Abstract
Local malaria transmission in the United Arab Emirates (UAE) came to an end in 1997. Nevertheless, UAE has been subjected to substantial importation of malaria cases from abroad, concerning both UAE nationals and immigrants from malarious countries with a total number of 2,119 cases in 2007. To evaluate a new DNA extraction technique using nested PCR, blood samples were collected from 132 individuals who presented to Infectious Diseases Department in Rashid Hospital, Dubai, and Central Department of Malaria Control with fever and persistent headache. Giemsa-stained blood films and ELISA test for malaria antibodies were carried out for detection of Plasmodium infection. Plasmodium infections were identified with the genus-specific primer set and species differentiation using nested PCR. A rapid procedure for diagnosis of malaria infections directly from dried blood spots using for the first time DNA extract from FTA Elute cards was evaluated in contrast to extraction techniques using FTA classic cards and rapid boiling technique. Our new simple technique for DNA extraction using FTA Elute cards was very sensitive giving a sensitivity of 100% compared to 94% using FTA classic cards and 62% in the rapid boiling technique. No complex preparation of blood samples was required prior to the amplification. The production cost of DNA isolation in our PCR assay was much less in comparable to that of other DNA extraction protocols. The nested PCR detected plasmodial infection and could differentiate P. falciparum from P. vivax, and also detected the mixed infection.
-
Key words: Plasmodium vivax, Plasmodium falciparum, imported malaria, UAE, nested PCR-DNA Extraction, FTA Elute cards
INTRODUCTION
Malaria is still one of the most prevalent parasitic diseases, particularly in tropical and subtropical developing countries [
1,
2]. Before and during the 1960s, malaria used to be a major public health problem in the United Arab Emirates (UAE), with hyperendemic foci particularly on the East coast, Ras Al Khaimah, the Central Plateau and Al Ain. Transmission was maintained by
Anopheles stephensi and
Anopheles culicifacies breeding mainly in deep wells, shallow wells, basins, drums, and irrigation channels ("farms"). The prevailing parasite species were
Plasmodium vivax and
Plasmodium falciparum, with a sporadic occurrence of
Plasmodium malariae. Local malaria transmission in UAE has come to an end in 1997. From 1998 to 2004, no autochthonous cases have been reported, and UAE was certified to be a malaria free country. Nevertheless, the country is subjected to substantial importation of malaria cases from abroad, concerning both UAE nationals and especially immigrants from malarious countries with a total number of cases of 2,119 in 2007 [
3].
Although microscopic examination of blood smears remains the gold standard in diagnosis of malaria, this method suffers from insufficient sensitivity and requires considerable expertise. To improve diagnosis, different serological tests and finally PCR were developed [
4]. Over the past years PCR-based genotyping of pathogens has become a central technique applied in diagnostics and molecular epidemiological studies. Methods for DNA preparations from blood samples in studies of epidemiological scale have to fulfill the following criteria: 1) rapid preparation and large through-put, 2) high reliability, 3) production of DNA of good quality for long term storage, 4) avoidance of cross contamination, and 5) reasonable cost [
5]. The present study aimed to evaluate the accuracy of a new commercially available DNA extraction technique using FTA Elute cards (Whatman, Maidstone, UK).
MATERIALS AND METHODS
All samples and data included in this study were obtained with informed consent in accordance with guidelines of Infectious Disease Department in Rashid Hospital, Dubai, UAE, and Central Department of Malaria Control in Sharjah, UAE.
Specimens
Blood specimens were collected from 132 individuals who presented with fever and persistent headache. Blood collected on EDTA was spotted on FTA Elute cards and FTA classic cards, and then stored at room temperature till used for DNA extraction. Sera were given a reference number, aliquoted, and stored at -80℃ until tested by ELISA.
Microscopy
Blood films were prepared and stained by Giemsa and examined for malaria plasmodia.
Serologic screening of malaria samples
The presence of antibodies to malaria was tested by ELISA test for malaria antibodies (DiaMed, Cressier FR, Switzerland). This test is based on binding of anti-Plasmodium antibodies present in serum samples to antigens immobilized on 96-well plates. The antigens are a mixture of a total extract of cultured P. falciparum and recombinant P. vivax merozoite surface protein-1 (MSP-1) and circumsporozoite protein (CSP), and the test was performed as recommended by the manufacturer. The cut-off value was calculated by multiplying the average optical density (OD) of the negative control wells by 4 (with a minimum value of 0.200). The assay was carried out using an automatic ELISA reader (Stat Fax 2100, Palm City, Florida, USA).
DNA template preparation
DNA extraction using FTA Elute cards
A 3-mm disk was punched out and placed in a microcentrifuge tube, and then the disk was rinsed in 500 µl dH2O by pulse vortexing 3 times for 5 sec each. Water was removed with quick spinning and, 50 µl sterile H2O was added. Heating was done at 95℃ for 30 min. Eluted DNA was used in PCR.
DNA extraction using FTA classic cards
A 1.2-mm disk was punched out from the dried blood spots on FTA classic cards and placed into PCR tube. The punch was washed with FTA purification reagent, and then with TE buffer, and dried. PCR master mix was added directly to the punch and PCR was done. To avoid the possible disadvantage that some parts of the disk may contain more DNA template than the other parts, which may affect the results of PCR amplification, 2 punches were cut and 2 PCR amplifications were done per disk in FTA Elute and FTA classic cards.
DNA extraction using rapid boiling technique
This was done according to Foley et al. [
6]. Briefly, 10 µl of blood was added to 500 µl of ice-cold 5 mM sodium phosphate buffer PH (8.0), vortexed, and spun for 2 min at 14,000 rpm. The supernatant was discarded, and washing was repeated twice. Then, 50 µl distilled water was added to the washed pellet, and boiling was done for 10 min. Finally, the sample was spun for 10 min at 14,000 rpm, and the pellet was discarded. A 5-µl of the supernatant was used as an elute for PCR.
Plasmodium infections were identified with a genus-specific primer set, and species differentiation was done using nested PCR assay as described by Snounou and Ndao [
7,
8]. Oligonucleotide primers for nested PCR were obtained from Alpha DNA (Montreal, Canada). These primers were designed based on the
Plasmodium small subunit ribosomal RNA (ssrRNA). Nested PCR amplification using Gen Amp PCR system 9700 (Applied Biosystems, Foster City, California, USA) was done, and analysis of PCR products was followed.
Nest 1
Each of 50 µl reaction mixture for nest 1 amplifications contained 5 µl DNA template, 2.2 µl primers (genus-specific, "rplu1 and rplu5") in a concentration of 25 pmole/µl, 25 µl PCR master mix (Go Taq green master mix) (Promega, Madison, Wisconsin, USA), and nuclease free water 15.6 µl.
Nest 1 amplification conditions
Step 1): hold at 94℃ for 4 min. Step 2): 35 cycles of denaturation at 94℃ for 30 sec, annealing at 55℃ for 1 min, and extension at 72℃ for 1 min. Final extension was at 72℃ for 4 min and hold at 4℃ for 48 hr or kept at -20℃ for a week.
Nest 2
Each of 20 µl reaction mixture for nest 2 amplifications contained 2 µl of nest 1 amplification as DNA template. The concentration of nest 2 primers and other constituents were identical to nest 1 amplifications except annealing temperature in step 3) of 58℃ for species-specific primers and 62℃ for genus-specific primers, rplu3 and rplu4, respectively. PCR products of nest 2 amplifications were analyzed by 2% gel electrophoresis stained by ethidium bromide. A 100-bp molecular marker (Promega) was used.
RESULTS
In total, 52 patients were identified as being infected with malaria by blood film analysis. Among them, 33 were identified as having P. vivax infection, 19 were having P. falciparum infection, and none was identified as having Plasmodium ovale, Plasmodium malariae, or mixed infections. All patients' blood samples were also tested by ELISA for anti-malaria antibodies and were then subjected to nested PCR assay.
By ELISA, 46 of 52 samples were observed to be malaria positive. In comparison to PCR assays, both microscopy and malaria antibody ELISA had lower sensitivities (
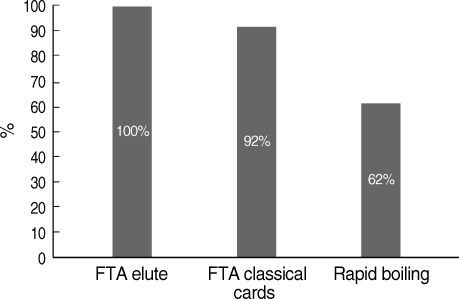
Table 1). Assay of sensitivities of the 3 DNA extraction techniques using genus-specific primer sets for the detection of malaria by nested PCR showed that the most sensitive method was FTA Elute cards giving 100% sensitivity, and the least sensitive was the rapid boiling technique giving 62% sensitivity (
Fig. 1).
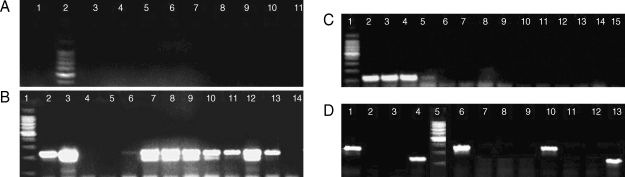
PCR analysis for genus and species determination was run as independent assays. With the genus-specific primers, 60 samples were detected as positive for the presence of
Plasmodium infection with a 240-bp PCR product in nest 2 PCR. Amplification with the species-specific primers gave rise to a 205-bp PCR product in 21 samples which correlated with
P. falciparum. In the other 35 samples, a 117-bp PCR product was observed, and this product correlated with
P. vivax. In the course of these diagnostic tests, 4 samples were observed to have both 117-bp and 205-bp fragments (
Fig. 2). These samples were from 4 patients with mixed infections, which were initially misdiagnosed at microscopy (
Table 2). The samples that gave discordant results were rescreened blindly by microscopy and PCR, and 6 of them produced concordant results (
Table 3).
DISCUSSION
Microscopy has historically been the mainstay of malaria diagnosis and continues to be the gold standard. However, disadvantages include the low sensitivity, subjectivity, and inadequacy for large-scale epidemiology studies [
9]. Thus, parasite densities of 4-40 parasites/L blood are rarely detected [
10], and in busy routine examination, the sensitivity is 10-fold lower. In addition, the number of false-negative findings in oligoparasitemic patients and false-positive findings due to artifacts is not negligible [
11]. Mixed infections are a particular challenge for microscopy. The reason obviously lies in the morphologic similarities between early developmental stages of malaria parasites of different species [
12]. As a result of these limitations, alternative techniques for the diagnosis of malaria have been developed [
10].
Our results showed that the sensitivity of microscopy was 88.2% compared to PCR results. Although ELISA antibody test is a sensitive and relatively specific assay, it is not applicable for differentiation between malaria species. Our study indicates that ELISA test for malaria antibodies has a sensitivity of 81.1% in comparison to PCR for identification of malaria genes; however, it is not applicable for differentiation between malaria species. Oh et al. [
13] found that ELISA for malaria antibodies was insufficiently sensitive for blood screening in Korea. However, Elghouzzi et al. [
14] found that performance of ELISA in their study has confirmed its potential as a new screening test for use in blood banks, as an alternative to immunofluorescence antibody test (IFAT) in prevention of transfusion-transmitted malaria in non-endemic countries.
Our comparative study of microscopy, the antibody-ELISA detection kits, and the PCR test showed that the results obtained by PCR were superior to those obtained by microscopy. The PCR test was able to detect malarial infections and mixed infections that were missed by microscopy which may be due to the presence of higher numbers of parasites of 1 species relative to the other, or the parasite densities were below the microscopic threshold. This is in agreement with Di Santi et al. [
15] who reported that PCR identified mixed infection that was missed by Giemsastained thick blood smears. Also, Sethabutr et al. [
16] demonstrated by the PCR technique that
P. falciparum DNA in the blood of infected patients could be detected transiently at a time when the parasite could no longer be detected microscopically. Efficient, rapid, and reproducible procedures for isolating high quality DNA before PCR gene amplification are essential for the diagnostic and molecular identification of pathogenic organisms [
17].
Collection of blood samples on filter papers has a history of more than 40 years. This simple and feasible collection and storage method has been adopted for broad use in diagnostic screening, drug monitoring, and genetic analysis [
18], being particularly suitable for molecular epidemiologic studies in remote areas with tropical climate, where transport and storage conditions are difficult [
19]. Here, we have reported on the application of nested PCR for diagnosis of malarial infection using 3 different DNA extraction techniques. The sensitivity of DNA extraction using FTA classic cards and rapid boiling technique was compared to extraction using FTA Elute cards.
The FTA Elute cards provided high sensitivity due to the yield of DNA free from inhibitors, since hemoglobin (a known DNA inhibitor) is pound to the FTA matrix. FTA Elute does exactly what its name suggests; elution of DNA and providing liquid DNA for downstream analysis. FTA Elute cards eliminated the long sample processing times, the high cost of using the purification kits to isolate DNA, and also the use of nucleic acid purification devices. The non-microbial growth and long-term room temperature storage of nucleic acid add further advantages to the FTA Elute card method. Comparing the results and the steps in the 3 techniques, in FTA Elute method, since DNA eluted into solution (liquid phase DNA manipulation), we were able to use multiple PCR reactions per punch. However, DNA stays on punch in classic cards, so 1 PCR reaction per punch was done.
PCR assay in epidemiological studies for malaria detection was determined using DNA templates from blood spot on FTA filter paper by Singh et al. [
20], who detected a high sensitivity with constant quality of specific products on agarose gels irrespective of the number of parasites number present in the sample. However, Zhong et al. [
21] evaluated 2 filter paper-based blood collection devices for the diagnosis of malaria by PCR amplification compared to whole-blood samples collected at the same time, and optimally frozen and transported. They demonstrated that IsoCode and FTA were satisfactory collection and processing devices for the subsequent amplification of plasmodial DNA. Both devices displayed good sensitivity for the subsequent PCR identification of single-species infections, but neither was sensitive for the detection of mixed infections. The reasons for decreased detection of mixed infections are unknown, but may reflect loss of template DNA through degradation or trapping of parasite DNA in the paper matrix.
Other researchers [
22] reported on the use of Tris-EDTA buffer-based extraction from blood dried on Whatman filter paper, methanol extraction, and Chelex extraction techniques regarding PCR for detection of
P. falciparum parasites from samples stored for 1-2 years. For a 3-mm Whatman filter paper method, the sensitivity was 100%, and for methanol and Chelex methods, it was 73% and 93%, respectively. Gonzalez et al. [
23] reported the use of different DNA extraction techniques, and they found that WBC lysis with proteinase K and heat inactivation was the best technique. Whereas, FTA cards performed better than untreated filter papers, and were nearly comparable to the sensitivity of WBC lysis.
Henning et al. [
5] showed that template preparation by the rapid boiling method, or using the isocode stix, provided increased sensitivity for the detection of multiple infections when compared to QIAamp or GTC/phenol/chloroform template preparation. Although the rapid boiling method offers high sensitivity and cost-effectiveness, long-term storage of template is critical. According to our results, we found that the rapid boiling technique is inexpensive but time consuming, and it was found to be the least sensitive.
FTA cards were found to be useful in overcoming problems regarding storage, infectivity, and transportation in a study done by Yamamura et al. [
24] who evaluated rapid molecular diagnostic system for
P. falciparum combined with DNA filter paper, loop-mediated isothermal amplification, and melting curve analysis. In a study on comparative detection of
Theileria equi infection using whole blood compared with pre-extracted DNA samples as PCR templates [
25], although minimal variations in limit of detection were observed among the methods compared, overall, the use of pre-extracted DNA samples and blood spotted on FTA classic cards had comparable detection limits. These results indicate that
T. equi infection can be efficiently detected directly from FTA classic cards by PCR without the need for pre-extraction of DNA from blood samples.
In a study to evaluate the sensitivities of DNA extraction and PCR methods for detection of
Giardia duodenalis in stool specimens, the FTA filter paper method was found to be the most efficient DNA extraction method, as it detected as few as 168 cysts/ml, while both the QIAamp stool mini-kit and phenolchloroform extraction method could detect 674 cysts/ml stool dilution. In addition to its high sensitivity, the FTA filter paper assay was simple to use and can be applied with a large number of samples at one time. The samples are also easy to handle and transport for further analysis [
26]. Li et al. [
27] reported that whole blood stored on a FTA filter paper provided a simple and economical method for collection and storage of specimens of HIV-1 DNA for later testing. Moreover, Muthukrishnan et al. [
28] has evaluated the usefulness of FTA classic cards for the collection, shipment, storage, and identification of the foot-and-mouth disease virus (FMDV) genome by RT-PCR and real-time RT-PCR.
In summary, we have described a nested PCR assay for the diagnosis of malaria evaluating a new simple technique for DNA extraction using for the fist time FTA Elute cards. The test detected plasmodial infection and could differentiate P. falciparum from P. vivax and detected the mixed infection. No complex treatment of the blood samples was required prior to the amplification. The blood spots on Elute cards were found to be very stable without any noticeable effects on the sensitivity of the assay. The production cost of DNA isolation using FTA Elute was much less compared to that of other DNA extraction protocols. We would like to present this DNA extraction technique as an effective diagnostic tool that is sensitive, specific, less costly, and less labor intensive than currently used extraction methods for the diagnosis of malaria. Moreover, our results encourage efforts to improve malaria antibody detection methods to increase its sensitivity and its differentiation between all plasmodia species in the field of blood screening.
References
- 1. OPS. Control de la malaria en las Américas: análisis crítico. Bull Oficina Sanit Panam 1986;101:522-539.
- 2. World Health Organization. World malaria situation in 1994. Part I. Population at risk. Wkly Epidemiol Rec 1997;72:269-274.
- 3. World Health Organization. Report on malaria situation in the United Arab Emirates-the fourth inter-country meeting of national malaria program managers. World Malaria Report 2005, WHO/HTM/MAL/2005.1102. 2004, Isfahan, Iran.
- 4. Chiodini PL, Moody AH. Techniques for the detection of malaria parasites. J R Soc Med 1989;82(suppl 17):41-43.
- 5. Henning L, Felger I, Beck HP. Rapid DNA extraction for molecular epidemiological studies of malaria. Acta Trop 1999;72:149-155.
- 6. Foley M, Randford-Cartwright LC, Babiker AH. Rapid and simple method for isolating malaria DNA from fingerprick samples of blood. Mol Biochem Parasitol 1992;53:241-244.
- 7. Snounou G. Detection and identification of the four malaria parasite species infecting humans by PCR amplification. Methods Mol Biol 1996;50:263-291.
- 8. Ndao M, Bandyayera E, Kokoskin E, Gyorkos TW, MacLean JD, Ward BJ. Comparison of blood smear, antigen detection, and nested-PCR methods for screening refugees from regions where malaria is endemic after a malaria outbreak in Quebec, Canada. J Clin Microbiol 2004;42:2694-2700.
- 9. Roy KB, Yajnik V, Roy A, Sharma VP. Detection of Plasmodium vivax in human blood using synthetic DNA probe. Indian J Malariol 1987;24:63-69.
- 10. Gilles HM. In Gilles HM, Warrell DA eds, Diagnostic methods in malaria. Bruce-Chwatt's Essential Malariology. 1993, 3rd ed. London, UK. Edward Arnold; pp 78-95.
- 11. Grant DB, Perinpanayagam MS, Shute PG, Zeitlin RA. A case of malignant tertian (Plasmodium falciparum) malaria after blood-transfusion. Lancet 1960;2:469-470.
- 12. Noedl H, Yingyuen K, Laoboonchai A, Fukuda M, Sirichaisinthop J, Miller RS. Sensitivity and specificity of an antigen detection ELISA for malaria diagnosis. Am J Trop Med Hyg 2006;75:1205-1208.
- 13. Oh JS, Kim JS, Lee CH, Nam DH, Kim SH, Park DW, Lee CK, Lim CS, Park GH. Evaluation of a malaria antibody enzyme immunoassay for use in blood screening. Mem Inst Oswaldo Cruz 2008;103:75-78.
- 14. Elghouzzi MH, Senegas A, Steinmetz T, Guntz P, Barlet V, Assal A, Gallian P, Volle P, Chuteau C, Beolet M, Berrebi S, Filisetti D, Doderer C, Abdelrahman T, Candolfi E. Multicentric evaluation of the DiaMed enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay malaria antibody test for screening of blood donors for malaria. Int J Transfu Med (Vox Sang) 2008;94:33-40.
- 15. Di Santi SM, Kirchgatter K, Brunialti SK, Oliveira AM, Ferreira SRS, Boulos M. PCR-based diagnosis to evaluate the performance of malaria reference centers. Rev Inst Med Trop Sao Paulo 2004;46:183-187.
- 16. Sethabutr O, Brown AE, Panyim S, Kain KC, Webster HK, Echeverria P. Detection of Plasmodium falciparum by polymerase chain reaction in a field study. J Infect Dis 1992;166:145-148.
- 17. Coyne SR, Craw PD, Norwood DA, Ulrich MP. Comparative analysis of the Schleicher and Schuell IsoCode Stix DNA isolation device and the Qiagen QIAamp DNA mini kit. J Clin Microbiol 2004;42:4859-4862.
- 18. Lindström B, Ericsson O, Alván G, Rombo L, Ekman L, Rais M, Sjöqvist F. Determination of chloroquine and its desethyl metabolite in whole blood: an application for samples collected in capillary tubes and dried on filter paper. Ther Drug Monit 1985;7:207-210.
- 19. Prior TW, Highsmith WE Jr, Friedman KJ, Perry TR, Scheuerbrandt G, Silverman LM. A model for molecular screening of newborns: simultaneous detection of Duchenne/Becker muscular dystrophies and cystic fibrosis. Clin Chem 1999;36:1756-1759.
- 20. Singh B, Bobogare A, Cox-Singh JC, Snounou G, Abdullah MS, Rahman HA. A genus- and species-specific nested polymerase chain reaction malaria detection assay for epidemiologic studies. Am J Trop Med Hyg 1999;60:687-692.
- 21. Zhong KJ, Salas CJ, Shafer R, Gubanov A, Gasser RA Jr, Magill AJ, Forney JR, Kain KC. Comparison of IsoCode STIX and FTA Gene Guard collection matrices as whole-blood storage and processing devices for diagnosis of malaria by PCR. J Clin Microbiol 2001;39:1195-1196.
- 22. Bereczky S, Mårtensson A, Gil JP, Färnert A. Short report: rapid DNA extraction from archive blood spots on filter paper for genotyping of Plasmodium falciparum. Am J Trop Med Hyg 2005;72:249-251.
- 23. Gonzalez JL, Loza A, Chacon E. Sensitivity of different Trypanosoma vivax specific primers for the diagnosis of livestock trypanosomosis using different DNA extraction methods. Vet Parasitol 2006;136:119-126.
- 24. Yamamura M, Makimura K, Ota Y. Evaluation of a new rapid molecular diagnostic system for Plasmodium falciparum combined with DNA filter paper, loop-mediated isothermal amplification, and melting curve analysis. Jpn J Infect Dis 2009;62:20-25.
- 25. Alhassan A, Iseki H, Kim C, Yokoyama N, Igarashi I. Comparison of polymerase chain reaction methods for the detection of Theileria equi infection using whole blood compared with pre-extracted DNA samples as PCR templates. Trop Anim Health Prod 2007;39:369-374.
- 26. Nantavisai K, Mungthin M, Tan-Ariya P, Rangsin R, Naaglor T, Leelayoova S. Evaluation of the sensitivities of DNA extraction and PCR methods for detection of Giardia duodenalis in stool specimens. J Clin Microbiol 2007;45:581-583.
- 27. Li CC, Beck IA, Seidel KD, Frenkel LM. Persistence of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 subtype B DNA in dried-blood samples on FTA filter paper. J Clin Microbiol 2004;42:3847-3849.
- 28. Muthukrishnan M, Singanallur NB, Ralla K, Villuppanoor SA. Evaluation of FTA cards as a laboratory and field sampling device for the detection of foot-and-mouth disease virus and serotyping by RT-PCR and real-time RT-PCR. J Virol Methods 2008;151:311-316.
Fig. 1Comparative sensitivity of different DNA extraction techniques for Plasmodium genus detection.

Fig. 2DNA extracted from malaria patients and amplified by nested PCR. Assays of sensitivities, using genus- and species-specific primer sets. (A) DNA by FTA Elute card. Lanes 1 & 3-11, positive samples, Plasmodium genus fragment (240 bp); 2, molecular marker 100 bp (Promega). (B) DNA by rapid boiling technique. Lanes 2-6 & 13-14, Plasmodium genus fragment (240 bp). DNA by FTA classic cards. Lanes 7-12, Plasmodium genus fragment (240 bp). Lane 1, molecular marker 100 bp (Promega). (C) Species-specific primers. Lanes 2-4, P. vivax fragment (117 bp); 5-15, negative results; 1, molecular marker 100 bp (Promega). (D) Species-specific primers in 3 samples; sample 1, lanes 1-4; sample 2, lanes 10-13 showing mixed infections with P. falciparum and P. vivax; sample 3, lanes 6-9 showing single infection with P. falciparum. Each sample was run against the 4 species primer sets. Lanes 1, P. falciparum fragment (205 bp); 2, P. ovale primer (negative); 3, P. malariae primer (negative); 4, P. vivax fragment (117 bp); 5, molecular marker 100 bp (Promega); 6, P. falciparum fragment (205 bp); 7, P. ovale primer (negative); 8, P. malariae primer (negative); 9, P. vivax fragment (negative); 10, P. falciparum fragment (205 bp); 11, P. ovale primer (negative); 12, P. malariae primer (negative); 13, P. vivax fragment (117 bp).

Table 1.Sensitivity of microscopy, ELISA, and PCR methods in the Plasmodium genus detection
Table 1.
|
Results |
No. positive (%) |
No. negative (%) |
Sensitivity (%)*
|
|
Microscopy |
52 (39.4) |
80 (60.6) |
88.2 |
|
ELISA |
46 (34.8) |
86 (65.2) |
81.1 |
|
PCR |
60 (45.5) |
72 (54.5) |
100.0 |
Table 2.Comparison of the genus and species detection using microscopy and PCR
Table 2.
|
Microscopy |
Nested PCR
|
Nested PCR total |
|
Negative |
Pv
|
Pf
|
|
Negative |
72 |
0 |
0 |
72 |
|
Pv
|
4 |
31 |
0 |
35 |
|
Pf
|
4 |
0 |
17 |
21 |
|
Pv + Pf
|
0 |
2 |
2 |
4 |
|
Microscopy total |
80 |
33 |
19 |
132 |
Table 3.Discordant results using microscopy and PCR
Table 3.
|
Number of cases |
PCR result |
Microscopy result |
Repeated PCR result |
Repeated microscopy result |
|
1 |
Pv
|
Negative |
Pv
|
Pv
|
|
2 |
Pv
|
Negative |
Pv
|
Pv
|
|
3 |
Pf
|
Negative |
Pf
|
Pf
|
|
4 |
Pv
|
Negative |
Pv
|
Negative |
|
5 |
Pv + Pf
|
Pf
|
Pv + Pf
|
Pf
|
|
6 |
Pf
|
Negative |
Pf
|
Negative |
|
7 |
Pv
|
Negative |
Pv
|
Pv
|
|
8 |
Pv + Pf
|
Pv
|
Pv + Pf
|
Pv
|
|
9 |
Pf
|
Negative |
Pf
|
Pf
|
|
10 |
Pv + Pf
|
Pf
|
Pv + Pf
|
Pv
|
|
11 |
Pf
|
Negative |
Pf
|
Pf
|
|
12 |
Pv + Pf
|
Pv
|
Pv + Pf
|
Pv
|