Abstract
We investigated the value of mitochondrial small subunit rRNA gene (mt SSU rDNA) PCR-RFLP as a taxonomic tool for Acanthamoeba isolates with close interrelationships. Twenty-five isolates representing 20 species were included in the analysis. As in nuclear 18S rDNA analysis, two type strains (A. astronyxis and A. tubiashi) of morphological group 1 diverged earliest from the other strains, but the divergence between them was less than in 18S riboprinting. Acanthamoeba griffini of morphological group 2 branched between pathogenic (A. culbertsoni A-1 and A. healyi OC-3A) and nonpathogenic (A. palestinensis Reich, A. pustulosa GE-3a, A. royreba Oak Ridge, and A lenticulata PD2S) strains of morphological group 3. Among the remaining isolates of morphological group 2, the Chang strain had the identical mitochondrial riboprints as the type strain of A. hatchetti. AA2 and AA1, the type strains of A. divionensis and A. paradivionensis, respectively, had the identical riboprints as A. quina Vil3 and A. castellanii Ma. Although the branching orders of A. castellanii Neff, A. polyphaga P23, A. triangularis SH621, and A. lugdunensis L3a were different from those in 18S riboprinting analysis, the results obtained from this study generally coincided well with those from 18S riboprinting. Mitochondrial riboprinting may have an advantage over nuclear 18S rDNA riboprinting because the mt SSU rDNAs do not seem to have introns that are found in the 18S genes of Acanthamoeba and that distort phylogenetic analyses.
-
Key words: Acanthamoeba, phylogenetic relationship, PCR-RFLP, mitochondrial SSU rDNA
INTRODUCTION
Acanthamoeba spp. are the most ubiquitous protozoa among environments such as soil, air, freshwater and ocean sediment (
De Jonckheere, 1991). Sometimes the amoebae can be carriers or vectors in the dispersion and dissemination of pathogenic microbes such as
Legionella spp.,
Listeria spp.,
Mycobacterium spp., and
Vibrio spp. (
Jadin, 1973;
Ly and Muller, 1990;
Field, 1991;
Thom et al., 1992;
Kong and Chung, 1996;
Chung et al, 1997). Furthermore, several members of the genus
Acanthamoeba play direct roles as human pathogens causing life-threatening granulomatous amebic encephalitis and vision-threatening keratitis (
Sisson et al., 1995).
Recent molecular systematic studies provided a new classification of the genus
Acathamoeba. Stothard et al. (
1998) classified 53 strains of
Acanthamoeba spp. into 12 Rns sequence types based on sequence analysis of 18S rDNA. The results obtained were inconsistent with some previous species designation and indicated that the taxonomy of
Acanthamoeba should be revised. Although 18S rDNA sequence data are useful for identification and differentiation of
Acanthamoeba isolates, generation of sequence data is too labor-intensive and expensive for routine identification and classification of
Acanthamoeba. Riboprinting, PCR-RFLP analysis of 18S rDNA, is a simpler and less expensive substitute for 18S rDNA sequence analysis (
Clark and Diamond, 1997). Chung et al., (
1998) applied riboprinting to subgenus classification of
Acantamoeba. The results were congruent with those of sequence analysis. However, 18S rDNA of some
Acanth-amoeba strains contains an intron, which therefore can generate misleading results (
Chung et al., 1998).
Mitochondrial DNA (mtDNA) is a molecular clone within mitochondriate eukaryotic cells like Acanthamoeba. Although variation of the mitochondrial genome size limited the availability of the RFLP analysis of whole mitochondrial genome as a phylogenetic tool, usefulness of mitochondrial small subunit (SSU) rDNA remains unknown. In this study, we evaluated PCR-RFLP of Acanthamoeba mitochondrial SSU rDNA as a phylogenetic tool and compared the results with those from nuclear riboprinting analysis.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Acanthamoeba
Twenty-five strains including 20 type strains of the genus
Acanthamoeba which were previously assigned to 20 species, were obtained from ATCC (
Table 1). They were cultured axenically in Proteose peptone-Yeast extract-Glucose (PYG) or Proteose peptone-Yeast extract-Glucose-Cysteine (PYGC) media at 25℃ or 37℃ (
Chung et al., 1996).
mtDNA of
Acanthamoeba was extracted using phenol and phenol/chloroform (1:1) and recovered by precipitation with cold absolute ethanol in the presence of sodium acetate (
Yagita and Endo, 1990). The DNA was stored at -20℃ until used as template DNA for PCR reactions.
The primers for the PCR, FP16; 5'-TTGTATAAACAATCGTTGGGTTTTATT-3', RP16; 5'-GTCCAGCAGCAGGTTCCCCTACCGCTA-3', are designed to hybridize to highly conserved sequences at the extreme 5' (P3) and 3' (P4) termini of mitochondrial SSU rDNA (
Lonergan and Gray, 1994). The PCR was done using a kit of premixed PCR reagents (Bioneer, Chongwon, Korea) and a thermal cycler (Perkin Elmer Cetus, CA, USA). Fifty µl scale premix was dissolved in 47 µl of distilled water and vortexed vigorously. One µl of template DNA and 1 µl of each primer (25 nmol concentration) were added to the premix and mixed thoroughly. The whole mixture was covered with 20 µl of mineral oil. Each PCR process was performed through 30 cycles at 94℃ for 1 min, 58℃ for 30 sec, and 72℃ for 2 min followed by an extension time of 10 min. After amplification, the mineral oil was removed by treating with chloroform and the amplified DNA was stored at -20℃ until used (
Chung et al., 1998).
The PCR products of 25 strains were electrophoresed in a 1.5% agarose gel with DNA size standards (Amplisize, Biorad, CA, USA). Eight kinds of restriction endonucleases (
Hae III,
Hsp92 I,
Hinf I,
Dde I,
Mbo I,
Sau96 I,
Rsa I, and
Taq I; Poscochem, Seoul, Korea), which have recognition sequences of four nucleotides, were used to generate comparative riboprints. The amplified DNA (1 µg) was digested with 5-10 units of the enzymes for 2 hr with recommended buffers at 37℃, except for
Taq I (67℃), and electrophoresed in a 2.5% agarose gel (agarose 3: Nusieve 1) for 1.5 hr. To differentiate small DNA fragments, which were unclear in the agarose gel, digested samples were electrophoretically separated in 12% polyacrylamide gels (
Chung et al., 1998). The gels were stained with ethidium bromide and photographed under an UV transilluminator.
Sequence divergence estimates were calculated by the Nei and Li equation (
1979) from a fragment comigration dataset which was obtained by comparison of the riboprints of 25
Acanthamoeba strains with each other. A phylogenetic tree was reconstructed by the unweighted pair group method with arithmetic averages (UPGMA) using the computer program Phylip, version 3.5 (
Felsenstein, 1989).
RESULTS
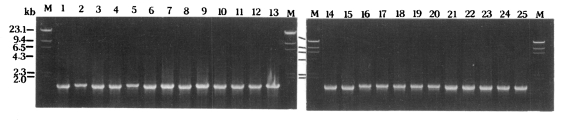
Only a single PCR product was amplified from each
Acanthamoeba strain (
Fig 1). The PCR products of 25
Acanthamoeba strains were approximately 1,550 nucleotides in length as predicted.
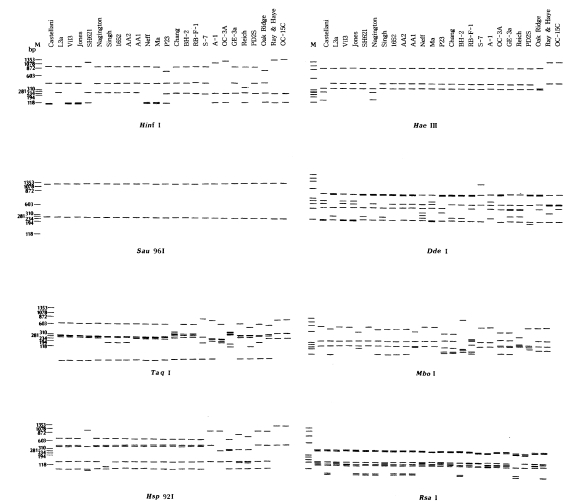
Mitochondrial riboprint patterns of 25
Acanthamoeba strains using eight restriction endonucleases are shown schematically in
Fig 2. The patterns of
A. divionensis AA2 and
A. paradivionensis AA1 were identical with all enzymes used. The Chang strain which was previously assigned to
A. castellanii had identical riboprints with BH-2, the type strain of
A. hatchetti. Vil3, the type strain of
A. quina had identical mitochondrial riboprints with the Ma strain of
A. castellanii.
Proportions of co-migrating fragments and estimated genetic distance between amoebae strains are shown in
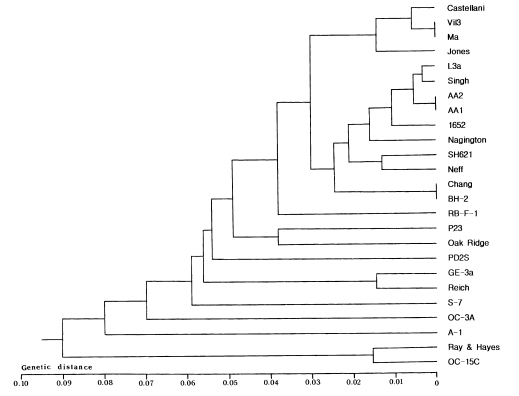
Table 2, and the dendrogram constructed based on the estimated genetic distance is presented in
Fig 3.
Acanthamoeba astronyxis Ray & Hayes and
A. tubiashi OC-15C of morphological group 1 (
Pussard and Pons, 1977) were the earliest branching strains. Among the remaining strains, the most divergent were
A. culbertsoni A-l and
A. healyi OC-3A, which belong to morphological group 3 and are known to be highly virulent.
Acanthamoeba griffini, with an intron in its nuclear 18S rDNA (
Gast et al., 1996;
Ledee et al., 1996) branched between virulent strains A-1 and OC-3A and avirulent strains GE-3a, Reich Oak Ridge and PD2S of morphological group 3. Strain P23 which is the neotype strain of
A. polyphaga of morphological group 2 formed a cluster with the Oak Ridge strain (the type strain of
A. royreba; morphological group 3). RB-F-1, the type strain of
A. stevensoni was the earliest branching strain among the remaining 15 strains of morphological group 2. The Castellani, Ma, Vil3, and Jones strains formed a cluster separated from the remaining ten strains. The Nagington, 1652, L3a, Singh, AA2 and AA1 strains formed another cluster.
DISCUSSION
Analysis of mtDNA, using either sequence or RFLP data, may permit the identification of problematic specimens (
Wells and Sperling, 1999). Among mitochondrial genes, the SSU rRNA gene has been widely and successfully applied to investigation of relationships at subgeneric levels as well as among very distantly related groups (
Flook and Rowell, 1997). Although RFLP analyses of the mitochondrial genome have been used in phylogenetic and taxonomic studies of
Acanthamoeba spp. (
Byers et al., 1983;
Yagita and Endo, 1990), the results were somewhat ambiguous partly because of the quite difference of genome size among strains. Recently, riboprinting of nuclear 18S rDNA has been widely applied to classification of morphologically indistinguishable protozoa including
Acanthamoeba and recognized as an inexpensive and rapid tool for taxonomic and phylogenetic studies (
Clark et al., 1995;
Clark and Diamond, 1997;
Chung et al., 1998). However, some strains of
Acanthamoeba have introns in their nuclear 18S rDNA (
Stothard et al., 1998) and identification of these strains can be problematic with nuclear riboprinting. PCR-RFLP analysis of mt SSU rDNA (mt riboprinting) has not been used previously for phylogenetic and taxonomic studies of
Acanthamoeba.
In this study, we obtained similar but not identical results from mt riboprinting as we obtained previously with nuclear 18S riboprinting. A dendrogram constructed in this study (
Fig 3) coincided generally with the grouping of Pussard and Pons (
1977) based on the morphological features of cysts. Some of the results strongly support the observations of Chung et al. (
1998) based on nuclear 18S riboprinting. For example, AA2 and AA1, the type strains of
A. divionensis and
A. paradivionensis respectively, showed the identical mt riboprints with all restriction enzymes used. Both strains were isolated simultaneously from soil of France by the same group of investigators (
Pussard and Pons, 1977), and differed slightly in mor-phology. Furthermore, they showed the same mt genome RFLP, alloenzyme (unpublished data) and nuclear riboprint patterns (
Chung et al., 1998). As Chung et al. (
1998) proposed, both strains should be a species and closely related with the Singh strain, the type strain of
A. rhysodes. Also, the Chang strain, previously assigned to
A. castellanii revealed the identical mt riboprints with BH-2, the type strain of
A. hatchetti. Both strains were pathogenic for mice (unpublished data) and were found to be closely related based on nuclear riboprinting. In addition, these strains had lots of comigrating DNA fragments on mtDNA RFLP analyses and revealed very similar alloenzyme patterns (unpublished data).
In contrast to our previous studies, L3a, the type strains of A. lugdunensis, which clustered with the Castellani, Vil3, Jones, and Ma strains in a dendrogram reconstructed by 18S riboprinting, formed a cluster with the Nagington, 1652, Singh, AA2, and AA1 strains here. The Neff, SH621, and P23 strains also branched at different positions in this dendrogram. Estimated divergence between A. astronyxis and A. tubiashi was lower in this study than in 18S riboprinting analysis. These differences may result from a difference in evolutionary rate between the mitochondrial and nuclear genes.
In spite of the likely difference in evolutionary rate between the mitochondrial and nuclear genomes, similar results with mt and nuclear riboprint patterns were observed with several strains assigned to different species. These results suggest that the taxonomic status of some species of the genus Acanthamoeba should be revised. This study has shown that mt riboprinting is another tool for the phylogenetic study of Acanthamoba. In addition, the mt riboprinting confirms the basic features of the evolutionary history of the genus as revealed in studies of the 18S rDNA. One important advantage is that it avoids problems caused by isolates with introns within nuclear 18S rDNA.
Notes
-
This authors wish to acknowledge the financial support of the Korea Research Foundation made in the program year of 1997 (No 1997-002-F00038).
References
- 1. Byers TJ, Bogler SA, Burianek LL. Analysis of mitochondrial DNA variation as an approach to systematic relationships in the genus Acanthamoeba. J Protozool 1983;30:198-203.
- 2. Chung DI, Kong HH, Kim TH, et al. Bacterial endosymbiosis within the cytoplasm of Acanthamoeba lugdunensis isolated from a contact lens storage case. Korean J Prasitol 1997;35:127-133. (in Korean).
- 3. Chung DI, Kong HH, Yu HS, Oh YM, Yee ST, Kim YJ. Biochemical and molecular characterization of a strain KA/S2 of Acanthamoeba castellanii isolated from Korean soil. Korean J Parasitol 1996;34:79-85.
- 4. Chung DI, Yu HS, Hwang MY, et al. Subgenus classification of Acanthamoeba by riboprinting. Korean J Parasitol 1998;36:69-80.
- 5. Clark CG, Diamond LS. Intraspecific variation and phylogenetic relationships in the genus Entamoeba as revealed by riboprinting. J Euk Microbiol 1997;44:142-154.
- 6. Clark CG, Martin DS, Diamond LS. Phylogenetic relationships among anuran trypanosomes as revealed by riboprinting. J Euk Microbiol 1995;42:92-96.
- 7. De Jonckheere JF. Ecology of Acanthamoeba. Rev Infect Dis 1991;13:S385-S387.
- 8. Felsenstein J. PHYLIP: Phylogenetic inference package (version 3.5). Cladistics 1989;5:164-166. manual, version 3.5. Department of Genetics, University of Washington.
- 9. Field BS. The role of amoebae in legionellosis. Clin Microbiol Newsletter 1991;13:92-93.
- 10. Flook PK, Rowell CHF. The effectiveness of mitochondrial rRNA gene sequences for the reconstruction of the phylogeny of an insect order (Orthoptera). Mol Phylogenet Evol 1997;8:177-192.
- 11. Gast RJ, Ledee DR, Fuerst PA, Byers TJ. Subgenus systematics of Acanthamoeba: four nuclear 18S rDNA sequence types. J Euk Microbiol 1996;43:498-504.
- 12. Jadin JB. De la meningoencephalite amibienne et du pouvoir pathogene des amibes limax. Annee Biologique 1973;12:305-342.
- 13. Kong HH, Chung DI. Bacterial endosymbionts of Acanthamoeba sp. isolated from cooling tower water. Japanese J Parasitol 1996;45:505-511.
- 14. Ledee DR, Hay J, Byers TJ, Seal DV, Kirkness CM. Acanthamoeba griffini: Molecular Characterization of a new corneal pathogen. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 1996;37:544-550.
- 15. Lonergan KM, Gray MW. The ribosomal RNA gene region in Acanthamoeba castellanii mitochondrial DNA. A case of evolutionary transfer of introns between mitochondria and plastids? J Mol Biol 1994;239:476-499.
- 16. Ly TMC, Muller HE. Ingested Listeria monocytogenes survive and multiply in protozoa. J Med Microbiol 1990;33:51-54.
- 17. Nei M, Li WH. Mathematical model for studying genetic variation in terms of restriction endonuclease. Proc Nat Acad Sci USA 1979;76:5269-5273.
- 18. Pussard M, Pons R. Morphologie de la paroi kystique et taxonomie du genre Acanthamoeba (Protozoa, Amoebida). Protistologica 1977;13:557-598.
- 19. Sisson JP, Kemper CA, Loveless M, McShane D, Visvesvara GS, Deresinski SC. Disseminated Acanthamoeba infection in patients with AIDS: Case reports and review. Clin Infect Dis 1995;20:1207-1216.
- 20. Stothard DR, Schroeder-Diedrich JM, Awwad MH, et al. The evolutionary history of the genus Acanthamoeba and the identification of eight new 18S rRNA gene sequence types. J Euk Microbiol 1998;45:45-54.
- 21. Thom S, Warhurst D, Drasar BS. Association of Vibrio cholerae with fresh water amoebae. J Med Microbiol 1992;36:303-306.
- 22. Well JD, Sperling FA. Molecular phylogeny of Chrysomya albiceps and C. rufifacies. J Med Entomol 1999;36:222-226.
- 23. Yagita K, Endo T. Restriction enzyme analysis of mitochondrial DNA of Acanthamoeba strains in Japan. J Protozool 1990;37:570-575.
Fig. 1Agarose gel electrophoretic patterns of PCR products from mitochondrial small subunit rRNA gene of 25 Acanthamoeba strains. Hind III digested λ phage DNA was used as the DNA size marker (M).

Fig. 2Schematic representation of mt riboprints of 25 strains of Acanthamoeba by eight restriction enzymes. Hae III digested ΦX174 DNA was used as the size marker (M).

Fig. 3Dendrogram of 25 Acanthamoeba strains constructed by UPGMA method using Phylip ver. 3.5 based on genetic divergence estimates.

Table 1.List of 25 strains of Acanthamoeba spp. analysed in this study
Table 1.
|
Number |
Strain |
ATCC No. |
Virulence |
Environmental source |
Geographic source |
Reference |
Former species designation |
|
1 |
Castellani |
30011 |
+ |
yeast culture |
England |
Douglas (1930) |
A. castellanii
|
|
2 |
L3a |
50240 |
+ |
swimming pool |
France |
Pussard & Pons (1977) |
A. lugdunensis
|
|
3 |
Vil3 |
50241 |
nd |
swimming pool |
France |
Pussard & Pons (1977) |
A. quina
|
|
4 |
Jones |
30461 |
+ |
keratitis |
USA |
Jones et al. (1975) |
A. polyphaga
|
|
5 |
SH621 |
50254 |
nd |
human feces |
France |
Pussard & Pons (1977) |
A. triangularis
|
|
6 |
Nagington |
30873 |
+ |
keratitis |
England |
Nagington et al. (1974) |
A. polyphaga
|
|
7 |
Singh |
30973 |
- |
soil |
England |
Singh (1952) |
A. rhysodes
|
|
8 |
1652 |
50253 |
- |
soil |
Morocco |
Pussard & Pons (1977) |
A. mauritaniensis
|
|
9 |
AA2 |
50238 |
- |
soil |
France |
Pussard & Pons (1977) |
A. divionensis
|
|
10 |
AA1 |
50251 |
- |
soil |
France |
Pussard & Pons (1977) |
A. paradivionensis
|
|
11 |
Neff |
30010 |
- |
soil |
USA |
Neff (1957) |
A. castellanii
|
|
12 |
Ma |
50370 |
+ |
keratitis |
USA |
Ma et al. (1981) |
A. castellanii
|
|
13 |
P23 |
30871 |
- |
fresh-water |
USA |
Page (1967) |
A. polyphaga
|
|
14 |
Chang |
30898 |
+ |
fresh water |
USA |
Byers et al. (1990) |
A. castellanii
|
|
15 |
BH-2 |
30730 |
+ |
ocean sediment |
USA |
Sawyer et al. (1977) |
A. hatchetti
|
|
16 |
RB-F-1 |
50388 |
nd |
ocean sediment |
USA |
Sawyer et al. (1993) |
A. stevensoni
|
|
17 |
S-7 |
30731 |
+ |
beach-bottom |
USA |
Sawyer (1971) |
A. griffini
|
|
18 |
A-1 |
30171 |
+ |
tissue culture |
USA |
Singh & Das (1970) |
A. culbertsoni
|
|
19 |
OC-3A |
30866 |
+ |
GAE |
USA |
Moura et al. (1992) |
A. healyi
|
|
20 |
GE-3a |
50252 |
- |
swimming pool |
France |
Pussard & Pons (1977) |
A. pustulosa
|
|
21 |
Reich |
30870 |
- |
soil |
Israel |
Reich (1933) |
A. palestinensis
|
|
22 |
PD2S |
30841 |
+ |
swimming pool |
France |
Molet & Ermolieff-Braun (1976) |
A. lenticulata
|
|
23 |
Oak Ridge |
30884 |
+ |
cell culture |
USA |
Willaert et al. (1978) |
A. royreba
|
|
24 |
Ray & Hayes |
30137 |
nd |
soil |
USA |
Ray & Hayes (1954) |
A. astronyxis
|
|
25 |
OC-15C |
30867 |
nd |
river |
USA |
Lewis & Sawyer (1979) |
A. tubiashi
|
Table 2.Proportional homologus fragments (values above the diagonal) and estimates of genetic divergence (values below the diagonal) among 25 Acanthamoeba strains based on the mitochondrial SSU rDNA PCR-RFLP
Table 2.
Group
|
|
II
|
III
|
I
|
|
No. |
Species |
Strain |
1 |
2 |
3 |
4 |
5 |
6 |
7 |
8 |
9 |
10 |
11 |
12 |
13 |
14 |
15 |
16 |
17 |
18 |
19 |
20 |
21 |
22 |
23 |
24 |
25 |
|
1 |
A. castellanii
|
Castellani |
— |
52/68 |
64/67 |
58/67 |
50/68 |
56/68 |
50/68 |
54/67 |
54/68 |
54/68 |
58/71 |
64/67 |
48/68 |
52/68 |
52/68 |
44/67 |
40/66 |
38/64 |
40/68 |
44/69 |
42/71 |
38/66 |
42/66 |
30/60 |
30/60 |
|
2 |
A. lugdunensis
|
L3a |
0.067 |
— |
54/67 |
50/67 |
60/68 |
58/68 |
66/68 |
60/67 |
66/68 |
66/68 |
60/71 |
54/67 |
50/68 |
58/68 |
58/68 |
52/67 |
42/66 |
34/64 |
36/68 |
50/69 |
46/71 |
46/66 |
42/62 |
28/60 |
30/60 |
|
3 |
A. quina
|
Vil3 |
0.011 |
0.054 |
— |
60/66 |
52/66 |
52/67 |
52/67 |
56/66 |
56/67 |
56/67 |
60/70 |
66/66 |
50/67 |
54/67 |
54/67 |
46/66 |
42/65 |
40/63 |
42/67 |
46/68 |
44/70 |
40/65 |
42/65 |
32/59 |
32/59 |
|
4 |
A. polyphaga
|
Jones |
0.036 |
0.073 |
0.024 |
— |
48/67 |
48/67 |
48/67 |
50/66 |
52/67 |
52/67 |
56/70 |
60/66 |
48/67 |
48/67 |
48/67 |
42/66 |
40/65 |
42/63 |
42/67 |
48/68 |
46/70 |
40/65 |
42/65 |
30/59 |
30/59 |
|
5 |
A. trisngularis
|
SH621 |
0.077 |
0.031 |
0.060 |
0.083 |
— |
56/68 |
62/68 |
56/67 |
62/68 |
62/68 |
64/71 |
54/67 |
50/68 |
56/68 |
56/68 |
52/67 |
40/66 |
34/64 |
36/68 |
50/69 |
46/71 |
46/66 |
44/66 |
28/60 |
30/60 |
|
6 |
A. polyphaga
|
Nagington |
0.049 |
0.049 |
0.063 |
0.083 |
0.049 |
— |
62/69 |
60/68 |
62/69 |
62/69 |
54/72 |
50/68 |
44/69 |
52/69 |
52/69 |
50/68 |
40/67 |
30/65 |
38/69 |
44/70 |
40/72 |
46/67 |
38/67 |
26/61 |
28/61 |
|
7 |
A. rhysodes
|
Singh |
0.077 |
0.007 |
0.063 |
0.083 |
0.023 |
0.027 |
— |
62/67 |
64/68 |
64/68 |
58/71 |
52/67 |
48/68 |
56/68 |
56/68 |
52/67 |
40/66 |
32/64 |
38/68 |
48/69 |
44/71 |
48/66 |
38/66 |
26/60 |
28/60 |
|
8 |
A. mauritaniensis
|
1652 |
0.054 |
0.028 |
0.041 |
0.069 |
0.045 |
0.031 |
0.019 |
— |
62/67 |
62/67 |
54/70 |
56/66 |
48/67 |
58/67 |
58/67 |
50/66 |
44/65 |
32/63 |
42/67 |
48/68 |
44/70 |
46/65 |
40/65 |
28/59 |
30/59 |
|
9 |
A. divionensis
|
AA2 |
0.058 |
0.007 |
0.045 |
0.063 |
0.023 |
0.027 |
0.015 |
0.019 |
— |
68/68 |
60/71 |
56/67 |
50/68 |
58/68 |
58/68 |
54/67 |
44/66 |
34/64 |
40/68 |
50/69 |
46/71 |
48/66 |
44/66 |
30/60 |
32/60 |
|
10 |
A. paradivionensis
|
AA1 |
0.058 |
0.007 |
0.045 |
0.063 |
0.023 |
0.027 |
0.015 |
0.019 |
0 |
— |
56/67 |
50/68 |
58/68 |
58/68 |
54/67 |
44/66 |
34/64 |
40/68 |
40/68 |
50/69 |
46/71 |
48/66 |
44/66 |
30/60 |
32/60 |
|
11 |
A. castellanii
|
Neff |
0.051 |
0.042 |
0.039 |
0.056 |
0.026 |
0.072 |
0.051 |
0.065 |
0.042 |
0.042 |
— |
60/70 |
50/71 |
54/71 |
54/71 |
50/70 |
40/69 |
38/67 |
40/71 |
50/72 |
48/74 |
44/69 |
44/69 |
32/63 |
30/63 |
|
12 |
A. castellanii
|
Ma |
0.011 |
0.054 |
0 |
0.024 |
0.054 |
0.077 |
0.063 |
0.041 |
0.045 |
0.045 |
0.039 |
— |
50/67 |
54/67 |
54/67 |
46/66 |
42/65 |
40/63 |
42/67 |
46/68 |
44/70 |
40/65 |
42/65 |
32/59 |
32/59 |
|
13 |
A. polyphaga
|
P23 |
0.087 |
0.077 |
0.073 |
0.083 |
0.077 |
0.112 |
0.087 |
0.083 |
0.077 |
0.077 |
0.088 |
0.073 |
— |
50/67 |
50/67 |
44/66 |
36/65 |
36/63 |
48/67 |
40/68 |
40/70 |
36/65 |
48/65 |
32/59 |
30/59 |
|
14 |
A. castellanii
|
Chang |
0.067 |
0.040 |
0.054 |
0.083 |
0.049 |
0.071 |
0.049 |
0.036 |
0.040 |
0.040 |
0.068 |
0.054 |
0.073 |
— |
68/68 |
50/67 |
48/66 |
30/64 |
38/68 |
50/69 |
46/71 |
40/66 |
42/66 |
30/60 |
30/60 |
|
15 |
A. hachetti
|
BH-2 |
0.067 |
0.040 |
0.054 |
0.083 |
0.049 |
0.071 |
0.049 |
0.036 |
0.040 |
0.040 |
0.068 |
0.054 |
0.073 |
0 |
— |
50/67 |
48/66 |
30/64 |
38/68 |
50/69 |
46/71 |
40/66 |
42/66 |
30/60 |
30/60 |
|
16 |
A. stevensoni
|
RB-F-1 |
0.105 |
0.063 |
0.090 |
0.113 |
0.063 |
0.077 |
0.063 |
0.069 |
0.054 |
0.054 |
0.084 |
0.090 |
0.101 |
0.073 |
0.073 |
— |
42/65 |
28/63 |
38/67 |
40/68 |
38/70 |
42/65 |
42/65 |
30/59 |
32/59 |
|
17 |
A. griffini
|
S-7 |
0.125 |
0.113 |
0.109 |
0.121 |
0.125 |
0.129 |
0.125 |
0.098 |
0.101 |
0.101 |
0.136 |
0.109 |
0.148 |
0.080 |
0.080 |
0.109 |
— |
34/62 |
30/66 |
42/67 |
38/69 |
36/64 |
36/64 |
28/58 |
28/58 |
|
18 |
A. culbertsoni
|
A-1 |
0.130 |
0.158 |
0.114 |
0.101 |
0.158 |
0.193 |
0.173 |
0.169 |
0.158 |
0.158 |
0.142 |
0.114 |
0.140 |
0.189 |
0.189 |
0.203 |
0.150 |
— |
36/64 |
30/65 |
30/67 |
28/62 |
36/62 |
26/56 |
26/56 |
|
19 |
A. healyi
|
OC-3A |
0.133 |
0.159 |
0.117 |
0.117 |
0.159 |
0.149 |
0.145 |
0.117 |
0.133 |
0.133 |
0.143 |
0.117 |
0.083 |
0.145 |
0.145 |
0.142 |
0.197 |
0.144 |
— |
36/69 |
40/71 |
34/66 |
40/66 |
30/60 |
30/60 |
|
20 |
A. pustulosa
|
GE-3a |
0.112 |
0.081 |
0.098 |
0.087 |
0.081 |
0.116 |
0.091 |
0.087 |
0.081 |
0.081 |
0.091 |
0.098 |
0.133 |
0.081 |
0.081 |
0.133 |
0.117 |
0.193 |
0.163 |
— |
64/72 |
40/67 |
36/67 |
24/61 |
26/61 |
|
21 |
A. palestinensis
|
Reich |
0.131 |
0.109 |
0.116 |
0.105 |
0.109 |
0.147 |
0.120 |
0.116 |
0.109 |
0.109 |
0.108 |
0.116 |
0.140 |
0.109 |
0.109 |
0.153 |
0.149 |
0.201 |
0.143 |
0.029 |
— |
36/69 |
36/69 |
26/63 |
26/63 |
|
22 |
A. lenticulata
|
PD2S |
0.138 |
0.090 |
0.121 |
0.121 |
0.090 |
0.094 |
0.080 |
0.086 |
0.080 |
0.080 |
0.112 |
0.121 |
0.148 |
0.125 |
0.125 |
0.109 |
0.144 |
0.199 |
0.166 |
0.129 |
0.163 |
— |
40/64 |
18/58 |
22/58 |
|
23 |
A. royreba
|
Oak Ridge |
0.113 |
0.113 |
0.109 |
0.109 |
0.101 |
0.142 |
0.138 |
0.121 |
0.101 |
0.101 |
0.112 |
0.109 |
0.076 |
0.113 |
0.113 |
0.109 |
0.144 |
0.136 |
0.125 |
0.155 |
0.163 |
0.118 |
— |
30/58 |
32/58 |
|
24 |
A. astronyxis
|
Ray & Hayes |
0.173 |
0.191 |
0.153 |
0.169 |
0.191 |
0.213 |
0.209 |
0.186 |
0.173 |
0.173 |
0.169 |
0.153 |
0.153 |
0.173 |
0.173 |
0.169 |
0.182 |
0.192 |
0.173 |
0.233 |
0.221 |
0.293 |
0.165 |
— |
46/52 |
|
25 |
A. tubiashi
|
OC-15C |
0.173 |
0.173 |
0.153 |
0.169 |
0.173 |
0.195 |
0.191 |
0.169 |
0.157 |
0.157 |
0.185 |
0.153 |
0.169 |
0.173 |
0.173 |
0.153 |
0.182 |
0.192 |
0.173 |
0.213 |
0.221 |
0.242 |
0.149 |
0.031 |
— |