Abstract
This study was done to provide an overview of the latest trichomoniasis status in Korea by finding disease clusters and analyzing temporal trends during 2012–2020. Data were obtained from the Health Insurance Review & Assessment Service (HIRA) of Korea. SaTScan and Joinpoint programs were used for statistical analyses. Gyeonggi-do had the highest average population and highest number of cases. The high incidence of T. vaginalis infections were observed among women aged 40–49 and 30–39 years (33,830/year and 33,179/year, respectively). Similarly, the 40–49 and 30–39 age group in men showed the highest average cases (1,319/year and 1,282/year, respectively). Jeollabuk-do was the most likely cluster, followed by Busan/Gyeongsangnam-do/Ulsan/Daegu and Jeju-do and Gwangju. Urban and rural differences were prominent. Trichomoniasis has decreased significantly in most clusters, except for Incheon. Trichomoniasis was decreasing in women recently after peaking around 2014. Men showed different trends according to age. Trichomoniasis was increasing in the 10–39 age groups, but decreasing in the 40–59 age groups. This study might provide an analytic basis for future health measures, policy-makers, and health authorities in developing effective system for prevention of trichomoniasis.
-
Key words: Trichomonas, HIRA, cluster, trend, spatial analysis, temporal analysis, SaTScan, Joinpoint
INTRODUCTION
Trichomoniasis is one of the most common sexually transmitted infection (STI) globally. The responsible pathogen,
Trichomonas vaginalis, is a flagellate protozoan that infects the human vagina, prostate gland, and urethra [
1]. The majority of women and men with trichomoniasis are asymptomatic [
2,
3], but it may cause vaginitis and cervicitis in women, and serious complications including infertility, preterm birth, and pelvic inflammatory disease [
4,
5]. Although the incidence is lower in men, it may cause nongonococcal urethritis, prostatitis, epididymitis, and infertility [
6,
7]. Cervical neoplasia [
8] and prostate cancer are known to be associated with trichomoniasis [
9]. It is also a high-risk factor for HIV and other STIs, and thus may pose a significant public health problem [
10]. According to the WHO, 170 million people are believed to be infected annually, and it is more prevalent than
Chlamydia trachomatis,
Neisseria gonorrhoeae, and syphilis combined. Domestically, 10.4% of women complaining of vaginal symptoms and signs have been reported to be infected in Korea [
11].
Korea has a complete full health-coverage of its population, and the clinical data from the Healthcare Bigdata Hub provided by the Health Insurance Review&Assessment Service (HIRA) of Korea has been used in this study, thereby representing the whole Korean population. Our study shows the results of a 9 year-survey.
We discuss the spatial infection clusters and infection trend present during this temporal window. SaTScan and Joinpoint programs were used to locate and statistically test these clusters and determine the most recent trend of trichomoniasis in Korea.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Ethics statement
This study was performed under the regulation of the IRB Committee of The Catholic University of Korea (MIRB-2020 1127-002). This research adhered to the tenets of the Declaration of Helsinki.
Data Source and Definition
The nationwide trichomoniasis cases for 9 years (2012–2020) from the 17 administrative districts in Korea and age-period cohorts (5-year interval) according to sex were obtained from the HIRA of Korea. (
https://opendata.hira.or.kr/home.do. [cited 2020 October]) The HIRA collects all relevant information from the records of all the patients at almost all hospitals and clinics in Korea, and the accuracy and reliability of its data have been systemically validated [
12].
The population data of 17 administrative divisions 2012–2020 were obtained from the Korean Statistical Information Service (
https://kosis.kr/index/index.do [cited 2021 October]). The geographical locations of the cases were set to the latitude and longitude of administrative center as the search point since the case data were compiled by administrative district unit. The population and number of cases were summed up as accumulated counts and numbers for the full period to evaluate overall trichomoniasis. Case numbers were adjusted for the particular district’s population (cases/1,000,000) to facilitate comparison between the different districts (
Table 1).
The cases were stratified into age groups, under 0–9, 10–19, 20–29, 30–39, 40–49, 50–59, 60–69, 70–79, and 80 years and over, according to sex (
Table 2). The total study period was evaluated initially, and it was further divided into tertiles (2012–2014, 2015–2017, 2018–2020) to evaluate the trend more specifically.
SaTScan (v10.0) [
13] was used to detect clusters and evaluate their significance through simulation. The discrete Poisson model was used since the case data were linked to their background population at risk. Spatial scan analysis detects clusters with maximum likelihood ratio by creating a circular window on a map and scanning the study area by varying the window size.
The window size determines a percentage of the population at risk within its boundaries [
14]. Spatial scan statistic works best for detecting spatial clusters, and may be effective in the study of small numbered cases, such as novel or infrequent outbreaks [
15,
16]. It is important to find an appropriate set value of cluster size because a large value could hide the effect of small core clusters, while a small value could overlook the regional pattern of clusters [
17]. Various studies have been performed to address this issue, and SaTScan has been progressively updated to address these results and implemented them on the new versions [
18,
19]. Therefore, we selected 50% window size for statistical analyses as per the users’ guide in the present study.
General trend of the disease according to administrative districts was determined through spatial variation in temporal trend analysis, by scanning for clusters with either increasing or decreasing rates.
Statistical significance of the clusters was calculated using the Monte Carlo simulations with an inference of 9,999 [
20] and expressed as
P-value. A significance level of alpha <0.05 was used as a standard. QGIS software (v3.16) was used to visualize cluster patterns on a map. The clusters and trends are shown in order of log likelihood ratio. The study analyzed data from 2012 to 2020.
Disease trend according to sex and age was determined using Joinpoint Regression Program (v4.9.0.0)(
https://surveillance.cancer.gov/joinpoint/) [
21,
22], The present study used crude rates computed by the Joinpoint software, whereby the number of new cases occurring in a specified population per year is expressed as the number of cases per 100,000 population at risk.
A maximum number of 1 joinpoint was used, making it possible to see whether the incidence is better explained by a single trend or by the existence of multiple trend segments during the study period. Briefly, joinpoint regression identifies best-fitting break-points (years) in which there was a significant change in the incidence rate (crude rates) [
23]. The results were summarized as annual percentage changes (APC) with the best model fit for each trend segment. Statistical significance was calculated with an inference of 9,999 and expressed as
P-value. A significance level of alpha <0.05 was used as a standard.
The results were also output in graphs by the software, where crude rates and years are displayed. In some cases, the years are displayed twice, because the crude rates are calculated by mid-year, and multiple trends reflect this aspect. The final selected models from statistically significant age groups according to sex were output into a single graph to view multiple models simultaneously.
RESULTS
General characteristics
A total of 1,178,505 trichomoniasis cases was reported, with an average of 130,689 cases/year during the study period of 2012 to 2020. Gyeonggi-do had the highest average population (12,726,986) and highest average number of cases (30,055). After adjusting for the population (cases/1,000,000), Busan had the highest average crude rate of 3,238. It also had the highest crude rate in 2016 at 4,535. Major cities tended to have a higher crude rate (
Table 1).
The 40–49 and 30–39 age groups in women showed the highest average cases of trichomoniasis (33,830 and 33,179/year, respectively). Similarly, 40–49 and 30–39 age groups in men showed the highest average cases (1,319 and 1,282/year, respectively). After adjusting for the population (cases/1,000,000), women and men in the 30–39 age group had the highest crude rate (8,956 and 335, respectively). Women tended to have a higher crude rate, but it peaked around 2014, and continued to decrease steadily. On the other hand, the 30–39 age group in men showed a peak around 2017 but remained high, or in the case of 40–49 age group, a stationary crude rate was observed (
Table 2).
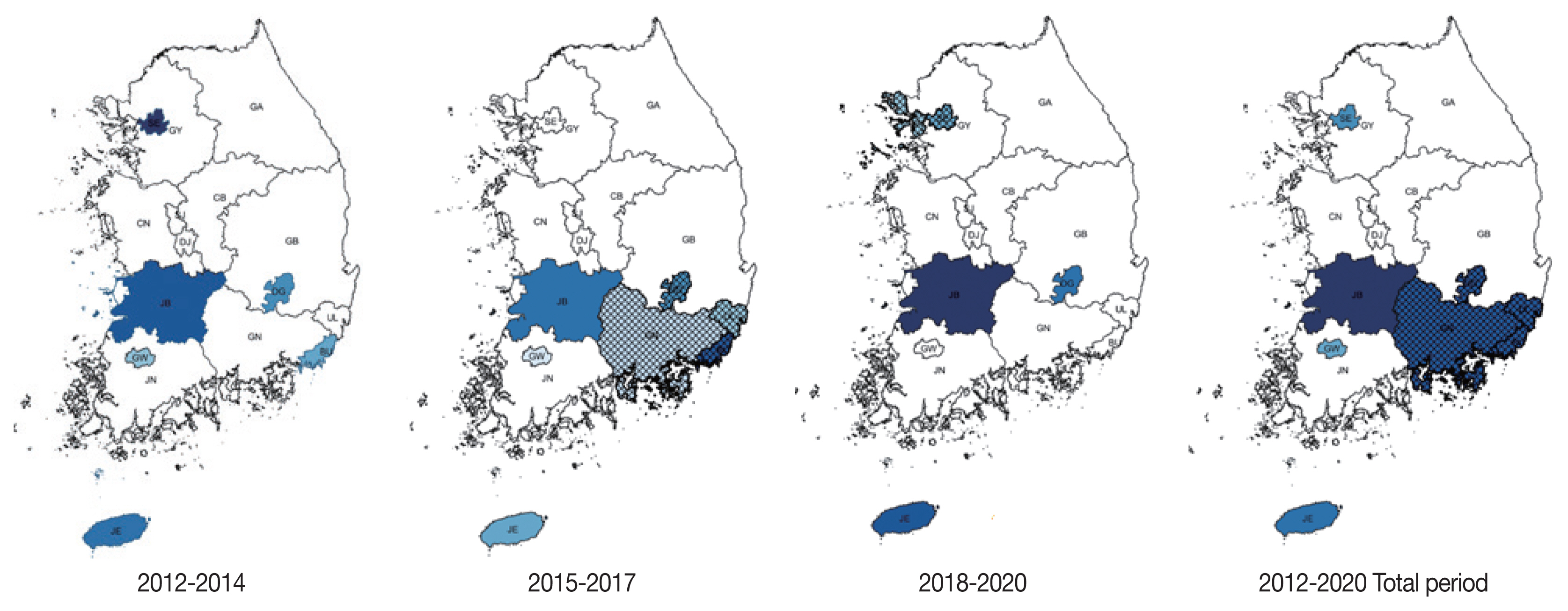
Jeollabuk-do was the most likely cluster (MLC) with relative risk (RR) and log likelihood ratio (LLR) of 1.70 and 7895.184 for the total study period. The joint cluster of Busan/Gyeongsangnam-do/Ulsan/Daegu was next (RR=1.27, LLR=5,771. 405), followed by Jeju-do (RR=1.86, LLR=4,159.725), Seoul (RR=1.19, LLR=2,998.914) and Gwangju (RR=1.12, LLR= 221.612). Urban and rural differences were prominent. Most major metropolitan areas except for Daejon and Sejong were clusters at some point during the study period. In contrast, only Jeollabuk-do and Gyeongsangnam-do were significant clusters among the provinces (
Table 3;
Fig. 1).
Major cities (Seoul, Daegu, Busan, Gwangju), Jeju-do and Jeollabuk-do were significant clusters at the first tertile of 2012–2014. During the second tertile of 2015–2017, Gyeongsangnam-do and Ulsan became significant clusters, while Seoul became not significant. On the third tertile, Incheon became a significant joint cluster together with Seoul. Gyeongsangnam-do, Busan and Ulsan were not further significant. Seen altogether, the southern regions seem to be significant clusters.
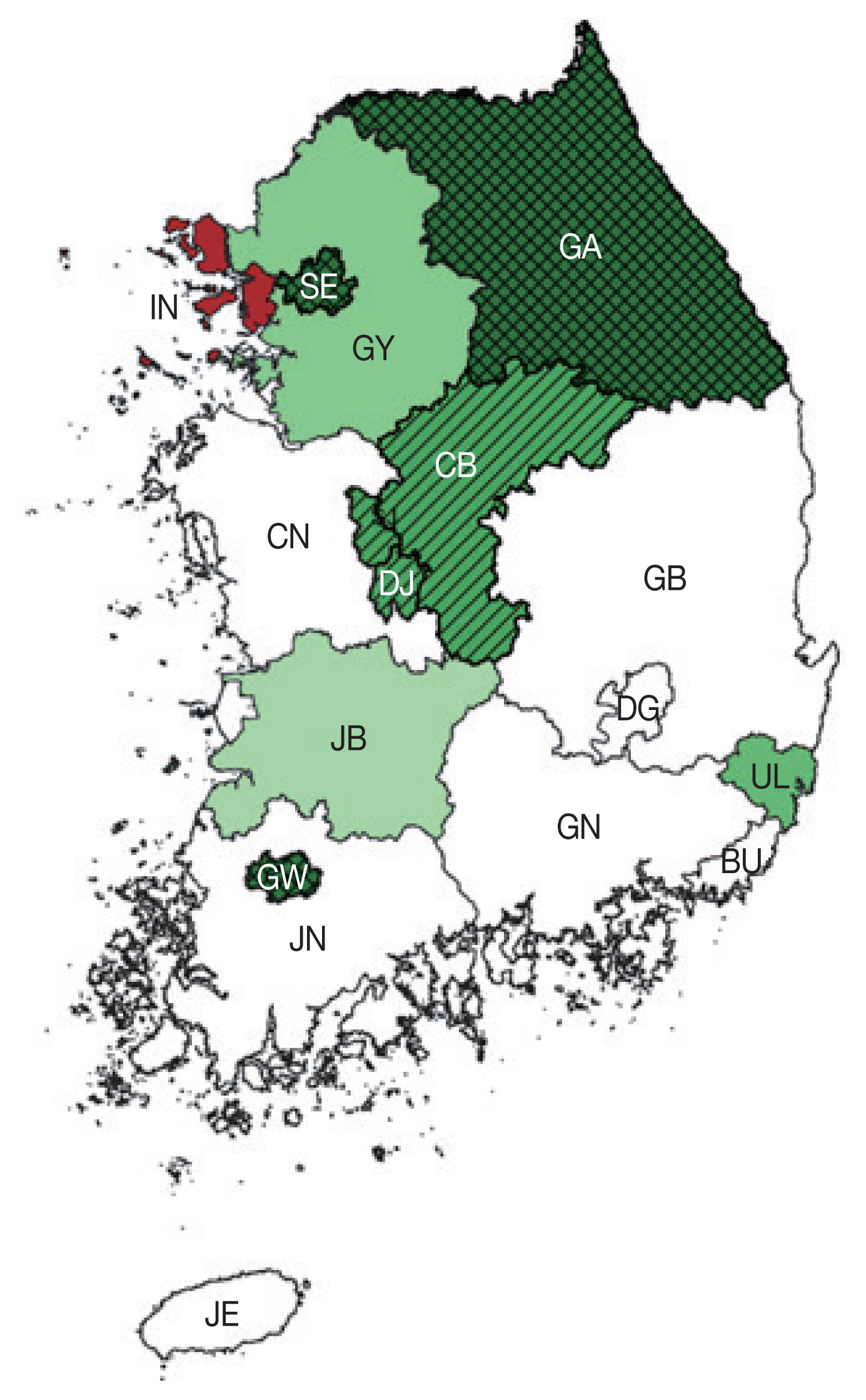
Spatial variation in temporal trends analysis
Temporal trends analysis for the whole study period showed that trichomoniasis rate was decreasing in most clusters. Incheon was the only cluster with increasing rate (0.72%, LLR=740.745). Chungcheongbuk-do/Sejong/Daejeon joint cluster (−8.83%, LLR=305.845) showed the greatest decrease. Gangwon-do/Gwangju/Seoul joint cluster (−7.34%, LLR=852.650), Ulsan (−0.0024%, LLR=289.338), Gyeonggi-do (−3.73%, LLR=216.829) and Jeollabuk-do (−2.52%, LLR=168.491) all showed significant decreases (
Table 4;
Fig. 2).
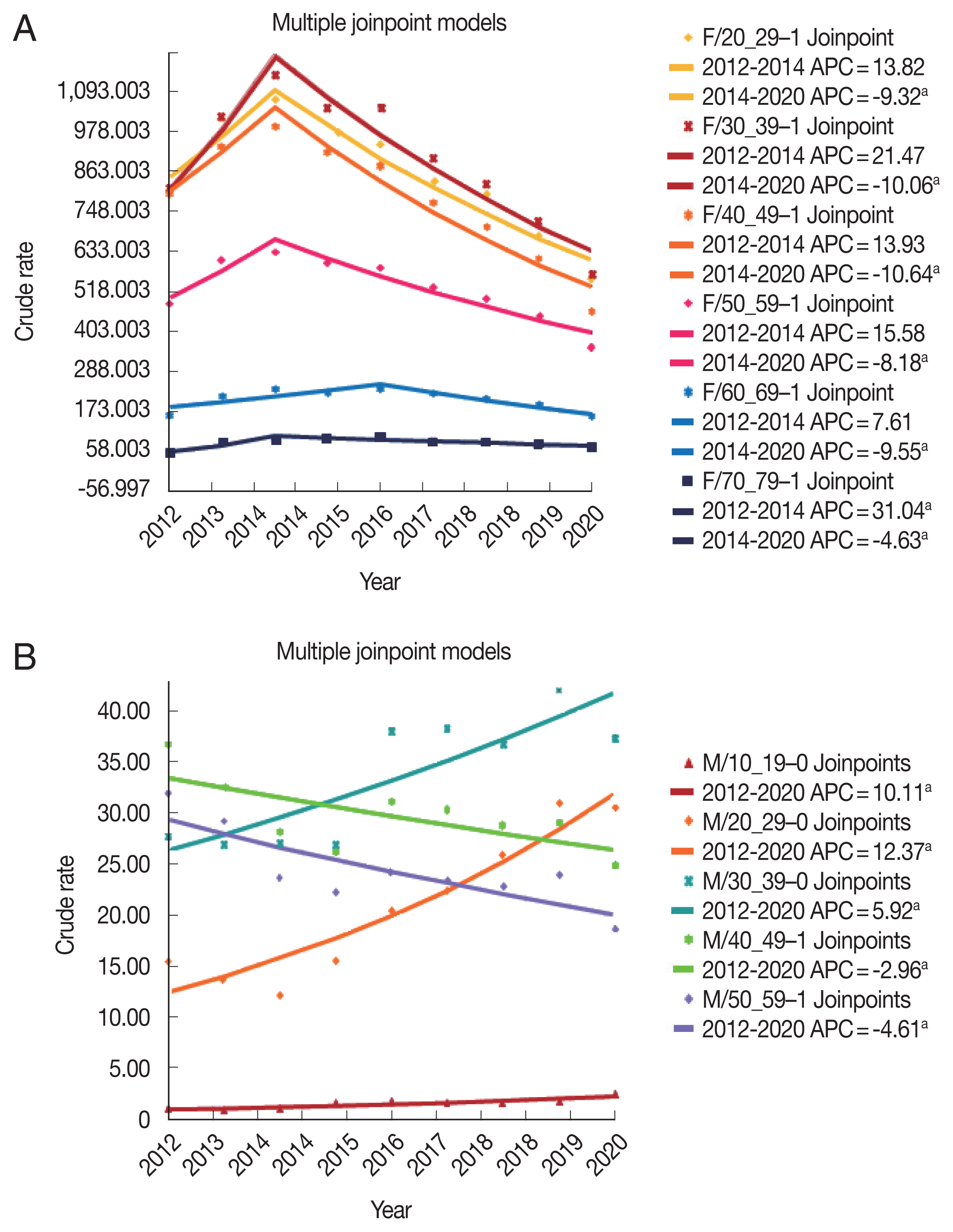
Changes in crude rate of women and men are shown in
Fig. 3. In women, the 20–59 age groups showed sharp increasing rates until 2014 (trend 1) but were not significant. From 2014 on, they showed significant decrease (trend 2). The 60–69 age group showed a more gradual rise and decrease, which was significant at trend 2. The 70–79 age group showed an even more gradual change, but it was significant throughout the whole period. Overall, trichomoniasis seems to be decreasing in women currently after peaking around 2014 (
Fig. 3A). Although the crude rate is far smaller than that of women, men showed different trends according to age. The 10–39 age groups showed significant increasing rates throughout the study period. In contrast, the 40–59 age groups showed significant decrease during the same period (
Fig. 3B).
A joinpoint was observed in all female age groups of 10–19 and older, although the increasing first trend was not significant except for the 70–79 age group (31%,
P=0.026). The first trend was seen mostly during 2012–2014.
Trichomonas infection decreased significantly during the second trend, which was mostly 2014–2020, in most age groups (all
P<0.05), except for the 10–19 and ≥80 age groups (
P=0.053 and 0.050, respectively). On the other hand, no joinpoint was observed in the male age groups. The 10–19, 20–29, and 30–39 age groups showed a significant increase while the 40–49 and 50–59 age groups showed significant decrease. Although not significant, increasing rates were observed in the 60–69 and older age groups (
Table 5).
DISCUSSION
The present study provides an overview of the latest Trichomonas infection status in Korea by determining trichomoniasis clusters and evaluating temporal trends according to districts and age or sex during 2012–2020.
The incidence and prevalence of trichomoniasis are known to be varied depending on the population, time, and region, but they are higher in women and older age groups compared to men or younger age groups [
24]. Joo et al. [
25] have reported that trichomoniasis emerged as the most common non-viral sexually transmitted diseases (STD) among the total population during 2009–2014. Some overlap occurs, but in the current study, we strived to further analyze more recent data statistically.
Gyeonggi-do had the highest average number of cases, not surprising as this province also has the highest average population. Busan had the highest average crude rate after adjusting for the population. Busan is one of the major metropolitan cities in Korea, and major cities tended to have a higher crude rate compared to the provinces.
The 40–49 and 30–39 age groups in women showed the highest average cases of trichomoniasis, and this was also observed in the same age groups of men. After adjusting for the population, both women and men in the 30–39 age group had the highest crude rate. These findings were consistent with that reported by Joo et al. [
25]. Women tended to have a higher crude rate, but it peaked around 2014 and decreased steadily. On the other hand, the 30–39 age group in men showed a peak around 2017 but remained high, or in the case of 40–49 age group, a stationary crude rate was observed.
Most major metropolitan areas were clusters at some point during the study period. This might have been caused by urban and rural differences, as a high population density or ready access to health resources in major cities seems to be the most probable cause.
Jeollabuk-do and Gyeongsangnam-do were clusters among the provinces. To our surprise, Jeollabuk-do was the most likely cluster for the whole study period, and this was a finding also noted by Joo et al. [
25]. They have reported this finding for 2009–2014, so trichomoniasis is still prevalent for over a decade. The cause is still unclear. Although Gyeongsangnam-do is a province, it is near or borders the major cities of Busan, Ulsan, and Daegu. This might have caused in it becoming a joint cluster. The southern regions seem to be significant clusters. Jeju-do is a province but being a semi-tropical island in the southern region, it is a favorite travelling destination. A large influx of outsiders may have caused in it being a cluster.
Trichomoniasis was decreasing in most clusters, except for Incheon. Incheon is a major metropolitan city and has several characteristics that might have had an influence in the outcome. Besides having a large population and industry itself, it also has a major seaport and airport that serves as a major transition point for adjacent Seoul and Gyeonggi-do, the largest city and province, respectively, in terms of population. A large number of people living in Incheon commutes to the surrounding areas. It also has many islands, which means limited health resources spread thinly over a vast area.
Chungcheongbuk-do/Sejong/Daejeon joint cluster showed the greatest decrease. Although Daejon is a major city, its nearby Chungcheongbuk-do has a low population compared to the other provinces. Sejong is a fairly new city that was only inaugurated in 2012. It is also a specialized city with mainly public and administrative organizations, so besides its size, its population composition tends to be different from other cities. These factors may have contributed to the significant decrease in trichomoniasis. A low population density might also have had an influence in Gwangwon-do. It was also decreasing in most metropolitan cities. Increased awareness of the disease and introduction of more sensitive diagnostic tests might have had an influence, as initially the incidence had risen around 2014, and then decreased steadily [
25].
Trichomoniasis cases increased in most female age groups during 2012–2014 but were not significant except for the elderly (70–79 age group). Kim et al. [
26] have reported a similar finding in a previous study. However, after around 2014, trichomoniasis decreased significantly in nearly all age groups. The Special Law on Sex Trade was enacted in September 2004. Prostitution has always been illegal in Korea, but up to then the authorities had turned a blind eye to it. Since then, prohibition was strictly implemented, and it might also have had an influence.
Trichomoniasis in the male age groups revealed a different trend. The 40–49 and 50–59 age groups showed significant decrease, but in comparison to the same age group in women, the decrease was progressively linear. The decrease might be explained like in women above. On the other hand, a marked age demarcation was noted around the age of 40. It showed a significantly progressive increasing trend in the age groups below 40. According to a 2012 study by the Ministry of Gender Equality and Family, runaway youths, that included at-risk youths and same age group students, have been exposed to various sex-related problems. At-risk youths, compared to their counterpart students, experienced 3 times more prostitution (11.0% vs. 3.3%). Sexual relationship was even higher, at-risk youths experiencing 6 times more than the comparable students (36.3% vs. 5.6%) [
http://www.mogef.go.kr/mp/pcd/mp_pcd_s001d.do;jsessionid=fqV5nBCWAC9phOl6rwJ-kN5h.mogef20?mid=plc502&bbtSn=691646]. Unfortunately, rapid changes in society might aggravate this kind of problem further, and it might also have an impact on future trends of the infection.
In conclusion, our study was able to recognize the current status and trend of trichomoniasis in Korea, augmenting the study by Joo et al. [
25]. This study might provide an analytic basis for future health measures and help policy-makers and health authorities in developing effective system for prevention of trichomoniasis.
Notes
-
The authors declare no conflict of interest related to this study.
ACKNOWLEDGMENT
This study was supported by a research grant from the Korean Association of Health Promotion (No. 2015-01), Republic of Korea.
Fig. 1Regional clusters for T. vaginalis infection from 2012 to 2020. Light to dark blue gradient represents increasing order of log likelihood ratio. Lattice patterns represent a joint cluster. Area codes represent administrative districts of the Korean government. SE, Seoul; BU, Busan; IN, Incheon; DG, Daegu; GW, Gwangju; DJ, Daejeon; UL, Ulsan; GY, Gyeonggi-do; GA, Gangwon-do; CB, Chungcheongbuk-do; CN, Chungcheongnam-do; JB, Jeollabuk-do; JN, Jeollanam-do; GB, Gyeongsangbuk-do; GN, Gyeongsangnam-do; JE, Jeju-do; SJ, Sejong.
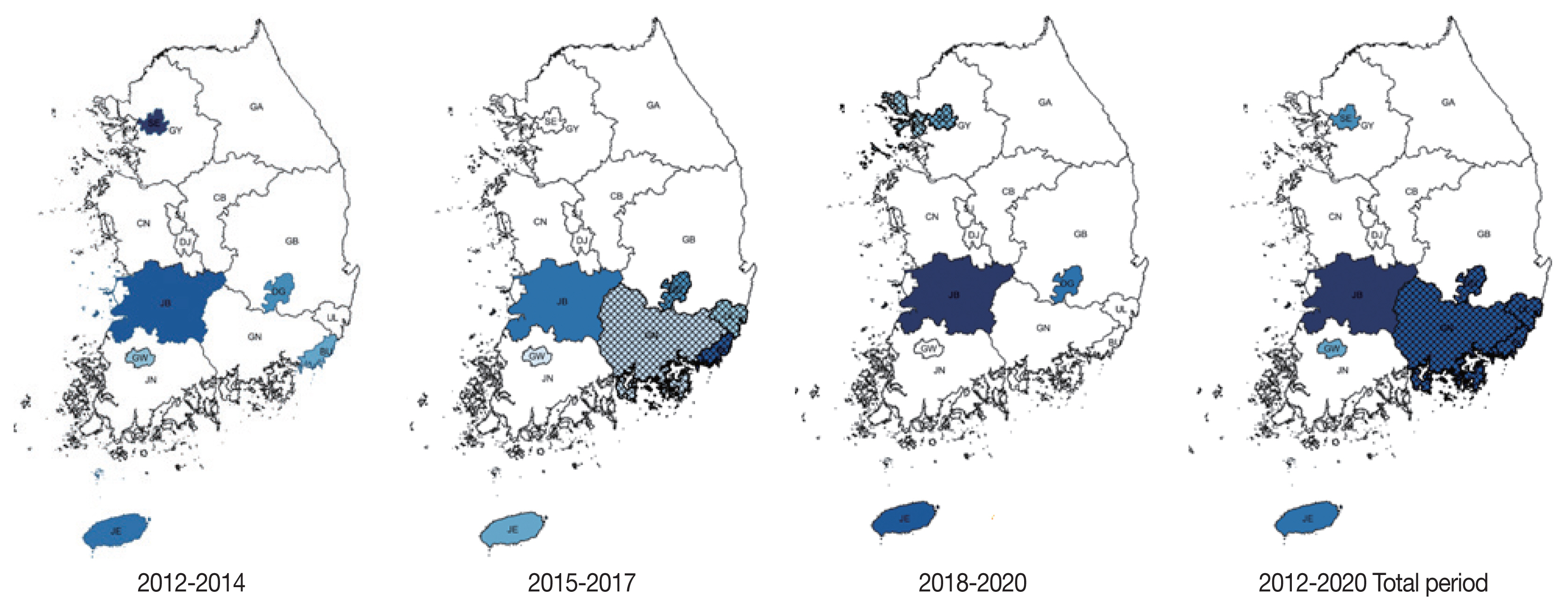
Fig. 2Spatiotemporal trend analysis of trichomoniasis according to districts. Green and red indicate decreasing and increasing rate of infection within the cluster, respectively. Light to dark green gradient represents increasing order of log likelihood ratio. Lattice patterns and dashed lines represent joint clusters in decreasing order of log likelihood ratio. Area codes represent administrative districts of the Korean government. SE, Seoul; BU, Busan; IN, Incheon; DG, Daegu; GW, Gwangju; DJ, Daejeon; UL, Ulsan; GY, Gyeonggi-do; GA, Gangwon-do; CB, Chungcheongbuk-do; CN, Chungcheongnam-do; JB, Jeollabuk-do; JN, Jeollanam-do; GB, Gyeongsangbuk-do; GN, Gyeongsangnam-do; JE, Jeju-do; SJ, Sejong.
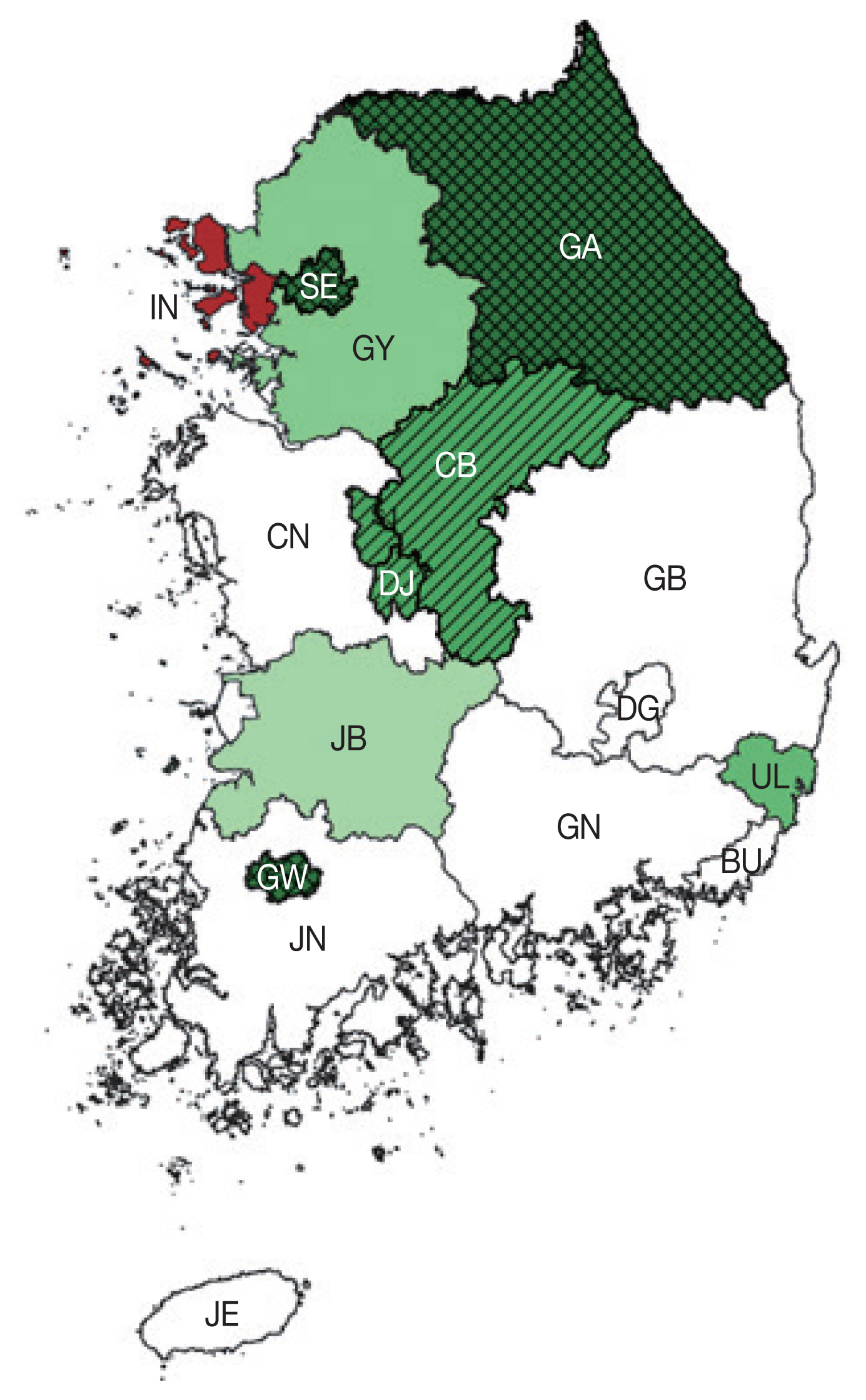
Fig. 3Trend analysis of trichomoniasis according to sex. (A) In women, the 20–59 age groups show sharp increasing rates until 2014 (trend 1), but are not significant. From 2014 on, they show significant decrease (trend 2). Annual Percentage Changes (APC) for the 20–29, 30–39, 40–49, and 50–59 age groups are −9.3, −10.1, −10.6, and −8.2, respectively. The 60–69 age group shows a more gradual rise and decrease (significant trend 2) with APC −9.6. The 70–79 age group shows an even more gradual change, but is significant throughout the whole period, with APC 31.0 and −4.6 in trend 1 and 2, respectively. (B) In men, the 10–39 age groups show significant increasing rates throughout the study period. APC for the 10–19, 20–29, and 30–39 age groups are 10.1, 12.4, and 5.9, respectively. In contrast, the 40–59 age groups show significant decrease during the same period. APC for 40–49 and 50–59 age groups are −3.0 and −4.6, respectively. Only significant trends are shown. Crude rates (adjusted cases per 100,000 population at risk) are calculated by mid-year in Joinpoint, so the program outputs 2014 (B) and 2018 (A) twice on the X axis to reflect multiple trends. aIndicates that the APC is significant at the alpha=0.05 level.

Table 1Trichomoniasis cases and adjusted infection rate for 2012–2020 according to administrative districts
Table 1
|
Average population |
Cases |
|
Total |
2012 |
2013 |
2014 |
2015 |
2016 |
2017 |
2018 |
2019 |
2020 |
Average |
|
Seoul (SE) |
9,935,068 |
260,892 |
31,920 |
39,794 |
39,697 |
28,798 |
28,665 |
25,362 |
25,716 |
22,619 |
18,321 |
28,988 |
|
Busan (BU) |
3,479,524 |
101,688 |
10,153 |
11,995 |
13,380 |
14,744 |
15,865 |
11,411 |
11,132 |
7,139 |
5,869 |
11,299 |
|
Incheon (IN) |
2,922,033 |
60,760 |
5,638 |
6,364 |
6,246 |
6,963 |
7,170 |
7,928 |
7,933 |
8,145 |
4,373 |
6,751 |
|
Daegu (DG) |
2,474,029 |
80,356 |
9,022 |
9,079 |
10,898 |
11,191 |
9,804 |
9,702 |
7,716 |
6,511 |
6,433 |
8,928 |
|
Gwangju (GW) |
1,465,451 |
37,281 |
4,126 |
5,447 |
6,561 |
5,694 |
4,704 |
2,962 |
2,812 |
2,768 |
2,207 |
4,142 |
|
Daejeon (DJ) |
1,505,918 |
22,801 |
2,047 |
3,172 |
3,444 |
3,295 |
3,703 |
2,783 |
2,016 |
1,591 |
750 |
2,533 |
|
Ulsan (UL) |
1,157,860 |
31,765 |
3,209 |
2,946 |
3,341 |
4,070 |
4,707 |
3,791 |
3,464 |
3,549 |
2,688 |
3,529 |
|
Gyeonggi-do (GY) |
12,726,986 |
270,493 |
24,131 |
33,382 |
35,730 |
35,062 |
32,439 |
32,086 |
29,050 |
26,477 |
22,136 |
30,055 |
|
Gangwon-do (GA) |
1,544,798 |
18,998 |
2,461 |
2,553 |
2,494 |
2,022 |
2,234 |
2,001 |
2,287 |
1,868 |
1,078 |
2,111 |
|
Chungcheongbuk-do (CB) |
1,587,489 |
30,868 |
3,809 |
3,966 |
4,149 |
4,143 |
4,874 |
3,212 |
2,528 |
2,440 |
1,747 |
3,430 |
|
Chungcheongnam-do (CN) |
2,088,983 |
35,073 |
3,223 |
5,004 |
5,240 |
3,387 |
3,943 |
3,636 |
3,907 |
3,293 |
3,440 |
3,897 |
|
Jeollabuk-do (JB) |
1,851,870 |
70,039 |
6,963 |
8,283 |
9,285 |
9,256 |
8,637 |
7,411 |
7,096 |
7,523 |
5,585 |
7,782 |
|
Jeollanam-do (JN) |
1,892,796 |
19,681 |
2,764 |
2,695 |
2,316 |
1,761 |
2,634 |
2,198 |
1,828 |
1,999 |
1,486 |
2,187 |
|
Gyeongsangbuk-do (GB) |
2,686,178 |
37,186 |
3,893 |
4,726 |
6,524 |
5,452 |
4,874 |
4,750 |
3,043 |
2,250 |
1,674 |
4,132 |
|
Gyeongsangnam-do (GN) |
3,355,458 |
73,496 |
7,654 |
8,636 |
9,168 |
9,473 |
11,371 |
8,868 |
8,423 |
5,615 |
4,288 |
8,166 |
|
Jeju-do (JE) |
635,639 |
26,737 |
2,948 |
3,466 |
3,262 |
2,998 |
2,921 |
2,736 |
2,916 |
2,881 |
2,609 |
2,971 |
|
Sejong (SJ) |
237,329 |
391 |
14 |
25 |
13 |
18 |
69 |
42 |
69 |
63 |
78 |
43 |
|
Total |
51,547,410 |
1,178,505 |
123,735 |
151,227 |
161,384 |
148,012 |
148,252 |
130,624 |
121,716 |
106,584 |
84,671 |
130,689 |
|
|
|
Adjusted casesa
|
|
2012 |
2013 |
2014 |
2015 |
2016 |
2017 |
2018 |
2019 |
2020 |
Average |
|
Seoul (SE) |
|
|
3,131 |
3,923 |
3,929 |
2,873 |
2,887 |
2,573 |
2,633 |
2,325 |
1,895 |
2,908 |
|
Busan (BU) |
|
|
2,869 |
3,400 |
3,802 |
4,196 |
4,535 |
3,288 |
3,235 |
2,091 |
1,730 |
3,238 |
|
Incheon (IN) |
|
|
3,172 |
3,153 |
3,755 |
3,825 |
3,331 |
3,290 |
2,611 |
2,202 |
2,186 |
3,058 |
|
Daegu (DG) |
|
|
2,250 |
2,544 |
2,505 |
2,799 |
2,886 |
3,203 |
3,222 |
3,341 |
1,808 |
2,729 |
|
Gwangju (GW) |
|
|
2,808 |
3,698 |
4,445 |
3,868 |
3,202 |
2,024 |
1,927 |
1,900 |
1,522 |
2,822 |
|
Daejeon (DJ) |
|
|
1,343 |
2,069 |
2,248 |
2,170 |
2,445 |
1,853 |
1,353 |
1,079 |
512 |
1,675 |
|
Ulsan (UL) |
|
|
2,797 |
2,547 |
2,864 |
3,468 |
4,015 |
3,254 |
2,998 |
3,091 |
2,366 |
3,045 |
|
Gyeonggi-do (GY) |
|
|
1,995 |
2,728 |
2,891 |
2,800 |
2,551 |
2,492 |
2,221 |
2,000 |
1,649 |
2,370 |
|
Gangwon-do (GA) |
|
|
1,599 |
1,655 |
1,615 |
1,305 |
1,441 |
1,291 |
1,482 |
1,212 |
699 |
1,367 |
|
Chungcheongbuk-do (CB) |
|
|
2,433 |
2,522 |
2,628 |
2,616 |
3,062 |
2,015 |
1,581 |
1,525 |
1,091 |
2,164 |
|
Chungcheongnam-do (CN) |
|
|
1,589 |
2,444 |
2,541 |
1,630 |
1,881 |
1,718 |
1,837 |
1,551 |
1,622 |
1,868 |
|
Jeollabuk-do (JB) |
|
|
3,717 |
4,422 |
4,961 |
4,950 |
4,632 |
3,996 |
3,863 |
4,136 |
3,096 |
4,197 |
|
Jeollanam-do (JN) |
|
|
1,447 |
1,413 |
1,215 |
922 |
1,383 |
1,159 |
971 |
1,070 |
803 |
1,154 |
|
Gyeongsangbuk-do (GB) |
|
|
1,443 |
1,751 |
2,416 |
2,017 |
1,805 |
1,765 |
1,137 |
844 |
634 |
1,535 |
|
Gyeongsangnam-do (GN) |
|
|
2,306 |
2,590 |
2,737 |
2,815 |
3,370 |
2,623 |
2,496 |
1,670 |
1,284 |
2,432 |
|
Jeju-do (JE) |
|
|
5,050 |
5,837 |
5,371 |
4,801 |
4,553 |
4,164 |
4,371 |
4,294 |
3,867 |
4,701 |
|
Sejong (SJ) |
|
|
124 |
205 |
83 |
85 |
284 |
150 |
220 |
185 |
219 |
173 |
|
Total |
|
|
2,429 |
2,957 |
3,144 |
2,872 |
2,868 |
2,523 |
2,349 |
2,056 |
1,634 |
2,537 |
Table 2Trichomoniasis and adjusted infection rate for 2012–2020 according to sex and age
Table 2
|
Age group |
Cases |
Average |
|
|
2012 |
2013 |
2014 |
2015 |
2016 |
2017 |
2018 |
2019 |
2020 |
|
Female |
0–9 |
94 |
104 |
108 |
71 |
102 |
83 |
102 |
69 |
45 |
86 |
|
10–19 |
2,923 |
3,407 |
3,611 |
3,063 |
3,135 |
2,900 |
2,722 |
2,250 |
1,806 |
2,869 |
|
20–29 |
25,893 |
32,105 |
33,717 |
29,219 |
30,250 |
26,821 |
25,890 |
21,939 |
17,861 |
27,077 |
|
30–39 |
32,159 |
39,862 |
43,634 |
39,300 |
38,680 |
32,364 |
29,251 |
24,647 |
18,712 |
33,179 |
|
40–49 |
34,625 |
40,986 |
43,639 |
40,146 |
38,377 |
33,067 |
29,426 |
25,218 |
18,987 |
33,830 |
|
50–59 |
18,847 |
24,284 |
25,761 |
24,898 |
24,551 |
22,390 |
21,341 |
19,282 |
15,550 |
21,878 |
|
60–69 |
3,768 |
5,038 |
5,753 |
5,975 |
6,705 |
6,562 |
6,508 |
6,314 |
5,557 |
5,798 |
|
70–79 |
1,000 |
1,480 |
1,744 |
1,762 |
1,845 |
1,702 |
1,737 |
1,649 |
1,485 |
1,600 |
|
≥80 |
143 |
248 |
288 |
287 |
333 |
307 |
340 |
354 |
323 |
291 |
|
|
Male |
0–9 |
4 |
5 |
3 |
7 |
2 |
5 |
2 |
0 |
1 |
3 |
|
10–19 |
40 |
29 |
33 |
52 |
58 |
47 |
42 |
46 |
64 |
46 |
|
20–29 |
540 |
476 |
426 |
553 |
730 |
807 |
932 |
1,113 |
1,093 |
741 |
|
30–39 |
1,159 |
1,106 |
1,081 |
1,052 |
1,472 |
1,448 |
1,371 |
1,527 |
1,325 |
1,282 |
|
40–49 |
1,665 |
1,476 |
1,278 |
1,178 |
1,396 |
1,342 |
1,248 |
1,236 |
1,049 |
1,319 |
|
50–59 |
1,258 |
1,182 |
982 |
932 |
1,033 |
1,006 |
990 |
1,049 |
815 |
1,027 |
|
60–69 |
252 |
246 |
183 |
248 |
290 |
314 |
321 |
359 |
345 |
284 |
|
70–79 |
51 |
46 |
34 |
55 |
58 |
69 |
62 |
64 |
65 |
56 |
|
≥80 |
7 |
6 |
7 |
6 |
6 |
11 |
7 |
8 |
19 |
9 |
|
|
Age group |
Adjusted casesa
|
Average |
|
|
2012 |
2013 |
2014 |
2015 |
2016 |
2017 |
2018 |
2019 |
2020 |
|
|
Female |
0–9 |
42 |
46 |
48 |
32 |
46 |
38 |
49 |
34 |
23 |
40 |
|
10–19 |
956 |
1,150 |
1,263 |
1,119 |
1,192 |
1,139 |
1,102 |
941 |
780 |
1,072 |
|
20–29 |
8,175 |
10,233 |
10,699 |
9,214 |
9,458 |
8,322 |
8,010 |
6,798 |
5,525 |
8,493 |
|
30–39 |
8,029 |
10,157 |
11,404 |
10,476 |
10,505 |
9,001 |
8,248 |
7,165 |
5,617 |
8,956 |
|
40–49 |
8,004 |
9,359 |
9,950 |
9,222 |
8,850 |
7,715 |
7,053 |
6,118 |
4,654 |
7,881 |
|
50–59 |
4,862 |
6,095 |
6,317 |
6,031 |
5,895 |
5,320 |
4,990 |
4,483 |
3,631 |
5,292 |
|
60–69 |
1,678 |
2,179 |
2,375 |
2,288 |
2,426 |
2,264 |
2,139 |
1,958 |
1,613 |
2,102 |
|
70–79 |
580 |
835 |
966 |
973 |
1,007 |
897 |
892 |
829 |
730 |
857 |
|
≥80 |
182 |
296 |
319 |
295 |
320 |
277 |
288 |
280 |
242 |
278 |
|
|
Male |
0–9 |
2 |
2 |
1 |
3 |
1 |
2 |
1 |
0 |
0 |
1 |
|
10–19 |
12 |
9 |
11 |
17 |
20 |
17 |
16 |
18 |
26 |
16 |
|
20–29 |
156 |
138 |
122 |
157 |
205 |
225 |
259 |
311 |
306 |
209 |
|
30–39 |
278 |
270 |
271 |
268 |
382 |
384 |
368 |
421 |
374 |
335 |
|
40–49 |
369 |
325 |
281 |
261 |
313 |
304 |
289 |
290 |
249 |
298 |
|
50–59 |
321 |
292 |
237 |
222 |
242 |
235 |
228 |
240 |
187 |
245 |
|
60–69 |
121 |
114 |
80 |
101 |
111 |
114 |
110 |
116 |
105 |
108 |
|
70–79 |
41 |
35 |
25 |
40 |
41 |
47 |
40 |
40 |
39 |
39 |
|
≥80 |
22 |
17 |
18 |
14 |
13 |
21 |
12 |
13 |
28 |
17 |
Table 3Regional clusters for T. vaginalis infection from 2012 to 2020
Table 3
|
District |
Cases |
Expected |
Relative risk |
Log likelihood ratioa
|
P-value |
|
2012–2014 |
Seoul |
111,411 |
86,718 |
1.38 |
4113.443 |
<0.001 |
|
Jeollabuk-do |
24,531 |
16,008 |
1.56 |
2034.825 |
<0.001 |
|
Jeju-do |
9,676 |
5,093 |
1.92 |
1651.701 |
<0.001 |
|
Daegu |
28,999 |
21,371 |
1.38 |
1293.497 |
<0.001 |
|
Busan |
35,528 |
30,162 |
1.19 |
486.738 |
<0.001 |
|
Gwangju |
16,134 |
12,588 |
1.29 |
472.969 |
<0.001 |
|
|
2015–2017 |
Busan, Gyeongsangnam-do, Ulsan, Daegu |
114,997 |
87,094 |
1.44 |
5231.682 |
<0.001 |
|
Busan |
42,020 |
28,928 |
1.50 |
2812.724 |
<0.001 |
|
Jeollabuk-do |
25,304 |
15,422 |
1.68 |
2766.880 |
<0.001 |
|
Daegu |
30,697 |
20,555 |
1.53 |
2296.591 |
<0.001 |
|
Jeju-do |
8,655 |
5,306 |
1.64 |
898.886 |
<0.001 |
|
Ulsan |
12,568 |
9,686 |
1.31 |
401.646 |
<0.001 |
|
Gyeongsangnam-do |
29,712 |
27,925 |
1.07 |
59.983 |
<0.001 |
|
Gwangju |
13,360 |
12,160 |
1.10 |
59.131 |
<0.001 |
|
|
2018–2020 |
Jeollabuk-do |
20,204 |
11,009 |
1.89 |
3213.317 |
<0.001 |
|
Jeju-do |
8,406 |
4,055 |
2.10 |
1808.039 |
<0.001 |
|
Daegu |
20,660 |
14,754 |
1.43 |
1108.866 |
<0.001 |
|
Incheon, Seoul |
87,107 |
76,650 |
1.19 |
917.320 |
<0.001 |
|
Seoul |
66,656 |
58,804 |
1.17 |
624.663 |
<0.001 |
|
Incheon |
20,451 |
17,846 |
1.16 |
193.043 |
<0.001 |
|
|
Total period |
Jeollabuk-do |
70,039 |
42,337 |
1.70 |
7895.184 |
<0.001 |
|
Busan, Gyeongsangnam-do, Ulsan, Daegu |
287,305 |
239,295 |
1.27 |
5771.405 |
<0.001 |
|
Jeju-do |
26,737 |
14,533 |
1.86 |
4159.725 |
<0.001 |
|
Seoul |
260,892 |
227,134 |
1.19 |
2998.914 |
<0.001 |
|
Gwangju |
37,281 |
33,504 |
1.12 |
211.612 |
<0.001 |
Table 4Spatiotemporal trends analysis of trichomoniasis according to administrative districts (2012–2020)
Table 4
|
Districts |
Cases |
Expected |
Trend inside clustera
|
Trend outside clustera
|
Relative risk |
Log likelihood ratiob
|
P-value |
|
Gangwon-do, Gwangju, Seoul |
317,171 |
295,956 |
−7.34 |
−4.18 |
1.10 |
852.650 |
<0.001 |
|
Incheon |
60,760 |
66,805 |
0.72 |
−5.36 |
0.90 |
740.745 |
<0.001 |
|
Chungcheongbuk-do, Sejong, Daejeon |
54,060 |
76,151 |
−8.83 |
−4.86 |
0.70 |
305.845 |
<0.001 |
|
Ulsan |
31,765 |
26,471 |
0.00c
|
−5.19 |
1.21 |
289.338 |
<0.001 |
|
Gyeonggi-do |
270,493 |
290,982 |
−3.73 |
−5.42 |
0.91 |
216.829 |
<0.001 |
|
Jeollabuk-do |
70,039 |
42,337 |
−2.52 |
−5.19 |
1.70 |
168.491 |
<0.001 |
Table 5Trichomoniasis trends according to sex and age
Table 5
|
Age group |
Trend 1 |
Trend 2 |
|
|
|
Period |
APCa
|
95% CI |
P-value |
Period |
APCa
|
95% CI |
P-value |
|
Female |
0–9 |
2012–2020 |
−3.6 |
−9.7~2.8 |
0.22 |
|
|
|
|
|
10–19 |
2012–2014 |
15.5 |
−17.1~60.8 |
0.29 |
2014–2020 |
−6.0 |
−11.8~0.1 |
0.05 |
|
20–29 |
2012–2014 |
13.8 |
−13.9~50.4 |
0.27 |
2014–2020 |
−9.3 |
−13.9~−4.5 |
0.01 |
|
30–39 |
2012–2014 |
21.5 |
−5.2~55.7 |
0.10 |
2014–2020 |
−10.1 |
−14.2~−5.7 |
0.00 |
|
40–49 |
2012–2014 |
13.9 |
−9.5~43.5 |
0.19 |
2014–2020 |
−10.6 |
−14.5~−6.5 |
0.00 |
|
50–59 |
2012–2014 |
15.6 |
−6.6~43.0 |
0.13 |
2014–2020 |
−8.2 |
−11.5~−4.7 |
0.00 |
|
60–69 |
2012–2016 |
7.6 |
−3.3~19.7 |
0.13 |
2016–2020 |
−9.6 |
−17.7~−0.6 |
0.04 |
|
70–79 |
2012–2014 |
31.0 |
5.6~62.7 |
0.03 |
2014–2020 |
−4.6 |
−7.5~−1.6 |
0.01 |
|
≥80 |
2012–2014 |
27.2 |
−8.8~77.4 |
0.12 |
2014–2020 |
−4.2 |
−8.2~0.0 |
0.05 |
|
|
Male |
0–9 |
2012–2020 |
−9.9 |
−26.4~10.4 |
0.26 |
|
|
|
|
|
10–19 |
2012–2020 |
10.1 |
3.3~17.3 |
0.01 |
|
|
|
|
|
20–29 |
2012–2020 |
12.4 |
8.2~16.7 |
0.00 |
|
|
|
|
|
30–39 |
2012–2020 |
5.9 |
2.5~9.5 |
0.00 |
|
|
|
|
|
40–49 |
2012–2020 |
−3.0 |
−5.7~−0.2 |
0.04 |
|
|
|
|
|
50–59 |
2012–2020 |
−4.6 |
−7.4~−1.8 |
0.01 |
|
|
|
|
|
60–69 |
2012–2020 |
0.2 |
−3.2~3.7 |
0.90 |
|
|
|
|
|
70–79 |
2012–2020 |
1.5 |
−3.0~6.3 |
0.46 |
|
|
|
|
|
≥80 |
2012–2020 |
3.4 |
−6.2~14.0 |
0.45 |
|
|
|
|
References
- 1. Ryu JS, Min DY. Trichomonas vaginalis and trichomoniasis in the Republic of Korea. Korean J Parasitol 2006;44:101-116. https://doi.org/10.3347/kjp.2006.44.2.101
- 2. Sutton M, Sternberg M, Koumans EH, McQuillan G, Berman S, Markowitz L. The prevalence of Trichomonas vaginalis infection among reproductive-age women in the United States, 2001–2004. Clin Infect Dis 2007;45:1319-1326. https://doi.org/10.1086/522532
- 3. Seña AC, Miller WC, Hobbs MM, Schwebke JR, Leone PA, Swygard H, Atashili J, Cohen MS. Trichomonas vaginalis infection in male sexual partners: implications for diagnosis, treatment, and prevention. Clin Infect Dis 2007;44:13-22. https://doi.org/10.1086/511144
- 4. Cotch MF, Pastorek JG 2nd, Nugent RP, Hillier SL, Gibbs RS, Martin DH, Eschenbach DA, Edelman R, Carey JC, Regan JA, Krohn MA, Klebanoff MA, Rao AV, Rhoads GG. Trichomonas vaginalis associated with low birth weight and preterm delivery. The Vaginal Infections and Prematurity Study Group. Sex Transm Dis 1997;24:353-360. https://doi.org/10.1097/00007435-199707000-00008
- 5. Moodley P, Wilkinson D, Connolly C, Moodley J, Sturm AW. Trichomonas vaginalis is associated with pelvic inflammatory disease in women infected with human immunodeficiency virus. Clin Infect Dis 2002;34:519-522. https://doi.org/10.1086/338399
- 6. Mitteregger D, Aberle SW, Makristathis A, Walochnik J, Brozek W, Marberger M, Kramer G. High detection rate of Trichomonas vaginalis in benign hyperplastic prostatic tissue. Med Microbiol Immunol 2012;201:113-116. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00430-011-0205-2
- 7. van Gerwen OT, Camino AF, Sharma J, Kissinger PJ, Muzny CA. Epidemiology, natural history, diagnosis, and treatment of Trichomonas vaginalis in men. Clin Infect Dis 2021;73:1119-1124. https://doi.org/10.1093/cid/ciab514
- 8. Zhang ZF, Begg CB. Is Trichomonas vaginalis a cause of cervical neoplasia? Results from a combined analysis of 24 studies. Int J Epidemiol 1994;23:682-690. https://doi.org/10.1093/ije/23.4.682
- 9. Sutcliffe S, Alderete JF, Till C, Goodman PJ, Hsing AW, Zenilman JM, De Marzo AM, Platz EA. Trichomonosis and subsequent risk of prostate cancer in the Prostate Cancer Prevention Trial. Int J Cancer 2009;124:2082-2087. https://doi.org/10.1002/ijc.24144
- 10. Kissinger P. Trichomonas vaginalis: a review of epidemiologic, clinical and treatment issues. BMC Infect Dis 2015;15:307-314. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12879-015-1055-0
- 11. Ryu JS, Chung HL, Min DY, Cho YH, Ro YS, Kim SR. Diagnosis of trichomoniasis by polymerase chain reaction. Yonsei Med J 1999;40:56-60. https://doi.org/10.3349/ymj.1999.40.1.56
- 12. Seo HJ, Kim SY, Lee YJ, Jang BH, Park JE, Sheen SS, Hahn SK. A newly developed tool for classifying study designs in systematic reviews of interventions and exposures showed substantial reliability and validity. J Clin Epidemiol 2016;70:200-205. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclinepi.2015.09.013
- 13. Kulldorff M. A spatial scan statistic. Commun Stat Theory Methods 1997;26:1481-1496. https://doi.org/10.1080/03610929708831995
- 14. Kulldorff M, Nagarwalla N. Spatial disease clusters: Detection and inference. Stat Med 1995;14:799-810. https://doi.org/https://doi.org/10.1002/sim.4780140809
- 15. Mathes RW, Lall R, Levin-Rector A, Sell J, Paladini M, Konty KJ, Olson D, Weiss D. Evaluating and implementing temporal, spatial, and spatio-temporal methods for outbreak detection in a local syndromic surveillance system. PLoS One 2017;12:e0184419. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0184419
- 16. Stelling J, Yih WK, Galas M, Kulldorff M, Pichel M, Terragno R, Tuduri E, Espetxe S, Binsztein N, O’Brien TF, Platt R; W-A Collaborative Group. Automated use of WHONET and SaTScan to detect outbreaks of Shigella spp. using antimicrobial resistance phenotypes. Epidemiol Infect 2010;138:873-883. https://doi.org/10.1017/S0950268809990884
- 17. Chen J, Roth RE, Naito AT, Lengerich EJ, MacEachren AM. Geovisual analytics to enhance spatial scan statistic interpretation: an analysis of U.S. cervical cancer mortality. Int J Health Geogr 2008;7:57-74. https://doi.org/10.1186/1476-072X-7-57
- 18. Wang W, Zhang T, Yin F, Xiao X, Chen S, Zhang X, Li X, Ma Y. Using the maximum clustering heterogeneous set-proportion to select the maximum window size for the spatial scan statistic. Sci Rep 2020;10:4900-4913. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-020-61829-y
- 19. Yoo H, Jung I. Optimizing the maximum reported cluster size for normal-based spatial scan statistics. CSAM 2018;25:373-383. https://doi.org/10.29220/CSAM.2018.25.4.373
- 20. Azage M, Kumie A, Worku A, Bagtzoglou AC. Childhood diarrhea exhibits spatiotemporal variation in northwest Ethiopia: a SaTScan spatial statistical analysis. PLoS One 2015;10:e0144690. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0144690
- 21. Clegg LX, Hankey BF, Tiwari R, Feuer EJ, Edwards BK. Estimating average annual per cent change in trend analysis. Stat Med 2009;28:3670-3682. https://doi.org/10.1002/sim.3733
- 22. Kim HJ, Fay MP, Feuer EJ, Midthune DN. Permutation tests for joinpoint regression with applications to cancer rates. Stat Med 2000;19:335-351. https://doi.org/10.1002/(SICI)1097-0258(20000215)19:3<335::AID-SIM336>3.0.CO;2-Z
- 23. Molnar A, Iancu M, Radu R, Borzan CM. A joinpoint regression analysis of syphilis and gonorrhea incidence in 15–19-year old adolescents between 2005 and 2017: a regional study. Int J Environ Res Public Health 2020;17:5385-5396. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph17155385
- 24. Ginocchio CC, Chapin K, Smith JS, Aslanzadeh J, Snook J, Hill CS, Gaydos CA. Prevalence of Trichomonas vaginalis and coinfection with Chlamydia trachomatis and Neisseria gonorrhoeae in the United States as determined by the Aptima Trichomonas vaginalis nucleic acid amplification assay. J Clin Microbiol 2012;50:2601-2608. https://doi.org/10.1128/JCM.00748-12
- 25. Joo SY, Goo YK, Ryu JS, Lee SE, Lee WK, Chung DI, Hong Y. Epidemiology of trichomoniasis in South Korea and increasing trend in incidence, health insurance review and assessment 2009–2014. PLoS One 2016;11:e0167938-e0167938. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0167938
- 26. Kim HY, Choe HS, Lee DS, Yoo JM, Lee SJ. Sexual behavior and sexually transmitted infection in the elderly population of South Korea. Investig Clin Urol 2019;60:202-209. https://doi.org/10.4111/icu.2019.60.3.202