Abstract
We measured changes in sonographic findings of patients with clonorchiasis after a treatment in a highly endemic area. A total of 347 residents showed positive stool results for Clonorchis sinensis eggs in a village in northeastern China, and were treated with praziquantel. Of them, 132 patients underwent abdominal sonography both before and 1 year after treatment, and the changes in sonographic findings of 83 cured subjects were compared. Diffuse dilatation of intrahepatic bile ducts (DDIHD) was found in 82 patients (98.2%) before and 80 (96.4%) after treatment, which was improved in 3, aggravated in 1, and unchanged in 79 patients. Increased periductal echogenicity (IPDE) was observed in 42 patients (50.6%) before and 45 (54.2%) after treatment, which was improved in 5, aggravated in 8, and unchanged in 70 patients. Floating echogenic foci in the gallbladder (FEFGB) was detected in 32 patients (38.6%) before and 17 (20.5%) after treatment, which was improved in 20, aggravated in 5, and unchanged in 58 patients. Improvement of FEFGB only was statistically significantly (P = 0.004). The present results confirm that DDIHD and IPDE persist but FEFGB decreases significantly at 1 year after treatment. In a heavy endemic area, the sonographic finding of FEFGB may suggest active clonorchiasis 1 year after treatment.
-
Key words: Clonorchis sinensis, praziquantel, abdominal sonography, dilatation of intrahepatic bile ducts, periductal echogenicity, floating echogenic foci in the gallbladder
INTRODUCTION
In spite of introduction of praziquantel,
Clonorchis sinensis remains a common food-borne pathogen in China, Taiwan, Vietnam, Korea, and far eastern Russia [
1]. Long-standing clonorchiasis (
C. sinensis infection) can lead to serious complications, including cholangiocarcinoma. Thus,
C. sinensis is a major public health concern and requires active control in endemic areas [
1-
5].
Clonorchiasis is diagnosed primarily by detection of eggs in feces [
1,
6]. However, since fecal examination is becoming difficult to perform, alternative diagnostic methods, including serology, intradermal test, and radiological examinations, have been developed [
1]. Among them, abdominal sonography has been widely used because the pathological changes of the intrahepatic bile duct and gallbladder induced by
C. sinensis are easily detected [
1,
7-
11].
The diagnostic sensitivity and specificity of sonography depend on the intensity of infection (as determined by egg counts, chronicity, endemicity, and treatment) [
9,
12,
13]. Even though many sonographic findings in various conditions have been described [
7,
8,
11-
14], there are few clinical studies which focused on the pathological changes in patients with clonorchiasis after treatment [
8,
14,
15].
In this study, we observed changes of sonographic findings, which represent pathological changes in the liver, in patients with clonorchiasis after treatment in a highly endemic area.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Subjected population
A total of 494 residents were subjected at a village in Zhaoyuan county in Heilongjiang province, China, where a clonorchiasis control program has operated since 2001. The subjects were recruited for the Korea-China International Collaboration project of clonorchiasis control, and screened by fecal examination and abdominal sonography. The project was approved by the Center for Disease Control and Prevention of Heilongjiang province, 2004.
The initial fecal examinations and treatment
Baseline characteristics such as gender and age were recorded. A fecal examination was performed on all subjects using the Kato-Katz method [
6]. Subjects with positive stool results for
C. sinensis were treated with praziquantel, 25 mg/kg × 3.
Before treatment, an experienced abdominal radiologist, unaware of the clinical information or the status of
C. sinensis infection, performed the sonographic examinations using an ultrasound scanner equipped with a 3-6 MHz convex-array transducer (SonoAce 5500; Medison, Seoul, Korea). Any evidence of diffuse dilatation of intrahepatic bile ducts (DDIHD), increased periductal echogenicity (IPDE), or floating echogenic foci in the gallbladder (FEFGB) was noted [
7,
12,
13]. The criteria we used for the diagnosis and grading of DDIHD, IPDE, and FEFGB are described in previous literature [
13]. DDIHD and IPDE were graded as mild, moderate, or severe, and FEFGB were classified as a few (5 or less) or many (more than 5) foci.
For patients who revisited 1 year after treatment, follow-up sonography was performed using the same methods and criteria. They also underwent fecal examination.
Statistical analysis
The changes of 3 sonographic findings (DDIHD, IPDE, and FEFGB) were each evaluated in patients with egg-negative conversion. To identify the sonographic findings showing significant changes after treatment, the sign test was performed. SPSS for Windows (version 11.0; SPSS Institute, Inc., Chicago, IL, USA) was used for the analysis. P values less than 0.05 were considered statistically significant.
RESULTS
Follow-up fecal examination in revisited subjects
Three hundred and forty-seven (70.2%) of 494 subjected residents showed positive stool results for
C. sinensis eggs and were treated with praziquantel. This group comprised 300 males and 194 females with a median age of 37 year (range; 15-78 year). Of the 494 subjects, 474 were examined by sonography, 142 were egg negative and 332 were positive (
Table 1). Of this group of 332 subjects, 132 patients revisited 1 year after treatment and underwent both the follow-up sonographic and fecal examinations. They comprised 100 males and 32 females with a median age of 37 year (range; 15-78 year). Of the 132 patients, 83 (62.9%) were egg-negative converted (= cured) and 47 were egg-positive, after 1 year. There were no significant differences in gender or age between the egg-negative conversion group and the egg-positive group (
Table 2).
In the initial (pre-treatment) sonography of the 83 cured patients after treatment, DDIHD, IPDE, and FEFGB were found in 82 (98.2%), 42 (50.6%), and 32 (38.6%), respectively (
Table 3). After treatment, DDIHD, IPDE, and FEFGB were found in 80 (96.4%), 45 (54.2%), and 17 (20.5%), respectively. DDIHD was improved in 3 (
Fig. 1), aggravated in 1, and unchanged in 79 patients. IPDE was improved in 5 (
Fig. 2), aggravated in 8, and unchanged in 70 patients. FEFGB was improved in 20 (
Fig. 3), aggravated in 5, and unchanged in 58 patients. Neither DDIHD nor IPDE showed significant changes (
P = 0.625 and
P = 0.581, respectively). However, FEFGB revealed a statistically significant improvement (
P = 0.004) (
Table 3).
DISCUSSION
In the present study, most (70.2%, 347 of 494) of the residents examined in Zhaoyuan were
C. sinensis egg positive. Zhaoyuan is located in the middle of the highest endemic zone in Heilongjiang province, northeast China [
13]. Men showed a higher egg-positive rate and heavier infection intensities than women, which is consistent with other epidemiological studies on clonorchiasis [
7,
12,
14,
16]. In such an endemic area of clonorchiasis, sonographic screening of the liver is important to detect any hidden cholangiocarcinoma as a complication [
3,
4,
9,
10,
17].
Sonographic findings in clonorchiasis patients demonstrate rather clearly pathological changes of the bile ducts and gallbladder. Prior studies using rabbits infected with
C. sinensis showed that DDIHD was due to bile duct obstruction and dilatation caused by the flukes [
8,
11]. IPDE results from periductal inflammation, and FEFGB is due to the presence of the flukes and/or debris of host tissue. As pathological changes reflect severity and chronicity of clonorchiasis, sonographic findings can also be correlated with the intensity and duration of
C. sinensis infection. A recent study in the same area reported that DDIHD, IPDE, and FEFGB showed significant correlations with intensity of
C. sinensis infection [
13].
According to recent literature [
9,
15,
18], dynamic CT and MR imaging show the flukes themselves in the intrahepatic bile duct, as well as the hypertrophic intrahepatic bile ducts during the hepatic arterial phase. These findings represent active infection. In a clinical report, IPDE and FEFGB were significantly associated with active clonorchiasis [
12]. IPDE showed a sensitivity and specificity for active clonorchiasis of 35% and 91%, respectively, and FEFGB had a sensitivity and specificity of 28% and 94%, respectively. However, DDIHD showed a low relationship with active clonorchiasis, with a sensitivity of 67% and a specificity of 48%. Previous reports also show that long-lasting DDIHD is of little value for diagnosis of active clonorchiasis in patients with praziquantel treatment [
8,
14].
The present study suggests that neither IPDE nor DDIHD was good diagnostic indicators of active clonorchiasis at least 1 year after the treatment trial. Although FEFGB indicated active clonorchiasis in the present study, it lacks sensitivity [
12]. FEFGB in subjects with egg-negative conversion after treatment (20.5%, 17 of 83) are probably attributable to a false negative fecal examination or to false images of flukes. We believe that false images are simple fluke-mimicking sludge in the gallbladder. In active clonorchiasis, FEFGB mostly indicates flukes and desquamated material in the gallbladder [
7,
11,
12]. This finding has rarely been documented in non-endemic areas with low intensity of
C. sinensis [
7,
12]. The relatively high frequency (38.6%) of FEFGB before treatment in the present study was related to a moderate or heavy endemicity and burden of clonorchiasis. Among the sonographic findings, only FEFGB can be resolved after cure, which is the only significant finding showing 1 year interval resolution after treatment. The present sonographic findings are most serious in their frequencies and degrees among all previous records because of the heavy endemicity in the present subjected population.
In conclusion, sonographic findings of DDIHD and IPDE remain unchanged but that of FEFGB decreases significantly 1 year after treatment. Thus, FEFGB may suggest active clonorchiasis after treatment in a heavy endemic area.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
This study was supported by a grant from the Education and Research Foundation, Seoul National University College of Medicine, 2006. We appreciate faculty members of Zhaoyuan CDC and Heilongjiang CDC for administrative aids required for the field works.
References
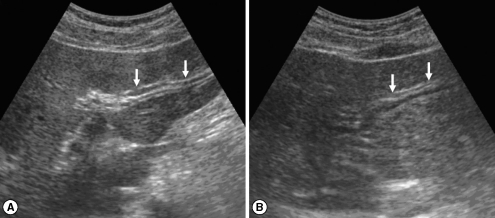
Fig. 1Sonograms of a patient with egg-negative conversion by treatment. Transverse scan before treatment (A) of the left hepatic lobe shows severe dilatation of the intrahepatic bile ducts (IHDs) (arrows). Diameter of the IHD is larger than that of the adjacent portal vein. Dilatation of the IHD is improved to mild degree (arrows) 1 year after treatment (B). IHD is dilated but its diameter is smaller than that of the adjacent portal vein.
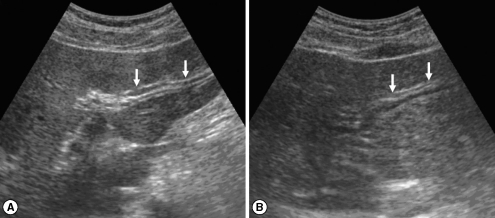
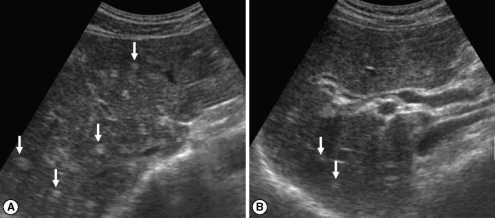
Fig. 2Sonograms of another patient with egg-negative conversion. Transverse scan before treatment (A) of the right hepatic lobe shows moderately increased periductal echogenicity (arrows). Increased periductal echogenicity is improved to mild degree (arrows) 1 A B year after treatment (B).
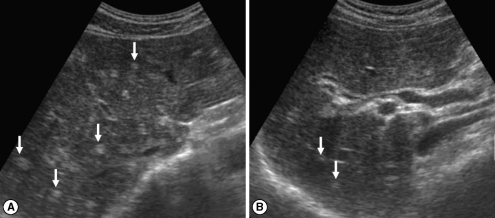
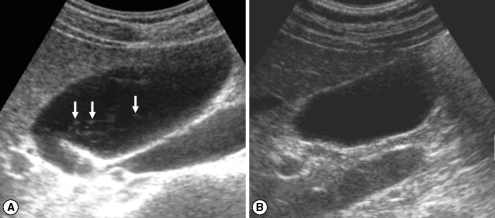
Fig. 3Sonograms of a patient with egg-negative conversion after treatment. Many floating echogenic foci (arrows) in the gallbladder before treatment (A) are no longer seen 1 A B year after treatment (B).
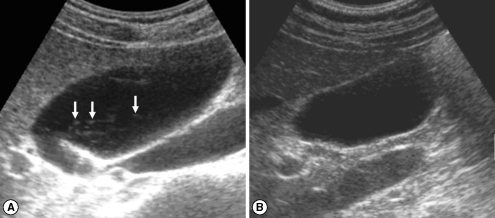
Table 1.Number of subjects by positive sonographic findings by EPG (eggs per gram of feces) grades before treatment, 2004
Table 1.
|
EPG grades |
No. of subjects |
Positive sonographic findings (%)
|
|
DDIHD (%) |
IPDE (%) |
FEFGB (%) |
|
0 |
142 |
139 (97.9) |
75 (52.8) |
51 (35.9) |
|
1-500 |
127 |
125 (98.4) |
75 (59.1) |
54 (42.5) |
|
501-2,000 |
112 |
110 (98.2) |
60 (53.6) |
38 (33.9) |
|
2,001- |
93 |
93 (100) |
39 (41.9) |
30 (32.3) |
|
Total |
474 |
467 (98.5) |
247 (52.1) |
173 (36.5) |
Table 2.Demographic characteristics and numbers of egg-negative conversion by EPG grades before treatment
Table 2.
|
Parameters |
Egg-negative conversion after treatment (n=83) |
Egg-positive after treatment (n=49) |
P value |
|
Age (year, mean + SD) |
12 - 78 (42.9 + 11.1) |
12 - 80 (42.3 + 12.8) |
0.77a
|
|
Male gender (%) |
41 (49.3) |
27 (55.1) |
0.65b
|
|
EPGs before treatment |
|
|
0.84b
|
|
<500 |
45 |
24 |
|
|
501-2,000 |
27 |
18 |
|
|
2,001 and over |
11 |
7 |
|
Table 3.Changes of sonographic findings in the egg-negative conversion group
Table 3.
|
Sonographic findings |
Changes by treatment |
No. of subjects (n = 83) |
P valuea
|
|
DDIHD |
Improved |
3 |
0.625 |
|
Aggravated |
1 |
|
|
Unchanged |
79 |
|
|
IPDE |
Improved |
5 |
0.581 |
|
Aggravated |
8 |
|
|
Unchanged |
70 |
|
|
FEFGB |
Improved |
20 |
0.004 |
|
Aggravated |
5 |
|
|
Unchanged |
58 |
|