Abstract
The α/β-tubulin heterodimer is the basic subunit of microtubules in eukaryotes. Polyclonal antibodies specific to recombinant α-tubulin of Giardia lamblia were made, and found effective as a probe to specifically detect G. lamblia by immunofluorescence assays. Nucleotide sequences of α-tubulin genes were compared between G. lamblia WB and GS strains, prototypes of assemblage A and assemblage B, respectively. A set of primers was designed and used to amplify a portion of the α-tubulin gene from G. lamblia. PCR-RFLP analysis of this α-tubulin PCR product successfully differentiated G. lamblia into 2 distinct groups, assemblages A and B. The results indicate that α-tubulin can be used as a molecular probe to detect G. lamblia.
-
Key words: Giardia lamblia, α-tubulin, immunofluorescence assay, PCR-RFLP
Giardia lamblia is a significant cause of diarrheal outbreaks worldwide, and infects a variety of mammalian hosts, including humans [
1]. Therefore, the development of a precise classification system for this organism is required to monitor possible sources of outbreaks as well as to identify the routes of infections. Two major lineages have been defined for human-derived
G. lamblia: assemblages A and B [
2] (otherwise referred to as groups I-II and groups III-IV [
3,
4] or as the 'Polish' and 'Belgian' genotypes [
5], respectively). Two antigenically distinct
G. lamblia strains, WB and GS, were established via an infection model using gerbils, and served as prototypes for assemblage A and B, respectively [
6]. Later,
G. lamblia GS was found as the most potent strain in infection of mice [
7]. In addition to these 2 groups, 3 additional assemblages of
G. lamblia were identified from animals: assemblages C and D from dogs [
8], and assemblage E from livestock [
9]. Furthermore, phylogenetic analysis of 4 house-keeping genes revealed that
G. lamblia includes at least 7 different lineages, assemblage A to G [
10].
Diverse genetic markers that successfully detect or classify
G. lamblia have been reported. Two sets of primers were designed based on the SSU-rDNA region of
G. lamblia: JW1 and JW2 [
11], and RH11 and RH4 [
12]. Primers specific to the
tim gene encoding triose-1-phosphate isomerase have been shown to differentiate assemblage A from assemblage B [
13]. Primers GGL and GGR were made for the unique
G. lamblia gene encoding giardin [
14]. In addition, we have designed a set of primers specific for
GLORF-C4, which allows classification of
G. lamblia into 2 assemblages, assemblage A and B [
15].
In the present study, we developed tools to detect G. lamblia using one of the abundant cytoskeletal components of this eukaryote, i.e., microtubules. We aimed to make an antigenic probe to detect G. lamblia, and a molecular tool not only to detect but also differentiate 2 representative G. lamblia assemblages. Most of all, α-tubulin comprising microtubules was used as an antigenic probe to detect G. lamblia. Searching of the G. lamblia genome database identified 2 genes for α-tubulin of G. lamblia WB, OFR#112079 and ORF#103676. Comparison of the nucleotide sequences of these ORFs revealed 6 synonymous mutations but no change in the amino acid sequence. Therefore, we used the ORF#103676 for further studies.
G. lamblia WB (ATCC#30957; American Type Cellular Collection, Manassas, Virginia, USA) strain was axenically cultivated using modified TYI-S-33 media [
16]. A 1,365 bp DNA fragment encoding α-tubulin was amplified from
G. lamblia WB using α-tubulin-ERI-F (5'-ATT
GAATTCATGCGTGAGTGCATCTC-3': underlined bases denote an EcoRI site) and α-tubulin-NotI-R (5'-GC
GCGGCCGCTCGTAGGCGTCGTCCTCC-3': underlined bases indicate a NotI site) primers, and then cloned into pGEX-4T-1 (Amersham Pharmacia, Buckinghamshire, UK) to produce pZhu30. GST-tagged recombinant α-tubulin protein (GST-α-tubulin) was expressed in
Escherichia coli BL21 (DE3), and then used to immunize Sprague-Dawley rats (3 times at 2 week-intervals, 200 µg for each immunization).
Specificity of the anti-α-tubulin polyclonal antibodies was then examined by western blot analysis.
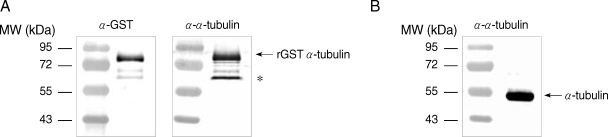
E. coli extracts expressing GST-α-tubulin were incubated with polyclonal goat anti-GST (Amersham Pharmacia) or rat anti-α-tubulin antibodies, and incubated with alkaline phosphatase (AP)-conjugated anti-goat IgG (Sigma, St. Louis, Missouri, USA) and AP-conjugated anti-rat IgG (Sigma), respectively. The immunoreactive protein was visualized using the nitroblue tetrazolium (NBT)/5-bromo-4-chloro-3-indolyl phosphate (BCIP) system (Promega, Madison, Wisconsin, USA). GST-α-tubulin was recognized as an immunoreactive protein of 77 kDa by both anti-GST and anti-α-tubulin antibodies (
Fig. 1A). Incubation of
E. coli lysates expressing GST-α-tubulin with anti-α-tubulin antibodies resulted in the appearance of an immunoreactive, non-specific band as indicated with an asterisk in
Fig. 1A. Native α-tubulin was also detected as a protein of 50 kDa in lysates of
Giardia trophozoites by western blot using anti-α-tubulin antibodies (
Fig. 1B).
The polyclonal antibodies against GST-α-tubulin were then used for an immunofluorescence assay (IFA) of
Giardia trophozoites as well as other protozoa, such as
Trichomonas vaginalis,
Entamoeba histolytica, and
Naegleria fowleri (
Fig. 2). Trophozoites of
T. vaginalis T016 were grown in a TYM medium [
17]. An axenic culture of
E. histolytica HM1 : IMSS (ATCC#30459) was grown in TYI-S-33 medium [
18], whereas
N. fowleri Carter NF69 (ATCC#30215) was cultured in CGV medium [
19]. Trophozoites were attached to glass slides coated with L-lysine in a humidified chamber.
G. lamblia and
T. vaginalis were then fixed with chilled 100% methanol at -28℃ for 10 min, and permeabilized with PBS/0.5% Triton X-100 for 10 min.
E. histolytica and
N. fowleri were fixed with 10% formalin for 30 min, incubated with 1 M NaOH for 5 min, and then permeabilized with 20% Tween 20 for 5 min at room temperature. After 1 hr-incubation in blocking buffer containing 5% goat serum and 3% bovine serum albumin (BSA), the cells were reacted with mouse anti-α-tubulin monoclonal antibodies specific to chicken α-tubulin (1 : 300 dilution; Sigma T9026, monoclonal anti-α-tubulin antibody produced in mouse clone DM 1A with microtubules from chicken embryo brain used as the immunogen) or rat anti-GST α-tubulin polyclonal antibodies (1 : 200 dilution) at 4℃ overnight. The cells were incubated with TRITC-conjugated anti-rat IgG or FITC-conjugated anti-mouse IgG (1 : 200 dilution; Jackson ImmunoResearch Lab, West Grove, Pennsylvania, USA) at 37℃ for 1 hr. As a control, the fixed trophozoites were incubated with mouse preimmune serum instead of commercial anti-α-tubulin antibodies or with rat preimmune serum for polyclonal anti-α-tubulin antibodies. The slides were reacted with 1 µg/ml 4'6-diamidino-2-phenylindole (DAPI; Sigma), and mounted with anti-fade mounting medium (Vectashilde; Vector, Burkingame, California, USA). The slides were then observed using a fluorescence microscope (Zeiss, Oberkochen, Germany).
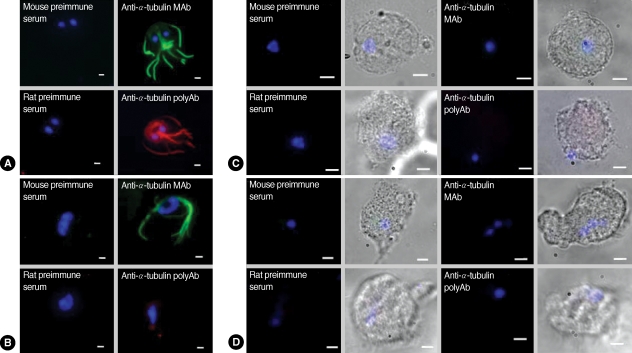
IFA using commercial α-tubulin antibodies or polyclonal anti-α-tubulin antibodies showed strong fluorescence mainly against cytoskeletal structures, such as the 8 flagella and a median body of
Giardia trophozoites (
Fig. 2A). In contrast, incubation with mouse preimmune serum or rat preimmune serum did not demonstrate any fluorescence in
Giardia trophozoites. The 2 antibodies were also tested for IFA with another flagellated protozoan,
T. vaginalis (
Fig. 2B). Reaction of
T. vaginalis with the monoclonal antibodies against α-tubulin generated green fluorescence at the flagella, but no red fluorescent signal was detected in
T. vaginalis upon incubation with polyclonal antibodies made against GST-α-tubulin. In contrast, IFA of
E. histolytica (
Fig. 2C) as well as
N. fowleri (
Fig. 2D) failed to produce any fluorescence using either of the 2 α-tubulin antibodies or the preimmune sera.
The results indicate that α-tubulin can be used as an antigenic probe to detect G. lamblia. Polyclonal antibodies against α-tubulin of G. lamblia did not show any cross-reactivity to other protozoa, T. vaginalis, E. histolytica, and N. fowleri. On the contrary, commercial monoclonal antibodies made against chicken microtubules reacted only with T. vaginalis and G. lamblia, suggesting that the epitope recognized by these monoclonal antibodies is also present in these 2 flagellates, however, it is absent in other 2 protozoa without flagella. The antigenic region working for these monoclonal antibodies may be more obviously presented in flagellates than amoebic protozoa. Reaction of polyclonal anti-α-tubulin antibodies only with G. lamblia, but not with other protozoa, suggests the presence of significant difference in composition of these tubulins.
We next examined whether the α-tubulin gene could be used to categorize
G. lamblia by PCR-RFLP. Genomic DNA was prepared from axenically cultivated
G. lamblia WB, GS (ATCC#50581), and K1 [
20] strains. Trophozoites of
T. vaginalis,
E. histolytica, and
N. fowleri were used a source of genomic DNA. In addition,
E. coli DH5α and
Vibrio vulnificus (ATCC#29307) were propagated in Luria Bertani broth with different saline concentrations (1 and 2% NaCl, respectively). DNAs of the above strains were prepared by phenol extraction as described [
20].
The α-tubulin gene from G. lamblia strain GS was amplified by using primers, α-tubulin-ERI-F and α-tubulin-NotI-R, and then sequenced using an automatic DNA sequencer (Applied Biosystems, Foster City, California, USA) to confirm difference in the genes encoding α-tubulins of 2 G. lamblia strains, WB and GS. Nucleotide sequences encoding α-tubulin of the GS strain were submitted to GenBank under the accession number, FJ-232540. Alignment of α-tubulin from the GS strain with the WB strain (ORF#103676) indicated 97% and 99% identity in their nucleotide and amino acid sequences, respectively (data not shown).
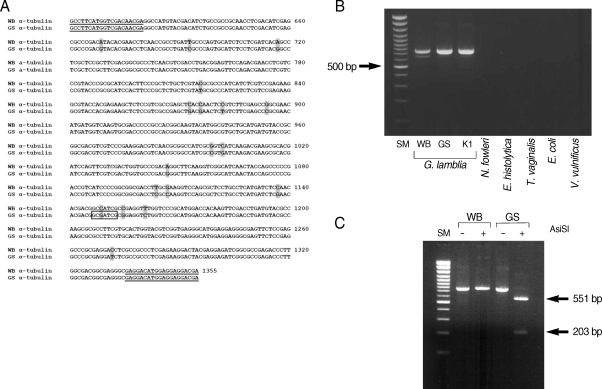
A search for restriction enzyme sites in the α-tubulin gene revealed that a recognition site for AisSI is present only in the GS strain, but absent from the WB strain (
Fig. 3A). We therefore designed a PCR-RFLP analysis of the α-tubulin gene to distinguish assemblage A from assemblage B of
G. lamblia. Two primers specific to the α-tubulin gene, genotype F and genotype R, were used to amplify the 3' portion of α-tubulin from
G. lamblia WB, GS, and K1 strains. The 2 primers were used to amplify a portion of the α-tubulin genes from 3 different
G. lamblia strains (WB, GS, and K1) as a PCR product of 754 bp (
Fig. 3B). These primers are specific for the α-tubulin gene from
G. lamblia, because PCR using the same set of primers failed to produce any DNA fragment from genomic DNA of other protozoa (
N. fowleri,
E. histolytica, and
T. vaginalis), or from bacteria (
E. coli and
V. vulnificus).
The α-tubulin gene was also evaluated as a probe to differentiate assemblages A and B in
G. lamblia by PCR-RFLP analysis (
Fig. 3C). The resultant PCR products were digested with AisSI (New England Biolab, Ipswich, Massachusetts, USA), which is present only in the PCR product derived from the GS strain, an assemblage B. As expected from the unique presence of the AsiSI site in the α-tubulin gene of the GS strain, the 754 bp PCR product derived from the GS strain was digested into 2 DNA fragments (551 bp and 203 bp), whereas the size of the α-tubulin PCR product from the WB strain was not affected by digestion with AsiSI.
Detection and classification of
G. lamblia is still an important problem, as this organism has attracted worldwide attention as a source of diarrheal outbreaks. Advanced technologies have been developed to detect
G. lamblia, which include labeling by fluorescent in situ hybridization and quantum dots-labeled IFA [
21], as well as real-time PCR [
22]. IFA coupled with immunomagnetic separation is currently one of the main methods to detect
Giardia [
23]. In addition, PCR-RFLP had been used frequently in field investigations on the occurrence of
Giardia among primary school children [
24] or in wild animals [
25]. Therefore, the identification and characterization of new markers is needed to improve current detection methods for
G. lamblia. Our study extends the list of molecular markers which can be used to detect and classify
G. lamblia.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
This work was supported by a grant from National Institute of Health, Korean Center for Disease Control and Prevention (2008-E0091-00).
References
- 1. Adam RD. The biology of Giardia spp. Microbiol Rev 1991;55:706-732.
- 2. Mayrhoefer G, Andrews RH, Ey PL, Chilton NB. Division of Giardia isolates from humans into two genetically distinct assemblages by electrophoretic analysis of enzymes encoded at 27 loci and comparison with Giardia muris. Parasitology 1995;111:11-17.
- 3. Andrews RH, Adams M, Boreham PF, Mayrhoefer G, Meloni BP. Giardia intestinalis: electrophoretic evidence for species complex. Int J Parasitol 1989;19:183-190.
- 4. Monis PT, Mayrhoefer G, Andrews RH, Homan WL, Limper L, Ey PL. Molecular genetic analysis of Giardia intestinalis isolates at the glutamate dehydrogenase locus. Parasitology 1996;11:1-12.
- 5. Homan WL, Van Enckevort FH, Limper L, Van Eys GJ, Schoone GJ, Kasprzak W, Majewska AC, Van Knapen F. Comparison of Giardia isolates from different laboratories by isoenzyme analysis and recombinant DNA probes. Parasitol Res 1992;78:316-323.
- 6. Aggarwal A, Nash TE. Comparison of two antigenically distinct Giardia lamblia isolates in gerbils. Am J Trop Med Hyg 1987;36:325-332.
- 7. Byrd LG, Conrad JT, Nash TE. Giardia lamblia infections in adult mice. Infect Immun 1994;62:3583-3585.
- 8. Monis PT, Andrews RH, Mayrhoefer G, Mackrill J, Kulda J, Isaac-Renton JL, Ey PL. Novel lineages of Giardia intestinalis identified by genetic analysis of organisms isolated from dogs in Australia. Parasitology 1998;116:7-19.
- 9. Ey PL, Mansouri M, Kulda J, Nohynkova E, Monis PT, Andrews RH, Mayrhoefer G. Genetic analysis of Giardia from hoofed farm animals reveals artiodactyls-specific and potentially zoonotic genotypes. J Eukaryot Microbiol 1997;44:626-635.
- 10. Monis PT, Andrews RH, Mayrhoefer G, Ey PL. Molecular systematics of the parasitic protozoan Giardia intestinalis. Mol Biol Evol 1999;16:1135-1144.
- 11. Weiss JB, Van Keulen H, Nash TE. Classification of subgroups of Giardia lamblia based upon ribosomal RNA gene sequence using polymerase chain reaction. Mol Biochem Parasitol 1992;54:73-86.
- 12. Hopkins RM, Meloni BP, Groth DM, Wetherall JD, Reynoldson JA, Thompson RC. Ribosomal RNA sequencing reveals differences between the genotypes of Giardia isolates recovered from humans and animals in Germany. J Parasitol 1997;83:44-51.
- 13. Baruch AC, Isaac-Renton J, Adam RD. The molecular epidemiology of Giardia lamblia: a sequence-based approach. J Infect Dis 1996;174:233-236.
- 14. Mahbubani MH, Bej AK, Perlin M, Schafer FW III, Jakubowski W, Atlas RM. Differentiation of Giardia duodenalis from other Giardia spp. by using polymerase chain reaction and gene probes. J Clin Microbiol 1992;30:74-78.
- 15. Yong TS, Park SJ, Hwang UW, Yang HW, Lee K, Min DY, Rim HJ, Wang Y, Feng Z. Ribosomal DNA sequencing for genotyping of Giardia lamblia recovered from humans in China and Korea. J Parasitol 2000;86:887-891.
- 16. Keister DB. Axenic culture of Giardia lamblia in TYI-S-33 medium supplemented with bile. Trans R Soc Trop Med Hyg 1983;77:487-488.
- 17. Diamond LS. The establishment of various trichomonads of animals and man in axenic cultures. J Parasitol 1957;43:488-490.
- 18. Diamond LS. Axenic cultivation of Entamoeba histolytica. Science 1961;134:336-337.
- 19. Willaert E. Isoelement et culture in vitro des amibes genre Naegleria. Ann Soc Belge Med Trop 1971;51:701-708.
- 20. Park SJ, Yong TS, Yang HW, Lee DH, Lee K. Axenic cultivation and characterization of Giardia lamblia isolated from humans in Korea. Korean J Parasitol 1999;37:121-125.
- 21. Zhang Q, Zhu L, Feng H, Ang S, Chau FS, Liu WT. Microbial detection in microfluidic devices through dual staining of quantum dots-labeled immunoassay and RNA hybridization. Anal Chum Acta 2006;556:171-177.
- 22. Bertrand I, Gantzer C, Chesnot T, Schwartzbrod J. Improved specificity for Giardia lamblia cysts quantification in wastewater by development of a real-time PCR method. J Microb Methods 2004;57:41-53.
- 23. Souza DS, Barreiros JT, Papp KM, Steindel M, Simoes CM, Barardi CR. Comparison between immunomagnetic separation, coupled with immunofluorescence, and the techniques of Faust et al. and of Lutz for diagnosis of Giardia lamblia cysts in human feces. Rev Inst Med Trop Sao Paulo 2003;45:339-342.
- 24. Ratanapo S, Mungthin M, Soontrapa S, Faithed C, Siripattanapipong S, Rangsin R, Naaglor T, Piyaraj P, Taamasri P, Leelayoova S. Multiple modes of transmission of giardiasis in primary school-children of a rural community, Thailand. Am J Trop Med Hyg 2008;78:611-615.
- 25. Robertson LJ, Forberg T, Hermansen L, Hamnes IS, Gjerde B. Giardia duodenalis cysts isolated from wild moose and reindeer in Norway: genetic characterization of PCR-RFLP and sequence analysis at two genes. J Wild Dis 2007;43:576-585.
Fig. 1Specificity of polyclonal antibodies against GST-α-tubulin of G. lamblia. (A) Extracts of E. coli expressing GST-α-tubulin were incubated with anti-GST or anti-GST-α-tubulin antibodies. (B) Native α-tubulin was detected only in Giardia trophozoites reacted with anti-GST-α-tubulin antibodies. Incubation of E. coli lysate expressing GST-α-ubulin with anti-GST-α-tubulin antibodies resulted in an immunoreactive and non-specific band as indicated by an asterisk.

Fig. 2IFA of G. lamblia (A), T. vaginalis (B), E. histolytica (C), and N. fowleri (D) using anti-α-tubulin antibodies. Trophozoites of G. lamblia and T. vaginalis were fixed with chilled 100% methanol at -20℃ for 10 min, and permeabilized with PBS/0.5% Triton X-100 for 10 min. E. histolytica and N. fowleri were fixed with 10% formalin for 30 min, incubated with 1 M NaOH for 5 min, and then permeabilized with 20% Tween 20 for 5 min at room temperature. Cells were then reacted with commercially available monoclonal antibodies against chicken α-tubulin (1 : 300 dilution) or with polyclonal antibodies against GST-α-tubulin of G. lamblia (1 : 200 dilution). Fixed trophozoites were also reacted with mouse preimmune or rat preimmune sera as controls for commercial monoclonal antibodies or polyclonal GST-α-tubulin antibodies, respectively. The slides were subsequently incubated with either TRITC-conjugated anti-rat IgG or FITC-conjugated anti-mouse IgG (1 : 200 dilution). To visualize nuclei, the cells were treated with 1 µg/ml 4'6-diamidino-2-phenylindole (DAPI), mounted with anti-fade mounting medium (Vectashilde; Vector), and then observed with a Zeiss fluorescent microscope (Zeiss). The bars represent 2 µm.

Fig. 3PCR-RFLP analysis of G. lamblia using the α-tubulin gene. (A) Aligned nucleotide sequences of the α-tubulin genes of G. lamblia WB (assemblage A) and GS (assemblage B) strains. The nucleotide sequences corresponding to the PCR primers, genotype F and genotype R, are underlined. Different bases between the 2 G. lamblia strains are shaded. A recognition site for AsiSI site is indicated in a box. (B) PCR detection of the α-tubulin gene in 2 groups of G. lamblia, other protozoa and bacteria. Using 2 primers, genotype F and genotype R, 754 bp α-tubulin DNA was amplified from the following genomic DNAs; lane 1, DNA size marker, 100 bp ladder; lane 2, WB (assemblage A G. lamblia); lane 3, GS (assemblage B G. lamblia); lane 4, K1 (assemblage B G. lamblia); lane 5, N. fowleri; lane 6, E. histolytica; lane 7, T. vaginalis; lane 7, E. coli DH5 αand ; lane 7, V. vulnificus. (C) Grouping of G. lamblia using α-tubulin primers. Using genomic DNAs derived from G. lamblia WB and GS strains as templates, PCR was carried out with primers, genotype F and genotype R, and the resultant PCR products were digested with AsiSI endonucleases. lane 1, DNA size marker, 100 bp ladder; lane 2, PCR product of G. lamblia WB; lane 3, PCR product of G. lamblia WB digested with AsiSI; lane 4, PCR product of G. lamblia GS; and lane 5, PCR product of G. lamblia GS digested with AsiSI.