Abstract
Paramyosin is a myofibrillar protein present in helminth parasites and plays multifunctional roles in host-parasite interactions. In this study, we identified the gene encoding paramyosin of Clonorchis sinensis (CsPmy) and characterized biochemical and immunological properties of its recombinant protein. CsPmy showed a high level of sequence identity with paramyosin from other helminth parasites. Recombinant CsPmy (rCsPmy) expressed in bacteria had an approximate molecular weight of 100 kDa and bound both human collagen and complement 9. The protein was constitutively expressed in various developmental stages of the parasite. Imunofluorescence analysis revealed that CsPmy was mainly localized in the tegument, subtegumental muscles, and the muscle layer surrounding the intestine of the parasite. The rCsPmy showed high levels of positive reactions (74.6%, 56/75) against sera from patients with clonorchiasis. Immunization of experimental rats with rCsPmy evoked high levels of IgG production. These results collectively suggest that CsPmy is a multifunctional protein that not only contributes to the muscle layer structure but also to non-muscular functions in host-parasite interactions. Successful induction of host IgG production also suggests that CsPmy can be applied as a diagnostic antigen and/or vaccine candidate for clonorchiasis.
-
Key words: Clonorchis sinensis, paramyosin, collagen, complement 9, antigenicity
INTRODUCTION
Paramyosin is an α-helical, rod-shaped filamentous protein found in numerous invertebrates. The protein mainly localizes in muscles, acting as a key component in the formation of large filaments in mollusca [
1] and likely playing an important role in specialized contractile activities [
1-
3]. Paramyosin has been also identified in numerous helminth parasites, including
Schistosoma mansoni [
4-
6],
Schistosoma japonicum [
7-
9],
Fasciola hepatica [
10],
Paragonimus westermani [
11],
Taenia solium [
12,
13],
Echinococcus granulosus [
14], and
Onchocerca volvulus [
15].
Besides their classical role as structural proteins that control the physiological contraction of muscle layers, paramyosins from helminth parasites have been proposed as immunoregulatory molecules that modulate the host's immune system by repressing the classical pathway of the complement cascade via inhibition of complement C1 function [
16]. They involved in immunological defense mechanism of parasites by acting as Fc receptors [
17,
18] and induced allergenic responses in humans [
19]. These results suggested that paramyosin of helminth parasites are multifunctional proteins acting not only as structural protein in muscle layers to control their contraction physiologically, but also as an immunoregulatory molecule interacting with the host immune system. In addition, immunogenic properties of paramyosins of helminth parasites make them potential vaccine candidates [
11,
20-
30].
In this study, we have identified a novel gene encoding a paramyosin from Clonorchis sinensis, a liver fluke that causes clonorchiasis in mammals, including humans, and characterized the biochemical and immunological properties of its recombinant protein.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Parasite
C. sinensis metacercariae were collected from naturally infected
Pseudorasbora parva caught in a pond located in Jinju, South Korea. All parasite materials used in this study were prepared as described previously [
31]. Briefly, Sprague-Dawley rats were infected by the oral administration of 100 metacercariae. Juvenile and adult worms in different developmental stages were collected from the bile ducts of rats 2, 4, 6, or 9 weeks after experimental infection. The worms were washed 5 times with cold physiological saline to remove any contamination from the hosts and were stored at -70℃, or used immediately for RNA preparation.
Synthesis of cDNA and PCR
C. sinensis adult worms were ground in liquid nitrogen and total RNA was isolated with a TRIzol reagent (Invitrogen, Carlsbad, California, USA) according to manufacturer's instructions. Single-stranded cDNA was synthesized from the total RNA using the SMART™ RACE cDNA Amplification Kit (Clontech, Palo Alto, California, USA). Double-stranded cDNA was amplified by PCR using 2 degenerate primers designed on the highly conserved amino acid regions of paramyosins from other helminth parasites. The forward primer used was 5'-CGWGATGCWAAYCGTCGTCTTACYGATTTRGA-3' and the reverse primer was 5'-AAYTGRCGYTTGTARGCYTTCATYTTCATTTG-3'. The thermal cycling profile for amplification was 94℃ for 4 min and 35 cycles of 94℃ for 1 min, 48℃ for 2 min, and 72℃ for 1 min, followed by a 72℃ extension for 10 min. The amplified PCR product was purified from gel, cloned into pGEM T-Easy vector (Promega, Madison, Wisconsin, USA) and transformed into Escherichia coli DH5α competent cells (Invitrogen). The nucleotide sequence of the cloned gene was determined using the Big-Dye Terminator Cycle Sequencing Ready Reaction Kit (PE Biosystem, UK) and an ABI automated DNA sequencer.
Rapid amplification of cDNA ends (RACE)
RACE procedures were performed with the SMART™ RACE cDNA Amplification Kit (Clontech) according to manufacturer's instructions. The first-strand cDNA was the template used for RACE. The 5'-RACE and 3'-RACE reactions were performed with gene-specific primer (GSP) and Universal Primer A Mix (UPM) according to manufacturer's instructions. Each GSP was designed on the nucleotide sequences obtained from the previous degenerate-primer PCR. GSP1 used for 5'-RACE was 5'-CACGCAGGCGACGTTCTTCTTCCAAGAA-3', and GSP2 for 3'-RACE was 5'-GAAGATGACCGACGAATGGTGCTTGAGC-3'. The amplified products were purified from the gel, cloned into pGEM T-Easy vector (Promega) and then sequenced.
Expression and purification of rCsPmy
The full-length CsPmy gene was amplified by PCR using the primers 5'-GTCGACATGAGTCACGAGTCGGAATCACAC-3', which contains a 5' Sal I site, and 5'-AAGCTTTTACATCATGCTCGTCGCGCGCGT-3', which harbors a 5' Hind III site. The PCR product was purified and ligated into pGEM T-Easy vector (Promega), followed by transformation into E. coli DH5α competent cells. After purification, plasmid DNA digested with Sal I and Hind III was ligated into pQE-30 expression vector (Qiagen, Valencia, California, USA) that predigested with the same enzymes. The resulting plasmid was transformed into E. coli M15 [pREP4] competent cells (Qiagen) and spread onto Luria-Bertani agar plates containing 100 µg/ml of ampicillin and 30 µg/ml of kanamycin. Selected clones were grown and induced with 1 mM isopropyl-1-thio-β-D-galactopyranoside. The cells were collected by centrifugation at 10,000 g for 15 min at 4℃, suspended in a native lysis buffer (50 mM NaH2PO4, 300 mM NaCl, 10 mM imidazole, pH 8.0), and sonicated on ice. The expressed protein was purified using a nickel-nitrilotriacetic acid (Ni-NTA) agarose column (Qiagen) containing complete protease inhibitor cocktail (Roche, Mannheim, Germany) under native conditions. The purity of the purified rCsPmy was analyzed by SDS-PAGE followed by Coomassie blue staining.
Production of specific antibody against rCsPmy (anti-rCsPmy)
Anti-rCsPmy was produced by immunizing BALB/c mice with the purified rCsPmy (50 µg) 3 times at 2-week intervals. Two weeks after the final boosting, the mice were sacrificed and the sera were collected. The IgG fraction was further isolated from the sera with a Protein G-Sepharose column (Amersham Biosciences, Piscataway, New Jersey, USA). The specificity of the antibody was confirmed by immunoblot analysis.
Collagen binding assay
To characterize the collagen binding properties of rCsPmy, a collagen binding assay was performed as previously described [
11]. Briefly, purified collagen type I (Sigma, St. Louis, Missouri, USA) was pre-washed with PBS (pH 7.2) containing 0.65 M NaCl, and immediately followed by equilibration with PBS. The pre-washed collagen (1 mg/ml) was separated on 8% SDS-PAGE and the proteins were transferred onto a nitrocellulose membrane (Millipore, Bedford, Massachusetts, USA). The membrane was cut into strips, and the strips were blocked with 3% skim milk in PBS containing 0.05% Tween 20 for 1 hr at room temperature. The strips were incubated with different concentrations (0-20 µg) of rCsPmy in blocking solution for 2 hr at room temperature. After several washes with PBST, the strips were probed with anti-rCsPmy diluted 1 : 1,000 for 2 hr at room temperature and washed with PBST several times. The strips were further incubated in horseradish peroxidase (HRP)-conjugated goat anti-mouse IgG (Sigma) diluted 1 : 1,000 for 2 hr at room temperature and washed with PBST several times. Immunoreactive bands were visualized with 4-chloro-1-naphthol (4CN, Sigma). Alternately, ELISA was also performed. Briefly, purified collagen (Sigma) was coated onto a 96-well microplate (Costar, Corning, New York, USA) at a concentration of 5 µg/ml and incubated overnight at 4℃. The plate was blocked with 200 µl PBST supplemented with 1% bovine serum albumin. Different concentrations of rCsPmy (0-10 µg) diluted in PBST were added to each well followed by incubation for 2 hr at 37℃. After washing the plate with PBST 3 times, anti-rCs-Pmy diluted 1 : 1,000 in PBST was added to each well followed by further incubation for 2 hr at 37℃. Several washes with PBST, HRP-conjugated goat anti-mouse IgG (Sigma) diluted 1 : 1,000 in PBST was added to each well and the plate was incubated for 2 hr at 37℃. After 3 washes with PBST, substrate mixture (0.05% o-phenylenediamine, 0.04% hydrogen peroxide/100 mM sodium citrate, pH 5.2) was added to each well and the plate was incubated for 30 min at room temperature. Reaction was stopped by the addition of 50 µl of 2.5 N H
2SO
4 and absorbance was measured at 492 nm with a Universal Microplate recorder EL800 (Bio-Tek, Winooski, Vermont, USA). All the experiments were performed in triplicate.
Purified rCsPmy (20 µg) subjected to SDS-PAGE was blotted onto a nitrocellulose membrane (Millipore), which was then cut into strips and blocked with 3% skim milk in PBST for 1 hr at room temperature. The strips were incubated with different concentrations (0-25 µg) of human complement 9 (C9, Quidel, San Diego, California, USA) in blocking solution for 2 hr at room temperature. After several washes with PBST, the strips were reacted with goat anti-human C9 antibody (Quidel) diluted 1 : 500 for 2 hr and then incubated with HRP-conjugated mouse anti-goat IgG (Sigma) diluted 1 : 1,000 for 2 hr at room temperature. Bands were visualized with 4CN (Sigma). For ELISA, rCsPmy was coated onto a 96-well microplate (Costar) at a concentration of 5 µg/ml by overnight incubation at 4℃. The plate was blocked with 200 µl PBST supplemented with 1% BSA, after which different concentrations of human C9 (Quidel, 0-10 µg) were added to each well. The plate was incubated for 2 hr at 37℃, washed with PBST 3 times, then incubated with goat anti-human C9 (Quidel) diluted 1 : 1,000 in PBST for 2 hr at 37℃. Several washes with PBST, HRP-conjugated mouse anti-goat IgG diluted 1 : 1,000 in PBST was added to each well and incubated for 2 hr at 37℃. After 3 washes with PBST, the plate was developed and analyzed with the same method as described above. All the experiments were performed in triplicate.
Semi-quantitative reverse transcription-PCR (RT-PCR)
The pattern of CsPmy mRNA transcription in various developmental stages of
C. sinensis, including metacercariae, juveniles, and adult worms, was analyzed as previously described [
31]. Total RNA was isolated from each developmental stage of the parasite using TRIzol reagent (Invitrogen) followed by treatment with RNase-free DNase (GIBCO BRL, Rockvile, Maryland, USA) to remove any DNA contamination. Reverse transcription and subsequent amplification of the CsPmy transcripts were performed with the ProtoScript® II RT-PCR Kit (Invitrogen) using equal amounts of total RNAs (1 µg each) and specific primers, according to manufacturer's instructions. Specific primers used were 5'-ATGAGTCACGAGTCGGAATCACAC-3' and 5'-TTACATCATGCTCGTCGCGCGCGT-3'. The amplification reaction was performed at 94℃ for 5 min, 94℃ for 1 min, 55℃ for 1 min, and 72℃ for 3 min for 25 cycles. As an internal control, the
C. sinensis actin gene was also amplified as previously described [
31]. Each amplified PCR product was analyzed on 1.2% agarose gel and stained with ethidium bromide.
To determine the localization of CsPmy in the parasite, immunoblotting and immunofluorescence assay (IFA) were performed. The excretory and secretory products (ESP) were prepared by incubating the adult C. sinensis in physiological saline for 3 hr at 37℃. The soluble fraction of the adult worms was prepared by homogenizing the adult worms in physiological saline containing Complete protease inhibitor cocktail (Roche) and centrifuging at 15,000 g for 15 min at 4℃. The supernatant was collected and used as the soluble fraction. The leftover pellet was resuspended in 8 M urea lysis buffer (8 M urea, 100 mM NaH2PO4, 10 mM Tris-HCl, pH 8.0), incubated at room temperature for 3 hr, and centrifuged at 15,000 g for 20 min at room temperature. This resulting supernatant was collected and used as the insoluble fraction. The ESP, soluble fraction, and insoluble fraction of C. sinensis adult worms were separated simultaneously by SDS-PAGE and transferred to a nitrocellulose membrane (Millipore). The membrane was blocked with PBST containing 3% skim milk for 1 hr and incubated with anti-rCsPmy diluted 1 : 1,000 in PBST at room temperature for 2 hr. After several washes with PBST, the membrane was incubated with HRP-conjugated goat anti-mouse IgG (Sigma) diluted 1 : 1,000 and developed with the same method as described above. For IFA, freshly prepared C. sinensis adult worms were washed several times with PBS (20 mM, pH 7.4) and fixed in 4% paraformaldehyde. The fixed worms were dehydrated using a graded ethanol series and embedded in paraffin. Paraffin sections (4 µm thickness) were mounted on slide glasses, deparaffinized, rehydrated and then rinsed with PBS. Slides were incubated with anti-rCsPmy diluted 1: 200 at room temperature for 2 hr and washed with PBS several times. After incubation with tetramethyl rhodamine isothiocyanate (TRITC)-conjugated goat anti-mouse IgG (Sigma) diluted 1 : 150 for 2 hr, the slides were washed with PBS several times and observed under a light/fluorescence microscope (Axioplot, Carl Zeiss, Jena, Germany). Counterstaining with Mayer's hematoxylin was also applied.
Antigenic property of rCsPmy
Serum samples (n = 75) used in this study were obtained from patients with clonorchiasis diagnosed by the egg detection method along with normal control serum samples (n = 20) collected from healthy individuals. Informed consent obtained from all individuals before admission was reviewed and approved by the Ethics Committee of the Gyeongsang National University College of Medicine, Jinju, South Korea. Immunoblot analysis was performed in order to determine the antigenicity of CsPmy. Purified rCsPmy was subjected to SDS-PAGE and transferred to a nitrocellulose membrane (Millipore). The membrane was cut into strips and the strips were blocked with PBST containing 3% skim milk for 1 hr at room temperature, followed by incubation with sera from patients with clonorchiasis or normal healthy controls diluted 1 : 200 at room temperature for 2 hr. After several washes with PBST, the membrane was incubated with HRP-conjugated goat anti-human IgG (Sigma) diluted 1 : 1,000 and developed as the same procedure as described above. To investigate CsPmy as an antigen which induced antibody production, Sprague-Dawley rats were subjected to intraperitoneal (n = 5) or intermuscular (n = 5) immunization with purified rCsPmy (50 µg). A control group of rats (n = 5) was injected with saline intraperitoneally. Rats were bled 4 weeks after immunization and the sera were used for ELISA to detect specific antibody.
RESULTS
Molecular characterization of CsPmy
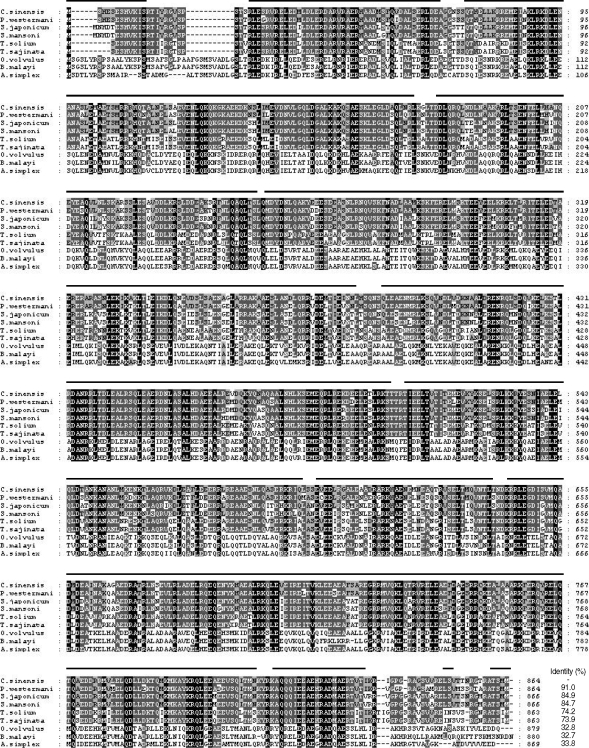
The full-length gene encoding CsPmy was identified by a combination of PCR using degenerate primers and RACE procedures. The CsPmy gene contains an open reading frame of 2,595 bp that encodes 864 amino acids. Primary sequence analysis of CsPmy suggested neither a signal peptide nor transmembrane domain was found in the sequence, although 4 putative N-glycosylation sites were identified at residues 71NSS73, 97NAS99, 215NLS217, and 559NKT561. Alignment of the deduced amino acid sequence of CsPmy with other known paramyosins from helminth parasites found significant sequence identity ranging from 32.7 to 91.0% (
Fig. 1). Specifically, the sequence identity was extremely high, up to 84.7%, when compared to paramyosins of treamtode parasites such as
S. mansoni,
S. japonicum, and
P. westermani. Secondary structure analysis suggested an extensive helical structure with repeated sequences of hydrophilic and charged amino acids expanded throughout the entire CsPmy sequence (
Fig. 1). The nucleotide sequence of CsPmy was deposited in the GenBank data base with the accession number EF071860.
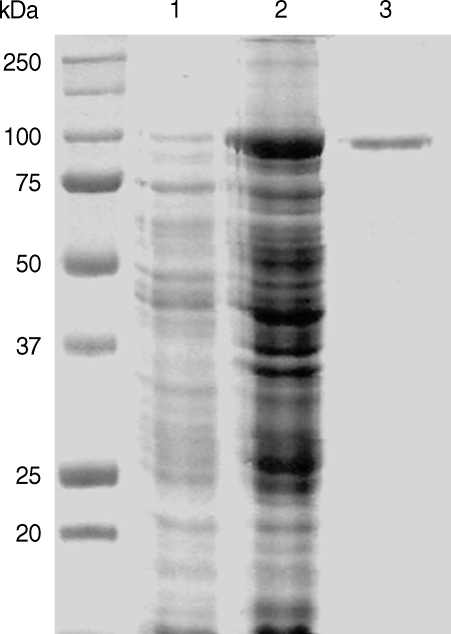
The full-length gene of CsPmy was cloned into a pQE-30 expression vector and expressed the recombinant protein in
E. coli. The rCsPmy was expressed as a soluble protein with an approximate molecular weight of 100 kDa, which corresponded well to the predicted size (99.4 kDa) derived from the primary sequence of the gene (
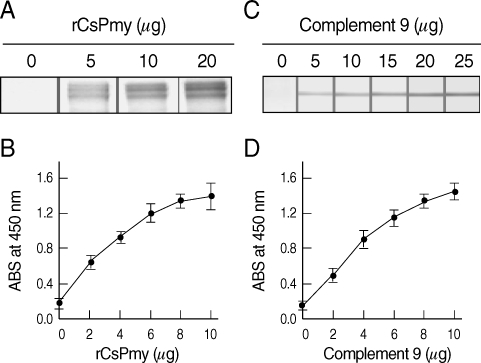
Fig. 2). To determine the nonstructural functions of CsPmy, the binding ability of rCsPmy to human collagen and C9 was determined by ELISA and immunoblot analyses. rCsPmy showed dose-dependent binding behavior to human collagen and C9 (
Fig. 3).
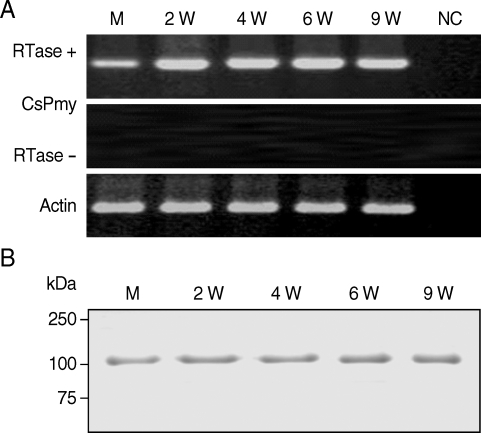
To analyze expression profile of RNA transcript of CsPmy in various developmental stages of
C. sinensis, a semi-quantitative RT-PCR was performed with the RNAs isolated from various developmental stages of the parasite. Amplification of the target gene from the RNAs of the metacercariae, juvenile (2-week old) and adult (4-, 6- and 9-week-old) worms suggested CsPmy was expressed in all developmental stages of the parasite tested (
Fig. 4A). Immunoblot analysis with anti-rCsPmy antibody also confirmed CsPmy was expressed in all developmental stages (
Fig. 4B).
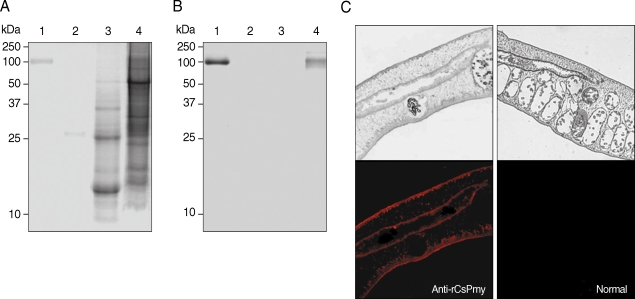
The localization of CsPmy in
C. sinensis was examined by immunoblot and IFA analyses. Immunoblot analysis using anti-rCsPmy antibody showed CsPmy was detected in the insoluble fraction of the adult worm, but not in the ESP or soluble fraction of the parasite (
Fig. 5A, B). IFA revealed strong reactivity of CsPmy in the tegument and subtegumental muscles as well as the cells surrounding the intestine (
Fig. 5C).
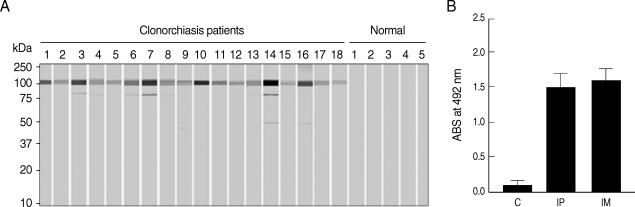
Immunoblot analysis showed positive reactivity of rCsPmy with sera from patients with clonorchiasis at a rate of 74.7% (56/75), compared the absence of reactivity seen with sera from normal healthy controls (
Fig. 6A). To further analyze the antigenic properties of CsPmy, the intraperitoneal or intramuscular immunization of purified rCsPmy was performed in rats and antibody levels against rCsPmy were tested by ELISA. In a normal control group, the mean value and standard deviation (SD) of the total IgG levels were 0.12 and 0.08, respectively. Meanwhile, the mean value and SD of the total IgG levels specific to rCsPmy for groups subjected to intraperitoneal or intermuscular immunization were 1.48 and 0.22, and 1.59 and 0.16, respectively (
Fig. 6B).
DISCUSSION
The CsPmy is a typical paramyosin in that it shares similar structural properties with paramyosins from other helminth parasites. Characteristic coiled-coil helical structure with repeated sequences of hydrophilic and charged amino acids, which is a typical structural property of paramyosins [
1], was found throughout the CsPmy sequence. The CsPmy was found to be expressed in various developmental stages from metacercariae to adults. Such a finding suggests an essential role of the protein in the life cycle of the parasite. The CsPmy was identified only in insoluble worm extract of the parasite, not in ESP or soluble worm extract. Localization studies of paramyosins from various helminth parasites have suggested additional non-muscular functions. Paramyosin from
T. solium (TPmy) was mainly present in the musculature but also detected in the tegument of the parasite [
13]. Paramyosin was localized in the post-acetabular glands of cercariae as well as on the tegument matrix and surface of lung schistosomula [
9,
32]. In
F. hepatica, paramyosin was localized within subtegumental muscle, on the surface of lamellae of the gut and the tegument of the adult parasite [
10]. A more recent study on
Paragonimus westermani also revealed PwPmy was found not only in the subtegumental muscle layer as well as muscles surrounding the oral sucker, pharynx, intestine and ovary, but also in tegument of the parasite [
11]. CsPmy was identified in subtegumental muscle, tegument and the muscle surrounding intestine of the parasite. Our data are consistent with previous studies of other helminth parasites. In addition, its localization in tegument further suggests CsPmy can possibly perform non-muscular functions interacting with the host's components.
Bacterially expressed rCsPmy was found to bind collagen in a dose-dependent manner. The ability of paramyosin from helminth parasites to bind collagen implies it performs significant, non-muscular functions in host-parasite interactions [
11,
12,
33-
35]. This is notable because paramyosin inhibits the classical complement cascade pathway of the host immune system possibly through competitively binding to the collagen-like regions of C1q [
16]. rCsPmy likewise demonstrated binding capacity to human C9. Although the mechanism of complement activation in
C. sinensis infection is not totally understood, it is well established that
S. mansoni paramyosin has an important immunomodulatory role in schistosomiasis by binding to C8 and C9 and thereby preventing assembly of the C5b-9n membrane attack complex (MAC) [
36]. Our finding that CsPmy binds to human collagen and C9 suggests it can possibly inhibit complement activation by binding to the complement components of the host. Therefore, it could potentially contribute to the immune evasion of
C. sinensis during infection. Further comprehensive studies are required to clarify the immuno-modulatory function of CsPmy in
C. sinensis infection.
Paramyosin also acts as an immunogen during infection with helminth parasites. Eight of 10 patients infected with
E. granulosus and 9 of 10 patients with
E. multilocularis revealed clear positive reactions against recombinant
E. granulosus paramyosin in ELISA [
14].
S. manosni paramyosin induced specific IgG1 and IgG4 productions in infected individuals [
37]. Paramyosin of
P. westermani showed positive reaction of 86.7% against the sera from patients with paragonimiasis and IgG1 and IgG4 were predominant IgG subclasses [
11]. Sera from patients with clonorchiasis also strongly reacted to rCsPmy (74.7%), which suggests CsPmy is a highly immunogenic antigen. Likewise, rats immunized with the rCsPmy also produced high levels of IgG in response to the protein. This coincides with previous studies on the vaccination/immunization of paramyosins from other helminth parasites [
11,
27,
38,
39]. Due to its high level of immunogenicity, paramyosin has been proposed as potential vaccine candidate in a number of helminthiases, including schistosomiasis [
20,
21,
28,
39,
40], filariasis [
22,
23] and cysticercosis [
27,
29]. We also found that rats vaccinated with rCsPmy (100 µg/rat) and challenged with 100 metacercariae of
C. sinensis showed reduced worm burden (11.6-20.6%) compared to control rats (our unpublished data). The worm burden was similarly reduced in both cases of intramuscular and intraperitoneal immunization with rCsPmy. The expression of CsPmy in all developmental stages of the parasite as well as on its surface could provide insights into the development of an anti-CsPmy vaccine, since the tegument of the parasite is constantly in contact with the immune system of the host. Our results collectively suggest CsPmy is an antigen that successfully induces host immune responses, and therefore is a potential vaccine candidate for clonorchiasis. Further comprehensive studies to evaluate the potential of rCwPmy as a vaccine against clonorchiasis are currently underway.
References
- 1. Cohen C, Szent-Györgyi AG, Kendrick-Jones J. Paramyosin and the filaments of molluscan "catch" muscles. I. Paramyosin: structure and assembly. J Mol Biol 1971;56:223-227.
- 2. Kagawa H, Gengyo K, McLachlan AD, Brenner S, Karn J. Paramyosin gene (unc-15) of Caenorhabditis elegans. Molecular cloning, nucleotide sequence and models for thick filament structure. J Mol Biol 1989;207:311-333.
- 3. Watabe S, Hartshorne DJ. Paramyosin and the catch mechanism. Comp Biochem Physiol B 1990;96:639-646.
- 4. Lanar DE, Pearce EJ, James SL, Sher A. Identification of paramyosin as schistosome antigen recognized by intradermally vaccinated mice. Science 1986;234:593-596.
- 5. Matsumoto Y, Perry G, Levine RJC, Blanton R, Mahmoud AAF, Aikawa M. Paramyosin and actin in schistosomal teguments. Nature 1988;333:76-78.
- 6. Schmidt J, Bodor O, Gohr L, Kunz W. Paramyosin isoforms of Schistosoma mansoni are phosphorylated and localized in a large variety of muscle types. Parasitology 1996;112:459-467.
- 7. Yang W, Waine GJ, Scully DG, Liu X, McManus DP. Cloning and partial nucleotide sequence of Schistosoma japonicum paramyosin: a potential vaccine candidate against schistosomiasis. Int J Parasitol 1992;22:1187-1191.
- 8. Nara T, Matsumoto N, Janucharut T, Matsuda H, Yamamoto K, Irimura T, Nakamura K, Aikawa M, Oswald I, Sher A, Kita K, Kojima S. Demonstration of the target molecule of a protective IgE antibody in secretory glands of Schistosoma japonicum larvae. Int Immunol 1994;6:963-971.
- 9. Gobert GN, Stenzel DJ, Jones MK, Allen DE, McManus DP. Schistosoma japonicum: immunolocalization of paramyosin during development. Parasitology 1997;114:45-52.
- 10. Cancela M, Carmona C, Rossi S, Frangione B, Göni F, Berasain P. Purification, characterization, and immunolocalization of paramyosin from the adult stage of Fasciola hepatica. Parasitol Res 2004;92:441-448.
- 11. Zhao QP, Moon SU, Na BK, Kim SH, Cho SH, Lee HW, Kong Y, Sohn WM, Jiang MS, Kim TS. Paragonimus westermani: biochemical and immunological characterizations of paramyosin. Exp Parasitol 2007;115:9-18.
- 12. Landa A, Laclette JP, Nicholson-Weller A, Shoemaker CB. cDNA cloning and recombinant expression of collagen-binding and complement inhibitor activity of Taenia solium paramyosin (AgB). Mol Biochem Parasitol 1993;60:343-347.
- 13. Laclette JP, Skelly PJ, Merchant MT, Shoemaker CB. Aldehyde fixation dramatically alters the immunolocalization pattern of paramyosin in platyhelminth parasites. Exp Parasitol 1995;81:140-144.
- 14. Mühlschlegel F, Sygulla L, Frosch P, Massetti P, Frosch M. Paramyosin of Echinococcus granulosus: cDNA sequence and characterization of a tegumental antigen. Parasitol Res 1993;79:660-666.
- 15. Limberger RJ, McReynolds LA. Filarial paramyosin: cDNA sequences from Dirofilaria immitis and Onchocerca volvulus. Mol Biochem Parasitol 1990;38:271-280.
- 16. Laclette JP, Shoemaker CB, Richter D, Arcos L, Pante N, Cohen C, Bing D, Nicholson-Weller A. Paramyosin inhibits complement C1. J Immunol 1992;148:124-128.
- 17. Kalinna B, McManus DP. An IgG (Fc gamma)-binding protein of Taenia crassiceps (Cestoda) exhibits sequence homology and antigenic similarity with schistosome paramyosin. Parasitology 1993;106:289-296.
- 18. Loukas A, Jones MK, King LT, Brindley PJ, McManus DP. Receptor for Fc on the surface of schistosomes. Infect Immun 2001;69:3646-3651.
- 19. Pérez-Pérez J, Fernández-Caldas E, Marañón F, Sastre J, Bernal ML, Rodriguez J, Bedate CA. Molecular cloning of paramyosin, a new allergen of Anisakis simplex. Int Arch Allergy Immunol 2000;123:120-129.
- 20. Pearce EJ, James SL, Hieny S, Lanar DE, Sher A. Induction of protective immunity against Schistosoma mansoni by vaccination with schistosome paramyosin (Sm97), a nonsurface parasite antigen. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 1988;85:5678-5682.
- 21. Flanigan TP, King CH, Lett RR, Nanduri J, Mahmoud AA. Induction of resistance to Schistosoma mansoni infection in mice by purified parasite paramyosin. J Clin Invest 1989;83:1010-1014.
- 22. Nanduri J, Kazura JW. Paramyosin-enhanced clearance of Brugia malayi microfilaremia in mice. J Immunol 1989;143:3359-3363.
- 23. Li BW, Chandrashekar R, Weil GJ. Vaccination with recombinant filarial paramyosin induces partial immunity to Brugia malayi infection in jirds. J Immunol 1993;150:1881-1885.
- 24. Ramirez BL, Kurtis JD, Wiest PM, Arias P, Aligui F, Acosta L, Peters P, Olds GR. Paramyosin: a candidate vaccine antigen against Schistosoma japonicum. Parasite Immunol 1996;18:49-52.
- 25. Taylor MG, Huggins MC, Shi F, Lin J, Tian E, Ye P, Shen W, Qian CG, Lin BF, Bickle QD. Production and testing of Schistosoma japonicum candidate vaccine antigens in the natural ovine host. Vaccine 1998;16:1290-1298.
- 26. Zhou S, Liu S, Song G, Xu Y, Sun W. Protective immunity induced by the full-length cDNA encoding paramyosin of Chinese Schistosoma japonicum. Vaccine 2000;18:3196-3204.
- 27. Vázquez-Talavera J, Solís CF, Terrazas LI, Laclette JP. Characterization and protective potential of the immune response to Taenia solium paramyosin in a murine model of cysticercosis. Infect Immun 2001;69:5412-5416.
- 28. McManus DP, Wong JY, Zhou J, Cai C, Zeng Q, Smyth D, Li Y, Kalinna BH, Duke MJ, Yi X. Recombinant paramyosin (rec-Sj-97) tested for immunogenicity and vaccine efficacy against Schistosoma japonicum in mice and water buffaloes. Vaccine 2001;20:870-878.
- 29. Solís CF, Ostoa-Saloma P, Lugo-Martínez VH, Johnston SA, Laclette JP. Genetic vaccination against murine cysticercosis by using a plasmid vector carrying Taenia solium paramyosin. Infect Immun 2005;73:1895-1897.
- 30. Petavy AF, Hormaeche C, Lahmar S, Ouhelli H, Chabalgoity A, Marchal T, Azzouz S, Schreiber F, Alvite G, Sarciron ME, Maskell D, Esteves A, Bosquet G. An oral recombinant vaccine in dogs against Echinococcus granulosus, the causative agent of human hydatid disease: a pilot study. PLoS Negl Trop Dis 2008;2:e125.
- 31. Na BK, Kang JM, Sohn WM. CsCF-6, a novel cathepsin F-like cysteine protease for nutrient uptake of Clonorchis sinensis. Int J Parasitol 2008;38:493-502.
- 32. Harrop R, Coulson PS, Wilson RA. Characterization, cloning and immunogenicity of antigens released by lung-stage larvae of Schistosoma mansoni. Parasitology 1999;118:583-594.
- 33. Laclette JP, Alagón A, Willms K, Torre-Blanco A. Purification of antigen B from Taenia solium cysticerci by affinity to mammalian collagen. J Parasitol 1990;76:273-275.
- 34. Ferreira CA, Barbosa MC, Silveira TC, Valenzuela JG, Vaz I da S Jr, Masuda A. cDNA cloning, expression and characterization of a Boophilus microplus paramyosin. Parasitology 2002;125:265-274.
- 35. Ferrer E, Moyano E, Benitez L, González LM, Bryce D, Foster-Cuevas M, Dávila I, Cortéz MM, Harrison LJ, Parkhouse RM, Gárate T. Cloning and characterization of Taenia saginata paramyosin cDNA. Parasitol Res 2003;91:60-67.
- 36. Deng J, Gold D, LoVerde PT, Fishelson Z. Inhibition of the complement membrane attack complex by Schistosoma mansoni paramyosin. Infect Immun 2003;71:6402-6410.
- 37. Ribeiro de Jesus A, Araújo I, Bacellar O, Magalhães A, Pearce E, Harn D, Strand M, Carvalho EM. Human immune responses to Schistosoma mansoni vaccine candidate antigens. Infect Immun 2000;68:2797-2803.
- 38. Richter D, Incani RN, Harn DA. Isotype responses to candidate vaccine antigens in protective sera obtained from mice vaccinated with irradiated cercariae of Schistosoma mansoni. Infect Immun 1993;61:3003-3011.
- 39. Yang W, Waine GJ, McManus DP. Antibodies to Schistosoma japonicum (Asian bloodfluke) paramyosin induced by nucleic acid vaccination. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 1995;212:1029-1039.
- 40. Bergquist R, Al-Sherbiny M, Barakat R, Olds R. Blueprint for schistosomiasis vaccine development. Acta Trop 2002;82:183-192.
Fig. 1Multiple alignment of putative polypeptide of Clonorchis sinensis paramyosin (CsPmy) with other helminth paramyosins. Paragonimus westermani (AY995190), Schistosoma japonicum (AF113871), S. mansoni (M35499), Taenia solium (AY686637), T. saginata (AJ439882), Onchocerca volvulus (M95813), Brugia malayi (U77590), and Anisakis simplex (AF173004). Percentage of sequence identity is represented as shading: black (100%), dark grey (55-88%), light grey (22-44%) and no shading (< 22%). Helical regions predicted by the Protean software of DNASTA package (DNASTAR) are indicated by a line over CsPmy.

Fig. 2Expression of recombinant CsPmy (rCsPmy). Lane 1, IPTG-uninduced E. coli lysate; lane 2, IPTG-induced E. coli lysate; lane 3, Ni-NTA affinity purified rCsPmy.

Fig. 3Collagen and complement 9 binding activity of rCsPmy. The binding activity of rCsPmy to collagen was determined by immunoblot (A) and ELISA (B). The binding activity of rCsPmy to complement 9 was determined by immunoblot (C) and ELISA (D).

Fig. 4Expression profile of the CsPmy in various developmental stages of C. sinensis. (A) Semi-quantitative RT-PCR. M, metacercariae; 2W - 9W, 2- to 9-week-old worms; NC, negative control without RNA template. (B) Immunoblot analysis. The CsPmy was probed by anti-rCsPmy mouse serum.

Fig. 5Localization of CsPmy in C. sinensis adult worm. (A) SDS-PAGE analysis. (B) Immunoblot analysis with anti-rCsPmy. Lane 1, purified rCsPmy; lane 2, C. sinensis ESP; lane 3, C. sinensis adult worm soluble extract; lane 4, C. sinensis adult worm insoluble extract. (C) Section of C. sinensis adult worms probed with anti-rCsPmy (left panel) or normal mouse serum (right panel). The magnification is × 100.

Fig. 6Antigenicity of the rCsPmy. (A) Immunoblot analyses with the sera of clonorchiasis patients. Representative reactions are shown. (B) Immunoglobulin G production in rats immunized with rCsPmy by intraperitoneal (IP) or intermuscular (IM) route and analyzed by ELISA. Control rats (C) were injected with saline.