Abstract
Non-biting midges are known to contain potent inhalant allergens. IgE antibody responses to the crude extract of Chironomus kiiensis adults, a dominant chironomid species in Korea, were examined. With the IgE-ELISA or passive cutaneous anaphylaxis reactions, increased levels of chironomid-specific IgE were detected in the skin test positive human sera, or immunized BALB/c mouse sera with the crude extract adsorbed to alum. IgE-immunoblot analysis showed major IgE-reacting protein band patterns, which reacted with more than 50% of the skin test positive human sera, at 110, 80, 73, 46, 40, 37, 34, and 31 kDa. The reactive band patterns were largely similar between skin test positive humans and immune BALB/c mice. However, the bands of 55, 31, 27, 26, 24, and 23 kDa were found only in sensitized humans, but not in immunized mice.
-
Key words: Chironomus kiiensis adults, chironomid, insect, hypersensitivity, allergens, IgE
INTRODUCTION
Very diverse, more than 10,000 species of chironomids, are distributed around the world. Presently in Korea, only about 50 has been reported out of 300 estimated species of chironomids. Also in 1993,
Chironomus kiiensis and
C. flaviplumus were reported to be the two most prevalent species of chironomids in Korea (
Ree, 1993). The latter emerges from eutrophic waters in urban areas, whereas the former is distributed mainly in rural areas, breeding in rice paddies, lakes, or other clean waters. Although the climates between Japan and Korea are similar,
C. yoshimatsui,
C. plumosus, and
Tokunagayusurika akamusi which are dominant species in Japan, are rarely found in Korea (
Ree and Kim, 1981).
Chironomid midges and larvae are known to contain potent allergens. Kimura et al. (
1990) reported that chironomid antigens were more abundant than mite antigens in the outdoor environment around the lake in the western part of Japan. Usually, sensitized subjects are frequently diagnosed as having bronchial asthma and less frequently as having conjunctivitis. Historically, it has been demonstrated that a midge,
Cladotanytarsus lewisi, occurred in enormous numbers in the Nile basins in Sudan and caused severe respiratory diseases in people living close to the Nile (
Kay et al., 1978). It has been reported that chironomid larvae were widely used as fish food in Germany, and that the significant number of people exposed to larvae suffered from allergic reactions (
Baur et al., 1982). Furthermore, the increasing frequency of IgE antibody responses to chironomids was found in patients with bronchial asthma in Japan (
Kino et al., 1987). In Korea, Park et al. (
1991) reported two cases of asthmatic patients allergic to
C. plumosus and
T. akamusi extracts. About 20% of the patients with respiratory allergic symptoms in Korea were reported to show positive reactions to the chironomid extracts (
Kim and Park, 1994). Since these two species are rarely found in Korea, the results indicated that their chironomid antigens contained cross-reactive materials with abundant chironomid species in Korea.
Hemoglobins, which are unique components of chironomids among insects, have been identified as the most important allergen in asthmatic patients (
Baur et al., 1986;
Cranston, 1988;
Kawai et al., 1996). Following studies have defined both the physical and chemical aspects of chironomid hemoglobins (
Mazur et al., 1987;
van Kampen et al., 1994a). On the other hand, nearly 40% of Japanese, Taiwanese, and Swedish sera from atopic patients were found to contain antibodies against crude extracts from a Japanese midge,
Cricotopus sylvestris, which has no hemoglobin (
van Kampen et al., 1994b). This result suggested the presence of other cross-reacting allergens except the hemoglobin. Presently, a few chironomid allergens have been reported, except for the hemoglobin; however, a protein with high molecular weight in the whole body extract of the chironomid adults was found to be more allergenic than the hemoglobin (
Matsuoka et al., 1988).
In the present study, IgE-immunoblot analyses were performed using both the sera of humans with skin test positives to the chironomid extract and immunized BALB/c mouse sera to identify the IgE-binding proteins in the whole body extract of C. kiiensis adults.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Preparation of the crude extract of C. kiiensis
Adults of
C. kiiensis were collected every 3 or 4 days from July to October in 1997 using 3 light-traps on a rice paddy at Dokyang-gu, Koyang-shi, Kyonggi-do, near Seoul, Korea. They were identified and selected under a stereomicroscope based on the key for morphological identification (
Ree, 1993). The selected midges were stored at -0℃ until used.
Frozen midges were defrosted, homogenized, and then extracted in 10 mM phosphate buffered saline (PBS, pH 7.4) followed by incubation for 10 hr at 4℃. The extracts were used for the ELISA or immunoblot analysis. Lyophilized midges were extracted in the modified Coca solution (0.9% NaCl, 0.25% NaHCO
3, 0.4% phenol), and 1:40 (w/v) diluted extracts were used for the skin prick test (
Park et al., 1991).
The skin prick test with C. kiiensis crude extract was performed with the patients who visited the allergy clinic of Severance Hospital, Yonsei University College of Medicine, Seoul, or those visited the Department of Allergy and Clinical Immunology, Ajou University Hospital in Suwon-shi, Kyonggi-do, Korea. Sera of the skin test positives were collected from June to August in 1998, and kept frozen at -0℃ until used.
Production of antisera in mice
Six-week-old 3 female BALB/c mice were immunized for the preparation of antiserum. Aluminum hydroxide gel (alum) was prepared as described (
Ree et al., 1996). Twenty micrograms of the crude extract in PBS were mixed with 1 ml of alum, and the mice were injected intraperitoneally with the crude extract-gel (0.1 ml, containing 2 µg of the crude extract and 14 mg of alum) at 0, 4 and 8 week intervals. At 5 and 9 weeks of immunization, the sera were collected.
ELISA was performed for the detection of human IgE as described previously (
Kim and Park, 1994). Briefly, the ELISA plates were coated with the crude extracts (10 µg/ml). After blocking with 10% newborn calf serum, each serum sample was added to the ELISA plates. Then, the plates were incubated with 1:1,000 diluted biotin-labelled goat anti-human IgE antibody (Sigma, St. Louis, USA). After washing, it was visualized with streptavidin-peroxidase and ABTS (2,2'-azido-ethly benzthiazoline sulfonic acid in citrate phosphate buffer), and the reaction was stopped with 2 N sodium azide. The absorbance was read at 410 nm.
The chironomid-specific serum IgE levels in the immunized mice were also measured by the ELISA as described (
Ree et al., 1996). The ELISA plates were coated with the crude extract and incubated with 1:2,000 diluted biotinylated anti-mouse IgE (Biodesign, Kennebunk, USA). Following the washes, 1:8,000 diluted peroxidase conjugated anti-biotin antibody (Vector, Burlingame, USA) was added before the incubation took place. Wells were developed with 0.05% orthophenylenediamine and 0.006% hydrogen peroxide in 0.1 M phosphate citrate buffer (pH 5.0). The absorbance was read at 490 nm.
The specific IgE levels in mice were measured in vivo by PCA reactions in rat skin (
Kawai and Konishi, 1988). Eight-week-old male Wistar rats were sensitized intradermally with 0.05 ml of a serial dilution of an antiserum. Four hours after the sensitization, a mixture of 0.5 ml of the chironomid crude extract (2 mg/ml) and 0.5 ml of 2% Evans blue in saline was injected intravenously. After 30 min, the rats were sacrificed, the dorsal skin reflected, and the reaction sites were measured.
The chironomid crude extract was electrophoresed on a 12% SDS-polyacrylamide gel and electrotransferred to the nitrocellulose membrane for IgE-immunoblot analysis. Nonspecific bindings were blocked with 3% bovine serum albumin and reacted with 1:10 dilution of human sera or 1:40 dilution of pooled immune mouse sera. After three washes, the membranes were incubated with1:500 diluted alkaline phosphatase conjugated anti-human IgE (Sigma) or peroxidase conjugated anti-mouse IgE (Nordic Immunology, Tilburg, Netherlands). The color was developed with the substrate for alkaline phosphatase (66 µl of 50 mg/ml of nitrobluetetrazolium and 33 µl of 50 mg/ml of 3-bromo-4-chloro-5-indolyl-phosphate in 10 mM Tris-HCl, pH 9.5, 100 mM NaCl, 5 mM MgCl2). For peroxidase, 2 mM diaminobenzidine solution containing 0.003% H2O2 was used for color development.
RESULTS
Chironomid midge proteins
Approximately 4,800
C. kiiensis adults were caught (
Fig. 1). A total weight of chironomid midges was about 1.3 g and the extracted protein in PBS from the midges was 133 mg.
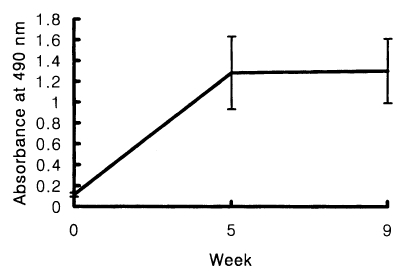
The positive cut-off value of the ELISA for the measurement of human serum IgE was 0.18. Chironomid-specific serum IgE were detected from 10 out of 15 skin test positives (66.7%). The absorbance range at 490 nm was between 0.25 and 1.33. The mean absorbance ± standard deviation was 0.65 ± 0.21. In immunized BALB/c mice, the increased levels of chironomid-specific IgE were detected by the ELISA, but no significant difference in the IgE levels between the sera obtained at 5 or 9 weeks of the first immunization (
Fig. 2).
Anti-chironomid IgE-mediated PCA reactions were easily recognized with
C. kiiensis adult extracts, indicating allergenicity of the extract in BALB/c mice. A blue spot larger than 5 × 5 mm on inner side of the rat skin was determined to be positive. The PCA titer was 1:320 with sera of 5 or 9 weeks of the immunization, and there was no blue spot detected with 1:640 diluted sera. When 1:20 diluted pooled serum was used, maximum sizes of the blue spots were 18 × 14 mm with serum obtained at 5 weeks of the first immunization and 16 × 15 mm with serum obtained at 9 weeks (
Fig. 3).
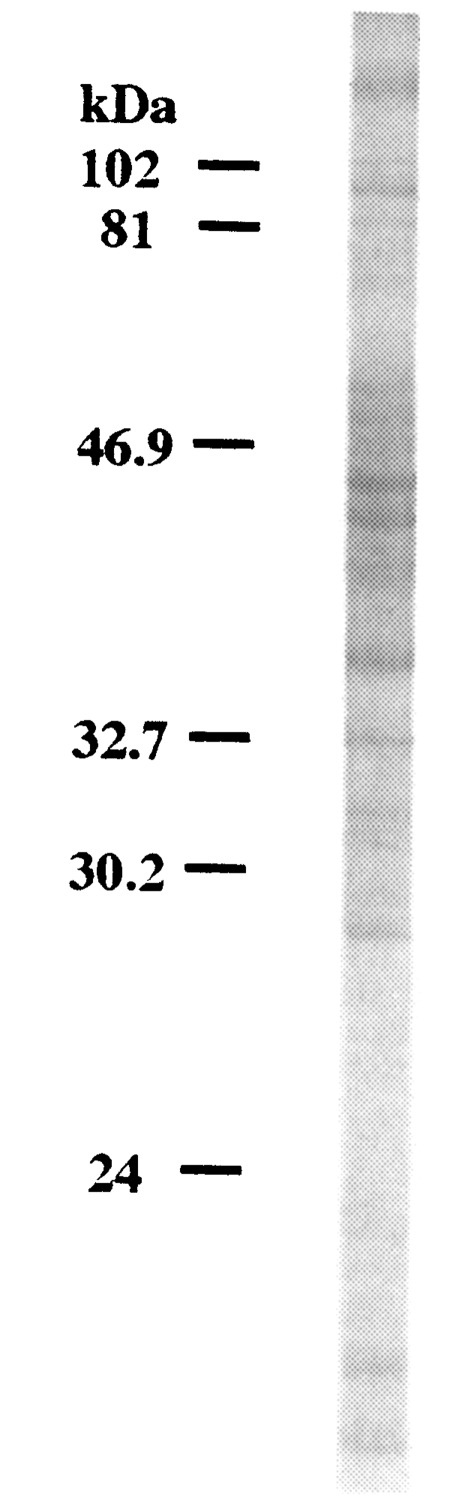
SDS-PAGE analysis of
C. kiiensis adult extract was performed. More than 20 protein bands were observed on a electrophoretic gel (
Fig. 4).
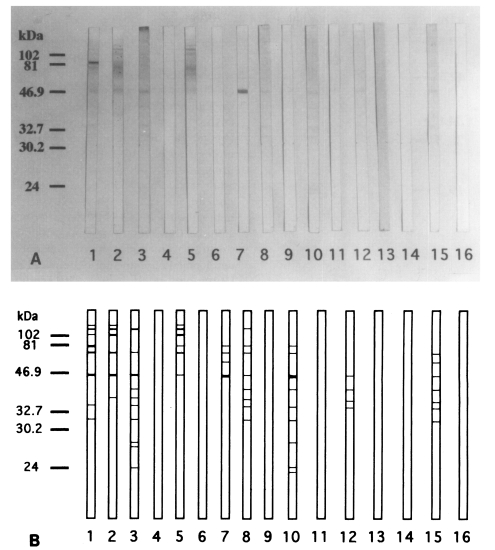
Although the ELISA showed the increasing levels of chironomid-specific IgE, the specific bands on the IgE-immunoblot were not consistent with the subjects with increased IgE levels. The reactive bands that seemed to be highly specific appeared in 9 out of 15 human serum samples. The IgE-reacting protein bands were visualized at 130, 110, 100, 80, 73, 55, 46, 40, 37, 34, 31, 27, 26, 24, and 23 kDa on the immunoblot analysis. The major IgE-reacting protein bands, which reacted with more than 50% of the subjects, were those revealed at 110, 80, 73, 46, 40, 37, 34, and 31 kDa (
Fig. 5).
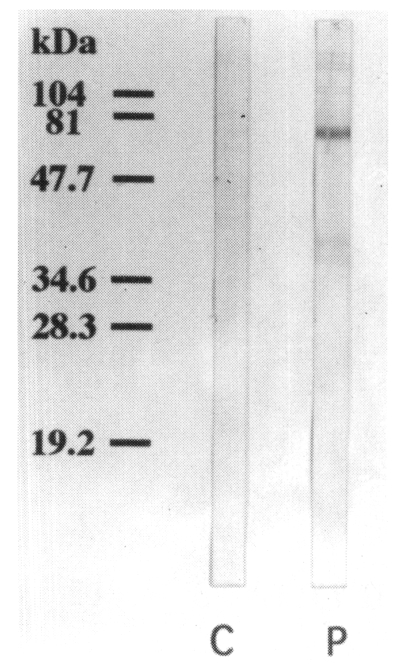
Using a pooled serum of the immune BALB/c mice, the IgE-reacting protein bands were visualized at 130, 110, 100, 80, 73, 46, 40, 37, and 34 kDa on the immunoblot analysis. The bands visualized at 73, 40 and 37 kDa were more prominent than other bands. No IgE-reacting bands were found in the control sera (
Fig. 6).
The reactive band patterns were largely similar between skin test positive humans and immunized BALB/c mice. The bands with molecular weight of 110, 80, 73, 46, 40, 37, and 34 kDa were recognized prominently in both humans and mice on the immunoblot analysis. However, the bands of 55, 31, 27, 26, 24, and 23 kDa were found only in sensitized humans, but not in immunized mice.
DISCUSSION
Most of the researches about chironomid allergens were carried out on the hemoglobin (
Baur et al., 1986). It has been reported that some chironomids have hemoglobins during the larval stage, and the larval hemoglobin degrades rapidly after the emergence. Some of the hemoglobins, however, are retained in the adult stage for several days, and they are believed to be the most important allergen in chironomid adults as well as in larvae (
Tee et al., 1987). Mazur et al. (
1987) reported two types of hemoglobins in chironomids: one is a 15-16 kDa monomer, and the other is a dimer with the molecular weight of 32 kDa. It was reported that the cross-reactivities between different chironomid species are common, and they also are derived from the hemoglobin components with common antigenic determinants predominantly (
Baur et al., 1983;
Kawai and Sakamoto, 1992). The cross-reactivity between
Chi t I, one of the most well-known chironomid hemoglobin component, and
C. sylvestris extracts was reported, which was also an evidence for common epitopes in both midge species (
van Kampen et al., 1994a).
It is believed, however, that there are other allergens besides the hemoglobins in chironomid extracts, especially in those from an adult stage. Matsuoka et al. (
1988) reported that children with asthma were more allergenic to the extracts from chironomid adults than the larvae. The same research group reported that the most allergenic substance with the molecular weight higher than 500 kDa, presumably vitellogenin in the chironomid adult female body and eggs. But, they could not detect IgE antibody to chironomid hemoglobins in 32 children with bronchial asthma. They found that hemoglobin degraded during the metamorphosis and noticed the developmental change of chironomid allergens (
Matsuoka et al., 1990). The study on the extracts of several different species of chironomids was performed, and another IgE-reacting protein with a different molecular weight was also reported (
Kawai and Konishi, 1988). However, these allergens have not been investigated further. Lee et al. (
1995) used
C. flaviplumus midges, which is a widely distributed chironomid species in Korea, to detect specific IgE responses in atopic children in Korea. At least 15 IgE binding bands of
C. flaviplumus extract were detected through an immunoblot analysis from 3 children, and 3 components with molecular weights of 32, 27, and 19 kDa showed relatively strong reactivity. The IgE reactions to the subjects, however, showed wide variations, and definite IgE-binding proteins to which over 50% of atopic subjects sera reacted were not found. Another study on
C. flaviplumus showed a 65 kDa protein to be the most reactive protein against IgE in the experimentally sensitized mice. Other allergens were also found with the molecular weights of 52, 35, 25, and 15 KDa. The IgE-binding protein of 15 kDa in the extracts was supposedly considered as
C. flaviplumus hemoglobin which was based on the molecular size shown by the immunoblot analysis (
Ree et al., 1996). Komase et al. (
1997) observed 24 IgE-binding components in
C. yoshimatsui extracts, but could not detect any IgE-binding protein to which over 50% of the patient sera reacted. They also noticed that only a limited number of patient sera reacted to midge proteins with molecular mass in the range of 16-32 kDa which corresponded to hemoglobins.
The present study showed the IgE-binding proteins with different molecular weights. There were no IgE-binding proteins found that were smaller than 20 kDa when using human sera with positive skin test to chironomid extracts or in experimentally sensitized BALB/c mice. This indicated that chironomid hemoglobin did not play any role in the IgE-immunoblot analysis in the present study. This result means that the SDS-PAGE analysis may be responsible for the lack of involvement of hemoglobins to the allergenicity of
C. kiiensis in this study. Kawai et al. (
1996) reported that a monomeric hemoglobin of
Polypedilum nubifer could bind to human IgE after the treatment with non-denaturing PAGE. The lack of allergenicity of hemoglobins from
C. kiiensis may also be attributable to the scarceness of remnant hemoglobins in the adult
C. kiiensis when compared to those of other
Chironomus species. It, on the other hand, is possible that the hemoglobin in the extract was presumably allergenic, but the serum samples used for the study did not contain IgE antibodies to chironomid hemoglobins. Several other IgE-binding proteins with molecular weights higher than the hemoglobin were rather easily detected through the immunoblot analysis in this study. The IgE-binding proteins in chironomids need more investigations, especially on their allergenicity to humans as well as their characteristics at a molecular level.
Yamashita et al. (
1989) suggested that there might be no cross-reactivity or, if any, only very low cross-reactivity between midge allergens and house dust mite, silk, shrimp, or mosquito allergens. However, the existence of cross-reactive allergens between chironomids and other arthropods has also been reported. Ito et al. (
1986) showed that 38% of the patients with asthma had a positive skin prick test with chironomid extract, and 80% of this group also had a positive prick test with house dust mites. Nagano et al. (
1992) showed evidently that cross-reactive epitopes to chironomids were expressed on the
Dermatophagoides pternyssinus with molecules of 45-53 kDa. Witteman et al. (
1995) showed the presence of cross-reactivities between chironomids and house dust mites, silverfish or cockroaches by means of RAST-inhibition studies. Pascual et al. (
1997) noticed cross-reactive bands between IgE-binding proteins from
Anisakis, German cockroach and chironomids at 30-43 kDa on immunoblot analysis. They also reported that none of the sera recognized allergens in the 14 kDa area, presumably chironomid hemoglobins. These cross-reactive allergens should be a part of chironomid allergens other than hemoglobins.
BALB/c mice were used in the study, because the strain was well known to produce high IgE among experimental mouse strains. As expected, the mice showed some similar IgE antibody binding responses to the potential allergens for humans on immunoblot analysis. Therefore, the experimental mouse, especially BALB/c strain, can be used successfully for the identification and characterization of allergens, including those from various insects. However, the different immune response to the same protein was also produced between the humans and mice. In nature, allergens in the dead and dry midges are exposed to humans. Once the midges become dry, they are broken into very tiny particles, and then many allergenic proteins in live midges tend to loose their allergenicity. Thus, the exposed antigens for humans in dry midges must be different, and only a limited sort of allergens could be inhaled to chironomid-sensitive people. The results obtained in the study using immunized mouse sera through an artificial immunization with chironomid extracts showed the IgE antibody reactive allergens, but did not show the allergens of interest, especially those in dry forms in nature. The pattern of the immunoblot findings between the humans and mice fail to represent the real difference in immune responses of the two races to the allergens, but showed the difference in immune responses caused by the different challenging allergens. Nevertheless, the immunized mice showing consistent immune reactions to the allergens will be useful for further characterization of allergens.
In summary, the IgE-immunoblot analysis demonstrated that the major IgE-reacting protein bands, which reacted with more than 50% of the skin test positive human sera, were those with the molecular weights of 110, 80, 73, 46, 40, 37, 34, and 31 kDa. The reactive band patterns were highly similar between skin test positive humans and immune BALB/c mice. However, the bands of 55, 31, 27, 26, 24, and 23 kDa were found only in sensitized humans, but not in immunized mice.
Notes
-
This study was supported by the Basic Medical Research Fund, the Ministry of Education, Korea, 1996-1997.
References
- 1. Baur X, Aschauer H, Mazur G, Dewair M, Prelicz H, Steigemann W. Structure, antigenic determinants of some clinically important insect allergens: chironomid hemoglobins. Science 1986;233:351-354.
- 2. Baur X, Dewair M, Fruhmann G, Aschauer H, Pfletschinger J, Braunitzer G. Hypersensitivity to chironomids (non-biting midges): localization of the antigenic determinants within certain polypeptide sequences of hemoglobins (erythrocruorins) of Chironomus thummi thummi (Diptera). J Allergy Clin Immunol 1982;69:66-76.
- 3. Baur X, Dewair M, Haegele K, Prelicz H, Scholl A, Tichy H. Common antigenic determinants of haemoglobin as bases of immunological cross reactivity between chironomid species (Diptera, Chironomidae): Studies with human and animal sera. Clin Exp Immunol 1983;54:599-607.
- 4. Cranston PS. Allergens of non-biting midges (Diptera: Chironomidae): a systematic survey of chironomid haemoglobins. Med Vet Entomol 1988;2:117-127.
- 5. Ito K, Miyamoto T, Shibuya T, et al. Skin test and radioallergosorbent test with extract of larval and adult midges of Tokunagayushrika akamusi (Diptera: Chironomidae) in asthmatic patients of the metropolitan area of Tokyo. Ann Allergy 1986;57:199-204.
- 6. Kawai K, Konishi K. Fundamental studies on chironomid allergy III. Allergen analyses of some adult Japanese chironomid midges (Chironomidae, Diptera). Arerugi 1988;37:944-951.
- 7. Kawai K, Sakamoto K. Cross-reactivities of murine IgE-inducing larval hemoglobins among various chironomid species. Jpn J Sanit Zool 1992;43:95-103.
- 8. Kawai K, Tagoh H, Yoshizaki K, Murakami G, Muraguchi A. Purification and characterization of an allergenic monomeric hemoglobin from a chironomid distributed worldwide, Polypedium nubifer. Int Arch Allergy Immunol 1996;110:288-297.
- 9. Kay AB, Gad EL, Rab MO, Stewart J, Erwa HH. Widespread IgE-mediated hypersensitivity in Northern Sudan to the chironomid Cladotanytarsus lewisi. Clin Exp Immunol 1978;34:106-110.
- 10. Kim YJ, Park HS. Skin reactivity and specific IgE antibody to two non-biting midges in Korean respiratory allergy patients. J Korean Med Sci 1994;9:21-28.
- 11. Kimura JY, Matsuoka H, Ishii A. ELISA inhibition method in detection of mite and chironomid antigens in environmentalsamples of dust, soil and air. Allergy 1990;45:167-173.
- 12. Kino T, Chihara J, Fukuda K, Sasaki Y, Shogaki Y, Oshima S. Allergy to insects in Japan. III. High frequency of IgE antibody responses to insects (moth, butterfly, caddis fly, and chironomid) in patients with bronchial asthma and immunochemical quantitation of the insect-related airborne particles smaller than 10 µm in diameter. J Allergy Clin Immunol 1987;79:857-866.
- 13. Komase Y, Sakata M, Azuma T, Tanaka A, Nakagawa T. IgE antibodies against midge and moth found in Japanese asthmatic subjects and comparison of allergenicity between these insects. Allergy 1997;52:75-81.
- 14. Lee KY, Kang HY, Kim DS, Kim KE, Jeong BJ, Ree HI. Immunological responses to Chironomus flaviplumus in atopic children. J Korean Soc Allergol 1995;15:250-261.
- 15. Matsuoka H, Ishii A, Kimura Y, Noono S. Developmental change of chironomid allergen during metamorphosis. Allergy 1990;45:115-120.
- 16. Matsuoka H, Ishii A, Noono S. Detection of IgE antibodies to larvae and adults of chironomids by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay. Allergy 1988;43:425-429.
- 17. Mazur G, Becker WM, Baur X. Epitope mapping of major insect allergens (chironomid hemoglobins) with monoclonal antibodies. J Allergy Clin Immunol 1987;80:876-883.
- 18. Nagano T, Ohta N, Okano M, Ono T, Masuda Y. Analysis of antigenic determinants shared by two different allergens recognized by human T cells: house dust mite (Dermatophagoides pteronyssinus) and chironomid midge (Chironomus yoshimatsui). Allergy 1992;47:554-559.
- 19. Park HS, Rhu NS, Cho DI, Kim JW. Two cases of bronchial asthma induced by Chironomus plumosus and Tokunagayusurika akamusi. J Korean Soc Allergol 1991;11:362-367.
- 20. Pascual CY, Crespo JF, San Martin S, et al. Cross-reactivity between IgE-binding proteins from Anisakis, German cockroach, and chironomids. Allergy 1997;52:514-520.
- 21. Ree HI. Breeding places of non-biting midges (Chironomidae, Diptera) in Korea. Korean J Entomol 1993;23:169-176.
- 22. Ree HI, Kim HS. Studies on Chironomidae (Diptera) in Korea I. Taxonomical study on adults of Chironominae. Proc Coll Nat Sci SNU 1981;6:1-126.
- 23. Ree HI, Lee SH, Kim YK, Jeon S, Chang JK, Kim YS. Identification and characterization of allergens of Chironomus flaviplumus adults (Chironomidae, Diptera) in mice. Korean J Parasitol 1996;34:35-47. (in Korean).
- 24. Tee RD, Cranston PS, Kay AB. Further characterisation of allergens associated with hypersensitivity to the "green nimitti" midge (Cladotanytarsus lewisi, Diptera: Chironomidae). Allergy 1987;42:12-19.
- 25. van Kampen V, Becker WM, Chen Z, et al. Analysis of B-cell epitopes in the Nterminal region of Chi t I component III using monoclonal antibodies. Mol Immunol 1994a;31:1133-1404.
- 26. van Kampen V, Liebers V, Czuppon A, Baur X. Chironomidae hemoglobin allergy in Japanese, Swedish, and German populations. Allergy 1994b;49:9-12.
- 27. Witteman AM, van den Oudenrijn S, van Leeuwen J, Akkerdaas J, van der Zee JS, Aalberse RC. IgE antibodies reactive with silverfish, cockroach and chironomid are frequently found in mite-positive allergic patients. Int Arch Allergy Immunol 1995;108:165-169.
- 28. Yamashita N, Ito K, Miyamoto T, et al. Allergenicity of Chironomidae in asthmatic patients. Ann Allergy 1989;63:423-426.
- 29. Yamashita N, Morita Y, Ito K, et al. Chironomidae as a cause of IgE-mediated histamine release in patients with asthma. Ann Allergy 1989;63:154-158.
Fig. 1
Chironomus kiiensis adults collected (◁: female, ◀: male). The bar indicates 2 mm.

Fig. 2BALB/c mice were immunized intraperitoneally with chironomid crude extract mixed with alum at 0, 4, 8 weeks of immunization. The increased levels of chironomid-specific IgE were detected in the immune BALB/c mice by the ELISA at 5 and 9 weeks.

Fig. 3Anti-chironomid IgE-mediated passive cutaneous anaphylaxis (PCA). Reactions were easily recognized with Chironomus kiiensis adult extracts, indicating allergenicity of the chironomid extract in BALB/c mice. The PCA titer was 1:320 with sera of 9 weeks of the immunization.

Fig. 4SDS-PAGE analysis of Chironomus kiiensis adult crude extract.

Fig. 5
A. Immunoblot analysis of 15 human sera of the skin test positive cases showed IgE-reacting protein bands at 130, 110, 100, 80, 73, 55, 46, 40, 37, 34, 31, 27, 26, 24, and 23 kDa (lane 1-15). The major IgE-reacting protein bands were those of 110, 80, 73, 46, 40, 37, 34, and 31 kDa. No IgE-reacting bands were noticed in the control serum (lane 16). B. Schematic representation of A.

Fig. 6Immunoblot analysis of the pooled immune BALB/c mouse sera. IgE-reacting protein bands of 130, 110, 100, 80, 73, 46, 40, 37, and 34 kDa are noticed on the immunoblot analysis (lane P). The bands of 73, 40, and 37 kDa were prominent than other bands. No IgE-reacting bands were noticed in the control serum (lane C).