Abstract
This pilot study aimed to investigate the effects of regional and seasonal variations on the prevalence of Theileria orientalis and the hematological profile of non-grazed dairy cows in Korea. A total of 365 clinically healthy lactating Holstein Friesian cows from 26 dairy farms in 7 provinces that were categorized into northern, central, and southern regions were sampled during the warm period from July to August and the cold period from October to December. The detection of T. orientalis major piroplasm surface protein gene and the hematology non-grazed dairy cows were analyzed using peripheral blood samples. The T. orientalis prevalence was 20.0% (73/365). The prevalence in the southern region was 35.9%, which was significantly higher than that in the central (21.6%) and northern (12.9%) regions (P<0.05). The prevalence during warm period was higher (43.0%) than that during the cold season (13.5%). The infected cows showed significantly lower erythrocyte counts in the southern region (5.8±0.6 M/μl) and during the warm period (5.8±0.7 M/μl) compared with those in the central and northern regions and during the cold season, which affected the extended RBC parameters, including hematocrit and hemoglobin concentrations. Our findings revealed the prevalence of T. orientalis in Korea, highlighting its high occurrence during warm periods and in certain geographical regions. Climatic factors could contribute to the health and productivity of cattle, as evidenced by the prevalence of T. orientalis and its negative impact on animals.
-
Key words: Theileria orientalis, tick-borne disease, dairy cattle, hematology
Introduction
The influence of climate change due to significant alterations in geophysical and meteorological conditions has become more evident in the past few decades. Rising global temperatures have resulted in unpredictable weather patterns and catastrophic events that have a major impact on the socioeconomic status of all countries [
1]. Such repercussions not only affect the quality of food, air, and water, but also induce changes in vector ecology and ecosystems, affecting various industries, human settlements, and agricultural sectors, such as crop and animal production systems [
2]. One of the consequences of climate change that affects the health of both humans and animals is the emergence and reemergence of vector-borne diseases (VBDs), alongside the increasing geographical distribution of vectors, especially insects and ticks [
3]. Previous studies have shown that increasing global temperatures due to climate change, particularly in temperate and polar regions, provide a more suitable environment for the survival of vectors, particularly ticks [
3]. Thus, this may result in the spread of tick-borne diseases (TBDs) that may affect both domesticated and wild animals [
4].
Theileria orientalis is a tick-borne parasite (TBP) that impairs the health and production of farm animals, especially cattle [
5]. It is mainly transmitted by the Asian long-horned tick
Haemaphysalis longicornis, which is widely distributed in many certain regions, such as Asian countries [
6–
10], Australia [
11], and New Zealand [
12], and has also been recently reported in the USA [
13]. Since
T. orientalis proliferates as piroplasms within red blood cells (RBCs), its main pathological effect is hemolytic anemia [
14]. Symptoms, such as weakness, lameness or recumbency, inappetence, mucosal pallor, jaundice, and hyperthermia, have been observed in a few clinical cases [
15,
16]. Previous studies on
T. orientalis have revealed that, unlike the lymphoproliferative
Theileria species, i.e.,
Theileria annulata and
Theileria parva, which cause lethal and morbid tropical or Mediterranean theileriosis and West Coast disease, it usually causes subclinical manifestations, which is why it is classified as “benign theileriosis” [
15]. However, more recent data revealed that this TBP could cause major economic damages due to increased treatment costs, reduced productivity and fertility, poor welfare, and even death of affected animals [
15,
17,
18].
Korea is a temperate Asian region facing the risk of notable shifts in climatic conditions [
19,
20], placing it at a high risk of dynamic VBD outbreaks. This has led to numerous studies in Korea assessing the prevalence of TBDs in livestock and wild animals, indicating that various TBPs, particularly
T. orientalis, are prevalent in certain regions of Korea [
10,
21–
23]. The influence of climatic factors, such as latitude and season, on the health of livestock, particularly dairy cattle infected with
T. orientalis, has not been extensively studied across Korea. The aim of this study is to conduct a nationwide pilot study to assess the effects of regional and seasonal variations on the prevalence of
T. orientalis and its impact on the hematological profile of non-grazed, clinically healthy, lactating dairy cows in Korea.
Materials and Methods
Ethics statement and sample collection
This study prioritized the welfare of the animals. All procedures and examinations were carefully conducted to minimize potential discomfort or harm to the animals. Qualified veterinarians and personnel ensured the well-being of the cattle included in this study. The farm owners were briefed on and consented to the study objectives. Necessary measures were taken to minimize harm during examinations, data were treated confidentially, and the results were presented transparently to advance cattle welfare.
The animals in this study were obtained from 26 dairy herds operating an all-year-round indoor non-grazing management system in 7 provinces in Korea. A veterinarian clinically assessed all cows during regular farm checkups; the enrolled animals presented with no clinical symptoms during the sampling period. A total of 365 lactating Holstein Friesian dairy cows were randomly selected for blood collection. A veterinarian collected the samples according to the ethical standards for animal care and handling. Peripheral blood was drawn via coccygeal venipuncture and collected in tubes treated with ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid (EDTA) for whole blood analysis. The samples were transported to the laboratory in an insulated box with coolant packs and immediately used for hematological analysis and the molecular detection of T. orientalis.
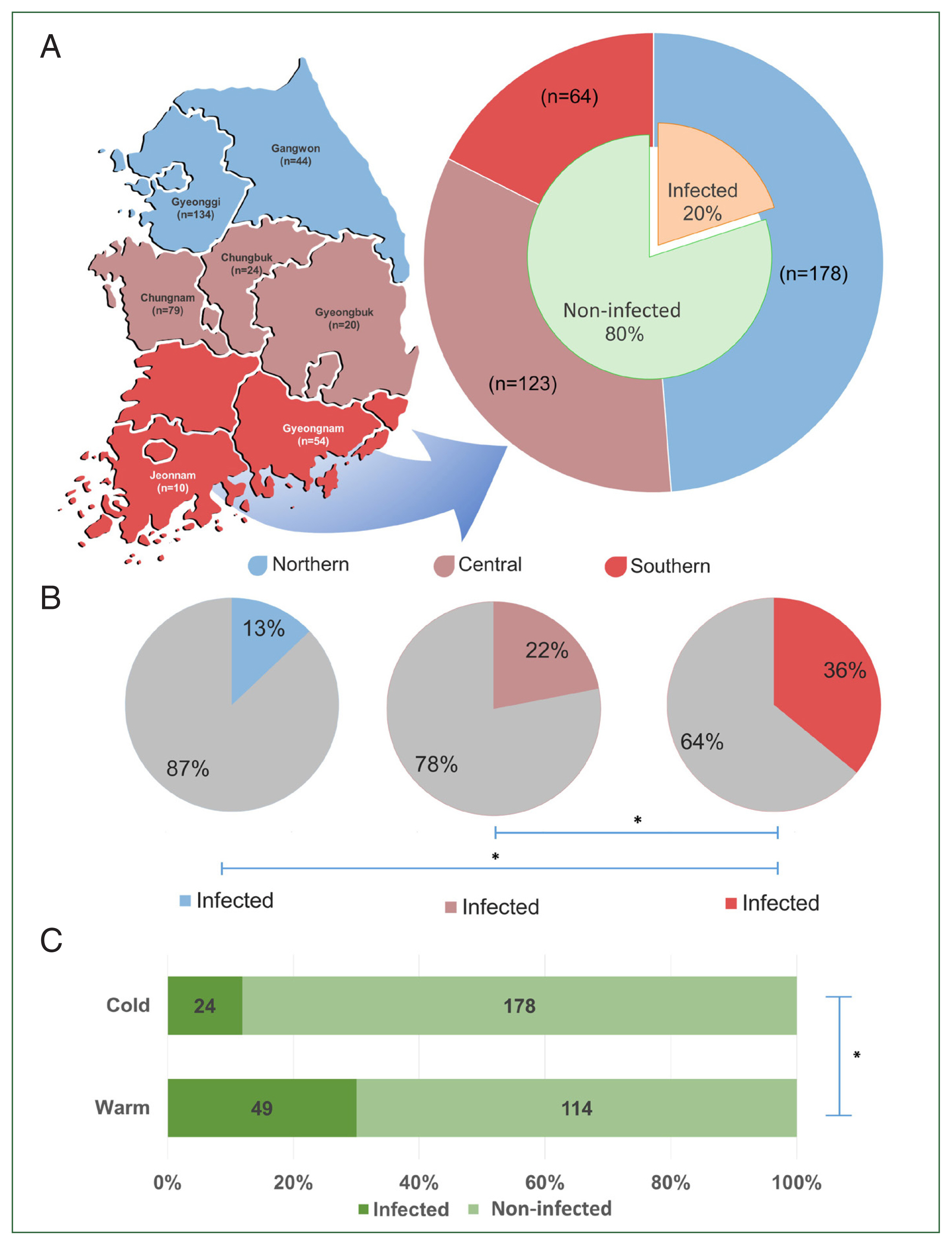
The provinces from which the samples were collected were selected by latitudinal regions: northern region (Gyeonggi and Gangwon Provinces), central region (Chungbuk, Chungnam, and Gyeongbuk provinces), and southern region (Gyeongnam and Jeonnam provinces) (
Fig. 1A). Sampling was conducted from July to December 2020, which was divided into 2 periods: the warm period or summer season (from July to August) and the cold period or autumn season (from late October to late December).
The peripheral blood samples were subjected to complete blood count (CBC) analysis. However, some samples were excluded from analysis due to blood coagulation. A total of 207 peripheral blood samples in good condition were used for CBC analysis. Field blood samples should be tested within 48 h of collection to prevent inaccurate measurements [
24]. Using an automated hematology analyzer (ProCyteDx, IDEXX Laboratories, Westbrook, ME, USA), the following CBC parameters were measured: RBCs and their parameters and indices, i.e., hematocrit (HCT), hemoglobin (HGB), mean corpuscular volume (MCV), mean corpuscular hemoglobin (MCH), and mean corpuscular hemoglobin concentration (MCHC); and white blood cells (WBCs) and their differential counts, i.e., neutrophils (NEU), lymphocytes (LYM), monocytes (MON), eosinophils (EOS), basophils (BAS), and platelets (PLT).
DNA was extracted from the peripheral blood samples stored in EDTA or heparinized tubes using Promega DNA isolation kits (Promega, Madison, WI, USA) in accordance with the standard protocol for blood extraction to detect
T. orientalis piroplasm. DNA concentration and purity were assessed using a NanoDrop spectrophotometer (Thermo Fisher Scientific, Waltham, MA, USA). Molecular detection was performed using PCR amplification of the major piroplasm surface protein (
mpsp) of known
T. orientalis genotypes with the following primer sequences: MPSP-Forward (5′-CTTTGCCTAGGATACTTCCT-3′) and MPSP-Reverse (5′-ACGGCAAGTGGTGAGAACT-3′) [
11]. In brief, a 20 μl reaction composed of 10 μl PCR premix (Bioneer Corp., Daejeon, Korea), 1 μl of each primer, 1 μl of the DNA sample, and 7 μl of sterile distilled water was prepared. The thermal cycling parameters were as follows: 5-min initial denaturation at 95°C; 30 cycles of 1-min denaturation, 1-min annealing, 1-min extension at 95°C, 58°C, and 72°C; and a 5-min final extension at 95°C. The presence of other TBPs, such as
Babesia spp. and Rickettsiales, including
Rickettsia spp.,
Ehrlichia spp., and
Anaplasma spp., were detected in the peripheral blood samples using PCR and the AccuPower Babesia PCR kit and Rickettsiales 3-plex PCR kit (Bioneer Corp.) respectively, to rule out the potential effects of other TBPs on the blood profile of the animals. By confirming their absence, we could specifically attribute any observed effects on the blood parameters to
T. orientalis infection, minimizing the confounding factors from other TBPs.
The prevalence between regions and season were compared using Pearson’s chi-square and Fisher’s exact tests. The differences in the means of CBC parameters between infected and non-infected cows, regions, and seasons were compared using one-way analysis of variance at 5% level, followed by the Tukey–Kramer (Honest Significant Difference) test. The analyses were performed using the Statistical Analysis Software (SAS 9.4).
Results
Of the screened TBPs, only
T. orientalis was detected in the sampled populations. The overall prevalence of
T. orientalis among cows was 20.0% (
Fig. 1A), with 73.1% of farms being affected by the infection. Significant differences in
T. orientalis prevalence (
P<0.05) were observed among different regions. The highest prevalence was found in the southern region (35.9%, 23/64), followed by the central (22.0%, 27/123), and northern (12.9%, 23/178) regions (
Fig. 1B). Additionally, a significant difference in the prevalence between seasons was observed, with the warm period showing a higher prevalence (43.0%) than the cold period (13.5%) (
P<0.05) (
Fig. 1C).
Significant differences were observed in several hematological parameters between
T. orientalis-infected and non-infected cows (
Table 1). Compared with non-infected cows, the infected dairy cows presented with lower RBC, HCT, and HGB values and higher MCV and MCH values.
The hematological profile revealed significant differences in certain CBC parameters between
T. orientalis-infected and non-infected dairy cows in Korea as categorized by latitudinal region (
Table 2). Within the normal range, significant variations were observed in the RBC, HCT, HGB, MCV, MCH, and PLT values, whereas the WBC count and its differentials remained unaffected. Moreover, the infected groups per region showed significantly lower RBC counts than the non-infected group. Specifically, the infected groups from the central and southern regions showed lower values than the infected cows from the northern region. A similar trend was observed for HCT, with modest differences observed between the infected and non-infected cows in the northern and central regions. In contrast, the lowest HCT levels were observed in the infected group from the southern region. Although no significant differences were observed in the HGB values between the infected and non-infected groups within all regions, a comparison between the regions revealed significantly lower HGB levels in the central and southern regions than in the northern region. No significant differences in the MCV values between the regions were observed, except in the southern region, where a significant difference was observed between the infected and non-infected groups. The MCH values exhibited a similar pattern, but the infected group from the northern region showed significantly higher MCH than the non-infected group from the southern region did. The infected group showed higher PLT levels in the central region, whereas no consistent pattern was observed in the other groups.
Seasonal variations in the hematological parameters between the infected and non-infected groups are summarized in
Table 3. Among the groups, the group infected in the warm period exhibited significantly lower RBC values, whereas this parameter did not differ significantly in other comparisons. The HCT values were the lowest in the infected group during the warm period, although this difference was only significant when compared with the non-infected group. No significant differences were observed between the infected and non-infected groups during the cold period. With regard to the HGB values, no significant differences were observed between the infected groups. However, the infected group presented with the lowest HGB values during the warm period compared with both groups during the cold period. The infected animals showed higher MCV and MCH values than the non-infected animals in both seasons did, albeit at modest levels. The MCHC values exhibited an erratic pattern, indicating no consistent differences. These findings revealed the influence of seasons on the hematological parameters among the infected and non-infected groups, with notable variations in the RBC and HCT values as observed during the warm period. However, the HGB, MCV, MCH, and MCHC values showed less pronounced differences among the groups.
Discussion
This is the first nationwide report on the prevalence of
T. orientalis among non-grazed lactating dairy cows in Korea. The 20.0% prevalence of this
T. orientalis infection recorded in this study was higher than that in previous regional studies in the country. For example, an earlier study reported that Holstein cattle in a farm in Jeolla Province, Korea, had a
T. orientalis infection rate of 13.2% during the non-grazing period [
25], whereas a more recent study in Gyeongsang province revealed a
T. orientalis infection rate of 4.2% among indoor-raised Holstein cattle [
10]. The high prevalence of
T. orientalis is considered a potential threat to the dairy cattle industry in Korea, as it has been observed to cause significant losses in other dairy industries [
17].
The prevalence of
T. orientalis in relation to the 2 climatic factors, latitudinal region and season, was analyzed. Our findings showed that a higher prevalence of
T. orientalis was recorded in regions that were closer to the equator. Since it is predicted that the southern regions of Korea are subject to warmer temperatures and higher weather variations than the northern regions [
19], the tick distribution could be more prevalent because of the more favorable warm habitat [
26]. This finding is similar to that of a study conducted in New Zealand from 2012 to 2013, where the prevalence of bovine anemia due to
Theileria-associated anemia was significantly higher in cattle herds on North Island, which experiences subtropical weather during the summer, than in those on South Island [
27]. A study conducted on Holstein cattle raised on Jeju Island, the southernmost province of Korea, revealed a notably high prevalence of
T. orientalis (96.2%) compared with their counterparts raised on the mainland, although the sampled animals were reported to graze from spring to autumn [
9].
The prevalence of
T. orientalis in Korea was significantly higher during the warm period (43.0%) than during the cold period (13.5%). This finding is partly consistent with that of an earlier study in which
T. orientalis was detected only during the summer [
10]. This is because invertebrate ectotherm vectors, such as ticks and insects, have better survival rates in warmer environments than in cooler environments [
3]. A previous study showed that the highest distribution of nymph and adult stages of
H. longicornis in different tick habitats in the northern part of Korea occurred during the summer [
28]. In contrast, a study in 2016 reported higher
T. orientalis infection rates among Holstein Friesian cows during the non-grazing period in November (4/15) than in August (0/10). However, the population size in our study was larger, and the seasonal categories had longer periods [
25]. It should be noted that the sampling in previous study was conducted on a single farm that practiced rotational grazing and non-grazing [
25]. It has not been determined how the non-grazed animals were infected with
T. orientalis because tick surveillance was not conducted. The proximity of farms to tick habitats, such as bush overgrowth, mountainsides, and paddy fields, could be associated with TBP transmission as TBP transmission also depends on vector ecology and landscape structure [
16,
29,
30]. Furthermore, other factors, such as sustained subclinical infection, host immunity and susceptibility, and other transmission routes, such as importation and vertical transmission, could have influenced the TBP transmission [
18].
The evaluation of hematological parameters in dairy cows infected with
T. orientalis revealed notable alterations in the RBC, HCT, HGB, MCV, and MCH values, which were specifically observed in the southern region based on the latitudinal region. Thus, these findings suggest a significant influence of the southern latitudinal region on the RBC count and its associated parameters in
T. orientalis-infected cattle. Moreover, these findings are consistent with those of previous studies, which emphasized the impact of season and latitudinal regions on these hematological parameters that can contribute to increased disease severity [
25]. However, the resultant changes in the MCV and MCH values indicate that
T. orientalis infection in the southern regions could lead to lower RBC levels and cause a higher rate of regenerative response against anemia, thus generating higher levels of these parameters [
31].
Regarding the seasonal variations in RBC parameters, the
T. orientalis-infected animals during the warm season exhibited significantly low RBC, HCT, and HGB values, which reveals that the combination of
T. orientalis infection and the warm season may affect the physiological status of cattle, leading to the deterioration of the RBC profile. Moreover, the moderate increase observed in the MCV and MCH parameters during the cold season among the infected animals could indicate a regenerative response in these animals, possibly resulting from previous hemolytic anemia caused by
T. orientalis during the summer [
31]. The observed differences in the MCV and HGB concentration compared which those in the normal group further confirm this hypothesis.
Changes in the peripheral blood profile of cattle due to warm ambient temperatures in the low latitudinal region and during the warm season could be attributed to the interplay between
T. orientalis infection and heat stress. Since the southern regions of temperate Asia more likely experience tropical monsoon climates, heatwave-related illnesses are projected to have a high occurrence [
20]. Rising temperatures cause heat stress, negatively affecting livestock health and reducing productivity and fertility [
32]. Moreover, the increasing number of vector ticks infesting animals in the lower regions with warmer habitats, as well as hot weather during the warm season, might cause a higher infection rate, which then affects the blood parameters. However, this was disproven in a previous study on
Babesia spp. [
33]. Further research is needed to determine whether tick infestation intensity affects
T. orientalis infection levels.
Theileria orientalis primarily affects RBCs in cattle showing no significant effects on WBCs or PLTs, a pattern that is consistently observed in previous studies [
25,
34]. Monitoring RBC-associated parameters in regions and seasons with a high prevalence of TBDs is essential. Notably, hematological changes observed occurred in asymptomatic animals, with values falling within the normal range. It is crucial to recognize that even asymptomatic cases of
T. orientalis infection can result in unquantified losses in dairy cows, as observed in a earlier study [
17]. Its potential impact on milk production needs to be further investigated. Subclinical infections may progress to clinical cases under additional stresses, such as parturition, lactation, or other factors that compromise the cows’ immune system [
11,
16]. Furthermore, if undetected and left untreated, asymptomatic animals can act as reservoirs for TBP, potentially transmitting the disease to more susceptible animals through established routes [
35].
Our findings revealed a higher prevalence of T. orientalis in the southern region and during the warm season in Korea. Although the clinically healthy animals exhibiting normal CBC parameters, our study revealed a modest yet statistically significant reduction in RBC parameters, particularly among infected animals in the southern region and during the warm season. This confirms the importance of adopting disease management strategies to address climate-driven disease dynamics, expanding disease vectors, and changing regional risks. Subclinical infections might impaire health in the affected animals. The studies on the productivity impact of subclinical T. orientalis infection in dairy cattle is limited. Further research is warranted to investigate this aspect to enhance our understanding of the economic implications and aid in developing targeted management strategies.
In conclusion, this study emphasizes the importance of comprehensive disease management strategies that encompass both clinical and subclinical cases, recognizing subclinical carriers as potential reservoirs for disease transmission as well as the economic implications, such as reduced productivity and the risk of disease spread, even in subclinical infections.
Notes
-
Conceptualization: Espiritu H, Cho YI
Data curation: Lee HW
Formal analysis: Espiritu H
Investigation: Espiritu H, Al Faruk MS
Methodology: Espiritu H, Lee HW
Project administration: Jin SJ, Cho YI
Resources: Lee HW, Jin SJ
Supervision: Cho YI
Writing – original draft: Espiritu H
Writing – review & editing: Lee SS, Cho YI
-
The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Acknowledgment
This study was supported by Sunchon National University Research Fund in 2023 (Grant number: 2023-0276).
Fig. 1The regions of Korea categorized based on their latitudinal location (A). The graph shows the population size per region (outer pie) and the overall prevalence of T. orientalis in Korea (inner pie). The regional prevalence of T. orientalis (B) and its prevalence during the cold and warm seasons (C). The significant difference between each group is indicated by asterisk (*).
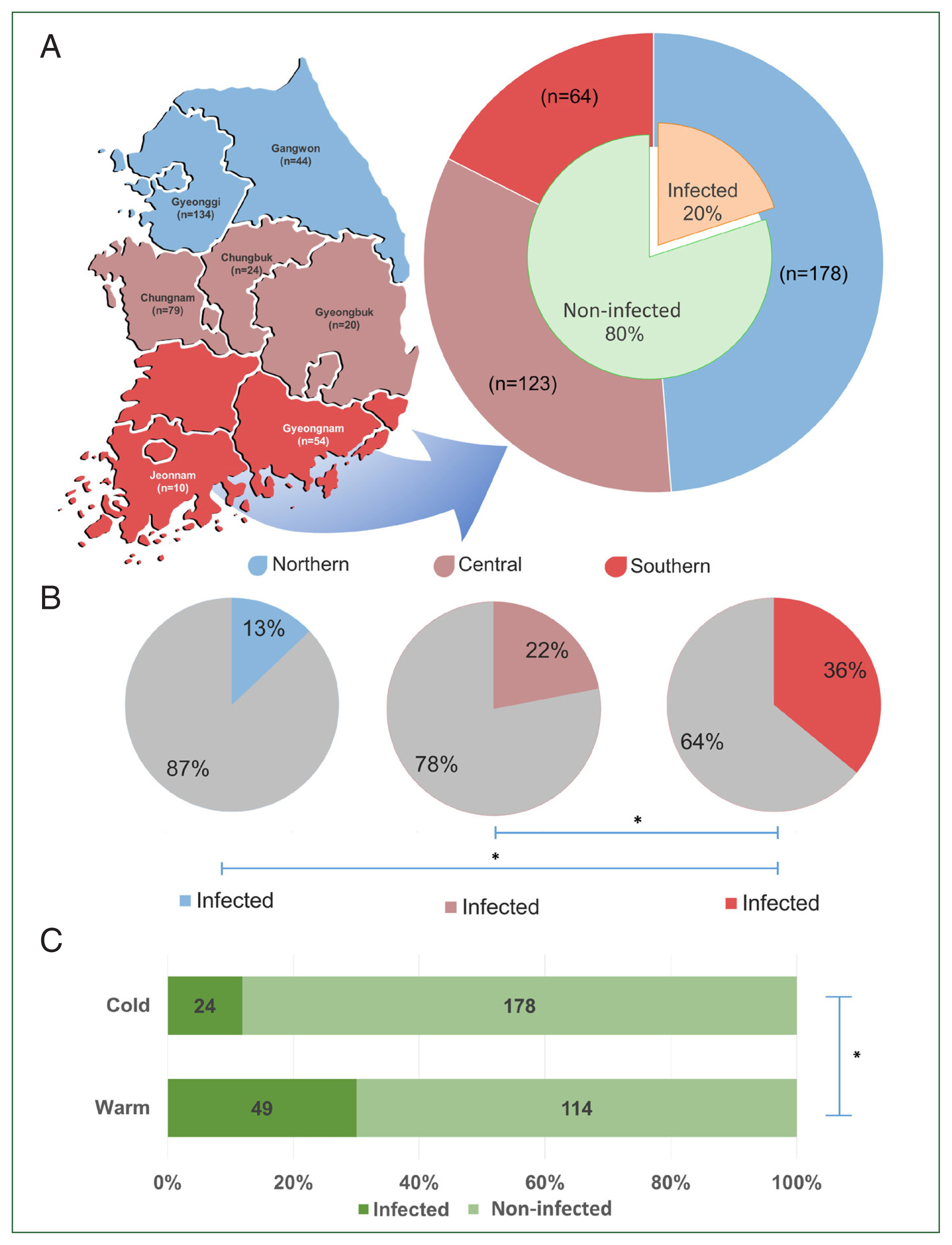
Table 1Comparison of the complete blood count parameters of T. orientalis-infected and non-infected non-grazing dairy cows
Table 1
|
Parameters (unit) |
Normal reference range†
|
Infected (n=64) |
Non-infected (n=142) |
P-value |
|
RBC (M/μl) |
4.5–9.4 |
5.9±0.7 |
6.4±0.5 |
<0.001 |
|
HCT (%) |
22.5–39.9 |
29.2±3.3 |
30.7±3.2 |
0.002 |
|
HGB (g/dl) |
7.4–12.8 |
9.6±1.1 |
9.9±1.0 |
0.044 |
|
MCV (fl) |
40.4–56.4 |
50.6±4.5 |
48.7±4.1 |
0.003 |
|
MCH (pg) |
11.5–18.5 |
16.8±1.3 |
16.2±1.3 |
0.003 |
|
MCHC (g/dl) |
30.2–33.5 |
33.1±0.9 |
33.2±1.0 |
0.448 |
|
WBC (K/μl) |
2.7–17.8 |
11.6±4.0 |
11.6±4.9 |
1.000 |
|
NEU (K/μl) |
0.7–7.0 |
5.2±2.0 |
4.8±1.4 |
0.096 |
|
LYM (K/μl) |
1.2–10.6 |
4.1±2.2 |
4.4±3.1 |
0.436 |
|
MONO (K/μl) |
0.02–2.2 |
1.9±1.2 |
1.9±1.2 |
0.687 |
|
EOS (K/μl) |
0.0–1.2 |
0.5±0.3 |
0.5±0.4 |
0.720 |
|
BASO (K/μl) |
0.0–0.04 |
0.02±0.03 |
0.02±0.02 |
0.241 |
|
PLT (K/μl) |
147.0–663.0 |
363.5±251.1 |
325.9±118.1 |
0.145 |
Table 2Changes in hematological parameters between T. orientalis-infected and non-infected with regards to latitudinal regions of Korea
Table 2
|
Parameters (unit) |
Normal reference range†
|
Northern |
Central |
Southern |
|
|
|
|
Infected (n=15) |
Non-infected (n=47) |
Infected (n=26) |
Non-infected (n=63) |
Infected (n=23) |
Non-infected (n=32) |
|
RBC (M/μl) |
4.5–9.4 |
6.3±0.6b
|
6.7±0.4a
|
5.7±0.8c
|
6.1±0.5b,c
|
5.8±0.6c
|
6.4±0.6a,b
|
|
|
HCT (g/dl) |
22.5–39.9 |
31.6±3.9a,b
|
32.3±2.6a
|
28.6±2.9c,d
|
29.6±3.1b,c,d
|
28.3±2.7d
|
30.7±3.1a,b,c
|
|
|
HGB (%) |
7.4–12.8 |
10.5±1.2a
|
10.3±0.9a
|
9.3±1.1b
|
9.7±1.0a,b
|
9.4±1.0b
|
9.9±1.1a,b
|
|
|
MCV (fl) |
40.4–56.4 |
50.8±3.8a,b
|
49.3±4.5a,b
|
50.1±3.4a,b
|
48.8±4.0a,b
|
51.2±6.0a
|
47.6±3.5b
|
|
|
MCH (pg) |
11.5–18.5 |
16.8±1.0a
|
16.4±1.4a,b
|
16.5±1.1a,b
|
16.2±1.3a,b
|
17.0±1.8a
|
15.7±1.0b
|
|
|
MCHC (g/dl) |
30.2–33.5 |
33.2±0.9 |
33.2±1.0 |
33.0±0.7 |
33.3±0.8 |
33.2±1.0 |
33.1±1.1 |
|
|
WBC (K/μl) |
2.7–17.8 |
12.2±5.9 |
11.3±4.9 |
10.9±3.5 |
11.5±5.1 |
12.0±3.0 |
12.4±4.2 |
|
|
NEU (K/μl) |
0.7–7.0 |
4.9±1.9 |
4.8±1.4 |
5.3±2.1 |
4.6±1.6 |
5.2±1.9 |
4.9±1.2 |
|
|
LYM (K/μl) |
1.2–10.6 |
4.6±2.9 |
4.1±3.2 |
3.8±2.0 |
4.3±3.3 |
4.1±1.9 |
5.0±2.9 |
|
|
MON (K/μl) |
0.02–2.2 |
2.2±1.7 |
1.9±1.3 |
1.6±0.9 |
1.9±1.2 |
2.0±1.1 |
2.1±1.2 |
|
|
EOS (K/μl) |
0.0–1.2 |
0.5±0.4 |
0.5±0.5 |
0.4±0.2 |
0.6±0.4 |
0.6±0.4 |
0.4±0.3 |
|
|
BAS (K/μl) |
0.0–0.04 |
0.03±0.05 |
0.02±0.02 |
0.02±0.02 |
0.02±0.02 |
0.02±0.02 |
0.02±0.02 |
|
|
PLT (K/μl) |
147.0–663.0 |
300.6±91.1b
|
340.0±93.9a,b
|
436.7±359a
|
308.4±123.0a,b
|
321.7±133.8a,b
|
339.7±137.5a,b
|
Table 3Changes in hematological (CBC) parameters between T. orientalis-infected and non-infected with regards to season in Korea
Table 3
|
Parameters (unit) |
Normal range†
|
Warm |
Cold |
|
|
|
Infected (n=49) |
Non-infected (n=72) |
Infected (n=15) |
Non-infected (n=70) |
|
RBC (M/μl) |
4.5–9.4 |
5.8±0.7b
|
6.3±0.5a
|
6.2±0.7a
|
6.5±0.5a
|
|
|
HCT (g/dl) |
22.5–39.9 |
28.6±2.8b
|
30.1±2.7a,b
|
31.2±4.3a
|
31.4±3.5a
|
|
|
HGB (%) |
7.4–12.8 |
9.4±0.99c
|
9.7±0.9b,c
|
10.4±1.3a
|
10.2±1.1a,b
|
|
|
MCV (fl) |
40.4–56.4 |
50.4±4.8a,b
|
48.3±3.7b
|
51.5±3.2a
|
49.2±4.5a,b
|
|
|
MCH (pg) |
11.5–18.5 |
16.7±1. 4a,b
|
15.9±1.1b
|
17.0±0.9a
|
16.5±1.3a,b
|
|
|
MCHC (g/dl) |
30.2–33.5 |
33.1±0.8a,b
|
32.9±0.9b
|
33.1±1.0a,b
|
33.5±1.0a
|
|
|
WBC (K/μl) |
2.7–17.8 |
11.3±3.2 |
12.2±4.7 |
12.7±6.1 |
11.1±5.00 |
|
|
NEU (K/μl) |
0.7–7.0 |
5.1±1.6 |
4.9±1.4 |
5.5±2.8 |
4.6±1.4 |
|
|
LYM (K/μl) |
1.2–10.6 |
3.9±1.9 |
4.6±3.2 |
4.4±3.0 |
4.2±3.1 |
|
|
MON (K/μl) |
0.02–2.2 |
1.8±1.0 |
2.2±1.4 |
2.1±1.7 |
1.7±1.0 |
|
|
EOS (K/μl) |
0.0–1.2 |
0.5±0.3 |
0.4±0.3 |
0.5±0.3 |
0.6±0.5 |
|
|
BAS (K/μl) |
0.0–0.04 |
0.02±0.02 |
0.02±0.02 |
0.03±0.05 |
0.02±0.02 |
|
|
PLT (K/μl) |
147.0–663.0 |
382.2±281.7 |
332.8±118.7 |
302.2±79.3 |
318.9±117.8 |
References
- 1. Oyhantçabal W, Vitale E, Lagarmilla P. Climate change and links to animal diseases and animal production. ConfOIE 2010;2010:179-186.
- 2. Lubroth J. Climate change and animal health risk. In Meybeck A, Lankosi J, Redfern S, Azzu N, Gitz V eds, Building Resilience for Adaptation to Climate Change in the Agriculture Secto. Rome, Italy. 2012, pp 63-70.
- 3. Rocklöv J, Dubrow R. Climate change: an enduring challenge for vector-borne disease prevention and control. Nat Immunol 2020;21(5):479-483. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41590-020-0648-y
- 4. Springer A, Glass A, Topp AK, Strube C. Zoonotic tick-borne pathogens in temperate and cold regions of europe-a review on the prevalence in domestic animals. Front Vet Sci 2020;7:604910. https://doi.org/10.3389/fvets.2020.604910
- 5. Grace D, Bett B, Lindahl J, Robinson T. Climate and livestock disease: assessing the vulnerability of agricultural systems to livestock pests under climate change scenarios. CCAFS Work Pap; 2015. 116:1-29 https://cgspace.cgiar.org/handle/10568/66595
- 6. Belotindos LP, Lazaro JV, Villanueva MA, Mingala CN. Molecular detection and characterization of Theileria species in the philippines. Acta Parasitol 2014;59(3):448-453. https://doi.org/10.2478/s11686-014-0256-9
- 7. Gebrekidan H, Nelson L, Smith G, Gasser RB, Jabbar A. An outbreak of oriental theileriosis in dairy cattle imported to Vietnam from Australia. Parasitology 2017;144(6):738-746. https://doi.org/10.1017/S0031182016002328
- 8. Jirapattharasate C, Adjou Moumouni PF, Cao S, Iguchi A, Liu M, et al. Molecular epidemiology of bovine babesia spp. and Theileria orientalis parasites in beef cattle from northern and northeastern Thailand. Parasitol Int 2016;65(1):62-69. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.parint.2015.10.005
- 9. Park J, Han YJ, Han DG, Chae JB, Chae JS, et al. Genetic characterization of theileria orientalis from cattle in the republic of Korea. Parasitol Res 2017;116(1):449-454. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00436-016-5316-7
- 10. Kwak D, Seo MG. Genetic diversity of bovine hemoprotozoa in South Korea. Pathogens 2020;9(9):1-9. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens9090768
- 11. Kamau J, De Vos AJ, Playford M, Salim B, Kinyanjui P, et al. Emergence of new types of Theileria orientalis in australian cattle and possible cause of theileriosis outbreaks. Parasit Vectors 2011;4:22. https://doi.org/10.1186/1756-3305-4-22
- 12. McFadden AMJ, Rawdon TG, Meyer J, Makin J, Morley CM, et al. An outbreak of haemolytic anaemia associated with infection of Theileria orientalis in naïve cattle. N Z Vet J 2011;59(2):79-85. https://doi.org/10.1080/00480169.2011.552857
- 13. Oakes VJ, Yabsley MJ, Schwartz D, LeRoith T, Bissett C, et al. Theileria orientalis ikeda genotype in cattle, virginia, USA. Emerg Infect Dis 2019;25(9):1653-1659. https://doi.org/10.3201/eid2509.190088
- 14. Kim S, Yu DH, Chae JB, Choi KS, Kim HC, et al. Pathogenic genotype of major piroplasm surface protein associated with anemia in Theileria orientalis infection in cattle. Acta Vet Scand 2017;59(1):1-5. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13028-017-0318-8
- 15. Watts JG, Playford MC, Hickey KL. Theileria orientalis: a review. N Z Vet J 2016;64(1):3-9. https://doi.org/10.1080/00480169.2015.1064792
- 16. Espiritu HM, Lee HW, Lee SS, Cho YI. A clinical case of bovine anemia due to Theileria orientalis group in a non-grazed dairy cow in the upper part of South Korea. Korean J Vet Res 2021;61(4):33.1-33.5. https://doi.org/10.14405/KJVR.2021.61.E33
- 17. Perera PK, Gasser RB, Firestone SM, Anderson GA, Malmo J, et al. Oriental theileriosis in dairy cows causes a significant milk production loss. Parasit Vectors 2014;7(1):1-8. https://doi.org/10.1186/1756-3305-7-73
- 18. Fukushima Y, Minamino T, Mikurino Y, Honkawa K, Horii Y, et al. Effects of Theileria orientalis infection on health status and productivity of dairy cows reared inside barns. Pathogens 2021;10(6):650. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens10060650
- 19. Jeung SJ, Sung JH, Kim BS. Assessment of the impacts of climate change on climatic zones over the Korean Peninsula. Adv Meteorol 2019;2019:5418041. https://doi.org/10.1155/2019/5418041
- 20. IPCC. The regional impacts of climate change: an assessment of vulnerability-a special report of the IPCC Working Group III. Environ Dev Econ 1998;5(3):333-340. https://doi.org/10.1017/s1355770x00220202
- 21. Seo MG, Ouh IO, Kwon OD, Kwak D. Molecular detection of Anaplasma phagocytophilum-like Anaplasma spp. and pathogenic A. phagocytophilum in cattle from South Korea. Mol Phylogenet Evol 2018;126:23-30. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ympev.2018.04.012
- 22. Seo MG, Kwon OD, Kwak D. Anaplasma bovis infection in a horse: first clinical report and molecular analysis. Vet Microbiol 2019;233:47-51. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.vetmic.2019.04.024
- 23. Chae JS, Adjemian JZ, Kim HC, Ko S, Klein TA, et al. Predicting the emergence of tick-borne infections based on climatic changes in Korea. Vector Borne Zoonotic Dis 2008;8(2):265-275. https://doi.org/10.1089/vbz.2007.0190
- 24. Espiritu H, Al Faruk MS, jaeLee G, Lopez BI, Lee SS, et al. Assessment of bovine blood sample stability for complete blood count and blood gases and electrolytes analysis during storage. Korean J Vet Serv 2019;42(4):265-274. https://doi.org/10.7853/KJVS.2019.42.4.265
- 25. Choi KS, Yu DH, Chae JS, Park BK, Yoo JG, et al. Seasonal changes in hemograms and Theileria orientalis infection rates among holstein cattle pastured in the mountains in the republic of Korea. Prev Vet Med 2016;127:77-83. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.prevetmed.2016.03.018
- 26. Medlock JM, Hansford KM, Bormane A, Derdakova M, Estrada-Peña A, et al. Driving forces for changes in geographical distribution of ixodes ricinus ticks in Europe. Parasit Vectors 2013;6(1):1-11. https://doi.org/10.1186/1756-3305-6-1
- 27. McFadden AMJ, Gias E, Heuer C, Stevens McFadden FJ, Pulford DJ. Prevalence and spatial distribution of cattle herds infected with Theileria orientalis in new zealand between 2012 and 2013. N Z Vet J 2016;64(1):55-59. https://doi.org/10.1080/00480169.2015.1090891
- 28. Chong ST, Kim HC, Lee IY, Kollars TM, Sancho AR, et al. Seasonal distribution of ticks in four habitats near the demilitarized zone, Gyeonggi-do (Province), Republic of Korea. Korean J Parasitol 2013;51(3):319-325. https://doi.org/10.3347/kjp.2013.51.3.319
- 29. Díaz-Cao JM, Adaszek Ł, Dzięgiel B, Paniagua J, Caballero-Gómez J, et al. Prevalence of selected tick-borne pathogens in wild ungulates and ticks in southern Spain. Transbound Emerg Dis 2022;69(3):1084-1094. https://doi.org/10.1111/TBED.14065
- 30. Matei IA, Estrada-Peña A, Cutler SJ, Vayssier-Taussat M, Varela-Castro L, et al. A review on the eco-epidemiology and clinical management of human granulocytic anaplasmosis and its agent in Europe. Parasites Vectors 2019;12(1):599. https://doi.org/10.1186/S13071-019-3852-6
- 31. Roland L, Drillich M, Iwersen M. Hematology as a diagnostic tool in bovine medicine. J Vet Diagn Invest 2014;26(5):592-598. https://doi.org/10.1177/1040638714546490
- 32. Forman S, Hungerford N, Yamakawa M, Yanase T, Tsai HJ, et al. Climate change impacts and risks for animal health in Asia. Rev Sci Tech 2008;27(2):581-597. https://doi.org/10.20506/RST.27.2.1814
- 33. Giglioti R, Oliveira HN, Santana CH, Ibelli AMG, Néo TA, et al. Babesia bovis and Babesia bigemina infection levels estimated by qPCR in Angus cattle from an endemic area of São Paulo state, Brazil. Ticks Tick Borne Dis 2016;7(5):657-662. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.TTBDIS.2016.02.011
- 34. Lawrence KE, Sanson RL, McFadden AMJ, Pulford DJ, Pomroy WE. The effect of month, farm type and latitude on the level of anaemia associated with Theileria orientalis Ikeda type infection in New Zealand cattle naturally infected at pasture. Res Vet Sci 2018;117:233-238. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rvsc.2017.12.021
- 35. Eamens GJ, Bailey G, Jenkins C, Gonsalves JR. Significance of Theileria orientalis types in individual affected beef herds in New South Wales based on clinical, smear and PCR findings. Vet Parasitol 2013;196(1–2):96-105. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.vetpar.2012.12.059
 , Hee-Woon Lee2
, Hee-Woon Lee2 , Md Shohel Al Faruk1,+
, Md Shohel Al Faruk1,+ , Su-Jeong Jin1
, Su-Jeong Jin1 , Sang-Suk Lee1
, Sang-Suk Lee1 , Yong-Il Cho1,*
, Yong-Il Cho1,*