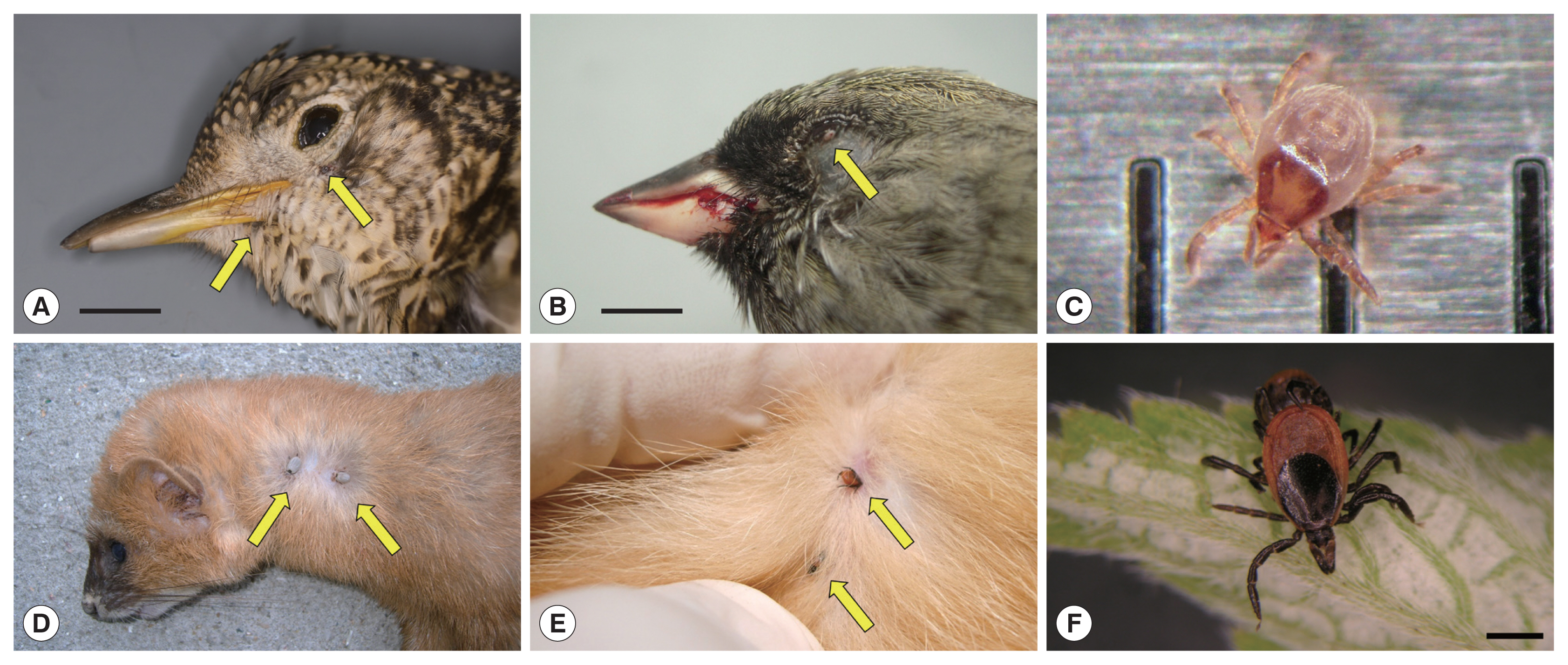
Fig. 2Typical morphological characteristics of the 2 tick genera, Haemaphysalis and Ixodes, collected from birds on Hong Island, Shinan County in the Republic of Korea; ventral views of (A) Haemaphysalis flava and (B) Ixodes turdus. Horizontal scale bars: 100 μm.

Table 1Number of ticks, by species and stage of development, collected from 711 avian carcasses on Hong Island (Hong-do), a migratory bird stopover in the Republic of Korea, in 2008 and 2009. Only bird species with ticks were represented
Table 1
|
Avian host |
No. carcasses |
No. with ticks (%)a
|
Tick species |
Stage of development |
|
|
Larvae |
Nymphs |
Total |
|
Scaly Thrush |
24 |
3 (12.5) |
Ixodes turdus
|
3 |
6 |
9 |
|
Zoothera aurea
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Pale Thrush |
41 |
2 (4.8) |
Ixodes turdus
|
0 |
3 |
3 |
|
Turdus pallidus
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Thick-billed Shrike |
1 |
1 (100) |
Haemaphysalis flava
|
0 |
2 |
2 |
|
Lanius tigrinus
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Black-faced Bunting |
66 |
1 (1.5) |
Ixodes turdus
|
0 |
1 |
1 |
|
Emberiza spodocephala
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Japanese White-eye |
23 |
1 (4.3) |
Haemaphysalis flava
|
0 |
1 |
1 |
|
Zosterops japonicus
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Total |
155 |
8 (5.2) |
|
3 |
13 |
16 |
References
- 1. Miyamoto K, Nakao M, Fujita H, Sato F. The ixodid ticks on migratory birds in Japan and isolation of Lyme disease spirochetes from bird-feeding ticks. Jpn J Sanit Zool 1993;44:315-326. https://doi.org/10.7601/mez.44.315
- 2. Proctor NS, Lynch PJ. Manual of Ornithology: Avian Structure and Function. Yale University Press; New Haven, USA. 1993.
- 3. Kinsey AA, Durden LA, Oliver JH Jr. Tick infestations of birds in coastal Georgia and Alabama. J Parasitol 2000;86:251-254. https://doi.org/10.1645/0022-3395(2000)086[0251:TIOBIC]2.0.CO;2
- 4. Morshed MG, Scott JD, Fernando K, Beati L, Mazerolle DF, Geddes G, Durden LA. Migratory songbirds disperse ticks across Canada, and first isolation of the Lyme disease spirochete, Borrelia burgdorferi, from the avian tick, Ixodes auritulus. J Parasitol 2005;91:780-790. https://doi.org/10.1645/GE-3437.1
- 5. Kim HC, Ko SJ, Choi CY, Nam HY, Chae HY, Chong ST, Klein TA, Sames WJ, Robbins RG, Chae JS. Migratory bird tick surveillance, including a new record of Haemaphysalis ornithophila Hoogstraal and Kohls 1959 (Acari: Ixodidae) from Hong-do (Hong Island), Republic of Korea. System Appl Acarol 2009;14:3-10. https://doi.org/10.11158/saa.14.1.1
- 6. Kang JG, Kim HC, Choi CY, Nam HY, Chae HY, Chong ST, Klein TA, Ko S, Chae JS. Molecular detection of Anaplasma, Bartonella, and Borrelia species in ticks collected from migratory birds from Hong-do Island, Republic of Korea. Vector-borne Zoonotic Dis 2013;13:216-225. https://doi.org/10.1089/vbz.2012.1149
- 7. Seo HJ, Noh J, Kim HC, Chong ST, Klein TA, Park CU, Choi CY, Kwon YS, Kim M, Min S, Park Y, Yoo MS, Cho YS. Molecular detection and phylogenetic analysis of Anaplasma and Borrelia species in ticks collected from migratory birds at Heuksan, Hong, and Nan islands, Republic of Korea. Vector-borne Zoonotic Dis 2021;21:20-31. https://doi.org/10.1089/vbz.2020.2629
- 8. Ishiguro F, Takada N, Masuzawa T, Fukui T. Prevalence of Lyme disease Borrelia spp. in ticks from migratory birds on the Japanese mainland. Appl Environ Microbiol 2000;66:982-986. https://doi.org/10.1128/AEM.66.3.982-986.2000
- 9. Bjöersdorff A, Bergstrom S, Massung RF, Haemig PD, Olson B. Ehrlichia-infected ticks on migrating birds. Emerg Inf Dis 2001;7:877-879. https://doi.org/10.3201/eid0705.017517
- 10. Waldenström J, Lundkvist A, Falk KI, Garpmo U, Bergström S, Lindegren G, Sjöstedt A, Mejlon H, Fransson T, Haemig PD, Olsen B. Migrating birds and tickborne encephalitis virus. Emerg Inf Dis 2007;13:1215. https://doi.org/10.3201/eid1308.061416
- 11. Pietzsch ME, Mitchell R, Jameson LJ, Morgan C, Medlock JM, Collins D, Chamberlain JC, Gould EA, Hewson R, Taylor MA, Leach S. Preliminary evaluation of exotic tick species and exotic pathogens imported on migratory birds into the British Isles. Vet Parasitol 2008;155:328-332. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.vetpar.2008.05.006
- 12. Oh MR, Moon KH, Kim SY, Kim YG, Choi CY, Kang CW, Kim HJ, Lee KK, Yun YM. Prevalence of Anaplasma sp. in Thrushes (Family Turdidae) in Jeju Island, Republic of Korea. J Vet Clin 2014;31:206-211. https://www.kci.go.kr/kciportal/ci/sereArticleSearch/ciSereArtiView.kci?sereArticleSearchBean.artiId=ART001886563
- 13. Choi CY, Kang CW, Kim EM, Lee S, Moon KH, Oh MR, Yamauchi T, Yun YM. Ticks collected from migratory birds, including a new record of Haemaphysalis formosensis, on Jeju Island, Korea. Exp Appl Acarol 2014;62:557-566. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10493-013-9748-9
- 14. Cumming GS, van Vuuren DP. Will climate change affect ectoparasite species ranges? Global Ecol Biogeogr 2006;15:486-497. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1466-822X.2006.00241.x
- 15. Thorup K, Tøttrup AP, Rahbek C. Patterns of phenological changes in migratory birds. Oecologia 2007;151:697-703. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00442-006-0608-8
- 16. Choi CY, Nam HY. Migrating dragonflies: famine relief for resident Peregrine falcons Falco peregrinus on islands. Forktail 2012;28:149-151. https://www.orientalbirdclub.org/forktail28
- 17. Ministry of Culture and Information. Natural Conservation Area Hanlasan and Hongdo (Natural Monument No. 187 & 170): Report of the Academic Survey of Mt. Hanlasan and Is. Hongdo. Ministry of Culture and Information; Seoul, Korea. 1968, pp 367-384.
- 18. Lee AN, Park YC. Terrestrial mammalian fauna in Dadohaehaesang National Park. J Nat Park Res 2010;1:150-156. (in Korean). https://www.earticle.net/Article/A181347
- 19. Hoogstraal H, Kohls GM. The Haemaphysalis ticks (Acarina: Ixodidae) of birds. 1. H. ornithophila n. sp. from Burma and Thailand. J Parasitol 1959;45:417-420. https://doi.org/10.2307/3274392
- 20. Yamaguti N, Tipton VJ, Keegan HL, Toshioka S. 1971;Ticks of Japan, Korea and the Ryukyu Islands. Brigham Young Univ Sci Bull Biol Series 15:1-226. https://scholarsarchive.byu.edu/byuscib/vol15/iss1/1
- 21. Ko S, Kang JG, Kim SY, Kim HC, Klein TA, Chong ST, Sames WJ, Yun SM, Ju YR, Chae JS. Prevalence of tick-borne encephalitis virus in ticks from southern Korea. J Vet Sci 2010;11:197-203. https://doi.org/10.4142/jvs.2010.11.3.197
- 22. Guglielmone AA, Robbins RG, Apanaskevich DA, Petney TN, Estrada-Peña A, Horak IG. The Hard Ticks of the World (Acari: Ixodida: Ixodidae). Dordrecht, Netherlands. Springer; 2014, pp 1-738 https://doi.org/10.1007/978-94-007-7497-1
- 23. Kim HC, Han SH, Chong ST, Klein TA, Choi CY, Nam HY, Chae HY, Lee H, Ko S, Kang JG, Chae JS. Ticks collected from selected mammalian hosts surveyed in the Republic of Korea during 2008–2009. Korean J Parasitol 2011;49:331-335. https://doi.org/10.3347/kjp.2011.49.3.331
- 24. Chae JB, Kang JG, Kim HC, Chong ST, Lee IY, Shin NS, Chae JS. Identification of tick species collected from wild boars and habitats of wild boars and domestic pigs in the Republic of Korea. Korean J Parasitol 2017;55:185-191. https://doi.org/10.3347/kjp.2017.55.2.185
- 25. Parola P, Paddock CD, Raoult D. Tick-borne rickettsioses around the world: emerging diseases challenging old concepts. Clin Microbiol Rev 2005;18:719-756. https://doi.org/10.1128/CMR.18.4.719-756.2005
- 26. Nakao M, Miyamoto K. Isolation of spirochetes from Japanese ixodid ticks, Ixodes tanuki, Ixodes turdus, and Ixodes columnae. Jpn J Sanit Zool 1993;44:49-52. https://doi.org/10.7601/mez.44.49
- 27. Fukunaga M, Hamase A, Okada K, Inoue H, Tsuruta Y, Miyamoto K, Nakao M. Characterization of spirochetes isolated from ticks (Ixodes tanuki, Ixodes turdus, and Ixodes columnae) and comparison of the sequences with those of Borrelia burgdorferi sensu lato strains. Appl Environ Microbiol 1996;62:2338-2344. https://doi.org/10.1128/aem.62.7.2338-2344.1996
- 28. Morris SR, Ertel MC, Wright MP. 2007The incidence and effects of ticks on migrating birds at a stopover site in Maine. Northeast Natural 2007;14:171-182. https://www.jstor.org/stable/4499908
- 29. Bing GC, Choi CY, Nam HY, Park JG, Hong GP, Kim SJ, Chae HY, Choi YB. Causes of mortality in birds at stopover islands. Korean J Ornithol 2012;19:23-31.
- 30. Beck KG, Zimmerman K, Schardt JD, Stone J, Lukens RR, Reichard S, Randall J, Cangelosi AA, Cooper D, Thompson JP. Invasive species defined in a policy context: recommendations from the federal invasive species advisory committee. Invasive Plant Sci Manag 2008;1:414-421. https://doi.org/10.1614/IPSM-08-089.1