Abstract
Free-living amoebae of the genus Acanthamoeba are causative agents of granulomatous amebic encephalitis and amebic keratitis. Because the virulence of Acanthamoeba culbertsoni cultured in the laboratory is restored by consecutive brain passages, we examined the genes induced in mouse brain-passaged A. culbertsoni by differential display reverse transcriptase polymerase chain reaction (DDRT-PCR). Enhanced A. culbertsoni virulence was observed during the second mouse brain passage, i.e., infected mouse mortality increased from 5% to 70%. Ten cDNAs induced during mouse brain passage were identified by DDRT-PCR and this was confirmed by northern blot analysis. BlastX searches of these cDNAs indicated the upregulations of genes encoding predictive NADH-dehydrogenase, proteasomal ATPase, and GDP-mannose pyrophosphorylase B, which have previously been reported to be associated with A. culbertsoni virulence factors.
-
Key words: Acanthamoeba culbertsoni, free-living ameba, mouse, DDRT-PCR, virulence
INTRODUCTION
Free-living amoebae of the genus
Acanthamoeba occur in various environments, and some cause granulomatous amebic encephalitis and amebic keratitis in humans (
Gardner et al., 1991;
Tan et al., 1993;
Cohen et al., 1987). Moreover, amebic virulence is attenuated by the long-term cultivation of amebas in vitro and can be recovered by serial mouse brain passages via intranasal infection (
Lee et al., 1983;
Marzur et al., 1994). Peroxidase and proteinase activities have also been reported to increase in
Acanthamoeba in parallel with the recovery of virulence by mouse brain passage (
Marzur et al., 1994). On recovering virulence, protease activities and some secretory products were found to be increased in pathogenic
Acanthamoeba (
Hadas et al., 1993). We speculated that virulence restoration also occurs in parallel with the upregulation of virulence-related gene expressions, and that the gene products of these genes may play roles in the pathogenesis of
Acanthamoeba. Accordingly, using DDRT-PCR, we identified upregulations in the transcription of some
A. culbertsoni genes during mouse brain passages.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Cultivation of amebas and mouse brain passages
Acanthamoeba culbertsoni (ATCC No. 30171) was axenically cultured at 37℃ in Casitone-Glucose-Vitamin (CGV) medium (
Willaert, 1971).
A. culbertsoni trophozoites (1 X 10
6) were inoculated intranasally into 8-week-old male ICR mice under anesthesia. Infected ICR mouse mortality was observed over 25 days post-infection. Amebas recovered from infected mice were also cultured in CGV medium for 1 week and were used to re-infect mice. In order to recover amebas, autopsies were performed immediately after sacrificing animals and portions of brain tissues were placed in CGV medium.
Preparation of A. culbertsoni DNA and RNA
The genomic DNA of A. culbertsoni was prepared by lysing 1 X 107 trophozoites in 1% SDS, and following this with phenol/chloroform extraction and ethanol precipitation. Total RNA was isolated from A. culbertsoni (in vitro cultivated, and from animals recovered from the 1st, 2nd and 3rd passages) using TRIZOL reagent (Gibco/BRL, Gaithersburg, Maryland, U.S.A.), according to the manufacturer's instructions.
DDRT-PCR
DDRT-PCR was performed as described previously (
Liang et al., 1992) using a No.1 RNA image kit (GenHunter, Nashville, TN). DNA-free RNAs were obtained by treating total RNA with RNase-free DNase I. Total RNA from long-term in vitro cultured and mouse brain passaged amebas were converted to cDNA using 1 of the 3 oligo-dTs provided in the kit (T
11A, T
11G, or T
11C). Reactions were initiated at 65℃ for 5 min and 37℃ for 10 min, 100 units of Superscript II reverse transcriptase (Gibco/BRL) was then added, and reaction mixes were incubated at 37℃ for 50 min and then at 75℃ for 5 min. Using a 20 ng portion of cDNA as a template, a pool of cDNA was generated by PCR using 1 of the arbitrary primers and an appropriate oligo-dT. Parameters for the PCR reaction were as follows; pre-incubation for 2 min at 94℃, 40 amplification cycles (30 sec at 94℃, 2 min at 40℃, 30 sec at 72℃), and a final extension for 10 min at 72℃, cDNA bands were visualized by including a trace amount of
32P (1 µCi/20 µl reaction) in the PCR reaction. The cDNAs generated were then separated on 6% SDS-urea polyacrylamide gels. Differentially displayed cDNAs were re-amplified using the same PCR conditions, and the re-amplified cDNAs were cloned into pGEM-T easy vector (Promega, Madison, Wisconsin, U.S.A.) for sequencing and Northern blot analysis.
cDNA probes were labeled with 32P using a Random labeling kit (Takara, Japan), and used to examine expression patterns after 3 cycles of infection and in long-term in vitro cultured amebas. For Northern hybridization, samples of total RNA (10 µg) were fractionated in 1% formaldehyde agarose gels, blotted on Hybond-N membranes by capillary transfer in 20× SSPE (3 M NaCl, 0.2 M NaH2PO4, 0.02 M EDTA) and immobilized on membranes using a UV-crosslinker. Blots were prehybridized in 5× SSPE, 50% formamide, 5× Denhardt's solution, 0.5% SDS and 100 µg/ml salmon sperm DNA for 2 hr at 42℃, and hybridization was continued overnight at 42℃ in the presence of a 32P labeled probe. Membranes were washed twice in 2× SSPE/0.1% SDS at room temperature for 15 min, and then twice at 60℃ for 30 min in 0.2× SSPE/0.5% SDS. Blots were hybridized with a labeled beta-actin DNA fragment, as an internal RNA control. mRNAs levels were measured using a Phosphoimager BAS 2500 (Fuji-Film Co. Ltd., Japan) and analyzed using TINA 2.0 software.
Sequence analysis
cDNA clones showing an increased hybridization pattern after mouse passages versus in vitro cultivated amebas were sequenced using the dideoxy nucleotide chain termination method. The reactions were run and analyzed on a capillary automated sequencing machine (ABI 377 XL90; Applied Biosystems). For data analysis, the nucleotide sequences of the selected cDNA clones were compared with entries in the EMBL and GenBank databases, and all 6 reading frames of the selected cDNA clones were also searched for proteins and proteins in other organisms homologous to the determined A. culbertsoni sequences using BlastX.
RESULTS
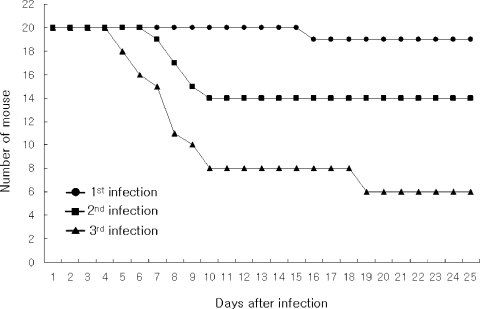
Mouse-passaged amebas showed increased virulence; from 5% of mortality in the fist infection to 70% in the third infection observed at 25 days of infection (
Fig. 1). DDRT-PCR was performed upon the mRNAs of brain-passaged amebas and upon the RNA of long-term in vitro cultured amebas using 24 combinations of 8 arbitrary primers and 3 oligo-dT
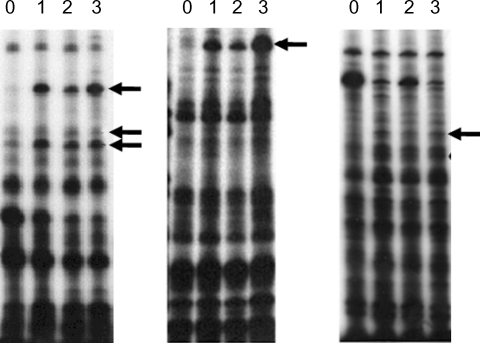
11 primers. Fifteen amebic cDNAs were found to show upregulated expression patterns following mouse brain passages, and were identified as shown in
Fig. 2. To confirm the elevated expressions of these selected cDNA clones in
A. culbertsoni we performed Northern blot hybridization. Ten of the 15 isolated cDNAs showed increased expressions in mouse brain-passaged amebas, ranging from 1.5 to 25-fold in 4G-1 and 3A-1 (
Fig. 3). DNA sequencing of 10 clones with a higher hybridization pattern in mouse brain-passaged amebas showed that 4 of these clones (3A-1, 3A-2, 3A-3 and 3G) had almost the same sequence. BlastX searches for 5 (3A-1, 3A-2, 3A-3, 3G and 4G-1) of these 10 clones failed to find any protein sequences in public databases. The sequences of the remaining 5 amplicons provided useful information with respect to their putative functions (
Table 1). One clone 2A showed homology to genes encoding p47 tumor suppressor protein of human and mouse. Interestingly their mRNAs rapidly increased at the first mouse brain passage and decreased marginally after the second and third passages. 7C showed homology to a mitochondrial metabolic enzyme - NADH-dehydrogenase subunit I. 7G-1 was found to be homologous to the proteasomal ATPase gene. 7G-2 matched ATP/GTP-binding fet5 mRNA, which is a known eukaryotic transcription factor of unknown function. 8G showed homology to GDP-mannose pyrophosphorylase B, a known virulence factor.
DISCUSSION
It has been postulated that the expressions of
A. culbertsoni genes that are directly or indirectly responsible for virulence, may be upregulated by consecutive brain passages, since the virulence of long-term cultured
A. culbertsoni in the laboratory is recovered by consecutive brain passages. DDRT-PCR has been applied to analyze tissues and developmental stages by comparing reverse transcribed cDNA from purified mRNA. For example, cancer cell-specific mRNA, human brain tissue-specific mRNA (
Sokolov et al., 1994), and developmental stage-specific mRNA in
Eimeria bovis of the coccidian parasite (
Abrahamsen et al., 1995) and in
Fasciola hepatica (
Reed et al., 1998) have been successfully identified using this technique. In the present study, DDRT-PCR produced 3 kinds of cDNA pools from mRNA templates when different oligo-dT
11-A, G or C primers were used during the reverse transcription reaction. Each cDNA pool was analyzed by PCR using the same oligo-dT
11-A, G, or C primer used for cDNA synthesis, and an arbitrary primer.
In this study, we examined differentially expressed genes in
A. culbertsoni after mouse brain passages and compared these with genes expressed after long-term in vitro culture, by DDRT-PCR. Ten differentially expressed clones in mouse brain-passaged amebas were identified by DDRT-PCR, and confirmed by Northern blot analysis. Based on sequencing analysis results, clone 2A showed homology to the human p47/p33 tumor suppressor protein. And, p47 tumor suppressor protein was reported to play an important role in cellular stress response to ultraviolet irradiation, during DNA repair and apoptosis (
Chen et al., 2003). Other amplicons were matched with NADH-dehydrogenase, proteasomal ATPase, ATP/GTP-binding fet5 mRNA, and GDP-mannose pyrophosphorylase B. The
Salmonella serotype Gallinarum containing mutated NADH dehydrogenase was reported to be less invasive than wild
Salmonella serotype Gallinarum, and showed no evidence of multiplication in the liver or spleen (
Li et al., 1998). In particular, proteasomal ATPase is known to function in the main degradation pathway of most proteins in the cytoplasm and nuclei of eukaryotic cells (
Hershko et al., 1998;
DeMartino et al., 1994). The proteasomal ATPase subunit was reported to recognize the polyubiquitin degradation signal (
Lam et al., 2002;
Aaron, 1994), and to be required for nitric oxide resistance (
Darwin et al., 2003). These findings suggest that the proteasomal degradation pathway of cellular protein and the nitric oxide protection mechanism are turned on during
A. culbertsoni infection in mice. In addition, ATP/GTP-binding fet5 mRNA is regulated by iron and upregulated in cells grown in iron-limited media, which suggests that Fet5 protein normally plays a role in the transport of iron (
Spizzo et al, 1997), an important factor in virulence change. In fungi, GDP-mannose pyrophosphorylase B gene deletion was found to be lethal (
Varki, 1999), and
Leishmania mexicana containing a mutated form of this gene, lost its ability to infect murine macrophages (
Attila et al., 2001). Moreover, GDP-mannose pyrophosphorylase B was suggested to be a virulence factor for other pathogens, and to play a significant role in host invasion (
Attila et al., 2001). Although it is difficult to conclude that any direct relationship exists between these induced genes and increased
A. culbertsoni virulence caused by mouse brain passage, proteasomal ATPase and GDP-mannose pyrophosphorylase B may be expected to participate in the virulence of amebic infection in the mouse brain.
The information gathered from the present study provides resources for further investigations into the molecular mechanisms of Acanthamoeba virulence. The availability of the cDNA sequence coding for Acanthamoeba should provide the opportunity to design experiments for recombinant protein and immunization of selected genes.
References
Fig. 1Survival rate of mice intranasally infected with A. culbertsoni; from 5% of mortality in the fist infection to 70% in the third infection observed at 20 days of infection.
Fig. 2Differential display using A, G or C-base anchored oligo-dT primers. PCR was carried out using single-strand cDNA produced from the total RNA from non-mouse brain passaged (0) and mouse brain passaged (1st, 2nd and 3rd) A. culbertsoni. Lane zero (non-mouse brain passage), 1, 2 and 3 (1st, 2nd and 3rd mouse brain passage) were compared by differential display using dT11A (or G, C) primer in combination with 8 arbitrary primers. Arrows indicate bands showing increased intensity after mouse brain passage.
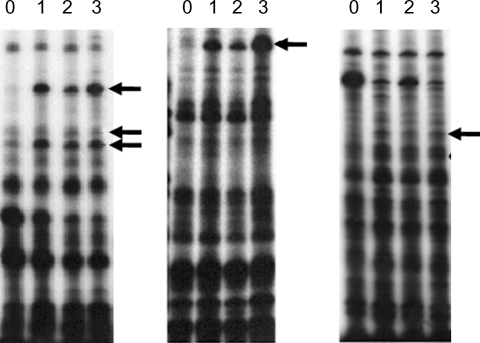
Fig. 3Northern blot analysis of A. culbertsoni RNA obtained before- mouse brain passage (0) or after mouse brain passage (1st, 2nd and 3rd mouse brain passages). The same membrane was stripped and re-hybridized with a non-regulated probe encoding A. culbertsoni actin as an RNA loading control. Signals were quantified using a Bio-Imaging Analyser System 2500 (Fuji-Film).
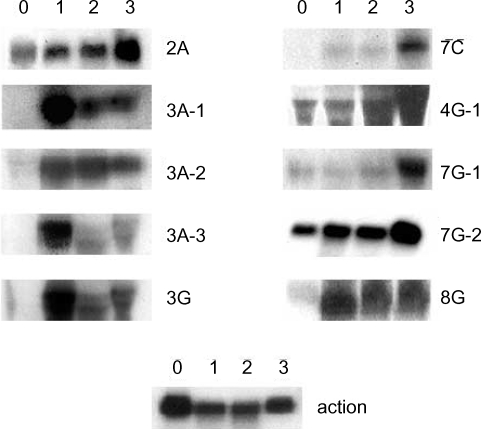
Table 1.Identification of clones selected by DDRT-PCR
Table 1.
|
Clonea)
|
cDNA size |
Northern blot analysisb)
|
Putative identification |
E-value |
Accession numberc)
|
|
8G |
138 bp (partial) |
3 |
GDP-mannose pyrophosphorylase B |
0.41 |
AY161267 |
|
7G-1 |
447 bp (partial) |
3 |
Proteasomal ATPase |
4e-47 |
AY161265 |
|
7G-2 |
252 bp (partial) |
2 |
ATP(GTP)-binding fet5 mRNA |
2e-07 |
AY161266 |
|
7C |
357 bp (partial) |
10 |
NADH-dehydrogenase (Acanthamoeba castellanii) |
1e-37 |
AY161264 |
|
2A |
231 bp (partial) |
2 |
P47 tumor suppressor protein |
2e-09 |
AY161262 |
|
4G-1 |
229 bp (partial) |
1.5 |
Novel gene |
|
AY161268 |
|
3G |
195 bp (partial) |
25 |
Novel gene |
|
AY161263 |
|
3A-1 |
191 bp (partial) |
25 |
Novel gene |
|
AY161263 |
|
3A-2 |
185 bp (partial) |
10 |
Novel gene |
|
AY161263 |
|
3A-3 |
191 bp (partial) |
25 |
Novel gene |
|
AY161263 |